The Application of Reference Dose Prediction Model to Human Health Water Quality Criteria and Risk Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Model Building
2.3. Derivation of Human Health Water Quality Criteria
2.4. Health Risk Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Prediction Models for Pesticide Class Chemicals
3.2. Determination of Other Water Quality Criteria Parameters
3.3. Health Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, Z.; Zheng, X.; Fan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, T.; Sun, Q.; Huang, Y. China national water quality criteria for the protection of freshwater life: Ammonia. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, L.L.; Borghoff, S.J.; Thompson, C.M. Comparison of threshold of toxicological concern (TTC) values to oral reference dose (RfD) values. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 113, 104651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, D.G.; Dourson, M. Reference dose (RfD): Description and use in health risk assessments. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. RTP 1988, 8, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority and World Health Organization. Review of the Threshold of Toxicological Concern (TTC) Approach and Development of New TTC Decision Tree; European Food Safety Authority: Parma, Italy; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kadry, A.M.; Skowronski, G.A.; Abdel-Rahman, M.S. Evaluation of the use of uncertainty factors in deriving RfDs for some chlorinated compounds. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 1995, 45, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Methodology for Deriving Ambient Water Quality Criteria for the Protection of Human Health (2000); USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- Alexeeff, G.V.; Broadwin, R.; Liaw, J.; Dawson, S.V. Characterization of the LOAEL-to-NOAEL uncertainty factor for mild adverse effects from acute inhalation exposures. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2002, 36, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, B.J.; Cox, K.; Bhat, V. Derivation of an oral reference dose (RfD) for di 2-ethylhexyl cyclohexan-1,4-dicarboxylate (DEHCH), an alternative to phthalate plasticizers. Regul Toxicol Pharm. 2018, 92, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsnelson, B.A.; Chernyshov, I.N.; Solovyeva, S.N.; Minigalieva, I.A.; Gurvich, V.B.; Valamina, I.E.; Makeyev, O.H.; Sahautdinova, R.R.; Privalova, L.I.; Tsaregorodtseva, A.E.; et al. Looking for the LOAEL or NOAEL Concentration of Nickel-Oxide Nanoparticles in a Long-Term Inhalation Exposure of Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Yan, Z.; Zheng, X.; Fan, J.; Wang, S.; Wei, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, P.; Guo, S. Transcriptome analysis of response mechanism to ammonia stress in Asian clam (Corbicula fluminea). Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 214, 105235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Council, N.R. Toxicity Testing in the 21st Century: A Vision and a Strategy; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; p. 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Yan, Z.; Zheng, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Q. Development of interspecies correlation estimation (ICE) models to predict the reproduction toxicity of EDCs to aquatic species. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, S.; Xu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, X.; Yan, Z. Reference dose prediction by using CDK molecular descriptors: A non-experimental method. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wang, P. Modeling the ecological status response of rivers to multiple stressors using machine learning: A comparison of environmental DNA metabarcoding and morphological data. Water Res. 2020, 183, 116004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zheng, L.; Yan, Z.; Huang, Y.; Feng, C.; Li, L.; Ling, J. Effective extrapolation models for ecotoxicity of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylene (BTEX). Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myint, K.Z.; Xie, X.Q. Recent Advances in Fragment-Based QSAR and Multi-Dimensional QSAR Methods. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 3846–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisaki, T.; Kaneko, M.A.n.; Hirota, M.; Matsuoka, M.; Kouzuki, H. Integration of read-across and artificial neural network-based QSAR models for predicting systemic toxicity: A case study for valproic acid. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2020, 45, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Yang, M.; Zhu, Q.; Wagner, E.D.; Plewa, M.J. Comparative Quantitative Toxicology and QSAR Modeling of the Haloacetonitriles: Forcing Agents of Water Disinfection Byproduct Toxicity. Env. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 8909–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veselinovic, J.B.; Veselinovic, A.M.; Toropova, A.P.; Toropov, A.A. The Monte Carlo technique as a tool to predict LOAEL. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 116, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toropova, A.P.; Toropov, A.A.; Marzo, M.; Escher, S.E.; Dome, J.L.; Georgiadis, N.; Benfenati, E. The application of new HARD-descriptor available from the CORAL software to building up NOAEL models. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 112, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilaoui, L.; Schilter, B.; Tran, L.