Recent Advances and Future Prospects on the Tailing Covering Technology for Oxidation Prevention of Sulfide Tailings
Abstract
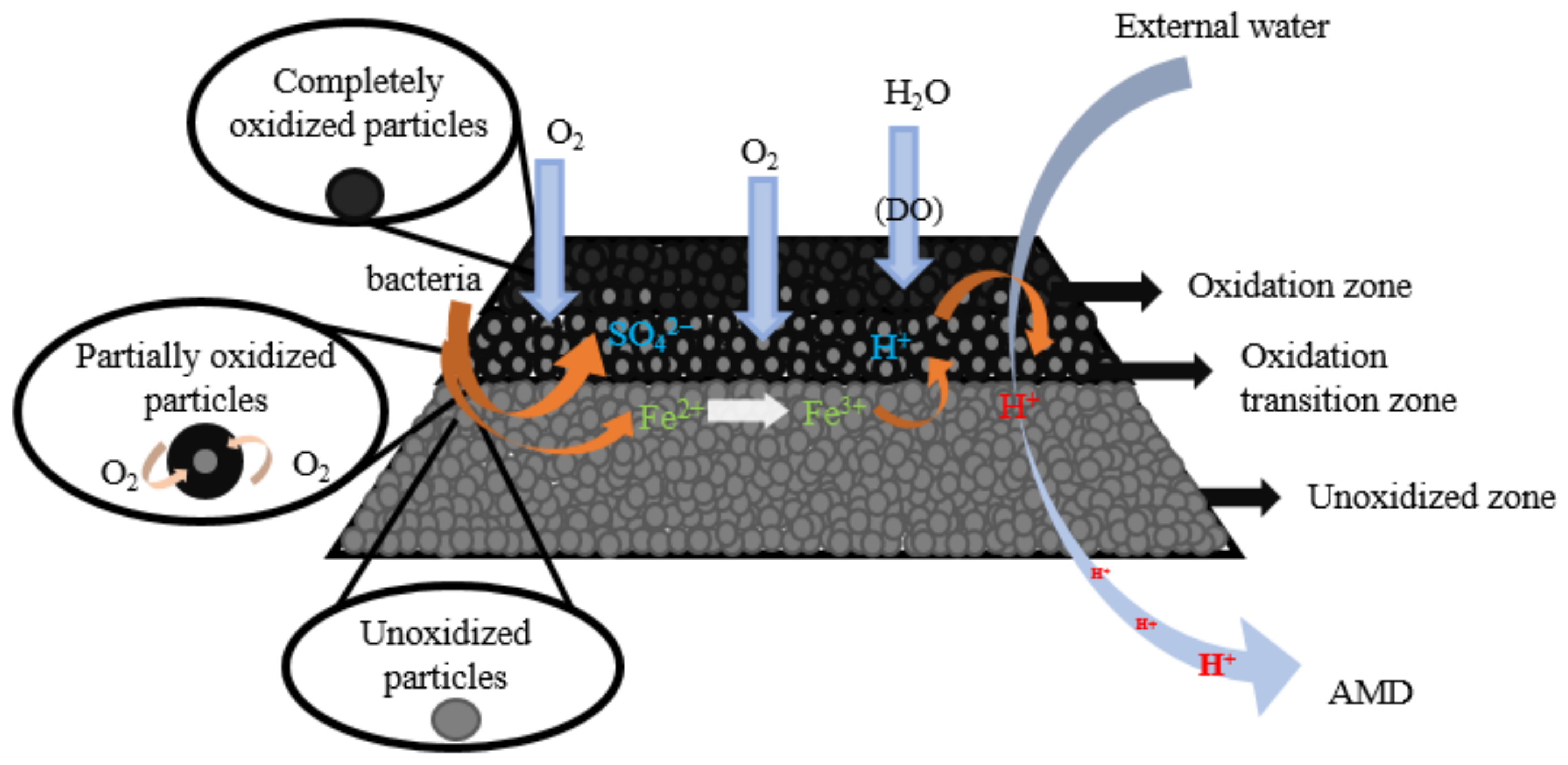
1. Introduction
2. Tailings Cover Technology
2.1. Wet Covers
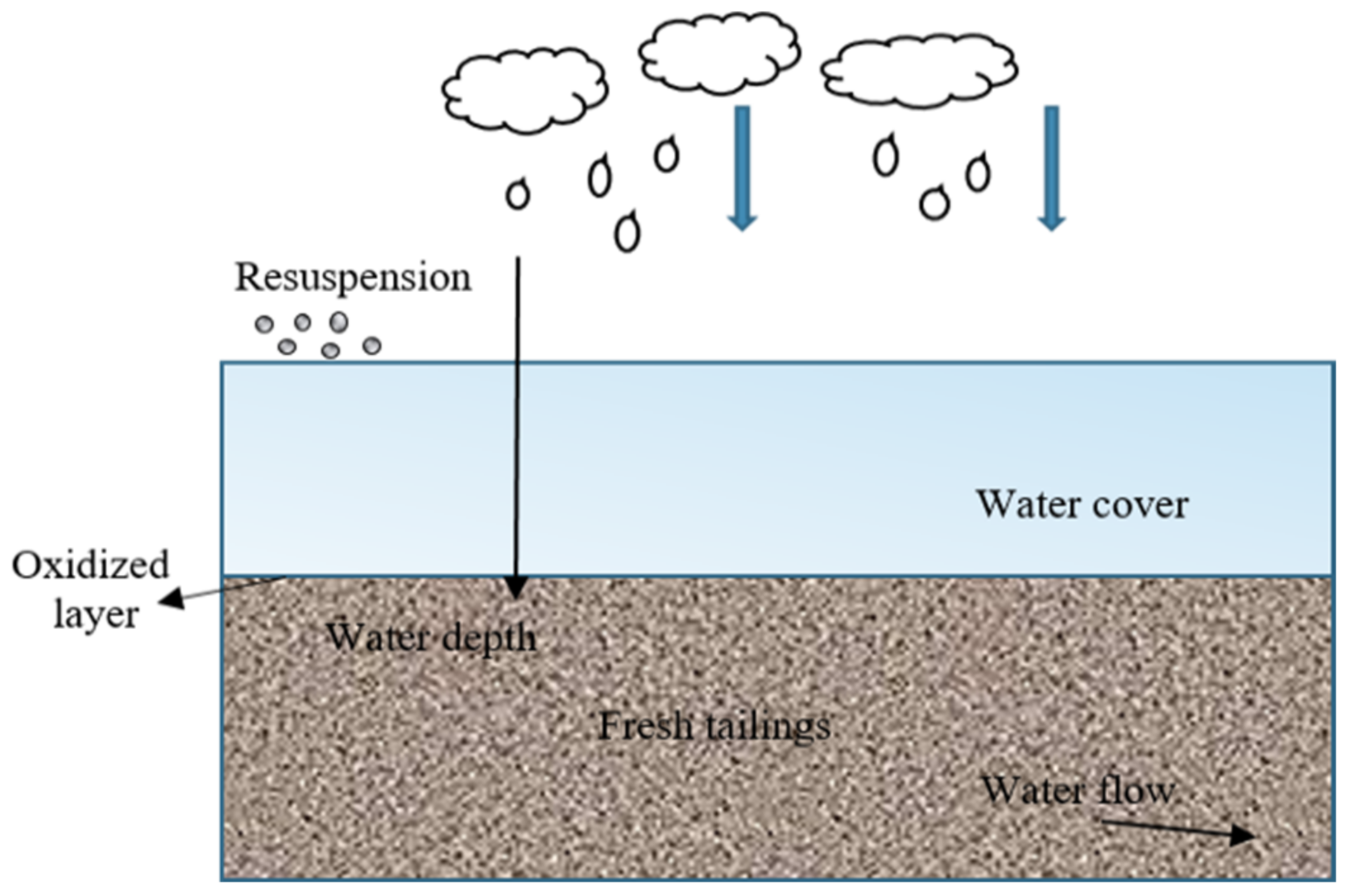
2.1.1. Flooded Cover
