Urinary Levels of 14 Metal Elements in General Population: A Region-Based Exploratory Study in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
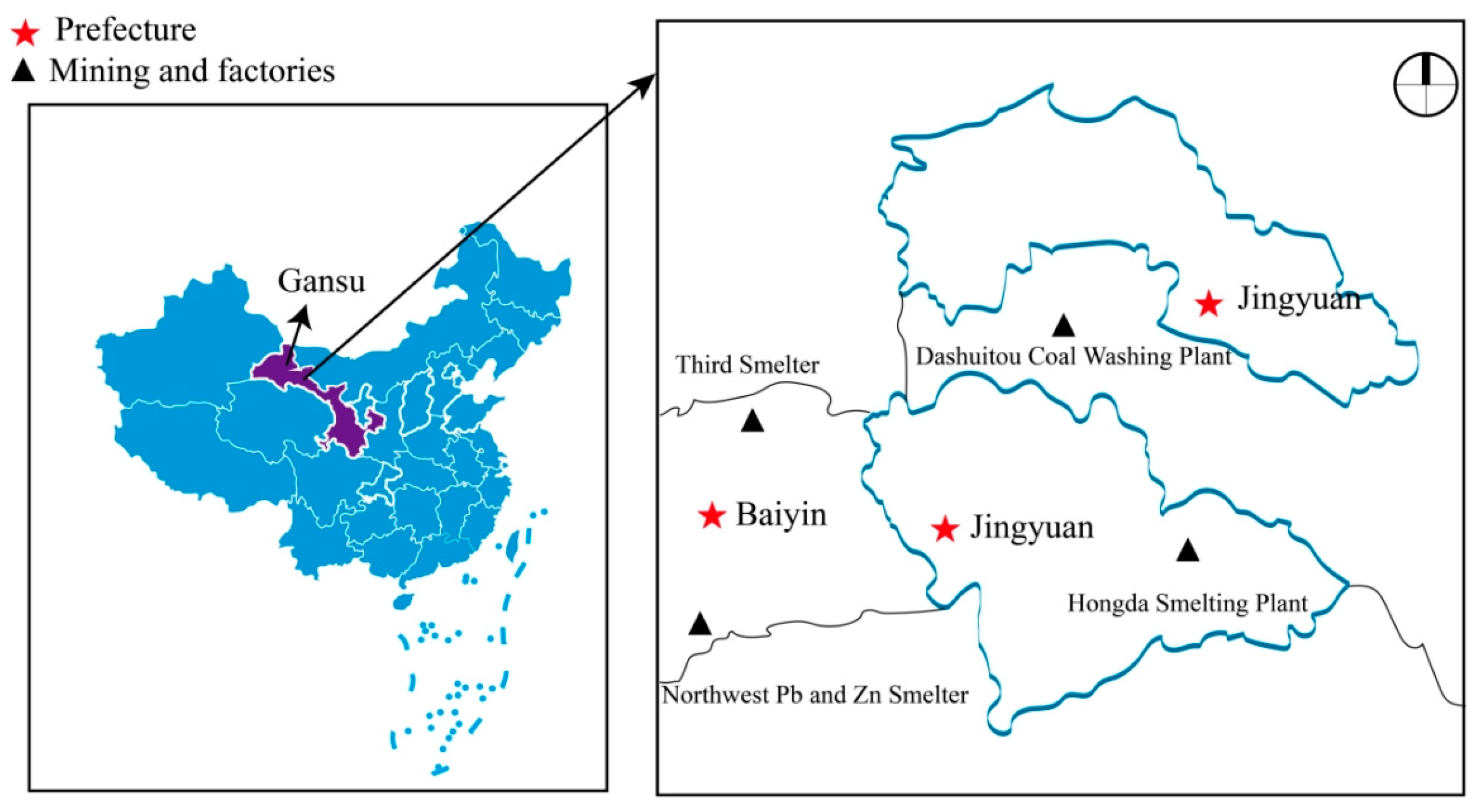
2.2. Study Population and Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Pretreatment and Instrument Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Participants’ Characteristics
3.2. Urinary Concentrations of 14 Metals
3.3. Factors Influencing the Element Levels in Urine
3.3.1. Gender-Related Differences in Urine Element Concentrations
3.3.2. Age-Related Differences in Urine Element Concentrations
3.3.3. Differences in Urine Element Concentration in Groups of People with or without Soil Contact
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Zhou, M.; Xiao, L.; Xu, T.; Yang, S.; Nie, X.; Xie, L.; Yu, L.; Mu, G.; et al. Systemic inflammation mediates the association of heavy metal exposures with liver injury: A study in general Chinese urban adults. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeker, J.D.; Rossano, M.G.; Protas, B.; Padmanahban, V.; Diamond, M.P.; Puscheck, E.; Daly, D.; Paneth, N.; Wirth, J.J. Environmental exposure to metals and male reproductive hormones: Circulating testosterone is inversely associated with blood molybdenum. Fertil. Steril. 2010, 93, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; Li, Q.; Guo, C.; Zhong, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Yu, Y. Urinary heavy metals in residents from a typical city in South China: Human exposure and health risks. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 15827–15837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Li, J. Environmental effects of heavy metals derived from the e-waste recycling activities in China: A systematic review. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2587–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fang, F.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kuang, Y.; Wu, M. Heavy metal contamination and health risks of indoor dust around Xinqiao Mining Area, Tongling, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2020, 26, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.H.; Hyun, Y.Y.; Lee, K.-B.; Chang, Y.; Ryu, S.; Oh, K.-H.; Ahn, C. Environmental Heavy Metal Exposure and Chronic Kidney Disease in the General Population. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2015, 30, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokadia, H.K.; Agarwal, S. Serum Heavy Metals and Obstructive Lung Disease Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Chest 2013, 143, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimeri, A.M.; Robb, S.W.; Hassan, S.M.; Hire, R.R.; Davis, M.B. Assessing Heavy Metal and PCB Exposure from Tap Water by Measuring Levels in Plasma from Sporadic Breast Cancer Patients, a Pilot Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 15683–15691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul, K.S.M.; Jayasinghe, J.S.; Chandana, E.P.S.; Jayasumana, C.; De Silva, P.M.C. Arsenic and human health effects: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 828–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasab, H.; Rajabi, S.; Eghbalian, M.; Malakootian, M.; Hashemi, M.; Mahmoudi-Moghaddam, H. Association of As, Pb, Cr, and Zn urinary heavy metals levels with predictive indicators of cardiovascular disease and obesity in children and adolescents. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.J.; O’Brien, K.M.; Jackson, B.P.; Karagas, M.R. Urine and toenail cadmium levels in pregnant women: A reliability study. Environ. Int. 2018, 118, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.L.; Zhang, R.Q.; Wang, X.; Shen, X.L.; Wang, P.L.; Sun, N.; Li, X.W.; Li, X.H.; Hai, C.X. Effects of sub-chronic, low-dose cadmium exposure on kidney damage and potential mechanisms. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.P.; Dai, S.J.; Yin, Z.Q.; Lu, H.K.; Jia, R.Y.; Xu, J.; Song, X.; Li, L.; Shu, Y.; Zhao, X.H. Toxicological assessment of combined lead and cadmium: Acute and sub-chronic toxicity study in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 65, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Song, J.; Li, Y.; Lai, Y.; Lin, J.; Pan, J.; Chi, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, G.; et al. Bioaccessibility and bioavailability adjusted dietary exposure of cadmium for local residents from a high-level environmental cadmium region. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocca, B.; Ruggieri, F.; Pino, A.; Rovira, J.; Calamandrei, G.; Martinez, M.A.; Domingo, J.L.; Alimonti, A.; Schuhmacher, M. Human biomonitoring to evaluate exposure to toxic and essential trace elements during pregnancy. Part A. concentrations in maternal blood, urine and cord blood. Environ. Res. 2019, 177, 108599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; Guo, Y.; Wang, B.; Xu, Y.; Chen, W. Associations between essential metals exposure and metabolic syndrome (MetS): Exploring the mediating role of systemic in flammation in a general Chinese population. Environ. Int. 2020, 140, 105802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gailer, J. Probing the bioinorganic chemistry of toxic metals in the mammalian bloodstream to advance human health. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2012, 108, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, T.R.; Zaman, S.Z.; Chowdhury, T.I.; Begum, B.A.; Islam, M.A.; Rahman, M.M. Status of metals in serum and urine samples of chronic kidney disease patients in a rural area of Bangladesh: An observational study. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Ge, X.; Xu, J.; Li, A.; Mei, Y.; Yin, G.; Wu, J.; Liu, X.; Wei, L.; Xu, Q. Association between urine metals and liver function biomarkers in Northeast China: A cross-sectional study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 231, 113163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, C.; Deng, Y.; Chen, P.; Luo, Q.; Cui, F.; Zhang, M.; Lu, W.; Zeng, Q. Urinary biomarker of strontium exposure is positively associated with semen quality among men from an infertility clinic. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godebo, T.R.; Paul, C.J.; Jeuland, M.A.; Tekle-Haimanot, R. Biomonitoring of metals and trace elements in urine of central Ethiopian populations. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vormittag, E.; Saldiva, P.; Anastacio, A.; Barbosa, F. High levels of metals/metalloids in blood and urine of residents living in the area affected by the dam failing in Barra Longa, District, Brazil: A preliminary human biomonitoring study. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 83, 103566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbioni, G.; Castaño, A.; Esteban López, M.; Göen, T.; Mol, H.; Riou, M.; Tagne-Fotso, R. Literature review and evaluation of biomarkers, matrices and analytical methods for chemicals selected in the research program Human Biomonitoring for the European Union (HBM4EU). Environ. Int. 2022, 169, 107458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaKind, J.S.; Pollock, T.; Naiman, D.Q.; Kim, S.; Nagasawa, A.; Clarke, J. Factors affecting interpretation of national biomonitoring data from multiple countries: BPA as a case study. Environ. Res. 2019, 173, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xue, K.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ju, A.; Wu, B.; Zhao, F.; Chen, C.; et al. Human biomonitoring of toxic and essential metals in younger elderly, octogenarians, nonagenarians and centenarians: Analysis of the Healthy Ageing and Biomarkers Cohort Study (HABCS) in China. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cui, X.; Lin, C.; Ma, J.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y. Reference levels and relationships of nine elements in first-spot morning urine and 24-h urine from 210 Chinese children. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2017, 220, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Lin, S.; Zhao, F.; Lv, Y.; Qu, Y.; Hu, X.; Yu, S.; Song, S.; Lu, Y.; Yan, H.; et al. Cohort profile: China National Human Biomonitoring (CNHBM)—A nationally representative, prospective cohort in Chinese population. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, N.; Murawski, A.; Schmied-Tobies, M.I.H.; Rucic, E.; Doyle, U.; Kämpfe, A.; Höra, C.; Hildebrand, J.; Schäfer, M.; Drexler, H.; et al. Lead, cadmium, mercury, and chromium in urine and blood of children and adolescents in Germany—Human biomonitoring results of the German Environmental Survey 2014–2017 (GerES V). Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2021, 237, 113822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Lee, C.K.; Moon, C.S.; Choi, I.J.; Lee, K.J.; Yi, S.-M.; Jang, B.-K.; Yoon, B.j.; Kim, D.S.; Peak, D.; et al. Korea National Survey for Environmental Pollutants in the Human Body 2008: Heavy metals in the blood or urine of the Korean population. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2012, 215, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoet, P.; Jacquerye, C.; Deumer, G.; Lison, D.; Haufroid, V. Reference values and upper reference limits for 26 trace elements in the urine of adults living in Belgium. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2013, 51, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo-Relloso, A.; Grau-Perez, M.; Briongos-Figuero, L.; Gomez-Ariza, J.L.; Garcia-Barrera, T.; Duenas-Laita, A.; Bobb, J.F.; Chaves, F.J.; Kioumourtzoglou, M.A.; Navas-Acien, A.; et al. The association of urine metals and metal mixtures with cardiovascular incidence in an adult population from Spain: The Hortega Follow-Up Study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 48, 1839–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Gou, X.