-A.; Mazzatorta, P.; Grigorov, M. Integrated computational methods for prediction of the lowest observable adverse effect level of food-borne molecules. Qsar Comb. Sci. 2007, 26, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowski, M.; Czerczak, S. A proposal for calculating the no-observed-adverse-effect level (NOAEL) for organic compounds responsible for liver toxicity based on their physicochemical properties. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2014, 27, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarn, J.A.; Engeli, B.E.; Schlatter, J.R. Study parameters influencing NOAEL and LOAEL in toxicity feeding studies for pesticides: Exposure duration versus dose decrement, dose spacing, group size and chemical class. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 61, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabovsky, J.; Fowles, J.; Hill, M.D.; Lewis, D.C. A health risk benchmark for the neurologic effects of styrene: Comparison with NOAEL/LOAEL approach. Risk Anal. 2001, 21, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyer, S.D.; Versteeg, D.J.; Belanger, S.E.; Chaney, J.G.; Raimondo, S.; Barron, M.G. Comparison of species sensitivity distributions derived from interspecies correlation models to distributions used to derive water quality criteria. Environ. Sci. Technol 2008, 42, 3076–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Lee, P.W.; Cao, S. China: Forward to the green pesticides via a basic research program. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 2613–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, E.; Moore, P. The effects of the herbicide metolachlor on agonistic behaviorin the crayfish, Orconectes rusticus. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 55, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Wang, w.; Zhou, J.; Yi, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z. Screening of high phytotoxicity priority pollutants and their ecological risk assessment in China’s surface waters. Chemosphere 2015, 128, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; He, H.; Yan, Z.; Gao, F.; Zheng, X.; Fan, J.; Wang, Y. Comparative analysis of freshwater species sensitivity distributions and ecotoxicity for priority pesticides: Implications for water quality criteria. Ecotoxicol Environ. Saf. 2019, 176, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, A.; Glen, R.C. Molecular similarity: A key technique in molecular informatics. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2004, 2, 3204–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Domenech, R.; de Julian-Ortiz, J.V.; Besalu, E. True prediction of lowest observed adverse effect levels. Mol. Divers. 