Co-Exposure of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Phthalates with Blood Cell-Based Inflammation in Early Pregnant Women
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Questionnaire Survey
2.3. Determinations of Urinary mPAEs and OH-PAHs
2.4. Quality Control
2.5. Blood Cell Examination
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of the Participants
3.2. Concentrations of Urine mPAEs, OH-PAHs, and Blood Cells
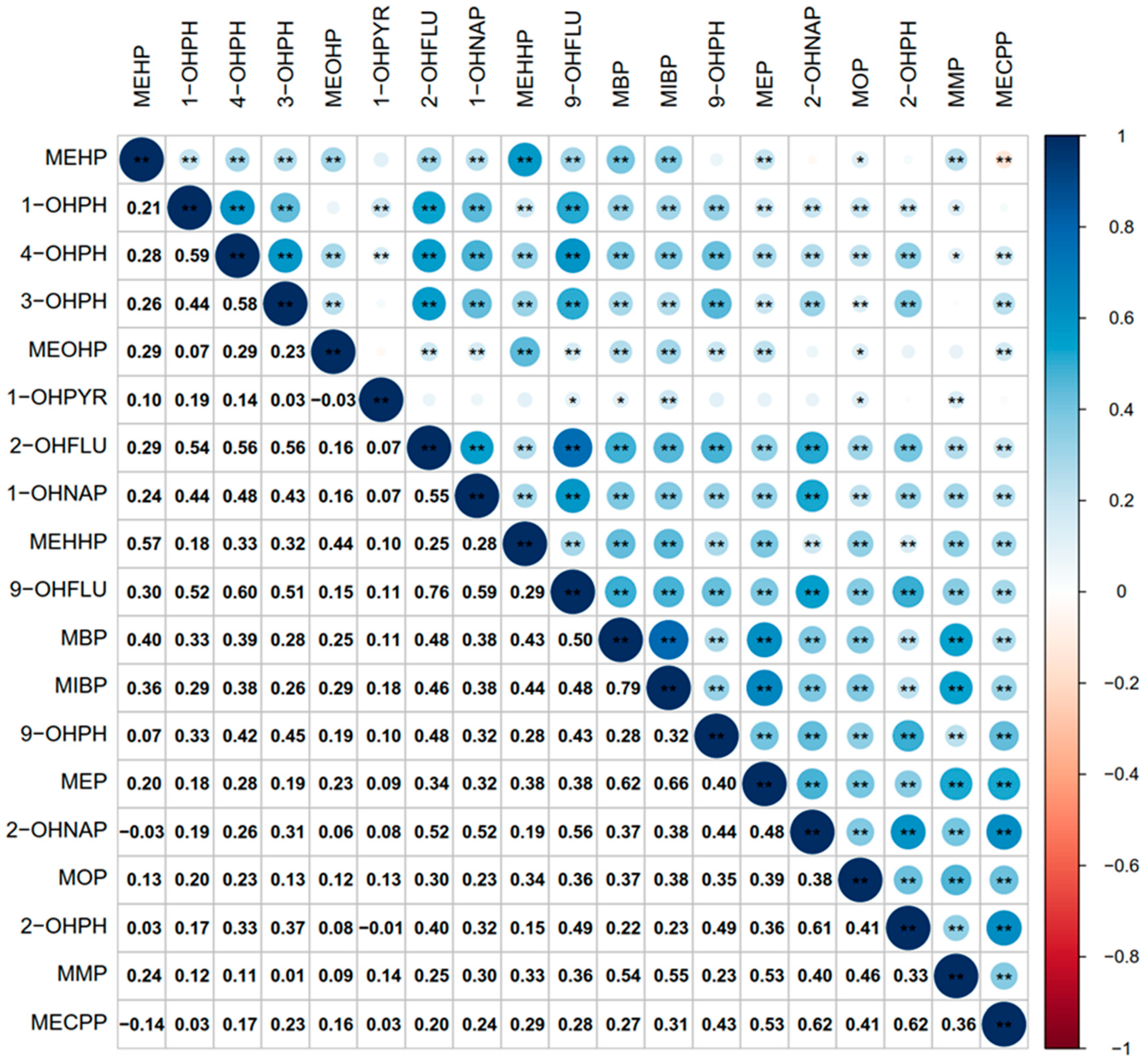
3.3. Correlation between OH-PAHs and mPAEs Metabolites
3.4. The Relationship between OH-PAHs and mPAEs and Blood Cell-Based Inflammatory Indicators
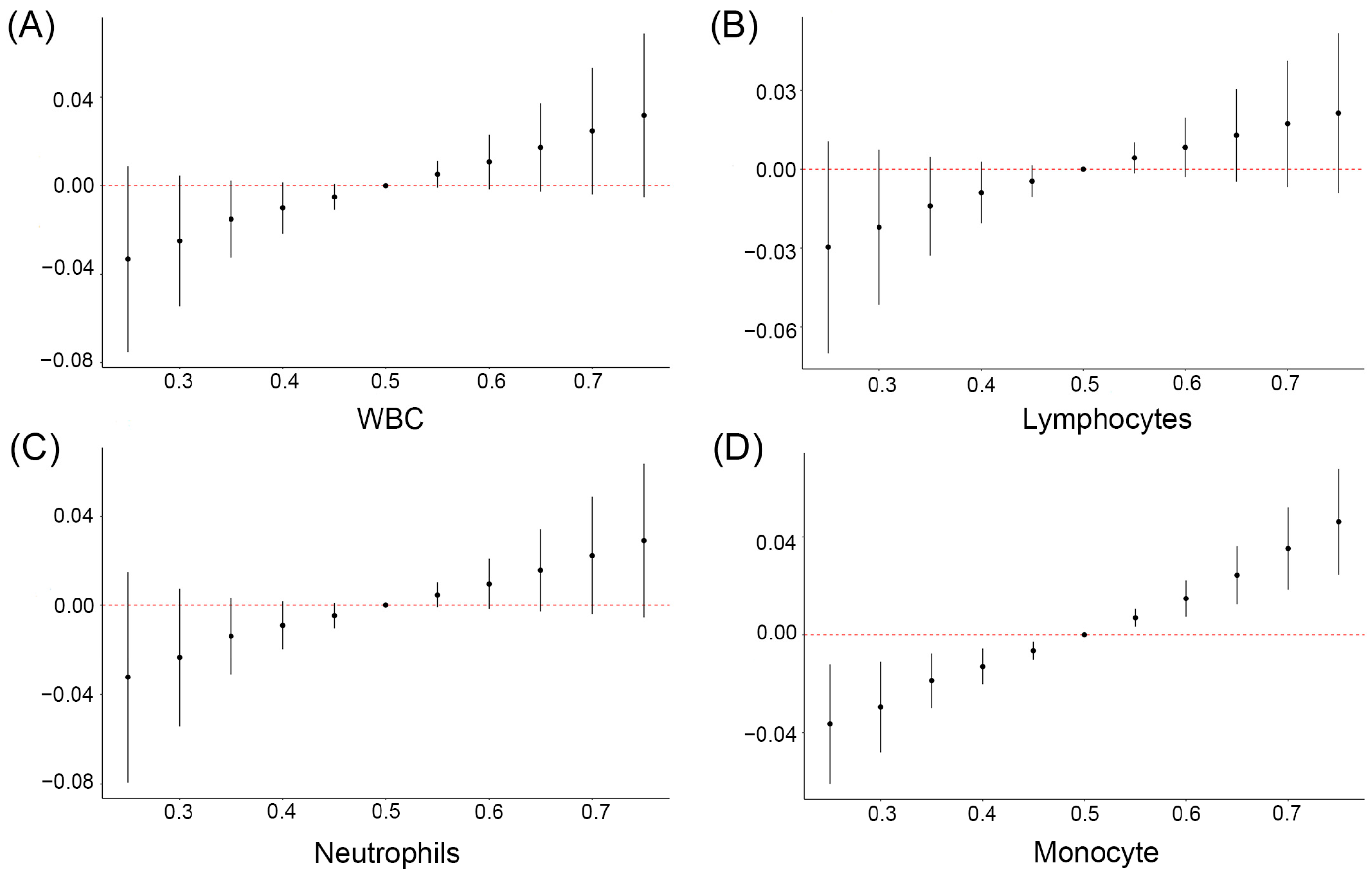
3.5. Identification of the Key mPAE or OH-PAH Metabolites Based on WBC
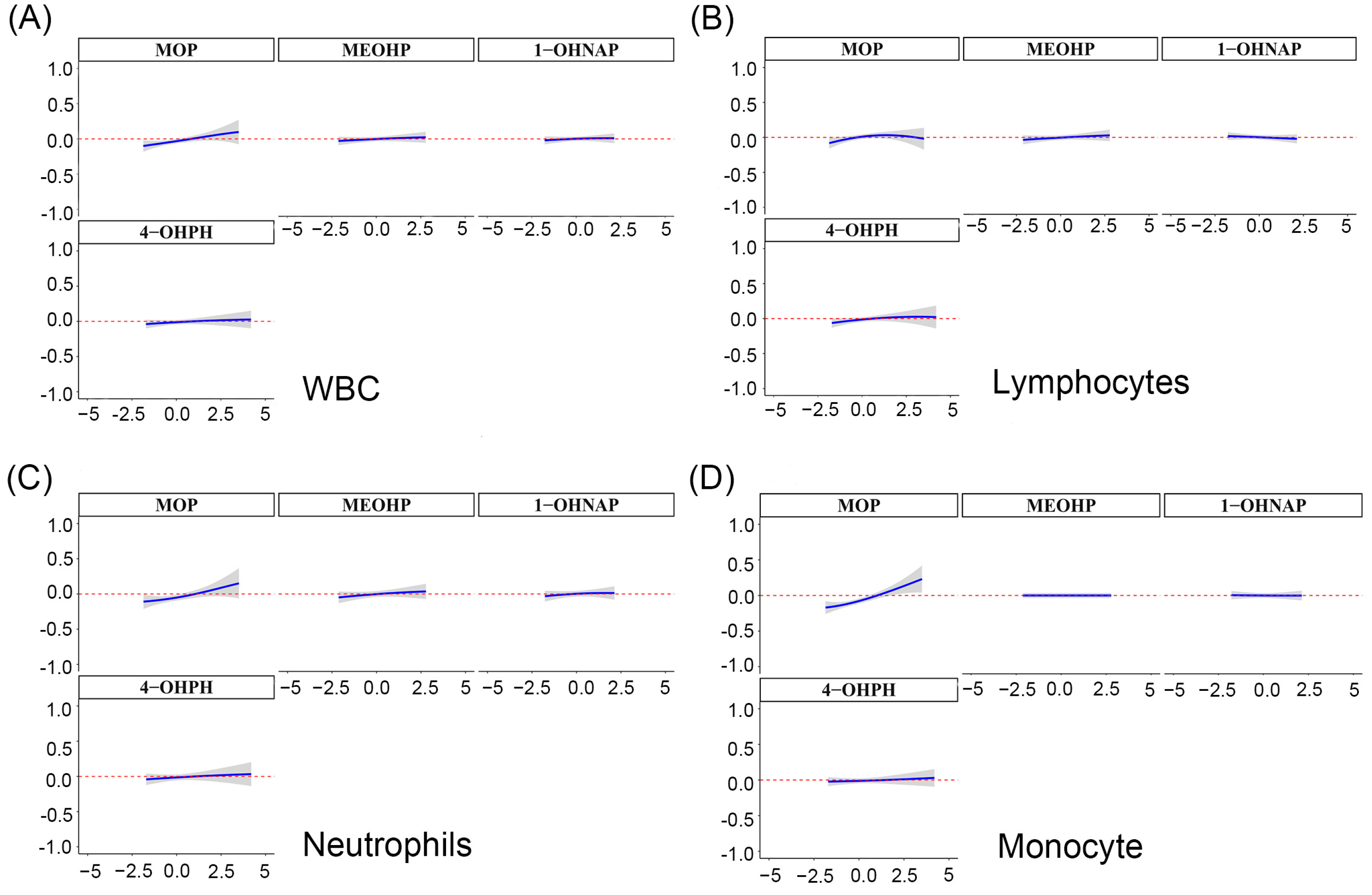
3.6. Relationship between Mixture of OH-PAHs and mPAEs and Blood Cell-Based Inflammatory Indicators Based on BKMR
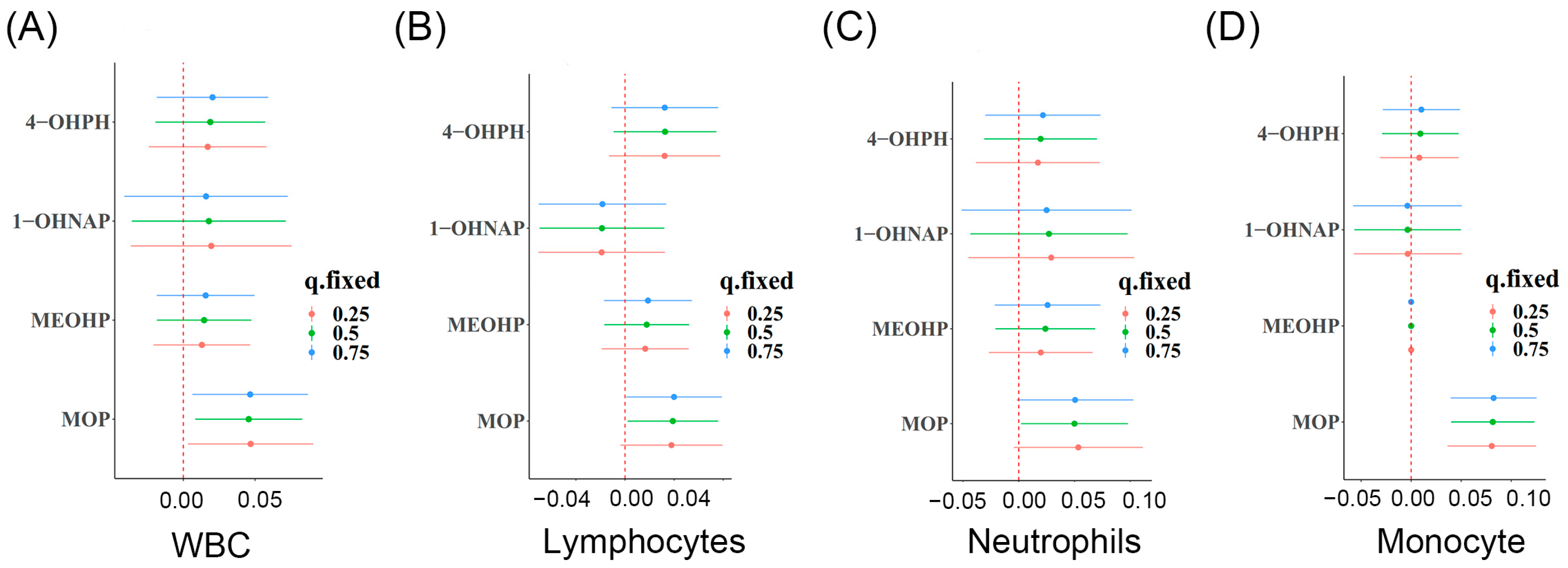
3.7. Quantile g-Computation to Explore the Relationship of Co-Exposure OH-PAHs and PAEs with Blood Cell-Based Inflammatory Biomarkers
3.8. Sensitivity Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, D.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Liang, H. An overview of phthalate acid ester pollution in China over the last decade: Environmental occurrence and human exposure. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 645, 1400–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrdina, A.I.H.; Kohale, I.N.; Kaushal, S.; Kelly, J.; Selin, N.E.; Engelward, B.P.; Kroll, J.H. The Parallel Transformations of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Body and in the Atmosphere. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 25004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Ebinghaus, R.; Temme, C.; Lohmann, R.; Caba, A.; Ruck, W. Occurrence and air-sea exchange of phthalates in the Arctic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 4555–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Wu, Y.; Xu, L.; Zeng, X.; Qin, Q.; Xu, X. Maternal urinary metabolites of PAHs and its association with adverse birth outcomes in an intensive e-waste recycling area. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, T.P.; Broe, A.; Lash, T.L.; Cronin-Fenton, D.P.; Ulrichsen, S.P.; Christiansen, P.M.; Cole, B.F.; Tamimi, R.M.; Sørensen, H.T.; Damkier, P. Phthalate Exposure and Breast Cancer Incidence: A Danish Nationwide Cohort Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1800–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Shao, H.; Ying, X.; Huang, W.; Hua, Y. The Endocrine Disruption of Prenatal Phthalate Exposure in Mother and Offspring. Front. Public. Health 2020, 8, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyńska, M.; Pośniak, M.; Dobrzyńska, E. Determination of phthalates in particulate matter and gaseous phase emitted into the air of the working environment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 17, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Lu, X.; Qiu, X.; Yin, F.; Faull, K.F.; Tseng, C.-H.; Zhang, J.; Fiehn, O.; Zhu, T.; Araujo, J.A.; et al. Arachidonic acid metabolism and inflammatory biomarkers associated with exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Huo, Y.; Toufektsian, M.C.; Ramos, S.I.; Ma, Y.; Tejani, A.D.; French, B.A.; Yang, Z. Activated platelets contribute importantly to myocardial reperfusion injury. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 290, H692–H699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, V.X.; Patel, S.; Jones, H.F.; Nielsen, T.C.; Mohammad, S.S.; Hofer, M.J.; Gold, W.; Brilot, F.; Lain, S.J.; Nassar, N.; et al. Maternal acute and chronic inflammation in pregnancy is associated with common neurodevelopmental disorders: A systematic review. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, J.A.; Gallagher, K.; Beck, C.; Kumar, R.; Gernand, A.D. Maternal-Fetal Inflammation in the Placenta and the Developmental Origins of Health and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 531543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, M.; Liu, L.; Guo, W.; Yang, H.; Chen, S.; Yu, J.; Li, M.; Fang, Q.; Lai, X.; et al. The association of co-exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and phthalates with blood cell-based inflammatory biomarkers in children: A panel study. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dymicka-Piekarska, V.; Wasiluk, A. Procalcitonin (PCT), contemporary indicator of infection and inflammation. Postep. Hig. Med. Dosw. 2015, 69, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Cao, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Du, P. Diagnostic and Predictive Values of Inflammatory Factors in Pathology and Survival of Patients Undergoing Total Cystectomy. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 9234067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Han, Y.; Qiu, X.; Chai, Q.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Xue, T.; et al. Organic Components of Personal PM(2.5) Exposure Associated with Inflammation: Evidence from an Untargeted Exposomic Approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 10589–10596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Huo, X.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X. Alterations in platelet indices link polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons toxicity to low-grade inflammation in preschool children. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 105043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshaarawy, O.; Zhu, M.; Ducatman, A.; Conway, B.; Andrew, M.E. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon biomarkers and serum markers of i20nflammation. A positive association that is more evident in men. Environ. Res. 2013, 126, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yin, W.; Li, P.; Hu, C.; Hou, J.; Wang, L.; Yuan, J.; Yu, Z. Seasonal exposure to phthalates and inflammatory parameters: A pilot study with repeated measures. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.W.; Cathey, A.L.; Watkins, D.J.; Rosario-Pabón, Z.Y.; Vélez-Vega, C.M.; Alshawabkeh, A.N.; Cordero, J.F.; Meeker, J.D. Associations of urinary phthalate metabolites and inflammatory biomarkers among pregnant women in Puerto Rico. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 854, 158773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q.; Liao, J.; Fang, D.; et al. Characteristics of exposure to 10 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon metabolites among pregnant women: Cohort of pregnant women in Zunyi, southwest China. Occup. Environ. Med. 2023, 80, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Fang, D.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, S.; Wang, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, H.; An, S.; He, C.; Chen, W.; et al. Exposure characteristics of phthalate metabolites among the Zunyi cohort of pregnant women in Southwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 58869–58880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Tian, K.