Biochar Derived from Urban Green Waste Can Enhance the Removal of Cd from Water and Reduce Soil Cd Bioavailability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soils and Biochars
2.2. Isothermal Adsorption
2.3. Pot Experiment
2.4. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
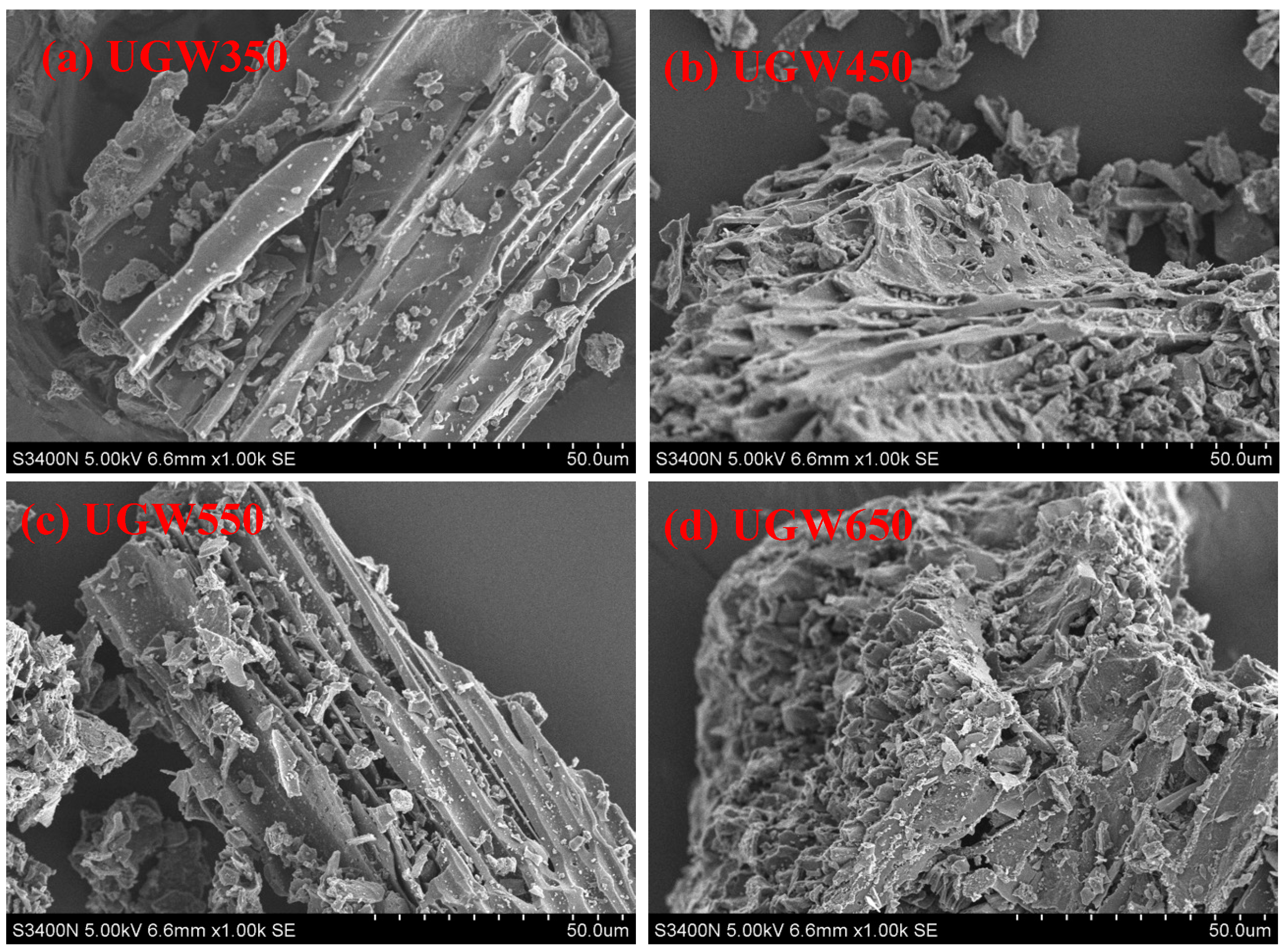
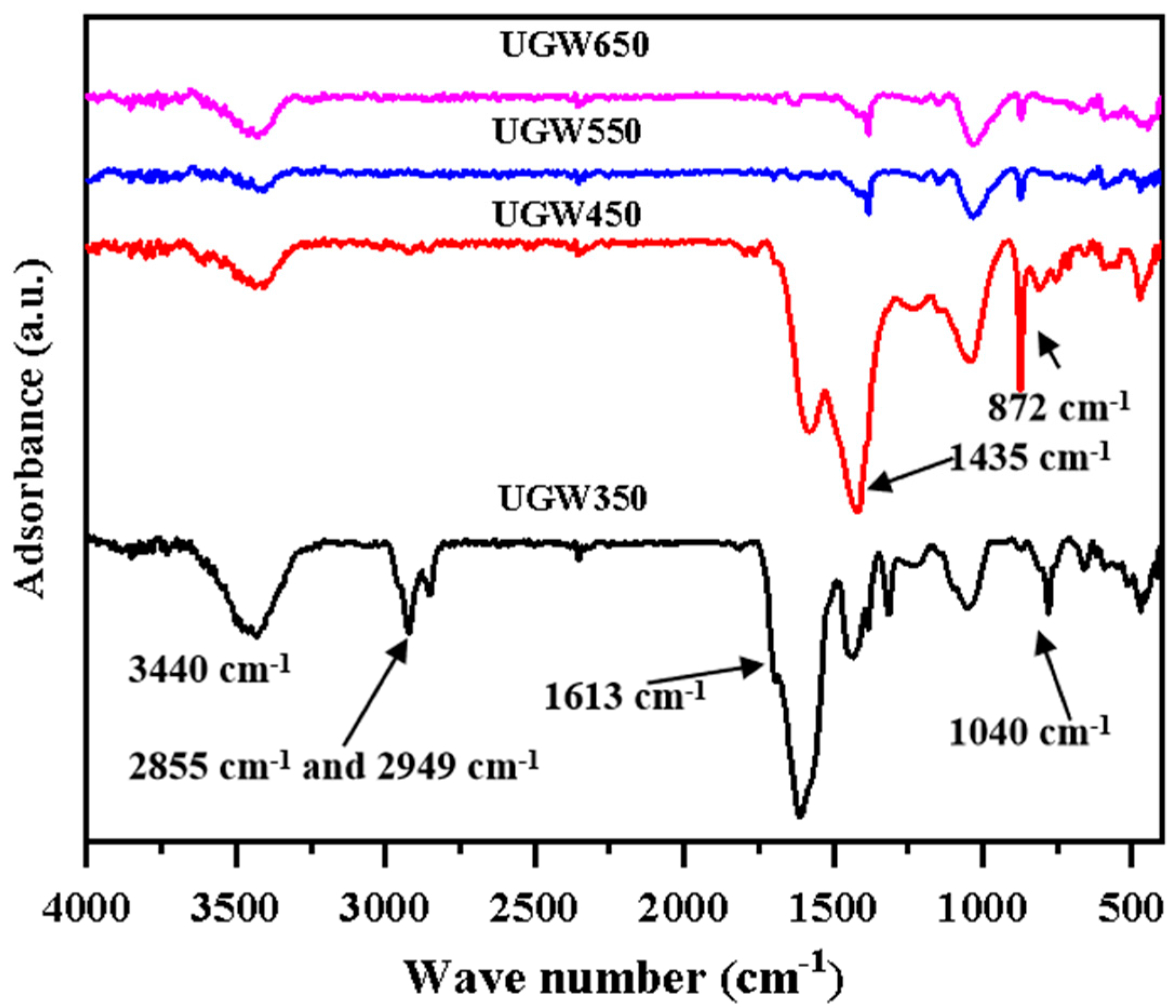
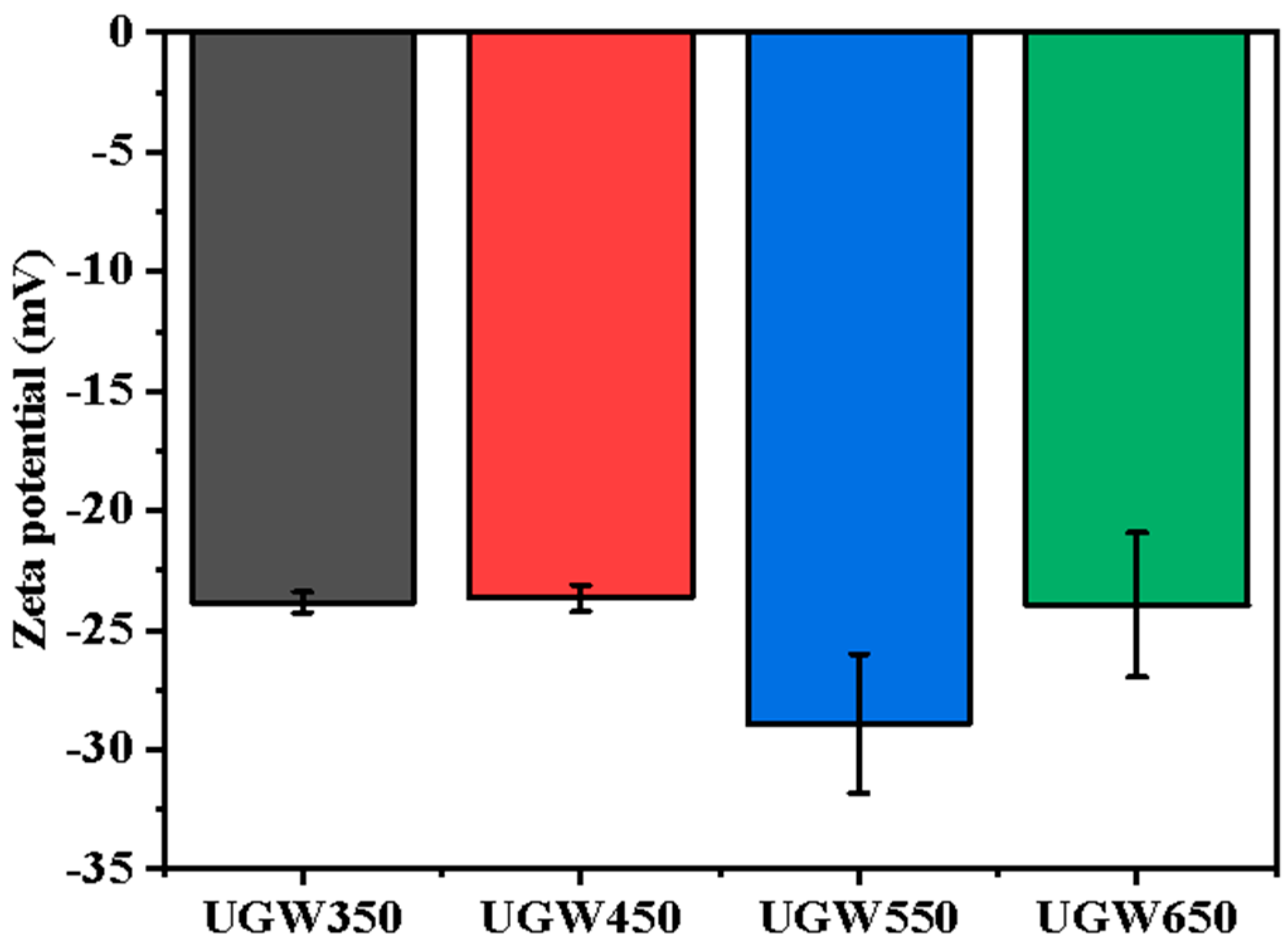
3.1. The Characters of the UGW-Biochar
3.1.1. Structural Elements
3.1.2. Surface Analysis
3.2. Adsorption Behavior of Cd Displayed by UGW Biochar
3.3. Conditioning Effect of UGW-Biochar on Cd-Contaminated Soils
3.3.1. Soil Available Cd
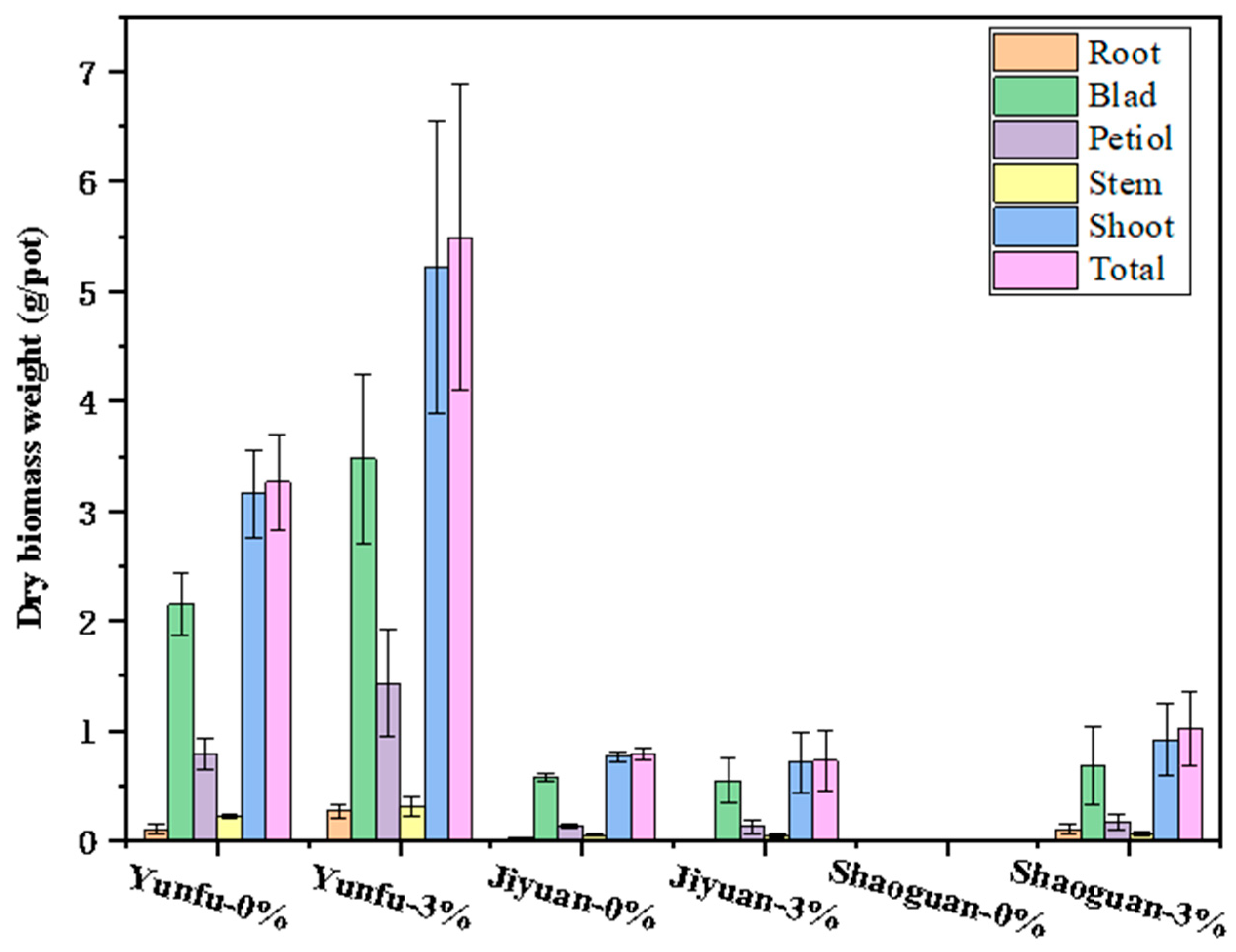
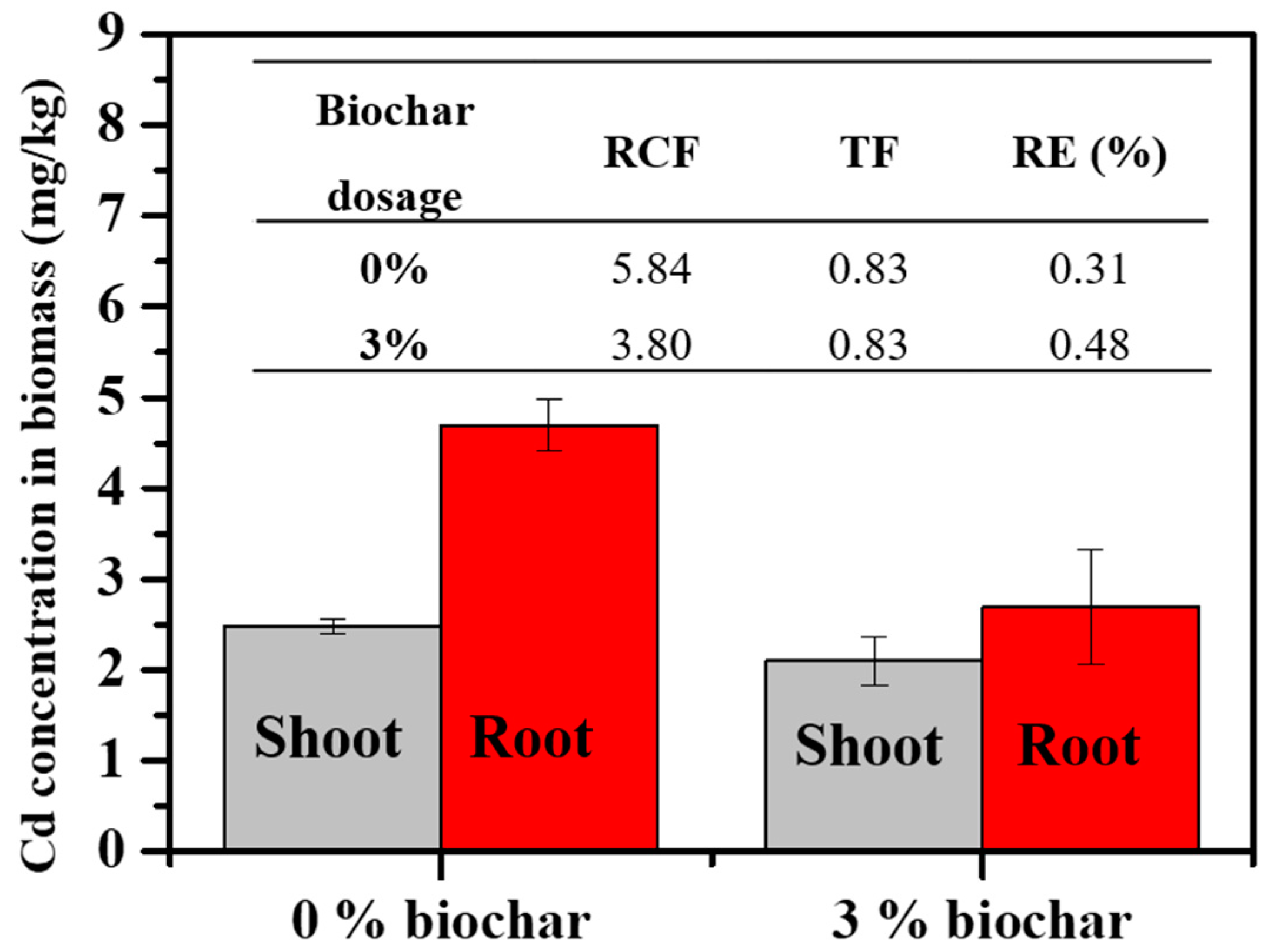
3.3.2. Cabbage Biomass and Cd Accumulation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bolan, N.S.; Makino, T.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Kim, P.-J.; Ishikawa, S.; Murakami, M.; Naidu, R.; Kirkham, M.B. Chapter Four—Cadmium Contamination and Its Risk Management in Rice Ecosystems. In Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; Volume 119, pp. 183–273. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Jin, Q.; Kavan, P. A Study of Heavy Metal Pollution in China: Current Status, Pollution-Control Policies and Countermeasures. Sustainability 2014, 6, 5820–5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tian, G.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, C.; Kong, L. Cadmium (Cd) Distribution and Contamination in Chinese Paddy Soils on National Scale. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17941–17952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Kopittke, P.M.; Zhao, F.-J. Cadmium Contamination in Agricultural Soils of China and the Impact on Food Safety. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, J.M.; Ippolito, J.A.; Watts, D.W.; Sigua, G.C.; Ducey, T.F.; Johnson, M.G. Biochar Compost Blends Facilitate Switchgrass Growth in Mine Soils by Reducing Cd and Zn Bioavailability. Biochar 2019, 1, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Guo, L.; Xiong, Q.; Liao, P.; Deng, X.; Pan, X.; Tan, X.; Xie, X.; Dai, Q.; Gao, H.; et al. Biochar-Mediated Cd Accumulation in Rice Grains through Altering Chemical Forms, Subcellular Distribution, and Physiological Characteristics. Biochar 2023, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järup, L. Cadmium Overload and Toxicity. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2002, 17, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, A. Cadmium Toxicity: Effects on Human Reproduction and Fertility. Rev. Environ. Health 2019, 34, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X.-H.; Yang, G.; Long, L.-L.; Chen, C.; Song, C.; Wu, J.; Gao, P.; Guan, D.-X. Biochar-Bacteria Partnership Based on Microbially Induced Calcite Precipitation Improves Cd Immobilization and Soil Function. Biochar 2023, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Mu, B.; Zhang, T.; Dong, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zong, L.; Wang, A. Synthesis of Biochar/Clay Mineral Nanocomposites Using Oil Shale Semi-Coke Waste for Removal of Organic Pollutants. Biochar 2023, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Tang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Q. Remediation of Cadmium-Contaminated Soil with Biochar Simultaneously Improves Biochar’s Recalcitrance. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhong, H.; Liu, G.; Dai, Z.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J. Remediation of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soils by Biochar: Mechanisms, Potential Risks and Applications in China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Fang, Z.; Bolan, N.; Bhatnagar, A.; Gao, B.; Hou, D.; Wang, S.; Song, H.; et al. Engineered Biochar for Environmental Decontamination in Aquatic and Soil Systems: A Review. Carbon Res. 2022, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Huang, W.; Lu, J.; Luo, S.; Czech, B.; Li, T.; Wang, H. Capture-Reduction Mechanism for Promoting Cr(VI) Removal by Sulfidated Microscale Zerovalent Iron/Sulfur-Doped Graphene-like Biochar Composite. Carbon Res. 2023, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Xu, L.; Buyong, F.; Chay, T.C.; Li, Z.; Cai, Y.; Hu, B.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X. Modified Biochar: Synthesis and Mechanism for Removal of Environmental Heavy Metals. Carbon Res. 2022, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Wang, N.; Jiang, S.; Li, F.; Luo, S.; Chen, A.; Li, H.; Lin, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; et al. Potential Implications of Biochar and Compost on the Stoichiometry-Based Assessments of Soil Enzyme Activity in Heavy Metal-Polluted Soils. Carbon Res. 2022, 1, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahori, A.H.