A Scoping Assessment of Implemented Toxicokinetic Models of Per- and Polyfluoro-Alkyl Substances, with a Focus on One-Compartment Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
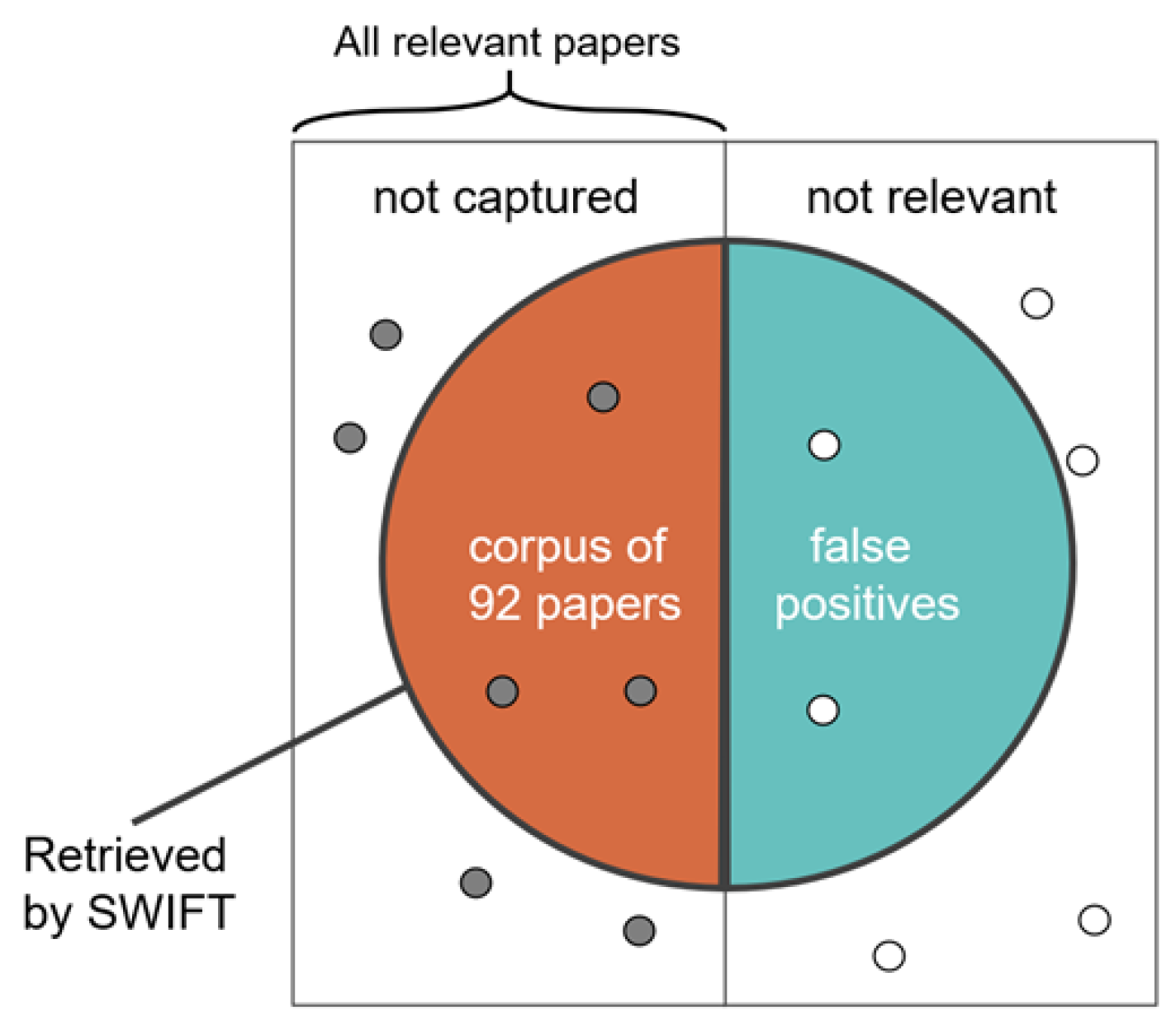
2.1. Literature Search and Screening
2.2. Data Extraction and Curation
2.3. Analyses
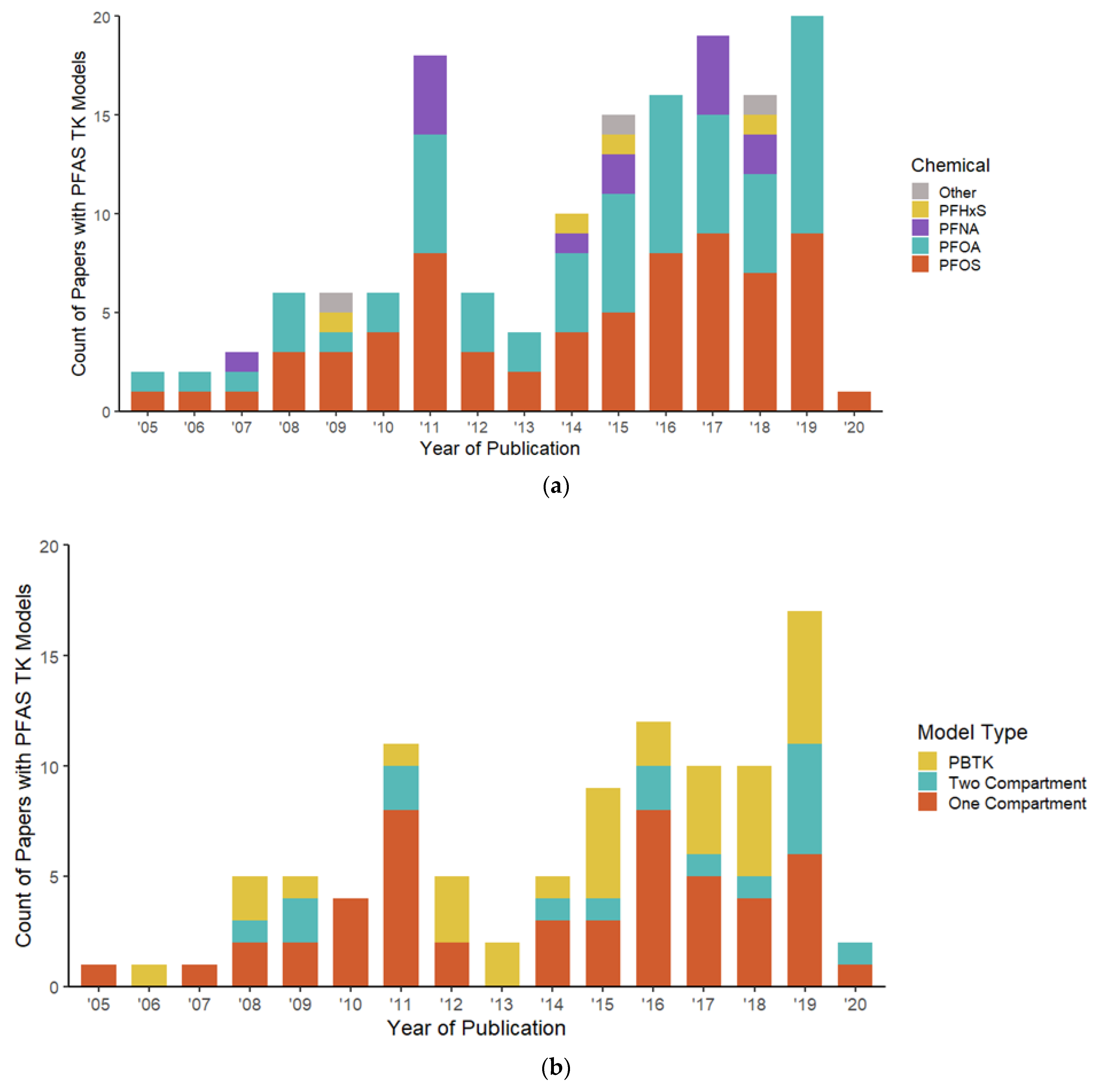
3. Results
3.1. Corpus of Extracted Texts
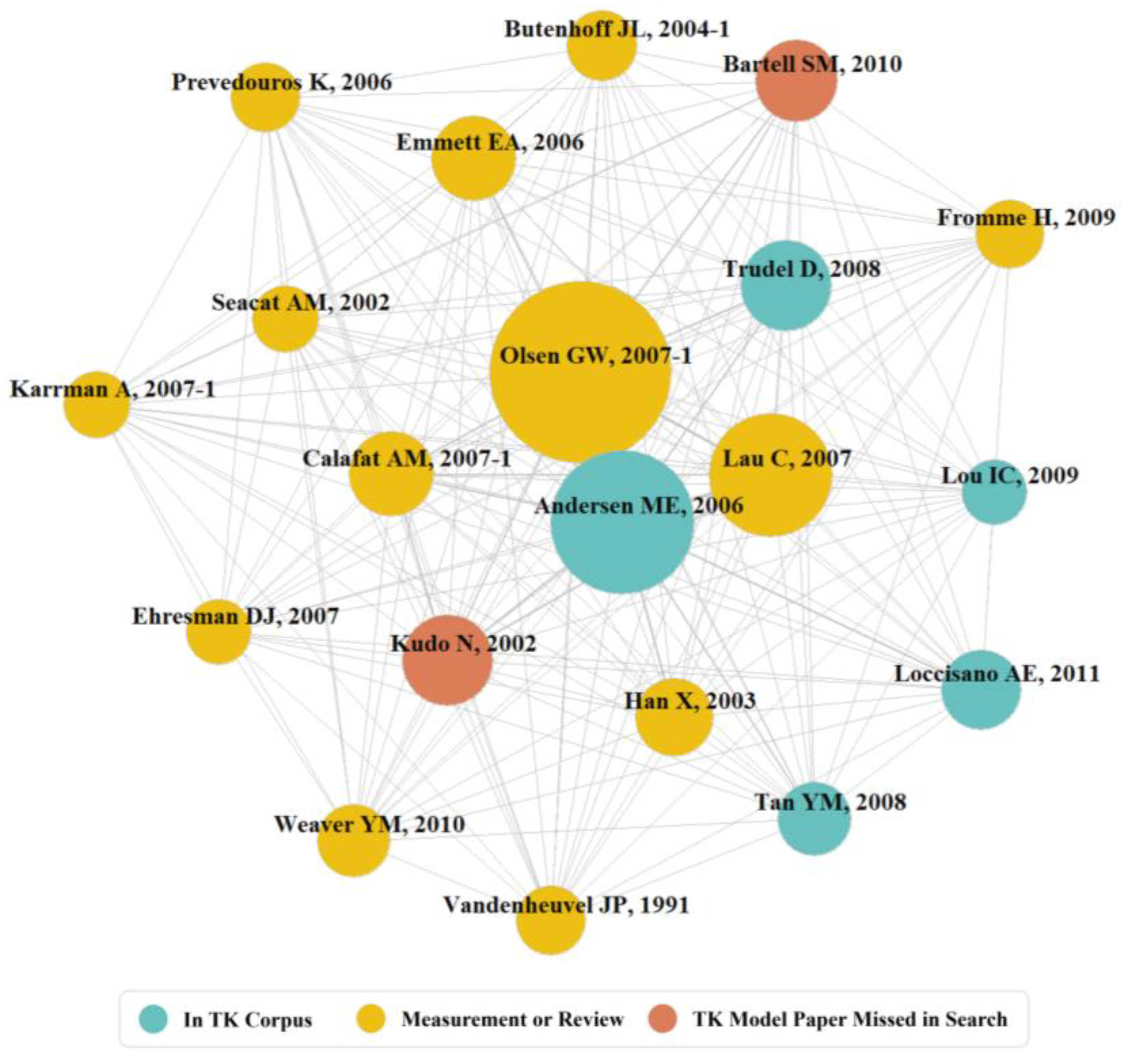
3.2. Exploring Evidence: Influential Publications Co-Citation
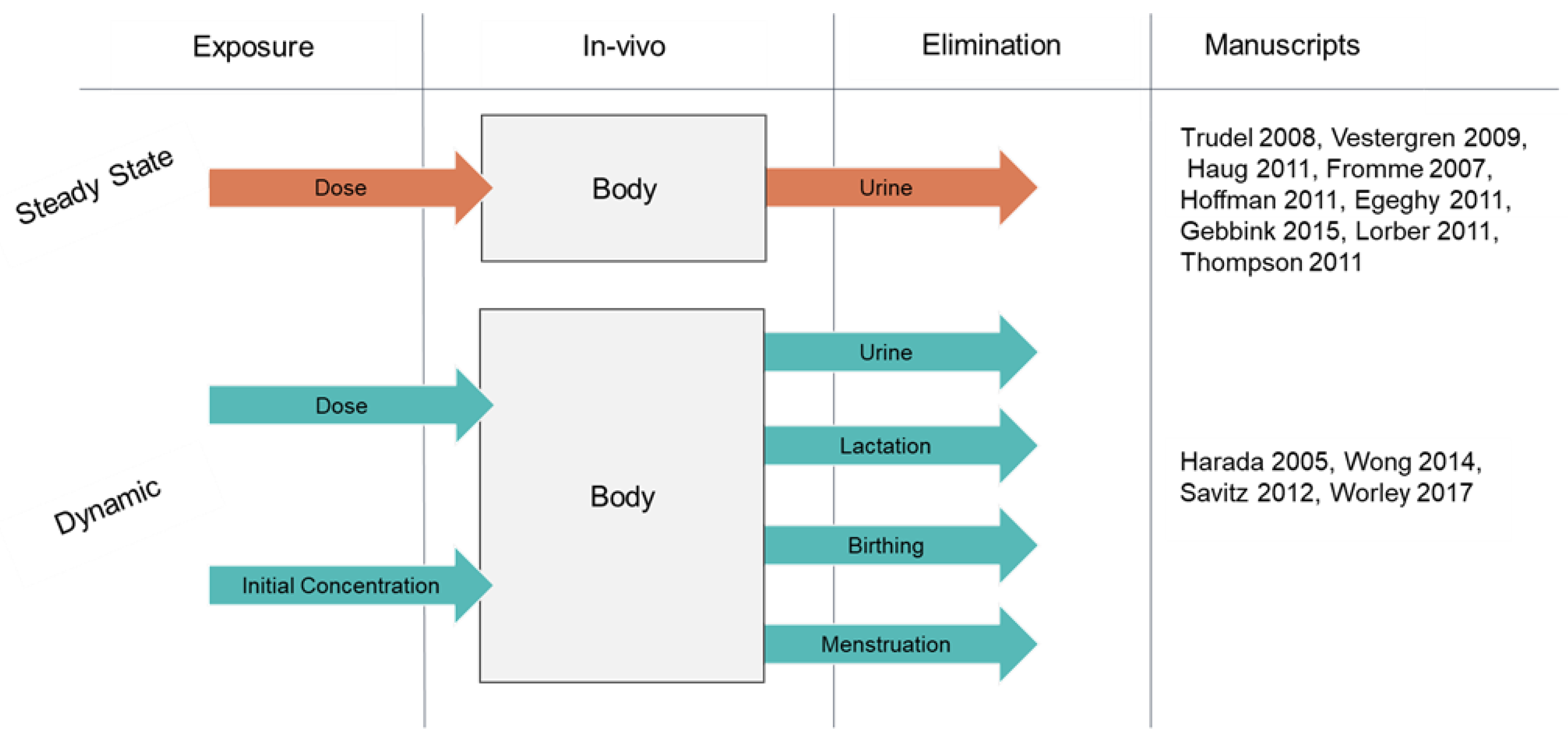
3.3. A Chronology of One-Compartment Models
4. Discussion
4.1. Search Effectiveness
4.2. One Compartment Models: Half-Lives and PFAS as a Class
4.3. Emerging TK Models and Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
References
- Organisation for Economic Cooperation Development. Toward a New Comprehensive Global Database of per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs): Summary Report on Updating the OECD 2007 List of per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs); Organisation for Economic Cooperation Development (OECD): Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vecitis, C.D.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Park, H.; Mader, B.T.; Hoffmann, M.R. Sonochemical degradation of perfluorooctanesulfonate in aqueous film-forming foams. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; DeWitt, J.C.; Higgins, C.P.; Cousins, I.T. A Never-Ending Story of per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs)? ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Prevedouros, K.; Cousins, I.T.; Buck, R.C.; Korzeniowski, S.H. Sources, fate and transport of perfluorocarboxylates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, R.C.; Franklin, J.; Berger, U.; Conder, J.M.; Cousins, I.T.; De Voogt, P.; Jensen, A.A.; Kannan, K.; Mabury, S.A.; van Leeuwen, S.P. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment: Terminology, classification, and origins. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2011, 7, 513–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cousins, I.T.; DeWitt, J.C.; Glüge, J.; Goldenman, G.; Herzke, D.; Lohmann, R.; Ng, C.A.; Scheringer, M.; Wang, Z. The high persistence of PFAS is sufficient for their management as a chemical class. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 2307–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giesy, J.P.; Kannan, K. Global distribution of perfluorooctane sulfonate in wildlife. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1339–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiatkowski, C.F.; Andrews, D.Q.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Bruton, T.A.; DeWitt, J.C.; Knappe, D.R.; Maffini, M.V.; Miller, M.F.; Pelch, K.E.; Reade, A. Scientific basis for managing PFAS as a chemical class. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calafat, A.M.; Kato, K.; Hubbard, K.; Jia, T.; Botelho, J.C.; Wong, L.-Y. Legacy and alternative per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the US general population: Paired serum-urine data from the 2013–2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 105048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Fourth National Report on Human Exposure to Environmental Chemicals, Updated Tables; CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform: Scotts Valley, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Göckener, B.; Weber, T.; Rüdel, H.; Bücking, M.; Kolossa-Gehring, M. Human biomonitoring of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in German blood plasma samples from 1982 to 2019. Environ. Int. 2020, 145, 106123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffek, A.; Conrad, A.; Kolossa-Gehring, M.; Lange, R.; Rucic, E.; Schulte, C.; Wellmitz, J. Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in blood plasma–Results of the German Environmental Survey for children and adolescents 2014–2017 (GerES V). Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 228, 113549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebbink, W.A.; Glynn, A.; Berger, U. Temporal changes (1997–2012) of perfluoroalkyl acids and selected precursors (including isomers) in Swedish human serum. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 199, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Kang, Q.Y.; Peng, H.; Ding, M.Y.; Zhao, F.R.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Dong, Z.M.; Zhang, H.F.; Yang, M.; Tao, S.; et al. Relationship between perfluorooctanoate and perfluorooctane sulfonate blood concentrations in the general population and routine drinking water exposure. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenton, S.E.; Ducatman, A.; Boobis, A.; DeWitt, J.C.; Lau, C.; Ng, C.; Smith, J.S.; Roberts, S.M. Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substance toxicity and human health review: Current state of knowledge and strategies for informing future research. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 606–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, N.; Lee, M.; Steenland, K. Epidemiological findings. In Toxicological Effects of Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 305–335. [Google Scholar]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Toxicological Profile for Perluoroalkyls; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Beesoon, S.; Zhu, L.; Martin, J.W. Biomonitoring of perfluoroalkyl acids in human urine and estimates of biological half-life. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10619–10627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worley, R.R.; Moore, S.M.; Tierney, B.C.; Ye, X.Y.; Calafat, A.M.; Campbell, S.; Woudneh, M.B.; Fisher, J. Per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in human serum and urine samples from a residentially exposed community. Environ. Int. 2017, 106, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Fletcher, T.; Pineda, D.; Lindh, C.H.; Nilsson, C.; Glynn, A.; Vogs, C.; Norström, K.; Lilja, K.; Jakobsson, K. Serum half-lives for short-and long-chain perfluoroalkyl acids after ceasing exposure from drinking water contaminated by firefighting foam. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 077004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, D.E.; Lau, C.; Pradeep, P.; Sayre, R.R.; Judson, R.S.; Tornero-Velez, R.; Wambaugh, J.F. A Machine Learning Model to Estimate Toxicokinetic Half-lives of Per- and Polyfluoro-alkyl Substances (PFAS) in Multiple Species. Toxics 2023, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-C.; Das, K.; Ehresman, D.J.; Ellefson, M.E.; Gorman, G.S.; Hart, J.A.; Noker, P.E.; Tan, Y.-M.; Lieder, P.H.; Lau, C. Comparative pharmacokinetics of perfluorobutyrate in rats, mice, monkeys, and humans and relevance to human exposure via drinking water. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 104, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, G.W.; Chang, S.-C.; Noker, P.E.; Gorman, G.S.; Ehresman, D.J.; Lieder, P.H.; Butenhoff, J.L. A comparison of the pharmacokinetics of perfluorobutanesulfonate (PFBS) in rats, monkeys, and humans. J. Toxicol. 2009, 256, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA, U.S. PFAS Strategic Roadmap: EPA’s Commitments to Action 2021–2024. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/pfas/pfas-strategic-roadmap-epas-commitments-action-2021-2024 (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Harada, K.; Inoue, K.; Morikawa, A.; Yoshinaga, T.; Saito, N.; Koizumi, A. Renal clearance of perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoate in humans and their species-specific excretion. Environ. Res. 2005, 99, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, N. Metabolism and pharmacokinetics. In Toxicological Effects of Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 151–175. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Nabb, D.L.; Russell, M.H.; Kennedy, G.L.; Rickard, R.W. Renal elimination of perfluorocarboxylates (PFCAs). Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, N.; Katakura, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, Y. Sex hormone-regulated renal transport of perfluorooctanoic acid. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2002, 139, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.-H.; Glover, K.P.; Han, X. Characterization of cellular uptake of perfluorooctanoate via organic anion-transporting polypeptide 1A2, organic anion transporter 4, and urate transporter 1 for their potential roles in mediating human renal reabsorption of perfluorocarboxylates. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 117, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.E.; Clewell, H.J.; Tan, Y.M.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Olsen, G.W. Pharmacokinetic modeling of saturable, renal resorption of perfluoroalkylacids in monkeys—Probing the determinants of long plasma half-lives. Toxicology 2006, 227, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Silva, A.O.; Armitage, J.M.; Bruton, T.A.; Dassuncao, C.; Heiger-Bernays, W.; Hu, X.C.; Kärrman, A.; Kelly, B.; Ng, C.; Robuck, A. PFAS exposure pathways for humans and wildlife: A synthesis of current knowledge and key gaps in understanding. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 631–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, K.L.; Randall, N.P.; Haddaway, N.R. A methodology for systematic mapping in environmental sciences. Environ. Evid. 2016, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuca, N.M.; Angrish, M.; Wilkins, A.; Thayer, K.; Hubal, E.A.C. Human exposure pathways to poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from indoor media: A systematic review protocol. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, B.E.; Phillips, J.; Miller, K.; Tandon, A.; Mav, D.; Shah, M.R.; Holmgren, S.; Pelch, K.E.; Walker, V.; Rooney, A.A. SWIFT-Review: A text-mining workbench for systematic review. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckland, M.; Gey, F. The relationship between recall and precision. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 1994, 45, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- East, A.; Egeghy, P.P.; Hubal, E.A.C.; Slover, R.; Vallero, D.A. Computational estimates of daily aggregate exposure to PFOA/PFOS from 2011 to 2017 using a basic intake model. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2021, 33, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wambaugh, J.F.; Barton, H.A.; Setzer, R.W. Comparing models for perfluorooctanoic acid pharmacokinetics using Bayesian analysis. J. Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn. 2008, 35, 683–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Small, H. Co-citation in the scientific literature: A new measure of the relationship between two documents. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 1973, 24, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondel, V.D.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Lambiotte, R.; Lefebvre, E. Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2008, 2008, P10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, Y.; Seong, J.; Stanescu, A.; Hwang, C.S. A comparison of network clustering algorithms in keyword network analysis: A case study with geography conference presentations. Int. J. Geospat. Environ. Res. 2020, 7, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Cavadas, A. Visualising the Collaboration Network of a European Marine Research Infrastructure: A Bibliometric and Social Network Analysis. U. Porto J. Eng. 2020, 6, 98–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osareh, F. Bibliometrics, Citation Analysis and Co-Citation Analysis: A Review of Literature I. Libri 1996, 46, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, H.; Deo, N. Detecting communities using bibliographic metrics. In Proceedings of GrC; 2006; pp. 293–298. Available online: https://www.eecs.ucf.edu/~deo/deo/IEEE-GrC.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- Garfield, E. Historiographic mapping of knowledge domains literature. J. Inf. Sci. 2004, 30, 119–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruchterman, T.M.; Reingold, E.M. Graph drawing by force-directed placement. Softw. Pract. Exp. 1991, 21, 1129–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seacat, A.M.; Thomford, P.J.; Hansen, K.J.; Olsen, G.W.; Case, M.T.; Butenhoff, J.L. Subchronic toxicity studies on perfluorooctanesulfonate potassium salt in cynomolgus monkeys. Toxicol. Sci. 2002, 68, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kärrman, A.; Ericson, I.; van Bavel, B.; Darnerud, P.O.; Aune, M.; Glynn, A.; Lignell, S.; Lindström, G. Exposure of perfluorinated chemicals through lactation: Levels of matched human milk and serum and a temporal trend, 1996–2004, in Sweden. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calafat, A.M.; Wong, L.-Y.; Kuklenyik, Z.; Reidy, J.A.; Needham, L.L. Polyfluoroalkyl chemicals in the US population: Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2003–2004 and comparisons with NHANES 1999–2000. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1596–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehresman, D.J.; Froehlich, J.W.; Olsen, G.W.; Chang, S.-C.; Butenhoff, J.L. Comparison of human whole blood, plasma, and serum matrices for the determination of perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS), perfluorooctanoate (PFOA), and other fluorochemicals. Environ. Res. 2007, 103, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, Y.M.; Ehresman, D.J.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Hagenbuch, B. Roles of Rat Renal Organic Anion Transporters in Transporting Perfluorinated Carboxylates with Different Chain Lengths. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 113, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuvel, J.P.V.; Kuslikis, B.I.; Van Rafelghem, M.J.; Peterson, R.E. Tissue distribution, metabolism, and elimination of perfluorooctanoic acid in male and female rats. J. Biochem. Toxicol. 