Abstract
A large amount of nano-/microparticles (MNPs) are released into water, not only causing severe water pollution, but also negatively affecting organisms. Therefore, it is crucial to evaluate MNP toxicity and mechanisms in water. There is a significant degree of similarity between the genes, the central nervous system, the liver, the kidney, and the intestines of zebrafish and the human body. It has been shown that zebrafish are exceptionally suitable for evaluating the toxicity and action mechanisms of MNPs in water on reproduction, the central nervous system, and metabolism. Providing ideas and methods for studying MNP toxicity, this article discusses the toxicity and mechanisms of MNPs from zebrafish.
1. Introduction
Due to the continuous development of human activities, plastic products have become an integral part of our daily lives. However, with large quantities of plastic waste being discharged into water bodies, the global environment is expected to release 33 billion tons plastics of by 2050. In the course of environmental evolution, it will gradually decompose into tiny plastic particles called microplastics (MPs) (100–5000 nm) and nanoplastics (NPs) (<100 nm) [1,2]. Among the most common nano-/microparticles (MNPs) are polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polystyrene (PS), and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) [3]. Due to the small size, large surface area, strong adsorption capacity, and permeability of MNPs, their distribution and action mode in water are different from traditional organic pollutants [4,5,6,7]. High persistence and extreme distribution are unique characteristics of MNPs compared to other polluting suspended substances in the environment. As a result, MNPs are potentially harmful to freshwater and marine ecosystems [8,9]. Plastic debris has already caused an estimated EU 21 billion of severe economic damage in the world’s oceans. At the same time, due to their high surface area and hydrophobicity, MNPs can act as carriers of pathogens and organic pollutants, together with which they aggravate toxicity [10,11,12,13]. In addition, MNPs can enter the food chain circulation directly or indirectly, causing metabolic disorders and intestinal microbiota disorders in the human body. In addition, they cause neurotoxicity, reproductive toxicity, immunotoxicity, etc., which constitute serious threats to human health (Figure 1) [11,14,15].
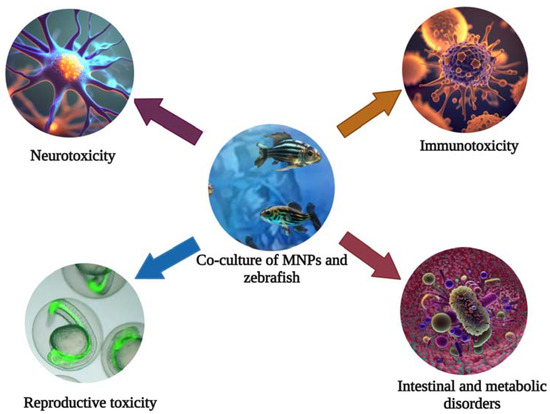
Figure 1.
The zebrafish can be used for toxicity evaluation and mechanistic studies of the nervous, reproductive, and immune systems of MNPs.
Therefore, to assess the toxicity of MNPs in water, many toxicity evaluation methods have been developed, including in vitro and in vivo methods. In vitro tests include chemical analysis and cytotoxicity tests [16,17]. These methods have limitations such as not reflecting real environmental conditions and complicated operation, and are time-consuming and laborious. A variety of animal models have been used to evaluate MNP toxicity in vivo, including mice, rats, rabbits, guinea pigs, and fish [18,19,20,21]. The zebrafish is a small freshwater fish. (I) Because of its small size, vitality, and reproductive ability, it is easy to raise and manage [22]; (II) its short life cycle, from fertilized egg to adult in about three months, allows for rapid large-scale experiments [23]; (III) Zebrafish larvae are transparent, and the development process of their internal structures and organs can be directly observed through a microscope. Therefore, they emerge in the field of toxicity evaluation of pollutants such as MNPs, heavy metals, pharmaceuticals, and algae in water [24].
This review summarizes the toxicity evaluation and mechanism research of the nervous, reproductive, and immune systems of the zebrafish used in MNPs, pointing out the challenges faced by the zebrafish in the toxicity evaluation of MNPs, and suggesting improved solutions, in order to facilitate better application of the zebrafish to toxicity evaluations of MNPs and exploration of their mechanisms of action.
2. Reliability of the Zebrafish for Toxicity Evaluation
Traditionally, mammals have been used to assess toxicity. Although the mammalian model has many advantages, it also has a number of disadvantages, such as its high cost, lengthy process time, and ethical and moral issues. Conversely, zebrafish are known for their fast population growth, short reproductive cycle, ease of experimental operation, high survival rate, and low feeding and maintenance costs [25,26]. Figure 2 illustrates the main advantages of using zebrafish in MNP research MNPs. These advantages include: (I) the genome of zebrafish has been completely sequenced, and the gene similarity to humans is as high as 87%. In addition, the pathological state of many diseases and genes related to disease etiology are highly conserved in humans [27,28]; (II) The transparent nature of zebrafish embryos and larvae provides an experimental advantage compared to other model organisms for studying the accumulation sites of fluorescence-labeled MNPs particles. In addition, transgenic zebrafish strains have become effective biological models for studying metabolic and immune diseases [29,30]; (III) The blood–brain barrier of zebrafish is similar to that of humans, and has been well used for central-nervous-system drug screening [31]; (IV) The nervous system of the zebrafish, which includes the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system, has social behaviors similar to human perception, movement, and emotion. Zebrafish have become widely used models in behavioral neuroscience, especially as disease models for Parkinson’s disease (PD), Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and depression [32,33,34]; (V) Zebrafish have similar metabolic organs and physiological structures to humans, such as the liver, kidney, and intestine. These organs can metabolize and eliminate harmful substances as shown in Figure 2 [35,36,37].
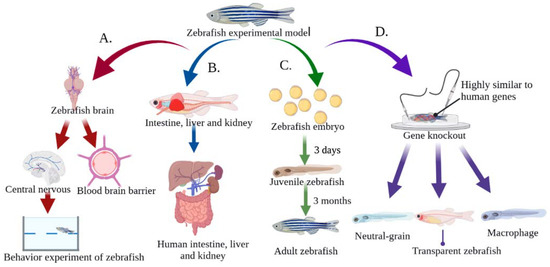
Figure 2.
Advantages of zebrafish for toxicity evaluation of MNPs. (A) The blood–brain barrier, central nervous system, and social behavior are similar to those of humans, making it an ideal animal model for studying neurotoxicity; (B) The intestine, liver and kidney are similar to those of humans, which makes them suitable for studying MNPs metabolism and immune diseases; (C) The reproductive and developmental toxicity of MNPs can be easily studied due to the short reproductive cycle of zebrafish and the large number of eggs laid. In addition, the embryos are transparent, so a microscope can be used to observe the cell division and organ formation process; (D) The genome of zebrafish has been fully sequenced, and is highly consistent with the human genome, and can be easily manipulated by genetic manipulation such as gene knockout and gene overexpression.