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, R.; Mahar, A.; Awasthi, M.K.; Shen, F.; Sial, T.A.; Kumbhar, F.; Wang, P.; et al. Use of Biochar as an Amendment for Remediation of Heavy Metal-Contaminated Soils: Prospects and Challenges. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, T.-T.; Wu, P.; Qin, Q.-Y.; Huang, Y.-N.; Wang, Y.-J.; Zhou, D.-M. Screening of Wheat Straw Biochars for the Remediation of Soils Polluted with Zn (II) and Cd (II). J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 362, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Qi, Z.; Wu, X.; Ji, R.; Chen, W. Biochar Nanoparticles-Mediated Transport of Organic Contaminants in Porous Media: Dependency on Contaminant Properties and Effects of Biochar Aging. Carbon Res. 2023, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Liang, X.; Huang, L.; Wei, L.; Zheng, X.; Albert, H.A.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z. Characterization of Biochars from Woody Agricultural Wastes and Sorption Behavior Comparison of Cadmium and Atrazine. Biochar 2022, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Lu, L.; Xiao, X.; Chen, B. Novel Insights into Effects of Silicon-Rich Biochar (Sichar) Amendment on Cadmium Uptake, Translocation and Accumulation in Rice Plants. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Huang, Y.; Huang, L.; Huang, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Liu, C.; Liu, Z. Combined Biochar and Soda Residues Increases Maize Yields and Decreases Grain Cd/Pb in a Highly Cd/Pb-Polluted Acid Udults Soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 306, 107198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Dai, W.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, J.; Huang, F.; Mei, C.; Huang, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, P.; Xiao, R. Effect of Rice Straw Biochar on Three Different Levels of Cd-Contaminated Soils: Cd Availability, Soil Properties, and Microbial Communities. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Shen, H.; Dong, S. Study on Eco-Utilization and Treatments of Highway Greening Waste. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Ge, Y.; Chang, J.; Shao, H.; Tang, Y. Garden Waste Biomass for Renewable and Sustainable Energy Production in China: Potential, Challenges and Development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 22, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drennan, M.F.; DiStefano, T.D. High Solids Co-Digestion of Food and Landscape Waste and the Potential for Ammonia Toxicity. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Din, M.F.M.; Taib, S.M.; Kamaludin, N.H.B.; Hanafi, N.; Ida, T.; Shamsuddin, M.S.; Chelliapan, S. Conversion of Landscape Waste into Bio-Coke Solid Fuel. In Green Engineering for Campus Sustainability; Yaser, A.Z., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 105–118. ISBN 9789811372605. [Google Scholar]
- Mukome, F.N.D.; Zhang, X.; Silva, L.C.R.; Six, J.; Parikh, S.J. Use of Chemical and Physical Characteristics To Investigate Trends in Biochar Feedstocks. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 2196–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, J.E.; Builes, S.; Heredia Salgado, M.A.; Tarelho, L.A.C.; Arroyave, C.; Aristizábal, A.; Chavez, E. Adsorption of Cadmium Using Biochars Produced from Agro-Residues. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 14592–14602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, I.; Zhang, G.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, F.; Dai, K. Ecological Restoration of an Acidic Cd Contaminated Soil Using Bamboo Biochar Application. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 84, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanli, Z.; Bo, S.U.N. Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Rice under Cadmium Contamination: Influence of Rice Cultivar versus Soil Type. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 1092–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Munir, M.A.M.; Liu, G.; Yousaf, B.; Mian, M.M.; Ali, M.U.; Ahmed, R.; Cheema, A.I.; Naushad, M. Contrasting Effects of Biochar and Hydrothermally Treated Coal Gangue on Leachability, Bioavailability, Speciation and Accumulation of Heavy Metals by Rapeseed in Copper Mine Tailings. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 191, 110244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, S.; Banik, C.; Laird, D.A. Estimating the Organic Oxygen Content of Biochar. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Yang, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Xiao, R. Adsorption of Cd(II) from Aqueous Solutions by Rape Straw Biochar Derived from Different Modification Processes. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Li, X.; Xing, J.; Xu, G. Adsorption of Potentially Toxic Elements in Water by Modified Biochar: A Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Lin, D.; Yang, K. Sorption Kinetics of 1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene to Biochars Produced at Various Temperatures. Biochar 2022, 4, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhou, D.; Zhu, L. Transitional Adsorption and Partition of Nonpolar and Polar Aromatic Contaminants by Biochars of Pine Needles with Different Pyrolytic Temperatures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5137–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Dai, Q.; You, Z. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Characterization of Aging-Related Properties of Original and Nano-Modified Asphalt Binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 101, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zeng, G.; Tan, X.; Huang, B.; Tang, X.; Wang, S.; Hua, Q.; Yan, Z. Competitive Adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cu(II) onto Chitosan-Pyromellitic Dianhydride Modified Biochar. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 506, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Zhang, L.; Tan, Z.; Huang, Q. Effect Mechanism of Biochar’s Zeta Potential on Farmland Soil’s Cadmium Immobilization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 19738–19748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Shang, J.; Li, B.; Flury, M. Surface and Colloid Properties of Biochar and Implications for Transport in Porous Media. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 2484–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-B.; Nguyen, T.-K.-T.; Chen, W.-H.; Chen, C.-W.; Bui, X.-T.; Patel, A.K.; Dong, C.-D. Hydrothermal and Pyrolytic Conversion of Sunflower Seed Husk into Novel Porous Biochar for Efficient Adsorption of Tetracycline. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 373, 128711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.-Z.; Huang, D.-L.; Liu, Y.-G.; Zhang, C.; Lai, C.; Zeng, G.-M.; Cheng, M.; Gong, X.-M.; Wan, J.; Luo, H. Investigating the Adsorption Behavior and the Relative Distribution of Cd2+ Sorption Mechanisms on Biochars by Different Feedstock. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 261, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, F.; Lamb, D.; Naidu, R.; Bolan, N.S.; Yan, Y.; Ok, Y.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Choppala, G. Cadmium Solubility and Bioavailability in Soils Amended with Acidic and Neutral Biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 1457–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, Z.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Zaheer, I.E.; Malik, A.; Riaz, M.A.; Shahid, M.R.; Rehman, M.Z.U.; Al-Wabel, M.I. A Critical Review of Mechanisms Involved in the Adsorption of Organic and Inorganic Contaminants through Biochar. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wabel, M.I.; Hussain, Q.; Usman, A.R.A.; Ahmad, M.; Abduljabbar, A.; Sallam, A.S.; Ok, Y.S. Impact of Biochar Properties on Soil Conditions and Agricultural Sustainability: A Review. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2124–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.S.; Adriano, D.C.; Duraisamy, P.; Mani, A.; Arulmozhiselvan, K. Immobilization and Phytoavailability of Cadmium in Variable Charge Soils. I. Effect of Phosphate Addition. Plant Soil 2003, 250, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, H.U.; Akbar, W.A.; Alatalo, J.M. A Comprehensive Literature Review on Cadmium (Cd) Status in the Soil Environment and Its Immobilization by Biochar-Based Materials. Agronomy 2022, 12, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, W.; Zheng, K.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Chen, R. Stabilization of Heavy Metal-Contaminated Soils by Biochar: Challenges and Recommendations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 139060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Tao, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Xu, J. Changes in Heavy Metal Bioavailability and Speciation from a Pb-Zn Mining Soil Amended with Biochars from Co-Pyrolysis of Rice Straw and Swine Manure. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Country | Yunfu | Jiyuan | Shaoguan | - | - | - | - |
