Association between Air Pollution and Lipid Profiles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Air Pollution and Blood Lipids
2.1. Association between Air Pollution and Blood Lipids
2.2. Air Pollutants
2.2.1. PM2.5
2.2.2. Other Air Pollutants
2.2.3. Air Pollutant Mixture
2.2.4. Indoor Air Pollution
2.3. Blood Lipid Indexes
2.3.1. Introduction to Blood Lipids
2.3.2. Indicators of Lipid Health
2.4. Vulnerable Population
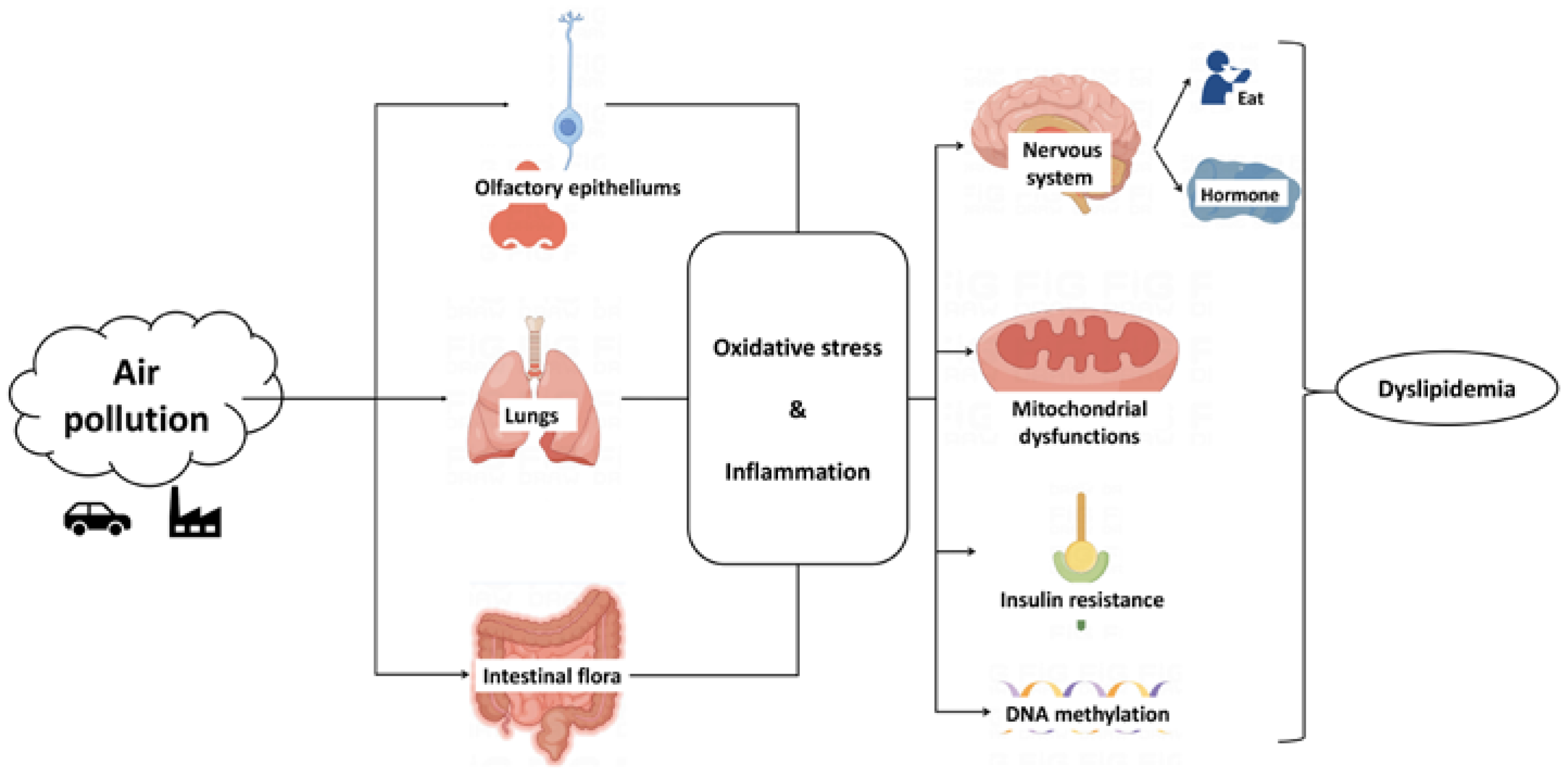
3. Potential Mechanism of Air Pollution Affecting Lipid Metabolism
3.1. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
3.2. Insulin Resistance
3.3. Hypothalamus
3.4. Epigenetic Changes
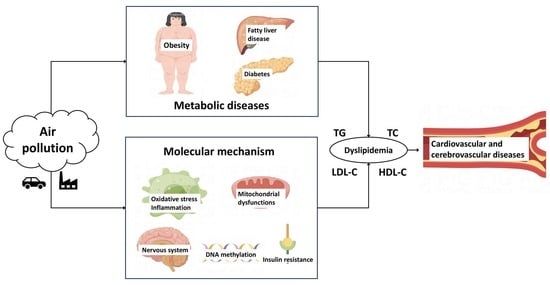
4. The Potential Diseases Related to Blood Lipid Disorders Caused by Air Pollution
4.1. Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Diseases
4.2. Metabolic Dysfunction Diseases
5. Summary and Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- GBD 2019 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1223–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Ambient (Outdoor) Air Pollution. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ambient-(outdoor)-air-quality-and-health (accessed on 16 August 2022).
- Mehta, A.; Shapiro, M.D. Apolipoproteins in vascular biology and atherosclerotic disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2022, 19, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esan, O.; Wierzbicki, A.S. Triglycerides and cardiovascular disease. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2021, 36, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontush, A. HDL and Reverse Remnant-Cholesterol Transport (RRT): Relevance to Cardiovascular Disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 1086–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaio, V.; Roquette, R.; Dias, C.M.; Nunes, B. Ambient air pollution and lipid profile: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Salam, M.T.; Toledo-Corral, C.; Watanabe, R.M.; Xiang, A.H.; Buchanan, T.A.; Habre, R.; Bastain, T.M.; Lurmann, F.; Wilson, J.P.; et al. Ambient Air Pollutants Have Adverse Effects on Insulin and Glucose Homeostasis in Mexican Americans. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sade, M.Y.; Kloog, I.; Liberty, I.F.; Schwartz, J.; Novack, V. The Association Between Air Pollution Exposure and Glucose and Lipids Levels. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 2460–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Meng, X.-C.; Huang, C.; Wang, J.; Liao, Y.-H.; Huang, Y.; Liu, R. Association between ambient air pollutants and lipid profile: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 262, 115140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinn, L.A.; Schneider, A.; McGarrah, R.W.; Ward-Caviness, C.; Neas, L.M.; Di, Q.; Schwartz, J.; Hauser, E.R.; Kraus, W.E.; Cascio, W.E.; et al. Association of long-term PM(2.5) exposure with traditional and novel lipid measures related to cardiovascular disease risk. Environ. Int. 2019, 122, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, S.; Young, B.N.; Clark, M.L.; Benka-Coker, M.L.; Bachand, A.M.; Brook, R.D.; Nelson, T.L.; Volckens, J.; Reynolds, S.J.; L’orange, C.; et al. Household air pollution from biomass-burning cookstoves and metabolic syndrome, blood lipid concentrations, and waist circumference in Honduran women: A cross-sectional study. Environ. Res. 2019, 170, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Z.-H.; Yang, B.-Y.; Zou, Z.-Y.; Ma, J.; Jing, J.; Wang, H.-J.; Dong, G.-H.; Ma, Y.-H.; Guo, Y.-M.; Chen, Y.-J. Exposure to ambient air pollution and blood lipids in children and adolescents: A national population based study in China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Chen, G.; Liu, F.; Li, N.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Lu, Y.; Xiang, H.; Guo, Y.; et al. Long-term effects of ambient air pollutants to blood lipids and dyslipidemias in a Chinese rural population. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, S.; Li, S.