Cadmium Exposure: Mechanisms and Pathways of Toxicity and Implications for Human Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion (ADME) Process of Cadmium in the Body
3. Oxidative Stress Caused by Cadmium
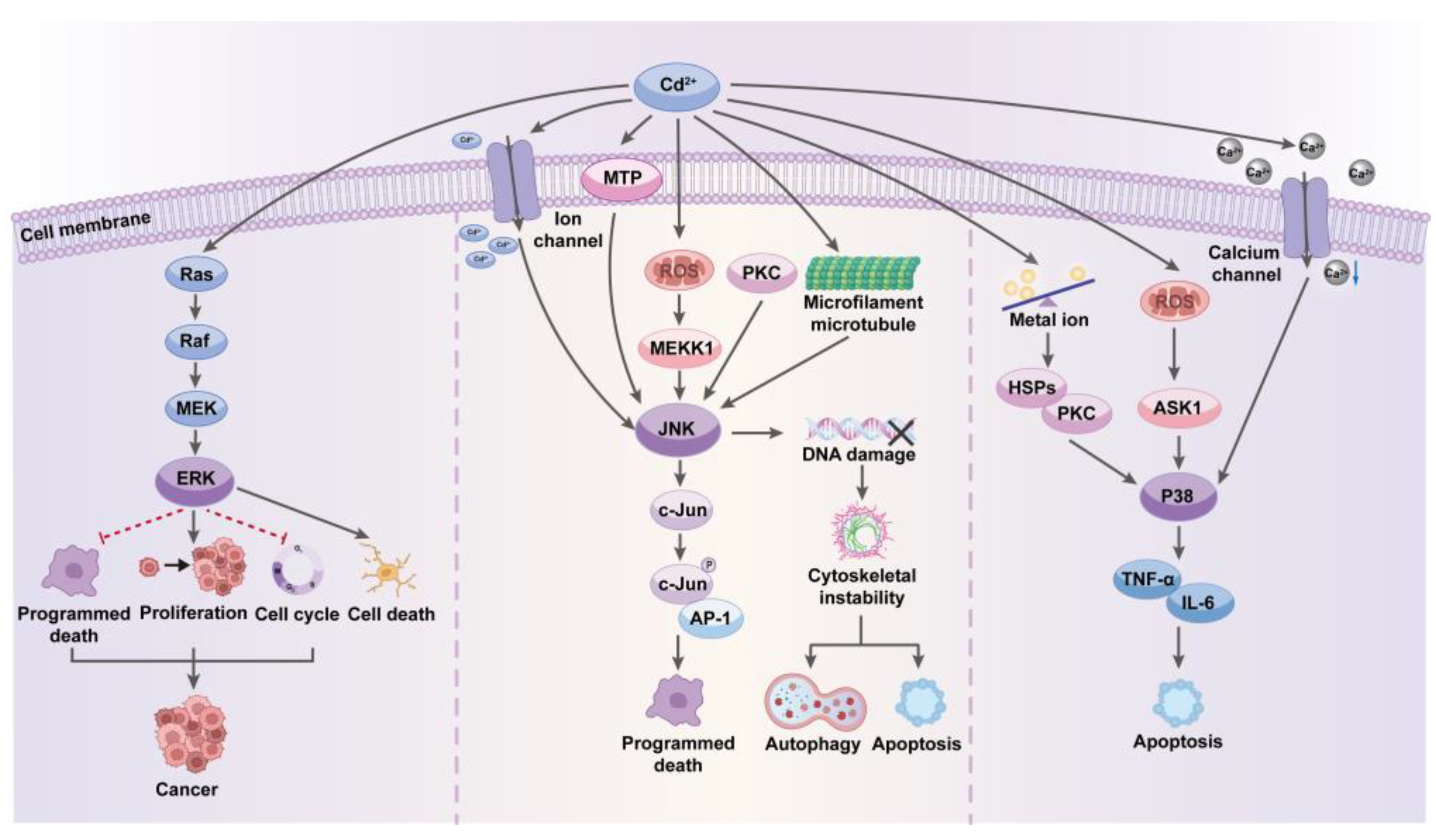
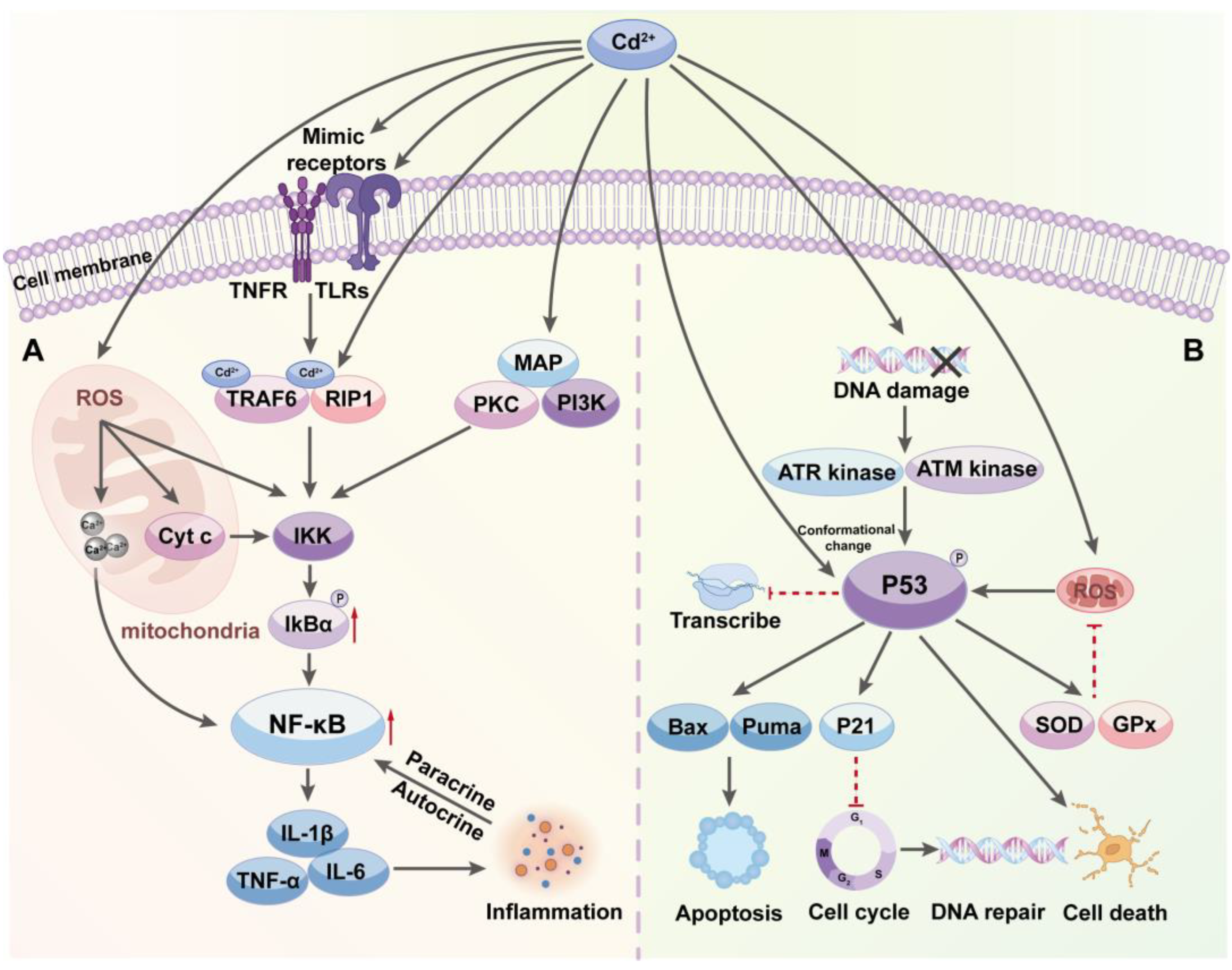
4. Cadmium Impact on Signal Transduction Pathways
5. Cadmium-Induced Epigenetic Alterations
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hayat, M.T.; Nauman, M.; Nazir, N.; Ali, S.; Bangash, N. Environmental hazards of cadmium: Past, present, and future. In Cadmium Toxicity and Tolerance in Plants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 163–183. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Chen, Z.; Song, W.; Hong, D.; Huang, L.; Li, Y. A review on cadmium exposure in the population and intervention strategies against cadmium toxicity. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawrot, T.S.; Staessen, J.A.; Roels, H.A.; Munters, E.; Cuypers, A.; Richart, T.; Ruttens, A.; Smeets, K.; Clijsters, H.; Vangronsveld, J. Cadmium exposure in the population: From health risks to strategies of prevention. Biometals 2010, 23, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elinder, C.-G. Cadmium: Uses, occurrence, and intake. In Cadmium and Health; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 23–64. [Google Scholar]
- Rietra, R.; Mol, G.; Rietjens, I.; Romkens, P. Cadmium in Soil, Crops and Resultant Dietary Exposure; Wageningen Environmental Research: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shakya, P.R.; Shrestha, P.; Tamrakar, C.S.; Bhattarai, P.K. Studies and determination of heavy metals in waste tyres and their impacts on the environment. Pak. J. Anal. Environ. Chem. 2006, 7, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Lee, H.J.; Hwang, J.-Y.; Ha, E.-H.; Park, H.; Ha, M.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, Y.-C.; Chang, N. Blood cadmium concentrations of male cigarette smokers are inversely associated with fruit consumption. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satarug, S.; Haswell-Elkins, M.R.; Moore, M.R. Safe levels of cadmium intake to prevent renal toxicity in human subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2000, 84, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charkiewicz, A.E.; Omeljaniuk, W.J.; Nowak, K.; Garley, M.; Nikliński, J. Cadmium Toxicity and Health Effects—A Brief Summary. Molecules 2023, 28, 6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, M.; Wilson, A.; Rajan, S.; Jonah, M. Biochemical pathways in cadmium toxicity. Mol. Biol. Toxicol. Met. 2000, 34–74. [Google Scholar]
- Sabolić, I.; Breljak, D.; Škarica, M.; Herak-Kramberger, C.M. Role of metallothionein in cadmium traffic and toxicity in kidneys and other mammalian organs. Biometals 2010, 23, 897–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomza-Marciniak, A.; Pilarczyk, B.; Marciniak, A.; Udała, J.; Bąkowska, M.; Pilarczyk, R. Cadmium, Cd. In Mammals and Birds as Bioindicators of Trace Element Contaminations in Terrestrial Environments: An Ecotoxicological Assessment of the Northern Hemisphere; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 483–532. [Google Scholar]
- Prozialeck, W.C.; Edwards, J.R. Early biomarkers of cadmium exposure and nephrotoxicity. Biometals 2010, 23, 793–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhardsson, L.; Skerfving, S. Concepts on biological markers and biomonitoring for metal toxicity. In Toxicology of Metals, Volume I; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; pp. 81–107. [Google Scholar]
