Removal of Particulate Matter by a Non-Powered Brush Filter Using Electrostatic Forces
Abstract
:1. Introduction
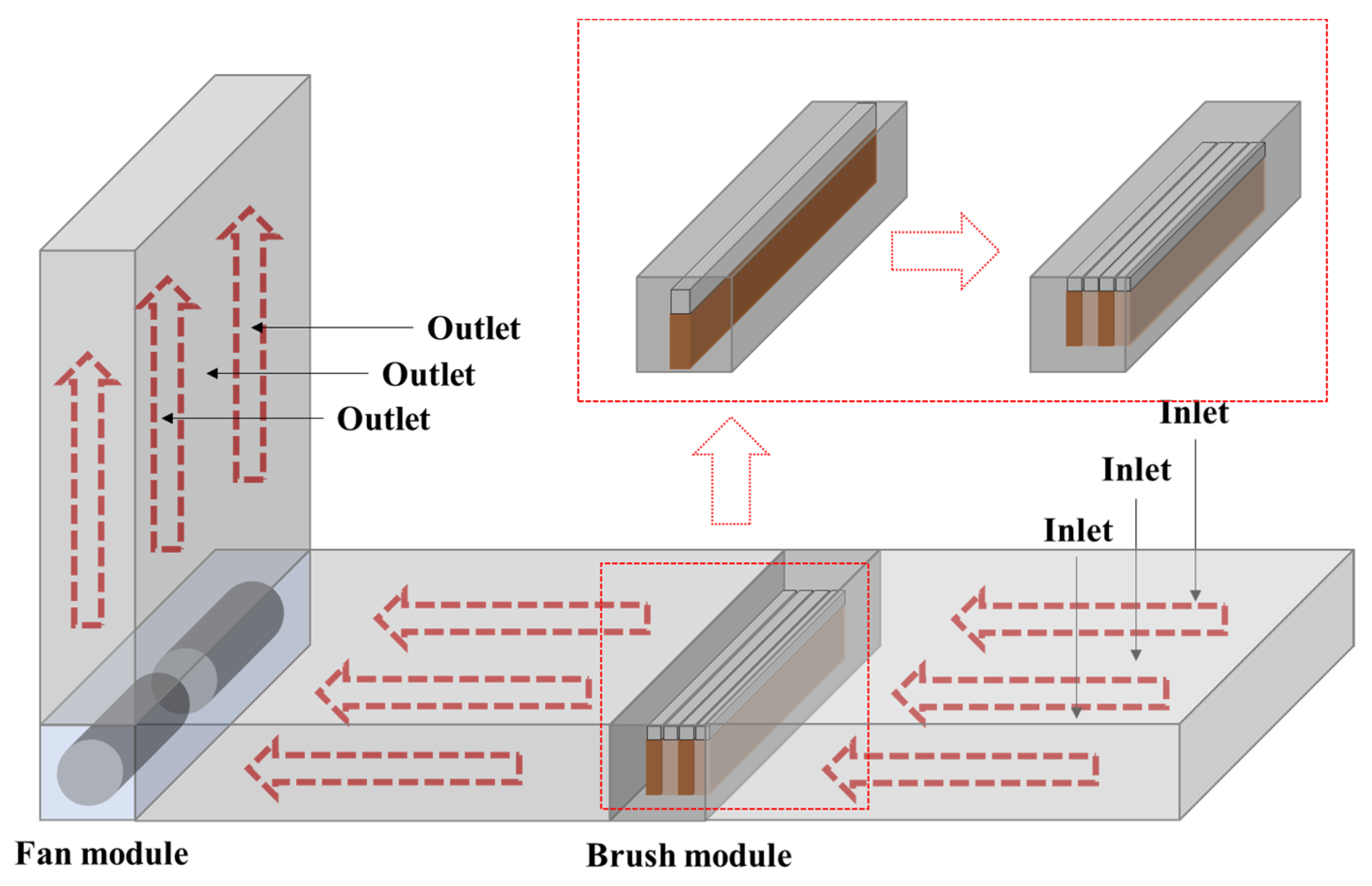
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Measurement of Electrostatic Force According to Brush Material
2.2. Removal Performance of Particulate Matter according to Brush Filter Material
2.3. Removal Performance of Particulate Matter according to Brush Filter Density
2.4. Calculation of the Brush Filter Replacement Cycle
3. Results
3.1. Electrostatic Force Generation according to Brush Material
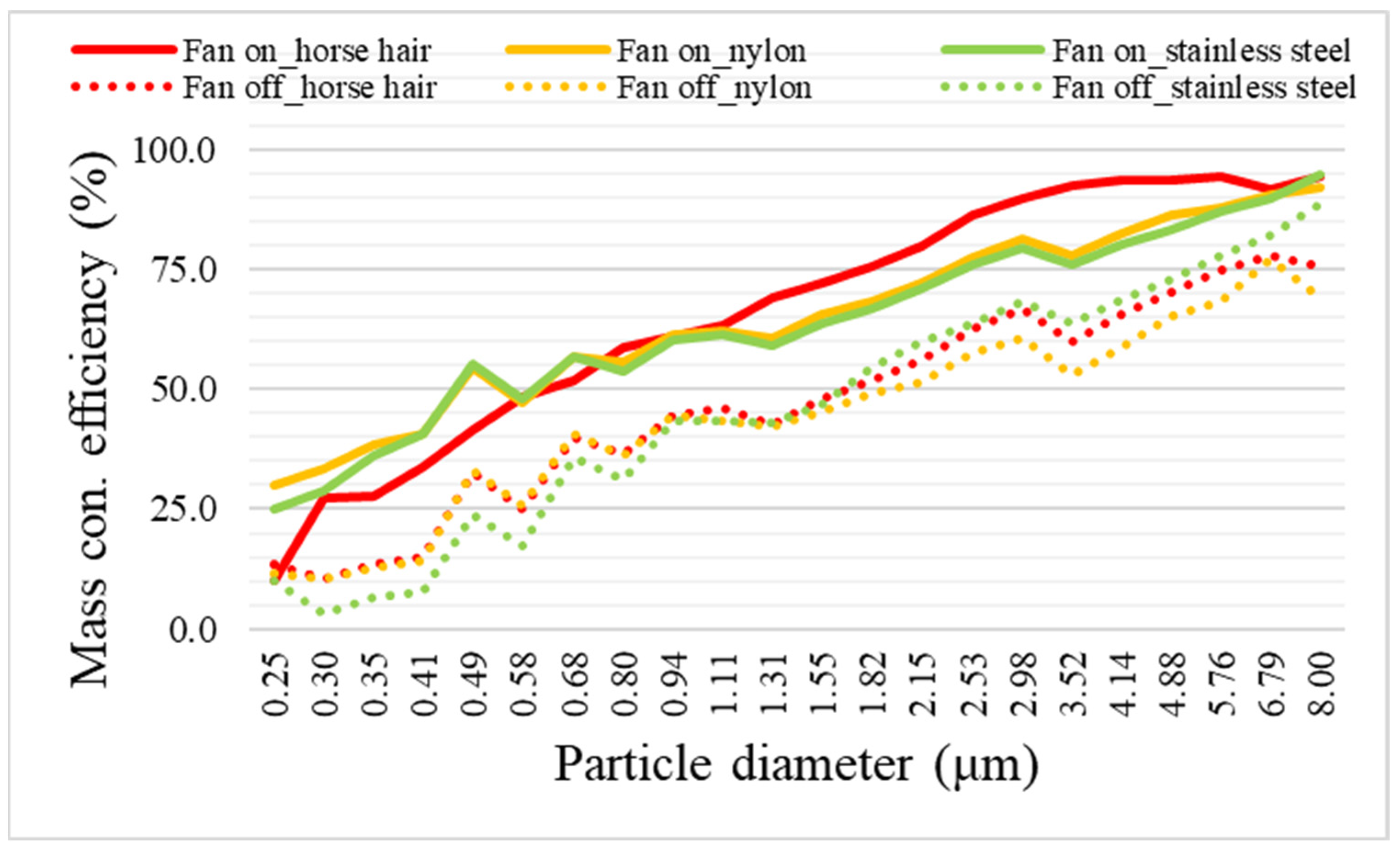
3.2. Particulate Matter Removal Performance according to Brush Filter Material
3.3. Particulate Matter Removal Performance according to Brush Filter Density
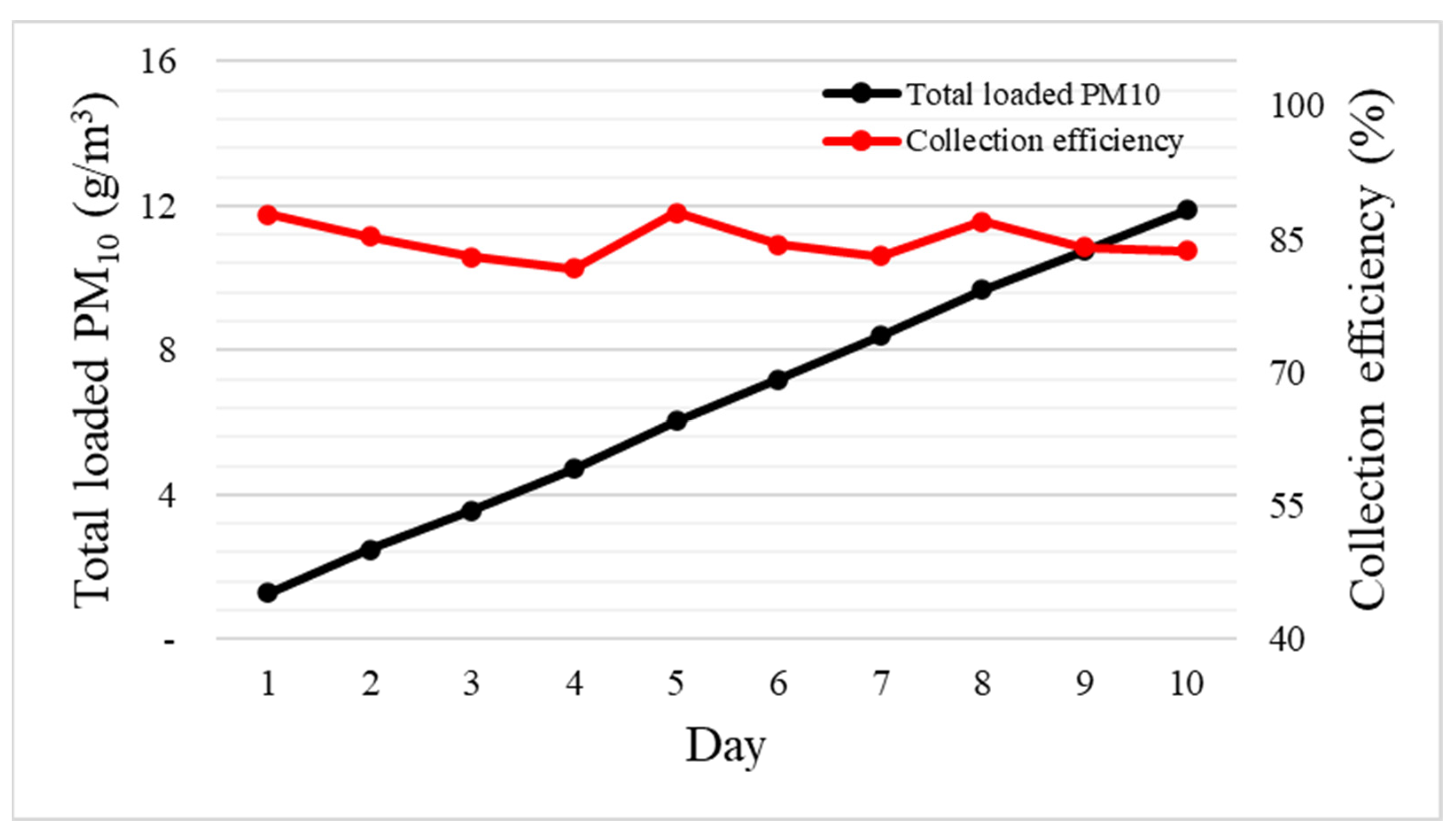
3.4. Calculation of the Brush Filter Replacement Cycle
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dockery, D.W.; Pope, C.A., III; Xu, X.; Spengler, J.D.; Ware, J.H.; Fay, M.E.; Ferris, B.G., Jr.; Speizer, F.E. An Association between Air Pollution and Mortality in Six U.S. Cities. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A.; Bates, D.V.; Raizenne, M.E. Health effects of particulate air pollution: Time for reassessment? Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.M. Studies of the source apportionment of airborne particulate matter in the United Kingdom. J. Aerosol Sci. 2000, 31, 106–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, R.; Ma, R.; Jerrett, M.; Goldberg, M.S.; Cakmak, S.; Pope, C.A.; Krewski, D. The spatial association between community air pollution and mortality: A new method of analyzing correlated geographic cohort data. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109 (Suppl. S3), 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.; Kwon, S.-B.; Cho, Y. Development and calibration of a particulate matter measurement device with wireless sensor network function. Int. J. Environ. Monit. Anal. 2013, 1, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.; Jang, Y.; Versoza, M.; Kim, G.; Park, D. A New Method of Removing Fine Particulates Using an Electrostatic Force. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittelson, D.B. Engines and nanoparticles: A review. J. Aerosol Sci. 1998, 29, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.; Figliozzi, M.; Monsere, C.M. Air Quality at Bus Stops: Empirical Analysis of Exposure to Particulate Matter at Bus Stop Shelters. Transp. Res. Rec. 2012, 2270, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, R.D.; Brook, J.R.; Urch, B.; Vincent, R.; Rajagopalan, S.; Silverman, F. Inhalation of Fine Particulate Air Pollution and Ozone Causes Acute Arterial Vasoconstriction in Healthy Adults. Circulation 2002, 105, 