Neuropathy with Cerebral Features Induced by Nitrous Oxide Abuse—A Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
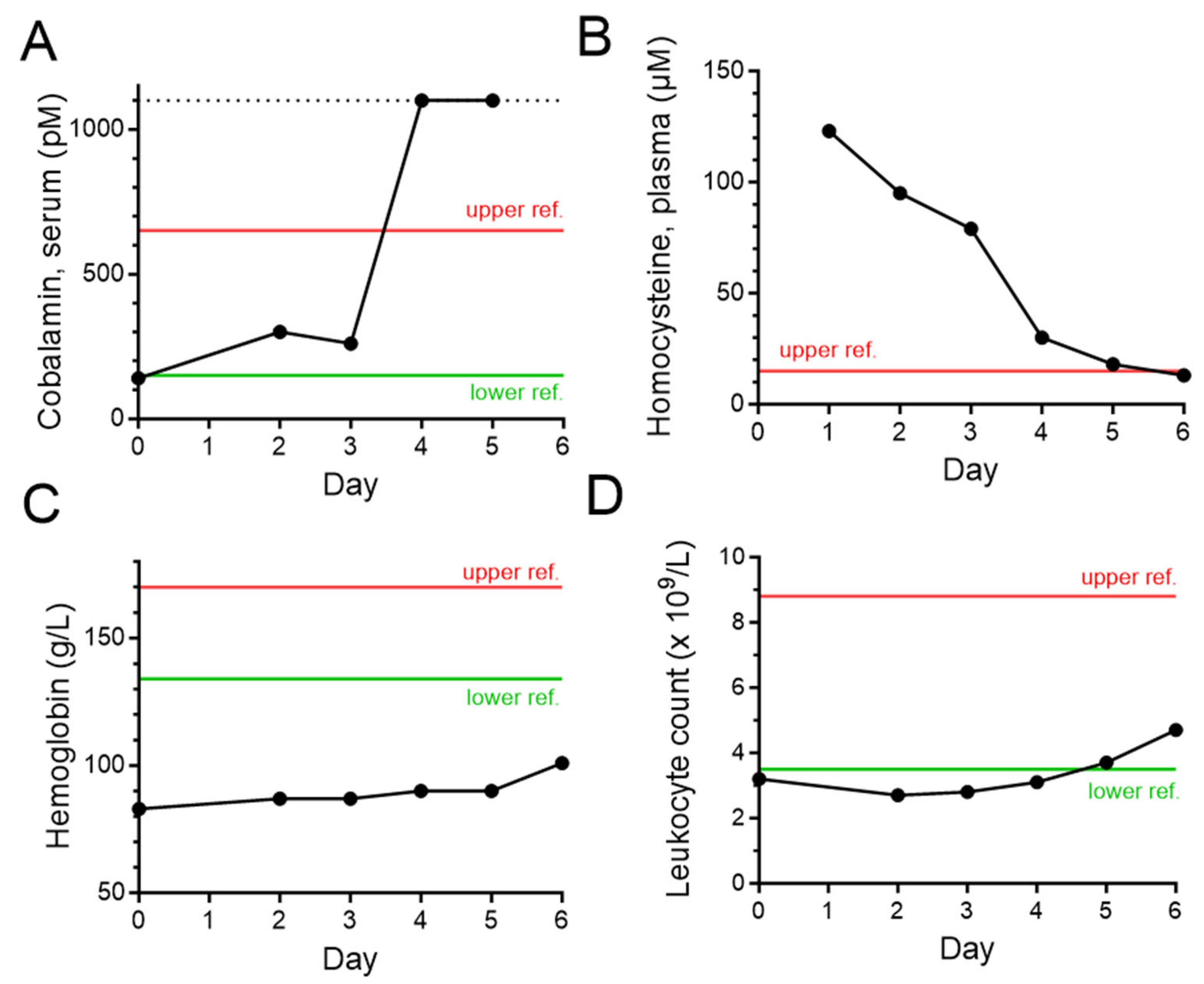
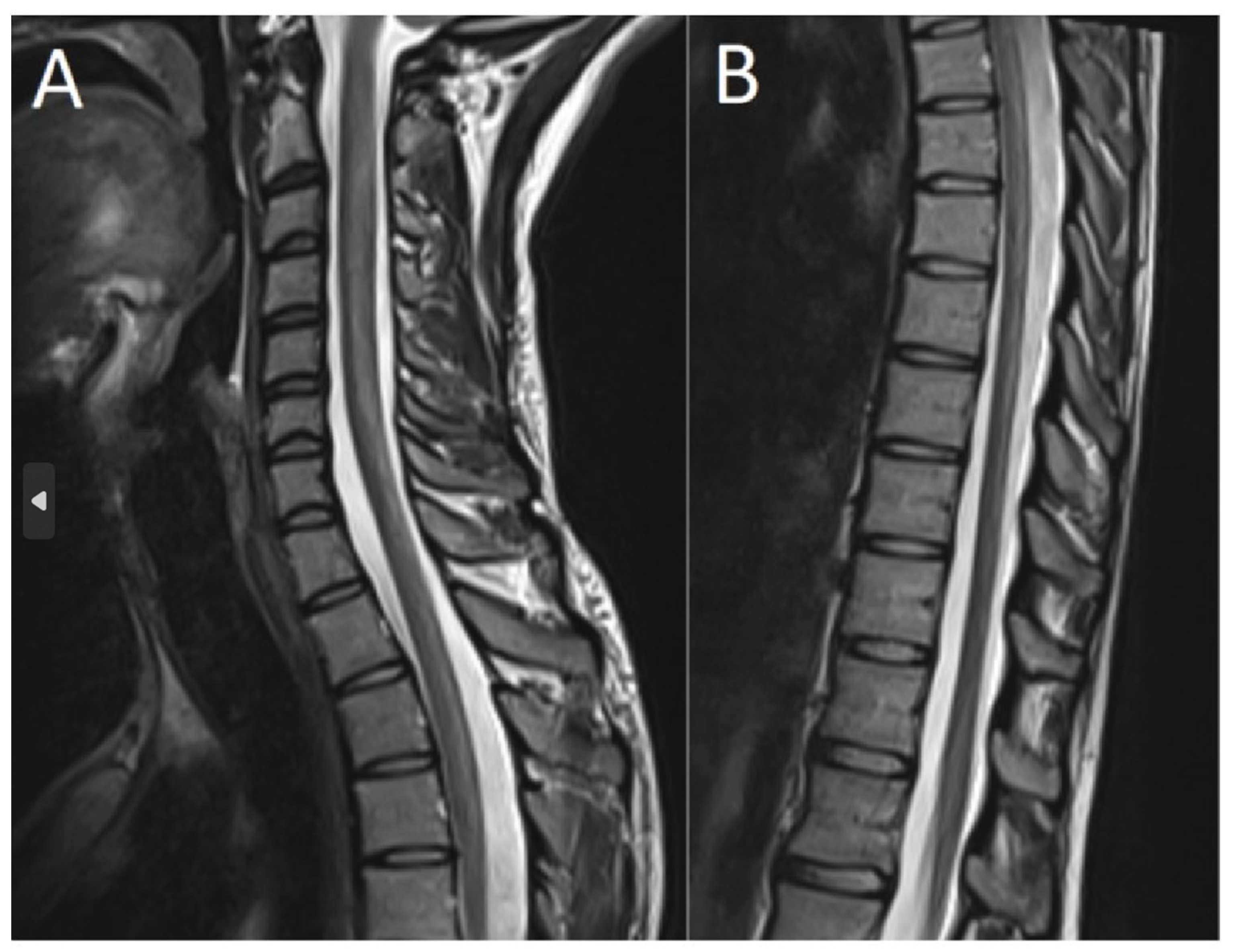
2. Case Description
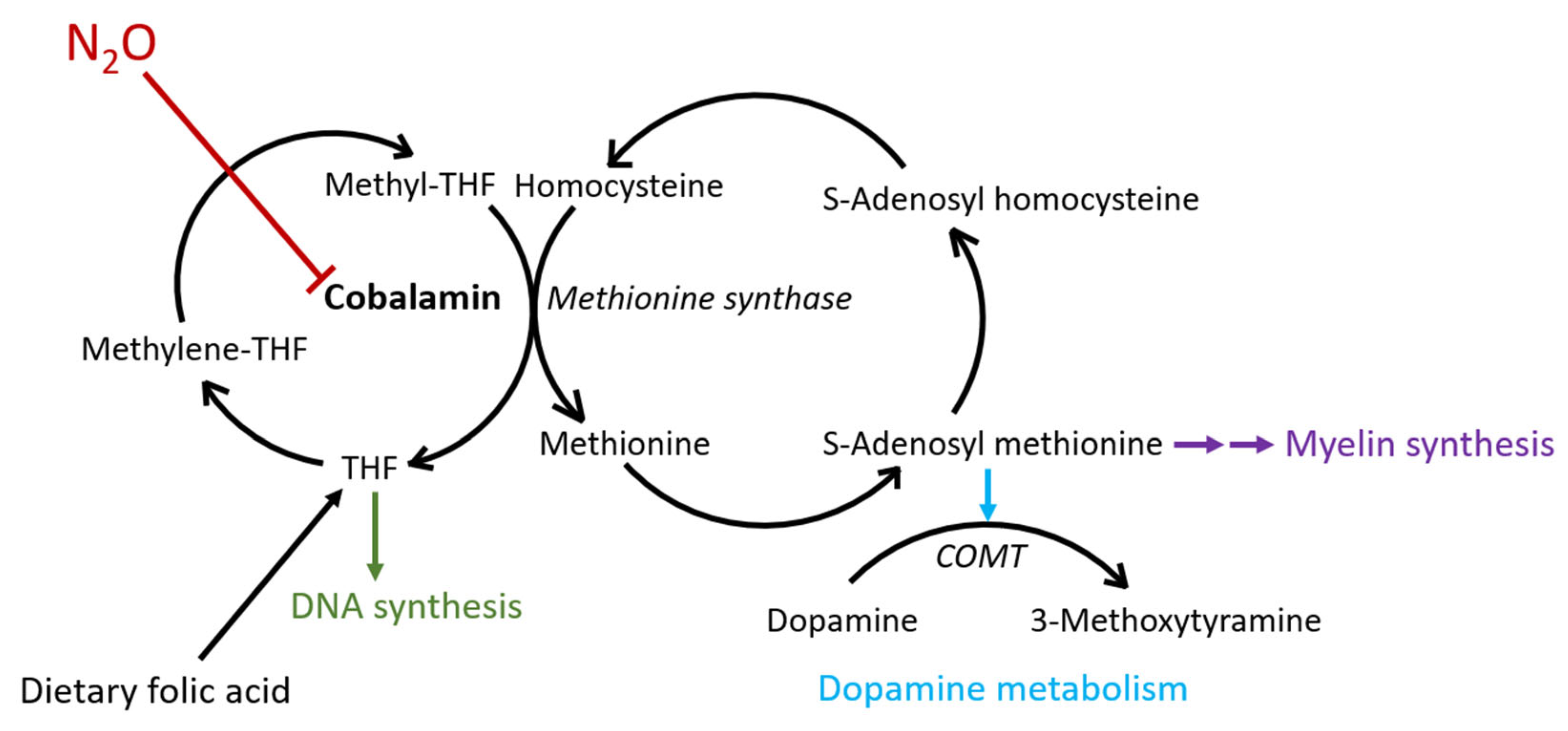
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction. Recreational Use of Nitrous Oxide: A Growing Concern for Europe; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornbein, T.F.; Eger, E.I., 2nd; Winter, P.M.; Smith, G.; Wetstone, D.; Smith, K.H. The Minimum Alveolar Concentration of Nitrous Oxide in Man. Anesth. Analg. 1982, 61, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jevtović-Todorović, V.; Todorović, S.M.; Mennerick, S.; Powell, S.; Dikranian, K.; Benshoff, N.; Zorumski, C.F.; Olney, J.W. Nitrous Oxide (laughing Gas) Is an NMDA Antagonist, Neuroprotectant and Neurotoxin. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 460–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, R.G.S.; Henderson, R.J.; Pratt, J.M. Reactions of Gases in Solution. Part III. Some Reactions of Nitrous Oxide with Transition-Metal Complexes. J. Chem. Soc. 1968, 2886–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, K.L.; Alberico, A.M. Postoperative Myeloneuropathy: A Preventable Complication in Patients with B12 Deficiency. J. Neurosurg. 1990, 72, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flippo, T.S.; Holder, W.D., Jr. Neurologic Degeneration Associated with Nitrous Oxide Anesthesia in Patients with Vitamin B12 Deficiency. Arch. Surg. 1993, 128, 1391–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassen, H.C.; Henriksen, E.; Neukirch, F.; Kristensen, H.S. Treatment of Tetanus; Severe Bone-Marrow Depression after Prolonged Nitrous-Oxide Anaesthesia. Lancet 1956, 270, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layzer, R.B.; Fishman, R.A.; Schafer, J.A. Neuropathy Following