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Su, Q.; Xiao, G. Heavy metal contamination and source in and agricultural soil in central Gansu Province, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Z.; Zhao, C. Heavy metal concentrations in gray calcareous soils of Baiyin region, Gansu Province, PR China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2000, 118, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Lin, C.; Yang, K.; Cheng, H.; Gu, X.; Wang, B.; Wu, l.; Ma, J. Lability, bioaccessibility, and ecological and health risks of anthropogenic toxic heavy metals in the arid calcareous soil around a nonferrous metal smelting area. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 136200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, T. Pollution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in urban soil in China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2016, 22, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.F.; Zhi-Guo, Q.I.; Han, S.Y. Study on Purification of Gansu Attapulgite Clay Minerals. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 26, 851–855+866. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Yang, H.; Ayyamperumal, R.; Liu, Y. Pollution, sources, and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in urban areas around industrialization and urbanization-Northwest China. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Yin, Y.; Li, Z.; Du, J.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Guo, W.; Qin, R.; Li, M.; Lv, H.; et al. Maternal exposure to metal mixtures during early pregnancy and fetal growth in the Jiangsu Birth Cohort, China. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; Lu, S. Exposure to heavy metals and its association with DNA oxidative damage in municipal waste incinerator workers in Shenzhen, China. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Chen, J.; Yan, G.; Yang, Y.; Luo, D.; Chen, X.; He, M.; Yuan, H.; Huang, Z.; Lu, Y. Plasma titanium level is positively associated with metabolic syndrome: A survey in China’s heavy metal polluted regions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, Y.; Kurano, M.; Tanaka, M.; Hisasue, T.; Sato, M.; Ono, Y.; Sato, T.; Shukuya, K.; Yatomi, Y. Midstream urine sampling is necessary for accurate measurement of the urinary level of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in healthy female subjects. Clin. Biochem. 2020, 79, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, H.T.T.; Watchalayann, P.; Nguyen, D.B.; Doan, H.N.; Liang, L. Environmental health risk assessment of heavy metal exposure among children living in an informal e-waste processing village in Viet Nam. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 133664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Xu, X.; Boezen, H.M.; Huo, X. Children with health impairments by heavy metals in an e-waste recycling area. Chemosphere 2016, 148, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, W.; Du, X.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Bassig, B.; Zhou, A.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, C.; Li, Z.; et al. A Case-Control Study of Prenatal Thallium Exposure and Low Birth Weight in China. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmied, A.; Murawski, A.; Kolossa-Gehring, M.; Kujath, P. Determination of trace elements in urine by inductively coupled plasma-tandem mass spectrometry—Biomonitoring of adults in the German capital region. Chemosphere 2021, 285, 131425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Gu, H.T.; Xie, X.Y.; Hou, F.; Liu, Q.; Wu, H.; Zhu, K.H.; Wan, Z.H.; Song, R.R. Urine metals concentrations and dyslexia among children in China. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Ren, L.; Liu, Y.; Ma, H.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Z.; Tang, Z.; Kang, L.; Liao, S. Urinary parabens in children from South China: Implications for human exposure and health risks. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akerstrom, M.; Barregard, L.; Lundh, T.; Sallsten, G. The relationship between cadmium in kidney and cadmium in urine and blood in an environmentally exposed population. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 268, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barregard, L.; Ellingsen, D.G.; Berlinger, B.; Weinbruch, S.; Sallsten, G. Normal variability of 22 elements in 24-hour urine samples—Results from a biobank from healthy non-smoking adults. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2021, 233, 113693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Q. Urinary copper/zinc ratio: A promising parameter for replacement of 24-hour urinary copper excretion for diagnosis of Wilson’s disease in children. World J. Pediatr. 2010, 6, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Commission of the Peoples Republic of China. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/gzdt/2010-12/13/content_1764682.htm (accessed on 13 December 2010).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (The U.S.). National Report on Human Exposure to Environmental Chemicals. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/exposurereport/ (accessed on 24 March 2022).