| Soil type | Udept | Ustalf | Udult | - | - | - | - |
| Biochar | - | - | - | UGW350 | UGW450 | UGW550 | UGW650 |
| Total N (g/kg) | 3.41 | 2.01 | 1.73 | 13.03 | 12.31 | 10.26 | 9.24 |
| Total P (g/kg) | 1.24 | 1.39 | 1.25 | 2.90 | 3.61 | 3.74 | 4.33 |
| pH(H2O) | 7.5 | 7.4 | 4.8 | 7.92 | 9.77 | 9.89 | 10.15 |
| Total Cd (mg/kg) | 1.97 | 14.02 | 4.16 | 0.35 | 0.25 | 0.22 | 0.25 |
| Available Cd (mg/kg) | 0.79 | 5.86 | 3.03 | - | - | - | - |
| Available P (mg/kg) | - | - | - | 560.6 | 784.8 | 271.3 | 220.9 |
| CEC (cmol/kg) | - | - | - | 6.7 | 10.7 | 3.9 | 4.4 |
| Biochar | C% | H% | O% | N% | H/C | O/C | (O+N)/C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UGW350 | 58.24 | 4.09 | 35.85 | 0.15 | 0.84 | 0.46 | 0.64 |
| UGW450 | 56.27 | 2.95 | 39.17 | 0.21 | 0.63 | 0.52 | 0.72 |
| UGW550 | 59.32 | 2.44 | 36.68 | 0.22 | 0.49 | 0.46 | 0.64 |
| UGW650 | 55.08 | 1.96 | 41.84 | 0.24 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.78 |
| Biochar | BET Surface Area | Total Pore Volume at P/P0 = 0.985 | Micropore Volume | Average Pore Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| m2/g | cm3/g | nm | ||
| GB350 | 1.7 | 4.7 × 10−3 | 2.6 × 10−4 | 11.1 |
| GB450 | 2.2 | 9.2 × 10−3 | 4.6 × 10−4 | 16.3 |
| GB550 | 2.2 | 18.9 × 10−3 | 6.0 × 10−4 | 34.7 |
| GB650 | 3.5 | 13.4 × 10−3 | 7.1 × 10−4 | 15.5 |
| Model | Parameters | UGW350 | UGW450 | UGW550 | UGW650 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freundlich Isotherm | KF (L/mg) | 2177.41 | 2875.97 | 2516.99 | 3287.77 |
| 1/n | 0.34 | 0.30 | 0.28 | 0.32 | |
| R2 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.98 | |
| Langmuir Isotherm | qm (mg/kg) | 5030.72 | 6011.15 | 5198.63 | 7431.96 |
| KL (L/mg) | 0.81 | 1.07 | 1.00 | 0.85 | |
| RL | 0.87 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.97 | |
| R2 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.98 | |
| Temkin Isotherm | b (J/mol) | 4.69 | 3.81 | 4.40 | 2.98 |
| Km (L/g) | 247.72 | 296.53 | 303.13 | 184.21 | |
| R2 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.94 |