Abuse of Nitrous Oxide. Neurology 1978, 28, 504–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layzer, R.B. Myeloneuropathy after Prolonged Exposure to Nitrous Oxide. Lancet 1978, 2, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amess, J.A.; Burman, J.F.; Rees, G.M.; Nancekievill, D.G.; Mollin, D.L. Megaloblastic Haemopoiesis in Patients Receiving Nitrous Oxide. Lancet 1978, 2, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.M. Folate–vitamin B12 Interrelationships in the Central Nervous System. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 1992, 51, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinn, J.J.; McCann, S.; Wilson, P.; Reed, B.; Weir, D.; Scott, J. Animal Model for Subacute Combined Degeneration. Lancet 1978, 2, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinn, J.J.; Weir, D.G.; McCann, S.; Reed, B.; Wilson, P.; Scott, J.M. Methyl Group Deficiency in Nerve Tissue: A Hypothesis to Explain the Lesion of Subacute Combined Degeneration. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 1980, 149, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, D.G.; Lindenbaum, J. Folate-Cobalamin Interactions. In Folate in Health and Disease; Bailey, L.B., Ed.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 237–285. ISBN 9780824792800. [Google Scholar]
- Savage, D.G.; Lindenbaum, J. Neurological Complications of Aquired Cobalamin Deficeincy: Clinical Aspects. In Folate in Health and Disease; Bailey, L.B., Ed.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 657–678. ISBN 9780824792800. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, S. Clinical Picture of Pernicious Anaemia prior to Introduction of Liver Therapy in 1926 and in Edinburgh Subsequent to 1944. Br. Med. J. 1957, 1, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Healton, E.B.; Savage, D.G.; Brust, J.C.; Garrett, T.J.; Lindenbaum, J. Neurologic