- Fang, X.; Qu, J.; Huan, S.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Jin, S.; Xia, W.; Xu, S.; Wu, Y.; et al. Associations of urine metals and metal mixtures during pregnancy with cord serum vitamin D Levels: A prospective cohort study with repeated measurements of maternal urinary metal concentrations. Environ. Int. 2021, 155, 106660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Xu, X.; Cui, F.; Chen, P.; Deng, Y.; Miao, Y.; Luo, Q.; Zeng, J.; et al. Individual and mixtures of metal exposures in associations with biomarkers of oxidative stress and global DNA methylation among pregnant women. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, S.; Xia, W.; Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Lu, B.; Wu, S.; Liao, J.; Liu, H.; Sun, X.; Zhou, A. Multiple metal exposure and platelet counts during pregnancy: A repeated measure study. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, L.; Zhu, M.; Lin, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, H.; Wang, J. Associations of exposure to multiple metals with blood pressure and hypertension: A cross-sectional study in Chinese preschool children. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Q.; Wu, H.B.; Niu, Q.S.; Jia, P.P.; Qin, Q.R.; Wang, X.D.; He, J.L.; Yang, W.J.; Huang, F. Exposure to multiple metals and the risk of hypertension in adults: A prospective cohort study in a local area on the Yangtze River, China. Environ. Int. 2021, 153, 106538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, P.K.; Kritz-Silverstein, D.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Milne, D.; Nielsen, F.; Gamst, A.; Morton, D.; Wingard, D. Plasma trace elements and cognitive function in older men and women: The rancho bernardo study. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2008, 12, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockitch, G.; Halstead, A.C.; Wadsworth, L.; Quigley, G.; Reston, L.; Jacobson, B. Age- and sex-specific pediatric reference intervals and correlations for zinc, copper, selenium, iron, vitamins A and E, and related proteins. Clin. Chem. 1988, 34, 1625–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, M.; Comfort, N.; Re, D.B. Sex-specific neurotoxic effects of heavy metal pollutants: Epidemiological, experimental evidence and candidate mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahter, M.; Akesson, A.; Liden, C.; Ceccatelli, S.; Berglund, M. Gender differences in the disposition and toxicity of metals. Environ. Res. 2007, 104, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mravunac, M.; Szymlek-Gay, E.A.; Daly, R.M.; Roberts, B.R.; Formica, M.; Gianoudis, J.; O’Connell, S.L.; Nowson, C.A.; Cardoso, B.R. Greater Circulating Copper Concentrations and Copper/Zinc Ratios are Associated with Lower Psychological Distress, But Not Cognitive Performance, in a Sample of Australian Older Adults. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, N.; Courbon, D.; Ducimetiere, P.; Zureik, M. Zinc, copper, and magnesium and risks for all-cause, cancer, and cardiovascular mortality. Epidemiology 2006, 17, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reunanen, A.; Knekt, P.; Marniemi, J.; Maki, J.; Maatela, J.; Aromaa, A. Serum calcium, magnesium, copper and zinc and risk of cardiovascular death. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 50, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mazdak, H.; Yazdekhasti, F.; Movahedian, A.; Mirkheshti, N.; Shafieian, M. The comparative study of serum iron, copper, and zinc levels between bladder cancer patients and a control group. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2010, 42, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laine, J.T.; Tuomainen, T.P.; Salonen, J.T.; Virtanen, J.K. Serum copper-to-zinc-ratio and risk of incident infection in men: The Kuopio Ischaemic Heart Disease Risk Factor Study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 35, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Peinado, M.; Robles, A.R.; Nogueras-Lopez, F.; Mir, M.V.; Lopez, M.J.O.; Navarro-Alarcon, M. Serum zinc and copper concentrations and ratios in cirrhotic patients: Correlation with severity index. Nutr. Hosp. 2018, 35, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, L.; Zurlo, F.; Ravussin, E. Aging and energy expenditure. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 53, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piers, L.S.; Soares, M.J.; McCormack, L.M.; O’Dea, K. Is there evidence for an age-related reduction in metabolic rate? J. Appl. Physiol. 