| Soils | Biochar Addition (%) | Soil pH | Available Cd (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yunfu | 0 | 7.5 ± 0.3 | 0.79 ± 0.17 |
| Yunfu | 3 | 7.5 ± 0.5 | 0.71 ± 0.15 |
| Jiyuan | 0 | 7.4 ± 0.3 | 5.86 ± 0.26 |
| Jiyuan | 3 | 7.5 ± 0.2 | 5.12 ± 0.22 |
| Shaoguan | 0 | 4.8 ± 0.1 | 3.03 ± 0.32 |
| Shaoguan | 3 | 5.9 ± 0.2 | 2.46 ± 0.19 |
| Soils | Biochar Addition (%) | Blade (Cd) (mg/kg) | Petiol (Cd) (mg/kg) | Stem (Cd) (mg/kg) | Shoot (Cd) (mg/kg) | Root (Cd) (mg/kg) | (Total Cd) (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yunfu | 0 | 2.93 ± 0.07 gh | 1.58 ± 0.32 gh | 1.31 ± 0.20 h | 2.48 ± 0.08 gh | 4.69 ± 2.80 fgh | 2.57 ± 0.14 gh |
| 3 | 2.55 ± 0.36 gh | 1.18 ± 0.16 h | 1.24 ± 0.25 h | 2.10 ± 0.27 gh | 2.69 ± 0.63 gh | 2.13 ± 0.24 gh | |
| Jiyuan | 0 | 65.63 ± 14.90 bc | 29.58 ± 2.96 d | 22.01 ± 3.25 de | 56.57 ± 11.80 c | NA | NA |
| 3 | 80.65 ± 23.56 a | 25.18 ± 9.11 d | 22.30 ± 4.14 de | 67.67 ± 19.86 b | NA | NA | |
| Shaoguan | 0 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| 3 | 13.35 ± 2.49 ef | 6.78 ± 1.13 fgh | 5.37 ± 1.70 fgh | 11.24 ± 2.33 fg | NA | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Jeyakumar, P.; Bolan, N.; Huang, L.; Rashid, M.S.; Liu, Z.; Wei, L.; Wang, H. Biochar Derived from Urban Green Waste Can Enhance the Removal of Cd from Water and Reduce Soil Cd Bioavailability. Toxics 2024, 12, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010008
Li X, Jeyakumar P, Bolan N, Huang L, Rashid MS, Liu Z, Wei L, Wang H. Biochar Derived from Urban Green Waste Can Enhance the Removal of Cd from Water and Reduce Soil Cd Bioavailability. Toxics. 2024; 12(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiang, Paramsothy Jeyakumar, Nanthi Bolan, Lianxi Huang, Muhammad Saqib Rashid, Zhongzhen Liu, Lan Wei, and Hailong Wang. 2024. "Biochar Derived from Urban Green Waste Can Enhance the Removal of Cd from Water and Reduce Soil Cd Bioavailability" Toxics 12, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010008
APA StyleLi, X., Jeyakumar, P., Bolan, N., Huang, L., Rashid, M. S., Liu, Z., Wei, L., & Wang, H. (2024). Biochar Derived from Urban Green Waste Can Enhance the Removal of Cd from Water and Reduce Soil Cd Bioavailability. Toxics, 12(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010008