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dai, M.; Gong, L.; Xiong, S.; Xie, Y.; Shen, X.; Zhou, Y. Single and joint associations of exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with blood coagulation function during pregnancy: A cross-sectional study. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 885, 163949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornung, R.W.; Reed, L.D. Estimation of Average Concentration in the Presence of Nondetectable Values. Appl. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 1990, 5, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmer, E.; Garland, A.; Kumar, A.; Doucette, S.; Houston, B.L.; Menard, C.E.; Leeies, M.; Turgeon, A.F.; Mahmud, S.; Houston, D.S.; et al. White blood cell count trajectory and mortality in septic shock: A historical cohort study. Can. J. Anaesth. 2022, 69, 1230–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Chen, C.; Li, Q. White blood cell counting at point-of-care testing: A review. Electrophoresis 2020, 41, 1450–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, M.D.; Sevoyan, M.; Hofseth, L.; Shivappa, N.; Hurley, T.G.; Hebert, J.R. The Dietary Inflammatory Index is associated with elevated white blood cell counts in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 69, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchett, D.; Reddy, A.B. Circadian Clocks in the Hematologic System. J. Biol. Rhythm. 2015, 30, 374–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrecque, N.; Cermakian, N. Circadian Clocks in the Immune System. J. Biol. Rhythm. 2015, 30, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhong, Y.; He, W.; Huang, S.; Li, Q.; Guo, C.; Ma, S.; Li, G.; Yu, Y. Co-exposure and health risks of parabens, bisphenols, triclosan, phthalate metabolites and hydroxyl polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons based on simultaneous detection in urine samples from guangzhou, south China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 115990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zhu, Y.-D.; Xu, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Yao, H.-Y.; Sheng, J.; Jin, Z.-X.; Ren, L.-L.; Huang, K.; Hao, J.