1998, 85, 2196–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolo, M.T.; Khandaker, M.U.; Amin, Y.M.; Abdullah, W.H.B.; Bradley, D.A.; Alzimami, K.S. Assessment of health risk due to the exposure of heavy metals in soil around mega coal-fired cement factory in Nigeria. Results Phys. 2018, 11, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamara, I.; Adie, G.U.; Giwa, A.S. Total and bio-accessible toxic metals in low-cost children toys sold in major markets in Ibadan, South West Nigeria. Sci. Afr. 2023, 20, e01613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malin Igra, A.; Warnqvist, A.; Rahman, S.M.; Ekström, E.-C.; Rahman, A.; Vahter, M.; Kippler, M. Environmental metal exposure and growth to 10 years of age in a longitudinal mother–child cohort in rural Bangladesh. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Zeng, Z.; Tian, Q.; Huang, J.; Zhong, Q.; Huo, X. Epidemiological evidence for the effect of environmental heavy metal exposure on the immune system in children. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 868, 161691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwegbue, C.M.A.; Obi, G.; Emoyan, O.O.; Odali, E.W.; Egobueze, F.E.; Tesi, G.O.; Nwajei, G.E.; Martincigh, B.S. Characterization of metals in indoor dusts from electronic workshops, cybercafes and offices in southern Nigeria: Implications for on-site human exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 159, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hongcan, L. Clinical application of rapid semi quantitative detection of urine zinc and quantitative detection of blood zinc. Stud. Trace Elem. Health 2014, 31, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Mocchegiani, E.; Romeo, J.; Malavolta, M.; Costarelli, L.; Giacconi, R.; Diaz, L.E.; Marcos, A. Zinc: Dietary intake and impact of supplementation on immune function in elderly. Age 2013, 35, 839–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoroddu, M.A.; Aaseth, J.; Crisponi, G.; Medici, S.; Peana, M.; Nurchi, V.M. The essential metals for humans: A brief overview. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2019, 195, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barneo-Caragol, C.; Martinez-Morillo, E.; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, S.; Lequerica-Fernandez, P.; Vega-Naredo, I.; Menendez, F.V.A. Strontium and oxidative stress in normal pregnancy. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 45, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Tang, L.; He, J.; Su, Y.; Cen, Y.; Yu, D.; Wu, B.; Lin, Y.; Chen, W.; Song, E.; et al. Urinary strontium and the risk of breast cancer: A case-control study in Guangzhou, China. Environ. Res. 2012, 112, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, J.J.; Avigliano, E.; Fernández Cirelli, A. Essential and non-essential metals in three lowland rivers of temperate South America (Argentina): Distribution and accumulation. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2022, 73, 127016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, M.; Soares, M.C.F.; Baisch, P.R.M.; Baisch, A.L.M.; da Silva, F.M.R. Biomonitoring of trace elements in urine samples of children from a coal-mining region. Chemosphere 2018, 197, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, L.; Lin, B.; Xiang, M.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wan, Y. Health implication of heavy metals exposure via multiple pathways for residents living near a former e-waste recycling area in China: A comparative study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Wang, H.; Du, C.; Yuan, T.-H.; Chen, C.; Yu, C.; Chan, C. Air-polluted environmental heavy metal exposure increase lung cancer incidence and mortality: A population-based longitudinal cohort study. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 152186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, X.; Cai, J.; Lin, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Wei, C.; Wei, Y.; Huang, S.; et al. Correlation between urinary contents of some metals and fasting plasma glucose levels: A cross-sectional study in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 228, 152186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Lv, Y.; Ji, S.; Ding, L.; Zhao, F.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Hu, X.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Effect of exposures to mixtures of lead and various metals on hypertension, pre-hypertension, and blood pressure: A cross-sectional study from the China National Human Biomonitoring. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 299, 118864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Lin, W.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; He, M.; Yu, L.; et al. Relationship between cumulative exposure to metal mixtures and heart rate among Chinese preschoolers. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

 : Range within 1.5. Interquartile range (IQR). ─: Median line. ○: Outlier. *: Extreme cases.
: Range within 1.5. Interquartile range (IQR). ─: Median line. ○: Outlier. *: Extreme cases.
 : Range within 1.5. Interquartile range (IQR). ─: Median line. ○: Outlier. *: Extreme cases.
