Battle of the Bites: The Effect of Sewage Effluent Exposure on Mosquitofish Biocontrol of Mosquitoes in Residential Louisiana
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Collection
2.2. Water Collection
2.3. Body Condition
2.4. Effluent-Contaminated Water Toxicity
2.5. Prey Capture Behavior
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Site Comparison
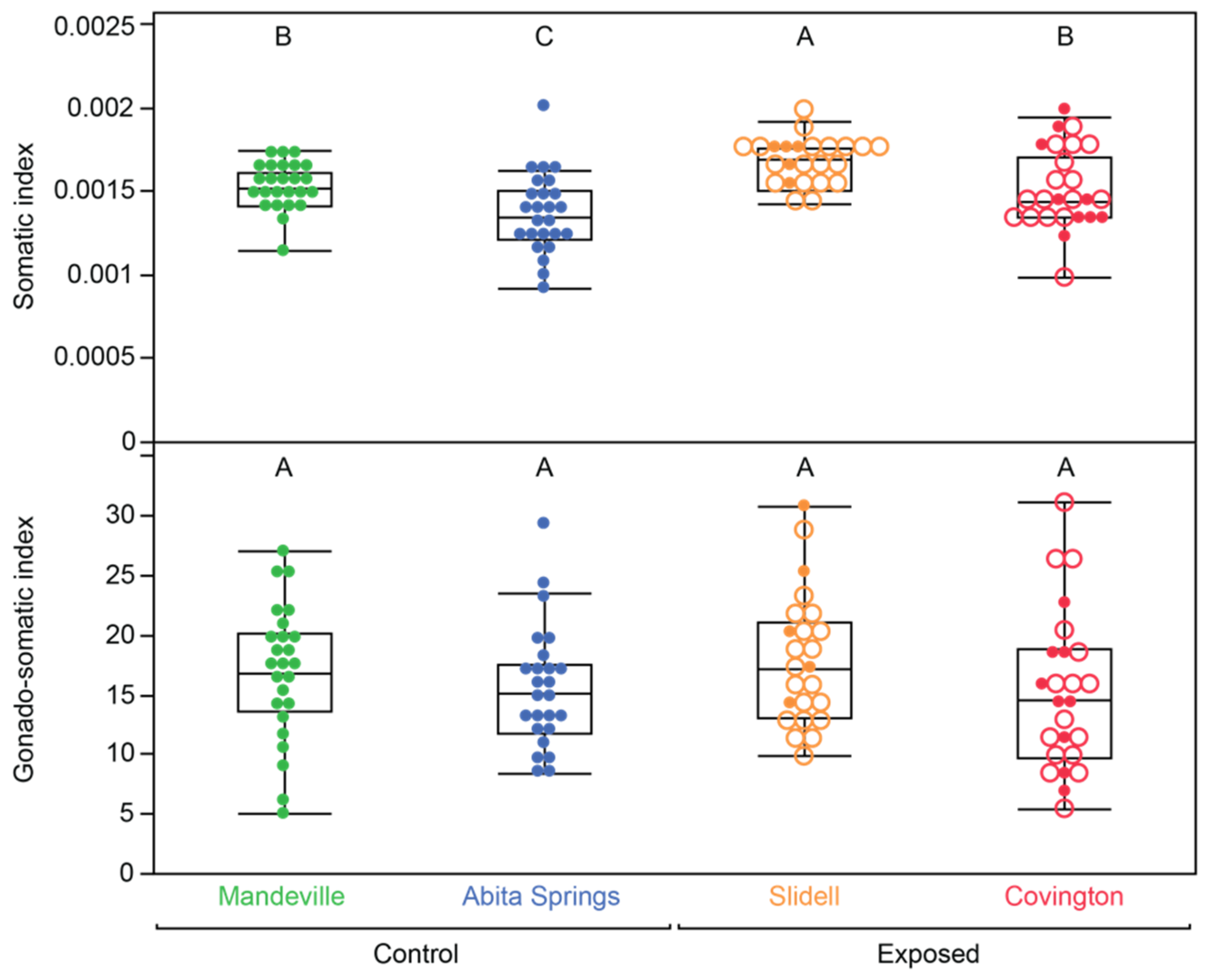
3.2. Body Condition
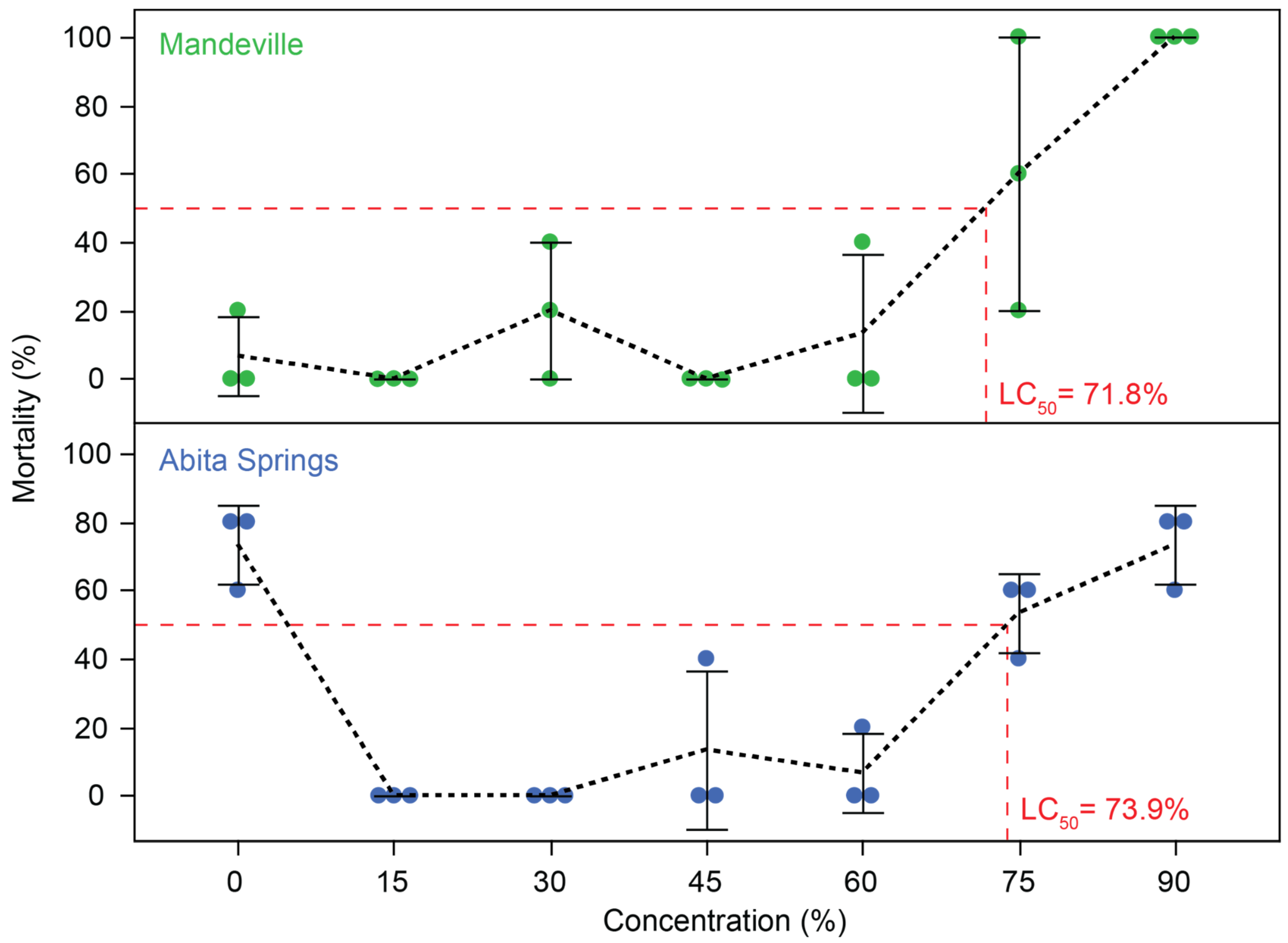
3.3. Effluent-Contaminated Water Toxicity
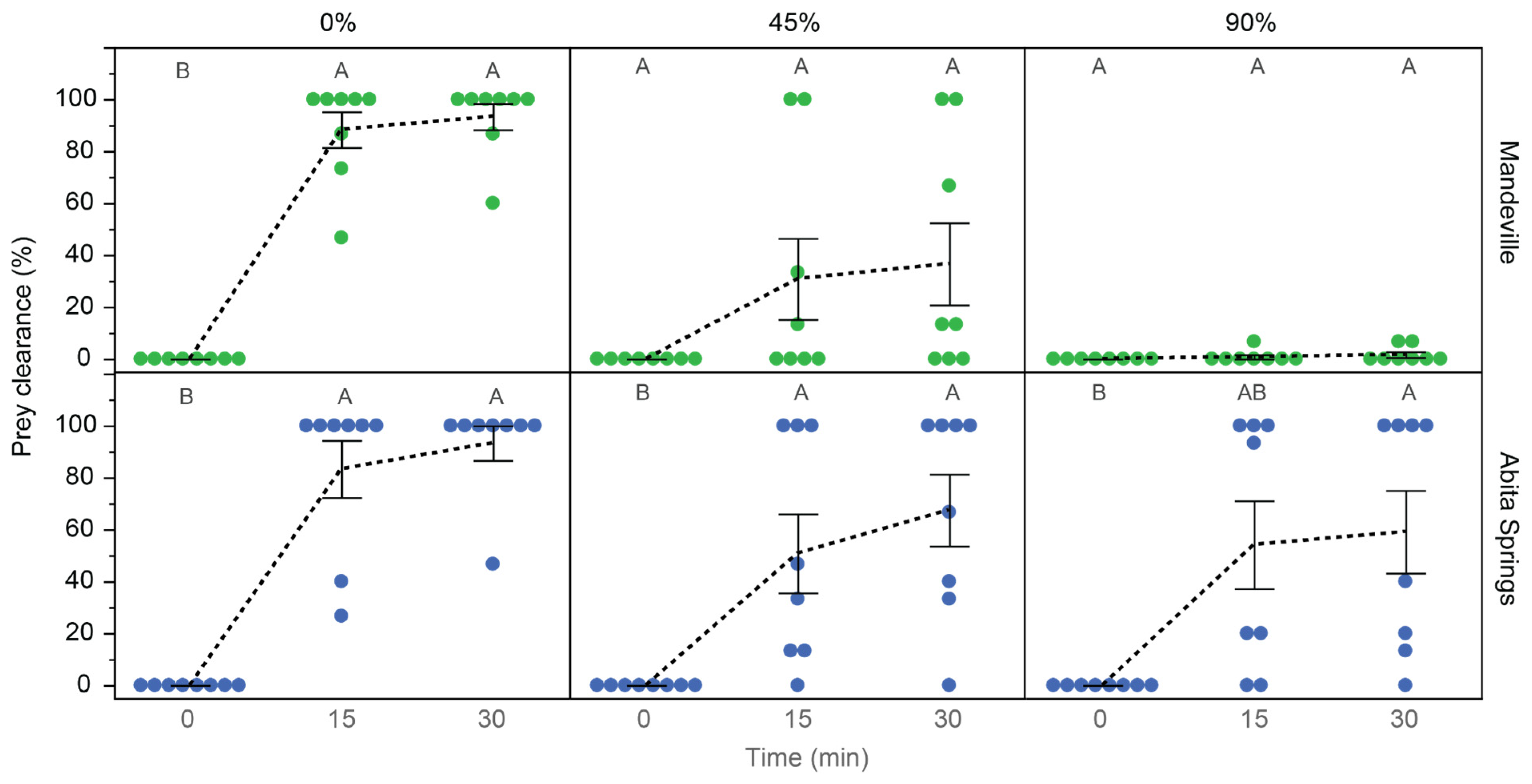
3.4. Prey Capture Behavior
4. Discussion
4.1. Effluent-Contaminated Water Acute Toxicity
4.2. Effluent-Contaminated Water Chronic Toxicity
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhattacharya, S.; Basu, P. The Southern House Mosquito, Culex Quinquefasciatus: Profile of a Smart Vector. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2016, 4, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Bermond, C.D. How Sewage Pollution Affects Distribution and Life History Traits of the Southern House Mosquito, Culex Quinquefasciatus. Master’s Thesis, The University of Southern Mississippi, Hattiesburg, MS, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chaves, L.F.; Keogh, C.L.; Nguyen, A.M.; Decker, G.M.; Vazquez-Prokopec, G.M.; Kitron, U.D. Combined Sewage Overflow Accelerates Immature Development and Increases Body Size in the Urban Mosquito Culex Quinquefasciatus. J. Appl. Entomol. 2011, 135, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calhoun, L.M.; Avery, M.; Jones, L.; Gunarto, K.; King, R.; Roberts, J.; Burkot, T.R. Combined Sewage Overflows (CSO) Are Major Urban Breeding Sites for Culex Quinquefasciatus in Atlanta, Georgia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 77, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krol, L.; Gorsich, E.E.; Hunting, E.R.; Govender, D.; van Bodegom, P.M.; Schrama, M. Eutrophication Governs Predator-Prey Interactions and Temperature Effects in Aedes Aegypti Populations. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jesús Crespo, R.; Harrison, M.; Rogers, R.; Vaeth, R. Mosquito Vector Production across Socio-Economic Divides in Baton Rouge, Louisiana. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. EPA No. 832-B-05-001 Handbook for Managing Onsite and Clustered (Decentralized) Wastewater Treatment Systems. 2005. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-06/documents/onsite_handbook.pdf (accessed on 3 October 2023).
