Effects of Pb(II) and Zn(II) Contamination on Adsorption, Desorption and Degradation of Cry1Ac Toxin Identical to Bt Transgenic Poplar in Black Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Sample
2.2. Bt Toxin and Heavy Metal Salt
2.3. Preparation of Bt Toxin Solution
2.4. Preparation of Soil Suspension
2.5. Preparation of Pb (II) and Zn(II) Solution
2.6. Adsorption Tests in Batch Mode
2.7. Desorption of Bt Toxin
2.8. Zeta Potential of Soil Particles and Bt Toxin
2.9. Degradation of Bt Toxin in Soil
2.10. Statistics
3. Results and Analysis
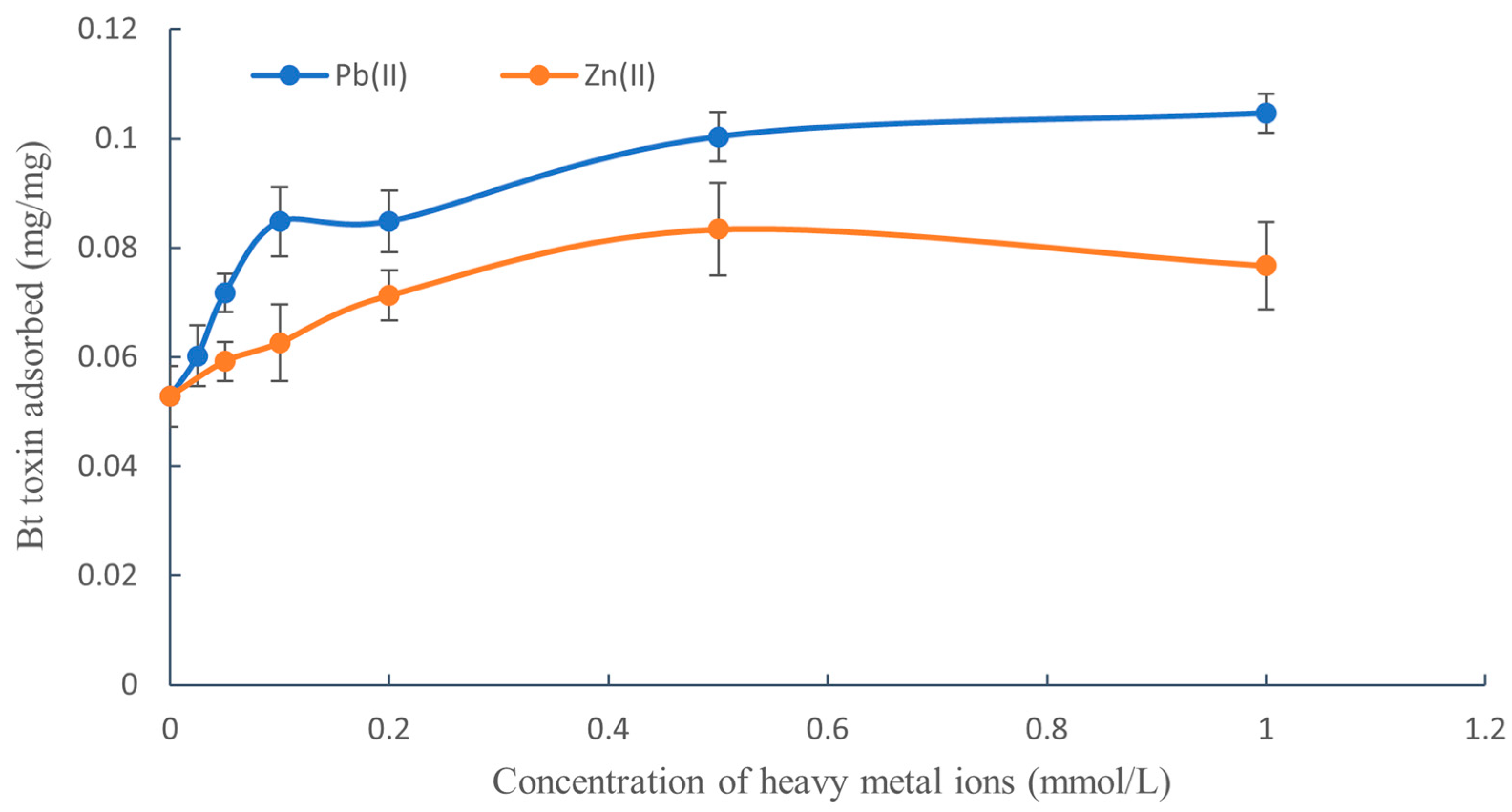
3.1. Effect of Pb(II) and Zn(II) Concentrations on the Adsorption of Bt Toxin
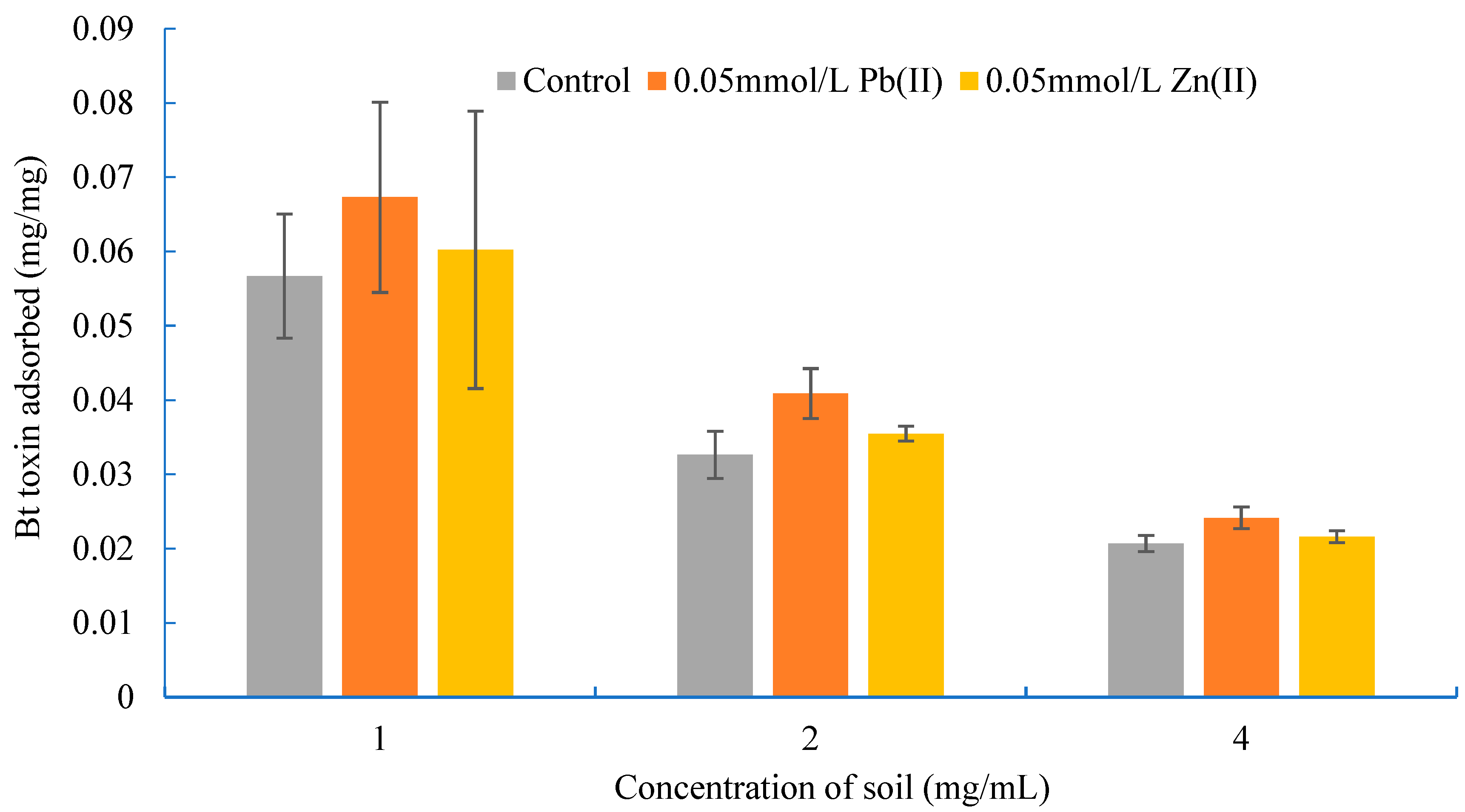
3.2. Effects of Soil Concentration on the Adsorption of Bt Toxin
3.3. Effects of Temperature on the Adsorption of Bt Toxin
3.4. The Effect of Lead and Zinc Ions on the Desorption of Bt Toxin from Black Soil
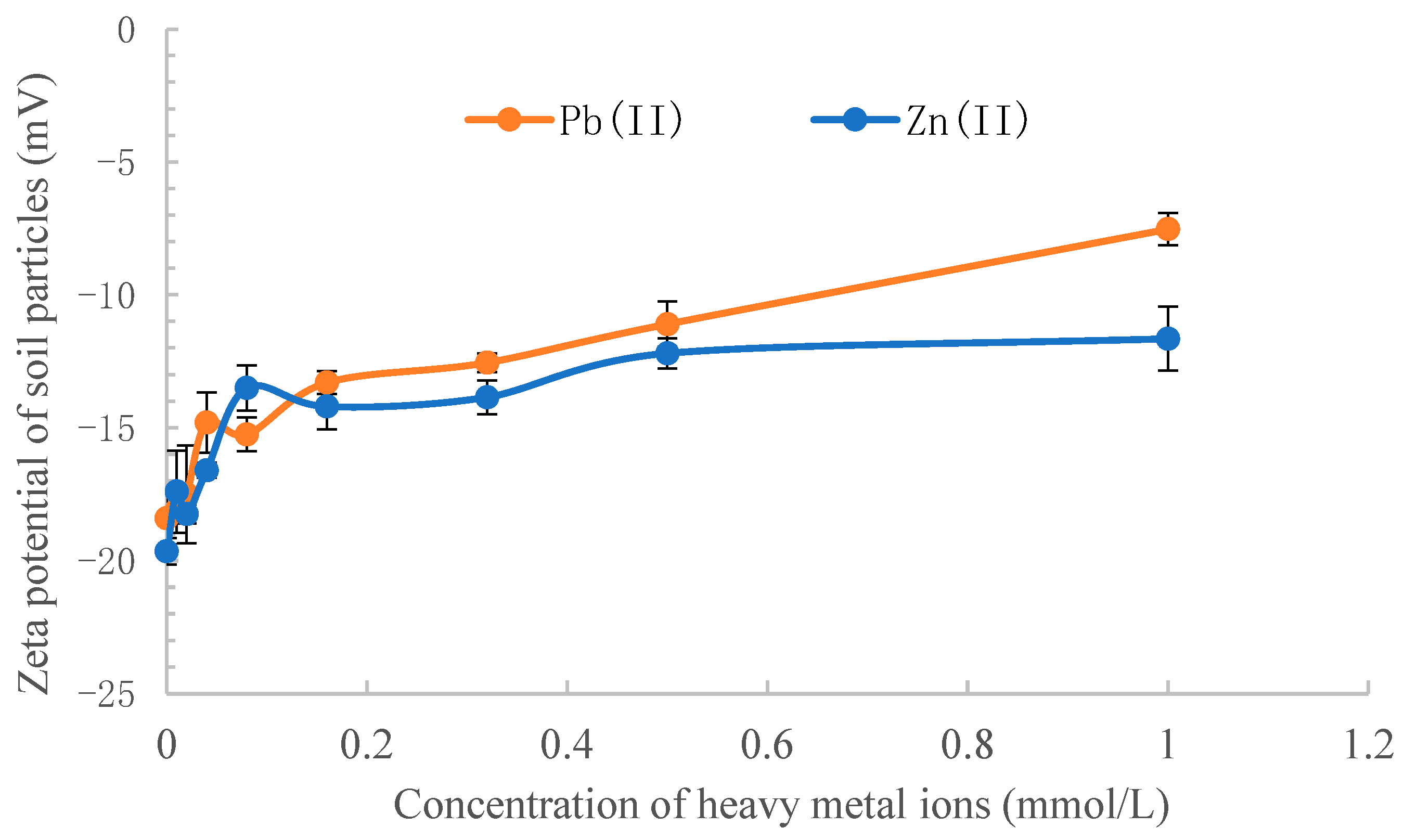
3.5. The Effect of Heavy Metal Ions on the Zeta Potential of Soil Particles
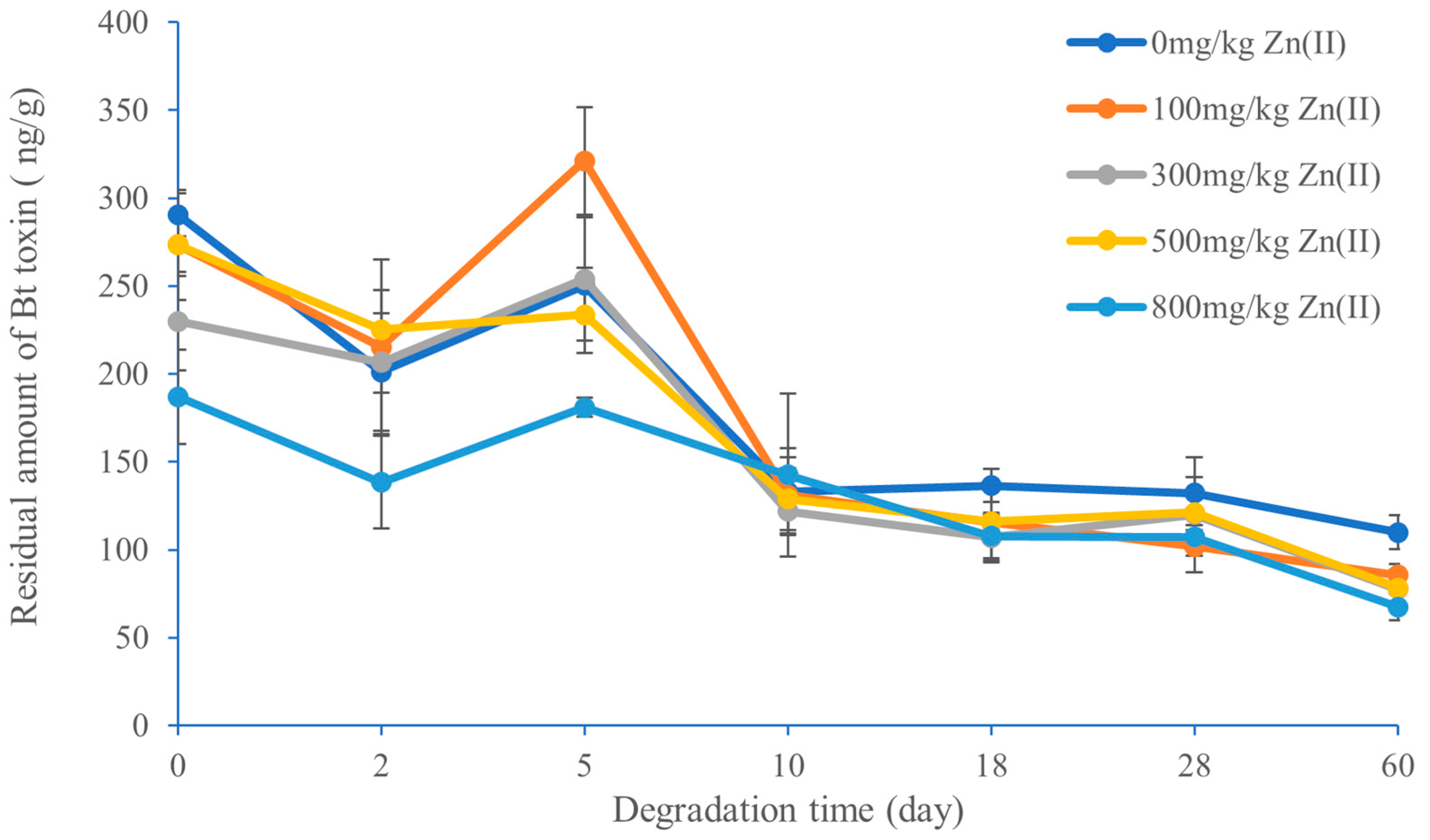
3.6. Effect of Pb(II) and Zn(II) Concentration on the Degradation of Bt Toxin in Black Soil
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tzfira, T.; Zuker, A.; Altman, A. Forest-tree biotechnology: Genetic transformation and its application to future forests. Trends Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, L.; Séguin, A. Recent advances in the genetic transformation of trees. Trends Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubouzet, J.G.; Strabala, T.J.; Wagner, A. Potential transgenic routes to increase tree biomass. Plant Sci. 2013, 212, 72–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R. Application of biological control technology in forest pest control. Seed Sci. Technol. 2021, 39, 41–42. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Dong, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ren, M.; Yang, M.; Wang, J. Dynamic monitoring of the impact of insect-resistant transgenic poplar field stands on arthropod communities. For. Ecol. Manage 2022, 505, 119921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, P.M.; Hamelin, R.C.; Filion, M. Alteration of soil rhizosphere communities following genetic transformation of white spruce. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 4128–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraclough, E.I.; Burgess, E.P.J.; Philip, B.A.; Wohlers, M.W.; Malone, L.A. Tritrophic impacts of Bt-expressing transgenic pine on the parasitoid Meteorus pulchricornis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) via its host Pseudocoremia suavis (Lepidoptera: Geometridae). Biol. Control 2009, 49, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Mi, D.; Ewald, D.; Wang, Y.; Liang, H.; Zhen, Z. Survival and escape of Agrobacterium tumefaciens in triploid hybrid lines of Chinese white poplar transformed with two insect-resistant genes. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2006, 26, 3555–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Hu, J. Research and application status of transgenic poplar in China. J. For. Eng. 2006, 20, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- James, C. Global biotechnology/GM crop commercialization development in 2014. China Biotechnol. 2015, 35, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.J.; Liu, L.P.; Fang, Z.X. Effects of planting transgenic cotton beneath transgenic poplar trees on the diversity of arthropod community in the transgenic poplar-cotton composite system. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2021, 64, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y. Changes in Environmental Behaviors of Trace Metals Involved in Poplar-Based Phytomanagement on Low-Phosphorus Calcareous Soil. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X. Bacterial Diversity and Screening of Heavy Metal Tolerant Endophytic Bacteria Associated with Poplar in Mining Areas. Master’s Thesis, Hunan University, Changsha, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Y. Review on the remediation of soil heavy metal pollution by poplar. Liaoning For. Sci. Technol. 2021, 4, 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- Pilipovića, A.; Zalesny, R.S., Jr.; Rončević, S.; Nikolić, N.; Orlović, S.; Beljin, J.; Katanić, M. Growth, physiology, and phytoextraction potential of poplar and willow established in soils amended with heavy-metal contaminated, dredged river sediments. J. Environ. Manage. 2019, 239, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yang, M.; Lu, M. Advances in biosafety studies on transgenic insect-resistant poplars in China. Biodivers. Sci. 2010, 18, 336–345. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, S.; Yuan, X.; Liang, Y.; Wang, H.; Leng, L.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Mo, D.; Zeng, G. In situ surface transfer process of Cry1Ac protein on SiO2: The effect of biosurfactants for desorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 341, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stotzky, G. Clays and humic acids affect the persistence and biological activity of insecticidal proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis in soil. Dev. Soil Sci. 2002, 28, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Tapp, H.; Stotzky, G. Persistence of the insecticidal toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strain, K.E.L.; Michael, J. The fate and transport of the Cry1Ab protein in an agricultural field and laboratory aquatic microcosms. Chemosphere 