-H.; et al. Season-dependent concentrations of urinary phthalate metabolites among Chinese pregnant women: Repeated measures analysis. Environ. Int. 2017, 104, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Deng, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Lyu, P.; Zhou, L.; Shi, Y.; Mao, W.; Yang, X.; et al. Phthalate acid esters and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons concentrations with their determining factors among Chinese pregnant women: A focus on dietary patterns. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 852, 158344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koniecki, D.; Wang, R.; Moody, R.P.; Zhu, J. Phthalates in cosmetic and personal care products: Concentrations and possible dermal exposure. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Lu, Y.; Teng, Y.; Tan, C.; Ren, W.; Cao, X. Occurrence and health risk assessment of phthalate esters in tobacco and soils in tobacco-producing areas of Guizhou province, southwest China. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.-J.; Lu, J.-F.; Wang, J.; Wei, S.-Q.; Hageman, K.J. Phthalate esters in biota, air and water in an agricultural area of western China, with emphasis on bioaccumulation and human exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.J.; Barr, D.B.; Reidy, J.A.; Kato, K.; Malek, N.A.; Hodge, C.C.; Hurtz, D.; Calafat, A.M.; Needham, L.L.; Brock, J.W. Glucuronidation patterns of common urinary and serum monoester phthalate metabolites. Arch. Toxicol. 2003, 77, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xie, Z.; Lan, J.; Li, T.; Yuan, D.; Yang, H.; Xing, B. Characteristics and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil seepage water in karst terrains, southwest China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornehag, C.-G.; Carlstedt, F.; Jönsson, B.A.; Lindh, C.H.; Jensen, T.K.; Bodin, A.; Jonsson, C.; Janson, S.; Swan, S.H. Prenatal Phthalate Exposures and Anogenital Distance in Swedish Boys. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, K.K.; McElrath, T.F.; Pace, G.G.; Weller, D.; Zeng, L.; Pennathur, S.; Cantonwine, D.E.; Meeker, J.D. Urinary Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Metabolite Associations with Biomarkers of Inflammation, Angiogenesis, and Oxidative Stress in Pregnant Women. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4652–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, A.