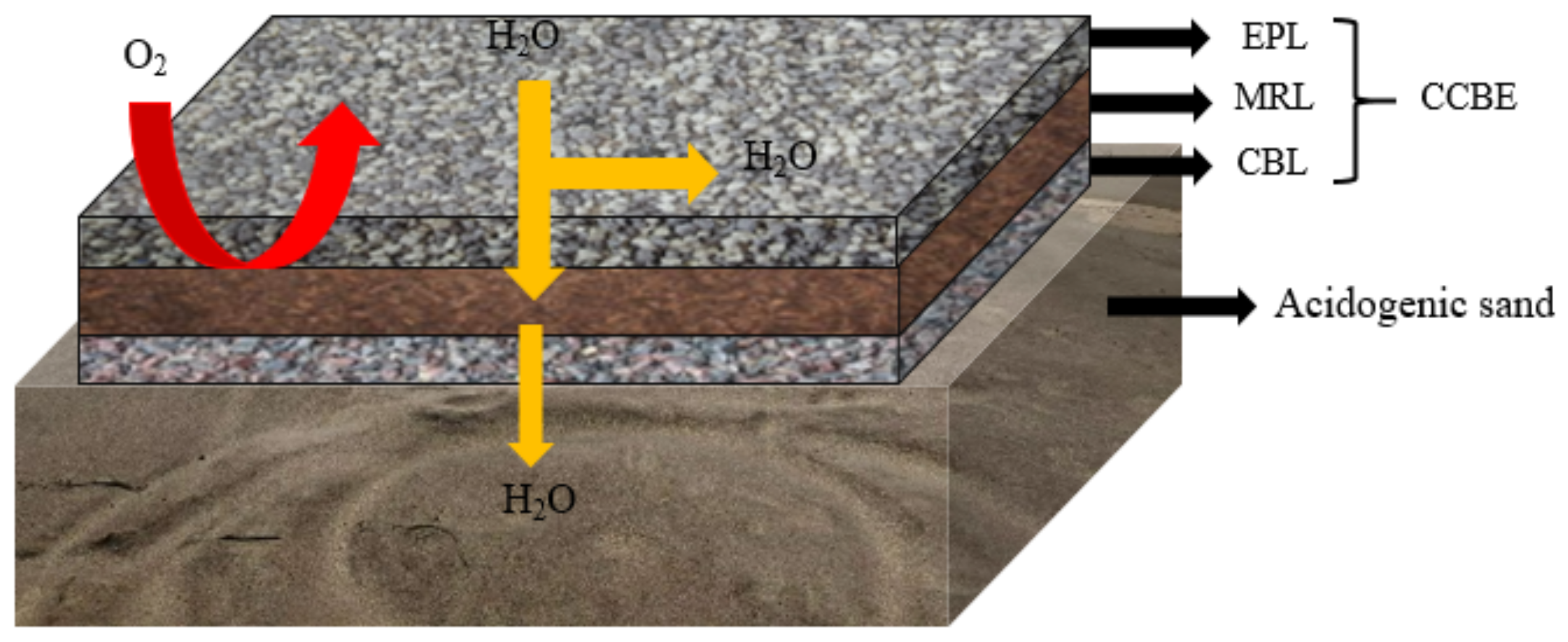
2.1.2. Cover with Capillary Barrier Effects (CCBE)
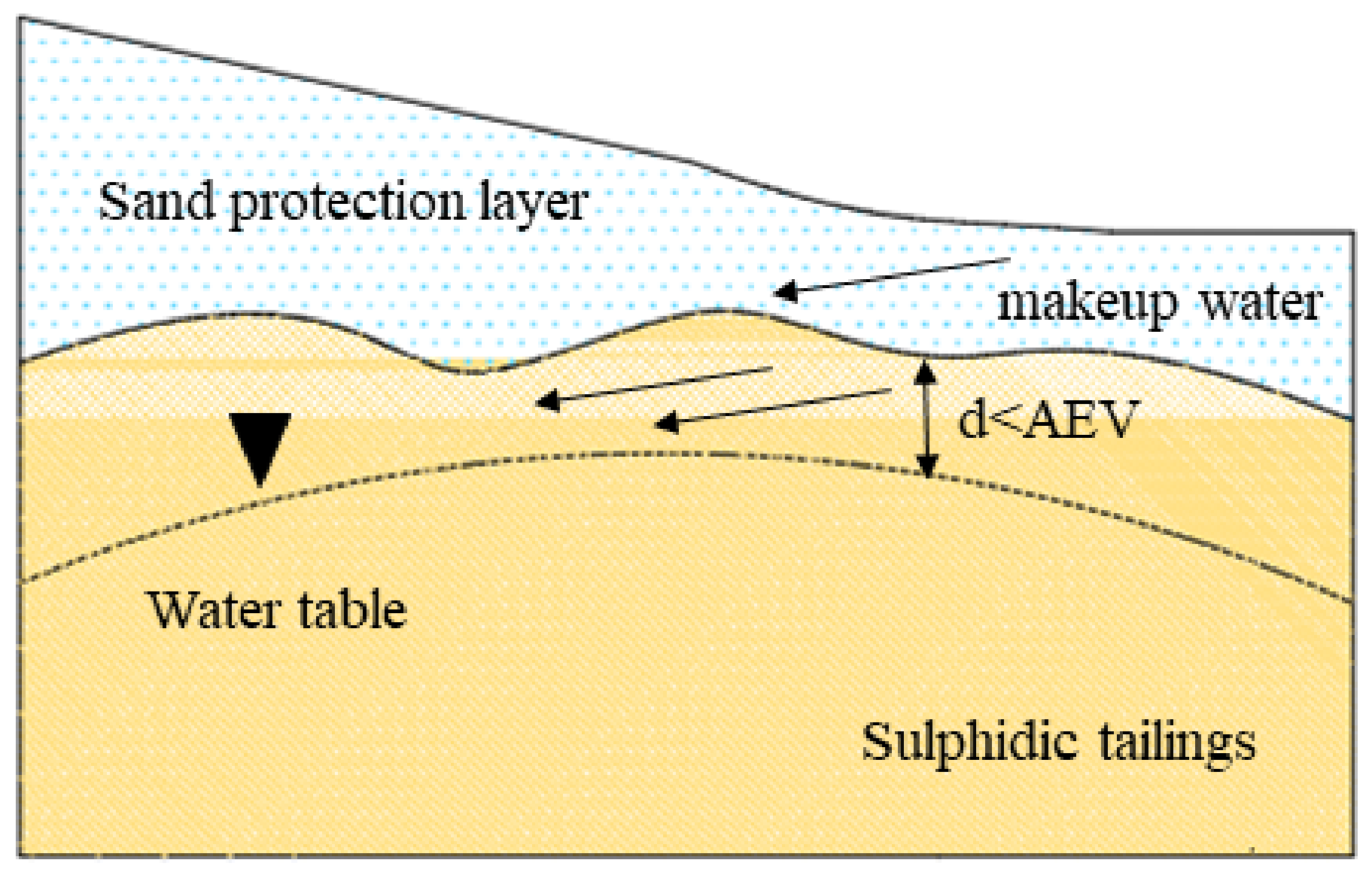
2.1.3. Elevated Water Table (EWT)
2.2. Dry Covers
2.2.1. Monolayer Cover
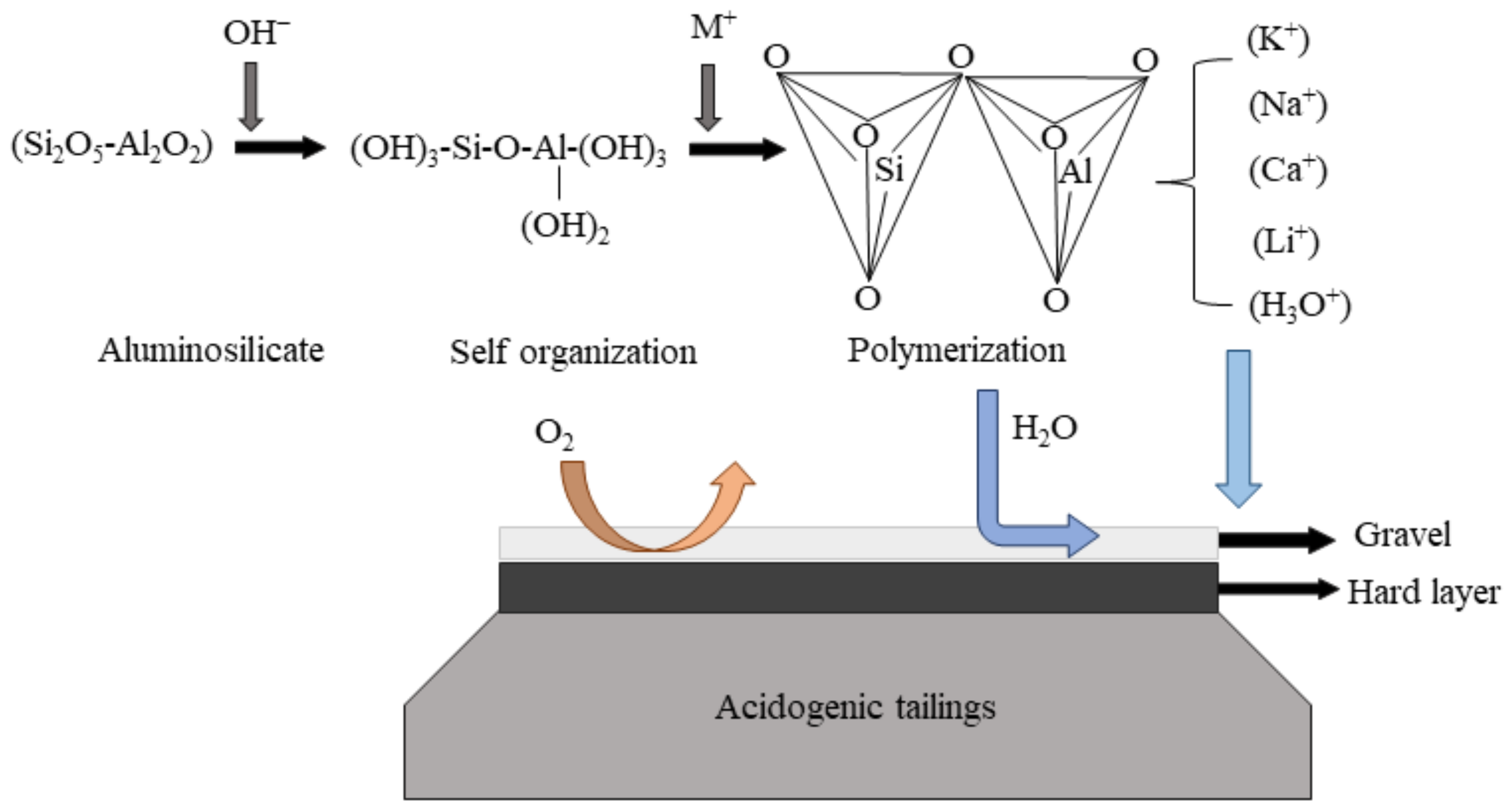
2.2.2. Stabilization Cover
| Structure | Main Criteria Weight | Cost Accounting (€/m2) | Normalized Cluster Value | Priority Order | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Above the Surface | Below Surface | |||||
| SPC a | Vegetation (100 mm) | PC stabilized tailings (1 m) | Economic, 33% Technical, 33% Social-Ecological, 33% | 26.32 | 0.172 | 3 |
| AAC b | Vegetation (100 mm) | AAC stabilized tailings (1 m) | Economic, 33% Technical, 33% Social-Ecological, 33% | 26.78 | 0.238 | 2 |
| AHCL c | Vegetation (100 mm) + Moraine (300 mm) + tailings (200 mm) + CaO + moraine (200 mm) | AAC stabilized tailings (300 mm) | Economic, 33% Technical, 33% Social-Ecological, 33% | 22.09 | 0.262 | 1 |
| Soil layer | 500 | |||||
| Multilayer | 2000–3000 | |||||
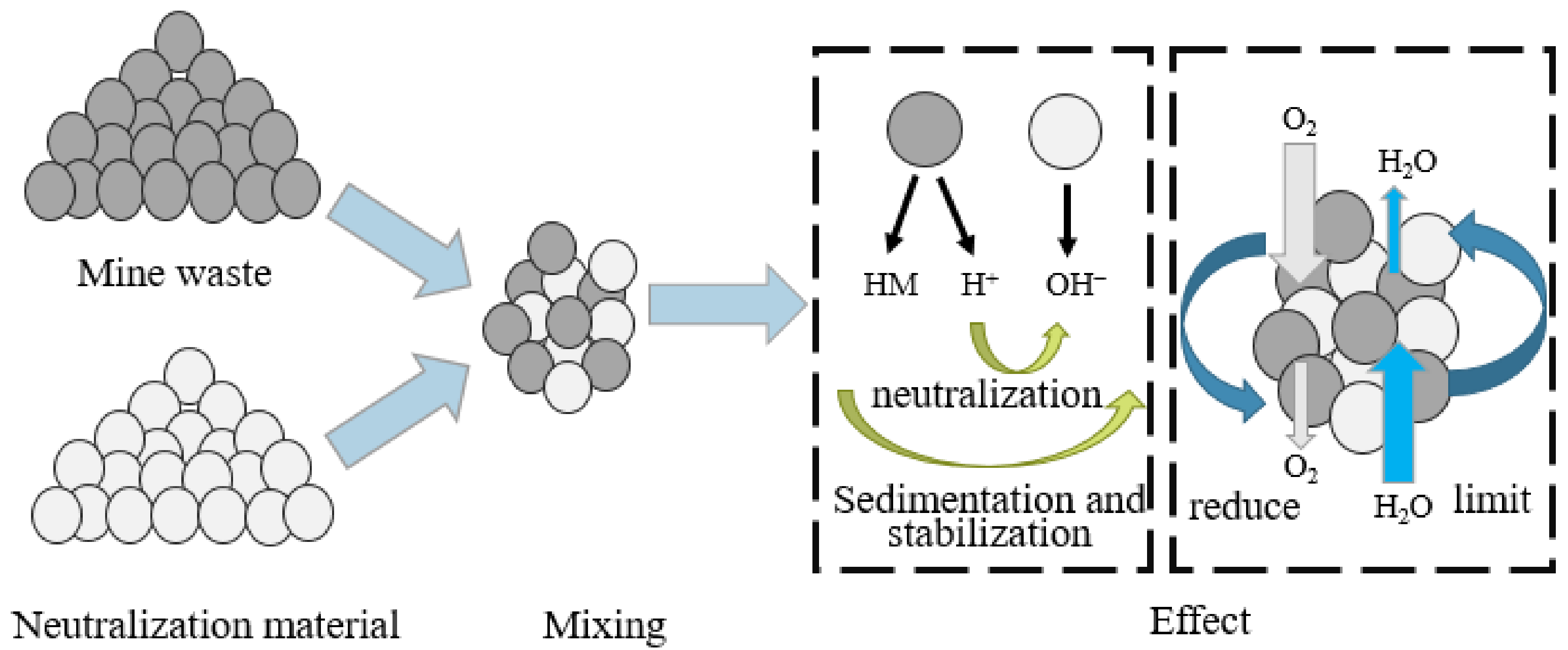
2.2.3. Benign Material Cover
2.3. Organic Reactive Barriers (ORB)
3. Future Perspectives
- (1)
- Most of the tailings covering schemes are limited to short-term research and lack of long-term problem monitoring. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct relatively long-term simulation experiments in the future research, and then it is necessary to predict the long-term treatment performance with appropriate geological simulation software so as to verify the lasting effectiveness of the scheme.