2015, 132, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, H.; Lu, X.; Shi, L.; Hao, J. Lead (II) pollution enhances the binding of transgenic toxin in brown and red soils: Equilibrium and kinetics. Int. J. Chem. Reac.Eng. 2013, 11, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Peng, Y.; Huang, T.; Hu, H.; Deng, Y.; Yu, X. Effects of ionic strength and sesquioxides on adsorption of toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki on soils. Pedosphere 2012, 22, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madliger, M.; Sander, M.; Schwarzenbach, R.P. Adsorption of transgenic insecticidal Cry1Ab protein to SiO2. 2. Patch-controlled electrostatic attraction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8877–8883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madliger, M.; Gasser, C.A.; Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Sander, M. Adsorption of transgenic insecticidal Cry1Ab protein to silica particles. Effects on transport and bioactivity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4377–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, W.; Hu, H.; Chen, D.; Yang, C. Remaining dynamics of Cry1Ab proteins from transgenic Bt corn in soil. J. Food Agric. Env. 2012, 10, 294–298. [Google Scholar]
- Pouresmaieli, M.; Ataei, M.; Forouzandeh, P.; Azizollahi, P.; Mahmoudifard, M. Recent progress on sustainable phytoremediation of heavy metals from soil. J. Environ. Manage. 2022, 10, 108482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Lu, X.; Duan, Q.; Huang, L.; Bi, J. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alburquerque, J.A.; Fuente, C.; Bernal, M.P. Improvement of soil quality after ‘‘alperujo’’ compost application to two contaminated soils characterised by differing heavy metal solubility. J. Environ. Manage 2011, 92, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.W.; Jiao, R.Z.; Dong, Y.H. Research progress in bioremediation of heavy-metal contaminated soil. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2017, 53, 146–155. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.X.; Liu, Y.L.; Ding, X.Z.; Xia, L.Q. An improved method for purifying Cry1Ac protein from Bacillus thuringiensis. Hunan Agric. Sci. 2011, 15, 117–119. [Google Scholar]
- Helassa, N.; Revault, M.; Quiquampoix, H.; Déjardin, P.; Staunton, S.; Noinville, S. Adsorption on montmorillonite prevents oligomerization of Bt Cry1Aa toxin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 356, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, M.; Madliger, M.; Schwarzenbach, R. Adsorption of transgenic insecticidal cry1Ab protein to SiO2. 1. Forces driving adsorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8870–8876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z. Bacillus Thuringiensis; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990; pp. 200–220. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Huang, Q.Y.; Chen, S.W.; Yu, Z.N. Adsorption of the insecticidal protein of Bacillus thuringiensis on montmorillonite, kaolinite, silica, goethite and Red soil. Appl. Clay Sci. 2005, 30, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crecchio, C.; Stotzky, G. Insecticidal activity and biodegradation of the toxin from Bacillus thruingiensis subsp. kustuki bound to humic acids from soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 463–470. [Google Scholar]
- Palm, C.J.; Donegan, K.; Harris, D.; Seidler, R.J. Quantification in soil of Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki δ-endotoxin from transgenic plants. Mol. Ecol. 1994, 3, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.M.; Li, Z.H.; Li, B.; Tian, X.L.; Duan, L.S.; Zhai, Z.X.; He, Z.P. Content and expression of Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal protein in transgenic cotton. J. Agric. Technol. 