2006, 10, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansch, C.; Steward, A.R. The use of substituent constants in the analysis of the structure--activity relationship in penicillin derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 1964, 7, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment the People’s Republic of China. Technical Guideline for Deriving Water Quality Criteria for the Protection of Human Health; Ministry of Ecology and Environment the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment the People’s Republic of China. Exposure Factors Handbook of Chinese Population (Adult Volume); China Evironmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Society, N. Nutrition and Dietary Guidelines for Chinese Residents; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.; Singh, S.; Thakur, S.; Lakhwani, M.; Khadikar, P.V.; Agrawal, V.K.; Supuran, C.T. QSAR study on murine recombinant isozyme mCAXIII: Topological vs structural descriptors. Arkivoc 2006, 14, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.P.; Paul, S.; Mitra, I.; Roy, K. On Two Novel Parameters for Validation of Predictive QSAR Models. Molecules 2009, 14, 1660–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Hua, R.M.; Li, X.D.; Zhou, T.T.; Yang, F.; Cao, H.Q.; Wu, X.W.; Tang, J. Residual Characteristic and Assessment of Organochlorine Pesticides in Water of Chaohu Lake Tributaries. In Proceedings of the Third National Symposium on Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, Tianjin, China, 1 October 2009; pp. 558–564. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, W.; Khalid, M.; Zhou, J.; Xu, L.; Hong, H. Evaluation and Fate of the Organic Chlorine Pesticides at the Waters in Jiulong River Estuary. Environ. Sci. 2001, 22, 88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.H.; Qi, S.H.; Wang, W. The characteristic distribution of organic chlorine pesticides in the water and sediment of Diaocha Lake in Hubei Province. Environ. Pollut. Control 2007, 29, 415–418. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.S.; Mai, B.X.; Fu, J.M.; Sheng, G.Y.; Hu, X. Studies on organochlorine pesticites (OCPs) in waters of Pearl River artery estuary water. China Environ. Sci. 2005, 25, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.S.; Teng, M.D.; Xu, C.M. Determination of Fourteen Organochlorine Pesticides in the Middle of Chishui River by Gas Chromatography. Arid. Environ. Monit. 2011, 25, 193–202. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, C.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, T.; Xiao, C.; Wu, L. Distribution characteristics and risk evaluation of organoclorine pesticides in runoff from typical area of Danjiangkou Reservoir. China Environ. Sci. 2012, 32, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar]
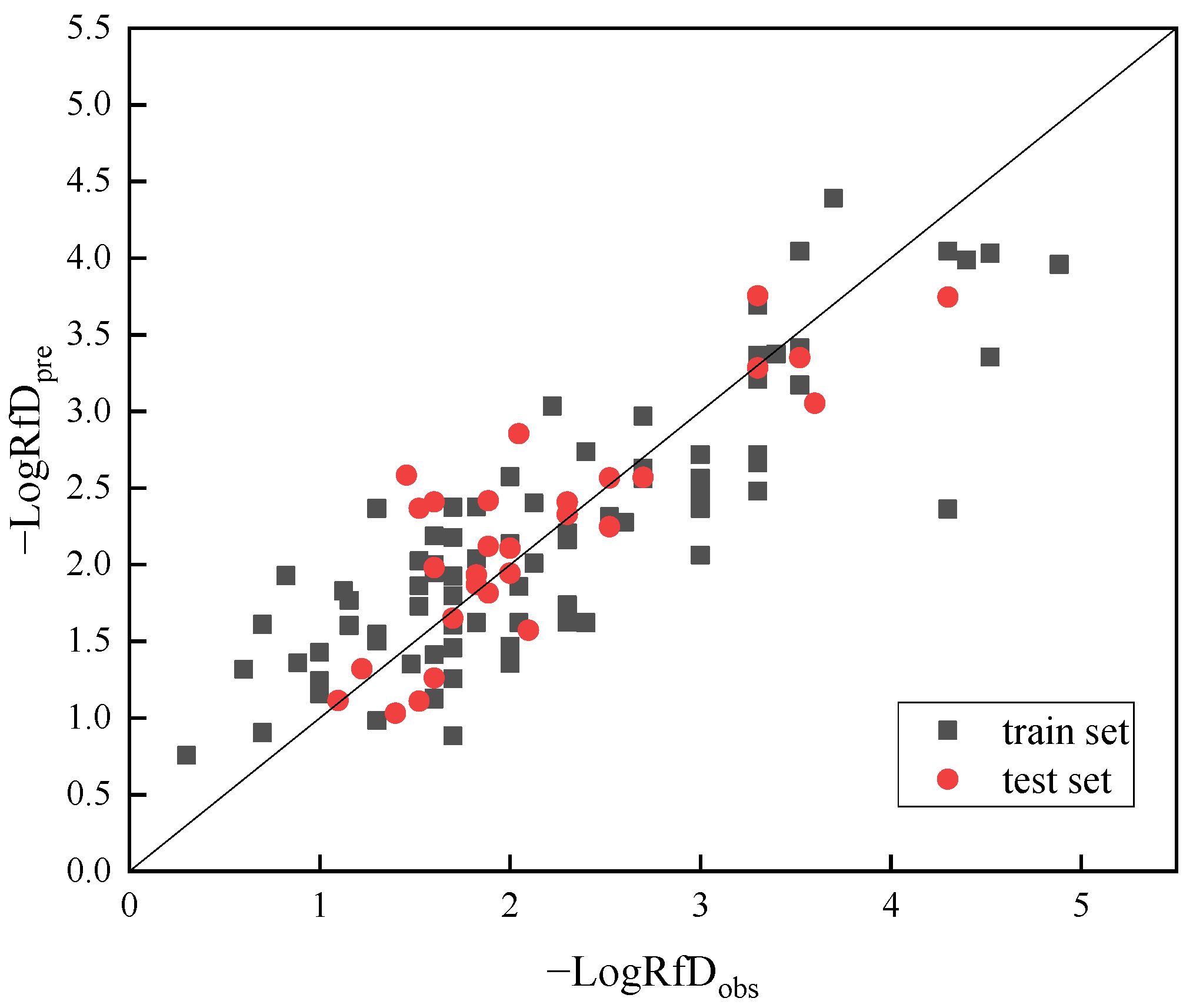
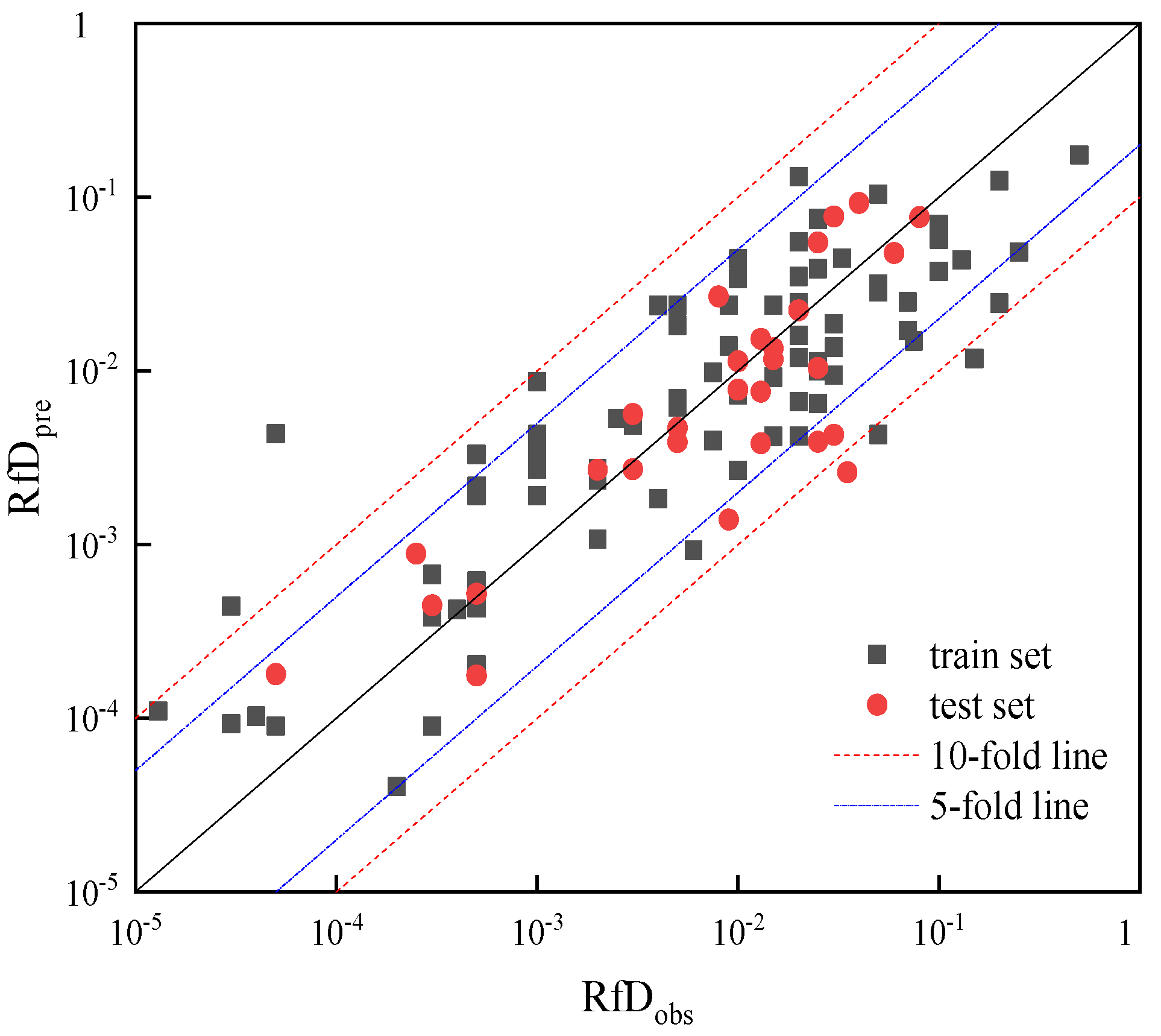
| No | Descriptor | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ui | Unsaturation index |