- Vazquez-Prokopec, G.M.; Vanden, E.J.L.; Kelly, R.; Mead, D.G.; Kolhe, P.; Howgate, J.; Kitron, U.; Burkot, T.R. The Risk of West Nile Virus Infection Is Associated with Combined Sewer Overflow Streams in Urban Atlanta, Georgia, USA. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1382–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, R.; Barrera, R.; Lewis, M.; Kluchinsky, T.; Claborn, D. Septic Tanks as Larval Habitats for the Mosquitoes Aedes Aegypti and Culex Quinquefasciatus in Playa-Playita, Puerto Rico. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2010, 24, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, M. Evaluating the Impact of Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems on Watershed Contamination, Choccolocco Creek Watershed, Alabama. Master’s Thesis, Auburn University, Auburn, AL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Irion, K.S. A Deal with the Devil: How Politics, Expediency and Economics Resulted in the Proliferation of Onsite Wastewater Systems for Subdivisions in Louisiana and the Effect That the Adoption of TMDLS Is Having on Wastewater Treatment; St. Tammany Parish Mosquito Abatement Department: Slidell, LA, USA, 2016; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Types of Septic Systems. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/septic/types-septic-systems (accessed on 3 October 2023).
- Nordlie, F.G. Physicochemical Environments and Tolerances of Cyprinodontoid Fishes Found in Estuaries and Salt Marshes of Eastern North America. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2006, 16, 51–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, W.E.; Henke, J.A.; Why, A.M. Gambusia affinis (Baird and Girard) and Gambusia holbrooki Girard (Mosquitofish). In A Handbook of Global Freshwater Invasive Species; Routledge: London, UK, 2012; pp. 261–273. [Google Scholar]
- St. Tammany Parish Mosquito Abatement Department. 2019 Annual Report; St. Tammany Parish Mosquito Abatement Department: Slidell, LA, USA, 2019; p. 8.
- Fryxell, D.C.; Arnett, H.A.; Apgar, T.M.; Kinnison, M.T.; Palkovacs, E.P. Sex Ratio Variation Shapes the Ecological Effects of a Globally Introduced Freshwater Fish. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20151970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, T. The Rate of Growth of Fishes. In 22nd Annual Report of the Fishery Board of Scotland; Edinburgh: London, UK, 1904; Volume 3, pp. 141–241. [Google Scholar]
- Heincke, F. Bericht über die Untersuchungen der Biologischen Anstalt auf Helgoland zur Naturgeschichte der Nutzfische. Die Beteil. Dtschl. Der Int. Meeresforsch. 1908, 4/5, 67–155. [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone, J. Report on Measurements of Plaice Made during the Year 1911. Trans. Liverp. Biol. Soc. 1912, 26, 85–102. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, R.D.; Valencia, A.H.; Geffen, A.J. The Origin of Fulton’s Condition Factor—Setting the Record Straight. Fisheries 2006, 31, 236–238. [Google Scholar]
- Ragheb, E. Length-Weight Relationship and Well-Being Factors of 33 Fish Species Caught by Gillnets from the Egyptian Mediterranean Waters off Alexandria. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2023, 49, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricker, W.E. Computation and Interpretation of Biological Statistics of Fish Populations. Fish. Res. Board Can. Bull. 1975, 191, 1–382. [Google Scholar]