- Bernard, A. Renal dysfunction induced by cadmium: Biomarkers of critical effects. Biometals 2004, 17, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, N.Y.; Bae, H.S.; Yu, S.D.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, H.; Choi, B.S.; Yu, I.J. Evaluation of factors associated with cadmium exposure and kidney function in the general population. Environ. Toxicol. 2013, 28, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noonan, C.W.; Sarasua, S.M.; Campagna, D.; Kathman, S.J.; Lybarger, J.A.; Mueller, P.W. Effects of exposure to low levels of environmental cadmium on renal biomarkers. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niede, R.; Benbi, D.K. Integrated review of the nexus between toxic elements in the environment and human health. AIMS Public Health 2022, 9, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lushchak, V.I. Free radicals, reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress and its classification. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 224, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercal, N.; Gurer-Orhan, H.; Aykin-Burns, N. Toxic metals and oxidative stress part I: Mechanisms involved in metal-induced oxidative damage. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2001, 1, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Qu, W.; Kadiiska, M.B. Role of oxidative stress in cadmium toxicity and carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nies, D.H.; Grass, G. Transition metal homeostasis. EcoSal Plus 2009, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schieber, M.; Chandel, N.S. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R453–R462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.T.; Kadhim, S.M.; Jassimand, A.; Abbas, S. Free radicals and human health. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. 2015, 4, 218–223. [Google Scholar]
- Branca, J.J.; Fiorillo, C.; Carrino, D.; Paternostro, F.; Taddei, N.; Gulisano, M.; Pacini, A.; Becatti, M. Cadmium-induced oxidative stress: Focus on the central nervous system. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobe, G.; Crane, D. Mitochondria, reactive oxygen species and cadmium toxicity in the kidney. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 198, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Cruz, E.Y.; Amador-Martínez, I.; Aranda-Rivera, A.K.; Cruz-Gregorio, A.; Chaverri, J.P. Renal damage induced by cadmium and its possible therapy by mitochondrial transplantation. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 361, 109961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossy-Wetzel, E.; Green, D.R. Caspases induce cytochrome c release from mitochondria by activating cytosolic factors. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 17484–17490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambeth, J.D. NOX enzymes and the biology of reactive oxygen. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, R.; Geng, X.; Li, F.; Ding, Y. NOX activation by subunit interaction and underlying mechanisms in disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.C.; Al-Naemi, H.A. Cadmium Toxicity: Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Tissue Injury. Occup. Dis. Environ. Med. 2019, 4, 144–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein-Khannazer, N.; Azizi, G.; Eslami, S.; Alhassan Mohammed, H.; Fayyaz, F.; Hosseinzadeh, R.; Usman, A.B.; Kamali, A.N.; Mohammadi, H.