The Effects and Mechanisms of pH and Dissolved Oxygen Conditions on the Release of Arsenic at the Sediment–Water Interface in Taihu Lake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.2. Experimental Mesocosms
2.3. Sampling and Analysis
2.4. Quality Assurance and Data Analyses
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Basic Physicochemical Properties of Sediments
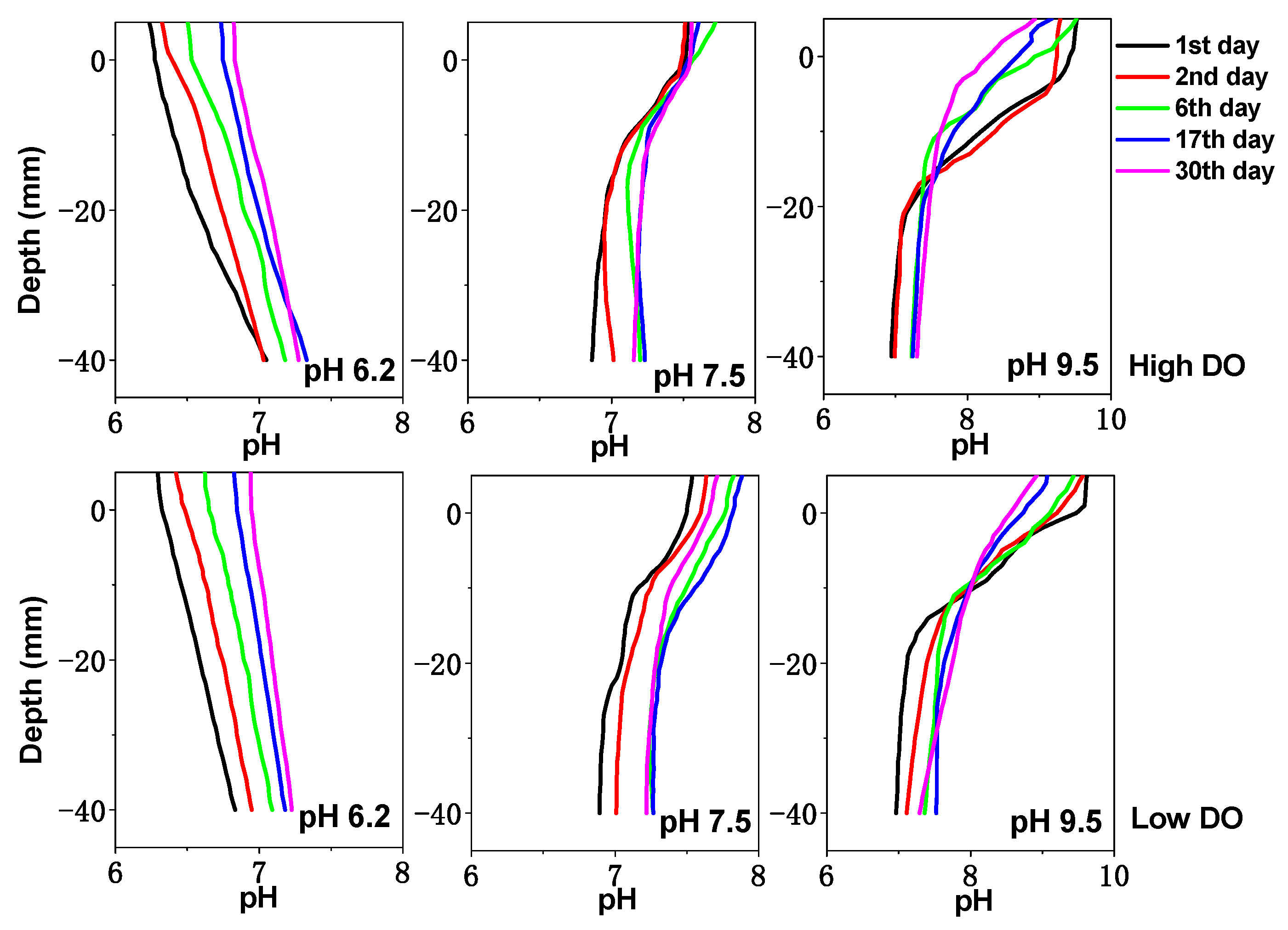
3.2. Effects of Initial pH of Water on Physicochemical Properties of Sediments under Different DO Conditions
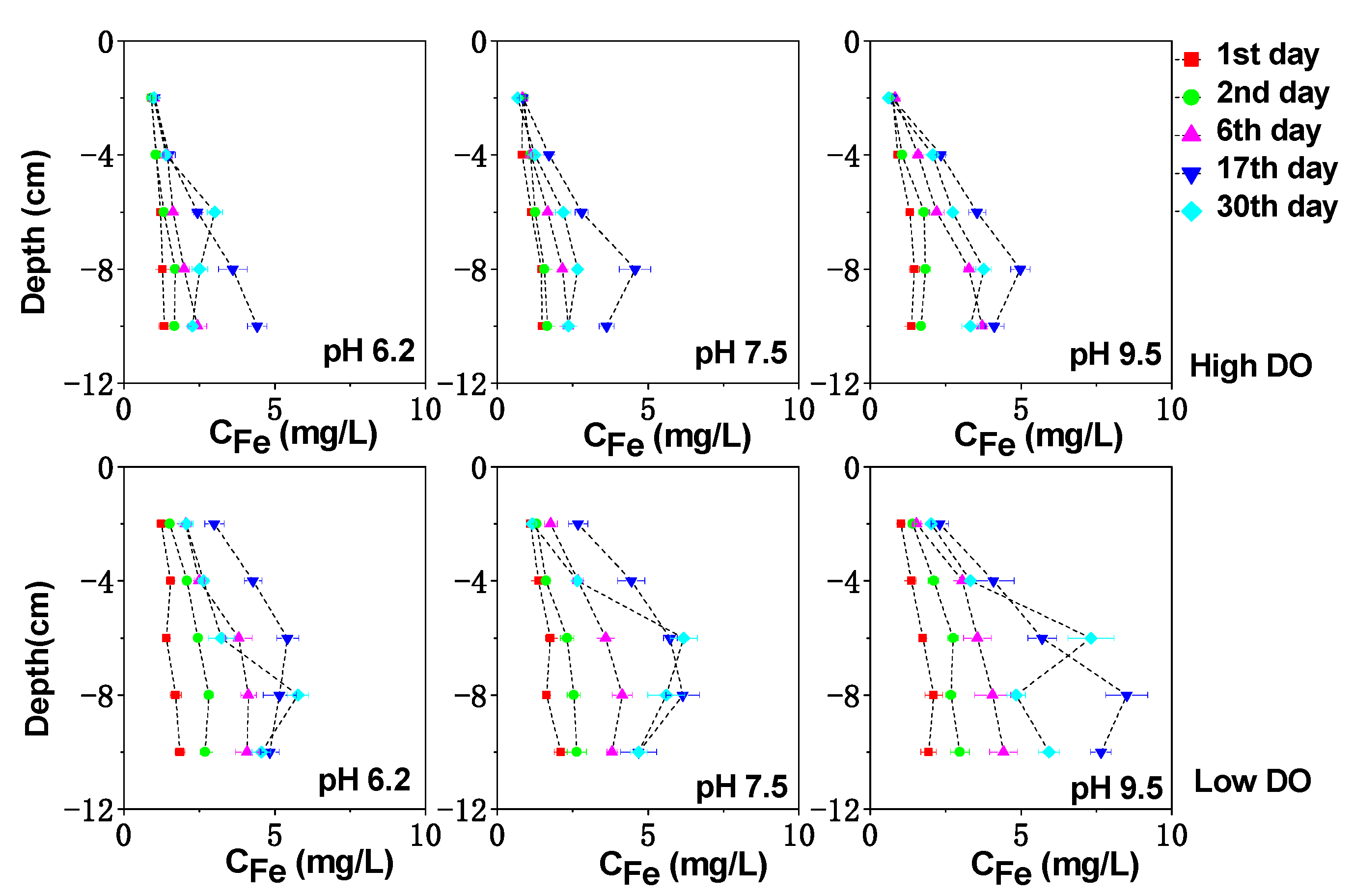
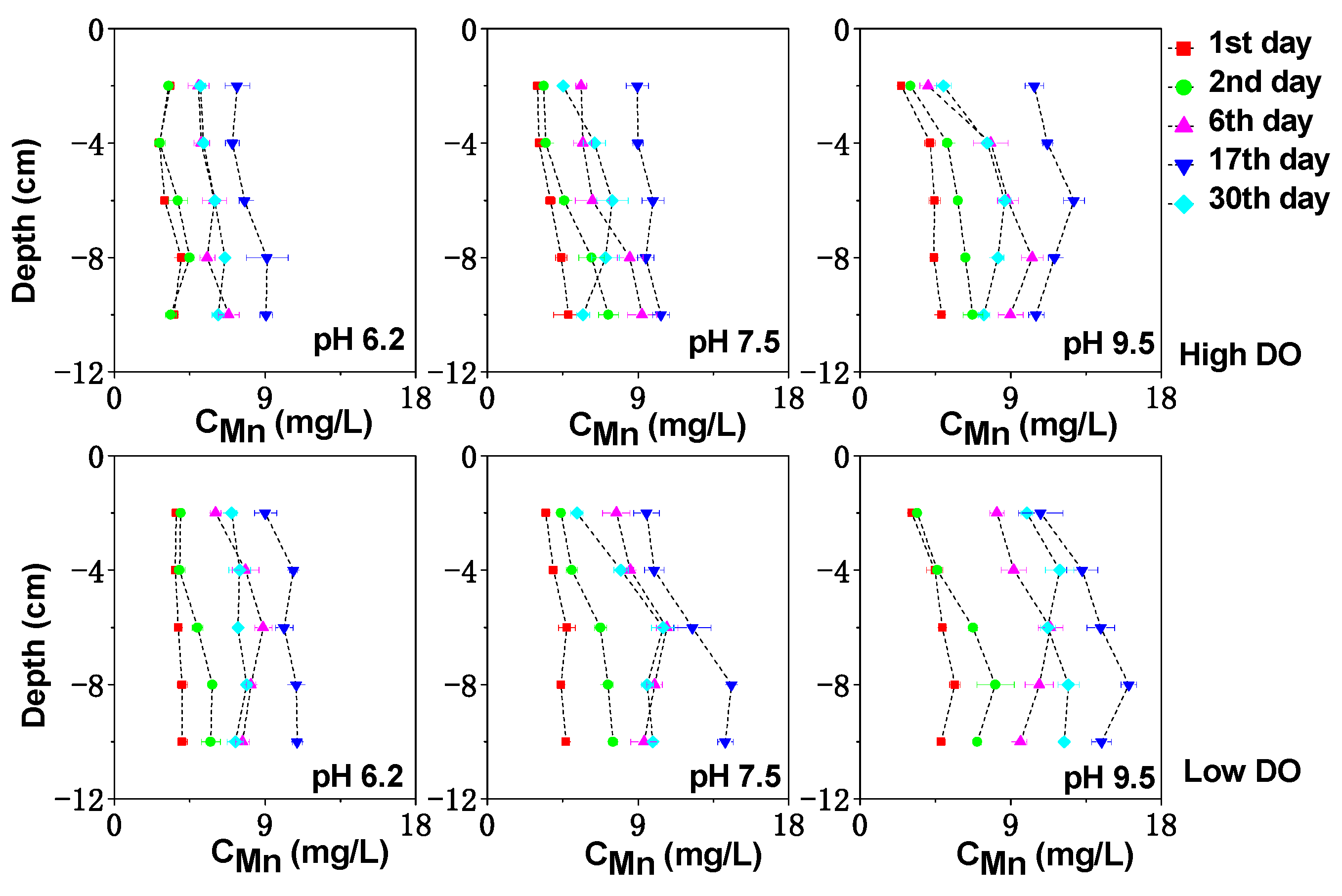
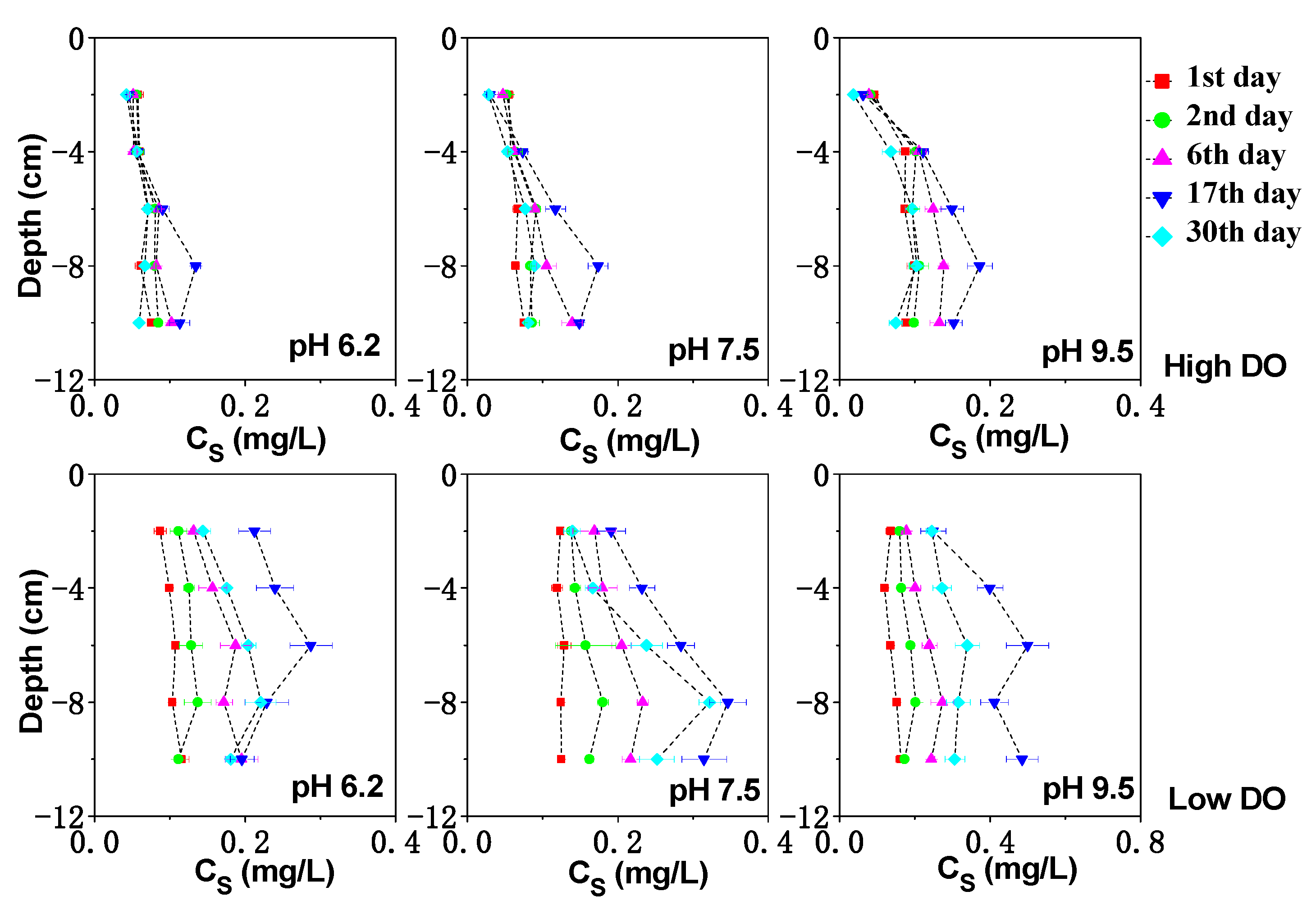
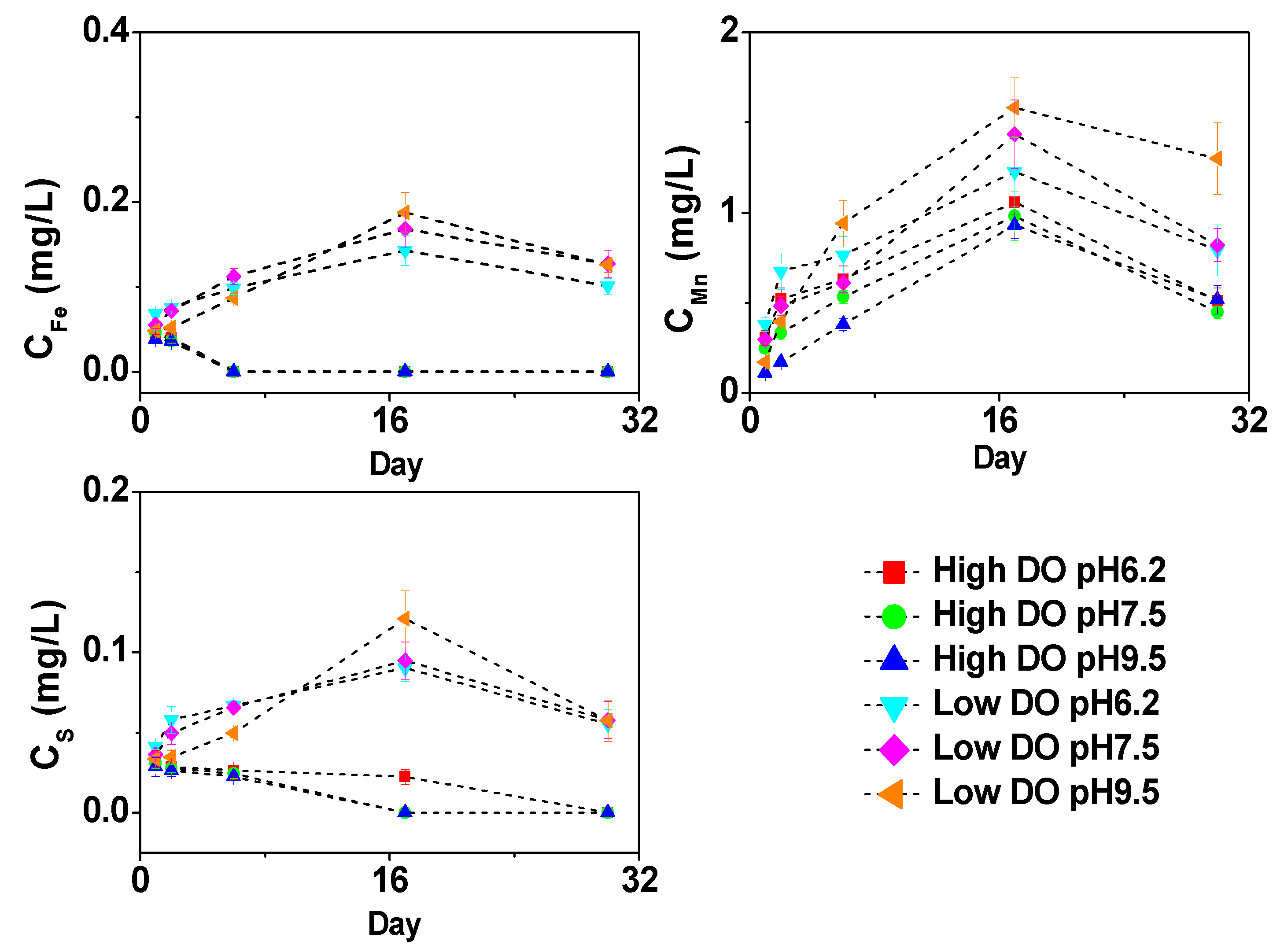
3.3. Effect of Initial pH on Dissolved Fe, Mn and S under Different DO Conditions
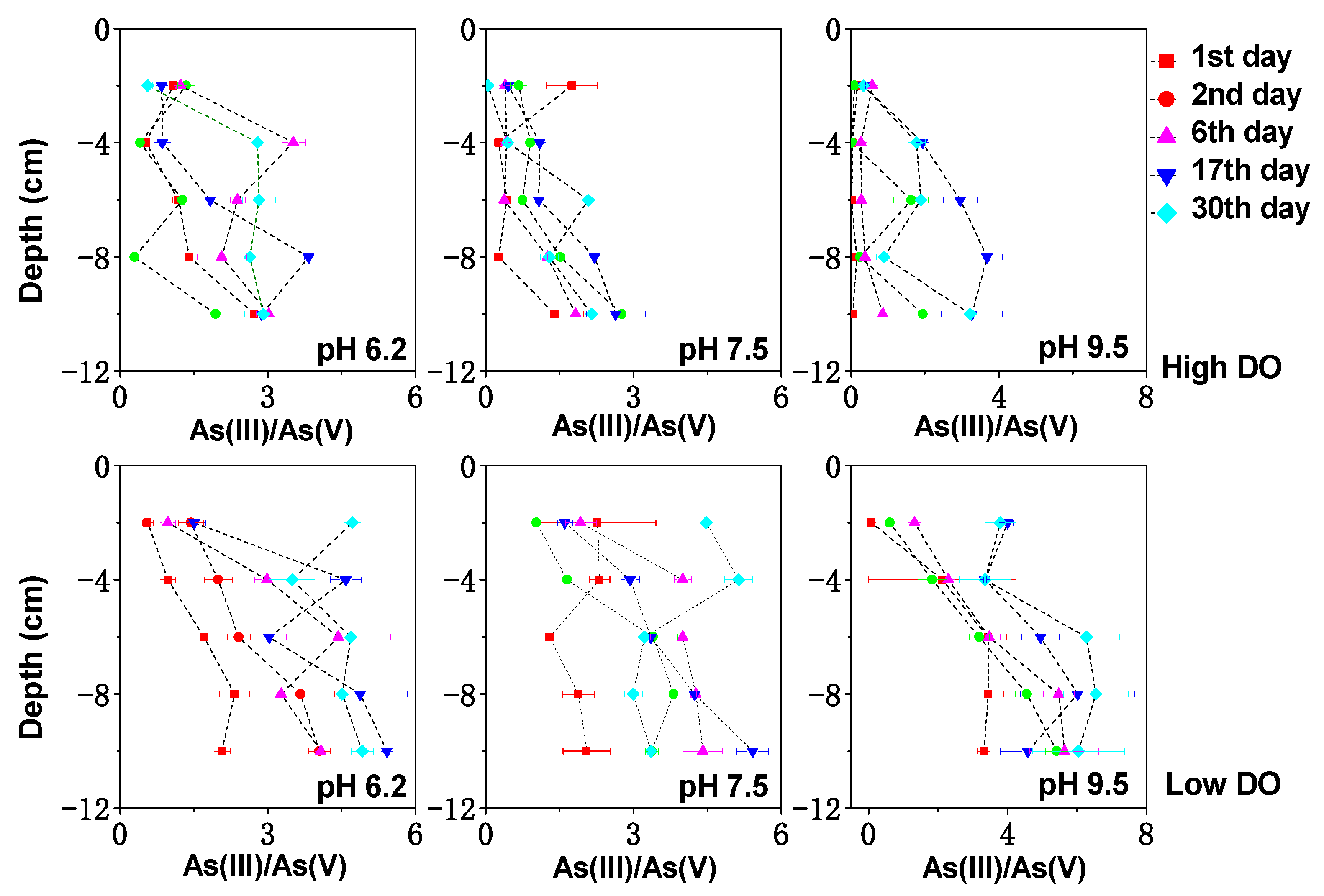
3.4. Effect of Initial pH on Dissolved As in Interstitial Water under Different DO Conditions
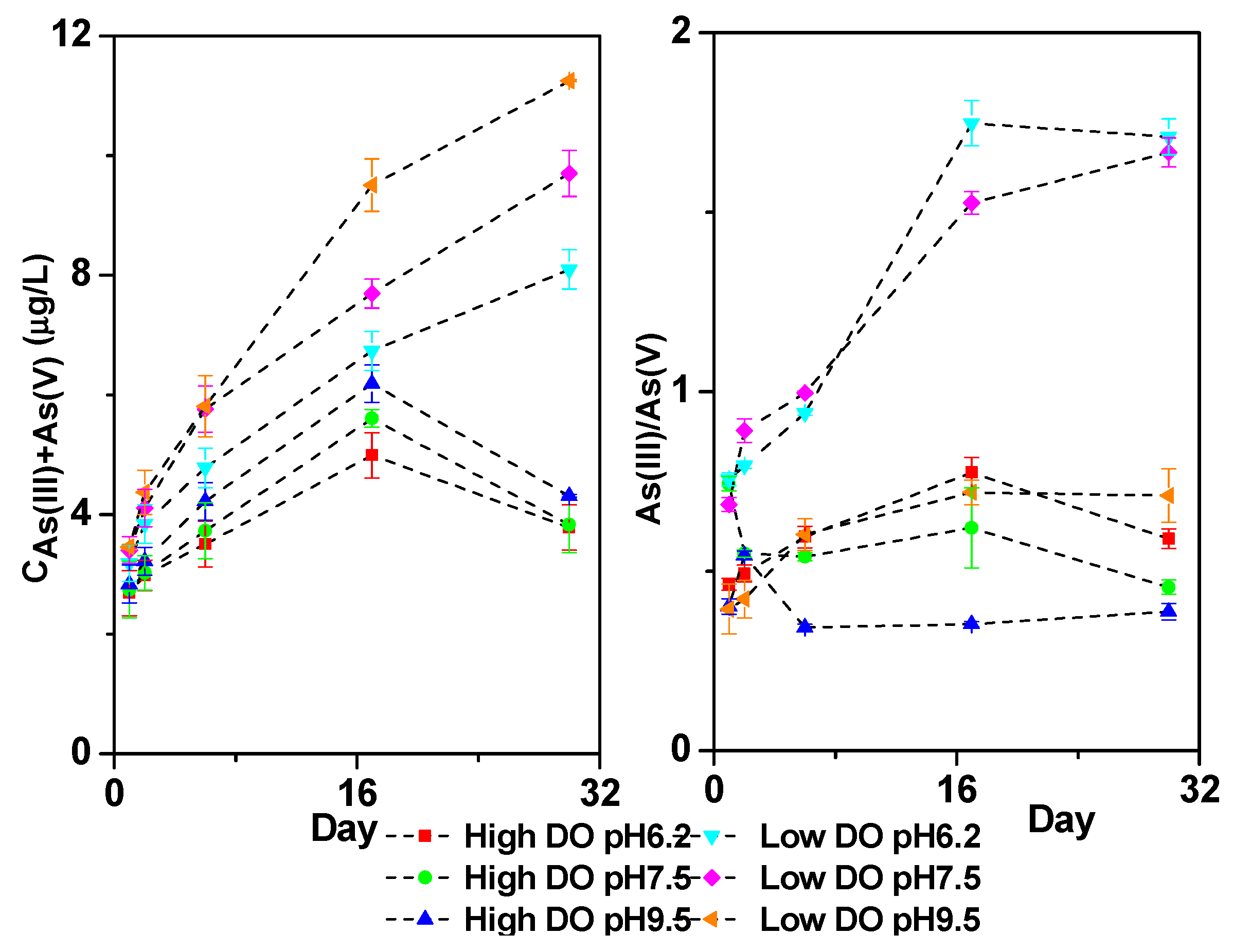
3.5. Effect of Initial pH on Dissolved As in Overlying Water under Different DO Conditions
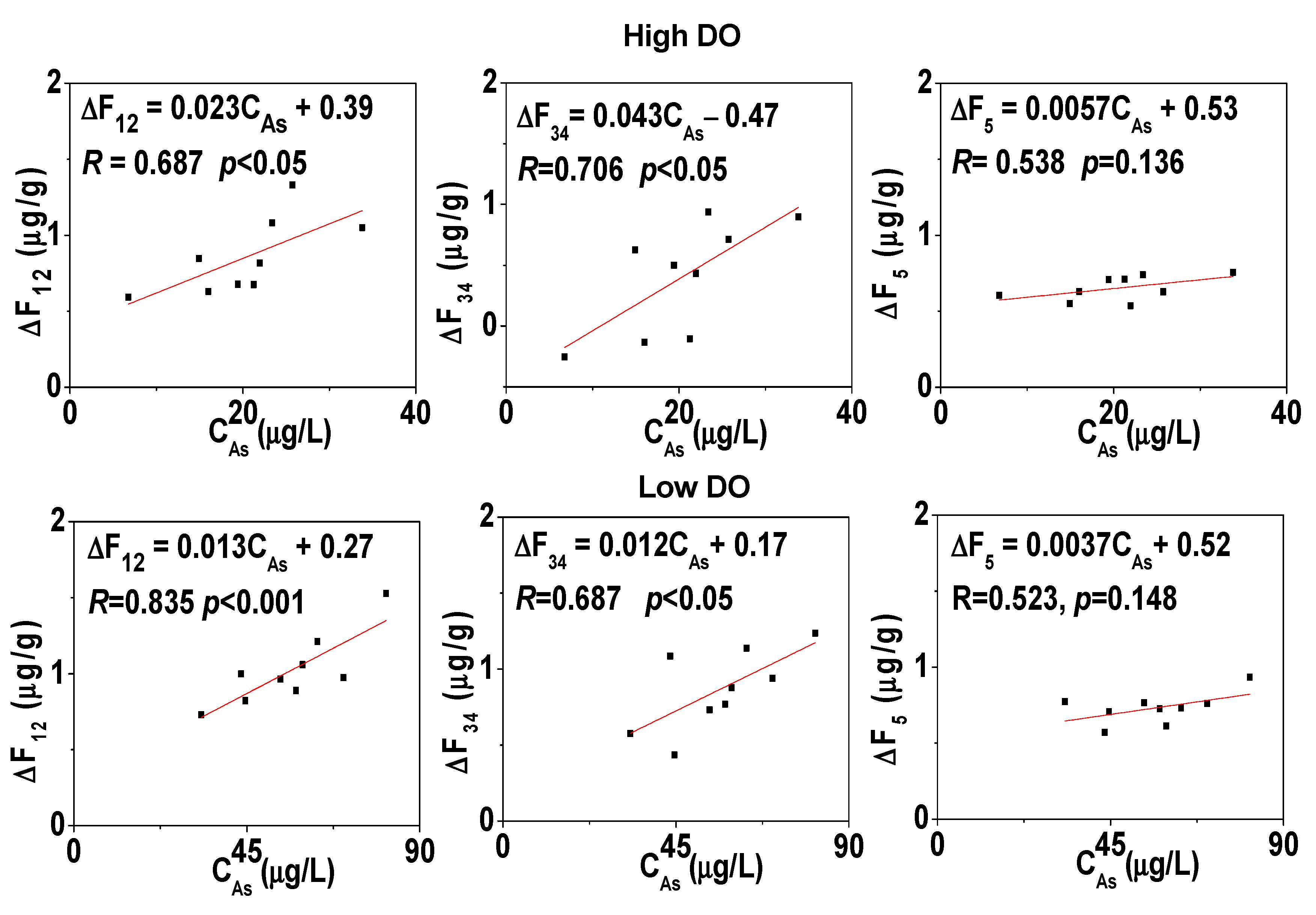
3.6. Cumulative Release Rate of Dissolved As, Fe, Mn, and S in Overlying Water
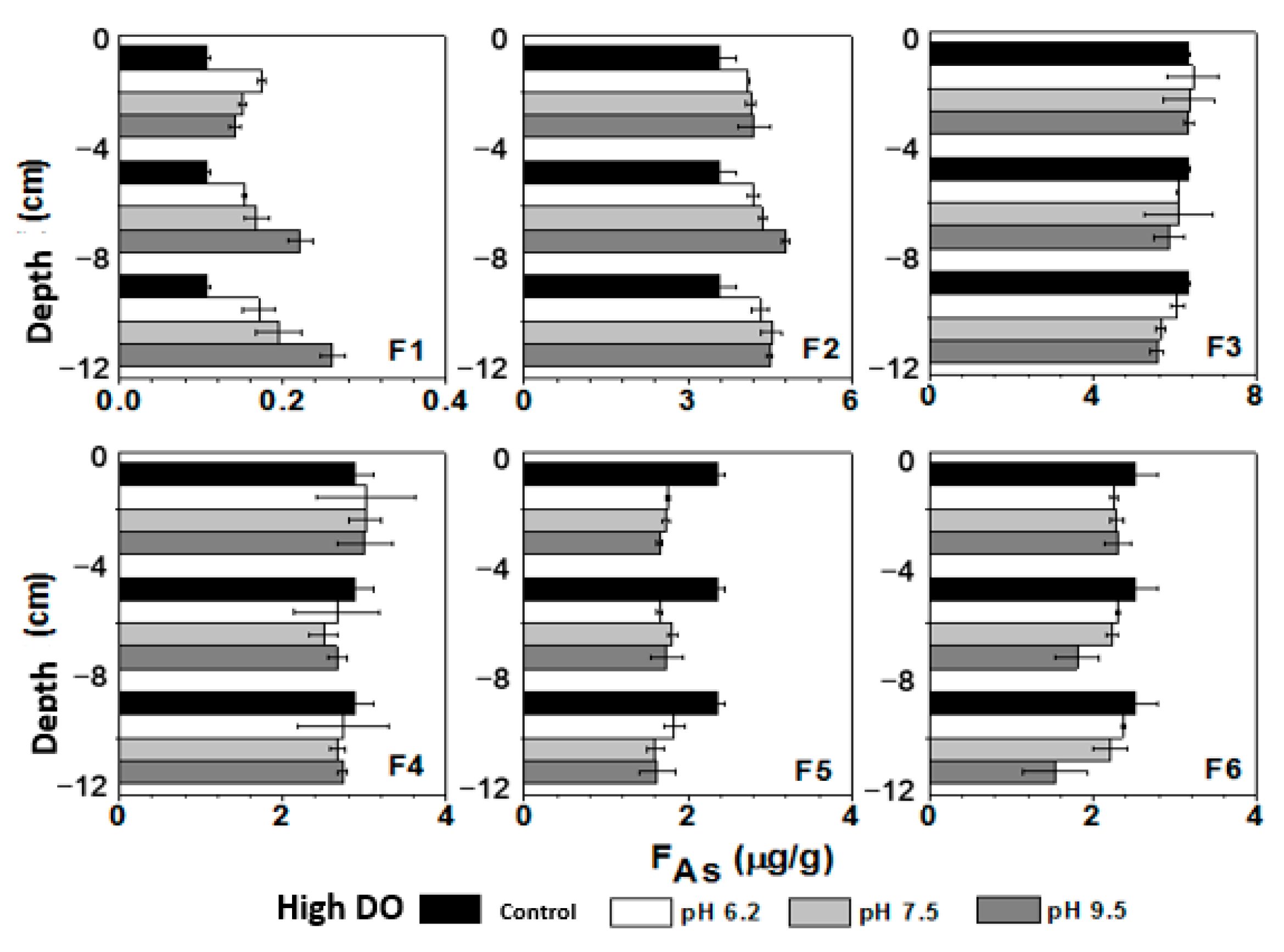
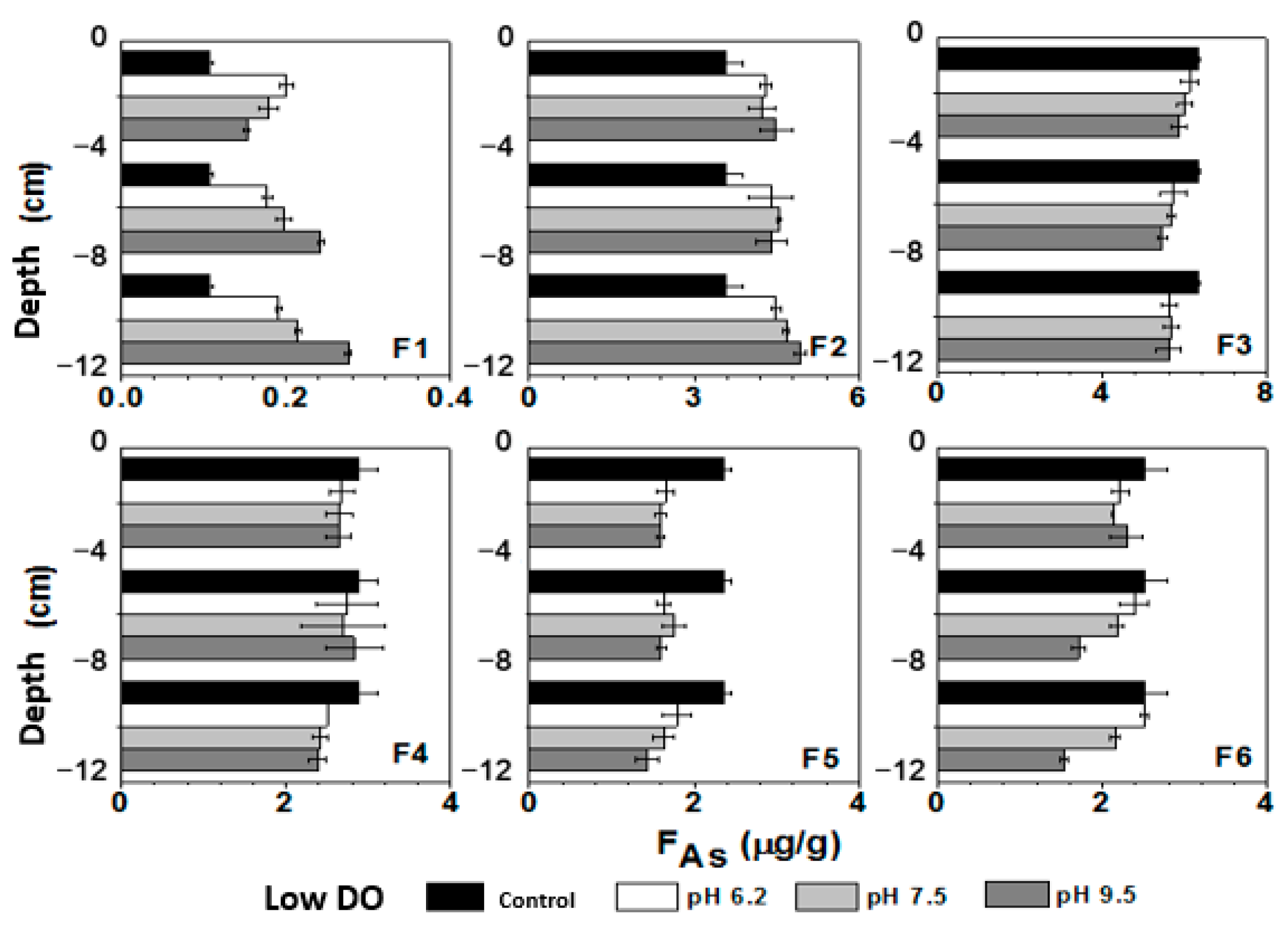
3.7. Influence of Initial pH of Water on Sediment As Components under Different DO Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, F.; Han, Y.; Shi, H.; Wang, G.; Zhou, M.; Chen, Y. Arsenic in the hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata: A review of benefits, toxicity, and metabolism. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 896, 165232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.S.; Pandey, P.K.; Martín-Ramos, P.; Corns, W.T.; Varol, S.; Bhattacharya, P.; Zhu, Y. A review on arsenic in the environment: Contamination, mobility, sources, and exposure. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 8803–8821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abebe, M.B.; Bossissi, N.; Thimo, G.; Gudrun, D.B.; Lieven, B. Distribution of metals in water, sediment and fish tissue. Consequences for human health risks due to fish consumption in Lake Hawassa, Ethiopia. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156968. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Zhu, G.; Chen, J.; Yang, T. In-situ observations of internal dissolved heavy metal release in relation to sediment suspension in lake Taihu. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 97, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Gu, W.Q.