: Range within 1.5. Interquartile range (IQR). ─: Median line. ○: Outlier. *: Extreme cases.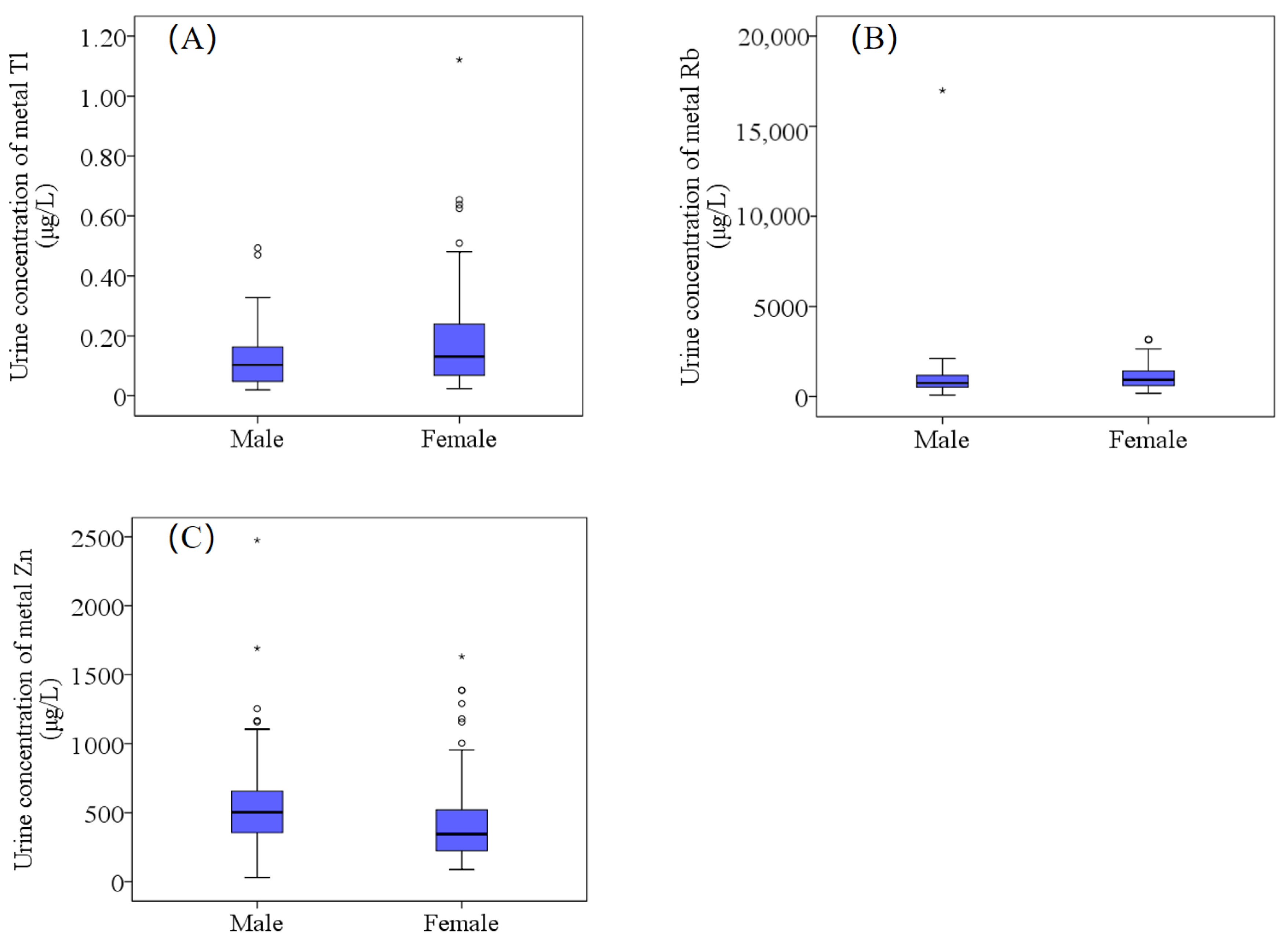
 : Range within 1.5. Interquartile range (IQR). ─: Median line. ○: Outlier. *: Extreme cases. Outside boxplots: ]: Significant differences between the two groups. ✱: p < 0.05. ✱✱: p < 0.01.
: Range within 1.5. Interquartile range (IQR). ─: Median line. ○: Outlier. *: Extreme cases. Outside boxplots: ]: Significant differences between the two groups. ✱: p < 0.05. ✱✱: p < 0.01.
 : Range within 1.5. Interquartile range (IQR). ─: Median line. ○: Outlier. *: Extreme cases. Outside boxplots: ]: Significant differences between the two groups. ✱: p < 0.05. ✱✱: p < 0.01.