| 2 | ATS1m | Broto–Moreau autocorrelation of a topological structure—lag 1/weighted by atomic masses |
| 3 | MAXDP | Maximal electrotopological positive variation |
| 4 | xp9 | Simple 9th order path chi index |
| 5 | SdssC_acnt | Count of (=C<) |
| 6 | ssi | Standardized Shannon Information or standardized information content |
| 7 | SHHBd | Sum of E-State indices for hydrogen bond donors |
| 8 | MATS8e | Moran autocorrelation—lag 8/weighted by atomic Sanderson electronegativities |
| 9 | MATS2m | Moran autocorrelation—lag 2/weighted by atomic masses |
| 10 | MATS2e | Moran autocorrelation—lag 2/weighted by atomic Sanderson electronegativities |
| 11 | SsssCH_acnt | Count of (>CH–) |
| 12 | piPC08 | Molecular multiple path count of order 08 |
| N | Rtra2 | Rtes2 | RMSEP | p | D-W | q2 | k | k’ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 0.762 | 0.683 | 0.434 | <0.05 | 1.952 | 0.648 | 0.983 | 1.016 |
| Trophic Levels | fl | Compounds | FCM | BL-BAF | F-BAF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0.019 | p-p’DDE | 1.000 | 5.33 × 107 | 3.24 × 104 |
| α-HCH | 1.000 | 1.97 × 104 | 365 | ||
| 3 | 0.026 | p-p’DDE | 13.30 | 5.18 × 108 | 4.30 × 105 |
| α-HCH | 24.70 | 3.55 × 105 | 9.00 × 103 | ||
| 4 | 0.030 | p-p’DDE | 1.128 | 3.81 × 107 | 3.65 × 104 |
| α-HCH | 1.003 | 1.25 × 104 | 366 |
| Compounds | RfD | BW | DI | FIi/kg · d−1 | BAF/L · kg−1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg · kg−1 · d−1 | kg | L · d−1 | FI2 | FI3 | FI4 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| p-p’DDE | 0.01 | 60.60 | 1.850 | 0.0126 | 0.0100 | 0.0075 | 3.24 × 104 | 4.30 × 105 | 3.65 × 104 |
| α-HCH | 0.0002 | 365 | 9.00 × 103 | 366 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Men, S.-H.; Xie, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, J.-Y.; Jiao, C.-Y.; Yan, Z.-G. The Application of Reference Dose Prediction Model to Human Health Water Quality Criteria and Risk Assessment. Toxics 2023, 11, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040318
Men S-H, Xie X, Zhao X, Zhou Q, Chen J-Y, Jiao C-Y, Yan Z-G. The Application of Reference Dose Prediction Model to Human Health Water Quality Criteria and Risk Assessment. Toxics. 2023; 11(4):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040318
Chicago/Turabian StyleMen, Shu-Hui, Xin Xie, Xin Zhao, Quan Zhou, Jing-Yi Chen, Cong-Ying Jiao, and Zhen-Guang Yan. 2023. "The Application of Reference Dose Prediction Model to Human Health Water Quality Criteria and Risk Assessment" Toxics 11, no. 4: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040318
APA StyleMen, S.-H., Xie, X., Zhao, X., Zhou, Q., Chen, J.-Y., Jiao, C.-Y., & Yan, Z.-G. (2023). The Application of Reference Dose Prediction Model to Human Health Water Quality Criteria and Risk Assessment. Toxics, 11(4), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11040318








