Simultaneous Method for Selected PBDEs and HBCDDs in Foodstuffs Using Gas Chromatography—Tandem Mass Spectrometry and Liquid Chromatography—Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Sorbents
2.2. Standards
2.3. Test Samples
2.4. Sample Treatment
2.5. Instrumental Analysis
2.5.1. GC-MS/MS (EI) Method
2.5.2. LC-MS/MS(ESI)
2.6. Quality Control
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. GC-MS/MS Method Development
3.2. LC-MS/MS Method Development
3.3. Optimisation of the Extraction and Clean-Up Method
3.3.1. Extraction Method
3.3.2. Optimisation of the Clean-Up Procedure
3.4. Method Validation
3.4.1. Linearity
3.4.2. Limit of Quantification (LOQ)
3.4.3. Trueness and Precision
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hajeb, P.; Castaño, A.; Cequier, E.; Covaci, A.; López Esteban, M.; Gonzalez Antuña, A.; Småstuen Haug, L.; Henríquez-Hernández, L.A.; Melymuk, L.; Pérez Luzardo, O.; et al. Critical review of analytical methods. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1193, 338828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietroń, W.J.; Małagocki, P. Quantification of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in food. A review. Talanta 2017, 167, 411–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covaci, A.; Harrad, S.; Abdallah, A.E.M.; Ali, N.; Law, J.R.; Herzke, D.; de Wit, C.A. Novel brominated flame retardants: A review of their analysis, environmental fate and behaviour. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 532–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papachlimitzou, A.; Barber, L.J.; Losada, S.; Bersuder, P.; Law, J.R. A review of the anaysis of novel brominated flame retardants. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1219, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuiderveen, E.A.R.; Slootweg, J.C.; de Boer, J. Novel brominated flame retardants—A review of their occurance in indoor air, dust, consumer goods and food. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavoloni, T.; Stramenga, A.; Stecconi, T.; Siracusa, M.; Bacchiocchi, S.; Piersanti, A. Single sample preparation for brominated flame retardants in fish and shellfish with dual detection: GC-MS/MS (PBDEs) and LC-MS/MS (HBCDs). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Scientific Opinion on polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in food. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Scientific Opinion on the update of the risk assessment of hexabromocyxlododecanes (HBCDDs) in food. EFSA J. 2021, 19, 6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretariat of the Stockholm Convention (SSC). Stockholm Convention on Persistant Organic Pollutants (POPs). (Revision 2019). Available online: http://chm.pops.int/TheConvention/Overview/TextoftheConvention/tabid/2232/Default.aspx (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- Parties and Signatoires of the Stockholm Convention. Available online: http://chm.pops.int/Countries/StatusofRatifications/PartiesandSignatoires/tabid/4500/Default.aspx (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- European Commision (EC). Commision Recommendation 2014/118/EU of 3. March 2014 on the monitoring of brominated flame retardants in food. Off. J. Eur. Commun. 