Residential Nitrogen Dioxide Exposure and Cause-Specific Cerebrovascular Mortality: An Individual-Level, Case-Crossover Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Granata, A.; Harshfield, E.L.; Moxon, J.V. Cerebrovascular Disorders. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2023, 23, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, A.J.S.; Werring, D.J. New Insights Into Cerebrovascular Pathophysiology and Hypertension. Stroke 2022, 53, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-J.; Li, Z.-X.; Gu, H.-Q.; Zhai, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, X.-Q.; Wang, Y.-L.; Yang, X.; Wang, C.-J.; Meng, X.; et al. China Stroke Statistics 2019: A Report From the National Center for Healthcare Quality Management in Neurological Diseases, China National Clinical Research Center for Neurological Diseases, the Chinese Stroke Association, National Center for Chronic and Non-communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention and Institute for Global Neuroscience and Stroke Collaborations. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2020, 5, 211–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendelson, S.J.; Prabhakaran, S. Diagnosis and Management of Transient Ischemic Attack and Acute Ischemic Stroke. JAMA 2021, 325, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaño, A.; Hanley, D.F.; Hemphill, J.C. Hemorrhagic stroke. In Interventional Neuroradiology; Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 229–248. [Google Scholar]
- Cobbold, A.T.; Crane, M.A.; Knibbs, L.D.; Hanigan, I.C.; Greaves, S.P.; Rissel, C.E. Perceptions of air quality and concern for health in relation to long-term air pollution exposure, bushfires, and COVID-19 lockdown: A before-and-after study. J. Clim. Chang. Health 2022, 6, 100137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Z.; Liu, F.; Yu, H.; Wu, S.; Xiang, H. Association between exposure to ambient air pollution and hospital admission, incidence, and mortality of stroke: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of more than 23 million participants. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2021, 26, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patz, J.A.; Tian, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Xiang, X.; Li, M.; Juan, J.; Song, J.; Cao, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Association between ambient air pollution and daily hospital admissions for ischemic stroke: A nationwide time-series analysis. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, C.P.; Bennett, K.E.; Hickey, A.; Kavanagh, P.; Broderick, B.; O’Mahony, M.; Williams, D.J. Short-Term Air Pollution as a Risk for Stroke Admission: A Time-Series Analysis. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 49, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Wang, Z.; Guo, X.; Xia, X.; Xue, J.; Jiang, G.; Gu, Y.; Han, S.; Yao, Q.; Cai, Z.; et al. Short-term effects of outdoor air pollution on acute ischaemic stroke occurrence: A case-crossover study in Tianjin, China. Occup. Environ. Med. 2020, 77, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.S.V.; Lee, K.K.; McAllister, D.A.; Hunter, A.; Nair, H.; Whiteley, W.; Langrish, J.P.; Newby, D.E.; Mills, N.L. Short term exposure to air pollution and stroke: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2015, 350, h1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Edgell, R.C.; Wei, J.; Li, H.; Qian, Z.; Feng, J.; Tian, F.; Wang, X.; Xin, Q.; Cai, M.; et al. Air pollution and stroke hospitalization in the Beibu Gulf Region of China: A case-crossover analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 255, 114814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Stowell, J.; Kan, H.; Liu, Y. Estimating PM2.5 concentrations in Northeastern China with full spatiotemporal coverage, 2005–2016. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 253, 112203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Hang, Y.; Lei, J.; Kan, H.; Meng, X. Optimizing modeling windows to better capture the long-term variation of PM2.5 concentrations in China during 2005–2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, P.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Shi, S.; Xue, T.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Chen, R.; et al. Mortality burden due to ambient nitrogen dioxide pollution in China: Application of high-resolution models. Environ. Int. 2023, 176, 107967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noël, T.; Loukos, H.; Defrance, D.; Vrac, M.; Levavasseur, G. Extending the global high-resolution downscaled projections dataset to include CMIP6 projections at increased resolution coherent with the ERA5-Land reanalysis. Data Brief. 2022, 45, 108669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, D.G.; Bland, J.M. How to obtain the P value from a confidence interval. BMJ 2011, 343, d2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milojevic, A.; Wilkinson, P.; Armstrong, B.; Bhaskaran, K.; Smeeth, L.; Hajat, S. Short-term effects of air pollution on a range of cardiovascular events in England and Wales: Case-crossover analysis of the MINAP database, hospital admissions and mortality. Heart 2014, 100, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Chen, X.; Guo, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, N.; Dai, J.; Gong, J.; Xiang, H. Ambient air pollution and cerebrovascular disease mortality: An ecological time-series study based on 7-year death records in central China. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 27299–27307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Yu, Y.; Yao, S.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, G.; Yao, Y.; Yao, X.; Wang, S.-L.; Zhang, Z. Acute effects of air pollution on ischaemic stroke onset and deaths: A time-series study in Changzhou, China. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e020425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versaci, F.; Anticoli, S.; Pezzella, F.R.; Mangiardi, M.; Giosa, A.D.; Marchegiani, G.; Calcagno, S.; Pietro, R.D.I.; Frati, G.; Sciarretta, S.; et al. Impact of weather and pollution on the rate of cerebrovascular events in a large metropolitan area. Panminerva Med. 2022, 64, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Wang, Q.; Wei, J.; Lu, W.; Wang, R.; Liu, T.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, L.; et al. Association of short-term exposure to ambient air pollution with mortality from ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. Eur. J. Neurol. 2022, 29, 1994–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Shi, W.; Yuan, K.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, W.; Li, C.; Xu, L.; Wu, L.; Sun, S.; Hong, F. Hourly Air Pollution Exposure and Emergency Hospital Admissions for Stroke: A Multicenter Case-Crossover Study. Stroke 2023, 54, 3038–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Stewart, J.D.; Eliot, M.N.; Yanosky, J.D.; Liao, D.; Tinker, L.F.; Eaton, C.B.; Whitsel, E.A.; Wellenius, G.A. Short-term exposure to air pollution and incidence of stroke in the Women’s Health Initiative. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 105065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, T.F.; Zha, Z.Q.; Sun, L.; Liu, L.L.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Meng, X.L.; Li, H.B.; Wang, H.L.; Nie, H.H.; et al. Ambient nitrogen dioxide and cardiovascular diseases in rural regions: A time-series analyses using data from the new rural cooperative medical scheme in Fuyang, East China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 51412–51421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Xu, R.; Wei, J.; Liu, T.; Ye, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, S.; Lv, Z.; et al. Short-Term Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution and Hospital Admissions for Sequelae of Stroke in Chinese Older Adults. GeoHealth 2022, 6, e2022GH000700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahad, O.; Lelieveld, J.; Birklein, F.; Lieb, K.; Daiber, A.; Münzel, T. Ambient Air Pollution Increases the Risk of Cerebrovascular and Neuropsychiatric Disorders through Induction of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münzel, T.; Gori, T.; Al-Kindi, S.; Deanfield, J.; Lelieveld, J.; Daiber, A.; Rajagopalan, S. Effects of gaseous and solid constituents of air pollution on endothelial function. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3543–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucking, A.J.; Lundback, M.; Mills, N.L.; Faratian, D.; Barath, S.L.; Pourazar, J.; Cassee, F.R.; Donaldson, K.; Boon, N.A.; Badimon, J.J.; et al. Diesel exhaust inhalation increases thrombus formation in man. Eur. Heart J. 2008, 29, 3043–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
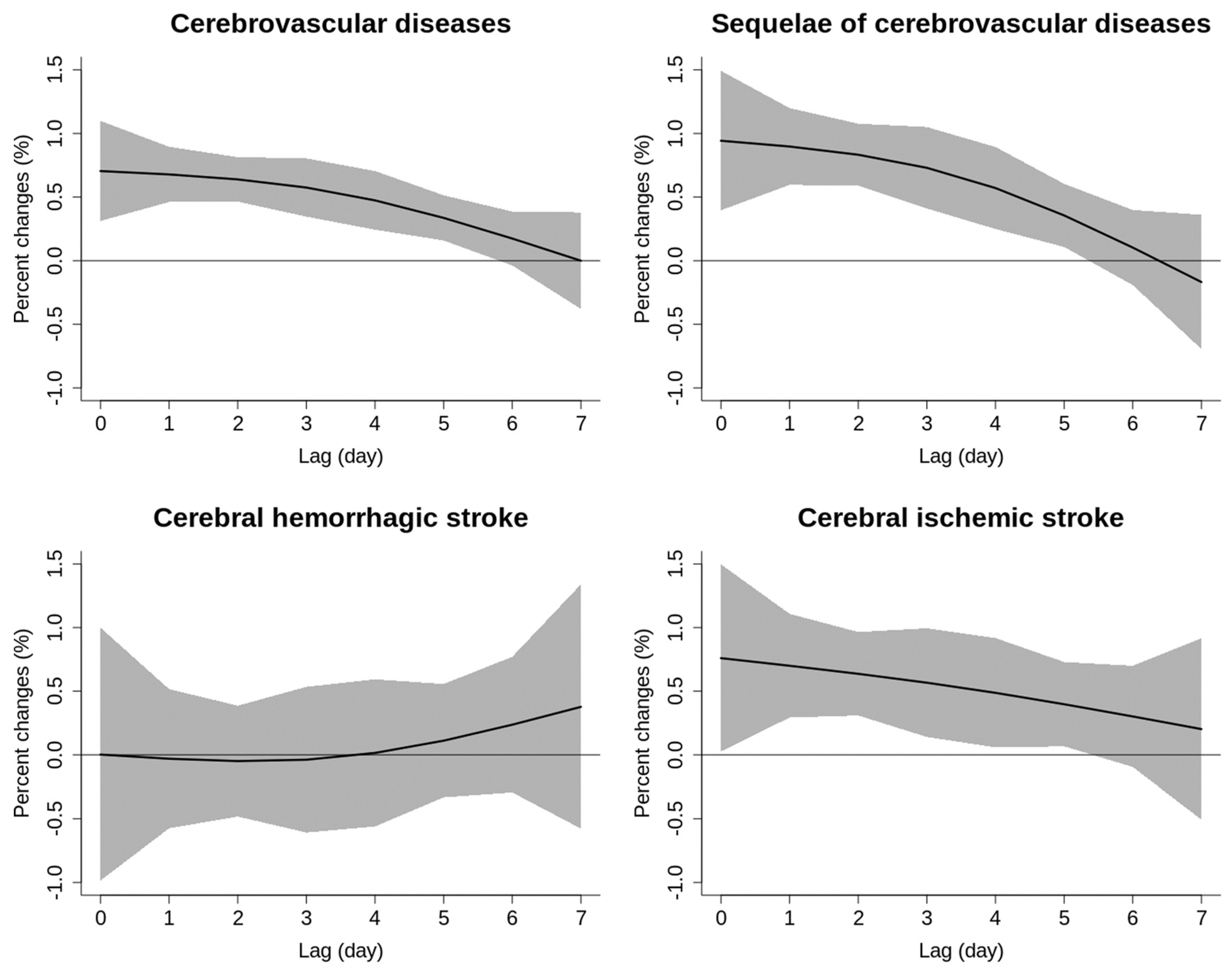
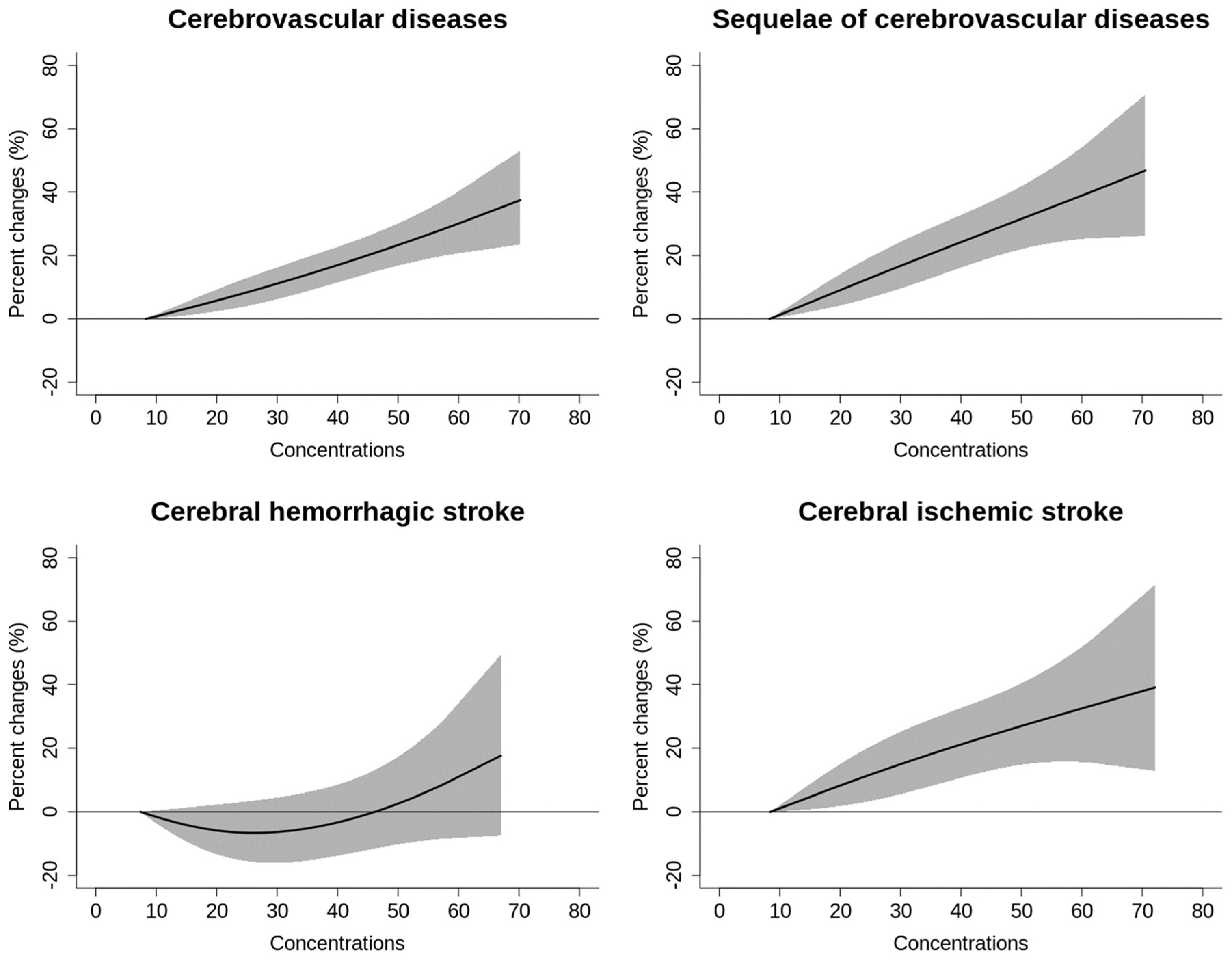
| Variable | Cases (n, %) |
|---|---|
| Cerebrovascular deaths | 219,147 (100.0) |
| Sequelae of cerebrovascular disease | 111,182 (50.7) |
| Hemorrhagic stroke | 37,539 (17.1) |
| Ischemic stroke | 60,217 (27.5) |
| Other types of cerebrovascular disease | 10,209 (4.7) |
| Sex | |
| Male | 108,916 (49.7) |
| Female | 110,231 (50.3) |
| Age (years) | |
| <80 | 67,437 (30.8) |
| ≥80 | 151,710 (69.2) |
| Season | |
| Warm | 96,437 (44.0) |
| Cold | 122,710 (56.0) |
| Education | |
| ≤9 years | 85,529 (39.0) |
| >9 years | 91,230 (41.6) |
| Unknown | 42,388 (19.4) |
| Marriage | |
| Single | 102,382 (46.7) |
| Married | 116,460 (53.1) |
| Unknown | 305 (0.2) |
| Variables | Mean | SD | Min | P25 | P50 | P75 | Max | IQR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO2 (μg/m3) | 23.8 | 12.5 | 1.6 | 15.7 | 20.9 | 28.4 | 133.7 | 12.7 |
| PM2.5 (μg/m3) | 43.1 | 29.4 | 1.0 | 22.7 | 35.2 | 54.6 | 440.3 | 31.9 |
| PM2.5–10 (μg/m3) | 27.2 | 18.7 | 0.0 | 16.0 | 23.3 | 34.6 | 442.1 | 18.6 |
| O3 (μg/m3) | 83.3 | 36.6 | 0.1 | 56.2 | 77.9 | 104.9 | 276.9 | 48.7 |
| Temperature (°C) | 15.9 | 8.5 | −7.1 | 8.5 | 15.9 | 23.1 | 34.8 | 14.6 |
| RH (%) | 72.9 | 14.6 | 21.1 | 64.6 | 75.4 | 83.8 | 100.0 | 19.2 |
| PM2.5 | PM2.5–10 | O3 | Temperature | RH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO2 | 0.54 * | 0.32 * | −0.18 * | −0.38 * | −0.30 * |
| PM2.5 | - | 0.65 * | −0.04 * | −0.37 * | −0.31 * |
| PM2.5–10 | - | - | −0.12 * | −0.14 * | −0.41 * |
| O3 | - | - | - | 0.52 * | −0.20 * |
| Temperature | - | - | - | - | 0.37 * |
| Categories | Cerebrovascular Diseases | Sequelae of Cerebrovascular Disease | Hemorrhagic Stroke | Ischemic Stroke |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 3.62 (2.56, 4.69) | 4.29 (2.81, 5.80) | 0.54 (−2.01, 3.15) | 4.30 (2.30, 6.33) |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 2.75 (1.26, 4.25) | 2.80 (0.70, 4.94) | 1.36 (−1.98, 4.82) | 3.64 (0.77, 6.58) |
| Female | 4.49 (2.99, 6.02) | 5.72 (3.63, 7.84) | −0.66 (−4.54, 3.37) | 4.91 (2.14, 7.75) |
| p | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.45 | 0.54 |
| Age | ||||