Aspects of Cobalamin Deficiency. Medicine 1991, 70, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garakani, A.; Jaffe, R.J.; Savla, D.; Welch, A.K.; Protin, C.A.; Bryson, E.O.; McDowell, D.M. Neurologic, Psychiatric, and Other Medical Manifestations of Nitrous Oxide Abuse: A Systematic Review of the Case Literature. Am. J. Addict. 2016, 25, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.G.; Leite, M.I.; Lunn, M.P.; Bennett, D.L.H. Whippits, Nitrous Oxide and the Dangers of Legal Highs. Pract. Neurol. 2015, 15, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordmark Grass, J.; Westerbergh, J.; Lindeman, E. Recurrent use of nitrous oxide can give rise to severe complications. Lakartidningen 2022, 119, 21157. (In Swedish) [Google Scholar]
- J Siddiqui, A.; Gautam, G.; Ågren, A.; Nordmark Grass, J. Life threatening thrombosis after massive consumption of laughing gas. Lakartidningen 2023, 120, 22151. [Google Scholar]
- van Riel, A.J.H.P.; Hunault, C.C.; van den Hengel-Koot, I.S.; Nugteren-van Lonkhuyzen, J.J.; de Lange, D.W.; Hondebrink, L. Alarming Increase in Poisonings from Recreational Nitrous Oxide Use after a Change in EU-Legislation, Inquiries to the Dutch Poisons Information Center. Int. J. Drug Policy 2022, 100, 103519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borch, K.; Liedberg, G. Prevalence and Incidence of Pernicious Anemia. An Evaluation for Gastric Screening. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1984, 19, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, N.A.; Poulsen, M.K.; Woo, M.A. Validity of the Montreal Cognitive Assessment Screener in Adolescents and Young Adults with and without Congenital Heart Disease. Nurs. Res. 2017, 66, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindeman, E.; Abdulhameed, I.; Nordmark Grass, J. Rapid Normalization of Homocysteine after Cessation of Nitrous Oxide Exposure: A Case Series. Clin. Toxicol. 