1991, 6, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmett, E.A.; Shofer, F.S.; Zhang, H.; Freeman, D.; Desai, C.; Shaw, L.M. Community exposure to perfluorooctanoate: Relationships between serum concentrations and exposure sources. J. Occup. Environ. Med. /Am. Coll. Occup. Environ. Med. 2006, 48, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butenhoff, J.L.; Kennedy Jr, G.L.; Frame, S.R.; O’Connor, J.C.; York, R.G. The reproductive toxicology of ammonium perfluorooctanoate (APFO) in the rat. Toxicology 2004, 196, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, G.W.; Burris, J.M.; Ehresman, D.J.; Froehlich, J.W.; Seacat, A.M.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Zobel, L.R. Half-life of serum elimination of perfluorooctanesulfonate, perfluorohexanesulfonate, and perfluorooctanoate in retired fluorochemical production workers. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Snow, T.A.; Kemper, R.A.; Jepson, G.W. Binding of perfluorooctanoic acid to rat and human plasma proteins. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2003, 16, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, C.; Anitole, K.; Hodes, C.; Lai, D.; Pfahles-Hutchens, A.; Seed, J. Perfluoroalkyl acids: A review of monitoring and toxicological findings. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 99, 366–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromme, H.; Tittlemier, S.A.; Völkel, W.; Wilhelm, M.; Twardella, D. Perfluorinated compounds–exposure assessment for the general population in Western countries. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2009, 212, 239–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartell, S.M.; Calafat, A.M.; Lyu, C.; Kato, K.; Ryan, P.B.; Steenland, K. Rate of decline in serum PFOA concentrations after granular activated carbon filtration at two public water systems in Ohio and West Virginia. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trudel, D.; Horowitz, L.; Wormuth, M.; Scheringer, M.; Cousins, I.T.; Hungerbuhler, K. Estimating consumer exposure to PFOS and PFOA. Risk Anal. 2008, 28, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.M.; Clewell, H.J.; Andersen, M.E. Time dependencies in perfluorooctylacids disposition in rat and monkeys: A kinetic analysis. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 177, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loccisano, A.E.; Campbell, J.L., Jr.; Andersen, M.E.; Clewell III, H.J. Evaluation and prediction of pharmacokinetics of PFOA and PFOS in the monkey and human using a PBPK model. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 59, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, I.C.; Wambaugh, J.F.; Lau, C.; Hanson, R.G.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Strynar, M.J.; Zehr, R.D.; Setzer, R.W.; Barton, H.A. Modeling Single and Repeated Dose Pharmacokinetics of PFOA in Mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 107, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fromme, H.; Schlummer, M.; Moller, A.; Gruber, L.; Wolz, G.; Ungewiss, J.; Bohmer, S.; Dekant, W.; Mayer, R.; Liebl, B.; et al. Exposure of an adult population to perfluorinated substances using duplicate diet portions and biomonitoring data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7928–7933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergren, R.; Cousins, I.T. Tracking the pathways of human exposure to perfluorocarboxylates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5565–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.; Lorber, M.; Toms, L.M.L.; Kato, K.; Calafat, A.M.; Mueller, J.F. Use of simple pharmacokinetic modeling to characterize exposure of Australians to perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (vol 36, pg 390, 2010). Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 647–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niisoe, T.; Harada, K.H.; Ishikawa, H.; Koizumi, A. Long-Term Simulation of Human Exposure to Atmospheric Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctanoate (PFO) in the Osaka Urban Area, Japan. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7852–7857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorber, M.; Egeghy, P.P. Simple intake and pharmacokinetic modeling to characterize exposure of Americans to perfluoroctanoic acid, PFOA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8006–8014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haug, L.S.; Huber, S.; Becher, G.; Thomsen, C. Characterisation of human exposure pathways to perfluorinated compounds—Comparing exposure estimates with biomarkers of exposure. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Kho, Y.L.; Shoeib, M.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, K.R.; Park, J.E.; Shin, Y.S. Occurrence of perfluorooctanoate and perfluorooctanesulfonate in the Korean water system: Implication to water intake exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, K.; Webster, T.F.; Bartell, S.M.; Weisskopf, M.G.; Fletcher, T.; Vieira, V.M. Private Drinking Water Wells as a Source of Exposure to Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) in Communities Surrounding a Fluoropolymer Production Facility. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egeghy, P.P.; Lorber, M. An assessment of the exposure of Americans to perfluorooctane sulfonate: A comparison of estimated intake with values inferred from NHANES data. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2011, 21, 150–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.Q.; Liu, W.; Li, X.N.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Y.S.; Zhou, J.; Jin, Y.H. Serum levels of perfluorinated compounds in the general population in Shenzhen, China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 3092–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitz, D.A.; Stein, C.R.; Bartell, S.M.; Elston, B.; Gong, J.; Shin, H.M.; Wellenius, G.A. Perfluorooctanoic Acid Exposure and Pregnancy Outcome in a Highly Exposed Community. Epidemiology 2012, 23, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.M.; Steenland, K.; Ryan, P.B.; Vieira, V.M.; Bartell, S.M. Biomarker-Based Calibration of Retrospective Exposure Predictions of Perfluorooctanoic Acid. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5636–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, F.; MacLeod, M.; Mueller, J.F.; Cousins, I.T. Enhanced elimination of perfluorooctane sulfonic acid by menstruating women: Evidence from population-based pharmacokinetic modeling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 8807–8814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebbink, W.A.; Berger, U.; Cousins, I.T. Estimating human exposure to PFOS isomers and PFCA homologues: The relative importance of direct and indirect (precursor) exposure. Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorber, M.; Eaglesham, G.E.; Hobson, P.; Toms, L.M.L.; Mueller, J.F.; Thompson, J.S. The effect of ongoing blood loss on human serum concentrations of perfluorinated acids. Chemosphere 2015, 118, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomis, M.I.; Vestergren, R.; Nilsson, H.; Cousins, I.T. Contribution of Direct and Indirect Exposure to Human Serum Concentrations of Perfluorooctanoic Acid in an Occupationally Exposed Group of Ski Waxers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7037–7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, S.; Vestergren, R.; Herzke, D.; Melhus, M.; Evenset, A.; Hanssen, L.; Brustad, M.; Sandanger, T.M. Exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances through the consumption of fish from lakes affected by aqueous film-forming foam emissions—A combined epidemiological and exposure modeling approach. The SAMINOR 2 Clinical Study. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Kim, S.K.; Shoeib, M.; Oh, J.E.; Park, J.E. Human exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) via house dust in Korea: Implication to exposure pathway. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 553, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, G.Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, L.Q.; Du, P.; Luo, X.X.; Wu, Q.N.; Zhu, L.Y. Impacts of daily intakes on the isomeric profiles of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in human serum. Environ. Int. 2016, 89–90, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avanasi, R.; Shin, H.M.; Vieira, V.M.; Savitz, D.A.; Bartell, S.M. Impact of Exposure Uncertainty on the Association between Perfluorooctanoate and Preeclampsia in the C8 Health Project Population. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avanasi, R.; Shin, H.M.; Vieira, V.M.; Bartell, S.M. Variability and epistemic uncertainty in water ingestion rates and pharmaco-kinetic parameters, and impact on the association between perfluorooctanoate and preeclampsia in the C8 Health Project popula-tion. Environ. Res. 2016, 146, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomis, M.I.; Vestergren, R.; MacLeod, M.; Mueller, J.F.; Cousins, I.T. Historical human exposure to perfluoroalkyl acids in the United States and Australia reconstructed from biomonitoring data using population-based pharmacokinetic modelling. Environ. Int. 2017, 108, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrick, R.L.; Buckholz, J.; Biro, F.M.; Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.Y.; Xie, C.C.; Pinney, S.M. Polyfluoroalkyl substance exposure in the Mid-Ohio River Valley, 1991-2012. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 228, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Jin, Y.H.; Dong, G.H. Human exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances near a fluorochemical industrial park in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 9194–9201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Hoppmann, S.; Du, P.; Li, H.; Evans, P.M.; Moestue, S.A.; Yu, W.; Dong, F.; Liu, H.; Liu, L. Pharmacokinetics of perfluorobutane after intra-venous bolus injection of Sonazoid in healthy Chinese volunteers. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dassuncao, C.; Hu, X.D.C.; Nielsen, F.; Weihe, P.; Grandjean, P.; Sunderland, E.M. Shifting Global Exposures to Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) Evident in Longitudinal Birth Cohorts from a Seafood-Consuming Population. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3738–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.D.C.; Tokranov, A.K.; Liddie, J.; Zhang, X.M.; Grandjean, P.; Hart, J.E.; Laden, F.; Sun, Q.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Sunderland, E.M. Tap Water Contributions to Plasma Concentrations of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in a Nationwide Prospective Cohort of US Women. Environ. Health Perspect. 2019, 127, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goeden, H.M.; Greene, C.W.; Jacobus, J.A. A transgenerational toxicokinetic model and its use in derivation of Minnesota PFOA water guidance. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 29, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedikoglou, K.; Costopoulou, D.; Vassiliadou, I.; Leondiadis, L. Preliminary assessment of general population exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances through diet in Greece. Environ. Res. 2019, 177, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balk, F.G.; Pütz, K.W.; Ribbenstedt, A.; Gomis, M.I.; Filipovic, M.; Cousins, I.T. Children’s exposure to perfluoroalkyl acids–a modelling approach. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2019, 21, 1875–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, K.; Saito, N.; Sasaki, K.; Inoue, K.; Koizumi, A. Perfluorooctane sulfonate contamination of drinking water in the Tama River, Japan: Estimated effects on resident serum levels. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2003, 71, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen Hubal, E.A.; Frank, J.J.; Nachman, R.; Angrish, M.; Deziel, N.C.; Fry, M.; Tornero-Velez, R.; Kraft, A.; Lavoie, E. Advancing systematic-review methodology in exposure science for environmental health decision making. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2020, 30, 906–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, R.; Scheringer, M.; MacLeod, M.; Moeckel, C.; Jones, K.C.; Hungerbühler, K. Intrinsic human elimination half-lives of polychlorinated biphenyls derived from the temporal evolution of cross-sectional biomonitoring data from the United Kingdom. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.E.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Chang, S.C.; Farrar, D.G.; Kennedy, G.L.; Lau, C.; Olsen, G.W.; Seed, J.; Wallacekj, K.B. Perfluoroalkyl acids and related chemistries - Toxicokinetics and modes of action. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 102, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomis, M.I.; Vestergren, R.; Borg, D.; Cousins, I.T. Comparing the toxic potency in vivo of long-chain perfluoroalkyl acids and fluorinated alternatives. Environ. Int. 2018, 113, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Gu, W.; Barrett, H.; Yang, D.; Tang, S.; Sun, J.; Liu, J.; Krause, H.M.; Houck, K.A.; Peng, H. A roadmap to the structure-related metabolism pathways of per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the early life stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Health Perspect. 2021, 129, 077004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonough, C.A.; Choyke, S.; Ferguson, P.L.; DeWitt, J.C.; Higgins, C.P. Bioaccumulation of novel per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances in mice dosed with an aqueous film-forming foam. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 5700–5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tal, T.; Vogs, C. Invited perspective: PFAS bioconcentration and biotransformation in early life stage Zebrafish and Its implications for human health protection. Environ. Health Perspect. 2021, 129, 071304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Choi, E.J.; Choi, G.W.; Lee, Y.B.; Cho, H.Y. Exploring sex differences in human health risk assessment for PFNA and PFDA using a PBPK model. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 311–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Shin, H.; Lee, Y.B.; Cho, H.Y. Sex-specific risk assessment of PFHxS using a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 1113–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loccisano, A.E.; Campbell, J.L.