2014, L65, 39–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zacs, D.; Perkons, I.; Abdulajeva, E.; Pasecnaja, E.; Bartkiene, E.; Bartkevics, V. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDD), dechlorane-related compounds (DRC) and emerging brominated flame retardants (EBFRs) in foods: The levels, profiles and dietary intake in Latvia. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietron, W.J.; Piskorska-Pliszczynska, J. Improved chromatography separation for polybrominated diphenyl ether congeners quantification in the food of animal origin. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacs, D.; Perkons, I.; Volkovs, V.; Bartkevics, V. Multi-analyte method for the analysis of legacy and alternative brominated and chlorinated flame retardants in food products of animal origin using gas chromtography—Magnetic sector high resolution mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2019, 230, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Z. Tetrabromobisfenol A, hexabromocyclododecane isomers and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in foodstuff from Beijing, China: Contamination levels, dietary exposure and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bichon, E.; Guiffard, I.; Vénisseau, A.; Lesquin, E.; Vaccher, V.; Marchand, P.; Le Bizec, B. Simultaneous analysis of historical, emerging and novel brominated flame retardants in food and feed using a common extraction and purification method. Chemosphere 2018, 205, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roszko, M.; Rzepkowska, M.; Szterk, A.; Szymczyk, K.; Jȩdrzejczak, R.; Bryła, M. Application of semi-permeable membrane dialysis/ion trap mass spectrometry technique to determine polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polychlorinated biphenyls in milk fat. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 748, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.; Dicks, P.; Mortimer, D.; Gem, M.; Smith, F.; Driffield, M.; White, S.; Rose, M. Simultaneous determination of PCDDs, PCDFs, PCBs and PBDEs in food. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.N.; Reiner, E.J.; Marvin, C.; Helm, P.; Riddell, N.; Dorman, F.; Misselwitz, M.; Shen, L.; Crozier, P.; Macpherson, K.; et al. Development of chromatography atmospheric pressure chemical ionization tandem mass spectrometry for analysis of halogenated flame retardants in wastewater. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacs, D.; Bartkevics, V. Analytical capabilities of high performance liquid chromatography—Atmospheric pressure photoionization—Orbitrap mass spectrometry (HPLC-APPI-Orbitrap-MS) for the trace determination of novel and emerging flame retardants in fish. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 898, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagalante, A.F.; Oswald, T.D. Analysis of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) by liquid chromatography with negative-ion atmospheric pressure photoionization tandem mass spectrometry (LC-NI-APPI/MS/MS): Application to house dust. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 2249–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.N.; Reiner, E.J.; Marvin, C.; Kolic, T.; Riddell, N.; Helm, P.; Dorman, F.; Misselwitz, M.; Brindle, I.D. Liquid chromatography-atmospheric pressure photoionization tandem mass spectrometry for analysis of 36 halogenated flame retardants in fish. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covaci, A.; Voorspoels, S.; Ramos, L.; Neels, H.; Blust, R. Recent developments in the analysis of brominated flame retardants and brominated natural compounds. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 2253, 145–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okšová, L.; Tölgyessy, P. Determination of hexabromocyclododecanes in fish using modified QuEChERS method with efficient extract clean-up prior to liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Separations 2020, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebbink, W.A.; van der Lee, M.K.; Peters, R.J.B.; Trag, W.A.; ten Dam, G.; Hoogenboom, R.L.A.P.; van Leeuwen, S.P.J. Brominated flame retardants in animal derived foods in the Netherlands between 2009 and 2014. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chessa, G.; Cossu, M.; Fiori, G.; Ledda, G.; Piras, P.; Sanna, A.; Brambilla, G. Occurence of hexabromocyclododecanes and tetrabromobisphenol A in fish and seafood from the sea of Sardinia—FAO 37.1.3. area: Their impact on human health within the European Union marine framework strategy directive. Chemosphere 2019, 228, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Dam, G.; Pardo, O.; Traag, W.; van der Lee, M.; Peters, R. Simultaneous extraction and determination of HBCD isomers and TBBPA by ASE and LC-MSMS in fish. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 898, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Hu, D.; Song, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, P. Determinations of hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) isomers in channel catfish, crayfish, hen eggs and fish feeds from China by isotopic dilution LC-MS/MS. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śmiełowska, M.; Zabiegała. B. Current trends in analytical strategies for determination of polybrominated dipheyl ethers (PBDEs) in samples with different matrix compositions—Part 1: Screening of new developments in sample preparation. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 132, 115255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawn, D.F.K.; Sadler, A.; Quade, S.C.; Sun, W.-F.; Lau, B.P.-Y.; Kosarac, I.; Hayward, S.; Ryan, J.J. Brominated flame retardants in Canadian chicken egg yolks. Food Addit. Contam. 2011, 28, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Bayen, S.; Kelly, B.C. Co-extraction and simultanous determination of multi-class hydrophobic organic contaminants in marine sediments and biota using GC-EI-MS/MS and LC-ESI-MS/MS. Talanta 2015, 143, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, S.V.; Boer, J. Advances in the gas chromatographic determination of persistent organic pollutants in the aquatic environment. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1186, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Merwe, J.P.; Hodge, M.; Whittier, J.M.; Lee, Y.S. Analysing persistent organic pollutants in eggs, blood and tissue of the green sea turtle (Chelonia mydas) using gas chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (GC-MS/MS). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 1719–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, A.R.; Mortimer, D.; Rose, M.; Smith, F.; Panton, S.; Garcia-Lopez, M. Bromine content and brominated flame retardants in food and animal feed from the UK. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portolés, T.; Sales, C.; Gómara, B.; Sancho, J.V.; Betrán, J.; Herrero, L.; González, M.J.; Hernández, F. Novel Analytical Approach for brominated flame retardants based on the use of gas chromatography-atmosperic pressure chemical ionization-tandem mass spectrometry with emphasis in highly brominated congeners. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9892–9899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bichon, E.; Guiffard, I.; Vénisseau, A.; Lesquin, E.; Vaccher, V.; Brosseaud, A.; Marchand, P.; Le Bizec, B. Simultaneous determination of 16 brominated flame retardants in food and feed of animal origin by fast gas chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry using atmospheric pressure chemical ionisation. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1459, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Method 1614A. Brominated Dipheyl Ethers Congeners in Water, Soil, Sediment, and Tissue by HRGC/HRMS. 2010. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPURL.cgi?Dockey=P1005EUE.txt (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- Kelly, K.; Parnell, K.; Tudela, K. Fast, Accurate Analysis of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs) in a Single Run, Including BDE-209; TN-2054; Phenomenex: Torrance, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mackintosh, S.A.; Pérez-Fuentetaja, A.; Zimmerman, L.R.; Pacepavicius, G.; Clapsadl, M.; Alaee, M.; Aga, D.S. Analytical performance of a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer compared to high resolution mass spectrometer for the analsis of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in fish. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2012, 747, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piersanti, A.; Tavoloni, T.; Bastari, E.; Lestingi, C.; Romanelli, S.; Rossi, R.; Saluti, G.; Moretti, S.; Galarini, R. A GC-EI-MS/MS Method for the determination of 15 polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in fish and shellfish tissues. Food Anal. Methods. 2018, 11, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, P.; Zuliani, T.; Milačič, R.; Ščančar, J. Development of an analytical method for the determination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in mussels and fish by gas chromatography—Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1524, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poma, G.; Malarvannan, G.; Voorspoels, S.; Symons, N.; Malysheva, S.V.; Van Loco, J.; Covaci, A. Determination of halogenated flame retardants in food: Optimization and validation of a method based on a two-step clean-up and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Control 2016, 65, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, A.R.; Camargo, A.; Martinez, D.L.; Altamirano, J.C. Dispersive solid-phase extraction as a simplified clean-up technique for biological sample extracts. Determination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 2490–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Method 1613B. Tetra-through Octa-Chlorinated Dioxins and Furans by Isotope Dilution HRGC/HRMS. 1994. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-08/documents/method_1613b_1994.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Method 1668C. Chlorinated Biphenyl Congeners in Water, Soil, Sediment, Biosolids, and Tissue by HRGC/HRMS. 2010. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPURL.cgi?Dockey=P100IJHQ.txt (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- Guidance on the Determination of Organobromine Contaminants. Available online: https://eurl-pops.eu/news/guidance-document-bcon-parameters/guidance-document-bcon-parameters-2 (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- EURL POPs. EURL Proficiency Test on the Determination of PCDD/Fs, PCBs, PBDEs and HBCDDs in Dried Citrus Pulp 2021; EURL-PT-DPB_2015-DCP, Version 1.0; EURL for halogenated POPs in Feed and Food, State Institute for Chemical and Veterinary Analysis: Freiburg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- EURL POPs. EURL Proficiency Test on the Determination of PCDD/Fs, PCBs, PBDEs and HBCDDs in Baby Food 2021; EURL-PT-DPB_2101-BF, Version 1.0; EURL for halogenated POPs in Feed and Food, State Institute for Chemical and Veterinary Analysis: Freiburg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- EURL POPs. EURL Proficiency Test on the Determination of PCDD/Fs, PCBs, BFRs, PFASs and CPs in Fish Fillet 2020; EURL-PT-POP-2001-Fl, Version 1.0; EURL for halogenated POPs in Feed and Food, State Institute for Chemical and Veterinary Analysis: Freiburg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
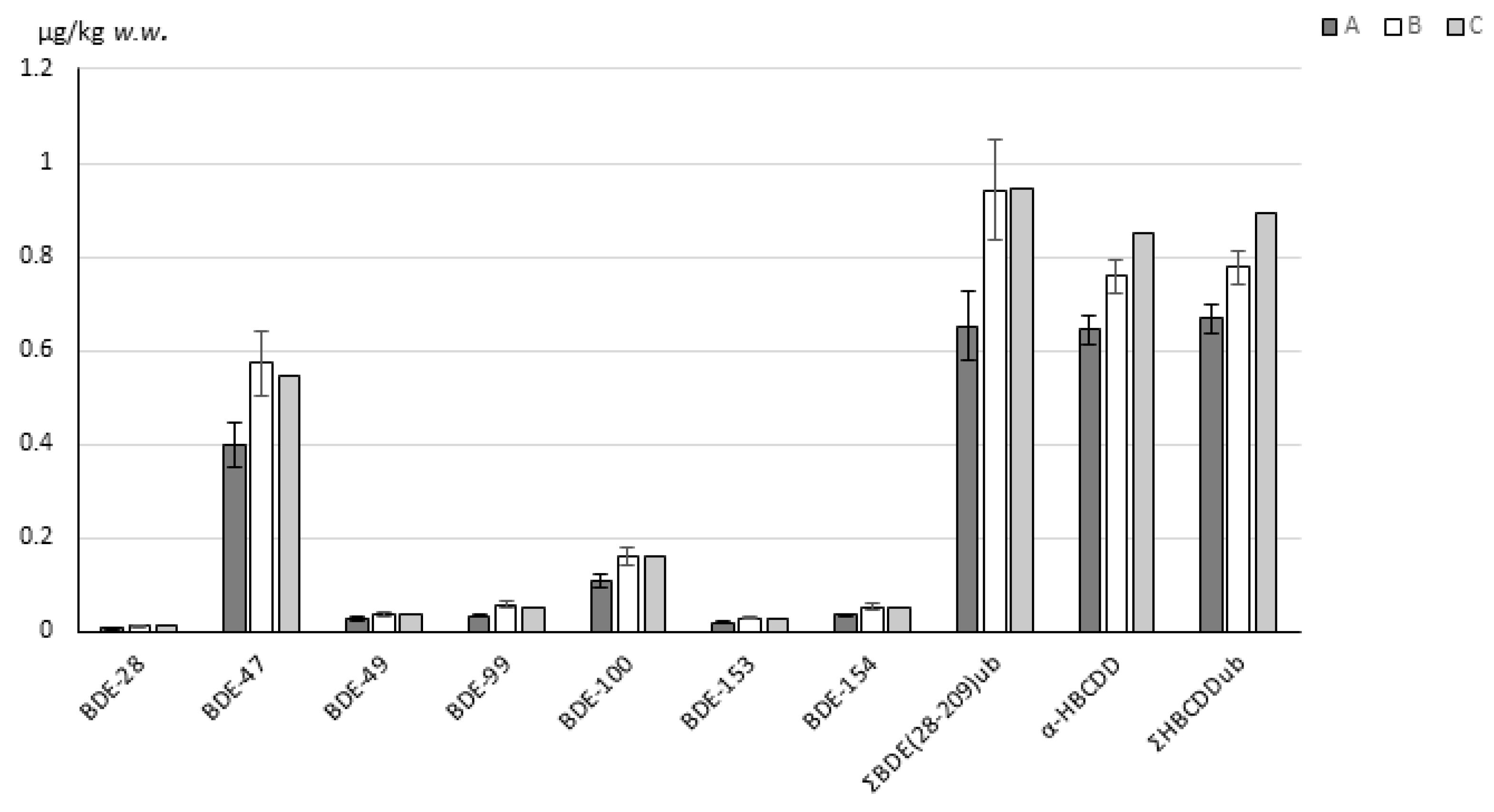
| Quantitative Transition/ion | Confirmative Transition/ions | Abundance Ratio (%RSD) a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BDE-28 | 407.8 → 248.0 (12 eV) | 405.8 → 246.0 (11 eV) | 0.97 (1.6) |
| 13C12-BDE-28 | 417.8 → 258.0 (13 eV) | 419.8 → 260.0 (8 eV) | 0.65 (1.4) |
| BDE-47, BDE-49 | 485.7 → 325.8 (14 eV) | 487.8 → 327.8 (12 eV) | 0.45 (2.4), 0.46 (0.6) |
| 13C12-BDE-47 | 497.7 → 337.8 (5 eV) | 499.7 → 339.8 (15 eV) | 1.00 (1.3) |
| BDE-99, BDE-100 | 565.6 → 405.8 (20 eV) | 563.6 → 403.8 (9 eV) | 0.63 (0.9), 0.61 (5.2) |
| 13C12-BDE-99, 13C12-BDE-100 | 577.6 → 417.8 (17 eV) | 575.6 → 415.8 (10 eV) | 0.74 (2.2), 0.72 (0.5) |
| BDE-153, BDE-154 | 643.7 → 483.8 (17 eV) | 645.7 → 485.8 (18 eV) | 0.70 (7.2), 0.66 (1.7) |
| 13C12-BDE-153, 13C12-BDE-154 | 655.7 → 495.8 (18 eV) | 657.7 → 497.8 (15 eV) | 0.58 (1.6), 0.56 (1.3) |
| BDE-183 | 723.4 → 563.6 (22 eV) | 721.4 → 561.6 (15 eV) | 0.93 (7.3) |
| 13C12-BDE-183 | 733.4 → 573.6 (16 eV) | 735.4 → 575.6 (12 eV) | 0.77 (3.5) |
| BDE-209 | 799.5 | 797.5, 801.5 | 0.83 (2.4), 0.83 (6.1) |
| 13C12-BDE-209 | 811.5 | 809.5 |
| Quantitative Transition | Confirmative Transition | Abundance Ratio (%RSD) a | Declustering Potential (V) | Entrance Potential (V) | Collision Cell Exit Potential (V) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-HBCDD | 640.5 → 78.9 (−72 V) | 640.5 → 80.9 (−72 V) | 0.93 (14) | −45 | −10 | −9 |
| 13C12-α-HBCDD | 652.6 → 80.9 (−52 V) | - | −35 | −10 | −9 | |
| ß-HBCDD | 640.5 → 80.9 (−58 V) | 640.5 → 78.9 (−58 V) | 1.04 (7.4) | −55 | −10 | −9 |
| 13C12-ß-HBCDD | 652.6 → 80.9 (−52 V) | - | −35 | −10 | −9 | |
| γ-HBCDD | 640.5 → 78.9 (−62 V) | 640.5 → 80.9 (−62 V) | 0.91 (13) | −40 | −10 | −9 |
