Examining the Correlational Interaction of Environmental Fluoride and Selenium and Its Impact on Dental Fluorosis in Coal-Burning Regions of Southwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
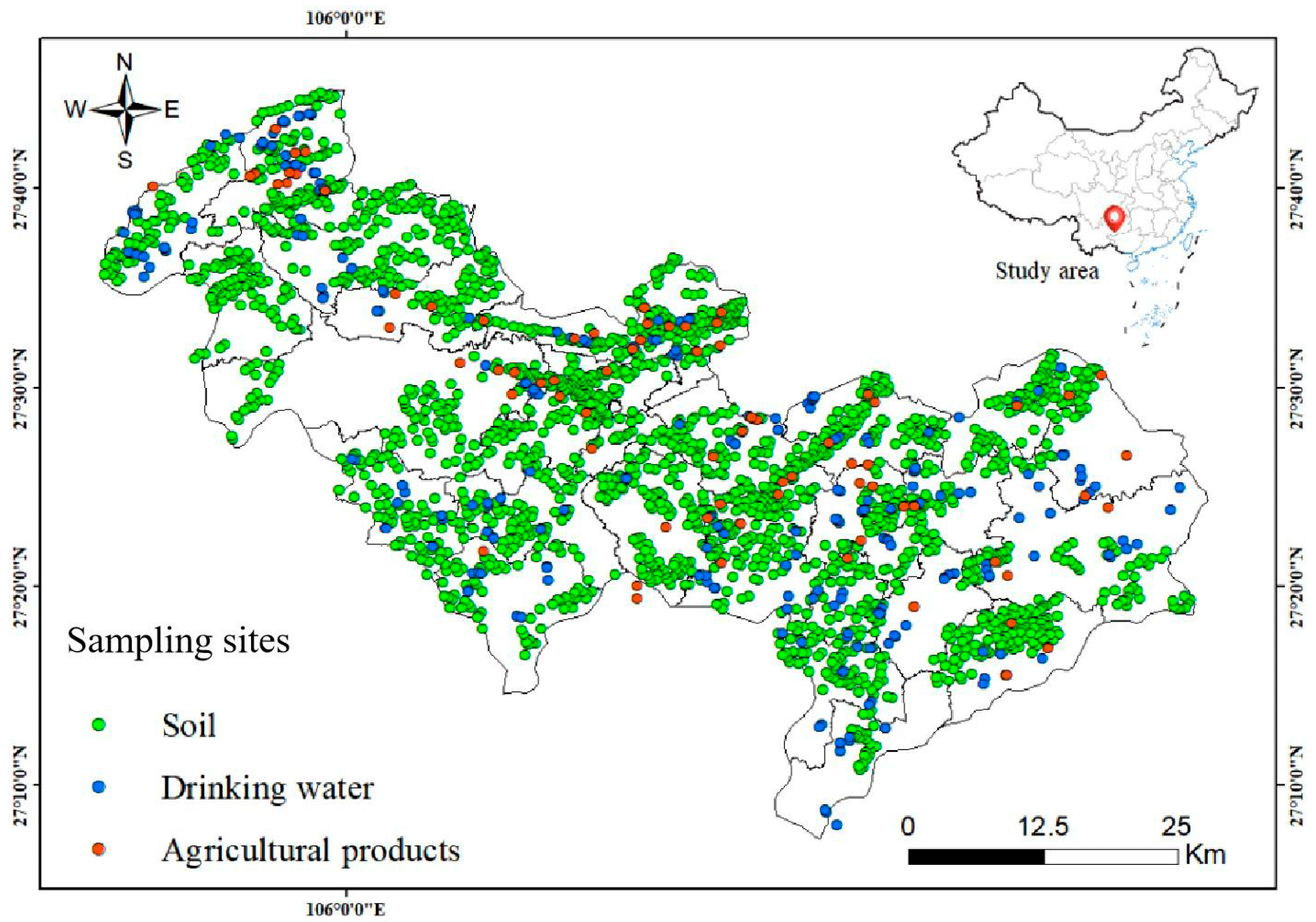
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Getis–Ord General G
3. Results
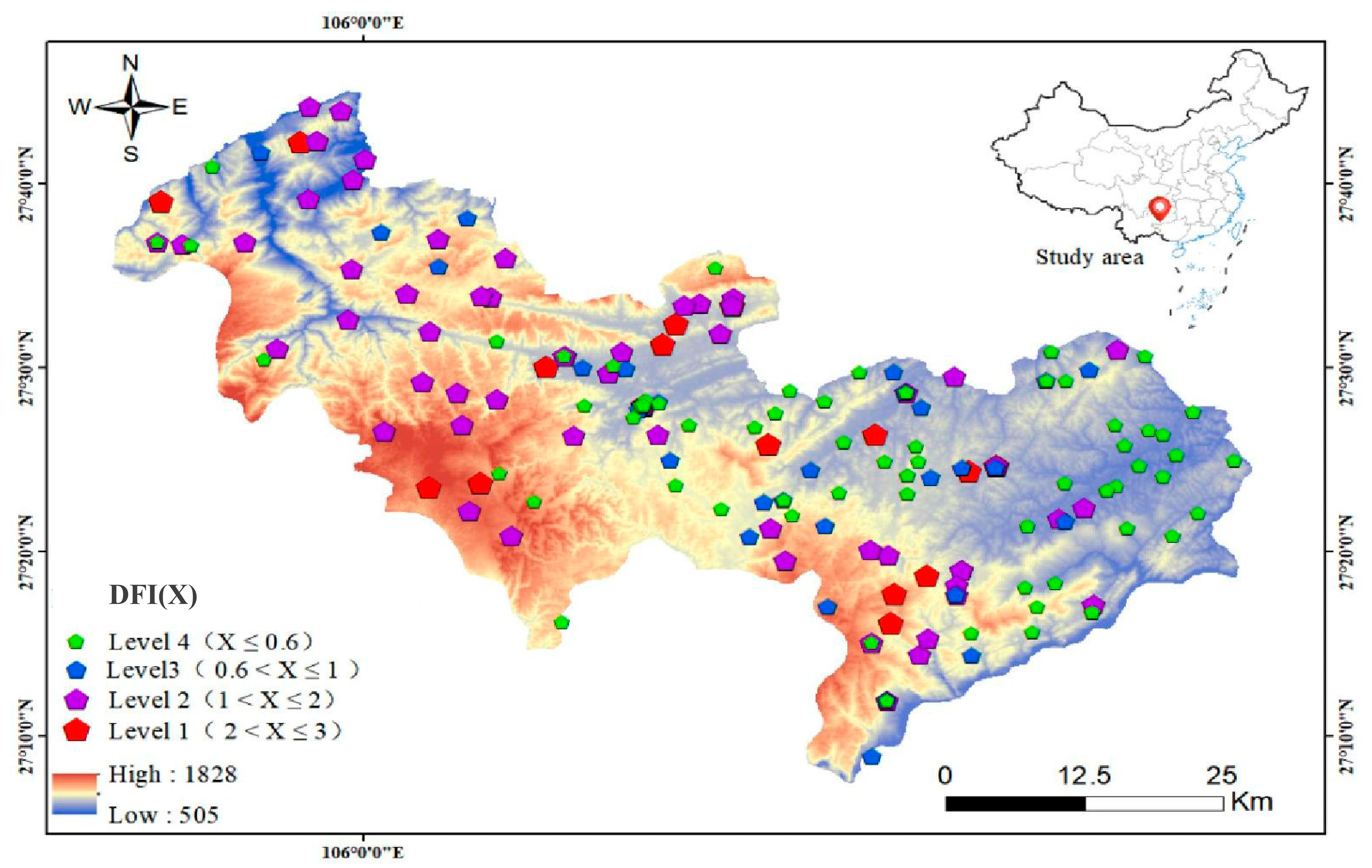
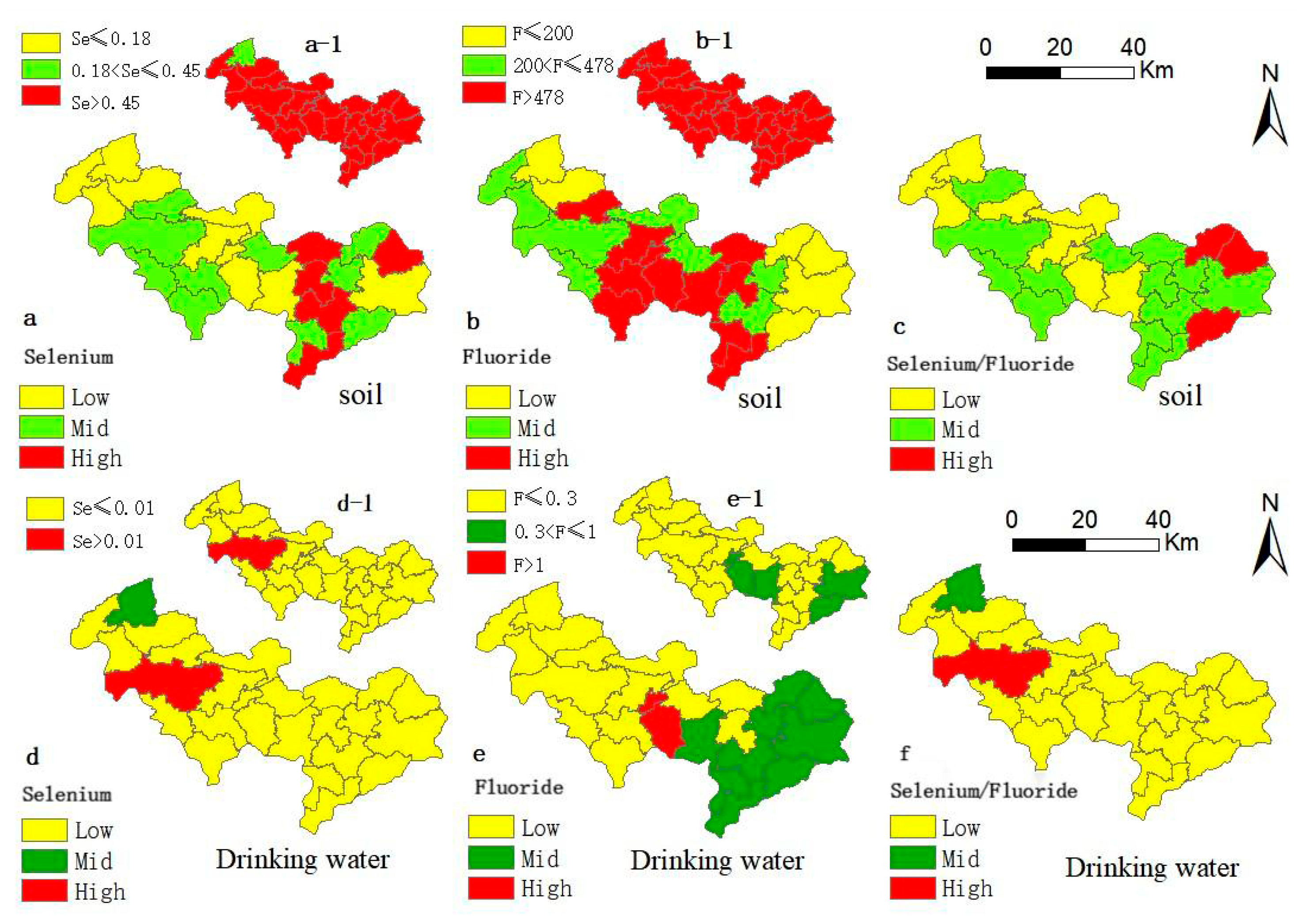
3.1. Spatial Geochemical Distribution Pattern of Environmental Selenium and Fluoride
3.1.1. Selenium and Fluoride in Soil and Drinking Water
3.1.2. Agricultural Products and Selenium
3.1.3. Spatial Distribution of Selenium, Fluoride, and Selenium/Fluoride in Soil and Drinking Water
3.1.4. Geochemical Anomalies and Limited Transfer
3.2. Correlations and Spatial Association of Selenium or Fluoride with DFI
3.2.1. Correlations with DFI
3.2.2. Association with DFI
3.3. The Generalized Additive Model (GAM) of Soil Selenium Content, Fluoride Content and Selenium/Fluoride with the Dean’s Dental Fluorosis Index