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Andersen, M.E.; Clewell, H.J. Comparison and evaluation of pharmacokinetics of PFOA and PFOS in the adult rat using a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 33, 452–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loccisano, A.E.; Campbell, J.L.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Andersen, M.E.; Clewell, H.J. Evaluation of placental and lactational pharmacokinetics of PFOA and PFOS in the pregnant, lactating, fetal and neonatal rat using a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model. Reprod. Toxicol. 2012, 33, 468–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovira, J.; Martinez, M.A.; Sharma, R.P.; Espuis, T.; Nadal, M.; Kumar, V.; Costopoulou, D.; Vassiliadou, I.; Leondiadis, L.; Domingo, J.L.; et al. Prenatal exposure to PFOS and PFOA in a pregnant women cohort of Catalonia, Spain. Environ. Res. 2019, 175, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worley, R.R.; Fisher, J. Application of physiologically-based pharmacokinetic modeling to explore the role of kidney transporters in renal reabsorption of perfluorooctanoic acid in the rat. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2015, 289, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.X.; Ng, C.A. A Permeability-Limited Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Model for Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in Male Rats. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9930–9939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrega, F.; Kumar, V.; Benfenati, E.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L.; Nadal, M. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling of perfluoroalkyl substances in the human body. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2015, 97, 814–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, A.S.; Kapraun, D.F.; Schlosser, P.M. A model template approach for rapid evaluation and application of physiologically based pharmacokinetic models for use in human health risk assessments: A case study on per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Toxicol. Sci. 2021, 182, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verner, M.A.; Ngueta, G.; Jensen, E.T.; Fromme, H.; Volkel, W.; Nygaard, U.C.; Granum, B.; Longnecker, M.P. A Simple Pharmacokinetic Model of Prenatal and Postnatal Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wambaugh, J.F.; Setzer, R.W.; Pitruzzello, A.M.; Liu, J.; Reif, D.M.; Kleinstreuer, N.C.; Wang, N.C.Y.; Sipes, N.; Martin, M.; Das, K.; et al. Dosimetric Anchoring of In Vivo and In Vitro Studies for Perfluorooctanoate and Perfluorooctanesulfonate. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 136, 308–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EPA. Notification of a Public Meetings of the Science Advisory Board Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) Review Panel. Fed. Reg. 2021, 86, 62526. [Google Scholar]




| Description | Results |
|---|---|
| Range of years published | 2005–2020 |
| Unique Sources (Journals, Books, etc) | 31 |
| Documents | 92 |
| Average years from publication | 7.45 |
| Average citations per study | 41.02 |
| Average citations per year per document | 4.406 |
| Total number of references | 2670 |
| Unique Authors | 358 |
| Authors per study | 3.89 |
| Node | DOI | Between-Ness | GCS | TK Model | Class | Objective | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Olsen GW, 2007 [56] | 10.1289/ehp.10009 | 19.3 | 760 | Yes | Measurement | Estimated half-life of PFOS, PFHS, and PFOA in fluorochemical production workers | |
| Lau C, 2007 [58] | 10.1093/toxsci/kfm128 | 11.9 | 2407 | No | Review | PFAS concentrations in environment, wildlife and humans. Toxicology and mode of action | |
| Andersen ME, 2006 [30] | 10.1016/j.tox.2006.08.004 | 11.0 | 193 | Yes | Dynamic PBTK Animal | Developed a PBPK model using renal resoprtion | |
| Trudel D, 2008 [61] | 10.1111/j.1539-6924.2008.01017.x | 5.9 | 472 | Yes | Steady State OCH | Estimated Daily intakes of PFOA and PFOS | |
| Calafat AM, 2007 [50] | 10.1289/ehp.10598 | 5.1 | 1012 | No | Measurement | Shared NHANES PFAS summary statistics | |
| Butenhoff JL, 2004 [55] | 10.1016/j.tox.2003.11.005 | 3.9 | 220 | No | Measurement | Gestational Rat observations for PFOA | |
| Emmett EA, 2006 [54] | 10.1097/01.jom.0000232486.07658.74 | 3.6 | 377 | No | Measurement | Determined serum PFOA levels of population living near production facility | |
| Kudo N, 2002 [28] | 10.1016/S0009-2797(02)00006-6 | 3.5 | 267 | Yes | Dynamic TC Animal | Evaluated role of sex hormones in renal clearance of PFOA in rats | |
| Han X, 2003 [57] | 10.1021/tx034005w | 2.9 | 392 | No | Measurement | Examined binding of PFOA to serum albumin in rats and humans | |