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F. The effects of cadmium exposure in the induction of inflammation. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2020, 42, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, M.; Nichols, L.; Dave, A.A.; Pittman, E.H.; Cheek, J.P.; Caroland, A.J.; Lotwala, P.; Drummond, J.; Bridges, C.C. Molecular Mechanisms of Cellular Injury and Role of Toxic Heavy Metals in Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, A.; Muñoz, M.F.; Argüelles, S. Lipid peroxidation: Production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 360438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadtman, E.; Levine, R. Free radical-mediated oxidation of free amino acids and amino acid residues in proteins. Amino Acids 2003, 25, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; O, W.; Li, W.; Jiang, Z.-G.; Ghanbari, H.A. Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 24438–24475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakem, R. DNA-damage repair; the good, the bad, and the ugly. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 589–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Simpson, E.R.; Brown, K.A. p53: Protection against tumor growth beyond effects on cell cycle and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 5001–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, S. Reactive oxygen species and cellular defense system. Free. Radic. Hum. Health Dis. 2015, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Sun, J.; Wu, B.; Yuan, Y.; Gu, J.; Bian, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z. Effects of cadmium and/or lead on autophagy and liver injury in rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 198, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Cruz, E.Y.; Arancibia-Hernández, Y.L.; Loyola-Mondragón, D.Y.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J. Oxidative stress and its role in Cd-induced epigenetic modifications: Use of antioxidants as a possible preventive strategy. Oxygen 2022, 2, 177–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakis, J.M.; Avruch, J. Mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 807–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waisberg, M.; Joseph, P.; Hale, B.; Beyersmann, D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of cadmium carcinogenesis. Toxicology 2003, 192, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeton, D.M.; Liu, Y. Multiple roles of cadmium in cell death and survival. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 188, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.; Steelman, L.S.; Shelton, J.G.; Lee, J.T.; Navolanic, P.M.; Blalock, W.L.; Franklin, R.; McCubrey, J.A. Regulation of cell cycle progression and apoptosis by the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2003, 22, 469–480. [Google Scholar]
