Strategies for Effective Management of Indoor Air Quality in a Kindergarten: CO2 and Fine Particulate Matter Concentrations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
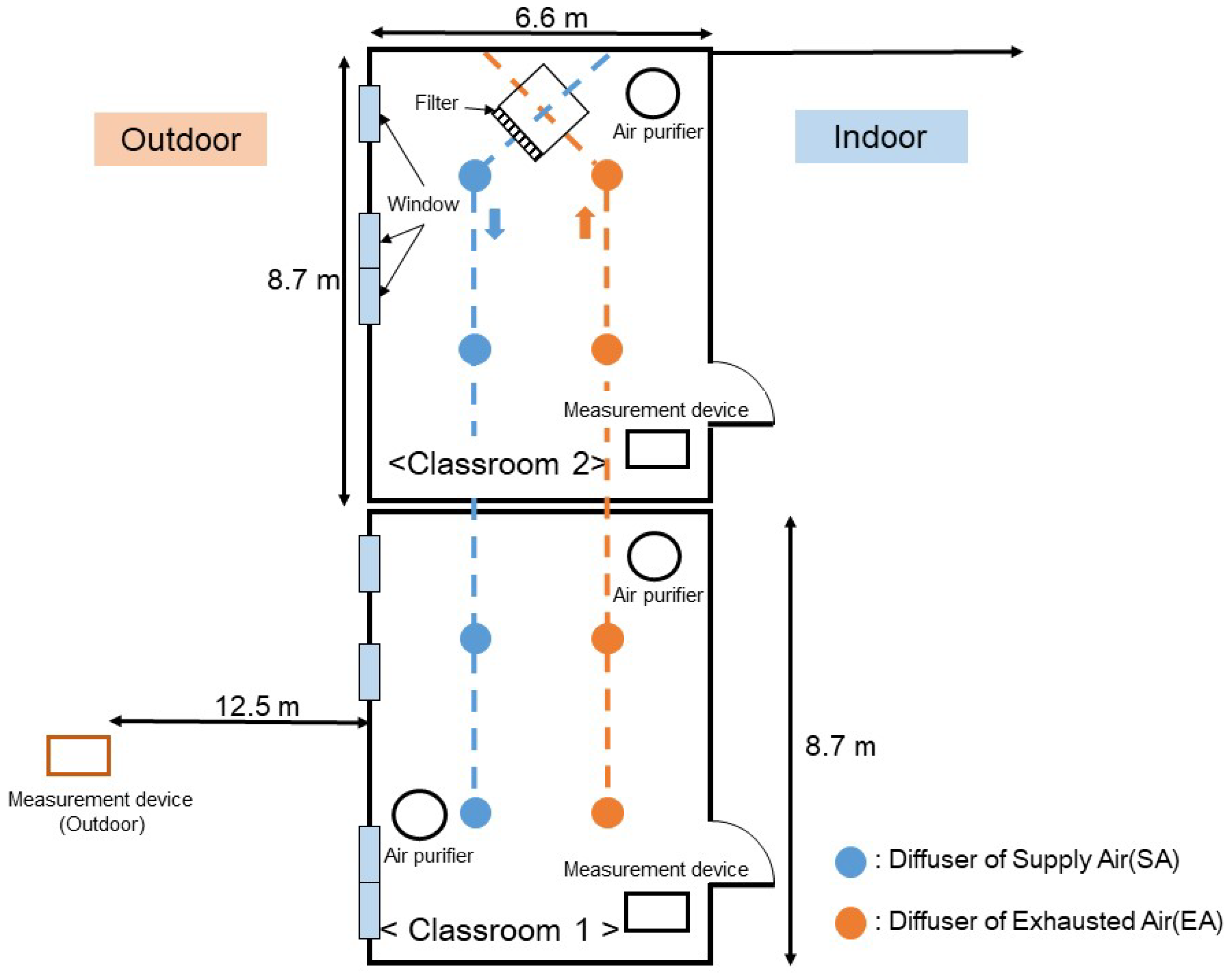
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Numerical Model
2.3. Defining the Parameters
3. Results
3.1. Comparing the Numerical Model with Measured Data
3.1.1. The Concentrations of CO2
3.1.2. The Concentrations of PM2.5
4. Discussion
4.1. Flowrate of Mechanical Ventilation
4.2. Decreasing the Concentration of PM2.5
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Indoor CO2 Concentration (ppm) = | |
| (t) | Indoor PM2.5 Concentration (μg/m3) = |
| Outdoor CO2 Concentration (ppm) | |
| Outdoor PM2.5 Concentration (μg/m3) | |
| Indoor Infiltration (m3/h) | |
| Indoor Filtration Rate (m3/h) | |
| Flow Rate of Supply via Mechanical Ventilation (m3/h) | |
| Exhaust Flow Rate by Mechanical Ventilation (m3/h) | |
| G | Amount of CO2 Generated in Room (ppm × m3/min) |
| Clean Air Delivery Rate (m3/h = State CADR) | |
| Efficiency of Air Cleaning Rate (m3/h = EACR) | |
| Deposition Rate of PM2.5 (h−1) | |
| V | Volume of Indoor (m3) |
| Collection Efficiency of PM2.5 Particles by Infiltration | |
| Collection Efficiency of PM2.5 Particles by Mechanical Ventilation |
References
- Jones, A.P. Indoor air quality and health. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 4535–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.; Nelson, W.C. National Human Activity Pattern Survey Data Base; USEPA: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 1995; p. NC2.