Zebrafish are also being used in toxicity assessment, according to many studies. Zebrafish have been shown to exhibit physiological responses and behavioral abnormalities as a result of exposure to environmental pollutants that are similar to those of mammals. As a result, zebrafish have been widely utilized in toxicity assessments, drug screening, and other fields, demonstrating their reliability for evaluating the biological effects of MNPs.
3. Toxicity of MNPs in Water to Zebrafish
Currently, the zebrafish used to evaluate MNP biotoxicity are manipulated by the exposure method [38,39], injecting MNPs directly into the aquaculture water or adding MNPs to the feed, and then exposing the zebrafish to the suspension for a specified period of time. Zebrafish behavior and physiological indicators can be observed during this period. As shown in Figure 3, acute toxicity of MNPs to zebrafish was evaluated by observing changes in growth, reproduction, behavior, and physiology. In addition, water-flow can also control MNP concentration and time to simulate dynamic MNP exposure environments.
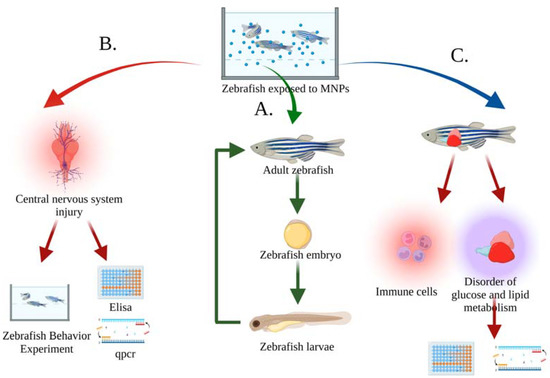
Figure 3.
Evaluation index of MNP toxicity in zebrafish in a water body. (A) Evaluation of the toxicity of MNPs on growth and reproduction by the damage and apoptosis of sperm, testis, and oocytes of adult zebrafish, as well as the increased rate of malformation and mortality of embryos [40,41,42]; (B) Evaluation of the behavioral and neurological toxicity of MNPs by increasing oxidative-stress level and apoptosis in the zebrafish brain, as well as behavioral experiments to detect memory, learning, and mental disorders in zebrafish [43,44,45]; (C) Evaluation of the toxicity of MNPs on the metabolism and immune system by the upregulation of immune-related gene expression and apoptosis, as well as the reduction of hepatic glucose and lipid metabolism, glucose, α-ketoglutarate, and lipid-related indicators [46,47,48].
3.1. Growth and Reproduction of Zebrafish
Exposure of zebrafish to MNPs in aqueous solution has adverse effects on the growth and reproduction of zebrafish: (I) It may cause damage to the chorionic membrane of zebrafish embryos or changes in water quality (such as hypoxia induction) [41], which may lead to premature hatching of embryos, and their inability to survive for a long time, resulting in an increase in the mortality of larvae [49]; (II) Zebrafish larvae were unable to survive for long in an aqueous solution containing 2 mg/mL MNPs, and their mortality rate increased to 32.4%; (III) Exposed larvae displayed edema of the yolk sac and pericardium, curvature of the spine, curvature of the tail, and a larger area of visual vesicles; (IV) When zebrafish embryos were exposed to 100 ppm of PET-NPs in aqueous solution, the survival rate decreased to 65%, while at 200 ppm the survival rate was almost zero [50]; (V) A previous study exposed adult zebrafish to PS-NPs for one month, and a large accumulation of PS-NPs, as well as an increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) was observed in the gonads and liver of the zebrafish [51]. It was found that high concentrations of MNPs resulted in apoptosis of male zebrafish testis, as well as a significant reduction in basement-membrane thickness, resulting in oxidative stress to female zebrafish oocytes, leading to apoptosis [40], and affecting egg morphology and yolk area of zebrafish offspring, resulting in malformations [52]; (VI) Upon exposure to PE-MPs in water for 15 days, adult zebrafish accumulated a large amount of PE-MP in their bodies, causing DNA damage to red blood cells and nuclear abnormalities, which may lead to genetic damage. In addition, the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) decreased, resulting in an imbalance in the redox state [53].
3.2. The Behavior and Nervous System of Zebrafish
According to studies, MNPs can cross the blood–brain barrier [54], and they accumulate in large amounts in the heads of zebrafish, causing an increase in oxidative stress levels and apoptosis in the brain [43,44], in addition to a decrease in the activity of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) in the brain of the zebrafish (the activity regulates brain function and is considered a biomarker of neurotoxicity in zebrafish), as well as inhibition of the synthesis of neurotransmitters (such as dopamine, melatonin, aminobutyric acid, and 5-hydroxytryptamine) [55,56], causing serious harm to the nervous system and inducing neurobehavioral disorders [57]. One study found that zebrafish swimming behavior and range of motion were significantly reduced when exposed to PC-MPs and PE-MPs in water. There were also emetic and electrophysiology abnormalities, learning and memory problems [58,59], and severe epileptic behaviors [45]. Meanwhile, avoidance and anxiety behaviors were observed in zebrafish larvae [60]. The above studies suggest that MNP exposure may negatively affect the nervous system and behavior of zebrafish. This provides a rapid method for assessing MNP toxic effects on aquatic organisms’ nervous systems and behavior.
3.3. Metabolism and Immune System of Zebrafish
MNPs are capable of crossing biological barriers and entering the circulatory system, where they reduce energy reserves through mechanical destruction, ultimately affecting the immune system [61]. (I) It was found that zebrafish exposed to MNPs had significant increases in mRNA and protein levels of genes associated with the innate immune system (interleukin-1α (IL-1α), IL-1β, nuclear factor-κb (NF-κb), and interferon) and apoptosis (casp3A and BCL2) [62]. Moreover, the number of white blood cells decreased, the accumulation of neutrophils in intestinal epithelium increased, and the immune function was abnormal [63]. At the same time, the metabolic system of zebrafish was adversely affected, resulting in abnormal liver and intestinal metabolism; (II) Zebrafish embryos exposed to PE-MPs showed an interference in the metabolism of triglycerides, total cholesterol, non-esterified fatty acids, total bile acids, glucose, and pyruvate; (III) When adult male zebrafish were exposed for 21 days to PS-MPs, a significant reduction in body weight was observed as well as a reduction in transcription levels associated with glucose and lipid metabolism in the liver. Furthermore, glucose, pyruvate, and alpha-ketoglutaric acid levels in the liver decreased. The liver also decreased in genes related to fatty-acid metabolism and amino-acid metabolism; (IV) In adult zebrafish exposed for 21 days to aqueous solutions of PE-MPs and PP-MPs, MPs induced oxidative stress, resulting in lipid peroxidation as well as stimulation of autophagy and apoptosis signal transduction pathways [64,65]. In combination, exposure to MNPs disrupts the immune system and glucose and lipid metabolism in zebrafish (Table 1) [46].