1534–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibald-Mulli, A.; Timonen, K.L.; Peters, A.; Heinrich, J.; Wölke, G.; Lanki, T.; Buzorius, G.; Kreyling, W.G.; de Hartog, J.; Hoek, G.; et al. Effects of particulate air pollution on blood pressure and heart rate in subjects with cardiovascular disease: A multicenter approach. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc, L.T.N.; Kim, M.; Bui, V.K.H.; Park, D.; Lee, Y.-C. Particulate Matter Exposure of Passengers at Bus Stations: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.O.; Thundiyil, J.G.; Stolbach, A. Clearing the Air: A Review of the Effects of Particulate Matter Air Pollution on Human Health. J. Med. Toxicol. 2012, 8, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, N.; Olivieri, O.; Girelli, D. Air particulate matter and cardiovascular disease: A narrative review. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 24, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styer, P.; McMillan, N.; Gao, F.; Davis, J.; Sacks, J. Effect of outdoor airborne particulate matter on daily death counts. Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samet, J.M.; Dominici, F.; Curriero, F.C.; Coursac, I.; Zeger, S.L. Fine particulate air pollution and mortality in 20 US cities, 1987–1994. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1742–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; He, G.; Chiu, K.Y.; Fan, M.; Liu, C.; Xue, A.; Liu, T.; Pan, Y.; Mu, Q.; Zhou, M. Particulate air pollution and mortality in 38 of China’s largest cities: Time series analysis. BMJ 2017, 356, j667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkerton, K.E.; Green, F.H.; Saiki, C.; Vallyathan, V.; Plopper, C.G.; Gopal, V.; Hung, D.; Bahne, E.B.; Lin, S.S.; Ménache, M.G.; et al. Distribution of particulate matter and tissue remodeling in the human lung. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocbach, A.; Herseth, J.I.; Låg, M.; Refsnes, M.; Schwarze, P.E. Particles from wood smoke and traffic induce differential pro-inflammatory response patterns in co-cultures. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 232, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Gao, D.; Liao, F.; Zhou, F.; Wang, X. The health effects of ambient PM2.5 and potential mechanisms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 128, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, Y.; Heo, J.; Kim, S.-W.; Jeon, K.; Yi, S.-M.; Hopke, P.K. Source apportionment of PM2.5 in Seoul, South Korea and Beijing, China using dispersion normalized PMF. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korea Transportation Safety Authority. 2020 Public transportation status survey-Report of Overall Results-; Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport: Sejong City, Republic of Korea, 2020.