- Cagnol, S.; Chambard, J.C. ERK and cell death: Mechanisms of ERK-induced cell death–apoptosis, autophagy and senescence. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Su, Q.; Yue, C.; Zou, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, H.; Song, R.; Liu, Z. The effect of oxidative stress-induced autophagy by cadmium exposure in kidney, liver, and bone damage, and neurotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanke, B.W.; Boudreau, K.; Rubie, E.; Winnett, E.; Tibbles, L.A.; Zon, L.; Kyriakis, J.; Liu, F.-F.; Woodgett, J.R. The stress-activated protein kinase pathway mediates cell death following injury induced by cis-platinum, UV irradiation or heat. Curr. Biol. 1996, 6, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martindale, J.L.; Holbrook, N.J. Cellular response to oxidative stress: Signaling for suicide and survival. J. Cell. Physiol. 2002, 192, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thévenod, F. Cadmium and cellular signaling cascades: To be or not to be? Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matés, J.M.; Segura, J.A.; Alonso, F.J.; Márquez, J. Intracellular redox status and oxidative stress: Implications for cell proliferation, apoptosis, and carcinogenesis. Arch. Toxicol. 2008, 82, 273–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, S.-M.; Wang, I.-C.; Yang, J.-L. Roles of JNK, p38 and ERK mitogen-activated protein kinases in the growth inhibition and apoptosis induced by cadmium. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoit, B.; Baillet, A.; Poüs, C. Cytoskeleton and associated proteins: Pleiotropic JNK substrates and regulators. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, J.; Cheng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Xu, D.; Kapron, C.M.; Liu, J. Low dose cadmium inhibits proliferation of human renal mesangial cells via activation of the JNK pathway. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Ravindran, G.; Krishnamurthy, V. A brief review on the effect of cadmium toxicity: From cellular to organ level. Int. J. Biotechnol. Res. 2013, 3, 17–36. [Google Scholar]
- Kefaloyianni, E.; Gourgou, E.; Ferle, V.; Kotsakis, E.; Gaitanaki, C.; Beis, I. Acute thermal stress and various heavy metals induce tissue-specific pro-or anti-apoptotic events via the p38-MAPK signal transduction pathway in Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lam.). J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 4427–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemmiche, S. Oxidative signaling response to cadmium exposure. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 156, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valko, M.; Rhodes, C.; Moncol, J.; Izakovic, M.; Mazur, M. Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2006, 160, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Tareq, A.M.; Emran, T.B.; Nainu, F.; Khusro, A.; Idris, A.M.; Khandaker, M.U.; Osman, H.; Alhumaydhi, F.A. Impact of heavy metals on the environment and human health: Novel therapeutic insights to counter the toxicity. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszowski, T.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I.; Gutowska, I.; Chlubek, D. Pro-inflammatory properties of cadmium. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2012, 59, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Andersson, R. NF-κB activation and inhibition: A review. Shock 2002, 18, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thévenod, F.; Lee, W.-K. Cadmium and cellular signaling cascades: Interactions between cell death and survival pathways. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1743–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepand, M.-R.; Aliomrani, M.; Hasani-Nourian, Y.; Khalhori, M.-R.; Farzaei, M.