Table 1.
Summary table of toxicity caused by different MNPs in zebrafish.
4. Exploring the Toxicological Mechanisms of MNPs in Water with Zebrafish
The genes, blood–brain barrier, and central nervous system of zebrafish are highly similar to those of humans, and at the same time, the zebrafish have the advantage of rapid reproduction, more eggs, zebrafish larvae transparent intestines, etc. Therefore, it is easy for researchers to examine how MNPs affect the nervous system, intestinal microorganisms, reproductive development, and immune system toxic mechanisms (Figure 4).
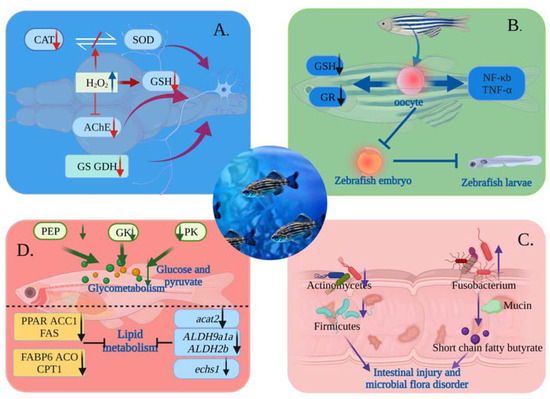
Figure 4.
Diagram of the toxicological mechanism of MNPs in water explored using zebrafish. (A) The mechanism of central nervous toxicity of MNPs: Excessive production of H2O2, inactivation of enzyme protein, disruption of the balance between CAT and SOD activities, inhibition of AChE activity, and significant reduction in the activity of GS and GDH, leading to brain neurodegeneration. (B) Mechanism of reproductive toxicity of MNPs: MNPs were transferred to oocytes of adult female zebrafish, causing reduction of GR and GSH contents, leading to oxidative stress in oocytes. At the same time, NF-b and TNF- expression was significantly upregulated, affecting the offspring’s growth and development. (C) Effect of MNPs on zebrafish gut: Increased abundance of Fusobacterium metabolized mucin into short-chain fatty butyrate and induce intestinal inflammation in zebrafish. The number of actinobacteria decreased, foreign bodies accumulated in the intestine, and the number of Firmicutes decreased, all of which resulted in reduced mucus production and damage to the intestinal barrier. (D) The mechanism of metabolic toxicity of MNPs: Reduction of PEP, GK, and PK in the glycolytic pathway led to insufficient glucose and pyruvate production, leading to disorders of glucose metabolism. Additionally, the expression levels of PPAR, ACC1, FAS, FABP6, ACO, CPT1, acat2, ALDH9a1a, ALDH2b, and echs1 genes were reduced, resulting in abnormal lipid metabolism.
4.1. Toxicological Mechanism of MNPs on Nervous System
Adult zebrafish were exposed for a long period of time to a PS-MNP solution in an attempt to detect the effects of MNPs on the oxidative stress system, the cholinergic system, the glutaminergic system, and the histological changes in the brain [44]. By reducing CAT activity, a key antioxidant defense mechanism, and glutathione (GSH) levels, PS-MPs induce oxidative stress. Overproduction of H2O2 inactivates enzyme proteins and disrupts CAT and SOD activity balance. GSH is also a powerful antioxidant, protecting cells against oxidative damage by removing ROS and pro-oxidants. It also plays an essential role in maintaining cell redox homeostasis. Cell detoxification requires GSH combined with MNPs. Additionally, excess H2O2 will cause glutathione to be oxidized into glutathione disulfide in the glutathione redox cycle [69], which contributes to oxidative stress reactions [70,71,72].
At the same time, AChE activity decreases and excess acetylcholine neurotransmitter (ACh) in synapses leads to interruption of normal nervous-system function, which can cause some neurodegenerative diseases (AD, dementia with Lewy bodies, PD, etc.) [73,74,75]. In zebrafish soaked in MNPs, abnormal neurobehavioral phenomena were observed which may have been the result of oxidative stress caused by the damage of the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and cell membrane, which may have led to blocking of the AChE enzyme production [76]. In addition, H2O2 and AChE metabolism are directly correlated. As an allosteric activator of AChE, H2O2 can change the structure and distribution of isomers in cells. It has an antagonistic effect on AChE activity [77].
The glutaminergic system is the main excitatory neurotransmitter system in the brain. Glutamate is considered the most abundant neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. It is crucial in many aspects of central-nervous-system function, including cognition, memory, and learning. Glutamine synthetase (GS) and glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) are two major enzymes involved in brain glutamate metabolism. GS maintains the balance of the glutamine–glutamine and ammonia cycles. Decreased GS activity leads to increased glutamate and ammonia concentrations. In the presence of excessive amounts of extracellular glutamate, glutamate receptors are overactivated, resulting in neuronal damage and cell death [78]. Studies have shown that MNPs immersed in the solution will transfer to the brain of zebrafish. They will interfere with glutamate metabolism, and significantly reduce GS and GDH, which may cause brain neurodegeneration. In addition, histological analysis of neuronal filament populations and myelin axon sites in the white layer of the brain showed that MNPs caused severe degradation of the brain-cell layer. This significantly reduced the number of neurons and nerve cells [44].
In conclusion, MNPs can cause central neurotoxic effects by negatively affecting various biomarkers in the central nervous system of zebrafish by negatively affecting various biomarkers. In doing so, CAT activity and GSH levels are reduced, resulting in oxidative damage, interfering with glutamatergic and cholinergic neurotransmitter systems, and resulting in brain cell apoptosis. Thus, zebrafish are a compelling choice as a model organism for neurotoxicity studies.
4.2. Toxicological Mechanism of MNPs Affecting Reproduction
The effects of exposure to PS-NPs on adult zebrafish (F0) and the effects of PS-NPs on zebrafish physiology have been investigated. The experiment produced four F1 groups: blank control, exposed female, exposed male, and exposed male and female. Detection of F1 embryos and larvae showed that NPs were present in yolk sacs, gastrointestinal tract, liver, and pancreas of female and male F1 embryos, and larvae exposure to NPs, possibly due to the high affinity of NPs for plasma proteins (lipid transport proteins, vitellinogen, and zona pellucinalis) [79] and its interaction with vitellinogen, promoted the transfer of PS-NPs to oocytes and eventually to the yolk sac of the embryo; thus, PS-NPs were transferred from females to offspring [80]. Furthermore, bradycardia was observed only in females and both male and female injected embryos. This may be associated with PS-NPs entering the cells and interacting with the myocardium of the heart, thereby altering cardiac function [40].