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lyth, O. Endemic Fluorisis in Kweichow, China. Lancet 1946, 247, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, J.; Liao, H. Review on Health Impacts from Domestic Coal Burning: Emphasis on Endemic Fluorosis in Guizhou Province, Southwest China. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 258, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siljander, M.; Uusitalo, R.; Pellikka, P.; Isosomppi, S.; Vapalahti, O. Spatiotemporal clustering patterns and sociodemographic determinants of COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) infections in Helsinki, Finland. Spat. Epidemiol. 2022, 41, 100493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Cheng, J.Z.; Yang, N.; Zhang, J.H.; Tu, C.L. Spatial correlation between the prevalence of dental fluorosis and the chemical elemental composition of drinking water sources in a typical coal-fired pollution fluorosis area. Chin. J. Epidemiol. 2023, 44, 891–898. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Tu, C.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Finkelman, R.B. Analysis of multiple pathways and levels of fluoride intake in fluorosis areas of Southwest China. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, W.; Li, X.X.; Wu, P. New Insights into Selenium Enrichment in the Soil of Northwestern Guizhou, Southwest China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 107, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovanović, J.; Antonijević, B.; Kolarević, S.; Milutinović-Smiljanić, S.; Mandić, J.; Vuković-Gačić, B.; Bulat, Z.; Ćurčić, M.; Kračun-Kolarević, M.; Sunjog, K.; et al. Genotoxicity of fluoride subacute exposure in rats and selenium intervention. Chemosphere 2021, 266, 128978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Zhang, L.; Miao, K.K.; Qian, W.; Zhang, Z.G. Effects of selenium intervention on chronic fluorosis-induced renal cell apoptosis in rats. Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 2013, 153, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Sun, Y.; Ke, L.; Ouyang, W.; Zhang, Z. Molecular mechanism of brain impairment caused by drinking-acquired fluorosis and selenium intervention. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 43, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J. Selenomethionine supplementation mitigates fluoride-induced liver apoptosis and inflammatory reactions by blocking Parkin-mediated mitophagy in mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, G.; Kang, Y.; Wu, B.; Sun, R.; Zhou, C.; Wu, D. Atmospheric emissions of F, As, Se, Hg, and Sb from coal-fired power and heat generation in China. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Xiao, X.; Zhan, X.A. Antagonistic effects of different selenium sources on growth inhibition, oxidative damage, and apoptosis induced by fluorine in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 3207–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 873-2017; Soil-Determination of Water Soluble Fluoride and Total Fluoride-Ion Selective Electrode Method. Environmental Protection Agency of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- GB/T 7484-1987; Water Quality—Determination of Fluoride—Ion Selective Electrode Method. Chinese Standardization Administration: Beijing, China, 1987.