- Alcaraz, C.; García-Berthou, E. Life History Variation of Invasive Mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki) along a Salinity Gradient. Biol. Conserv. 2007, 139, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Methods for Measuring the Acute Toxicity of Effluents and Receiving Waters to Freshwater and Marine Organisms, 5th ed.; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- Watson, R.J. The Effects of an Artificially Elevated Thermal Environment and Seasonal Acclimatization on the Thermal Tolerance of the Western Mosquitofish, Gambusia affinis; The University of Texas at Arlington: Arlington, TX, USA, 2008; ISBN 0-549-70788-3. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, D.K. What Is the Proper Way to Apply the Multiple Comparison Test? Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2018, 71, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapointe, B.E.; Herren, L.W.; Paule, A.L. Septic Systems Contribute to Nutrient Pollution and Harmful Algal Blooms in the St. Lucie Estuary, Southeast Florida, USA. Harmful Algae 2017, 70, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, J.D.; Campbell, J. Investigating Reactive Nitrogen Sources That Stimulate Algal Blooms in Baffin Bay; Corpus Christi: Coastal Bend Bays and Estuaries Program: Corpus Christi, TX, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick, S.W.; Gerberich, J.C.; Kronenberger, J.A.; Angeloni, L.M.; Funk, W.C. Locally Adapted Traits Maintained in the Face of High Gene Flow. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, K.M.; Klerks, P.L.; Leberg, P.L. Adaptation to Sea Level Rise: Does Local Adaptation Influence the Demography of Coastal Fish Populations? J. Fish Biol. 2010, 77, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, M.; DeWitt, T.J.; Schlupp, I.; García de León, F.J.; Herrmann, R.; Feulner, P.G.D.; Tiedemann, R.; Plath, M. Toxic Hydrogen Sulfide and Dark Caves: Phenotypic and Genetic Divergence across Two Abiotic Environmental Gradients in Poecilia mexicana. Evolution 2008, 62, 2643–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhanot, R.; Hundal, S.S. Acute Toxic Effects of Untreated Sewage Water in Labeo Rohita (Hamilton, 1822). J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2019, 7, 1351–1355. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, R.; Dua, A. 96 h LC50, Behavioural Alterations and Histopathological Effects Due to Wastewater Toxicity in a Freshwater Fish Channa Punctatus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 5100–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, R.; Dua, A. Acute Toxicity, Behavioural and Morphological Alterations in Indian Carp, Labeo rohita H., on Exposure to Municipal Wastewater of Tung Dhab Drain, Punjab, India. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2014, 3, 1716–1720. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, P.B. Study on the Toxic Effects of Wastewater in Catfish (Heteropneustes fossilis). Life Sci. Int. Res. J. 2018, 5, 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, V.K.; David, M. Behaviour and Respiratory Dysfunction as an Index of Malathion Toxicity in the Freshwater Fish, Labeo Rohita (Hamilton). Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 8, 233–237. [Google Scholar]
- Ruffier, P.J.; Boyle, W.C.; Kleinschmidt, J. Short-Term Acute Bioassays to Evaluate Ammonia Toxicity and Effluent Standards. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1981, 53, 367–377. [Google Scholar]