- Li, S.; Chen, S.; Zhu, L.; Chen, X.; Yao, C.; Shen, X. Concentrations and risk assessment of selected monoaromatic hydrocarbons in buses and bus stations of Hangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2004–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Zhao, W.; Yan, X.; Shu, T.; Xiong, Q.; Chen, F. Pollution Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of Airborne Heavy Metals Collected from Beijing Bus Stations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 9658–9671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Baek, C.M.; Moon, S.-Y.; Jang, D.-H.; Park, H.-M. Analysis of the Effect of Different Types of Roadside Bus Stops on the Characteristics of Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5). Int. J. Highw. Eng. 2019, 21, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.B.; Heo, K.J.; Sin, C.H.; Zhao, Y.; Lee, B.U. A Study on the Shapes of Aerosol Particles at a Bus Stop in the Eastern Part of Seoul. Part. Aerosol Res. 2016, 12, 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, D.B.; Ray, P.D.; Stinson, A.E.; Park, J. Determinants of exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) for waiting passengers at bus stops. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 5174–5182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Railroad Research Institute. Development of Particulate Matter Reduction System for Bus Station; Ministry of Environment: Sejong City, Republic of Korea, 2021.
- Shin, E.-C.; Ko, J.-H.; Lyeo, H.-K.; Kim, Y.-H. Derivation of a governing rule in triboelectric charging and series from thermoelectricity. Phys. Rev. Res. 2022, 4, 023131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersh, S.; Montgomery, D. Static electrification of filaments: Experimental techniques and results. Text. Res. J. 1955, 25, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henniker, J. Triboelectricity in polymers. Nature 1962, 196, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, P.; He, X.; Dai, G.; Zheng, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, A.C.; Xu, C.; et al. Quantifying the triboelectric series. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Guo, L.; Xue, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, P.; He, X.; Dai, G.; Jiang, P.; et al. Quantifying and understanding the triboelectric series of inorganic non-metallic materials. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, J.A. Clearing the Air: The Importance of Filter Replacement for Welding Fume Extraction Systems. Occup. Health Saf. 2017, 86, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aussawasathien, D.; Teerawattananon, C.; Vongachariya, A. Separation of micron to sub-micron particles from water: Electrospun nylon-6 nanofibrous membranes as pre-filters. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 315, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, K.M.; Park, H.-S.; Bae, G.-N.; Jung, J.H. Antimicrobial nanoparticle-coated electrostatic air filter with high filtration efficiency and low pressure drop. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 533, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Most Positive → Most Negative | Publication Year and Reference |
|---|---|
| wool → nylon → cotton → silk → PVC → PE → PTFE | 1955 |
| nylon → wool → silk → cotton → NR → S → PE → PVC → PTFE | 1962 |