It was also found that glutathione reductase (GR) activity and mercaptan levels were reduced in larval brains, muscles, and testes. GR may have an important role to play in early development. Its decreased activity may lead to long-term physiological effects after maturity and increase the sensitivity of organisms to other environmental stressors. It is also possible that the reduction in mercaptan levels is due to the consumption of mercaptan (such as GSH) during PS-NPs detoxification. Therefore, PS-NPs will increase offspring susceptibility to oxidative stress. In conclusion, PS-NPs may bioaccumulate and be passed on to offspring, altering the antioxidant system, but do not cause significant physiological damage [41].
Meanwhile, isolated zebrafish oocytes were incubated for 6 h with different doses of PS-NPs and the effects of PS-NPs on the zebrafish oocytes were quantified by real-time PCR. PS-NPs induced oxidative stress in oocytes and increased ROS production in the cells, affecting immune regulatory genes that play a critical role in oocyte maturation. Therefore, PS-NPs can inhibit DNA repair and apoptosis pathways, causing cell death. In addition, they led to significant upregulation of pro-inflammatory response genes (NF-κb and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)), indicating disruption of the normal ovulation process; therefore, PS-NPs impair reproductive function in zebrafish.
4.3. Effect of MNPs on Gut Histopathology and Microbiota in Zebrafish
The toxicological effects of MNPs are closely related to their size [81]. Since NPs have a large specific surface area and complex surface structure, their retention and purification time in the organism are longer, and their bioaccumulation rate is higher than MPs. Following MNP uptake in zebrafish, the gut is the main site of accumulation [82]. Zebrafish were exposed to PS-MNPs of different sizes for 30 days, which resulted in a change in intestinal tissues and microbial fractions. MNPs damaged gastrointestinal histology size-dependently. Smaller MNPs accumulated more in the intestine [83,84]. According to histological analysis, the intestinal tissue was severely damaged by necrosis and exfoliation of the top of the intestinal villi. This was followed by abrasion of crypt cells, structural tissue lysis, and vacuolization of intestinal epithelial cells [85].
Furthermore, Fusobacteria numbers increased, Firmicutes and Actinobacteria numbers decreased slightly, and the abundance and diversity of intestinal microbes decreased significantly. The increase in Fusobacteria could cause intestinal injury. Fusobacteria metabolize carbohydrates (including mucin) into short-chain fatty butyrate, which causes intestinal inflammation. There is even a cancer risk [86,87]. Additionally, actinomycetes have gained worldwide attention for their ability to synthesize secondary metabolites that remove foreign bodies. Therefore, a reduction in actinomycetes may explain MNP damage [88]. In addition, some Firmicutes produce butyrate, which provides nourishment and energy to epithelial and intestinal cells. It also increases mucus production and decreases inflammation, which may impair the integrity of the intestinal barrier if Firmicutes are reduced in abundance [89,90,91]. To conclude, long-term exposure to MPs may lead to intestinal flora disorders, inflammation of the intestinal tract, and cytokines that influence immunity. It may also trigger a series of immune responses and produce oxidative stress, which could threaten the health of the zebrafish’s microbiota and immune system.
4.4. Toxicological Mechanisms of MNPs Causing Metabolic Disorders
By exposing adult zebrafish to PS-MPs for 21 days, it was shown that PS-MPs had hepatic effects related to glucose and lipid metabolism [48]. Results indicated that PS-MPs may cause liver metabolic disorders in zebrafish by blocking the digestive tract and inhibiting enzyme production [92,93]. In addition, the liver is primarily responsible for bioaccumulation, metabolism, and detoxification. Therefore, analysis of the major genes involved in glucose and lipid metabolism in zebrafish liver showed that the expression levels of rate-limiting enzyme genes such as cytoplasmic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEP), glucokinase (GK), and pyruvate kinase (PK) in the glycolytic pathway were reduced. Therefore, glucose and pyruvate production were insufficient, resulting in glucose metabolism disorders [94,95,96]. At the same time, alterations in several genes that regulate hepatic lipogenesis, for example, decreased expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) family genes, acetyl-coa carboxylase 1 (ACC1), and fatty acid synthase (FAS) genes, have been associated with downregulation of triglyceride (TG) [97]. In addition, the reduction of α-ketoglutarate and isocitrate dehydrogenase (ICD), which are involved in tricarboxylic acid cycle energy metabolism, implies that MP exposure reduced energy metabolism in zebrafish. Furthermore, this study showed that the expression of fatty acid binding protein 6 (FABP6), which regulates lipid transport and acyl-coa oxidase (ACO), which participates in lipid oxidation, and carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (CPT1), was reduced [46,98].
In addition, reduced gene expression levels of acat2 (which protects hepatocytes from excess cholesterol [99]), as well as of ALDH9a1a and ALDH2b (aldehydes are irreversibly converted into acids in the liver, and large increases in aldehydes may result in enzyme inactivation and DNA damage, among other things [100,101]), and echs1 (enoyl-coa hydratase 1 is an important gene in fatty acid metabolism [102]) further confirmed that MP exposure can affect glucose, lipid, and amino acid metabolism. In addition, it provides substantial information regarding MPS-induced metabolic disorders in aquatic animals [47].
The zebrafish has provided a preliminary understanding of MNP toxic mechanisms in the nervous system, gut microbiota, reproductive development, and immune system. Furthermore, it provides an excellent animal model for future studies, treatment, and attenuation of MNPs toxic effects.
5. Limitations and Possible Solutions
MNPs have complex effects and mechanisms, which require accurate, sensitive, and repeatable methods to evaluate. As an animal model for toxicity assessment, zebrafish are widely used in MNP toxicity assessment. Despite its many advantages in assessing MNP toxicity in water, the zebrafish is used as a non-mammal model. There may be some problems with toxicity assessment results, such as species differences, repeatability, and a lack of long-term toxicity research. It is imperative to take these limitations into account when assessing MNP toxicity with the zebrafish.
(I) MNP particles have a very small size and large surface area, making their behavior and effects in water complex, so it is difficult to accurately simulate the real situation. To simulate the real situation in water, further study and optimization of the zebrafish exposure experiment design and method is necessary.
(II) The experimental results of different laboratories may differ due to zebrafish physiological characteristics and reproduction mode. To improve reproducibility and comparability of experiments, it is necessary to strictly follow the currently developed uniform experimental operating procedures and standards (as FET test) [103]. However, researchers still need to continuously promote the construction of standards to make zebrafish, as a model organism for toxicity evaluation toxicity, more perfect. In addition, for persuasive purposes, genetically consistent or inbred animal strains should be used.
(III) Lack of long-term toxicity studies: Most studies are short-term exposure experiments, with limited long-term data available. The reason for this is that zebrafish exposure experiments typically use high concentrations of compounds. By doing so, toxic effects of low concentrations of compounds can be evaluated rapidly. However, they cannot assess the potential toxic effects of low concentrations. A long-term exposure test can be used to better simulate the actual situation and explore MNPs’ long-term toxic effects. To enhance persuasion, more long-term exposure experiments are needed.
