Prediction of the Quantitative Biodistribution of Inhaled Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Using the Physiologically Based Toxicokinetic Modelling Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Dataset
2.2. TiO2-NPs PBTK Model Structure
2.3. Mathematical Description of the TiO2-NPs PBTK Model
2.4. Model Parameterization
2.5. The TiO2-NPs PBTK Model Validation
2.6. Sensitivity Analysis
3. Results
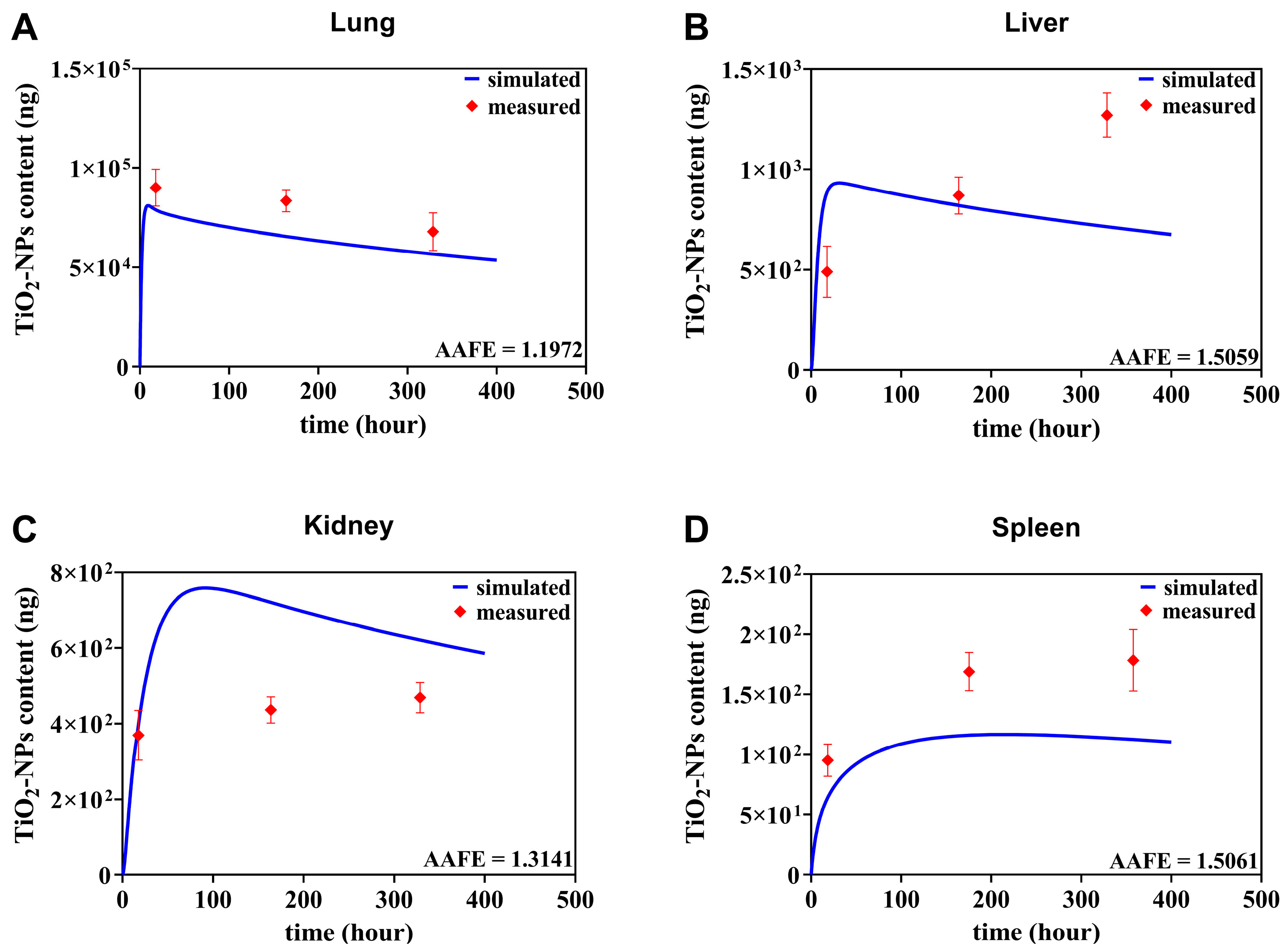
3.1. TiO2-NPs PBTK Model Prediction
3.2. The TiO2-NPs PBTK Model Evaluation with an Independent Data
3.3. The TiO2-NPs PBTK Model Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raj, L.F.A.A.; Annushrie, A.; Namasivayam, S.K.R. Anti Bacterial Efficacy of PhotoCatalytic Active Titanium DiOxide (TiO2) Nanoparticles Synthesized via Green Science Principles against Food Spoilage Pathogenic Bacteria. Microbe 2025, 7, 100331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, P.; Liu, J.; Yu, J. New Understanding of the Difference of Photocatalytic Activity among Anatase, Rutile and Brookite TiO2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 20382–20386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huuskonen, P.; Porras, S.P.; Scholten, B.; Portengen, L.; Uuksulainen, S.; Ylinen, K.; Santonen, T. Occupational Exposure and Health Impact Assessment of Diisocyanates in Finland. Toxics 2023, 11, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.M.; Johnston, H.J.; Gaiser, B.; Pinna, N.; Caputo, G.; Culha, M.; Kelestemur, S.; Altunbek, M.; Stone, V.; Roy, J.C.; et al. A Cross-Species and Model Comparison of the Acute Toxicity of Nanoparticles Used in the Pigment and Ink Industries. NanoImpact 2018, 11, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estillore, A.D.; Trueblood, J.V.; Grassian, V.H. ChemInform Abstract: Atmospheric Chemistry of Bioaerosols: Heterogeneous and Multiphase Reactions with Atmospheric Oxidants and Other Trace Gases. ChemInform 2016, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Sun, L.; Mei, D.; Liu, C.; Xia, T.; Li, J.; Meng, H. Engineering Inhalable Nanomedicines to Navigate Lung Barriers for Effective Pulmonary Fibrosis Therapy. Nano Today 2025, 64, 102778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Cao, S.; Dong, P.; Gao, J.; Wang, J. High Antibacterial Activity of Ultrafine TiO2/Graphene Sheets Nanocomposites under Visible Light Irradiation. Mater. Lett. 2013, 93, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun, N.H.; Mydin, R.B.S.M.N.; Sreekantan, S.; Saharudin, K.A.; Basiron, N.; Aris, F.; Wan Mohd Zain, W.N.; Seeni, A. Bactericidal Capacity of a Heterogeneous TiO2/ZnO Nanocomposite against Multidrug-Resistant and Non-Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Strains Associated with Nosocomial Infections. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 12027–12034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Rosa, S.; Pérez-Reyes, O. Neurotoxicity and Oxidative Stress Development in Adult Atya Lanipes Shrimp Exposed to Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles. Toxics 2023, 11, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grande, F.; Tucci, P.; Bevacqua, E.; Occhiuzzi, M.A. TiO2-NPs Toxicity and Safety: An Update of the Findings Published over the Last Six Years. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2023, 23, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Z. Long-Term Exposure to Polystyrene Nanoparticles at Environmentally Relevant Concentration Causes Suppression in Heme Homeostasis Signal Associated with Transgenerational Toxicity Induction in Caenorhabditis Elegans. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laomettachit, T.; Puri, I.K.; Liangruksa, M. A two-step model of TiO2 nanoparticle toxicity in human liver tissue. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 334, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Riviere, J.E. Pharmacokinetics of metallic nanoparticles. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2014, 7, 189–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Magaye, R.; Castranova, V.; Zhao, J. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles: A review of current toxicological data. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Lin, Z. Exploring the potential and challenges of developing physiologically-based toxicokinetic models to support human health risk assessment of microplastic and nanoplastic particles. Environ. Int. 2024, 186, 108617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaessig, F.C. PBPK Modeling of Slightly Soluble Silver Nanomaterials and Regulatory Acceptance. Small 2020, 16, 1907667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grech, A.; Brochot, C.; Dorne, J.-L.; Quignot, N.; Bois, F.Y.; Beaudouin, R. Toxicokinetic models and related tools in environmental risk assessment of chemicals. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, S.A. (Ed.) Regulatory Guidelines on the Reporting of Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modeling Analysis. In Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modeling and Simulations; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, D.M.; Siccardi, M. Optimizing nanomedicine pharmacokinetics using physiologically based pharmacokinetics modelling. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 3963–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Chaudhary, S.; Patel, J.K. Metallic Gold Nanoparticles: In Vivo Pharmacokinetics and X-Ray Contrast Imaging Studies. In Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Nanoparticulate Drug Delivery Systems; Patel, J.K., Pathak, Y.V., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 209–223. [Google Scholar]
- Ruark, C. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic model: Distribution processes. In Physiologically Based Pharmaco-Kinetic (PBPK) Modeling; Fisher, J.B., Lin, Z., Fisher, J.W., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 139–160. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Cui, Y.-Q.; Guo, W.-B.; Yang, L.; Miao, A.-J. Regulation of cadmium bioaccumulation in zebrafish by the aggregation state of TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachler, G.; von Goetz, N.; Hungerbühler, K. A Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model for Ionic Silver and Silver Nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 3365–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, W.-C.; Cheng, Y.-H.; Riviere, J.E.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Kreyling, W.G.; Lin, Z. Development of a Multi-Route Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Model for Nanomaterials: A Comparison between a Traditional versus a New Route-Specific Approach Using Gold Nanoparticles in Rats. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; He, Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Tang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Jiao, Z.; Cai, W.; Xiang, X. Application of Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling in Preclinical Studies: A Feasible Strategy to Practice the Principles of 3Rs. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreyling, W.G.; Holzwarth, U.; Schleh, C.; Hirn, S.; Wenk, A.; Schäffler, M.; Haberl, N.; Semmler-Behnke, M.; Gibson, N. Quantitative Biokinetics over a 28-Day Period of Freshly Generated, Pristine, 20 Nm Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle Aerosols in Healthy Adult Rats after a Single Two-Hour Inhalation Exposure. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2019, 16, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, F.J.; Asgharian, B.; Schroeter, J.D.; Price, O. Improvements and additions to the Multiple Path Particle Dosime-try model. J. Aerosol Sci. 2016, 99, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burda, B.U.; O’Connor, E.A.; Webber, E.M.; Redmond, N.; Perdue, L.A. Estimating Data from Figures with a web-based Program: Considerations for a Systematic Review. Res. Synth. Methods 2017, 8, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Qian, Z.; Huang, L.; Wang, M.; Wang, Q. Physiologically Based Toxicokinetic and Toxicodynamic (PBTK-TD) Modelling of Cis-Bifenthrin in Carassius auratus and Xenopus laevis Accounting for Reproductive Toxicity. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, R.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ma, M.; Wang, Z. In vitro to in vivo extrapolation for predicting human equivalent dose of phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals: PBTK model development, biological pathways, outcomes and performance. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 897, 165271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbek, O.; Genc, D.E.; Ulgen, K.O. Advances in Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modeling of Nanomaterials. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2024, 7, 2251–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Riviere, J.E. A Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model for Polyethylene Glycol-Coated Gold Nanoparticles of Different Sizes in Adult Mice. Nanotoxicology 2016, 10, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gakis, G.P.; Krikas, A.; Neofytou, P.; Tran, L.; Charitidis, C. Modelling the Biodistribution of Inhaled Gold Nanoparticles in Rats with Interspecies Extrapolation to Humans. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2022, 457, 116322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutumova, E.O.; Akberdin, I.R.; Egorova, V.S.; Kolesova, E.P.; Parodi, A.; Pokrovsky, V.S.; Zamyatnin, A.A., Jr.; Kolpakov, F.A. Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model for Predicting the Biodistribution of Albumin Nanoparticles after Induction and Recovery from Acute Lung Injury. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, L.M.; MacCalman, L.; Haber, L.T.; Kuempel, E.D.; Tran, C.L. Bayesian Evaluation of a Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Model of Long-Term Kinetics of Metal Nanoparticles in Rats. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 73, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlander, U.; Li, D.; Jolliet, O.; Emond, C.; Johanson, G. Toward a General Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Model for Intravenously Injected Nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 625–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yuan, M.; Madison, C.A.; Eitan, S.; Wang, Y. Blood-Brain Barrier Crossing Using Magnetic Stimulated Nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2022, 345, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parhiz, H.; Shuvaev, V.V.; Li, Q.; Papp, T.E.; Akyianu, A.A.; Shi, R.; Yadegari, A.; Shahnawaz, H.; Semple, S.C.; Mui, B.L.; et al. Physiologically Based Modeling of LNP-Mediated Delivery of mRNA in the Vascular System. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2024, 35, 102175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalishwaralal, K.; Azeez Nazeer, A.; Induja, D.K.; Keerthana, C.K.; Shifana, S.C.; Anto, R.J. Enhanced Extracellular Vesicles Mediated Uttroside B (Utt-B) Delivery to Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell: Pharmacokinetics Based on PBPK Modelling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 703, 149648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.P.; Delp, M.D.; Lindstedt, S.L.; Rhomberg, L.R.; Beliles, R.P. Physiological Parameter Values for Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Models. Toxicol. Ind. Health 1997, 13, 407–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aborig, M.; Malik, P.R.V.; Nambiar, S.; Chelle, P.; Darko, J.; Mutsaers, A.; Edginton, A.N.; Fleck, A.; Osei, E.; Wettig, S. Biodistribution and Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling of Gold Nanoparticles in Mice with Interspecies Extrapolation. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosens, I.; Minnema, J.; Boere, A.J.F.; Duistermaat, E.; Fokkens, P.; Vidmar, J.; Löschner, K.; Bokkers, B.; Costa, A.L.; Peters, R.J.B.; et al. Biodistribution of Cerium Dioxide and Titanium Dioxide Nanomaterials in Rats after Single and Repeated Inhalation Exposures. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2024, 21, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, L.; Jia, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y. The Construction and Application of Physiologically Based Toxicokinetic Models for Acrylamide, Glycidamide and Their Biomarkers in Rats and Humans. Chemosphere 2022, 292, 133458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Niu, Z. Health Risk Assessment of Trihalomethanes Mixtures from Daily Water-Related Activities via Multi-Pathway Exposure Based on PBPK Model. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 163, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Duan, X.; Liu, A. Effects of Inhalation Frequency on Inhalation/Exposure Dose of Hazardous Nanoparticles and Toxic Gases during Cigarette Smoking. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 240, 113709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golasik, M.; Herman, M.; Olbert, M.; Librowski, T.; Szklarzewicz, J.; Piekoszewski, W. Toxicokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Titanium in Ionic Form after Intravenous and Oral Administration. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 247, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento-González, A.; Encinar, J.R.; Marchante-Gayón, J.M.; Sanz-Medel, A. Titanium Levels in the Organs and Blood of Rats with a Titanium Implant, in the Absence of Wear, as Determined by Double-Focusing ICP-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 393, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, A.T.; Herity, L.B.; Kornblum, Z.A.; Madden, A.J.; Gabizon, A.; Kabanov, A.V.; Ajamie, R.T.; Bender, D.M.; Kulanthaivel, P.; Sanchez-Felix, M.V.; et al. Pharmacokinetic and Screening Studies of the Interaction between Mononuclear Phagocyte System and Nanoparticle Formulations and Colloid Forming Drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 526, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreyling, W.G.; Holzwarth, U.; Haberl, N.; Kozempel, J.; Hirn, S.; Wenk, A.; Schleh, C.; Schäffler, M.; Lipka, J.; Semmler-Behnke, M.; et al. Quantitative Biokinetics of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles after Intravenous Injection in Rats: Part 1. Nanotoxicology 2017, 11, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wang, H.; Grice, J.E.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Xu, Z.P.; Roberts, M.S. Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model for Long-Circulating Inorganic Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelclova, D.; Zdimal, V.; Kacer, P.; Fenclova, Z.; Vlckova, S.; Syslova, K.; Navratil, T.; Schwarz, J.; Zikova, N.; Barosova, H.; et al. Oxidative Stress Markers Are Elevated in Exhaled Breath Condensate of Workers Exposed to Nanoparticles during Iron Oxide Pigment Production. J. Breath Res. 2016, 10, 016004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLeod, L.; Bharadwaj, L.; Epp, T.Y.; Waldner, C.L. Ecological Analysis of Associations between Groundwater Quality and Hypertension and Cardiovascular Disease in Rural Saskatchewan, Canada Using Bayesian Hierarchical Models and Administrative Health Data. Environ. Res. 2018, 167, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.Q.; Tomenson, J.A.; Warheit, D.B.; Fryzek, J.P.; Golden, A.P.; Ellis, E.D. A Review and Meta-Analysis of Occupational Titanium Dioxide Exposure and Lung Cancer Mortality. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2018, 60, e356–e367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Organ | Parameter | Description | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whole body | QC | Total blood flow | 6.0345 | L/h |