| nylon → wool → silk → paper → cotton → PE → PP → PVC → Si → PTFE | 1987 |
| quartz → nylon → wool → silk → cotton → paper → metals → rubber → PTFE → PVC | 1998 |
| fur → glass → silk → wood → rubber → plastic | 2015 |
| Copy paper → nylon → PP → quartz → PE → PDMS → PTFE → PVC | 2019 |
| wool → PP → silk → nylon→ NR → cellulose → Al → Si → quartz → S → PE → PTFE → PDMS → PVC | 2022 |
| Friction Plate | Flow Velocity (m/s) | Horse Hair (kV) | Nylon (kV) | Stainless Steel (kV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC | 0 | −0.84 ± 0.03 | −0.83 ± 0.01 | −0.57 ± 0.02 |
| 0.6 | −1.58 ± 0.01 | −1.25 ± 0.01 | −0.93 ± 0.01 | |
| 0.8 | −1.68 ± 0.02 | −1.32 ± 0.01 | −0.94 ± 0.01 | |
| 1.0 | −1.78 ± 0.02 | −1.39 ± 0.02 | −0.96 ± 0.01 |
| Horse Hair | Nylon | Stainless | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fan on | Inlet (μg/m3) | 298.2 ± 36.4 | 323.2 ± 176.1 | 307.9 ± 53.4 |
| Outlet (μg/m3) | 53.3 ± 8.5 | 77.4 ± 22.3 | 80.8 ± 11.7 | |
| Efficiency (%) | 82.1 ± 3.4 | 76.1 ± 4.7 | 73.7 ± 4.5 | |
| Fan off | Inlet (μg/m3) | 304.8 ± 39.9 | 305.3 ± 47 | 311.6 ± 36.5 |
| Outlet (μg/m3) | 127.3 ± 25.9 | 141.5 ± 24.8 | 130.8 ± 21.2 | |
| Efficiency (%) | 58.2 ± 8.4 | 53.6 ± 9.2 | 58.0 ± 7.3 | |
| Brush Type | Number of Brushes | Inlet (μg/m3) | Outlet (μg/m3) | Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horse hair | 1 | 298.2 ± 36.4 | 53.3 ± 8.5 | 82.1 ± 3.4 |
| 2 | 319.2 ± 42.8 | 46.9 ± 7.8 | 85.3 ± 2.7 | |
| 3 | 321.6 ± 42.6 | 46.3 ± 7.1 | 85.6 ± 2.5 | |
| 4 | 299.5 ± 41.6 | 32.7 ± 5.2 | 89.1 ± 2.3 | |
| 5 | 325.7 ± 50.6 | 33.8 ± 4.7 | 89.6 ± 2.2 | |
| Nylon | 1 | 323.2 ± 176.1 | 77.4 ± 22.3 | 76.1 ± 4.7 |
| 2 | 309.5 ± 41.8 | 62.0 ± 8.9 | 80.0 ± 4.2 | |
| 3 | 314.6 ± 53.6 | 55.4 ± 8.5 | 82.4 ± 3.5 | |
| 4 | 310.3 ± 46.6 | 40.7 ± 8.2 | 86.9 ± 3.1 | |
| 5 | 332.9 ± 63.6 | 38.9 ± 8.0 | 88.3 ± 3.2 | |
| Stainless steel | 1 | 307.9 ± 53.4 | 80.8 ± 11.7 | 73.7 ± 4.5 |
| 2 | 312.3 ± 43.6 | 71.1 ± 13.4 | 77.2 ± 5.1 | |
| 3 | 316.7 ± 51.1 | 63.2 ± 9.6 | 80.0 ± 3.6 | |
| 4 | 261.3 ± 32.5 | 48.1 ± 9.9 | 81.6 ± 4.2 | |
| 5 | 307.6 ± 179.3 | 55.2 ± 10.7 | 82.1 ± 3.8 |
| Day | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Efficiency (%) | 88 ± 3.2 | 85 ± 3.2 | 83 ± 4.7 | 82 ± 4.0 | 88 ± 3.3 | 84 ± 3.9 | 83 ± 4.0 | 87 ± 3.2 | 84 ± 5.1 | 84 ± 3.9 |
| Day | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Holding capacity (g/m3) | 1.27 | 2.49 | 3.55 | 4.73 | 6.03 | 7.19 | 8.39 | 9.68 | 10.77 | 11.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heo, J.; Lee, J.; Yoon, M.; Park, D. Removal of Particulate Matter by a Non-Powered Brush Filter Using Electrostatic Forces. Toxics 2023, 11, 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110891
Heo J, Lee J, Yoon M, Park D. Removal of Particulate Matter by a Non-Powered Brush Filter Using Electrostatic Forces. Toxics. 2023; 11(11):891. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110891
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeo, Jaeseok, Jooyeon Lee, Minyoung Yoon, and Duckshin Park. 2023. "Removal of Particulate Matter by a Non-Powered Brush Filter Using Electrostatic Forces" Toxics 11, no. 11: 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110891
APA StyleHeo, J., Lee, J., Yoon, M., & Park, D. (2023). Removal of Particulate Matter by a Non-Powered Brush Filter Using Electrostatic Forces. Toxics, 11(11), 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110891