- Pandian, T.J.; Sheela, S.G. Hormonal Induction of Sex Reversal in Fish. Aquaculture 1995, 138, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angus, R.A.; McNatt, H.B.; Howell, W.M.; Peoples, S.D. Gonopodium Development in Mormal Male and 11-Ketotestosterone-Treated Female Mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis): A Quantitative Study Using Computer Image Analysis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2001, 123, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Chen, S.; Chen, H.; Ying, G.; Chen, D.; Liu, J.; Liang, Y.; Wu, R.; Fang, X.; Zhang, C.; et al. Rapid Masculinization and Effects on the Liver of Female Western Mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis) by Norethindrone. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Hitch, A.; Purcell, K.; Klerks, P.; Leberg, P. Life History Variation along a Salinity Gradient in Coastal Marshes. Aquat. Biol. 2009, 8, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautenberg, G.E.; Amé, M.V.; Monferrán, M.V.; Bonansea, R.I.; Hued, A.C. A Multi-Level Approach Using Gambusia affinis as a Bioindicator of Environmental Pollution in the Middle-Lower Basin of Suquía River. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 706–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.K.; Kwan, T.N.; Purser, J.; Patil, J.G. Masculinization of Adult Gambusia holbrooki: A Case of Recapitulation of Protogyny in a Gonochorist? Biology 2022, 11, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, A.R. Morphometric Analysis of Endocrine Status in Western Mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis) Inhabiting Bayou DeSiard (Ouachita Parish, LA). Master’s Thesis, University of Louisiana at Monroe, Monroe, LA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Polverino, G.; Karakaya, M.; Spinello, C.; Soman, V.R.; Porfiri, M. Behavioural and Life-History Responses of Mosquitofish to Biologically Inspired and Interactive Robotic Predators. J. R. Soc. Interface 2019, 16, 20190359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deaton, R.; Cureton, J.C. Female Masculinization and Reproductive Life History in the Western Mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis). Environ. Biol. Fishes 2011, 92, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.-P.; Yang, Y.; Shu, H.; Ying, G.-G.; Zhao, J.-L.; Fang, G.-Z.; Xin, L.; Shi, W.-J.; Yao, L.; Cheng, X.-M. Masculinization and Reproductive Effects in Western Mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis) after Long-Term Exposure to Androstenedione. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, L.G.; Lambright, C.S.; Orlando, E.F.; Guillette, L.J., Jr.; Ankley, G.T.; Gray, L.E., Jr. Masculinization of Female Mosquitofish in Kraft Mill Effluent-Contaminated Fenholloway River Water Is Associated with Androgen Receptor Agonist Activity. Toxicol. Sci. 2001, 62, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, D.E.; Bailey, R.M. The Poeciliid Fishes (Cyprinodontiformes): Their Structure, Zoogeography, and Systematics. Bull. AMNH 1963, 126, 176. [Google Scholar]
- Leusch, F.D.L.; Chapman, H.F.; Kay, G.W.; Gooneratne, S.R.; Tremblay, L.A. Anal Fin Morphology and Gonadal Histopathology in Mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki) Exposed to Treated Municipal Sewage Effluent. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2006, 50, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, C.L. Morphogenesis of the Gonopodium in Gambusia affinis Affinis. J. Morphol. 1941, 69, 161–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, W.M.; Denton, T.E. Gonopodial Morphogenesis in Female Mosquitofish, Gambusia affinis Affinis, Masculinized by Exposure to Degradation Products from Plant Sterols. Environ. Biol. Fishes 1989, 24, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholdt, L.L.; Ehrhardt, D.A.; Michael, A.G. A Guide to the Use of the Mosquito Fish, Gambusia affinis for Mosquito Control; Navy Environmental and Preventive Medicine Unit No. 2: Norfolk, VA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Liney, K.E.; Hagger, J.A.; Tyler, C.R.; Depledge, M.H.; Galloway, T.S.; Jobling, S. Health Effects in Fish of Long-Term Exposure to Effluents from Wastewater Treatment Works. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahamonde, P.A.; Munkittrick, K.R.; Martyniuk, C.J. Intersex in Teleost Fish: Are We Distinguishing Endocrine Disruption from Natural Phenomena? Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 192, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, W.M.; Black, D.A.; Bortone, S.A. Abnormal Expression of Secondary Sex Characters in a Population of Mosquitofish, Gambusia affinis Holbrooki: Evidence for Environmentally-Induced Masculinization. Copeia 1980, 1980, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, J.A.; Goodbred, S.L.; Sobiech, S.A.; Olivier, H.M.; Draugelis-Dale, R.O.; Alvarez, D.A. Effects of Wastewater Discharges on Endocrine and Reproductive Function of Western Mosquitofish (Gambusia spp.) and Implications for the Threatened Santa Ana Sucker (Catostomus santaanae); U.S. Department of the Interior, Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; ISBN 1-4959-2591-9.
- Jobling, S.; Nolan, M.; Tyler, C.R.; Brighty, G.; Sumpter, J.P. Widespread Sexual Disruption in Wild Fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2498–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.-Y.; Liu, Y.-S.; Chen, X.-W.; Liang, Y.-Q.; Liu, S.-S.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Hu, L.-X.; Shi, W.-J.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.-L.; et al. Feminization and Masculinization of Western Mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis) Observed in Rivers Impacted by Municipal Wastewaters. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockmeier, E.K.; Ogino, Y.; Iguchi, T.; Barber, D.S.; Denslow, N.D. Effects of 17β-Trenbolone on Eastern and Western Mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki and G. affinis) Anal Fin Growth and Gene Expression Patterns. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 128–129, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, C.L. Gonopodial Characteristics Produced in the Anal Fins of Females of Gambusia affinis Affinis by Treatment with Ethinyl Testosterone. Biol. Bull. 1941, 80, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajda, A.M.; Barber, L.B.; Gray, J.L.; Lopez, E.M.; Bolden, A.M.; Schoenfuss, H.L.; Norris, D.O. Demasculinization of Male Fish by Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluent. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 103, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbach, C.; Císař, P.; Šauer, P.; Klicnarová, J.; Schmidt-Posthaus, H.; Golovko, O.; Kocour Kroupová, H. Synthetic Progestin Etonogestrel Negatively Affects Mating Behavior and Reproduction in Endler’s Guppies (Poecilia wingei). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 663, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matkin, C.; Felgenhauer, B.; Klerks, P. Gonadal Histology of Adult Western Mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis) Following Early Life Exposure to 17α-Ethynylestradiol, 17β-Trenbolone, and/or Atrazine. Res. Prepr. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinck, J.E.; Blazer, V.S.; Schmitt, C.J.; Papoulias, D.M.; Tillitt, D.E. Widespread Occurrence of Intersex in Black Basses (Micropterus spp.) from U.S. Rivers, 1995–2004. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 95, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cyrana, M.V.; Ledet, A.J.; Bart, H.L., Jr. Ovarian Masculinization and Reproductive Impairment in 3 Species of Groundfish in and around the Hypoxic Zone in the Gulf of Mexico. Fish. Bull. 2023, 121, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fentress, J.A.; Steele, S.L.; Bart, H.L.; Cheek, A.O. Reproductive Disruption in Wild Longear Sunfish (Lepomis megalotis) Exposed to Kraft Mill Effluent. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
