Puerarin Prevents Bisphenol S Induced Lipid Accumulation by Reducing Liver Lipid Synthesis and Promoting Lipid Metabolism in C57BL/6J Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
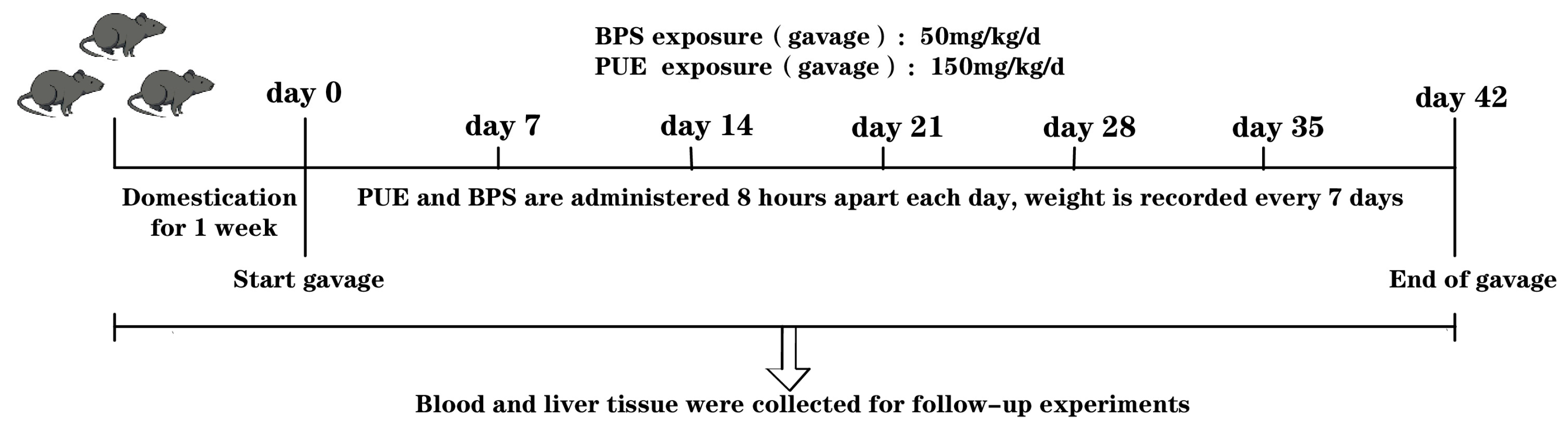
2.1. Animal Experiments
2.2. Sample Collection In Vivo
2.2.1. Blood Sampling
2.2.2. Organ Sampling
2.3. Histological Stains
2.3.1. Oil Red O Stain
2.3.2. H&E Stain
2.4. Measurements of Biochemical Parameters and Oxidative Stress Parameters
2.5. Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
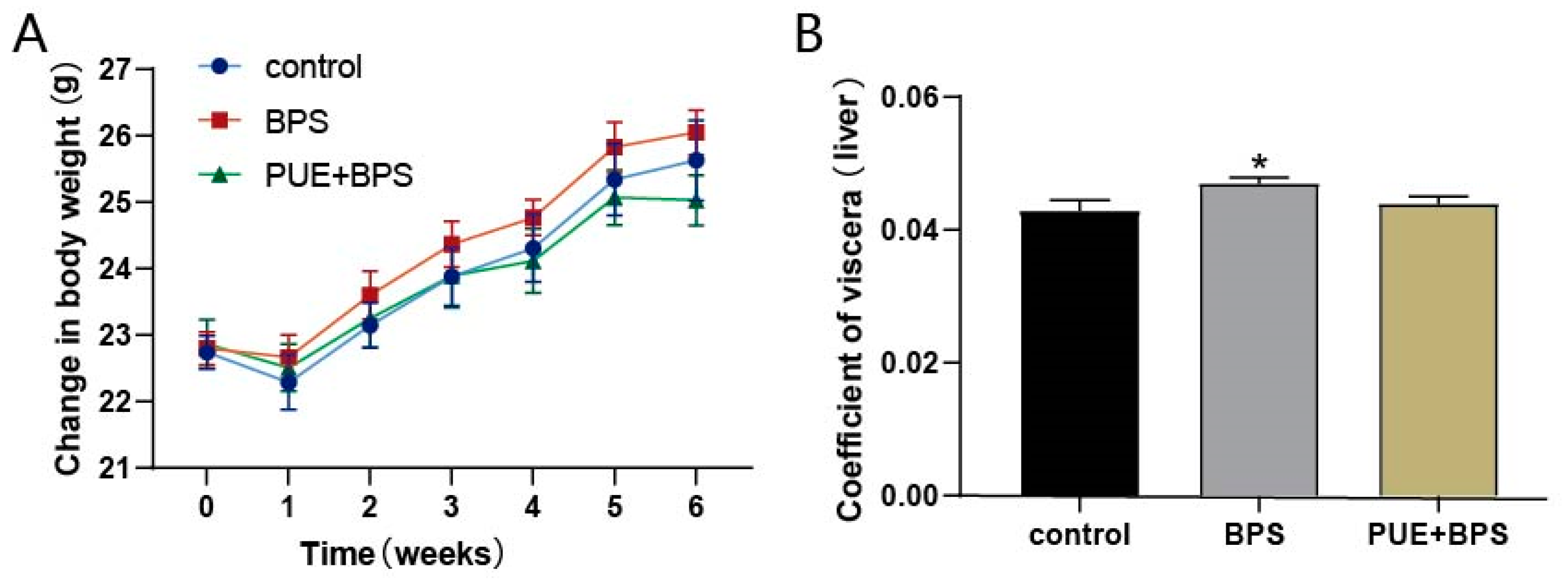
3.1. Body Weight and Organ Coefficient
3.2. Changes of Serum Lipid and Liver Function Indexes in Each Group
3.3. Changes in Oxidative Stress Levels in Liver Tissues of Mice in Each Group
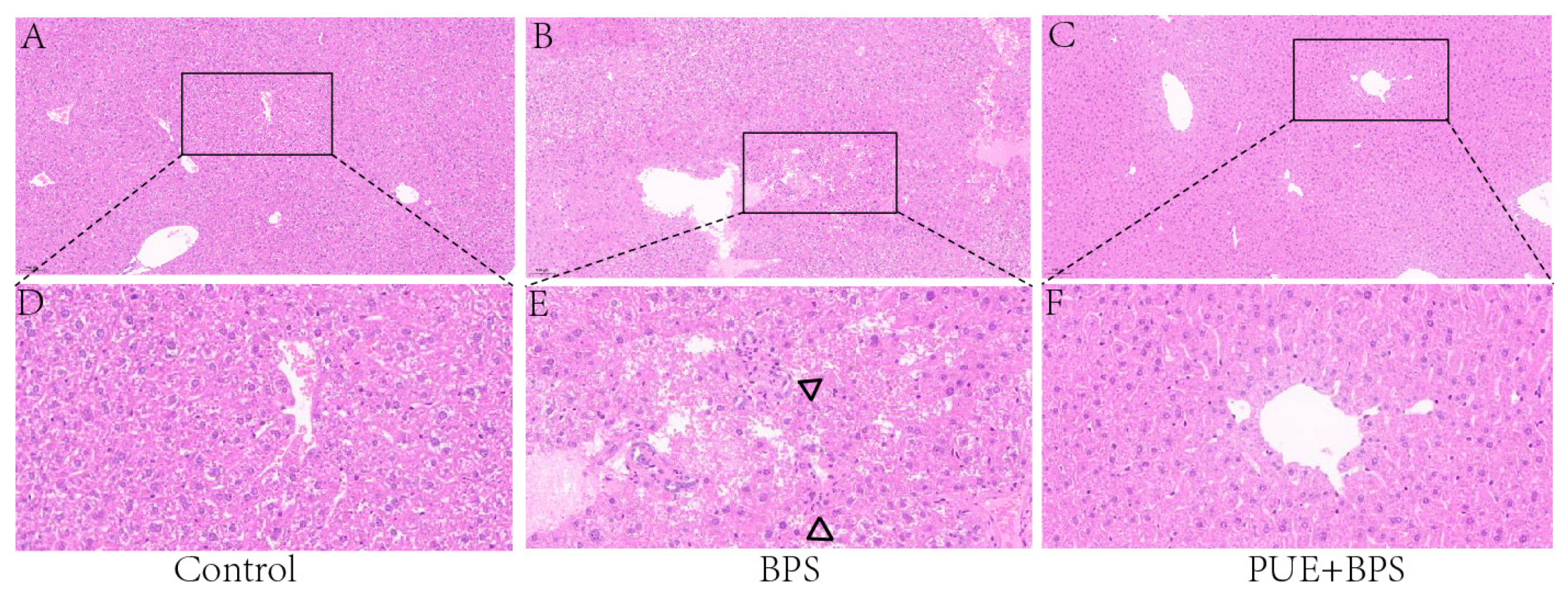
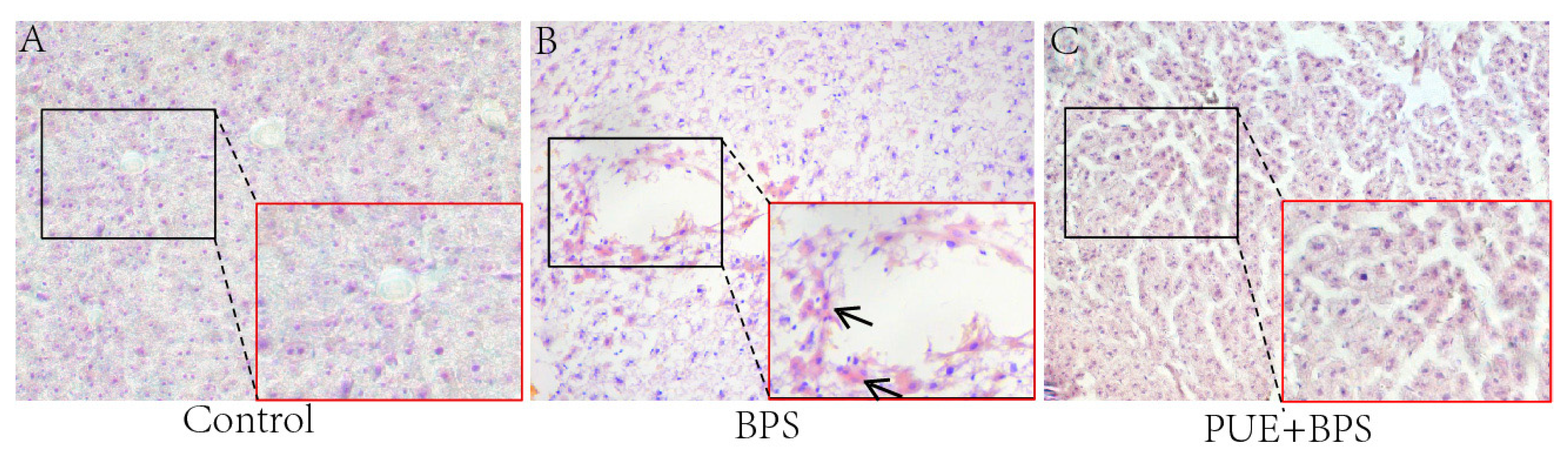
3.4. Changes in H&E and Oil Red O Staining of Liver Tissues in Each Group
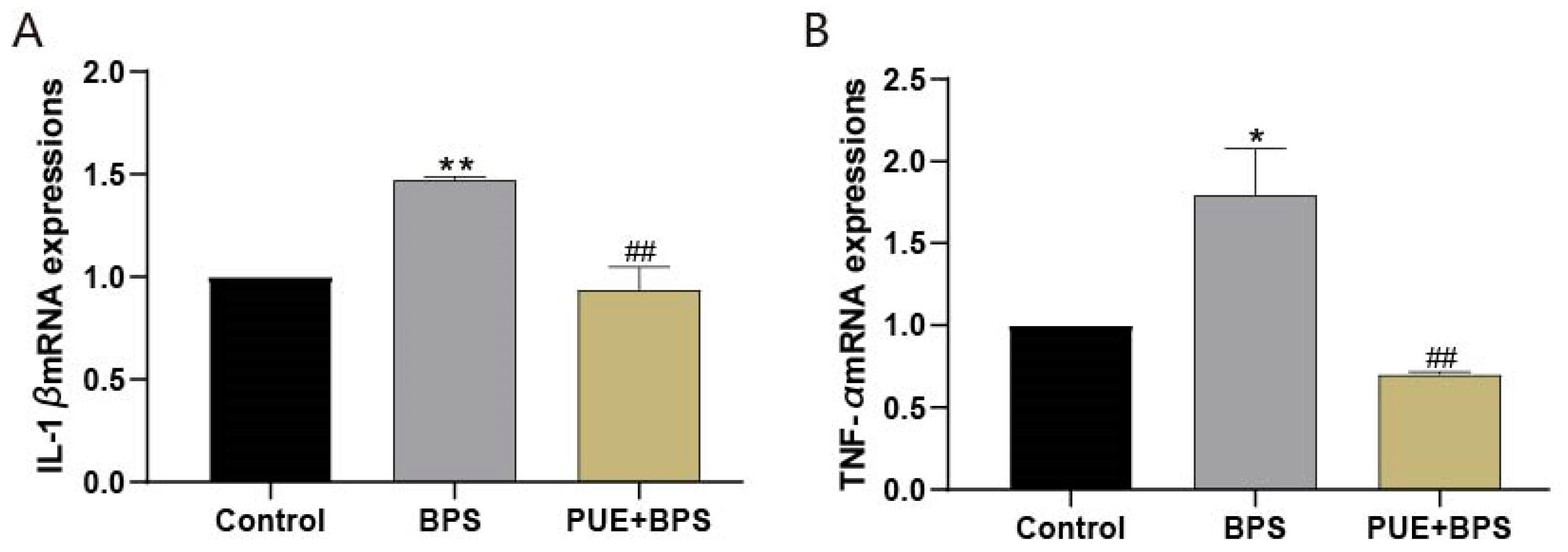
3.5. The mRNA Expression of SREBP1C, FASN, Cpt1a, Cpt1b, PPARγ, PPARα, CD36, IL-1β, and TNF-α in the Liver Tissues of Each Group of Mice
3.6. Changes in Protein Levels of SREBP1C, FASN, Cpt1b, and PPARγ in the Liver Tissues of Mice in Each Group
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, L.H.; Zhang, X.M.; Wang, F.; Gao, C.J.; Chen, D.; Palumbo, J.R.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, E.Y. Occurrence of bisphenol S in the environment and implications for human exposure: A short review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glausiusz, J. Toxicology: The plastics puzzle. Nature 2014, 508, 306–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Gao, R.; Liang, W.; Wei, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, F. Assessment of BPA and BPS exposure in the general population in Guangzhou, China—Estimation of daily intakes based on urinary metabolites. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 315, 120375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndaw, S.; Remy, A.; Denis, F.; Marsan, P.; Jargot, D.; Robert, A. Occupational exposure of cashiers to bisphenol S via thermal paper. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 298, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Profita, M.; Fabbri, E.; Spisni, E.; Valbonesi, P. Comparing effects and action mechanisms of BPA and BPS on HTR-8/SVneo placental cellsdagger. Biol. Reprod. 