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Tang, G.; Yang, C.M. Combined impacts of algae-induced variations in water soluble organic matter and heavy metals on bacterial community structure in sediment from Chaohu Lake, a eutrophic shallow lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthyala, S.C.; Bhaskar, D.R.V. Assessment of metals pollution and subsequent ecological risk in water, sediments and vegetation from a shallow lake: A case study from Ranipet industrial town, Tamil Nadu, India. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 103, 1786–1803. [Google Scholar]
- Sudip, S.; Selim Reza, A.H.M.; Kanti, R.M. Arsenic geochemistry of the sediments of the shallow aquifer and its correlation with the groundwater, Rangpur, Bangladesh. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 166. [Google Scholar]
- Amarathunga, U.; Diyabalanage, S.; Bandara, U.G.C.; Chandrajith, R. Environmental factors controlling arsenic mobilization from sandy shallow coastal aquifer sediments in the Mannar Island, Sri Lanka. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 100, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medunić, G.; Fiket, Ž.; Ivanić, M. Arsenic contamination status in Europe, Australia, and other parts of the world. In Arsenic in Drinking Water and Food; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2020; pp. 183–233. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Du, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, S.; Xu, Q. The effects of acidification on arsenic concentration and speciation in offshore shallow water system. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 181, 113930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, N.K.; Hossein, N.A.; Boshir, A.M.; Amin, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, J.L. Adsorption and desorption behavior of arsenite and arsenate at river sediment-water interface. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115497. [Google Scholar]
- Stollenwerk, K.G.; Breit, G.N.; Welch, A.H.; Yount, J.C.; Whitney, J.W.; Foster, A.L.; Uddin, M.N.; Majumder, R.K.; Ahmed, N. Arsenic attenuation by oxidized aquifer sediments in Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 379, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, C.F.; Swartz, C.H.; Badruzzaman, A.B.; Keon-Blute, N.; Yu, W.; Ali, M.A.; Jay, J.; Beckie, R.; Niedan, V.; Brabander, D.; et al. Arsenic mobility and groundwater extraction in Bangladesh. Science 2002, 298, 1602–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, S.; Hering, J.G. Comparison