-H.; Sanadgol, N. Mechanisms and pathogenesis underlying environmental chemical-induced necroptosis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 37488–37501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Đukić-Ćosić, D.; Baralić, K.; Javorac, D.; Djordjevic, A.B.; Bulat, Z. An overview of molecular mechanisms in cadmium toxicity. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2020, 19, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, M.; Fernandes, E. Zinc, cadmium and nickel increase the activation of NF-κB and the release of cytokines from THP-1 monocytic cells. Metallomics 2011, 3, 1238–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijit, M.; Caracciolo, V.; Melillo, A.; Amicarelli, F.; Giordano, A. Role of p53 in the regulation of cellular senescence. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méplan, C.; Mann, K.; Hainaut, P. Cadmium induces conformational modifications of wild-type p53 and suppresses p53 response to DNA damage in cultured cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 31663–31670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruiswijk, F.; Labuschagne, C.F.; Vousden, K.H. p53 in survival, death and metabolic health: A lifeguard with a licence to kill. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos, W.P.; Kaina, B. DNA damage-induced cell death: From specific DNA lesions to the DNA damage response and apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2013, 332, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipič, M. Mechanisms of cadmium induced genomic instability. Mutat. Res./Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2012, 733, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, J.D.; Castro, R.E.; Steer, C.J.; Rodrigues, C.M. p53 and the regulation of hepatocyte apoptosis: Implications for disease pathogenesis. Trends Mol. Med. 2009, 15, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, W.K.; Paules, R.S. DNA damage and cell cycle checkpoints. FASEB J. 1996, 10, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzuto, R.; Giorgi, C.; Romagnoli, A.; Pinton, P. Ca2+ signaling, mitochondria and cell death. Curr. Mol. Med. 2008, 8, 119–130. [Google Scholar]
- Gerzen, O.P.; Votinova, V.O.; Potoskueva, I.K.; Tzybina, A.E.; Nikitina, L.V. Direct Effects of Toxic Divalent Cations on Contractile Proteins with Implications for the Heart: Unraveling Mechanisms of Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Thijs, L.; Cauwenberghs, N.; Wei, F.F.; Jacobs, L.; Luttun, A.; Verhamme, P.; Kuznetsova, T.; Nawrot, T.S. Left ventricular structure and function in relation to environmental exposure to lead and cadmium. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e004692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangheluwe, P.; Sepulveda, M.R.; Missiaen, L.; Raeymaekers, L.; Wuytack, F.; Vanoevelen, J. Intracellular Ca2+-and Mn2+-transport ATPases. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4733–4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, P.; Liu, N.; Wang, Q.; Luo, J.; Wang, L. Cadmium induces apoptosis in freshwater crab Sinopotamon henanense through activating calcium signal transduction pathway. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xu, Y.; Xu, B.; Guo, M.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Ma, H.; Chen, Z.; Luo, Y.; Huang, S. CaMKII is involved in cadmium activation of MAPK and mTOR pathways leading to neuronal cell death. J. Neurochem. 2011, 119, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Xu, C.; Ran, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Gu, J.; Liu, X.; Bian, J.