: Range within 1.5. Interquartile range (IQR). ─: Median line. ○: Outlier. *: Extreme cases. Outside boxplots: ]: Significant differences between the two groups. ✱: p < 0.05. ✱✱: p < 0.01.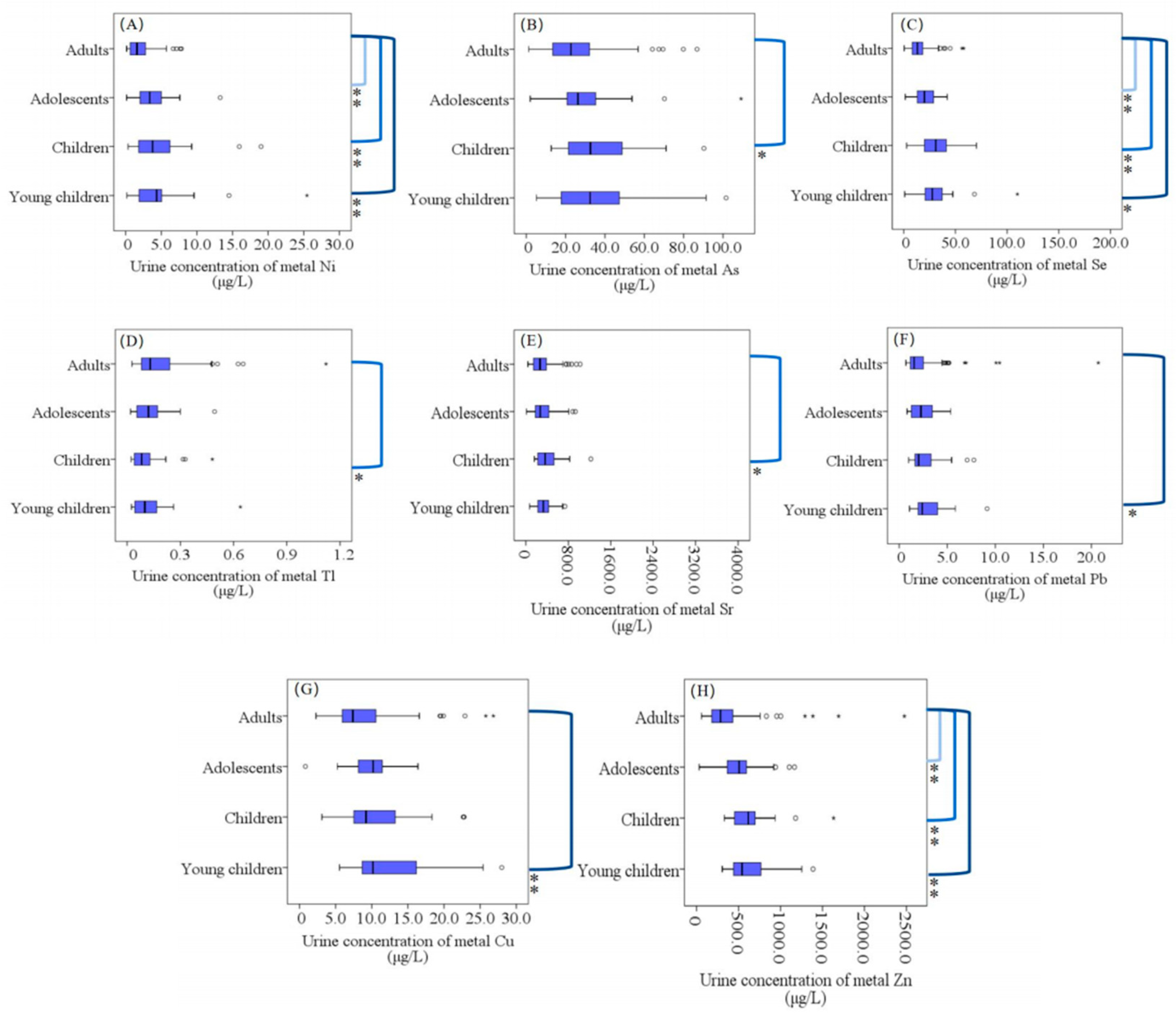
 : Range within 1.5. Interquartile range (IQR). ─: Median line. ○: Outlier. *: Extreme cases.
: Range within 1.5. Interquartile range (IQR). ─: Median line. ○: Outlier. *: Extreme cases.
 : Range within 1.5. Interquartile range (IQR). ─: Median line. ○: Outlier. *: Extreme cases.
: Range within 1.5. Interquartile range (IQR). ─: Median line. ○: Outlier. *: Extreme cases.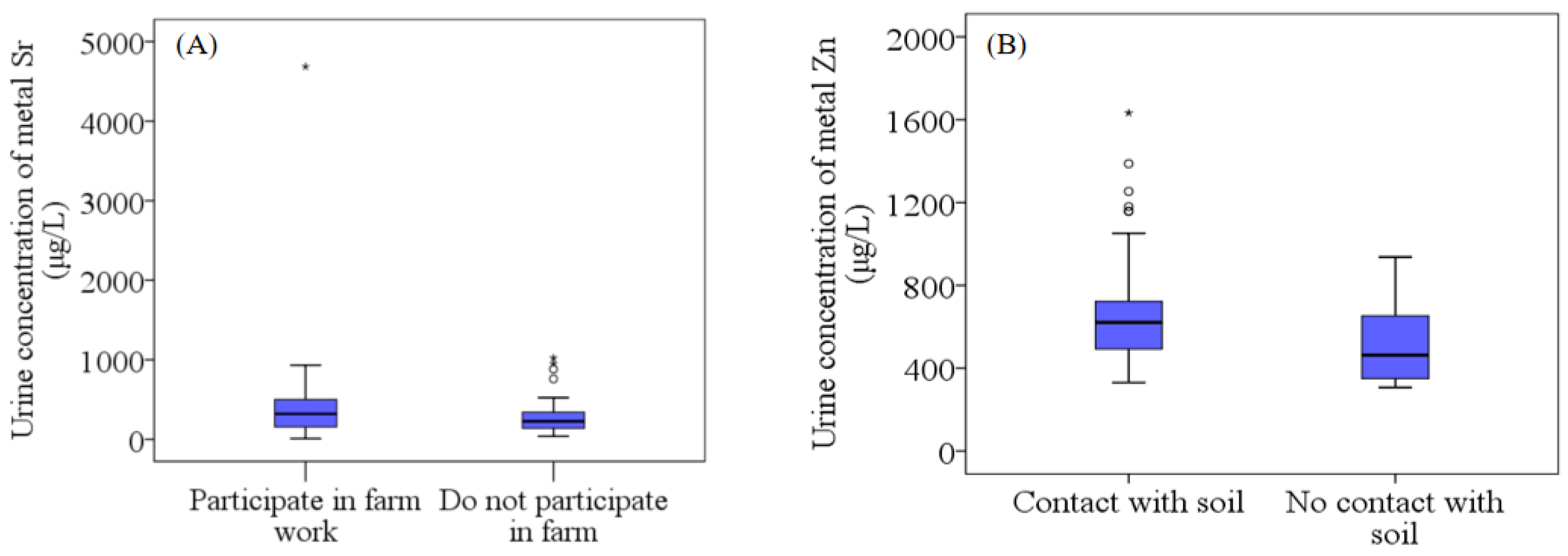
| Characteristics | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Male | 84 (46.4%) |
| Female | 97 (53.6%) |
| Age (years) | 29 ± 23 |
| Young children (1–5) | 28 (15.5%) |
| Children (6–11) | 29 (16.0%) |
| Adolescents (12–18) | 33 (18.2%) |
| Adults (>18) | 91 (50.3%) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 20.6 ± 5.3 |
| Does farm work | |
| Yes | 61 (33.7%) |
| No | 62 (34.2%) |
| Soil exposure due to playing outdoors | |
| Yes | 42 (23.2%) |
| No | 16 (8.8%) |
| Annual family income (Yuan/year) | |
| <25,000 | 47 (26.0%) |
| 25,000–50,000 | 109 (60.2%) |
| >50,000 | 25 (13.8%) |
| Urinary Elements | LOD (µg/L) | DF (%) | GM (µg/L) (95%CI) | Percentile (µg/L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5th | 25th | 50th | 75th | 95th | ||||
| Cr | 0.63 | 87.8 | 1.13 (0.99, 1.30) | <LOD | 0.72 | 0.99 | 1.59 | 3.55 |
| Ni | 0.25 | 89.0 | 1.96 (1.59, 2.40) | <LOD | 0.93 | 2.54 | 4.47 | 9.30 |
| As | 0.01 | 100.0 | 24.58 (21.82, 27.70) | 7.48 | 16.14 | 25.57 | 38.20 | 70.16 |
| Se | 0.76 | 97.8 | 16.4 (14.11, 18.95) | 3.65 | 9.56 | 17.25 | 29.70 | 55.64 |
| Sr | 0.02 | 100.0 | 267.6 (234.7, 305.1) | 70.82 | 164.3 | 290.8 | 432.0 | 807.1 |
| Cd | 0.01 | 98.3 | 0.53 (0.46, 0.62) | 0.16 | 0.36 | 0.59 | 0.90 | 1.82 |