2023, 61, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, B. Molecular Biology of the Cell; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 9781317563754. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.-J.; Huang, C.-S. Nitrous Oxide-Induced Subacute Combined Degeneration Presenting with Dystonia and Pseudoathetosis: A Case Report. Acta Neurol. Taiwan 2016, 25, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsao, D.; Diatchenko, L.; Dokholyan, N.V. Structural Mechanism of S-Adenosyl Methionine Binding to Catechol O-Methyltransferase. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettström, C.; Tournavitis, A.; Eriksson, L. Large amounts of nitrous oxide can give rise to psychiatric and neruologic symptoms. Lakartidningen 2023, 120, 22146. (In Swedish) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chiew Angela, L.; Raubenheimer Jacques, E.; Ingrid, B.; Buckley Nicholas, A.; Therese, B.; Betty, C.; Jonathan, B. Just “Nanging” around—Harmful Nitrous Oxide Use. A Retrospective Case Series and Review of Internet Searches, Social Media Posts and the Coroner’s Database. Intern. Med. J. 2021, 52, 1724–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.J.G.; Reid, M.; Schon, F.; Poole, N.A. Just Say N2O—Nitrous Oxide Misuse: Essential Information for Psychiatrists. BJPsych Adv. 2020, 26, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alt, R.S.; Morrissey, R.P.; Gang, M.A.; Hoffman, R.S.; Schaumburg, H.H. Severe Myeloneuropathy from Acute High-Dose Nitrous Oxide (N2O) Abuse. J. Emerg. Med. 2011, 41, 378–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Halleux, C.; Juurlink, D.N. Diagnosis and Management of Toxicity Associated with the Recreational Use of Nitrous Oxide. CMAJ 2023, 195, E1075–E1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodsky, L.; Zuniga, J. Nitrous Oxide: A Psychotogenic