of arsenic(V) and arsenic(III) sorption onto iron oxide minerals: Implications for arsenic mobility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4182–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Clark, M.W.; Yee, L.H.; Comarmond, M.J.; Payne, T.E.; Burton, E.D. Effects of pH, competing ions and aging on arsenic (V) sorption and isotopic exchange in contaminated soils. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 105, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Yan, X.L.; Liao, X.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Lin, L.Y.; Shan, T.Y. Study on stabilization of soils contaminated by arsenic and heavy metals by iron-manganese bimetallic materials. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 36, 4164–4172. [Google Scholar]
- Huyen, D.T.; Tabelin, C.B.; Thuan, H.M.; Dang, D.H.; Truong, P.T.; Vongphuthone, B.; Kobayashi, M.; Igarashi, T. The solid-phase partitioning of arsenic in unconsolidated sediments of the Mekong Delta, Vietnam and its modes of release under various conditions. Chemosphere 2019, 233, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, X.; Xiu, W.; He, W.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, A. Controls of organic matter bioreactivity on arsenic mobility in shallow aquifers of the Hetao Basin, PR China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 571, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftabtalab, A.; Rinklebe, J.; Shaheen, S.M.; Niazi, N.K.; Moreno-Jiménez, E.; Schaller, J.; Knorr, K.H. Review on the interactions of arsenic, iron (oxy)(hydr) oxides, and dissolved organic matter in soils, sediments, and groundwater in a ternary system. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Li, P.; Wang, Y. Effects of different dissolved organic matter on microbial communities and arsenic mobilization in aquifers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 125146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Song, W.; Zheng, J.; Luo, Y.; Qi, G.; Lü, S.; Lü, X.; Zhou, B.; Lü, C.; He, J. Factors and pathways regulating the release and transformation of arsenic mediated by reduction processes of dissimilated iron and sulfate. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.X.; Yin, G.C.; Chen, Z.L.; Lin, Q.T.; Huang, R.L.; Liu, D.L.; Peng, H.L.; Huang, L.; Wang, X.; Jiang, X.L. Influencing mechanism of Eh, pH and iron on the release of arsenic in paddy soil. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2017, 38, 2530–2537. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Schaefer, M.V.; Wang, Y.; Gan, Y.; Yu, K.; Deng, Y.; Fendorf, S. Experimental constraints on redox-induced arsenic release and retention from aquifer sediments in the central Yangtze River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberle, A.; Besold, J.; Kerl, C.F.; Lezama-Pacheco, J.S.; Fendorf, S.; Planer-Friedrich, B. Arsenic fate in peat controlled by the pH-dependent role of reduced sulfur. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6682–6692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Sun, F.; Su, H.; Tao, Y.; Chang, H. Multiple risk assessment of heavy metals in surface water and sediment in Taihu Lake, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13120. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.K. Methods for Agro-Chemical Analysis of Soil; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Dufailly, V.; Noël, L.; Guérin, T. Optimisation and critical evaluation of a collision cell technology ICP-MS system for the determination of arsenic in foodstuffs of animal origin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 611, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, H.; Goto, K.; Yotsuyanagi, T.; Nagayama, M. Spectrophotometric determination of iron (II) with 1, 10-phenanthroline in the presence of large amounts of iron (III). Talanta 1974, 21, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogo, J.K.; Popowsky, M. Spectrophotometric determination of hydrogen sulfide. Anal. Chem. 1949, 21, 732–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.G.; Sun, G.X.; Lei, M.; Teng, M.; Liu, Y.X.; Chen, N.C.; Wang, L.H.; Carey, A.M.; Deacon, C.; Raab, A.; et al. High percentage inorganic arsenic content of mining impacted and nonimpacted Chinese rice. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5008–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Uroic, M.K.; Xie, W.Y.; Zhu, Y.G.; Chen, B.D.; McGrath, S.P.; Jörg, F.; Zhao, J.F. Phytochelatins play a key role in arsenic accumulation and tolerance in the aquatic macrophyte Wolffia globosa. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 165, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cao, X.; Lin, C.; Chen, X. Arsenic content and fractionation in the surface sediments of the Guangzhou section of the Pearl River in Southern China. J. Hazard Mater. 