- Feng, Y.; Yang, Q.; Tong, X.; Chen, L. Evaluating land ecological security and examining its relationships with driving factors using GIS and generalized additive model. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 633, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Li, H.; Ding, Z.X.; Hu, Z.B.; Chen, F.; Wang, K.; Peng, Z.H.; Shen, H.B. Spatial statistical analysis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China. Geospat. Health. 2020, 15, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swetnam, T.L.; Lynch, A.M.; Falk, D.A.; Yool, S.R.; Guertin, D.P. Discriminating disturbance from natural variation with LiDAR in semi-arid forests in the southwestern USA. Ecosphere 2015, 6, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.A. The Atlas of Endemic Diseases and Their Environments in the People’s Republic of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F.; Wu, Y.; Islam, M.U.; Jiang, X.; Wang, B.; He, S.; Lin, X.; Sun, Y.; Chen, G.; Chen, X.; et al. Selenium levels in soil and tea as affected by soil properties in Jiangxi Province, China. BMC Plant Biology 2024, 24, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Yuan, T.; Hu, Z.; Liang, J.; Zhu, G.; Pang, C.; Zheng, H. Selenium in selenium-rich rice sold in China and risk assessment. Food Addit. Contam. Part B Surveill. 2022, 15, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H. Preliminary Study on the Effects of Selenium Application on Agronomic Traits, Yield and Selenium, Cadmium, and Lead Accumulation in Rapeseed Grains. Master’s thesis, Yangtze University, Jingzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Zhao, A.; Ke, H.; Chen, H. Geo-Environmental Factors’ Influence on the Prevalence and Distribution of Dental Fluorosis: Evidence from Dali County, Northwest China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, M.; Lu, J.; Yang, K.; Wang, K.; Liu, M.; Luo, H.; Pang, L.; Wang, B. Fluorine in the environment in an endemic fluorosis area in Southwest, China. Environ. Res. 2020, 184, 109300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Liao, C.; Sun, D.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Q. Soil exposure is the major fluoride exposure pathways for residents from the high-fluoride karst region in Southwest China. Chemosphere 2023, 310, 136831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.A.; Zhu, W.; Wang, W.; Li, R.; Hou, S.; Wang, D.; Yang, L. Selenium in soil and endemic diseases in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 284, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.R.; Shang, Y.J.; Zhang, S. Measuring the spatiotemporal variations of vegetation net primary productivity in Inner Mongolia using spatial autocorrelation. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Prete, D.; Xue, S.; Nan, Z.; Zang, F.; Zhang, Q. Accumulation and interaction of fluoride and cadmium in the soil-wheat plant system from the wastewater irrigated soil of an oasis region in northwest China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 595, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Liang, D.; Lei, L.; Zhang, R.; Lin, Z. Selenium geochemical distribution in the environment and predicted human daily dietary intake in northeastern Qinghai, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 11224–11235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.K. Geochemical and Spatial Appraisal of Fluoride in the Soils of Indo-Gangetic Plains of India Using Multivariate Analysis. Soil Air Water 2012, 40, 1392–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombik, E.; Bombik, A.; Rymuza, K. The influence of environmental pollution with fluorine compounds on the level of fluoride in soil, feed and eggs of laying hens in Central Pomerania, Poland. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wei, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, T.; Li, F.; Liu, J.; Gao, Z. Spatial Distribution and Genesis of Fluoride in Groundwater, Qingshui River Plain, China. Water 2025, 17, 2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Chi, Q.; Wu, H.; Zhang, B.; Xu, S.; Han, Z.; Nie, L.; Liu, H.; Liu, D.; et al. Geochemical characteristics of fluorine (F) in mainland China’s pedosphere: On the basis of the China Geochemical Baselines project. J. Geo. Explor. 2020, 219, 106635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.C.; Li, Z.; Gu, M.; Liu, M.; Li, L. Spatial and vertical distribution and pollution assessment of soil fluorine in a lead-zinc mining area in the Karst region of Guangxi, China. Plant. Soil. Environ. 2010, 56, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xie, Z.; Xu, J.; Wu, W. Preliminary study on guideline on soil health quality index of fluorine and method of its evaluation in China. J. Zhejiang Univ. 2005, 31, 593–597. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Z.; Liu, X.; Meng, W.; Li, C.; He, S.; Yan, C.; Wang, F. Geochemical characteristics of fluorine in soils and its environmental quality in central district of Guiyang. Res. Environ. Sci. 2018, 31, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Dinh, Q.T.; Cui, Z.; Huang, J.; Tran, T.A.T.; Wang, D.; Yang, W.; Zhou, F.; Wang, M.; Yu, D.; Liang, D. Selenium distribution in the Chinese environment and its relationship with human health: A review. Environ. Int. 2018, 112, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5749-2022; Standards for Drinking Water Quality. National Committee for Standardization: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Umer, M.F. A Systematic Review on Water Fluoride Levels Causing Dental Fluorosis. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehbandi, R.; Moore, F.; Keshavarzi, B. Geochemical sources, hydrogeochemical behavior, and health risk assessment of fluoride in an endemic fluorosis area, central Iran. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.K.; Mishra, V.K.; Sharma, D.K.; Damodaran, T. Fluoride in the environment and its metabolism in humans. Rev. Environ. Countam. T. 2011, 211, 121. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.; Li, W.; Tang, Y.; Yong, Z.; Peng, F. The sources, pathway, and preventive measures for fluorosis in Zhijin County, Guizhou, China. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, B. The antagonistic effect of selenium on dental fluorosis and the expression of beclin1 mice. J. Tongji Univ. 2020, 41, 426–430. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y. Research progress on brick-tea type fluorosis in Tibet Plateau. Prev. Med. 2022, 34, 156–160. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Zhong, Z.H.; Huang, Q.; Wang, L.; Yong, K.W.; Zhang, M.Z.; Luo, X.J.; Yan, W. Correlation between prevalence of dental fluorosis and soil chemical elements in endemic fluorosis areas. Chin. J. Endem. 2013, 32, 303–308. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Xue, W.; Kao, X.; Gao, Y.; Muhammad, N.; Song, D. Selenium increases expression of HSP70 and antioxidant enzymes to lessen oxidative damage in Fincoal-type fluorosis. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 34, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angwa, L.M.; Jiang, Y.; Pei, J.; Sun, D. Antioxidant phytochemicals for the prevention of fluoride-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis: A review. Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 2021, 200, 1418–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Yan, M.; Yang, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, G.; Schmidt-Vogt, D.; Xu, Y.; Xu, J. Spatial distribution and temporal variation of high fluoride contents in groundwater and prevalence of fluorosis in humans in Yuanmou County, Southwest China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 235, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Type | Selenium | Fluoride | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Min | Max | Means | SD | Median | Min | Max | Means | SD | Median | |
| Soil | 2023 | 0.06 | 14.30 | 0.78 | 0.66 | 0.64 | 84.00 | 6.93 × 103 | 1.11 × 103 | 7.15 × 102 | 9.11 × 102 |
| Drinking water | 274 | nd | 2.68 × 10−2 | 4.70 × 10−3 | 2.10 × 10−2 | nd | 1.58 × 10−2 | 2.53 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.15 |
| Total | 2297 | 0.06 | 14.30 | 1.58 × 10−2 | 6.93 × 103 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, N.; Wang, J.; Li, L. Examining the Correlational Interaction of Environmental Fluoride and Selenium and Its Impact on Dental Fluorosis in Coal-Burning Regions of Southwest China. Toxics 2025, 13, 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110940
Yang N, Wang J, Li L. Examining the Correlational Interaction of Environmental Fluoride and Selenium and Its Impact on Dental Fluorosis in Coal-Burning Regions of Southwest China. Toxics. 2025; 13(11):940. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110940
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Na, Jianying Wang, and Longbo Li. 2025. "Examining the Correlational Interaction of Environmental Fluoride and Selenium and Its Impact on Dental Fluorosis in Coal-Burning Regions of Southwest China" Toxics 13, no. 11: 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110940
APA StyleYang, N., Wang, J., & Li, L. (2025). Examining the Correlational Interaction of Environmental Fluoride and Selenium and Its Impact on Dental Fluorosis in Coal-Burning Regions of Southwest China. Toxics, 13(11), 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110940