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, N.; Liu, F.; Huang, S.; Liu, S.; Lu, Y.; Mao, Z.; et al. Is long-term PM(1) exposure associated with blood lipids and dyslipidemias in a Chinese rural population? Environ. Int. 2020, 138, 105637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuinn, L.A.; Coull, B.A.; Kloog, I.; Just, A.C.; Tamayo-Ortiz, M.; Osorio-Yáñez, C.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Wright, R.J.; Téllez-Rojo, M.M.; Wright, R.O. Fine particulate matter exposure and lipid levels among children in Mexico city. Environ. Epidemiol. 2020, 4, e088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, W.-Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, G.; Choi, S.; Kim, S.R.; Hong, Y.-C.; Park, S.M. Exposure to ambient fine particulate matter is associated with changes in fasting glucose and lipid profiles: A nationwide cohort study. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-J.; Kwon, H.; Yun, J.M.; Cho, B.; Park, J.-H. Interaction between visceral adiposity and ambient air pollution on LDL cholesterol level in Korean adults. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yao, Y.; Xie, W.; Wang, B.; Guan, T.; Han, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhu, T.; Xue, T. Association of long-term exposure to PM(2.5) with blood lipids in the Chinese population: Findings from a longitudinal quasi-experiment. Environ. Int. 2021, 151, 106454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chen, G.; Pan, Y.; Xia, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Silang, Y.; Chen, J.; Xu, H.; Zeng, C.; et al. Association of long-term exposure to ambient air pollutants with blood lipids in Chinese adults: The China Multi-Ethnic Cohort study. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-S.; Gui, Z.-H.; Zou, Z.-Y.; Yang, B.-Y.; Ma, J.; Jing, J.; Wang, H.-J.; Luo, J.-Y.; Zhang, X.; Luo, C.-Y.; et al. Long-term exposure to ambient air pollution and metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents: A national cross-sectional study in China. Environ. Int. 2021, 148, 106383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, H.; He, W.; Chen, G.; Lu, P.; Xu, R.; Yu, P.; Ye, T.; Guo, S.; Li, S.; et al. The association between ambient air pollution and blood lipids: A longitudinal study in Shijiazhuang, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Gong, J.; Wang, G.; Ge, W.; Chen, R.; Meng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Kan, H. Associations of long-term exposure to ambient nitrogen dioxide with indicators of diabetes and dyslipidemia in China: A nationwide analysis. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaio, V.; Roquette, R.; Monteiro, A.; Ferreira, J.; Lopes, D.; Dias, C.M.; Nunes, B. PM10 exposure interacts with abdominal obesity to increase blood triglycerides: A cross-sectional linkage study. Eur. J. Public Health 2022, 32, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ge, M.; Pei, Z.; He, J.; Wang, C. Nonlinear associations between environmental factors and lipid levels in middle-aged and elderly population in China: A national cross-sectional study. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Pang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Luo, H.; Han, Y.; Ma, S.; Li, L.; Yuan, J.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, R. Abnormal fasting blood glucose enhances the risk of long-term exposure to air pollution on dyslipidemia: A cross-sectional study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 237, 113537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, M.; Xiao, X.; Xu, S.-L.; Lin, S.; Wu, Q.-Z.; Chen, G.-B.; Yang, B.-Y.; Hu, L.-W.; Zeng, X.-W.; et al. Long-term PM0.1 exposure and human blood lipid metabolism: New insight from the 33-community study in China. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 303, 119171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Song, Y.; Shi, L.; Jiang, J.; Wan, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zou, Z.; Ma, J. Long-term effects of ambient PM(2.5) constituents on metabolic syndrome in Chinese children and adolescents. Environ. Res. 2023, 220, 115238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, C.; Xu, H.; Brook, R.D.; Liu, S.; Yi, T.; Wang, Y.; Feng, B.; Zhao, M.; Wang, X.; et al. Ambient Air Pollution Is Associated With HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) Dysfunction in Healthy Adults. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Y. Short-term exposure to air pollution and its interaction effects with two ABO SNPs on blood lipid levels in northern China: A family-based study. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.-Z.; Guo, P.-Y.; Xu, S.-L.; Zhou, Y.; Jalaludin, B.; Leskinen, A.; Knibbs, L.D.; Heinrich, J.; Morawska, L.; Yim, S.H.-L.; et al. Associations of Particulate Matter Sizes and Chemical Constituents with Blood Lipids: A Panel Study in Guangzhou, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 5065–5075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Xia, W.; Liang, G.; Xu, S.; Zhao, X.; Wang, D.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, H. Association of fine particulate matter with glucose and lipid metabolism: A longitudinal study in young adults. Occup. Environ. Med. 2021, 78, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Nan, B.; Huang, Q.; Du, X.; Tian, M.; Liu, L.; Xin, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Dynamic recovery after acute single fine particulate matter exposure in male mice: Effect on lipid deregulation and cardiovascular alterations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 414, 125504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Hu, D.; Li, L.; Cui, L.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Deng, F.; Guo, X. Joint effect of multiple air pollutants on lipid profiles in obese and normal-weight young adults: The key role of ozone. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292, 118247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Su, Y.; Jing, R.; Qi, J.; Qi, X.; Xie, Z.; Cui, B. Acute and lag effects of ambient fine particulate matter on the incidence of dyslipidemia in Chengdu, China: A time-series study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 37919–37929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roswall, N.; Poulsen, A.H.; Hvidtfeldt, U.A.; Hendriksen, P.F.; Boll, K.; Halkjær, J.; Ketzel, M.; Brandt, J.; Frohn, L.M.; Christensen, J.H.; et al. Exposure to ambient air pollution and lipid levels and blood pressure in an adult, Danish cohort. Environ. Res. 2023, 220, 115179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Hou, L.; Zhu, S.; Yi, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, F.; Li, X.; Pan, A.; Song, P. Lipid Variability and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases and All-Cause Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.-Y.; Bloom, M.S.; Markevych, I.; Qian, Z.; Vaughn, M.G.; Cummings-Vaughn, L.A.; Li, S.; Chen, G.; Bowatte, G.; Perret, J.L.; et al. Exposure to ambient air pollution and blood lipids in adults: The 33 Communities Chinese Health Study. Environ. Int. 2018, 119, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-N.; Ha, B.; Seog, W.; Hwang, I.-U. Long-term exposure to air pollution and the blood lipid levels of healthy young men. Environ. Int. 2022, 161, 107119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Hansell, A.L.; Blangiardo, M.; Burton, P.R.; De Hoogh, K.; Doiron, D.; Fortier, I.; Gulliver, J.; Hveem, K.; Mbatchou, S.; et al. Long-term exposure to road traffic noise, ambient air pollution, and cardiovascular risk factors in the HUNT and lifelines cohorts. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2290–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupcikova, Z.; Fecht, D.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Clark, C.; Cai, Y.S. Road traffic noise and cardiovascular disease risk factors in UK Biobank. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 2072–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yuan, X.; Ni, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ke, P.; Xu, M.; Zhao, Z. Associations between residential greenness and blood lipids in Chinese elderly population. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2022, 45, 2329–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skutecki, R.; Cymes, I.; Dragańska, E.; Glińska-Lewczuk, K.; Buciński, A.; Drozdowski, M.; Romaszko, J. Are the Levels of Lipid Parameters Associated with Biometeorological Conditions? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadif, R.; Goldberg, S.; Gourmelen, J.; Ozguler, A.; Goldberg, M.; Zins, M.; Henny, J. Seasonal variations of lipid profiles in a French cohort. Atherosclerosis 2019, 286, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, L.; Zheng, P.; Jia, G. Application of wearable devices for monitoring cardiometabolic dysfunction under the exposome paradigm. Chronic Dis. Transl. Med. 2023, 9, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lin, Y.; Yang, H.; Ling, W.; Liu, L.; Zhang, W.; Lu, D.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, G. Internal Exposure and Distribution of Airborne Fine Particles in the Human Body: Methodology, Current Understandings, and Research Needs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 6857–6869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, Q. Prospects for ozone pollution control in China: An epidemiological perspective. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Lyu, X.; Cheng, H.; Ling, Z.; Guo, H. Overview on the spatial–temporal characteristics of the ozone formation regime in China. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2019, 21, 916–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, E.S.; Fedak, K.M.; Good, N.; Balmes, J.; Brook, R.D.; Clark, M.L.; Cole-Hunter, T.; Devlin, R.B.; L’orange, C.; Luckasen, G.; et al. Acute differences in blood lipids and inflammatory biomarkers following controlled exposures to cookstove air pollution in the STOVES study. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2022, 32, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Fu, Y.; Lai, Z. Investigation of Health of Workers Occupationally Exposed to Cooking Oil Fume. J. Environ. Health 2005, 22, 366–368. [Google Scholar]
- Dehghani, S.; Yousefi, S.; Oskoei, V.; Tazik, M.; Moradi, M.S.; Shaabani, M.; Vali, M. Ecological study on household air pollution exposure and prevalent chronic disease in the elderly. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packard, C.J.; Boren, J.; Taskinen, M.-R. Causes and Consequences of Hypertriglyceridemia. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Yang, H.; Song, B.-L. Mechanisms and regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarese, E.P.; Robinson, J.G.; Kowalewski, M.; Kołodziejczak, M.; Andreotti, F.; Bliden, K.; Tantry, U.; Kubica, J.; Raggi, P.; Gurbel, P.A. Faculty Opinions recommendation of Association Between Baseline LDL-C Level and Total and Cardiovascular Mortality after LDL-C Lowering: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2018, 319, 1566–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zeng, F.-F.; Liu, Z.-M.; Zhang, C.-X.; Ling, W.-H.; Chen, Y.-M. Effects of blood triglycerides on cardiovascular and all-cause mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 61 prospective studies. Lipids Health Dis. 2013, 12, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, E.; Kong, S.Y.; Ro, Y.S.; Ryu, H.H.; Shin, S.D. Serum Cholesterol Levels and Risk of Cardiovascular Death: A Systematic Review and a Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, J.; Xiao, G.; Chen, S.; Wang, H. Urban particulate air pollution linked to dyslipidemia by modification innate immune cells. Chemosphere 2023, 319, 138040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Cai, J.; Kan, H. Response by Li et al to Letters Regarding Article, “Particulate Matter Exposure and Stress Hormone Levels: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Crossover Trial of Air Purification”. Circulation 2017, 136, 1209–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangwar, R.S.; Bevan, G.H.; Palanivel, R.; Das, L.; Rajagopalan, S. Oxidative