Agent. Compr. Psychiatry 1975, 16, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, S.; Johnsson, M. Serious and multi-faceted consequences of nitrous oxide use. Lakartidningen 2023, 120, 23116. (In Swedish) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Consumption of Foodstuffs of Animal Origin. Preliminary Data 2021. The Swedish Board of Agriculture. Website in Swedish. Available online: https://jordbruksverket.se/om-jordbruksverket/jordbruksverkets-officiella-statistik/jordbruksverkets-statistikrapporter/statistik/2022-03-17-livsmedelskonsumtion-av-animalier.-preliminara-uppgifter-2021 (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Lindenbaum, J.; Healton, E.B.; Savage, D.G.; Brust, J.C.; Garrett, T.J.; Podell, E.R.; Marcell, P.D.; Stabler, S.P.; Allen, R.H. Neuropsychiatric Disorders Caused by Cobalamin Deficiency in the Absence of Anemia or Macrocytosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 318, 1720–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lindeman, E.; Melin, S.; Paucar, M.; Ågren, R. Neuropathy with Cerebral Features Induced by Nitrous Oxide Abuse—A Case Report. Toxics 2023, 11, 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11120959
Lindeman E, Melin S, Paucar M, Ågren R. Neuropathy with Cerebral Features Induced by Nitrous Oxide Abuse—A Case Report. Toxics. 2023; 11(12):959. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11120959
Chicago/Turabian StyleLindeman, Erik, Sara Melin, Martin Paucar, and Richard Ågren. 2023. "Neuropathy with Cerebral Features Induced by Nitrous Oxide Abuse—A Case Report" Toxics 11, no. 12: 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11120959
APA StyleLindeman, E., Melin, S., Paucar, M., & Ågren, R. (2023). Neuropathy with Cerebral Features Induced by Nitrous Oxide Abuse—A Case Report. Toxics, 11(12), 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11120959