| Sb | 0.10 | 30.9 | - | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.22 | 3.52 |
| Tl | 0.04 | 68.5 | 0.11 (0.09, 0.12) | <LOD | <LOD | 0.11 | 0.19 | 0.48 |
| Pb | 1.77 | 47.0 | - | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 3.03 | 5.81 |
| Al | 2.39 | 100.0 | 34.69 (31.03, 38.77) | 12.20 | 21.88 | 33.40 | 50.73 | 154.4 |
| Fe | 1.44 | 100.0 | 38.36 (30 43, 39.53) | 5.19 | 25.18 | 35.80 | 62.23 | 160.4 |
| Cu | 0.16 | 100.0 | 9.02 (8.28, 9.83) | 3.77 | 6.68 | 9.03 | 11.88 | 21.10 |
| Zn | 0.40 | 100.0 | 397.0 (353.4, 446.0) | 124.1 | 257.5 | 418.0 | 634.7 | 1166 |
| Rb | 0.05 | 100.0 | 850.0 (763.4, 946.4) | 363.6 | 552.6 | 809.7 | 1310 | 2142 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Guo, S.; Hua, L.; Wang, B.; Chen, Q.; Liu, L.; Xiang, L.; Sun, H.; Zhao, H. Urinary Levels of 14 Metal Elements in General Population: A Region-Based Exploratory Study in China. Toxics 2023, 11, 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11060488
Zhang Z, Guo S, Hua L, Wang B, Chen Q, Liu L, Xiang L, Sun H, Zhao H. Urinary Levels of 14 Metal Elements in General Population: A Region-Based Exploratory Study in China. Toxics. 2023; 11(6):488. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11060488
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zining, Sai Guo, Liting Hua, Beibei Wang, Qiusheng Chen, Lu Liu, Li Xiang, Hongwen Sun, and Hongzhi Zhao. 2023. "Urinary Levels of 14 Metal Elements in General Population: A Region-Based Exploratory Study in China" Toxics 11, no. 6: 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11060488
APA StyleZhang, Z., Guo, S., Hua, L., Wang, B., Chen, Q., Liu, L., Xiang, L., Sun, H., & Zhao, H. (2023). Urinary Levels of 14 Metal Elements in General Population: A Region-Based Exploratory Study in China. Toxics, 11(6), 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11060488