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Chen, L.; Hu, J.; Wu, C.; et al. Urinary concentrations of phthalate metabolites associated with changes in clinical hemostatic and hematologic parameters in pregnant women. Environ. Int. 2018, 120, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xia, W.; Wu, C.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, J.; Ji, F.; Luan, H.; Xu, S.; Cai, Z. Variations of phthalate exposure and metabolism over three trimesters. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, W.A.; Lagoo-Deenadayalan, S.; Whitworth, N.S.; Stopple, J.A.; Barber, W.H.; Hale, E.; Brackin, M.N.; Cowan, B.D. First-trimester human chorionic villi express both immunoregulatory and inflammatory cytokines: A role for interleukin-10 in regulating the cytokine network of pregnancy. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 1999, 41, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, K.K.; McElrath, T.F.; Mukherjee, B.; Loch-Caruso, R.; Meeker, J.D. Associations between Maternal Biomarkers of Phthalate Exposure and Inflammation Using Repeated Measurements across Pregnancy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Huo, X.; Luo, X.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X. E-waste polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) exposure leads to child gut-mucosal inflammation and adaptive immune response. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 53267–53281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, T.; Liu, X.; Ji, Q.; Zhu, X.; Sun, J.; Wang, Q.; Yao, H.; Niu, Y.; et al. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons exposure and hematotoxicity in occupational population: A two-year follow-up study. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 378, 114622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Huo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X. Cardiovascular endothelial inflammation by chronic coexposure to lead (Pb) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from preschool children in an e-waste recycling area. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiNatale, B.C.; Schroeder, J.C.; Francey, L.J.; Kusnadi, A.; Perdew, G.H. Mechanistic insights into the events that lead to synergistic induction of interleukin 6 transcription upon activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and inflammatory signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 24388–24397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jepsen, K.; Abildtrup, A.; Larsen, S. Monophthalates promote IL-6 and IL-8 production in the human epithelial cell line A549. Toxicol. Vitr. 2004, 18, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Feng, W.; Kuang, D.; Deng, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, S.; He, M.; Zhang, X.; Wu, T.; Guo, H. The effects of heavy metals and their interactions with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on the oxidative stress among coke-oven workers. Environ. Res. 2015, 140, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristics | n | Mean ± SD or Percent (%) or Median (Lower Quartile, Upper Quartile) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 318 | 26.22 ± 4.7 |
| Pre-pregnancy BMI (kg/m2) | 318 | 22.10 ± 4.22 |
| Ethnicity | ||
| Ethnic Han | 312 | 98.11 |
| Minority | 6 | 1.8 |
| Education level | ||
| High school or below | 232 | 72.95 |
| College or beyond | 86 | 27.04 |
| Marital status | ||
| Married | 277 | 87.11 |
| Single | 39 | 12.26 |
| Divorced | 2 | 0.62 |
| Smoking | 20 | 6.28 |
| Passive smoking | 313 | 98.43 |
| Activities | ||
| Little or no | 167 | 52.52 |
| 1–2/week | 41 | 12.89 |
| ≥3/week | 110 | 34.59 |
| Drink | 27 | 8.49 |
| WBC | 318 | 8.09 (6.80, 9.58) |
| Lymphocyte | 318 | 1.80 (1.50, 2.18) |
| Neutrophile granulocyte | 318 | 5.73 (4.60, 6.94) |
| Monocyte | 318 | 0.40 (0.32, 0.48) |
| Platelet | 318 | 241.5 (202, 274) |
| NLR | 318 | 3.11 (2.43, 3.94) |
| PLR | 318 | 130.50 (109.44, 155.56) |
| SII | 318 | 727.00 (552.05, 942.74) |
| Urinary Metabolites | >LOD (%) | Median (25th, 75th) | Creatinine Correction Median (25th, 75th) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-OH-NAP (μg/L) | 70.05 | 0.65 (<LOD, 2.06) | 0.47 (0.006, 1.56) |
| 2-OH-NAP (μg/L) | 82.03 | 1.00 (0.10, 4.42) | 1.09 (0.10, 3.20) |
| 9-OH-FLU (μg/L) | 91.15 | 0.39 (0.16, 0.81) | 0.29 (0.13, 0.60) |
| 2-OH-FLU (μg/L) | 99.22 | 0.53 (0.25, 1.04) | 0.44 (0.19, 0.85) |
| 4-OH-PHE (μg/L) | 62.5 | 0.03 (<LOD, 0.07) | 0.023 (0.009, 0.05) |
| 9-OH-PHE (μg/L) | 86.46 | 0.02 (0.008, 0.07) | 0.019 (0.007, 0.06) |
| 3-OH-PHE (μg/L) | 95.57 | 0.30 (0.10, 0.77) | 0.22 (0.08, 0.71) |