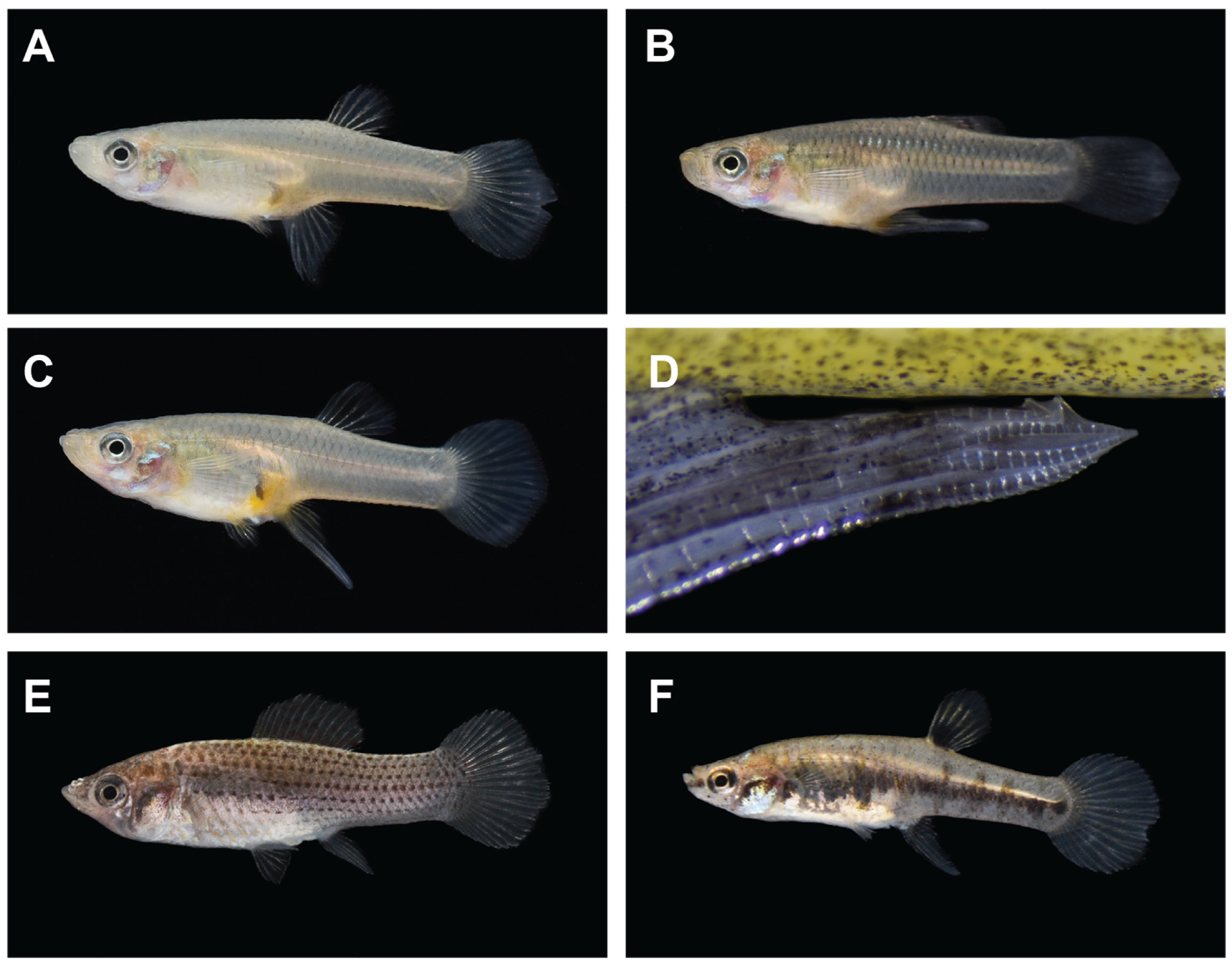



| Pair 1: Mandeville (Control) and Slidell (Exposed) | Pair 2: Abita Springs (Control) and Covington (Exposed) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trait | r2 | F1,11 | p | r2 | F1,7 | p |
| pH | 0.116 | 1.438 | 0.2557 | 0.040 | 0.289 | 0.6078 |
| Oxidation-reduction potential (mV) | 0.627 | 18.457 | 0.0013 | 0.003 | 0.024 | 0.8822 |
| Conductivity (µS/cm) | 0.802 | 44.646 | <0.0001 | 0.092 | 0.709 | 0.4275 |
| Salinity (psu) | 0.818 | 49.294 | <0.0001 | 0.059 | 0.440 | 0.5282 |
| Total dissolved solids (mg/L) | 0.805 | 45.417 | <0.0001 | 0.057 | 0.422 | 0.5365 |
| Temperature (°C) | 0.029 | 0.328 | 0.5783 | 0.298 | 2.972 | 0.1284 |
| Dissolved oxygen (mg/L) | 0.055 | 0.645 | 0.4391 | 0.382 | 4.335 | 0.0758 |
| Pair 1: Mandeville (Control) and Slidell (Exposed) | Pair 2: Abita Springs (Control) and Covington (Exposed) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trait | r2 | F1,47 | p | r2 | F1,48 | p |
| Standard Length (mm) | 0.274 | 17.707 | 0.0001 | 0.054 | 2.746 | 0.104 |
| Total Weight (g) | 0.144 | 7.911 | 0.0071 | 0.013 | 0.636 | 0.429 |
| Gonad Weight (g) | 0.107 | 5.638 | 0.0217 | 0.036 | 1.793 | 0.1869 |
| Somatic index (SI) | 0.252 | 15.832 | 0.0002 | 0.090 | 4.723 | 0.0347 |
| Somatic index, eviscerated (SIE) | 0.211 | 12.554 | 0.0009 | 0.073 | 3.769 | 0.0581 |
| Gonadosomatic index (GSI) | 0.006 | 0.266 | 0.6085 | 0.002 | 0.084 | 0.7737 |
| Trait | r2 | F1,47 | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Length (mm) | 0.155 | 8.629 | 0.0051 |
| Total Weight (g) | 0.130 | 7.008 | 0.011 |
| Gonad Weight (g) | 0.134 | 7.282 | 0.0096 |
| Somatic index (SI) | 0.001 | 0.052 | 0.8207 |
| Somatic index, eviscerated (SIE) | 0.004 | 0.211 | 0.648 |
| Gonadosomatic index (GSI) | 0.002 | 0.110 | 0.7417 |
| Population | Concentration (%) | Mean | SE | Min | Max | r2 | F4,35 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mandeville (control) | 0 | 98.3 | 1.66 | 86.7 | 100 | 0.92 | 94.32 | <0.0001 |
| 45 | 40.0 | 15.94 | 0 | 100 | 0.14 | 1.38 | 0.2593 | |
| 90 | 3.4 | 1.27 | 0 | 6.7 | 0.16 | 1.64 | 0.1865 | |
| Abita Springs (control) | 0 | 97.5 | 2.50 | 80 | 100 | 0.84 | 46.19 | <0.0001 |
| 45 | 74.2 | 11.98 | 13.3 | 100 | 0.41 | 6.11 | 0.0008 | |
| 90 | 63.3 | 14.80 | 0 | 100 | 0.30 | 3.75 | 0.0121 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kane, E.A.; Yadav, S.V.K.; Fogle, A.; D’Souza, N.A.; DeLisi, N.; Caillouët, K.A. Battle of the Bites: The Effect of Sewage Effluent Exposure on Mosquitofish Biocontrol of Mosquitoes in Residential Louisiana. Toxics 2024, 12, 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12040259
Kane EA, Yadav SVK, Fogle A, D’Souza NA, DeLisi N, Caillouët KA. Battle of the Bites: The Effect of Sewage Effluent Exposure on Mosquitofish Biocontrol of Mosquitoes in Residential Louisiana. Toxics. 2024; 12(4):259. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12040259
Chicago/Turabian StyleKane, Emily A., Shubham V. K. Yadav, Adeline Fogle, Nigel A. D’Souza, Nicholas DeLisi, and Kevin A. Caillouët. 2024. "Battle of the Bites: The Effect of Sewage Effluent Exposure on Mosquitofish Biocontrol of Mosquitoes in Residential Louisiana" Toxics 12, no. 4: 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12040259
APA StyleKane, E. A., Yadav, S. V. K., Fogle, A., D’Souza, N. A., DeLisi, N., & Caillouët, K. A. (2024). Battle of the Bites: The Effect of Sewage Effluent Exposure on Mosquitofish Biocontrol of Mosquitoes in Residential Louisiana. Toxics, 12(4), 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12040259