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, Z. CaMKII mediates cadmium induced apoptosis in rat primary osteoblasts through MAPK activation and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Toxicology 2018, 406, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Shao, C.; Tan, Y.; Cai, L. Cadmium and its epigenetic effects. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venza, M.; Visalli, M.; Biondo, C.; Oteri, R.; Agliano, F.; Morabito, S.; Caruso, G.; Caffo, M.; Teti, D.; Venza, I. Epigenetic effects of cadmium in cancer: Focus on melanoma. Curr. Genom. 2014, 15, 420–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimta, A.-A.; Schitcu, V.; Gurzau, E.; Stavaru, C.; Manda, G.; Szedlacsek, S.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Biological and molecular modifications induced by cadmium and arsenic during breast and prostate cancer development. Environ. Res. 2019, 178, 108700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; Freeman, J.L.; Xie, J.; Zhao, H. The Role of Dynamic Epigenetic Changes in Modulating Homeostasis after Exposure to Low-dose Environmental Chemicals. Genom. Epigenom. Biomark. Toxicol. Dis. Clin. Ther. Actions 2022, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Lauria, G.; Carocci, A.; Catalano, A. The effects of cadmium toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, D.R.; Taalab, Y.M.; Heinze, S.; Tariba Lovaković, B.; Pizent, A.; Renieri, E.; Tsatsakis, A.; Farooqi, A.A.; Javorac, D.; Andjelkovic, M. Toxic-metal-induced alteration in miRNA expression profile as a proposed mechanism for disease development. Cells 2020, 9, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Pacheco, M.; Hidalgo-Miranda, A.; Romero-Córdoba, S.; Valverde, M.; Rojas, E. MRNA and miRNA expression patterns associated to pathways linked to metal mixture health effects. Gene 2014, 533, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anetor, J.I. Rising environmental cadmium levels in developing countries: Threat to genome stability and health. Niger. J. Physiol. Sci. 2012, 27, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, A. Cadmium toxicity: Effects on human reproduction and fertility. Rev. Environ. Health 2019, 34, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, C.; Galdiero, M.; Pivonello, C.; Salzano, C.; Gianfrilli, D.; Piscitelli, P.; Lenzi, A.; Colao, A.; Pivonello, R. The environment and male reproduction: The effect of cadmium exposure on reproductive function and its implication in fertility. Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 73, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, F.; Zheng, W. Cadmium Exposure: Mechanisms and Pathways of Toxicity and Implications for Human Health. Toxics 2024, 12, 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12060388
Qu F, Zheng W. Cadmium Exposure: Mechanisms and Pathways of Toxicity and Implications for Human Health. Toxics. 2024; 12(6):388. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12060388
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Fei, and Weiwei Zheng. 2024. "Cadmium Exposure: Mechanisms and Pathways of Toxicity and Implications for Human Health" Toxics 12, no. 6: 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12060388
APA StyleQu, F., & Zheng, W. (2024). Cadmium Exposure: Mechanisms and Pathways of Toxicity and Implications for Human Health. Toxics, 12(6), 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12060388