stress pathways of air pollution mediated toxicity: Recent insights. Redox Biol. 2020, 34, 101545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Pérez, R.D.; Taborda, N.A.; Gómez, D.M.; Narvaez, J.F.; Porras, J.; Hernandez, J.C. Inflammatory effects of particulate matter air pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 42390–42404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Solt, A.C.; Henríquez-Roldán, C.; Torres-Jardón, R.; Nuse, B.; Herritt, L.; Villarreal-Calderón, R.; Osnaya, N.; Stone, I.; García, R.; et al. Long-term air pollution exposure is associated with neuroinflammation, an altered innate immune response, disruption of the blood-brain barrier, ultrafine particulate deposition, and accumulation of amyloid beta-42 and alpha-synuclein in children and young adults. Toxicol. Pathol. 2008, 36, 289–310. [Google Scholar]
- Della Guardia, L.; Shin, A.C. White and brown adipose tissue functionality is impaired by fine particulate matter (PM2.5) exposure. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 100, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.D.; Corkey, B.E.; Istfan, N.W.; Apovian, C.M. Hyperinsulinemia: An Early Indicator of Metabolic Dysfunction. J. Endocr. Soc. 2019, 3, 1727–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campolim, C.M.; Weissmann, L.; de Oliveira Ferreira, C.K.; Zordão, O.P.; Dornellas, A.P.S.; de Castro, G.; Zanotto, T.M.; Boico, V.F.; Quaresma, P.G.F.; Lima, R.P.A.; et al. Short-term exposure to air pollution (PM(2.5)) induces hypothalamic inflammation, and long-term leads to leptin resistance and obesity via Tlr4/Ikbke in mice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, J.; Yang, X.; Bigambo, F.M.; Snijders, A.M.; Wang, X.; Hu, W.; Lv, W.; Xia, Y. The effect of ambient ozone exposure on three types of diabetes: A meta-analysis. Environ. Health 2023, 22, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Guardia, L.; Wang, L. Fine particulate matter induces adipose tissue expansion and weight gain: Pathophysiology. Obes. Rev. 2023, 24, e13552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberzettl, P.; O’toole, T.E.; Bhatnagar, A.; Conklin, D.J. Exposure to Fine Particulate Air Pollution Causes Vascular Insulin Resistance by Inducing Pulmonary Oxidative Stress. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 1830–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Xu, X.; Bai, Y.; Wang, T.-Y.; Rao, X.; Wang, A.; Sun, L.; Ying, Z.; Gushchina, L.; Maiseyeu, A.; et al. Air Pollution–Mediated Susceptibility to Inflammation and Insulin Resistance: Influence of CCR2 Pathways in Mice. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, M.; Yao, Z. Recent progress in understanding protein and lipid factors affecting hepatic VLDL assembly and secretion. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihailescu, D.V.; Vora, A.; Mazzone, T. Lipid Effects of Endocrine Medications. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2011, 13, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, G.; Chen, R.; Li, R.; Wang, H.; Jiang, A.; Li, Z.; Kong, L.; Fonken, L.K.; Rajagopalan, S.; et al. Central IKK2 Inhibition Ameliorates Air Pollution-Mediated Hepatic Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Dysfunction in Mice With Type II Diabetes. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 164, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poursafa, P.; Kamali, Z.; Fraszczyk, E.; Boezen, H.M.; Vaez, A.; Snieder, H. DNA methylation: A potential mediator between air pollution and metabolic syndrome. Clin. Epigenetics 2022, 14, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, R.; Cai, J.; Cui, X.; Huang, N.; Kan, H. Short-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution and genome-wide DNA methylation: A randomized, double-blind, crossover trial. Environ. Int. 2018, 120, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopalan, S.; Al-Kindi, S.G.; Brook, R.D. Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Disease: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 2054–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brook, R.D.; Rajagopalan, S.; PopeIII, C.A.; Brook, J.R.; Bhatnagar, A.; Diez-Roux, V.; Holguin, F.; Hong, Y.; Luepker, R.V.; Mittleman, M.A.; et al. Particulate matter air pollution and cardiovascular disease: An update to the scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2010, 121, 2331–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.-Y.; Guo, Y.; Markevych, I.; Qian, Z.; Bloom, M.S.; Heinrich, J.; Dharmage, S.C.; Rolling, C.A.; Jordan, S.S.; Komppula, M.; et al. Association of Long-term Exposure to Ambient Air Pollutants With Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease in China. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e190318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.S.V.; Lee, K.K.; McAllister, D.A.; Hunter, A.; Nair, H.; Whiteley, W.; Langrish, J.P.; Newby, D.E.; Mills, N.L. Short term exposure to air pollution and stroke: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2015, 350, h1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.; Lin, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, J.; Lin, H. Long-term exposure to ambient fine particulate matter chemical composition and in-hospital case fatality among patients with stroke in China. Lancet Reg. Health-West. Pac. 2023, 32, 100679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, R.; Yin, P.; Meng, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, C.; Ji, J.S.; Qiu, Y.; Kan, H.; et al. Long-term exposure to ozone and cardiovascular mortality in China: A nationwide cohort study. Lancet Planet Health 2022, 6, e496–e503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouimet, M.; Barrett, T.J.; Fisher, E.A. HDL and Reverse Cholesterol Transport. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1505–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rader, D.J.; Hovingh, G.K. HDL and cardiovascular disease. Lancet 2014, 384, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghi, S.; Elkind, M.S. Lipids and Cerebrovascular Disease: Research and Practice. Stroke 2015, 46, 3322–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Guo, Y.; Nima, Q.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lu, R.; Baimayangji; Ma, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xu, H.; et al. Exposure to air pollution is associated with an increased risk of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Cao, W.; Yu, S.; Zhan, S.; Sun, F. Long-term exposure to air pollution, habitual physical activity and risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A prospective cohort study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 235, 113440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, J.; Xia, H.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, G.; Cai, Y. Long-Term Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter and the Risk of Chronic Liver Diseases: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Liang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Sun, Z.; Duan, J. Melatonin Alleviates PM(2.5)-Induced Hepatic Steatosis and Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease in ApoE(-/-) Mice. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 8688643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Chen, L.; Bennett, E.; Wheeler, A.J.; Southam, K.; Yen, S.; Johnston, F.; Zosky, G.R. Can Maternal Exposure to Air Pollution Affect Post-Natal Liver Development? Toxics 2023, 11, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Chen, R.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Q.; Li, R.; Gu, W.; Zhong, M.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.-C.; Sun, Q.; et al. Lipid metabolic adaption to long-term ambient PM(2.5) exposure in mice. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heeren, J.; Scheja, L. Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and lipoprotein metabolism. Mol. Metab. 2021, 50, 101238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFilippis, A.P.; Blaha, M.J.; Martin, S.S.; Reed, R.M.; Jones, S.R.; Nasir, K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Budoff, M.J. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and serum lipoproteins: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2013, 227, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, A.J.; Pinyol, M.; Solà, E.; Catalan, M.; Cofán, M.; Herreras, Z.; Amigó, N.; Gilabert, R.; Sala-Vila, A.; Ros, E.; et al. Relationship between noninvasive scores of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nuclear magnetic resonance lipoprotein abnormalities: A focus on atherogenic dyslipidemia. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2017, 11, 551–561.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duell, P.B.; Welty, F.K.; Miller, M.; Chait, A.; Hammond, G.; Ahmad, Z.; Cohen, D.E.; Horton, J.D.; Pressman, G.S.; Toth, P.P.; et al. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Cardiovascular Risk: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2022, 42, e168–e185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, J.D.; Sparks, C.E.; Adeli, K. Selective Hepatic Insulin Resistance, VLDL Overproduction, and Hypertriglyceridemia. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 2104–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phung, T.L.; Roncone, A.; Jensen, K.L.d.M.; Sparks, C.E.; Sparks, J.D. Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Activity Is Necessary for Insulin-dependent Inhibition of Apolipoprotein B Secretion by Rat Hepatocytes and Localizes to the Endoplasmic Reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 30693–30702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparks, J.D.; Phung, T.L.; Bolognino, M.; Sparks, C.E. Insulin-mediated inhibition of apolipoprotein B secretion requires an intracellular trafficking event and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation: Studies with brefeldin A and wortmannin in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Biochem. J. 1996, 313, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfrum, C.; Stoffel, M. Coactivation of Foxa2 through Pgc-1beta promotes liver fatty acid oxidation and triglyceride/VLDL secretion. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Li, C.; Zhao, F.; Zhu, J.; Wang, S.; Sun, G. The Association between Childhood Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution and Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Lu, X.; Liu, F.; Gu, D. Ambient air pollution and body weight status in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, R.; Amemiya, T.; Yoshino, M.; Komori, T.; Shibata, N.; Hirata, Y. Adverse effects of obesity on lipid and lipoprotein levels in the patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes in the young. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 1990, 10, S225–S230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Li, Z.; Guo, L.; Zheng, L.; Yu, S.; Yang, H.; Zou, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L.; et al. An update on overweight and obesity in rural Northeast China: From lifestyle risk factors to cardiometabolic comorbidities. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Shi, J.; Ma, Y.; Yu, N.; Zheng, P.; Chen, Z.; Wang, T.; Jia, G. Association between Air Pollution and Lipid Profiles. Toxics 2023, 11, 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110894
Zhang Y, Shi J, Ma Y, Yu N, Zheng P, Chen Z, Wang T, Jia G. Association between Air Pollution and Lipid Profiles. Toxics. 2023; 11(11):894. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110894
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yi, Jiaqi Shi, Ying Ma, Nairui Yu, Pai Zheng, Zhangjian Chen, Tiancheng Wang, and Guang Jia. 2023. "Association between Air Pollution and Lipid Profiles" Toxics 11, no. 11: 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110894
APA StyleZhang, Y., Shi, J., Ma, Y., Yu, N., Zheng, P., Chen, Z., Wang, T., & Jia, G. (2023). Association between Air Pollution and Lipid Profiles. Toxics, 11(11), 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110894