(IV) Zebrafish cannot replace the mammalian model completely: Although zebrafish have many advantages, their physiological characteristics and living environment are fundamentally different from those of humans. In practical applications, it is therefore necessary to establish a mutual verification mechanism between zebrafish and various animal models and combination methods. This will enable us to conduct a more comprehensive assessment of the biological toxicity of MNPs (Figure 5).
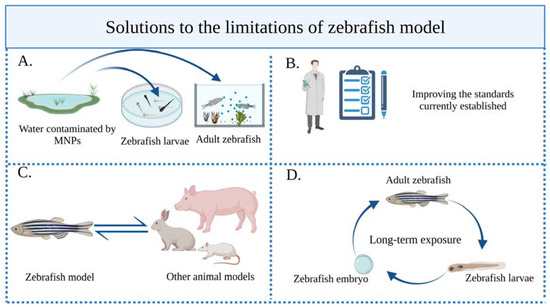
Figure 5.
Solutions to the limitations of zebrafish. (A) To optimize the zebrafish exposure experiments, larval or adult zebrafish should be exposed to real MNPs in contaminated water. (B) The current unified experimental operating procedures and standards must be strictly followed, and researchers still need to promote the construction of standards, so that the toxicity evaluation of zebrafish as a model organism can be more perfect. (C) The mutual verification mechanism for animal models must be strengthened. (D) Long-term exposure experiments should be carried out to expose adult zebrafish to MNPs over a long period of time and there should be generation studies from adult fish to offspring, and then to offspring adult respawning to comprehensively investigate MNP toxic mechanisms.
In addition, computer simulations and molecular biology technologies can also be used to study MNP toxicity mechanism and action targets. This provides a theoretical basis for more accurate and rapid evaluation methods.
6. Conclusions
Water pollution caused by MNPs has become a global environmental issue. The zebrafish has emerged as a promising animal model to understand the toxic impacts and mechanisms of MNPs in water. It provides a novel solution for mitigating MNP pollution. The focus of future research will be on zebrafish research and optimization, and will incorporate the rapid evaluation of several parameters of different indicators, as well as gene-editing technology for the construction of zebrafish mutation models, including genetic and psychiatric disease models, so that zebrafish research can be conducted more efficiently, accurately, and reliably. Furthermore, it is imperative to bolster fundamental research on MNP pollution and better understand its physical and chemical characteristics, environmental behavior, and biological mechanisms. This will provide a more comprehensive and accurate theoretical foundation for zebrafish toxicity evaluations.
Author Contributions
D.S., J.Z. and L.J. contributed to the conceptualization of this review; P.L., W.Z., J.M. and H.Y. analyzed the literature and wrote the manuscript; D.S., P.L., H.Y. and J.M. completed the figure drawings; Y.X., Y.F., J.D., D.S., L.W. and K.Z. revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Basic Scientific Research Project of Wenzhou Science and Technology Bureau (S2020005) and Wenzhou University Master’s Innovation Fund Project (3162023003048, 3162023003051).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| MNPs | Nano-/microplastics |
| MPs | Microplastics |
| NPs | Nanoplastics |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| PVC | Polyvinyl chloride |
| PET | Polyethylene terephthalate |
| PD | Parkinson’s syndrome |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| AChE | Activity of acetylcholinesterase |
| IL-1α | Interleukin-1α |
| NF-κb | Nuclear factor-κb |
| CAT | Catalase |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| ACh | Acetylcholine neurotransmitter |
| GS | Glutamine synthetase |
| GDH | Glutamate dehydrogenase |
| GR | Glutathione reductase |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| PEP | Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase |
| GK | Glucokinase |
| PK | Pyruvate kinase |
| PPAR | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor |
| ACC1 | Acetyl-coa carboxylase 1 |
| FAS | Fatty acid synthase |
| ICD | Isocitrate dehydrogenase |
| FABP6 | Fatty acid binding protein 6 |
| ACO | Acyl-coa oxidase |
| CPT1 | Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 |
| Echs1 | Enoyl-coa hydratase 1 |
| TG | Triglyceride |
References
- Prata, J.C.; da Costa, J.P.; Lopes, I.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Environmental exposure to microplastics: An overview on possible human health effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Shelver, W.L. Micro- and nanoplastic induced cellular toxicity in mammals: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Kauffman, A.E.; Li, L.; McFee, W.; Cai, B.; Weinstein, J.; Lead, J.R.; Chatterjee, S.; Scott, G.I.; Xiao, S. Health impacts of environmental contamination of micro- and nanoplastics: A review. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2020, 25, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; He, Y.; Yan, Y.; Junaid, M.; Wang, J. Characteristics, Toxic Effects, and Analytical Methods of Microplastics in the Atmosphere. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, B.; Dissanayake, P.D.; Bolan, N.S.; Dar, J.Y.; Kumar, M.; Haque, M.N.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Ramanayaka, S.; Biswas, J.K.; Tsang, D.C.W.; et al. Challenges and opportunities in sustainable management of microplastics and nanoplastics in the environment. Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, P.; Chen, H.; Ma, J.; Fang, Y.; Qu, L.; Yang, Q.; Peng, B.; Zhang, X.; Jin, L.; Sun, D. Research progress on extraction technology and biomedical function of natural sugar substitutes. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 952147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Wang, L.; Ji, H.; Fang, Y.; Lei, P.; Zhang, X.; Jin, L.; Sun, D.; Dong, H. Toxic Mechanism and Biological Detoxification of Fumonisins. Toxins 2022, 14, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chao, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q. Research progress of nanoplastics in freshwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, A.A. Plastic pollution: When do we know enough? J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetto, F.; Corcione, C.E.; Rizzo, A.; Maffezzoli, A. Production and Characterization of Polyethylene Terephthalate Nanoparticles. Polymers 2021, 13, 3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, V.; Sharma, S.; Gupta, S.; Ghosal, A.; Nadda, A.K.; Jose, R.; Sharma, P.; Kumar, S.; Singh, P.; Raizada, P. Prevalence and implications of microplastics in potable water system: An update. Chemosphere 2023, 317, 137848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xia, X.; Lv, X.; Song, E.; Song, Y. Iron-bearing nanoparticles trigger human umbilical vein endothelial cells ferroptotic responses by promoting intracellular iron level. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Lv, X.; Yang, B.; Qin, Q.; Song, E.; Song, Y. Tetrachlorobenzoquinone exposure triggers ferroptosis contributing to its neurotoxicity. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; He, Y.; Cheng, R.; Li, Q.; Qian, Z.; Lin, X. Recent advances in toxicological research and potential health impact of microplastics and nanoplastics in vivo. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 40415–40448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, M.A.; Gedik, K.; Gaga, E.O. Atmospheric micro (nano) plastics: Future growing concerns for human health. Air Qual. Atmosphere Health 2023, 16, 233–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Dong, G.; Liang, M.; Wu, X.; Xian, M.; An, Y.; Zhan, J.; Xu, L.; Xu, J.; Sun, W.; et al. Toxicity of micro(nano)plastics with different size and surface charge on human nasal epithelial cells and rats via intranasal exposure. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 136093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, M.; Martins, M.A.; Soares, A.M.V.; Cuesta, A.; Oliveira, M. Polystyrene nanoplastics alter the cytotoxicity of human pharmaceuticals on marine fish cell lines. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 69, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Shelver, W.L. Micro- and Nanoplastic-Mediated Pathophysiological Changes in Rodents, Rabbits, and Chickens: A Review. J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 1480–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.; Jeong, J.; Song, K.S.; Sung, J.H.; Oh, S.M.; Choi, J. Inhalation toxicity of polystyrene micro(nano)plastics using modified OECD TG 412. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Chen, Q.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Liang, W.; Su, L.; Shi, H. Distribution and translocation of micro- and nanoplastics in fish. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2021, 51, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, C.Q.Y.; Valiyaveettil, S.; Tang, B.L. Toxicity of Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Mammalian Systems. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Kong, A.; Shelton, D.; Dong, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, F.; Bai, C.; Huang, K.; Mo, W.; Chen, S.; et al. Early life stage transient aristolochic acid exposure induces behavioral hyperactivity but not nephrotoxicity in larval zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 238, 105916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.; Ma, J.; Fang, Y.; Lei, P.; Wang, L.; Qu, L.; Wu, W.; Jin, L.; Sun, D. Advances in Zebrafish for Diabetes Mellitus with Wound Model. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, J.; Zang, L.; Nishimura, N.; Shimada, Y. Zebrafish: An emerging model to study microplastic and nanoplastic toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horzmann, K.A.; Freeman, J.L. Making Waves: New Developments in Toxicology with the Zebrafish. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2018, 163, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, B.; Mally, A.; Liedtke, D. Zebrafish Embryos and Larvae as Alternative Animal Models for Toxicity Testing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clément, Y.; Torbey, P.; Gilardi-Hebenstreit, P.; Crollius, H.R. Enhancer-gene maps in the human and zebrafish genomes using evolutionary linkage conservation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 2357–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batel, A.; Borchert, F.; Reinwald, H.; Erdinger, L.; Braunbeck, T. Microplastic accumulation patterns and transfer of benzo[a]pyrene to adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) gills and zebrafish embryos. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, R.; Voy, C.; Chen, S.; Di Giulio, R.T. Nanoplastics Decrease the Toxicity of a Complex PAH Mixture but Impair Mitochondrial Energy Production in Developing Zebrafish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 8405–8415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, T.; Miao, X.; Yi, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Lee, S.M.-Y.; Zheng, Y. Zebrafish: A promising in vivo model for assessing the delivery of natural products, fluorescence dyes and drugs across the blood-brain barrier. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 125, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalueff, A.V.; Stewart, A.M.; Gerlai, R. Zebrafish as an emerging model for studying complex brain disorders. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuna, H.; Hutcheson, D.A.; Duncan, R.N.; McPherson, A.D.; Scoresby, A.N.; Gaynes, B.F.; Tong, Z.; Fujimoto, E.; Kwan, K.M.; Chien, C.-B.; et al. High-resolution analysis of central nervous system expression patterns in zebrafish Gal4 enhancer-trap lines. Dev. Dyn. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Anat. 2015, 244, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, G.J.; Zhang, C.; Ojiaku, P.; Bell, V.; Devkota, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Effects of ethanol exposure on nervous system development in zebrafish. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 299, 255–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goessling, W.; Sadler, K.C. Zebrafish: An important tool for liver disease research. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1361–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Jin, Q.; Gao, C.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Z.; Guo, G.; Peng, J. Unraveling Differential Transcriptomes and Cell Types in Zebrafish Larvae Intestine and Liver. Cells 2022, 11, 3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugman, S. The zebrafish as a model to study intestinal inflammation. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 64, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulukan, E.; Şenol, O.; Baran, A.; Kankaynar, M.; Yıldırım, S.; Kızıltan, T.; Bolat, İ.; Ceyhun, S.B. Nano-sized polystyrene plastic particles affect many cancer-related biological processes even in the next generations; zebrafish modeling. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 838, 156391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Silic, M.R.; Schaber, A.; Wasel, O.; Freeman, J.L.; Sepúlveda, M.S. Exposure route affects the distribution and toxicity of polystyrene nanoplastics in zebrafish. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 724, 138065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, A.; Maity, S.; Banerjee, S.; Dutta, S.; Adhikari, M.; Guchhait, R.; Biswas, C.; De, S.; Pramanick, K. Toxicological impacts of nanopolystyrene on zebrafish oocyte with insight into the mechanism of action: An expression-based analysis. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 830, 154796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.A.; Trevisan, R.; Massarsky, A.; Kozal, J.S.; Levin, E.D.; Di Giulio, R.T. Maternal transfer of nanoplastics to offspring in zebrafish (Danio rerio): A case study with nanopolystyrene. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 643, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malafaia, G.; de Souza, A.M.; Pereira, A.C.; Gonçalves, S.; da Costa Araújo, A.P.; Ribeiro, R.X.; Rocha, T.L. Developmental toxicity in zebrafish exposed to polyethylene microplastics under static and semi-static aquatic systems. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 700, 134867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, M.; Zhao, X.; Wu, F.; Wang, C.; Wang, C.; White, J.C.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, L.; Yan, S.; Tian, S. Charge-specific adverse effects of polystyrene nanoplastics on zebrafish (Danio rerio) development and behavior. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliakbarzadeh, F.; Rafiee, M.; Khodagholi, F.; Khorramizadeh, M.R.; Manouchehri, H.; Eslami, A.; Sayehmiri, F.; Mohseni-Bandpei, A. Adverse effects of polystyrene nanoplastic and its binary mixtures with nonylphenol on zebrafish nervous system: From oxidative stress to impaired neurotransmitter system. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 317, 120587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, C.W.; Ching-Fong Yeung, K.; Chan, K.M. Acute toxic effects of polyethylene microplastic on adult zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qin, Z.; Huang, Z.; Bao, Z.; Luo, T.; Jin, Y. Effects of polyethylene microplastics on the microbiome and metabolism in larval zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 282, 117039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Duan, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wei, Y.; Sun, H. Immunotoxicity responses to polystyrene nanoplastics and their related mechanisms in the liver of zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae. Environ. Int. 2022, 161, 107128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Bao, Z.; Wan, Z.