| BW | Total body weight | 0.263 | kg | |
| TV | Total body volume | 0.263 | kg | |
| Liver | Vli | Liver volume | 0.00983 | L |
| Vlicab | Liver capillary volume | 0.00023 | L | |
| Vlitis | Liver tissue volume | 0.0096 | L | |
| Qli | Liver blood flow | 1.05 | L/h | |
| Lung | Vlu | Lung volume | 0.00167 | L |
| Vlucab | Lung capillary volume | 0.00047 | L | |
| Vlutis | Lung tissue volume | 0.0012 | L | |
| Qlu | Lung blood flow | 6.0345 | L/h | |
| Kidney | Vki | Kidney volume | 0.00221 | L |
| Vkicab | Kidney capillary volume | 0.00031 | L | |
| Vkitis | Kidney tissue volume | 0.0019 | L | |
| Qki | Kidney blood flow | 0.8509 | L/h | |
| Spleen | Vspl | Spleen volume | 0.00065 | L |
| Vsplcab | Spleen capillary volume | 0.00012 | L | |
| Vspltis | Spleen tissue volume | 0.00053 | L | |
| Qspl | Spleen blood flow | 0.0736 | L/h | |
| Rest of body | Vrob | Rest of body volume | 0.2613 | L |
| Vrobcab | Rest of body capillary volume | 0.0102 | L | |
| Vrobtis | Rest of body tissue volume | 0.2511 | L | |
| Qrob | Rest of body blood flow | 4.06 | L/h | |
| Venous blood | Vven | Venous blood volume | 0.0106 | L |
| Arterial blood | Vart | Arterial blood volume | 0.0025 | L |
| Organ | Parameter | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liver | Xli | 489.2806 | dimensionless |
| Pli | 47.4101 | dimensionless | |
| Klimax | 263.8254 | 1/h | |
| Kli50 | 0.3592 | h | |
| Kliout | 19.4813 | 1/h | |
| Klipcs_feces | 0.0884 | 1/h | |
| Spleen | Xspl | 130.1283 | dimensionless |
| Pspl | 150 | dimensionless | |
| Ksplmax | 240 | 1/h | |
| Kspl50 | 1000 | h | |
| Ksplout | 0.9507 | 1/h | |
| Kidney | Xki | 0.0199 | dimensionless |
| Pki | 209 | dimensionless | |
| Kkimax | 0.9929 | 1/h | |
| Kki50 | 13.6432 | h | |
| Kkiout | 20 | 1/h | |
| Kkid_urine | 0.00005 | 1/h | |
| Rob | Xrob | 0.0001 | dimensionless |
| Prob | 10.8944 | dimensionless | |
| Krobmax | 0.000001 | 1/h | |
| Krob50 | 0.008 | h | |
| Krobout | 0.00005 | 1/h | |
| Tracheobronchial | Ktrach_feces | 0.3099 | 1/h |
| alveoli | Kalvpcs_trach | 8.3465 | 1/h |
| Kalv_inter | 0.353 | 1/h | |
| Kinter_alv | 0.09 | 1/h | |
| Kalvout | 0.0109 | 1/h | |
| Kalv50 | 202.1309 | h | |
| Kalvmax | 0.000004 | 1/h | |
| Lung | Kinter_max | 0.000050504 | 1/h |
| Kinter50 | 628.416 | h | |
| Kinterout | 0.0672 | 1/h | |
| Plu | 30359 | dimensionless | |
| Xlu | 49.1745 | dimensionless | |
| Upper airway | Kupp_robtis | 0.05 | 1/h |
| Kupp_feces | 0.008 | 1/h |
| Parameter | Liver (t1/2, h) | Kidney (t1/2, h) | Spleen (t1/2, h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2-NPs | 452.8 | 179.6 | 350.7 |
| Ti iron | 1.9 a | 3.3 a | 2.1 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Wan, B.; Cui, X. Prediction of the Quantitative Biodistribution of Inhaled Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Using the Physiologically Based Toxicokinetic Modelling Method. Toxics 2025, 13, 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100858
Wang J, Liu Z, Wan B, Cui X. Prediction of the Quantitative Biodistribution of Inhaled Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Using the Physiologically Based Toxicokinetic Modelling Method. Toxics. 2025; 13(10):858. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100858
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jintao, Zhangyu Liu, Bin Wan, and Xinguang Cui. 2025. "Prediction of the Quantitative Biodistribution of Inhaled Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Using the Physiologically Based Toxicokinetic Modelling Method" Toxics 13, no. 10: 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100858
APA StyleWang, J., Liu, Z., Wan, B., & Cui, X. (2025). Prediction of the Quantitative Biodistribution of Inhaled Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Using the Physiologically Based Toxicokinetic Modelling Method. Toxics, 13(10), 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100858