2002, 10, 215–219. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Liu, N.; Gao, J.B.; Zhang, M.; Cao, F. Adsorption thermodynamics of toxin (65 kDa) and protoxin (130 kDa) from Bacillus thuringiensis by several minerals. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2011, 9, A5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Huang, Q.Y.; Cai, P.; Yu, Z.N. Adsorption and insecticidal activity of toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis on rectorite. Pedosphere 2007, 17, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeton, T.P.; Bulla, L.A.J. Ligand specificity and affinity of BT-R1, the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1A toxin receptor from Manduca sexta, expressed in mammalian and insect cell cultures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 3419–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janot, J.M.; Boissière, M.; Thami, T.; Tronel-Peyroz, E.; Helassa, N.; Noinville, S.; Quiquampoix, H.; Staunton, S.; Déjardin, P. Adsorption of alexa-labeled Bt toxin on mica, glass, and hydrophobized glass: Study by normal scanning confocal fluorescence. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1661–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.H.; Chen, D.Q.; Hu, H.Q.; Zhuang, G.Q. Degradation and residue of Bt protein in several soils. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2009, 28, 169–173. [Google Scholar]
- Helassa, N.; M’Charek, A.; Quiquampoix, H.; Noinville, S.; Déjardin, P.; Frutos, R.; Staunton, S. Effects of physicochemical interactions and microbial activity on the persistence of Cry1Aa Bt (Bacillus thuringiensis) toxin in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| pH | AK (mg/kg) | AP (mg/kg) | AN (mg/kg) | SS (g/kg) | OM (g/kg) | Zn (mg/kg) | Pb (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.44 | 1257.49 | 24.20 | 211.01 | 2.89 | 69.45 | 122.3 | 33.72 |