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Polystyrene microplastic exposure disturbs hepatic glycolipid metabolism at the physiological, biochemical, and transcriptomic levels in adult zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sökmen, T.Ö.; Sulukan, E.; Türkoğlu, M.; Baran, A.; Özkaraca, M.; Ceyhun, S.B. Polystyrene nanoplastics (20 nm) are able to bioaccumulate and cause oxidative DNA damages in the brain tissue of zebrafish embryo (Danio rerio). Neurotoxicology 2020, 77, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashirova, N.; Poppitz, D.; Klüver, N.; Scholz, S.; Matysik, J.; Alia, A. A mechanistic understanding of the effects of polyethylene terephthalate nanoplastics in the zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryo. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasamma, S.; Audira, G.; Siregar, P.; Malhotra, N.; Lai, Y.-H.; Liang, S.-T.; Chen, J.-R.; Chen, K.H.-C.; Hsiao, C.-D. Nanoplastics Cause Neurobehavioral Impairments, Reproductive and Oxidative Damages, and Biomarker Responses in Zebrafish: Throwing up Alarms of Wide Spread Health Risk of Exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasco, M.; Gavaia, P.J.; Bensimon-Brito, A.; Cordelières, F.P.; Santos, T.; Martins, G.; de Castro, D.T.; Silva, N.; Cabrita, E.; Bebianno, M.J.; et al. Effects of pristine or contaminated polyethylene microplastics on zebrafish development. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, A.P.d.C.; da Luz, T.M.; Rocha, T.L.; Ahmed, M.A.I.; e Silva, D.D.D.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Malafaia, G. Toxicity evaluation of the combination of emerging pollutants with polyethylene microplastics in zebrafish: Perspective study of genotoxicity, mutagenicity, and redox unbalance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 432, 128691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, J.A.; Kozal, J.S.; Jayasundara, N.; Massarsky, A.; Trevisan, R.; Geitner, N.; Wiesner, M.; Levin, E.D.; Di Giulio, R.T. Uptake, tissue distribution, and toxicity of polystyrene nanoparticles in developing zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 194, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yin, D.; Jia, Y.; Schiwy, S.; Legradi, J.; Yang, S.; Hollert, H. Enhanced uptake of BPA in the presence of nanoplastics can lead to neurotoxic effects in adult zebrafish. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 609, 1312–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lei, Y.; Cai, Y.; Liang, Q.; Nie, S.; Jia, Y.; Chen, S.; Huang, C.; et al. Leachate from plastic food packaging induced reproductive and neurobehavioral toxicity in zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 231, 113189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lackmann, C.; Wang, W.; Seiler, T.-B.; Hollert, H.; Shi, H. Microplastics Lead to Hyperactive Swimming Behaviour in Adult Zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 224, 105521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chen, Q.; Qiu, W.; Ma, C.; Gao, Z.; Chu, W.; Shi, H. Concurrent water- and foodborne exposure to microplastics leads to differential microplastic ingestion and neurotoxic effects in zebrafish. Water Res. 2022, 219, 118582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.; Luzio, A.; Matos, C.; Bellas, J.; Monteiro, S.M.; Félix, L. Microplastics alone or co-exposed with copper induce neurotoxicity and behavioral alterations on zebrafish larvae after a subchronic exposure. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 235, 105814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Rowe, D.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastic ingestion decreases energy reserves in marine worms. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, R1031–R1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabezanahary, A.N.A.; Piette, M.; Missawi, O.; Garigliany, M.-M.; Kestemont, P.; Cornet, V. Microplastics alter development, behavior, and innate immunity responses following bacterial infection during zebrafish embryo-larval development. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 136969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limonta, G.; Mancia, A.; Benkhalqui, A.; Bertolucci, C.; Abelli, L.; Fossi, M.C.; Panti, C. Microplastics induce transcriptional changes, immune response and behavioral alterations in adult zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobori, D.C.; Feidantsis, K.; Dimitriadi, A.; Datsi, N.; Ripis, P.; Kalogiannis, S.; Sampsonidis, I.; Kastrinaki, G.; Ainali, N.M.; Lambropoulou, D.A.; et al. Dose-Dependent Cytotoxicity of Polypropylene Microplastics (PP-MPs) in Two Freshwater Fishes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobori, D.C.; Dimitriadi, A.; Feidantsis, K.; Samiotaki, A.; Fafouti, D.; Sampsonidis, I.; Kalogiannis, S.; Kastrinaki, G.; Lambropoulou, D.A.; Kyzas, G.Z.; et al. Differentiation in the expression of toxic effects of polyethylene-microplastics on two freshwater fish species: Size matters. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 830, 154603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Lv, M.; Zhao, X.; Ji, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, L. The combined toxic effects of polyvinyl chloride microplastics and di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate on the juvenile zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 440, 129711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhou, D.; Yang, S.; Shi, Z.; Pan, H.; Jin, Q.; Ding, Z. Neurotoxicity of polystyrene nanoplastics with different particle sizes at environment-related concentrations on early zebrafish embryos. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 872, 162096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Geng, J.; Ding, L.; Ren, H. Uptake and Accumulation of Polystyrene Microplastics in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) and Toxic Effects in Liver. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4054–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.H.; Jeong, J.A.; Choi, E.K.; Jeong, T.-Y. Antioxidant enzyme activity in Daphnia magna under microscopic observation and shed carapace length as an alternative growth endpoint. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 794, 148771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Wang, L. Metal accumulation and antioxidant defenses in the freshwater fish Carassius auratus in response to single and combined exposure to cadmium and hydroxylated multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 275, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.; Félix, L.; Luzio, A.; Parra, S.; Cabecinha, E.; Bellas, J.; Monteiro, S.M. Toxicological effects induced on early life stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio) after an acute exposure to microplastics alone or co-exposed with copper. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Bhagat, J.; Tiwari, E.; Khandelwal, N.; Darbha, G.K.; Shyama, S.K. Metal oxide nanoparticles and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons alter nanoplastic’s stability and toxicity to zebrafish. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidel, A.J.; Assmann, K.L.; Werlang, C.C.; Bertoncello, K.T.; Francescon, F.; Rambo, C.L.; Beltrame, G.M.; Calegari, D.; Batista, C.B.; Blaser, R.E.; et al. Subchronic atrazine exposure changes defensive behaviour profile and disrupts brain acetylcholinesterase activity of zebrafish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2014, 44, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashirzade, A.A.; Zabegalov, K.N.; Volgin, A.D.; Belova, A.S.; Demin, K.A.; de Abreu, M.S.; Babchenko, V.Y.; Bashirzade, K.A.; Yenkoyan, K.B.; Tikhonova, M.A.; et al. Modeling neurodegenerative disorders in zebrafish. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 138, 104679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Cao, H. Zebrafish and Medaka: Important Animal Models for Human Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.K.; Pal, R.; Siddiqi, N.J.; Sharma, B. Acetylcholinesterase from Human Erythrocytes as a Surrogate Biomarker of Lead Induced Neurotoxicity. Enzym. Res. 2015, 2015, e370705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcimartín, A.; López-Oliva, M.E.; González, M.P.; Sánchez-Muniz, F.J.; Benedí, J. Hydrogen peroxide modifies both activity and isoforms of acetylcholinesterase in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Redox Biol. 2017, 12, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadsetan, S.; Kukolj, E.; Bak, L.K.; SØrensen, M.; Ott, P.; Vilstrup, H.; Schousboe, A.; Keiding, S.; Waagepetersen, H.S. Brain Alanine Formation as an Ammonia-Scavenging Pathway during Hyperammonemia: Effects of Glutamine Synthetase Inhibition in Rats and Astrocyte—Neuron Co-Cultures. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Lin, L.; Wei, A.; Sepúlveda, M.S. Protein Corona Analysis of Silver Nanoparticles Exposed to Fish Plasma. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Barnoud, J.; Monticelli, L. Polystyrene Nanoparticles Perturb Lipid Membranes. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendra, M.; Pereiro, P.; Yeste, M.P.; Mercado, L.; Figueras, A.; Novoa, B. Size matters: Zebrafish (Danio rerio) as a model to study toxicity of nanoplastics from cells to the whole organism. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y. Microplastics as a Vector for HOC Bioaccumulation in Earthworm Eisenia fetida in Soil: Importance of Chemical Diffusion and Particle Size. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 12154–12163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigorakis, S.; Mason, S.A.; Drouillard, K.G. Determination of the gut retention of plastic microbeads and microfibers in goldfish (Carassius auratus). Chemosphere 2017, 169, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.-M.; Byeon, E.; Jeong, H.; Kim, M.-S.; Chen, Q.; Lee, J.-S. Different effects of nano- and microplastics on oxidative status and gut microbiota in the marine medaka Oryzias melastigma. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Huang, A.; Cao, S.; Sun, F.; Wang, L.; Guo, H.; Ji, R. Effects of nanoplastics and microplastics on toxicity, bioaccumulation, and environmental fate of phenanthrene in fresh water. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Q.; Dong, S.; Wang, X.; Yan, C. Combined effects of micro-/nano-plastics and oxytetracycline on the intestinal histopathology and microbiome in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engevik, M.A.; Danhof, H.A.; Ruan, W.; Engevik, A.C.; Chang-Graham, A.L.; Engevik, K.A.; Shi, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Brand, C.K.; Krystofiak, E.S.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum Secretes Outer Membrane Vesicles and Promotes Intestinal Inflammation. mBio 2021, 12, e02706–e02720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostic, A.D.; Chun, E.; Robertson, L.; Glickman, J.N.; Gallini, C.A.; Michaud, M.; Clancy, T.E.; Chung, D.C.; Lochhead, P.; Hold, G.L.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum potentiates intestinal tumorigenesis and modulates the tumor-immune microenvironment. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.; Saez, J.M.; Davila Costa, J.S.; Colin, V.L.; Fuentes, M.S.; Cuozzo, S.A.; Benimeli, C.S.; Polti, M.A.; Amoroso, M.J. Actinobacteria: Current research and perspectives for bioremediation of pesticides and heavy metals. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collinder, E.; Björnhag, G.; Cardona, M.; Norin, E.; Rehbinder, C.; Midtvedt, T. Gastrointestinal Host–Microbial Interactions in Mammals and Fish: Comparative Studies in Man, Mice, Rats, Pigs, Horses, Cows, Elks, Reindeers, Salmon and Cod. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2003, 15, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Klein, S.; Gordon, J.I. Human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 2006, 444, 1022–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, T. Chapter 35—Immunoprotective Effects of Probiotics in the Elderly. In Foods and Dietary Supplements in the Prevention and Treatment of Disease in Older Adults; Watson, R.R., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 363–372. ISBN 978-0-12-418680-4. [Google Scholar]
- Barletta, M.; Lima, A.R.A.; Costa, M.F. Distribution, sources and consequences of nutrients, persistent organic pollutants, metals and microplastics in South American estuaries. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 1199–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizraji, R.; Ahrendt, C.; Perez-Venegas, D.; Vargas, J.; Pulgar, J.; Aldana, M.; Patricio Ojeda, F.; Duarte, C.; Galbán-Malagón, C. Is the feeding type related with the content of microplastics in intertidal fish gut? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 116, 498–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santangeli, S.; Notarstefano, V.; Maradonna, F.; Giorgini, E.; Gioacchini, G.; Forner-Piquer, I.; Habibi, H.R.; Carnevali, O. Effects of diethylene glycol dibenzoate and Bisphenol A on the lipid metabolism of Danio rerio. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, M.; Wang, X.; Tu, W.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Bioaccumulation in the gut and liver causes gut barrier dysfunction and hepatic metabolism disorder in mice after exposure to low doses of OBS. Environ. Int. 2019, 129, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Lei, P.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Fang, Y.; Yan, X.; Yang, Q.; Peng, B.; Jin, L.; Sun, D. Advances in lncRNAs from stem cell-derived exosome for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 986683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.; Zhang, G.; He, L.; Ma, S.; Ma, H.; Zhai, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y. Canagliflozin Attenuates Hepatic Steatosis and Atherosclerosis Progression in Western Diet-Fed ApoE-Knockout Mice. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2022, 16, 4161–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oaxaca-Castillo, D.; Andreoletti, P.; Vluggens, A.; Yu, S.; van Veldhoven, P.P.; Reddy, J.K.; Cherkaoui-Malki, M. Biochemical characterization of two functional human liver acyl-CoA oxidase isoforms 1a and 1b encoded by a single gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 360, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parini, P.; Jiang, Z.-Y.; Einarsson, C.; Eggertsen, G.; Zhang, S.-D.; Rudel, L.L.; Han, T.-Q.; Eriksson, M. ACAT2 and human hepatic cholesterol metabolism: Identification of important gender-related differences in normolipidemic, non-obese Chinese patients. Atherosclerosis 2009, 207, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalby, P.A.; Aucamp, J.P.; George, R.; Martinez-Torres, R.J. Structural stability of an enzyme biocatalyst. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 1606–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Dai, J. Proteomic analysis of male zebrafish livers chronically exposed to perfluorononanoic acid. Environ. Int. 2012, 42, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Sun, M.; Tang, J. Enoyl-coenzyme A hydratase in cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2015, 448, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobanska, M.; Scholz, S.; Nyman, A.-M.; Cesnaitis, R.; Gutierrez Alonso, S.; Klüver, N.; Kühne, R.; Tyle, H.; de Knecht, J.; Dang, Z.; et al. Applicability of the fish embryo acute toxicity (FET) test (OECD 236) in the regulatory context of Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).