2010, 183, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, M.F.; Bernasconi, S.M.; Barbieri, A.; McKenzie, J.A. Preservation of organic matter and alteration of its carbon and nitrogen isotope composition during simulated and in situ early sedimentary diagenesis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 3573–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Tan, X.; Ali, I.; Wu, X.; Cao, J.; Xu, Y.X.; Shi, L.; Gao, W.P.; Ruan, Y.L.; Chen, C. Comparison of organic matter (OM) pools in water, suspended particulate matter, and sediments in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China: Implication for dissolved OM tracking, assessment, and management. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 845, 157257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Wu, J.; Yang, P.; Zhu, M. Coupled manganese redox cycling and organic carbon degradation on mineral surfaces. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 8801–8810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Jing, C. A review of arsenic interfacial geochemistry in groundwater and the role of organic matter. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2019, 183, 109550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Min, X.; Ke, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Yan, X.; Xu, H.; Fei, J.C.; Li, Y.C.; Liu, D.G.; et al. Release behaviors of arsenic and heavy metals from arsenic sulfide sludge during simulated storage. Minerals 2019, 9, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhanna, R.; Naveau, A.; Bueno, M.; Shmeit, M.; Ismail, F.; Fontaine, C.; Porel, G.; Bassil, J.; Caner, L. Concomitant behavior of arsenic and selenium from the karst infillings materials of the fractured carbonate Dogger Aquifer (Hydrogeological Experimental Site, Poitiers, France). Chemosphere 2021, 275, 129935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Hu, Y.; Guo, C.; Ke, C.; Lu, G.; Dang, Z. Mobilization of arsenic during reductive dissolution of As (V)-bearing jarosite by a sulfate reducing bacterium. J. Hazard Mater. 2021, 402, 123717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, S.G.; Arya, D.B.; Sunil, S.; Shaji, P.; Devi, A.; Sreevalsan, S.; Pulickal, A.K. Abundance, geo-microbial role and community diversity of sulfate-reducing bacteria in tropical estuarine sediments. Watershed Ecol. Environ. 2023, 5, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Meng, X.; Jing, C. Influence of sulfur on the mobility of arsenic and antimony during oxic-anoxic cycles Differences and competition. Geochim. Cosmoshim. Acta 2020, 288, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.E. Surface and complexation effects on the rate of Mn (II) oxidation in natural waters. Geochim. Cosmoshim. Acta 1980, 44, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.B. Microbial communities and interactions in low pH environments. In Acidophiles: Life in Extremely Acidic Environments; Caister Academic Press Limited: Poole, UK, 2016; pp. 121–138. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, P.; Zhu, C. Arsenic Eh–pH diagrams at 25 C and 1 bar. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 1673–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, M.V.; Guo, X.X.; Gan, Y.Q.; Benner, S.G.; Griffin, A.M.; Gorski, C.A.; Wang, Y.X.; Fendorf, S. Redox controls on arsenic enrichment and release from aquifer sediments in central Yangtze River Basin. Geochim. Cosmoshim. Acta 2017, 204, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedley, P.L.; Kinniburgh, D.G. A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 517–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Guo, H.; Zhao, B.; Wang, A.; Han, S.; Dong, H. Experiment-based geochemical modeling of Arsenic (V) and Arsenic (III) adsorption onto aquifer sediments from an inland basin. J. Hydrol. 2020, 588, 125094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drahota, P.; Peřestá, M.; Trubač, J.; Mihaljevič, M.; Vaněk, A. Arsenic fractionation and mobility in sulfidic wetland soils during experimental drying. Chemosphere 2021, 277, 130306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotaras, D.; Nikolopoulos, D. Arsenic occurrence and fate in the environment; a geochemical perspective. J. Earth Sci. Clim. Chang. 2015, 6, 269. [Google Scholar]
- Darma, A.; Yang, J.; Bloem, E.; Możdżen, K.; Zandi, P. Arsenic biotransformation and mobilization: The role of bacterial strains and other environmental variables. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R 2021, 29, 1763–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiao, C.; Adeyeye, O.; Yang, W.; Liang, X. Source and mobilization mechanism of iron, manganese and arsenic in groundwater of Shuangliao City, Northeast China. Water 2020, 12, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguffin, S.C.; Abu-Ali, L.; Tappero, R.V.; Pena, J.; Rohila, J.S.; McClung, A.M.; Reid, M.C. Influence of manganese abundances on iron and arsenic solubility in rice paddy soils. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2020, 276, 50–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, P.; Sharma, A. Role of iron in controlling speciation and mobilization of arsenic in subsurface environment. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4916–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, Z.; Bostick, B.C.; Zheng, Y.; Huq, M.R.; Rahman, M.M.; Ahmed, K.M.; van Geen, A. Evidence of decoupling between arsenic and phosphate in shallow groundwater of Bangladesh and potential implications. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 77, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, T.; Xu, J.; Cheng, G.; Wang, L. Inorganic Chemistry, 4th ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Beaulieu, B.; Ramirez, R.E. Arsenic remediation field study using a sulfate reduction and zero-valent iron PRB. Ground Water Monit. Remediat. 2013, 33, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saalfield, S.L.; Bostick, B.C. Changes in iron, sulfur, and arsenic speciation associated with bacterial sulfate reduction in ferrihydrite-rich systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 8787–8793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Day, P.A.; Vlassopoulos, D.; Root, R.; Rivera, N. The influence of sulfur and iron on dissolved arsenic concentrations in the shallow subsurface under changing redox conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13703–13708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVore, C.L.; Rodriguez-Freire, L.; Villa, N.; Soleimanifar, M.; Gonzalez-Estrella, J.; Ali, A.M.S.; LezamaPacheco, J.; Ducheneaux, C.; Cerrato, J.M. Mobilization of As, Fe, and Mn from Contaminated Sediment in Aerobic and Anaerobic Conditions: Chemical or Microbiological Triggers? ACS Earth Space Chem. 2022, 6, 1644–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Minamikawa, R.; Hattori, K.H.; Kurishima, K.; Kihou, N.; Yuita, K. Arsenic behavior in paddy fields during the cycle of flooded and non-flooded periods. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Bowers, B.; Kim, D.; Lee, B.; Jun, Y.S. Dissolved organic matter affects arsenic mobility and iron (III)(hydr) oxide formation: Implications for managed aquifer recharge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 14357–14367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| TAs (mg/kg) | Fe (g/kg) | Mn (g/kg) | FeOOH (g/kg) | MnOOH (g/kg) | TOC (%) | pH | Moisture Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18.15 | 35.42 | 1.41 | 24.01 | 0.85 | 1.44 | 7.56 | 52.4 |
| FeHDO | MnHDO | SHDO | FeLDO | MnLDO | SLDO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As (pH 6.2) | 0.965 ** | 0.985 ** | 0.734 | 0.886 * | 0.803 | 0.875 |
| As (pH 7.5) | 0.986 ** | 0.924 * | 0.721 | 0.942 * | 0.790 | 0.891 * |