| 1-OH-PHE (μg/L) | 83.59 | 0.08 (0.01, 0.24) | 0.06 (0.01, 0.17) |
| 2-OH-PHE (μg/L) | 77.34 | 0.09 (0.02,0.55) | 0.07 (0.01, 0.34) |
| 1-OH-PYR (μg/L) | 74.22 | 0.01 (<LOD, 0.06) | 0.01 (0.0002, 0.04) |
| MMP (μg/L) | 68.75 | 2.15 (<LOD, 6.99) | 1.48 (0.03, 4.91) |
| MEP (μg/L) | 97.66 | 17.55 (6.92, 37.30) | 13.17 (5.42, 31.91) |
| MIBP (μg/L) | 99.22 | 19.59 (9.74, 36.56) | 14.52 (7.28, 27.01) |
| MBP (μg/L) | 100 | 96.13 (39.29, 175.50) | 64.23 (28.92, 144.39) |
| MEHP (μg/L) | 78.39 | 3.69 (0.74, 8.87) | 2.30 (0.29, 7.96) |
| MOP (μg/L) | 65.63 | 0.12 (<LOD, 0.25) | 0.85 (0.04, 0.17) |
| MBZP (μg/L) | 40.25 | 0.03 (<LOD, 0.15) | 0.03 (0.01, 0.11) |
| MEOHP (μg/L) | 88.54 | 10.84 (4.07, 38.97) | 9.67 (3.67, 32.53) |
| MEHHP (μg/L) | 90.36 | 12.77 (5.07, 25.91) | 8.75 (3.10, 21.69) |
| MECPP (μg/L) | 78.12 | 130.40 (32.19, 2490.23) | 134.74 (23.58, 2372.43) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Wang, T.; Luo, L.; He, Q.; Guo, F.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Xie, Y.; Shang, X.; et al. Co-Exposure of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Phthalates with Blood Cell-Based Inflammation in Early Pregnant Women. Toxics 2023, 11, 810. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11100810
Yang Y, Wang T, Luo L, He Q, Guo F, Chen Z, Liu Y, Liu X, Xie Y, Shang X, et al. Co-Exposure of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Phthalates with Blood Cell-Based Inflammation in Early Pregnant Women. Toxics. 2023; 11(10):810. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11100810
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yunxiao, Ting Wang, Lei Luo, Qian He, Fangfei Guo, Zhongbao Chen, Yijun Liu, Xingyan Liu, Yan Xie, Xuejun Shang, and et al. 2023. "Co-Exposure of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Phthalates with Blood Cell-Based Inflammation in Early Pregnant Women" Toxics 11, no. 10: 810. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11100810
APA StyleYang, Y., Wang, T., Luo, L., He, Q., Guo, F., Chen, Z., Liu, Y., Liu, X., Xie, Y., Shang, X., Shen, X., Zhou, Y., & Tian, K. (2023). Co-Exposure of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Phthalates with Blood Cell-Based Inflammation in Early Pregnant Women. Toxics, 11(10), 810. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11100810