- WH Organization. Air Quality Guidelines Global Update 2021: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Talbott, E.O.; Arena, V.C.; Rager, J.R.; Clougherty, J.E.; Michanowicz, D.R.; Sharma, R.K.; Stacy, S.L. Fine particulate matter and the risk of autism spectrum disorder. Environ. Res. 2015, 140, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Liu, D.; Wu, W. PM2.5 exposure and pediatric health in e-waste dismantling areas. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 89, 103774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, B.F.A.; Ignotti, E.; Artaxo, P.; do Nascimento Saldiva, P.H.; Junger, W.L.; Hacon, S. Risk assessment of PM2.5 to child residents in Brazilian Amazon region with biofuel production. Environ. Health 2012, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norbäck, D.; Björnsson, E.; Janson, C.; Widström, J.; Boman, G. Asthmatic symptoms and volatile organic compounds, formaldehyde, and carbon dioxide in dwellings. Occup. Environ. Med. 1995, 52, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragsdale, S.W. Life with Carbon Monoxide. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 39, 165–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, A.H.; Patz, J.A. Reactive Nitrogen and Human Health: Acute and Long-term Implications. AMBIO 2002, 31, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, M.; Le Trionnaire, S.; Chopra, M.; Fox, B.; Whatmore, J. Emerging role of hydrogen sulfide in health and disease: Critical appraisal of biomarkers and pharmacological tools. Clin. Sci. 2011, 121, 459–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zoughool, M.; Krewski, D. Health effects of radon: A review of the literature. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2009, 85, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuraimi, M.S.; Tham, K.W.; Sekhar, S.C. The effects of ventilation operations in determining contributions of VOCs sources in air-conditioned tropical buildings. Build. Environ. 2003, 38, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.Y.; Tung, T.C.; Burnett, J. Influence of ventilation on indoor radon level. Build. Environ. 1997, 32, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahyuddin, N.; Awbi, H. A Review of CO2 Measurement Procedures in Ventilation Research. Int. J. Vent. 2012, 10, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaughnessy, R.J.; Sextro, R.G. What Is an Effective Portable Air Cleaning Device? A Review. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2006, 3, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidelines for Indoor Air Quality Management in Preschools; Ministry of the Environment: Sejong-si, Republic of Korea, 2021.
- Park, S.-M.; Lee, H.-S.; Yang, Y.; Lee, S.-Y.; Park, J.C. A Survey of the Indoor Air Quality in the Child Care Center. J. Korean Soc. Living Environ. Syst. 2017, 24, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phee, Y.G.; Jung, J.H.; Nam, M.R. Exposure assessment of PM2.5 in manufacturing industry office building. J. Korean Soc. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2013, 23, 356–366. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.; Hong, K.; Shin, D.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, S.; Hwang, C.-H.; Noh, K.-C. Field Tests of Indoor Air Cleaners for Removal of PM2.5 and PM10 in Elementary School Classrooms in Seoul, Korea. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2022, 22, 210383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, K.-C.; Yook, S.-J. Evaluation of clean air delivery rates and operating cost effectiveness for room air cleaner and ventilation system in a small lecture room. Energy Build. 2016, 119, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheff, P.A.; Paulius, V.K.; Huang, S.W.; Conroy, L.M. Indoor Air Quality in a Middle School, Part I: Use of CO2 as a Tracer for Effective Ventilation. Appl. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2000, 15, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.; Schito, E. Definition of Optimal Ventilation Rates for Balancing Comfort and Energy Use in Indoor Spaces Using CO2 Concentration Data. Buildings 2020, 10, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacitto, A.; Amato, F.; Moreno, T.; Pandolfi, M.; Fonseca, A.; Mazaheri, M.; Stabile, L.; Buonanno, G.; Querol, X. Effect of ventilation strategies and air purifiers on the children’s exposure to airborne particles and gaseous pollutants in school gyms. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 712, 135673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelot, N.; Marchand, C.; Ramalho, O.; Delmas, V.; Carrega, M. Monitoring indoor air quality in French schools and day-care centers. HVAC&R Res. 2013, 19, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M. An analysis on the concentration characteristics of PM2.5 in Seoul, Korea from 2005 to 2012. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 50 (Suppl. 1), 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, N.R.; da Graça, G.C. Impact of outdoor PM2.5 on natural ventilation usability in California’s nondomestic buildings. Appl. Energy 2017, 189, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.-M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kwon, S.-B.; Park, D.-S.; Park, J.-H.; Cho, K.-C. The Distribution Characteristics of Carbon Dioxide in Indoor School Spaces. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 27, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, K.-C.; Oh, M.-D. Variation of clean air delivery rate and effective air cleaning ratio of room air cleaning devices. Build. Environ. 2015, 84, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Kim, Y.; Hong, K.; Lee, G.; Park, I.; Han, B. The Actual Efficacy of an Air Purifier at Different Outdoor PM2.5 Concentrations in Residential Houses with Different Airtightness. Toxics 2022, 10, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Yoo, C.; Kim, Y. Effective Opening Area and Installation Location of Windows for Single Sided Natural Ventilation in High-rise Residences. J. Asian Arch. Build. Eng. 2012, 11, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SPS-KACA002-132:2021; Indoor Air Cleaner. Korea Air Cleaning Association: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2021.
