Applying Artificial Neural Networks to Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Forager Honey Bees (Apis mellifera) for Ecological Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
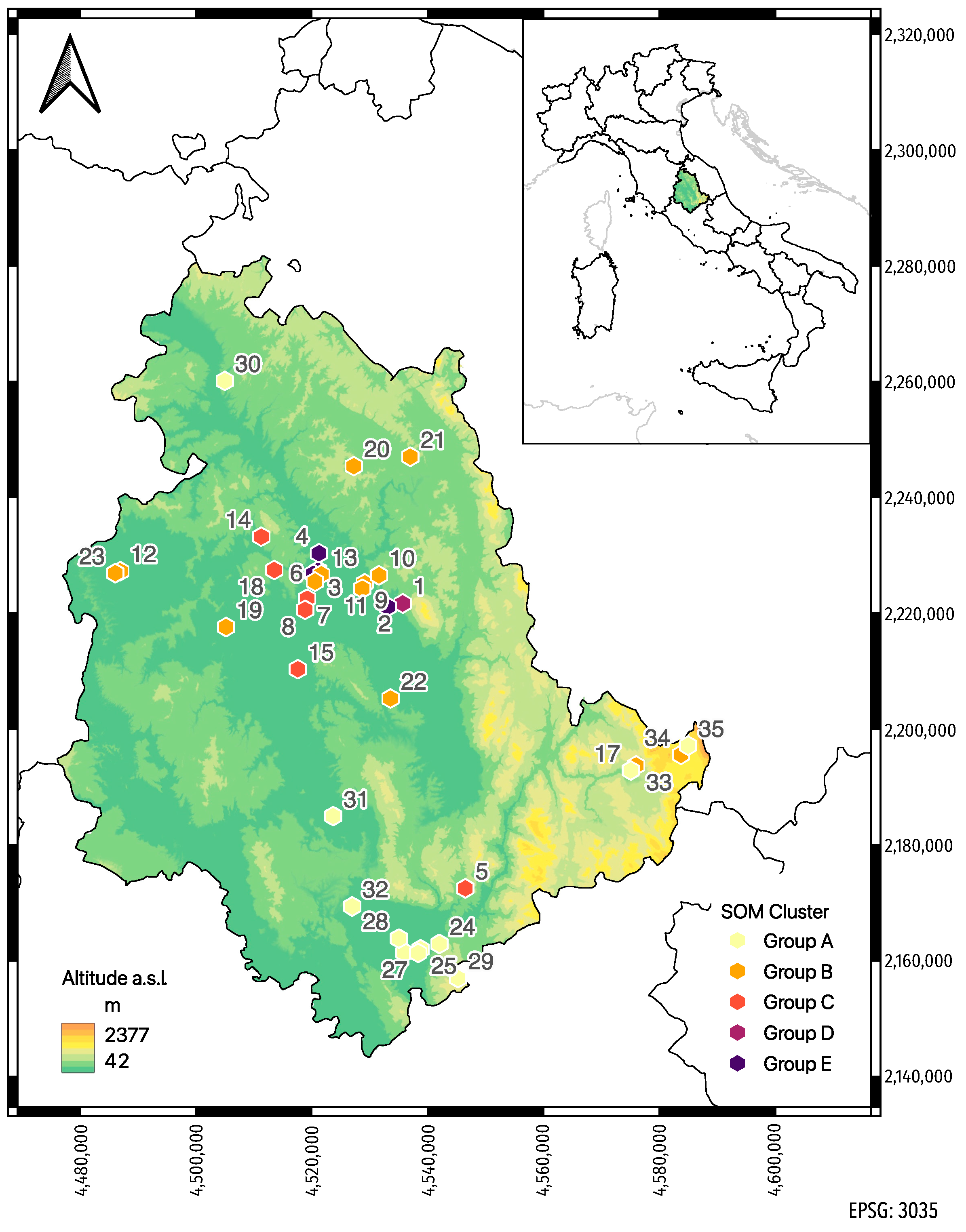
2.1. Honey Bee Sampling
2.2. Oxidative Stress Biomarkers
2.3. Modeling Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Biomarker Activities
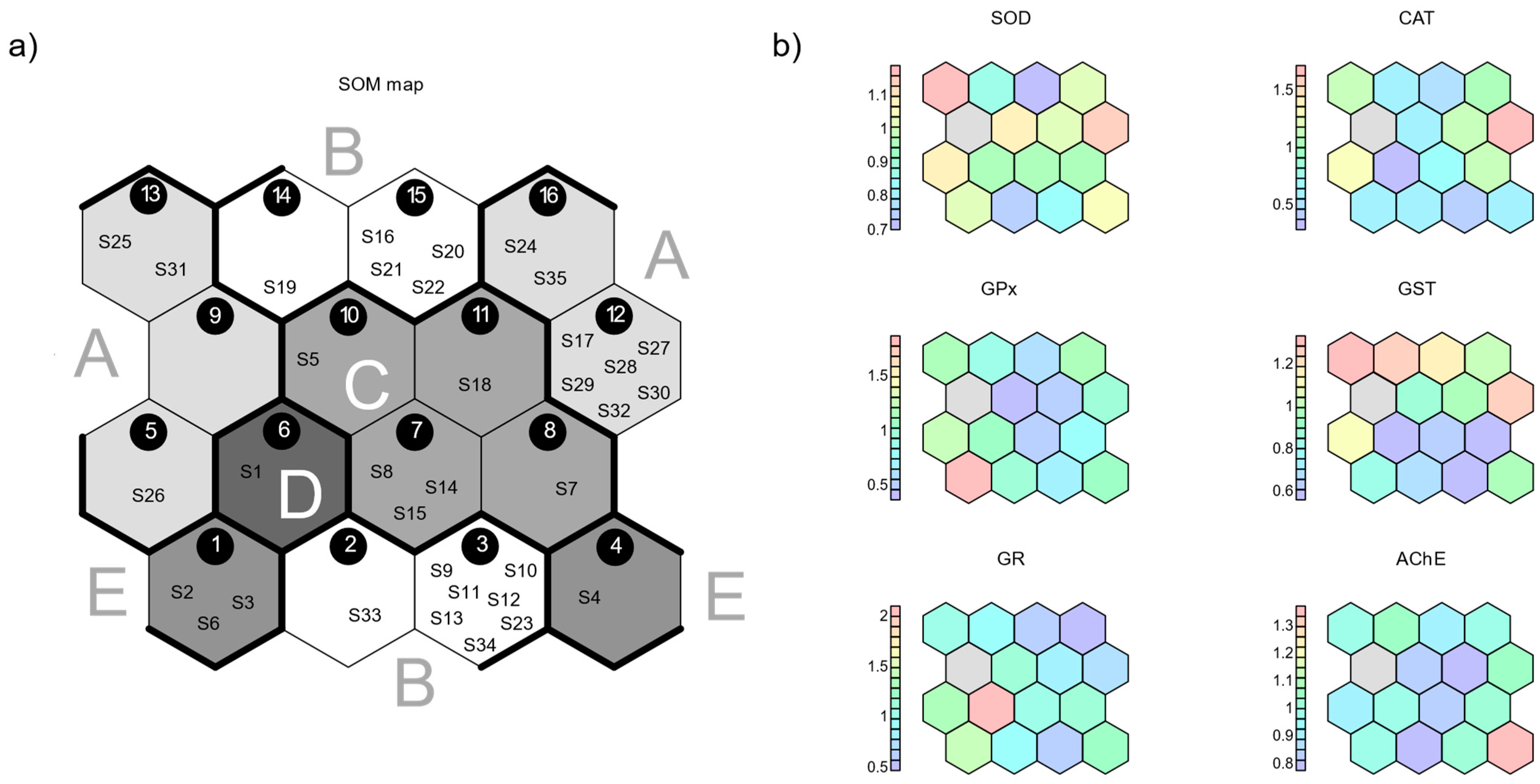
3.2. Self-Organizing Map
3.3. Correlations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ollerton, J. Pollinator Diversity: Distribution, Ecological Function, and Conservation. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2017, 48, 353–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, S.G.; Biesmeijer, J.C.; Kremen, C.; Neumann, P.; Schweiger, O.; Kunin, W.E. Global Pollinator Declines: Trends, Impacts and Drivers. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderplanck, M.; Lapeyre, B.; Brondani, M.; Opsommer, M.; Dufay, M.; Hossaert-McKey, M.; Proffit, M. Ozone Pollution Alters Olfaction and Behavior of Pollinators. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devillers, J.; Pham-Delegue, M.-H. (Eds.) Honey Bees: Estimating the Environmental Impact of Chemicals; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-0-429-21876-7. [Google Scholar]
- Di Fiore, C.; De Cristofaro, A.; Nuzzo, A.; Notardonato, I.; Ganassi, S.; Iafigliola, L.; Sardella, G.; Ciccone, M.; Nugnes, D.; Passarella, S.; et al. Biomonitoring of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, Heavy Metals, and Plasticizers Residues: Role of Bees and Honey as Bioindicators of Environmental Contamination. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 44234–44250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Noi, A.; Casini, S.; Campani, T.; Cai, G.; Caliani, I. Review on Sublethal Effects of Environmental Contaminants in Honey Bees (Apis mellifera), Knowledge Gaps and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goretti, E.; Pallottini, M.; Rossi, R.; La Porta, G.; Gardi, T.; Cenci Goga, B.T.; Elia, A.C.; Galletti, M.; Moroni, B.; Petroselli, C.; et al. Heavy Metal Bioaccumulation in Honey Bee Matrix, an Indicator to Assess the Contamination Level in Terrestrial Environments. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATSDR (Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry). Substance Priority List Dates and Notices and Related Information; ATSDR: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fränzle, S. Adsorption to Chitin—A Viable and Organism-Protecting Method for Biomonitoring Metals Present in Different Environmental Compartments Getting Contacted with Arthropods. Ann. Bot. 2015, 5, 13065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, A.C.; Dörr, A.J.M.; Abete, M.C.; Prearo, M. Seasonal Variability of Detoxificant Response and Heavy Metal Accumulation in Tissues of Both Sexes in Tinca tinca (L.) from Lake Trasimeno. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2010, 20, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, A.C.; Burioli, E.; Magara, G.; Pastorino, P.; Caldaroni, B.; Menconi, V.; Dörr, A.J.M.; Colombero, G.; Abete, M.C.; Prearo, M. Oxidative Stress Ecology on Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas from Lagoon and Offshore Italian Sites. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, A.C.; Magara, G.; Pastorino, P.; Zaccaroni, A.; Caldaroni, B.; Andreini, R.; Righetti, M.; Silvi, M.; Dörr, A.J.M.; Prearo, M. Ecotoxicity in Hyriopsis bialatus of Copper and Zinc Biocides Used in Metal-Based Antifouling Paints. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 18245–18258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccardo, M.; Bertoli, M.; Pastorino, P.; Barceló, D.; Provenza, F.; Lesa, D.; Anselmi, S.; Elia, A.; Prearo, M.; Pizzul, E.; et al. Lethal and Sublethal Responses of Hydropsyche pellucidula (Insecta, Trichoptera) to Commercial Polypropylene Microplastics after Different Preconditioning Treatments. Toxics 2021, 9, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monchanin, C.; Burden, C.; Barron, A.B.; Smith, B.H. Heavy metal pollutants: The hidden pervasive threat to honey bees and other pollinators. In Advances in Insect Physiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; Volume 64, pp. 255–288. ISBN 978-0-443-13249-0. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, M.M.; Tran, L.; McKee, C.G.; Ortega Polo, R.; Newman, T.; Lansing, L.; Griffiths, J.S.; Bilodeau, G.J.; Rott, M.; Marta Guarna, M. Honey Bees as Biomonitors of Environmental Contaminants, Pathogens, and Climate Change. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 134, 108457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, A.; Ammendola, A.; Battistella, S.; Naccarato, A.; Pallavicini, A.; Simeon, E.; Tagarelli, A.; Giulianini, P.G. Apis mellifera ligustica, Spinola 1806 as Bioindicator for Detecting Environmental Contamination: A Preliminary Study of Heavy Metal Pollution in Trieste, Italy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H.; Belousov, V.V.; Chandel, N.S.; Davies, M.J.; Jones, D.P.; Mann, G.E.; Murphy, M.P.; Yamamoto, M.; Winterbourn, C. Defining Roles of Specific Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Cell Biology and Physiology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 499–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliani, I.; Campani, T.; Conti, B.; Cosci, F.; Bedini, S.; D’Agostino, A.; Ammendola, A.; Di Noi, A.; Gori, A.; Casini, S. Multi-Biomarker Approach and IBR Index to Evaluate the Effects of Different Contaminants on the Ecotoxicological Status of Apis mellifera. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, T.V.; Kojić, D.; Orčić, S.; Vukašinović, E.L.; Blagojević, D.P.; Purać, J. Laboratory Bioassays on the Response of Honey Bee (Apis mellifera L.) Glutathione S-Transferase and Acetylcholinesterase to the Oral Exposure to Copper, Cadmium, and Lead. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 6890–6897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alburaki, M.; Steckel, S.J.; Chen, D.; McDermott, E.; Weiss, M.; Skinner, J.A.; Kelly, H.; Lorenz, G.; Tarpy, D.R.; Meikle, W.G.; et al. Landscape and Pesticide Effects on Honey Bees: Forager Survival and Expression of Acetylcholinesterase and Brain Oxidative Genes. Apidologie 2017, 48, 556–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bale, J.S.; Hayward, S.A.L. Insect Overwintering in a Changing Climate. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 980–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danks, H.V. Key Themes in the Study of Seasonal Adaptations in Insects I. Patterns of Cold Hardiness. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2005, 40, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danks, H.V. Insect Adaptations to Cold and Changing Environments. Can. Entomol. 2006, 138, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, H.-N.; Lee, S.-G.; Yun, S.-H.; Kim, H.K.; Choi, Y.S.; Kim, G.-H. Comparative Analyses of Cu-Zn Superoxide Dismutase (SOD1) and Thioredoxin Reductase (TrxR) at the MRNA Level between Apis mellifera L. and Apis cerana F. (Hymenoptera: Apidae) Under Stress Conditions. J. Insect Sci. 2016, 16, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalouette, L.; Williams, C.M.; Hervant, F.; Sinclair, B.J.; Renault, D. Metabolic Rate and Oxidative Stress in Insects Exposed to Low Temperature Thermal Fluctuations. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2011, 158, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ma, W.; Shen, J.; Long, D.; Feng, Y.; Su, W.; Xu, K.; Du, Y.; Jiang, Y. Tolerance and Response of Two Honeybee Species Apis cerana and Apis mellifera to High Temperature and Relative Humidity. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badiou-Bénéteau, A.; Carvalho, S.M.; Brunet, J.-L.; Carvalho, G.A.; Buleté, A.; Giroud, B.; Belzunces, L.P. Development of Biomarkers of Exposure to Xenobiotics in the Honey Bee Apis mellifera: Application to the Systemic Insecticide Thiamethoxam. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 82, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, S.M.; Belzunces, L.P.; Carvalho, G.A.; Brunet, J.-L.; Badiou-Beneteau, A. Enzymatic Biomarkers as Tools to Assess Environmental Quality: A Case Study of Exposure of the Honeybee Apis mellifera to Insecticides: Biomarker Responses in Honeybees Exposed to Pesticides. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 2117–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolić, T.V.; Purać, J.; Orčić, S.; Kojić, D.; Vujanović, D.; Stanimirović, Z.; Gržetić, I.; Ilijević, K.; Šikoparija, B.; Blagojević, D.P. Environmental Effects on Superoxide Dismutase and Catalase Activity and Expression in Honey Bee. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 90, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenci-Goga, B.T.; Sechi, P.; Karama, M.; Ciavarella, R.; Pipistrelli, M.V.; Goretti, E.; Elia, A.C.; Gardi, T.; Pallottini, M.; Rossi, R.; et al. Cross-Sectional Study to Identify Risk Factors Associated with the Occurrence of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Honey Bees Apis mellifera) in Umbria, Central Italy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 9637–9645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein Measurement with the Folin Phenol Reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enzyme Nomenclature. Recommendations 1992. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 223, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A New and Rapid Colorimetric Determination of Acetylcholinesterase Activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohonen, T. Self-Organizing Maps; Springer Series in Information Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; Volume 30, ISBN 978-3-540-67921-9. [Google Scholar]
- Vesanto, J.; Alhoniemi, E. Clustering of the Self-Organizing Map. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2000, 11, 586–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehrens, R.; Kruisselbrink, J. Flexible Self-Organizing Maps in Kohonen 3.0. J. Stat. Softw. 2018, 87, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-S.; Tison, J.; Lek, S.; Giraudel, J.-L.; Coste, M.; Delmas, F. Application of a Self-Organizing Map to Select Representative Species in Multivariate Analysis: A Case Study Determining Diatom Distribution Patterns across France. Ecol. Inform. 2006, 1, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- RStudio Team RStudio. Integrated Development Environment for R; RStudio Team RStudio: Boston, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, S.B.; Sivakoff, F.S.; Meuti, M.E.; Gardiner, M.M. Metals Could Challenge Pollinator Conservation in Legacy Cities. J. Insect Conserv. 2023, 27, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goretti, E.; Pallottini, M.; La Porta, G.; Elia, A.C.; Gardi, T.; Petroselli, C.; Gravina, P.; Bruschi, F.; Selvaggi, R.; Cappelletti, D. Bioaccumulation of Trace Elements along the Body Longitudinal Axis in Honey Bees. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, N.; Zhang, K.; Hladun, K.R.; Rust, M.; Chen, Y.-F.; Zhu, Z.-Y.; Liu, T.-X.; Trumble, J.T. Joint Effects of Cadmium and Copper on Apis mellifera Forgers and Larvae. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 237, 108839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migula, P.; Laszczyca, P.; Augustyniak, M.; Wilczek, G.; Rozpedek, K.; Kafel, A.; Woloszyn, M. Antioxidative Defence Enzymes in Beetles from a Metal Pollution Gradient. Biol. Bratisl. 2004, 59, 645–654. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, F.C.F.; Van Gestel, C.A.M.; Amorim, M.J.B. Impact of Chromium on the Soil Invertebrate Model Enchytraeus crypticus (Oligochaeta) in Standard Reproduction and Full Life Cycle Tests. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpi-Koski, J.; Penttinen, O.-P.; Väisänen, A.O.; Van Gestel, C.A.M. An Uptake and Elimination Kinetics Approach to Assess the Bioavailability of Chromium, Copper, and Arsenic to Earthworms (Eisenia andrei) in Contaminated Field Soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 15095–15104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, K.; Cleare, X.; Li-Byarlay, H. The Life Span and Levels of Oxidative Stress in Foragers Between Feral and Managed Honey Bee Colonies. J. Insect Sci. 2022, 22, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li-Byarlay, H.; Huang, M.H.; Simone-Finstrom, M.; Strand, M.K.; Tarpy, D.R.; Rueppell, O. Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) Drones Survive Oxidative Stress Due to Increased Tolerance Instead of Avoidance or Repair of Oxidative Damage. Exp. Gerontol. 2016, 83, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gizaw, G.; Kim, Y.; Moon, K.; Choi, J.B.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, J.K. Effect of Environmental Heavy Metals on the Expression of Detoxification-Related Genes in Honey Bee Apis mellifera. Apidologie 2020, 51, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.B.; Roberts, S.P.; Elekonich, M.M. Age and Natural Metabolically-Intensive Behavior Affect Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Mechanisms. Exp. Gerontol. 2008, 43, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.P.; Campbell, S.D.; Michaud, D.; Charbonneau, M.; Hilliker, A.J. Null Mutation of Copper/Zinc Superoxide Dismutase in Drosophila Confers Hypersensitivity to Paraquat and Reduced Longevity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 2761–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganger, R.; Garla, R.; Mohanty, B.P.; Bansal, M.P.; Garg, M.L. Protective Effects of Zinc Against Acute Arsenic Toxicity by Regulating Antioxidant Defense System and Cumulative Metallothionein Expression. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 169, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicewicz, Ł.; Nicewicz, A.W.; Kafel, A.; Nakonieczny, M. Set of Stress Biomarkers as a Practical Tool in the Assessment of Multistress Effect Using Honeybees from Urban and Rural Areas as a Model Organism: A Pilot Study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 9084–9096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Li, X.; Shen, J.; Du, Y.; Xu, K.; Jiang, Y. Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Apis mellifera Adaptations to High Temperature and High Humidity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 184, 109599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, S.R.; Bach, D.M.; Rondeau, N.C.; Sam, J.; Lovinger, N.L.; Lopatkin, A.J.; Snow, J.W. Honey Bee SHSP Are Responsive to Diverse Proteostatic Stresses and Potentially Promising Biomarkers of Honey Bee Stress. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Meng, F.; Jia, H.; Guo, X.; Xu, B. The Identification and Oxidative Stress Response of a Zeta Class Glutathione S-Transferase (GSTZ1) Gene from Apis cerana cerana. J. Insect Physiol. 2012, 58, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Li, G.; Guo, D.; Li, H.; Liu, Q.; Xu, B.; Guo, X. Response Mechanisms to Heat Stress in Bees. Apidologie 2021, 52, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Biomarker | n | Min | Max | Median | iqr | Mean | SD | 95% CI | % Variation | Spatial Autocorrelation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOD | 35 | 6.10 | 18.31 | 13.28 | 4.16 | 13.57 | 2.86 | 0.98 | 200% | −0.113 (p < 0.001) |
| CAT | 35 | 3.67 | 45.02 | 14.12 | 14.45 | 19.81 | 11.80 | 4.05 | 1128% | −0.185 (p < 0.001) |
| GPx | 35 | 3.51 | 31.98 | 12.90 | 8.15 | 14.26 | 6.57 | 2.26 | 811% | −0.020 (p = 0.620) |
| GST | 35 | 10.73 | 40.91 | 23.01 | 10.89 | 22.36 | 8.13 | 2.79 | 281% | −0.095 (p = 0.001) |
| GR | 35 | 14.96 | 137.74 | 49.29 | 24.71 | 52.05 | 24.53 | 8.43 | 821% | −0.050 (p = 0.296) |
| AChE | 35 | 45.11 | 104.35 | 65.97 | 13.33 | 65.93 | 13.41 | 4.61 | 131% | −0.010 (p = 0.342) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
La Porta, G.; Magara, G.; Goretti, E.; Caldaroni, B.; Dörr, A.J.M.; Selvaggi, R.; Pallottini, M.; Gardi, T.; Cenci-Goga, B.T.; Cappelletti, D.; et al. Applying Artificial Neural Networks to Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Forager Honey Bees (Apis mellifera) for Ecological Assessment. Toxics 2023, 11, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11080661
La Porta G, Magara G, Goretti E, Caldaroni B, Dörr AJM, Selvaggi R, Pallottini M, Gardi T, Cenci-Goga BT, Cappelletti D, et al. Applying Artificial Neural Networks to Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Forager Honey Bees (Apis mellifera) for Ecological Assessment. Toxics. 2023; 11(8):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11080661
Chicago/Turabian StyleLa Porta, Gianandrea, Gabriele Magara, Enzo Goretti, Barbara Caldaroni, Ambrosius Josef Martin Dörr, Roberta Selvaggi, Matteo Pallottini, Tiziano Gardi, Beniamino T. Cenci-Goga, David Cappelletti, and et al. 2023. "Applying Artificial Neural Networks to Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Forager Honey Bees (Apis mellifera) for Ecological Assessment" Toxics 11, no. 8: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11080661
APA StyleLa Porta, G., Magara, G., Goretti, E., Caldaroni, B., Dörr, A. J. M., Selvaggi, R., Pallottini, M., Gardi, T., Cenci-Goga, B. T., Cappelletti, D., & Elia, A. C. (2023). Applying Artificial Neural Networks to Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Forager Honey Bees (Apis mellifera) for Ecological Assessment. Toxics, 11(8), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11080661