2021, 105, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.L.; Luan, Y.L.; Shen, H.M.; Guo, Y. Long-term stability of several endocrine disruptors in the first morning urine samples and their associations with lifestyle characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 157873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Z.; Wang, D.; Liu, W.; Li, R.; Yan, S.; Jia, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, W. Perinatal exposure to Bisphenol S (BPS) promotes obesity development by interfering with lipid and glucose metabolism in male mouse offspring. Environ. Res. 2019, 173, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhu, F.; Wang, Y.; Fang, M.; et al. Environmental endocrine disruptor Bisphenol A induces metabolic derailment and obesity via upregulating IL-17A in adipocytes. Environ. Int. 2023, 172, 107759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, T.; Hu, W.; Wang, X.; Xu, B.; Lin, Z.; Hofer, T.; Stefanoff, P.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Association between exposure to a mixture of phenols, pesticides, and phthalates and obesity: Comparison of three statistical models. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Wang, D.; Yan, S.; Li, R.; Yan, J.; Teng, M.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, W. Effects of perinatal exposure to BPA and its alternatives (BPS, BPF and BPAF) on hepatic lipid and glucose homeostasis in female mice adolescent offspring. Chemosphere 2018, 212, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina-Pérez, I.; Olivas-Martínez, A.; Mustieles, V.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Molina-Molina, J.M.; Olea, N.; Fernández, M.F. Bisphenol F and bisphenol S promote lipid accumulation and adipogenesis in human adipose-derived stem cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 152, 112216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianfrancesco, M.A.; Paquot, N.; Piette, J.; Legrand-Poels, S. Lipid bilayer stress in obesity-linked inflammatory and metabolic disorders. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 153, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, S.R.; Cross, E.; Sanna, F.; Hodson, L. Dysregulation of hepatic metabolism with obesity: Factors influencing glucose and lipid metabolism. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2022, 81, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trefts, E.; Gannon, M.; Wasserman, D.H. The liver. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R1147–R1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, J.D.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. SREBPs: Activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.W.; Ding, X.F.; Cao, H.J.; Ni, Q.Z.; Zhu, B.; Ma, N.; Zhang, F.K.; Wang, Y.K.; Xu, S.; Chen, T.W.; et al. Ochratoxin A Induces Steatosis via PPARgamma-CD36 Axis. Toxins 2021, 13, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Qin, H.; Liao, M.; Zheng, E.; Luo, X.; Xiao, A.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Wei, L.; Zhao, L.; et al. CD36 promotes de novo lipogenesis in hepatocytes through INSIG2-dependent SREBP1 processing. Mol. Metab. 2022, 57, 101428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougarne, N.; Weyers, B.; Desmet, S.J.; Deckers, J.; Ray, D.W.; Staels, B.; De Bosscher, K. Molecular Actions of PPARalpha in Lipid Metabolism and Inflammation. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 760–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naiman, S.; Huynh, F.K.; Gil, R.; Glick, Y.; Shahar, Y.; Touitou, N.; Nahum, L.; Avivi, M.Y.; Roichman, A.; Kanfi, Y.; et al. SIRT6 Promotes Hepatic Beta-Oxidation via Activation of PPARalpha. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 4127–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Wang, W.; Kenzior, A.; Olsen, L.; Krishnan, J.; Persons, J.; Medley, K.; Peuß, R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; et al. Enhanced lipogenesis through Ppargamma helps cavefish adapt to food scarcity. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, 2272–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, T.; Feng, Y.; Tong, Y.; Jia, Y.; Wang, C.; Cui, R.; Qu, K.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J. PPARgamma Alleviates Sepsis-Induced Liver Injury by Inhibiting Hepatocyte Pyroptosis via Inhibition of the ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3 Signaling Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 1269747. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.; Yoo, J.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, H.J. Lonicera caerulea Extract Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Free Fatty Acid-Induced HepG2 Hepatocytes and in High Fat Diet-Fed Mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.X.; Zhang, H.; Peng, C. Puerarin: A review of pharmacological effects. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 961–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anukulthanakorn, K.; Parhar, I.S.; Jaroenporn, S.; Kitahashi, T.; Watanbe, G.; Malaivijitnond, S. Neurotherapeutic Effects of Pueraria mirifica Extract in Early- and Late-Stage Cognitive Impaired Rats. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Jia, H.; Yu, M.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Tian, D.; Zhang, H.; Zou, Z. Salvia miltiorrhiza and Pueraria lobata, two eminent herbs in Xin-Ke-Shu, ameliorate myocardial ischemia partially by modulating the accumulation of free fatty acids in rats. Phytomedicine 2021, 89, 153620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Yuan, M.H.; Zhang, C.Y.; Liu, H.M.; Liu, J.R.; Wei, A.L.; Ye, Q.; Zeng, B.; Li, M.F.; Guo, Y.P.; et al. Puerariae Lobatae radix flavonoids and puerarin alleviate alcoholic liver injury in zebrafish by regulating alcohol and lipid metabolism. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 134, 111121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H.; Chen, C.; Liu, R.; Hou, H.; Luo, Q.; Yu, Q.; Ouyang, H.; Feng, Y.; et al. alpha-D-1,3-glucan from Radix Puerariae thomsonii improves NAFLD by regulating the intestinal flora and metabolites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 299, 120197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, W.; Feng, Y.; Hou, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, Q.; Luo, Y.; Ouyang, H.; et al. Radix Puerariae thomsonii polysaccharide (RPP) improves inflammation and lipid peroxidation in alcohol and high-fat diet mice by regulating gut microbiota. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209 Pt A, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- en Braver-Sewradj, S.P.; van Spronsen, R.; Hessel EV, S. Substitution of bisphenol A: A review of the carcinogenicity, reproductive toxicity, and endocrine disruption potential of alternative substances. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2020, 50, 128–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, K.; Luo, J.; Sun, J.; Ge, H.; Wang, Z. Associations of urinary bisphenol A and its alternatives bisphenol S and F concentrations with depressive symptoms among adults. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Huh, D.A.; Moon, K.W. Urinary bisphenol concentrations and its association with metabolic disorders in the US and Korean populations. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 295, 118679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; He, Q.Z.; Zhu, B.Q.; Zeng, H.C. Oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis is involved in bisphenol S-induced reproductive toxicity in male C57BL/6 mice. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 1839–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Z.; Wu, Z.Y.; Zhu, B.Q.; Wang, Y.X.; Kan, Y.Q.; Zeng, H.C. The BDNF-TrkB-CREB Signalling Pathway Is Involved in Bisphenol S-Induced Neurotoxicity in Male Mice by Regulating Methylation. Toxics 2022, 10, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.L.; Nakib, D.; Perciani, C.T.; MacParland, S.A. The immune niche of the liver. Clin. Sci. 2021, 135, 2445–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramskov Tetzlaff, C.N.; Svingen, T.; Vinggaard, A.M.; Rosenmai, A.K.; Taxvig, C. Bisphenols B, E, F, and S and 4-cumylphenol induce lipid accumulation in mouse adipocytes similarly to bisphenol A. Environ. Toxicol. 2020, 35, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.A.; Baek, H.; Choi, M.; Park, J.; Son, S.J.; Seo, H.J.; Jung, J.; Seong, J.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, S. Adipogenic effects of prenatal exposure to bisphenol S (BPS) in adult F1 male mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Tian, S.; Yan, J.; Jia, M.; Yan, S.; Li, R.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, Z. Effects of perinatal exposure to BPA, BPF and BPAF on liver function in male mouse offspring involving in oxidative damage and metabolic disorder. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; He, J.; Xu, T.; Han, H.; Zhu, Z.; Meng, L.; Pang, Q.; Fan, R. Bisphenol A(BPA), BPS and BPB-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis mediated by mitochondria in human neuroblastoma cell lines. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Wang, J.; Liao, Y.; Shu, L. Puerarin alleviates depressive-like behaviors in high-fat diet-induced diabetic mice via modulating hippocampal GLP-1R/BDNF/TrkB signaling. Nutr. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 997–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, J.W.; Yang, H.K.; Jun, M.S.; Lee, B.C. Puerarin Attenuates Obesity-Induced Inflammation and Dyslipidemia by Regulating Macrophages and TNF-Alpha in Obese Mice. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepino, M.Y.; Kuda, O.; Samovski, D.; Abumrad, N.A. Structure-function of CD36 and importance of fatty acid signal transduction in fat metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2014, 34, 281–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, J.L.; Liu, Y.Y.; Li, Z.Z.; Zhuang, Q.Z.; Tang, W.Z.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, X.Z. Amentoflavone prevents ox-LDL-induced lipid accumulation by suppressing the PPARgamma/CD36 signal pathway. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2021, 431, 115733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, L.; Chi, W.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Song, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Jia, J.; Pilo, M.G.; Wang, J.; et al. Cholesterol biosynthesis supports the growth of hepatocarcinoma lesions depleted of fatty acid synthase in mice and humans. Gut 2020, 69, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Huang, K.; Zhao, J.; Le, S.; Jiang, L.; Liu, H.; Yang, P.; Xiao, X.; et al. B-cell lymphoma 6 alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice through suppression of fatty acid transporter CD36. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Deng, Z.T.; Huang, S.; Ning, M.; Feng, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, Q.S.; Leng, Y. Alisol B Alleviates Hepatocyte Lipid Accumulation and Lipotoxicity via Regulating RARalpha-PPARgamma-CD36 Cascade and Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis in Mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Gene | Primer | Sequences (5′ → 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| FASN | Forward | CGGAGTCGCTTGAGTATA |