- Malik, N. Field studies of dependence of air infiltration on outside temperature and wind. Energy Build. 1978, 1, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forecast Research Department. Report of Global Atmosphere Watch 2021; National Institute of Meteorological Sciences: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2022. [Google Scholar]










| Date | Classroom | Time | Number of People (Men/Women/Children) | (m3/h) | (m3/h) | (m3/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | ||||||
| 3 January 2023 | 1 | 9:00~9:30 | 1/2/8 | 26 | 230 | 240 |
| 9:30~10:30 | 1/2/11 | |||||
| 10:30~12:20 | 1/2/0 | |||||
| 12:20~14:50 | 1/2/11 | |||||
| 14:50~15:30 | 1/2/0 | |||||
| (b) | ||||||
| 3 January 2023 | 2 | 9:00~9:50 | 0/2/7 | 16 | 254 | 324 |
| 9:50~11:00 | 0/2/11 | |||||
| 11:00~12:40 | 1/2/0 | |||||
| 12:40~15:10 | 0/2/11 | |||||
| 15:10~15:30 | 0/1/4 | 143 | ||||
| (c) | ||||||
| 11 January 2023 | 1 | 9:00~9:40 | 1/2/6 | 26 | 142 | 120 |
| 9:40~11:00 | 1/1/0 | 143 | ||||
| 11:00~12:00 | 26 | |||||
| 12:00~13:00 | 1/2/10 | 143 | ||||
| 13:00~15:00 | 420 | |||||
| 15:00~15:30 | 0/2/0 | 571 | ||||
| (d) | ||||||
| 11 January 2023 | 2 | 9:00~9:30 | 1/1/2 | 16 | 154 | 210 |
| 9:30~11:00 | 1/2/7 | |||||
| 11:00~12:30 | 1/2/0 | |||||
| 12:30~15:00 | 2/2/8 | |||||
| 15:00~15:30 | 1/2/0 | 207 | ||||
| (a) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Classroom 1 | Number of People (Men/Women/Children) | (m3/h) | (m3/h) |
| 9:00~11:00 | 1/2/11 | 26 | 142 (Measured) Indoor 345 Scenario 1 |
| 11:00~12:30 | 1/2/0 | ||
| 12:30~15:00 | 0/2/15 | ||
| 15:00~16:00 | 0/2/0 | ||
| 16:00~17:30 | 0/2/11 | ||
| 17:30~18:00 | 1/2/0 | ||
| (b) | |||
| Classroom 2 | Number of People (Men/Women/Children) | (m3/h) | (m3/h) |
| 9:00~10:00 | 0/2/4 | 16 | 154 (Measured) Indoor 345 Scenario 1 |
| 10:00~10:30 | 0/0/0 | ||
| 10:30~11:30 | 0/2/8 | ||
| 11:30~12:00 | 0/2/0 | ||
| 12:00~15:00 | 0/2/15 | ||
| 15:00~15:30 | 0/2/6 | ||
| 15:30~16:30 | 0/2/13 | ||
| 16:30~18:00 | 0/2/2 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.; Kim, Y.; Hong, K.-J.; Lee, G.; Kim, H.-J.; Shin, D.; Han, B. Strategies for Effective Management of Indoor Air Quality in a Kindergarten: CO2 and Fine Particulate Matter Concentrations. Toxics 2023, 11, 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110931
Lee D, Kim Y, Hong K-J, Lee G, Kim H-J, Shin D, Han B. Strategies for Effective Management of Indoor Air Quality in a Kindergarten: CO2 and Fine Particulate Matter Concentrations. Toxics. 2023; 11(11):931. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110931
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Doyeon, Younghun Kim, Kee-Jung Hong, Gunhee Lee, Hak-Joon Kim, Dongho Shin, and Bangwoo Han. 2023. "Strategies for Effective Management of Indoor Air Quality in a Kindergarten: CO2 and Fine Particulate Matter Concentrations" Toxics 11, no. 11: 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110931
APA StyleLee, D., Kim, Y., Hong, K.-J., Lee, G., Kim, H.-J., Shin, D., & Han, B. (2023). Strategies for Effective Management of Indoor Air Quality in a Kindergarten: CO2 and Fine Particulate Matter Concentrations. Toxics, 11(11), 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110931