| <80 | 3.32 (1.39, 5.28) | 3.32 (1.39, 5.28) | −0.30 (−3.74, 3.27) | 1.71 (−2.00, 5.57) |
| ≥80 | 3.75 (2.49, 5.04) | 4.84 (2.73, 6.95) | 1.49 (−2.24, 5.37) | 5.27 (2.92, 7.68) |
| p | 0.71 | 0.49 | 0.50 | 0.12 |
| Season | ||||
| Warm | 5.35 (3.13, 7.62) | 8.95 (5.75, 12.24) | −1.86 (−6.81, 3.34) | 4.50 (2.20, 6.86) |
| Cold | 2.91 (1.70, 4.14) | 2.76 (1.08, 4.47) | 1.06 (−1.91, 4.12) | 2.82 (−1.23, 7.04) |
| p | 0.06 | <0.001 * | 0.33 | 0.49 |
| Education | ||||
| Low | 4.68 (2.93, 6.47) | 5.45 (3.08, 7.87) | −0.89 (−5.56, 4.01) | 5.46 (2.13, 8.91) |
| High | 2.05 (0.48, 3.64) | 2.67 (0.35, 5.05) | 0.89 (−2.43, 4.33) | 2.15 (−0.77, 5.15) |
| p | 0.03 * | 0.10 | 0.55 | 0.15 |
| Marriage | ||||
| Single | 5.14 (3.58, 6.73) | 5.07 (3.00, 7.18) | 2.17 (−2.33, 6.87) | 6.57 (3.60, 9.62) |
| Married | 2.33 (0.89, 3.79) | 3.53 (1.41, 5.69) | −0.19 (−3.26, 2.97) | 2.40 (−0.28, 5.17) |
| p | 0.01 * | 0.31 | 0.40 | 0.04 * |
| Cerebrovascular Diseases | Sequelae of Cerebrovascular Diseases | Hemorrhagic Stroke | Ischemic Stroke | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No adjustment | 3.62 (2.56, 4.69) | 4.29 (2.81, 5.80) | 0.54 (−2.01, 3.15) | 4.30 (2.30, 6.33) |
| + PM2.5 | 2.95 (1.79, 4.13) | 3.86 (2.23, 5.52) | 0.63 (−2.19, 3.54) | 2.77 (0.60, 5.00) |
| + PM2.5–10 | 2.89 (1.78, 4.02) | 3.19 (1.64, 4.76) | 0.99 (−1.71, 3.77) | 3.55 (1.45, 5.68) |
| + O3 | 3.29 (2.23, 4.36) | 3.93 (2.44, 5.44) | 0.49 (−2.07, 3.11) | 3.87 (1.87, 5.91) |
| + all | 2.81 (1.64, 3.99) | 3.53 (1.90, 5.20) | 0.81 (−2.03, 3.74) | 2.73 (0.54, 4.97) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, Y.; Cai, R.; Su, X.; Li, Q.; Jin, S.; Shi, W.; Chen, R.; Wang, C.; He, J. Residential Nitrogen Dioxide Exposure and Cause-Specific Cerebrovascular Mortality: An Individual-Level, Case-Crossover Study. Toxics 2024, 12, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010010
Qian Y, Cai R, Su X, Li Q, Jin S, Shi W, Chen R, Wang C, He J. Residential Nitrogen Dioxide Exposure and Cause-Specific Cerebrovascular Mortality: An Individual-Level, Case-Crossover Study. Toxics. 2024; 12(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Yifeng, Renzhi Cai, Xiaozhen Su, Qi Li, Shan Jin, Wentao Shi, Renjie Chen, Chunfang Wang, and Jia He. 2024. "Residential Nitrogen Dioxide Exposure and Cause-Specific Cerebrovascular Mortality: An Individual-Level, Case-Crossover Study" Toxics 12, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010010
APA StyleQian, Y., Cai, R., Su, X., Li, Q., Jin, S., Shi, W., Chen, R., Wang, C., & He, J. (2024). Residential Nitrogen Dioxide Exposure and Cause-Specific Cerebrovascular Mortality: An Individual-Level, Case-Crossover Study. Toxics, 12(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12010010