| Reverse | CACAGGGACCGAGTAATG | |
| Cpt1a | Forward | GGAGAATGCCAGGAGGTC |
| Reverse | GGTGTCAAATGGGAAGGA | |
| PPARγ | Forward | CACAATGCCATCAGGTTT |
| Reverse | CTCGCAGATCAGCAGACT | |
| PPARα | Forward | CAAGTGCCTGTCTGTCGG |
| Reverse | CAGGTAGGCTTCGTGGAT | |
| CD36 | Forward | ATTCTCATGCCAGTCGGA |
| Reverse | TTTGCTGCTGTTCTTTGC | |
| SREBP-1c | Forward | TCTCCTAGAGCGAGCGTT |
| Reverse | AGGGCATCTGAGAACTCC | |
| Cpt1b | Forward | AGACTGTGCGTTCCTGTA |
| Reverse | TTGGAGACGATGTAAAGG | |
| GAPDH | Forward | CCTCGTCCCGTAGACAAAATG |
| Reverse | TGAGGTCAATGAAGGGGTCGT | |
| IL-1β | Forward | GATGGCTTATTACAGTGGC |
| Reverse | TAGTGGTGGTCGGAGATT | |
| TNF-α | Forward | ACGCTCTTCTGCCTGCTG |
| Reverse | CTTGTCACTCGGGGTTCG | |
| β-actin | Forward | CACCCGCGAGTACAACCTC |
| Reverse | CCCATACCCACCATCACACC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Z.-Y.; Luo, L.; Kan, Y.-Q.; Qin, M.-L.; Li, H.-T.; He, Q.-Z.; Zeng, H.-C. Puerarin Prevents Bisphenol S Induced Lipid Accumulation by Reducing Liver Lipid Synthesis and Promoting Lipid Metabolism in C57BL/6J Mice. Toxics 2023, 11, 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11090736
Wu Z-Y, Luo L, Kan Y-Q, Qin M-L, Li H-T, He Q-Z, Zeng H-C. Puerarin Prevents Bisphenol S Induced Lipid Accumulation by Reducing Liver Lipid Synthesis and Promoting Lipid Metabolism in C57BL/6J Mice. Toxics. 2023; 11(9):736. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11090736
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Zi-Yao, Li Luo, Ya-Qi Kan, Mei-Lin Qin, Hai-Ting Li, Qing-Zhi He, and Huai-Cai Zeng. 2023. "Puerarin Prevents Bisphenol S Induced Lipid Accumulation by Reducing Liver Lipid Synthesis and Promoting Lipid Metabolism in C57BL/6J Mice" Toxics 11, no. 9: 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11090736
APA StyleWu, Z.-Y., Luo, L., Kan, Y.-Q., Qin, M.-L., Li, H.-T., He, Q.-Z., & Zeng, H.-C. (2023). Puerarin Prevents Bisphenol S Induced Lipid Accumulation by Reducing Liver Lipid Synthesis and Promoting Lipid Metabolism in C57BL/6J Mice. Toxics, 11(9), 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11090736