| As (pH 9.5) | 0.961 ** | 0.978 ** | 0.713 | 0.882 * | 0.869 | 0.782 |
| pK (FeS) | pK (FeS2) | |
|---|---|---|
| pH 6.2 | 9.23–10.05 | 14.37–15.54 |
| pH 7.5 | 9.14–9.96 | 14.21–15.37 |
| pH 9.5 | 8.89–9.89 | 13.78–15.25 |
| Linear Equation | Linear Equation | |
|---|---|---|
| pH 6.2 | pK(FeS)= −0.018 CAs + 10.14 r = −0.892 * | pK(FeS2)= −0.026 CAs + 15.70 r = −0.894 * |
| pK(FeS)= −0.26 RAs + 10.42 r = −0.903 * | pK(FeS2)= −0.37 RAs + 16.08 r = −0.897 * | |
| pH 7.5 | pK(FeS)= −0.016 CAs + 10.03 r = −0.923 * | pK(FeS2)= −0.022 CAs + 15.46 r = −0.916 * |
| pK(FeS)= −0.38 RAs + 10.69 r = −0.903 * | pK(FeS2)= −0.52 RAs + 16.38 r = −0.898 * | |
| pH 9.5 | pK(FeS)= −0.015 CAs + 9.97 r = −0.883 * | pK(FeS2)= −0.022 CAs + 15.37 r = −0.872 |
| pK(FeS)= −0.33 RAs + 10.65 r = −0.917 * | pK(FeS2)= −0.48 RAs + 16.35 r = −0.908 * |
| mg/(m2∙d) | pH 6.2 | pH 7.5 | pH 9.5 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low DO | High DO | Low DO | High DO | Low DO | High DO | |
| rFe | 0.73 | −0.47 | 0.92 | −0.42 | 1.11 | −0.50 |
| rMn | 6.31 | 3.61 | 8.99 | 4.56 | 14.27 | 5.60 |
| rS | 0.38 | −0.45 | 0.51 | −0.49 | 0.76 | −0.51 |
| rAs | 0.053 | 0.013 | 0.069 | 0.014 | 0.083 | 0.017 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, L.; Yan, C.; Yang, F.; Zhen, Z.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, W. The Effects and Mechanisms of pH and Dissolved Oxygen Conditions on the Release of Arsenic at the Sediment–Water Interface in Taihu Lake. Toxics 2023, 11, 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110890
Zeng L, Yan C, Yang F, Zhen Z, Yang J, Chen J, Huang Y, Xiao Y, Zhang W. The Effects and Mechanisms of pH and Dissolved Oxygen Conditions on the Release of Arsenic at the Sediment–Water Interface in Taihu Lake. Toxics. 2023; 11(11):890. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110890
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Liqing, Changzhou Yan, Fan Yang, Zhuo Zhen, Jiaming Yang, Jielun Chen, Yujie Huang, Yuhui Xiao, and Wen Zhang. 2023. "The Effects and Mechanisms of pH and Dissolved Oxygen Conditions on the Release of Arsenic at the Sediment–Water Interface in Taihu Lake" Toxics 11, no. 11: 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110890
APA StyleZeng, L., Yan, C., Yang, F., Zhen, Z., Yang, J., Chen, J., Huang, Y., Xiao, Y., & Zhang, W. (2023). The Effects and Mechanisms of pH and Dissolved Oxygen Conditions on the Release of Arsenic at the Sediment–Water Interface in Taihu Lake. Toxics, 11(11), 890. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11110890