| Bartell SM, 2010 [60] | 10.1289/ehp.0901252 | 2.8 | 340 | Yes | Dynamic OCH | Detemined decline of PFOA in serum samples after filtration intervention in water district | |
| Karrman A, 2007 [49] | 10.1289/ehp.9491 | 2.7 | 520 | No | Measurement | Compared occurance of PFAS in breastmilk and primiparous women serum | |
| Ehresman DJ, 2007 [51] | 10.1016/j.envres.2006.06.008 | 2.5 | 310 | No | Measurement | Evaluated PFAS concentration across human blood-based matrices (blood, plasma, serum) | |
| Prevedouros K, 2006 [4] | 10.1021/es0512475 | 2.5 | 2374 | No | Review | Reviewed fate and transport of PFAS in the environment | |
| Fromme H, 2009 [59] | 10.1016/j.ijheh.2008.04.007 | 2.5 | 228 | No | Review | Reviewed enviromental and biomonitoring data for PFOS, PFOA and precursors | |
| Seacat AM, 2002 [48] | 10.1093/toxsci/68.1.249 | 2.4 | 618 | No | Measurement | Identified lowest measurable responses for PFOS in humans using monkeys | |
| Lou IC, 2009 [64] | 10.1093/toxsci/kfn234 | 2.0 | 97 | Yes | Dynamic OCH, TCH, PBTK | Characterize pharmacokinetics of PFOA in mice to estimate exposure | |
| Tan YM, 2008 [62] | 10.1016/j.toxlet.2007.12.007 | 1.9 | 70 | Yes | PBTK Animal | Evaluated determinants of disposition of PFOA and PFOS in rats, monkeys | |
| Loccisano AE, 2011 [63] | 10.1016/j.yrtph.2010.12.004 | 1.7 | 94 | Yes | PBTK Animal/Human | Predicts/evaluates PFOA/PFOS pharmacokinetics for monkeys and humans | |
| Vandenheuvel JP, 1991 [53] | 10.1002/jbt.2570060202 | 1.5 | 278 | No | Measurement | Exploration of sex differences in elimination of PFOA in rats | |
| Weaver YM, 2010 [52] | 10.1093/toxsci/kfp275 | 1.4 | 126 | No | Measurement | Evaluated PFAS of differing chain length as substrates of renal transporters |
| Document | DOI | GCS | LCS | Model Structure | Model Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trudel D, 2008 [61] | 10.1111/j.1539-6924.2008.01017.x | 286 | 15 | Steady State | Validation of exposure estimates |
| Vestergren R, 2009 [66] | 10.1021/es900228k | 242 | 9 | Steady State | Validation of exposure estimates |
| Haug LS, 2011 [70] | 10.1016/j.envint.2011.01.011 | 203 | 7 | Steady State | Validation of exposure estimates |
| Harada K, 2005, [25] | 10.1016/j.envres.2004.12.003 | 171 | 10 | Dynamic | Evaluation of sex-based differences in elimination |
| Fromme H, 2007 [65] | 10.1021/es071244n | 163 | 10 | Steady State | Validation of exposure estimates |
| Wong F, 2014 [77] | 10.1021/es500796y | 90 | 6 | Dynamic | Evaluation of sex-based differences in elimination |
| Hoffman K, 2011 [72] | 10.1289/ehp.1002503 | 90 | 0 | Steady State | Estimate relative contributions of contaminated drinking water to serum concentation |
| Savitz DA, 2012 [75] | 10.1097/EDE.0b013e31824cb93b | 82 | 3 | Dynamic | Assess association between exposure and pregnancy outcomes |
| Egeghy PP, 2011 [73] | 10.1038/jes.2009.73 | 79 | 0 | Steady State | Validation of exposure estimates |
| Worley RR, 2017 [19] | 10.1016/j.envint.2017.06.007 | 68 | 2 | Dynamic | Determination of half-lifes to characterize exposure |
| Gebbink WA, 2015 [78] | 10.1016/j.envint.2014.10.013 | 66 | 5 | Steady State | Identification of relative source contributions and precursors |
| Lorber M, 2011 [69] | 10.1021/es103718h | 60 | 7 | Steady State | Validation of exposure estimates |
| Thompson J, 2010 [67] | 10.1016/j.envint.2010.02.008 | 56 | 14 | Steady State | Characterization of exposure from serum concentrations |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
East, A.; Dawson, D.E.; Brady, S.; Vallero, D.A.; Tornero-Velez, R. A Scoping Assessment of Implemented Toxicokinetic Models of Per- and Polyfluoro-Alkyl Substances, with a Focus on One-Compartment Models. Toxics 2023, 11, 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020163
East A, Dawson DE, Brady S, Vallero DA, Tornero-Velez R. A Scoping Assessment of Implemented Toxicokinetic Models of Per- and Polyfluoro-Alkyl Substances, with a Focus on One-Compartment Models. Toxics. 2023; 11(2):163. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020163
Chicago/Turabian StyleEast, Alexander, Daniel E. Dawson, Sydney Brady, Daniel A. Vallero, and Rogelio Tornero-Velez. 2023. "A Scoping Assessment of Implemented Toxicokinetic Models of Per- and Polyfluoro-Alkyl Substances, with a Focus on One-Compartment Models" Toxics 11, no. 2: 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020163
APA StyleEast, A., Dawson, D. E., Brady, S., Vallero, D. A., & Tornero-Velez, R. (2023). A Scoping Assessment of Implemented Toxicokinetic Models of Per- and Polyfluoro-Alkyl Substances, with a Focus on One-Compartment Models. Toxics, 11(2), 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020163