| Types of Ions | Concentration (mmol/L) | Amount of Bt Toxin Adsorbed (mg) | Amount of Bt Toxin Desorbed (mg) | Desorption Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb(II) | 0 | 0.2752 | 0.0887 | 32.22% |
| Pb(II) | 0.05 | 0.3330 | 0.0974 | 29.25% |
| Zn(II) | 0 | 0.2752 | 0.0887 | 32.22% |
| Zn(II) | 0.05 | 0.2990 | 0.0802 | 26.83% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, L.; Yang, P.; Maimaitiniyazi, R. Effects of Pb(II) and Zn(II) Contamination on Adsorption, Desorption and Degradation of Cry1Ac Toxin Identical to Bt Transgenic Poplar in Black Soil. Toxics 2023, 11, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020089
Wang Y, Zhou X, Zhang F, Zhang L, Yang P, Maimaitiniyazi R. Effects of Pb(II) and Zn(II) Contamination on Adsorption, Desorption and Degradation of Cry1Ac Toxin Identical to Bt Transgenic Poplar in Black Soil. Toxics. 2023; 11(2):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020089
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yongji, Xueyong Zhou, Fenguo Zhang, Lihong Zhang, Pingguo Yang, and Rehanguli Maimaitiniyazi. 2023. "Effects of Pb(II) and Zn(II) Contamination on Adsorption, Desorption and Degradation of Cry1Ac Toxin Identical to Bt Transgenic Poplar in Black Soil" Toxics 11, no. 2: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020089
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhou, X., Zhang, F., Zhang, L., Yang, P., & Maimaitiniyazi, R. (2023). Effects of Pb(II) and Zn(II) Contamination on Adsorption, Desorption and Degradation of Cry1Ac Toxin Identical to Bt Transgenic Poplar in Black Soil. Toxics, 11(2), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020089