| 13C12-γ-HBCDD | 652.6 → 80.9 (−52 V) | - | −35 | −10 | −9 |
| Analyte | Spike Level (µg/kg) | Intra-Day Precision (%) | Inter-Day Precision (%) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDE-28 | 0.01 | 4.0 | 10.9 | 102 |
| 0.3 | 1.5 | 16.4 | 95 | |
| BDE-47 | 0.01 | 5.8 | 10.4 | 101 |
| 0.3 | 3.1 | 4.3 | 112 | |
| BDE-49 | 0.01 | 4.9 | 8.0 | 106 |
| 0.3 | 5.2 | 9.1 | 119 | |
| BDE-99 | 0.01 | 5.1 | 13.1 | 102 |
| 0.3 | 3.3 | 12.8 | 96 | |
| BDE-100 | 0.01 | 4.3 | 12.6 | 105 |
| 0.3 | 1.9 | 13.7 | 98 | |
| BDE-153 | 0.01 | 5.6 | 9.6 | 98 |
| 0.3 | 1.8 | 11.3 | 97 | |
| BDE-154 | 0.01 | 4.6 | 11.4 | 105 |
| 0.3 | 2.6 | 12.4 | 106 | |
| BDE-183 | 0.01 | 6.1 | 11.9 | 99 |
| 0.3 | 3.2 | 11.1 | 102 | |
| BDE-209 | 0.01 | 7.1 | 8.3 | 105 |
| 0.1 | 2.8 | 10.4 | 94 | |
| 3 | 1.6 | 18.4 | 88 | |
| α-HBCDD | 0.01 | 11.3 | 10.7 | 96 |
| 0.3 | 5.1 | 5.2 | 98 | |
| β-HBCDD | 0.01 | 3.7 | 6.9 | 85 |
| 0.3 | 5.6 | 5.3 | 99 | |
| γ-HBCDD | 0.01 | 6.9 | / a | 85 b |
| 0.3 | 2.7 | 5.9 | 106 |
| Dried Citrus Pulp | Fish Fillet | Baby Food | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Result (µg/kg w.w.) | Trueness (%) | Result (µg/kg w.w.) | Trueness (%) | Result (µg/kg w.w.) | Trueness (%) | |
| BDE-28 | 0.009 | 98 | 0.013 | 113 | <LOQ (0.003) | (113) |
| BDE-47 | 0.120 | 101 | 0.573 | 104 | 0.251 | 117 |
| BDE-49 | 0.014 | 113 | 0.037 | 100 | <LOQ (0.006) | (119) |
| BDE-99 | 0.159 | 102 | 0.057 | 111 | 0.312 | 109 |
| BDE-100 | 0.035 | 105 | 0.161 | 100 | 0.067 | 108 |
| BDE-153 | 0.016 | 105 | 0.028 | 97 | 0.030 | 92 |
| BDE-154 | 0.014 | 105 | 0.053 | 102 | 0.024 | 100 |
| BDE-183 | 0.008 | 109 | <LOQ | n.d. | 0.040 | 113 |
| BDE-209 | 0.598 | 85 | 0.009 | n.d. | 0.297 | 86 |
| ΣBDE(28-209)ub | 0.975 | 90 | 0.942 | 100 | 1.03 | 103 |
| α-HBCDD | 0.086 | n.d. | 0.758 | 89 | 0.0946 | 105 |
| β-HBCDD | 0.059 | n.d. | <LOQ | n.d. | <LOQ | n.d. |
| γ-HBCDD | 1.21 | 127 | 0.010 | n.d. | 0.019 | n.d. |
| ΣHBCDDub | 1.35 | 127 | 0.778 | 87 | 0.124 | n.d. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lipičar, E.; Fras, D.; Javernik, N.; Prosen, H. Simultaneous Method for Selected PBDEs and HBCDDs in Foodstuffs Using Gas Chromatography—Tandem Mass Spectrometry and Liquid Chromatography—Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Toxics 2023, 11, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010015
Lipičar E, Fras D, Javernik N, Prosen H. Simultaneous Method for Selected PBDEs and HBCDDs in Foodstuffs Using Gas Chromatography—Tandem Mass Spectrometry and Liquid Chromatography—Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Toxics. 2023; 11(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleLipičar, Eva, Danijela Fras, Nino Javernik, and Helena Prosen. 2023. "Simultaneous Method for Selected PBDEs and HBCDDs in Foodstuffs Using Gas Chromatography—Tandem Mass Spectrometry and Liquid Chromatography—Tandem Mass Spectrometry" Toxics 11, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010015
APA StyleLipičar, E., Fras, D., Javernik, N., & Prosen, H. (2023). Simultaneous Method for Selected PBDEs and HBCDDs in Foodstuffs Using Gas Chromatography—Tandem Mass Spectrometry and Liquid Chromatography—Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Toxics, 11(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010015