- (2)
- The availability of water and oxygen is greatly reduced after physical covering treatment. However, the internal reactions caused by covering, such as side reactions, the proliferation and activity changes of aerobic and anaerobic bacteria, and the protective effect of precipitation coating on the surface of particles, magnify the microscopic oxidation process of sulfide minerals. Thus, the micro-oxidation process after the implementation of the technology should be studied, and the periodic oxidation reactions of sulfide minerals under different conditions and different oxidation states are encouraged to be analyzed.
- (3)
- The management of mine environment should focus on sustainability, in which ecological restoration is an important part. Therefore, the tailing covering system can be combined with vegetation restoration as synergistic technology for both pollution control and ecological restoration.
- (4)
- The introduction of cheap materials into the treatment scheme has showed great economic advantages. The long-term stability, as well as the leaching and migration of harmful substances and harmful side reactions of new materials, especially industrial wastes, can be further investigated in depth. In addition, the application of new materials and new technologies can be comprehensively evaluated for their environmental impacts.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adiansyah, J.S.; Rosano, M.; Vink, S.; Keir, G. A framework for a sustainable approach to mine tailings management: Disposal strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 108, 1050–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.; Hallberg, K. Acid mine drainage remediation options: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 338, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azapagic, A. Developing a framework for sustainable development indicators for the mining and minerals industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2004, 12, 639–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, S.; Vivo, B.D.; Lima, A.; Frattasio, G.; Kříbek, B.; Nyambe, I.; Majer, V. Prioritising environmental risk at the regional scale by a GIS aided technique: The Zambian Copperbelt Province case study. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 144, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anawar, H.M. Sustainable rehabilitation of mining waste and acid mine drainage using geochemistry, mine type, mineralogy, texture, ore extraction and climate knowledge. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 158, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, M.J.; Choi, B.Y.; Lee, G.; Hwang, Y.H.; Yang, J.S.; O’Loughlin, E.J.; Kwon, M.J. Water quality changes in acid mine drainage streams in Gangneung, Korea, 10 years after treatment with limestone. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 159, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, M.C.; Pérez-Sirvent, C.; Martínez-Sánchez, M.; Vidal, J.; Tovar, P.J.; Bech, J. Abandoned mine sites as a source of contamination by heavy metals: A case study in a semi-arid zone. J. Geochem. Explor. 2008, 96, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niane, B.; Moritz, R.; Guédron, S.; Ngom, P.M.; Pfeifer, H.R.; Mall, I.; Poté, J. Effect of recent artisanal small-scale gold mining on the contamination of surface river sediment: Case of Gambia River, Kedougou region, southeastern Senegal. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 144, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, A.; Komnitsas, K.; Halikia, I. Use of organic covers for acid mine drainage control. Miner. Eng. 2000, 13, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcil, A.; Koldas, S. Acid Mine Drainage (AMD): Causes, treatment and case studies. J. Clean. Prod. 2006, 14, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Couperthwaite, S.J.; Millar, G.J. Alternative neutralisation materials for acid mine drainage treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 22, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, S. Research on treatment of mine wastewater using sulfide precipitation floatation. Tech. Equip. Environ. Pollut. Control 2004, 5, 60–62. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nariyan, E.; Wolkersdorfer, C.; Sillanpää, M. Sulfate removal from acid mine water from the deepest active European mine by precipitation and various electrocoagulation configurations. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 227, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pat-Espadas, A.M.; Portales, R.L.; Amabilis-Sosa, L.E.; Gomez, G.; Vidal, G. Review of Constructed Wetlands for Acid Mine Drainage Treatment. Water 2018, 10, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.C.; Papirio, S.; Luongo, V.; Nancharaiah, Y.V.; Cennamo, P.; Esposito, G.; Hullebusch, E.V.; Lens, P. Comparative performance of anaerobic attached biofilm and granular sludge reactors for the treatment of model mine drainage wastewater containing selenate, sulfate and nickel. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 345, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Dong, Y.; Lin, H. Research progress of source control technologies of acid mine drainage. Saf. Environ. Eng. 2020, 27, 7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Swanson, D.A.; Barbour, S.L.; Wilson, G.W. Dry-site versus wet-site cover design. Proceeding of the 4th Interational Conference on Acid Rock Drainage, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 31 May–6 June 1997; Volume 4, pp. 1595–1610. [Google Scholar]
- Garcilaso, I. European Commission, 2004a. Reference Document on Best Available Techniques for Management of Tailings and Waste-Rock in Mining Activities, BREF Code MTWR, July; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Aachib, M.; Mbonimpa, M.; Aubertin, M. Measurement and Prediction of the Oxygen Diffusion Coefficient in Unsaturated Media, with Applications to Soil Covers. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2004, 156, 163–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, M.; Aubertin, M. Evaluation de l’effet du degre de saturation sur la diffusion et la consommation d’oxygene dans des residus miniers sulfureux. In Proceedings of the 8th Joint IAH-CNC and CGS Groundwater Specialty Conference and 90th Canadian Geotechnical Conference, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 21–24 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Romano, C.G.; Mayer, K.U.; Jones, D.R.; Ellerbroek, D.A.; Blowes, D.W. Effectiveness of various cover scenarios on the rate of sulfide oxidation of mine tailings. J. Hydrol. 2003, 271, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.M.; Parbhakar-Fox, A. Mineralogical and geochemical characterization of the Old Tailings Dam, Australia: Evaluating the effectiveness of a water cover for long-term AMD control. Appl. Geochem. 2016, 68, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanful, E.K.; Verma, A. Oxidation of flooded mine tailings due to resuspension. Can. Geotech. J. 1999, 36, 826–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneault, B.; Campbell, P.; Tessier, A.; Vitre, R.D. Geochemical changes in sulfidic mine tailings stored under a shallow water cover. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1066–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanful, M.A.S.; Ernest, K. A design approach for selecting the optimum water cover depth for subaqueous disposal of sulfide mine tailings. Rev. Can. Géotech. 2005, 42, 207–228. [Google Scholar]
- Lottermoser, B.G. Mine Wastes: Characterization, Treatment and Environmental Impacts; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kalonji-Kabambi, A.; Bussière, B.; Demers, I. Hydrogeochemical Behavior of Reclaimed Highly Reactive Tailings, Part 2: Laboratory and Field Results of Covers Made with Mine Waste Materials. Minerals 2020, 10, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aachib, M.; Aubertin, M. Essais en colonne sur des couvertures avec effets de barrière capillaire. In Proceedings of the 51st Canadian Geotechnical Conference, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 4–7 October 1998; Volume 2, pp. 837–844. [Google Scholar]
- Bussière, B.; Aubertin, M.; Chapuis, R.P. The behavior of inclined covers used as oxygen barriers. Can. Geotech. J. 2003, 40, 512–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, T.; Bussiere, B.; Aubertin, M.; Molson, J. Comparative performance of cover systems to prevent acid mine drainage from pre-oxidized tailings: A numerical hydro-geochemical assessment. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2018, 214, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussière, B.; Aubertin, M.; Mbonimpa, M.; Molson, J.W.; Chapuis, R.P. Field experimental cells to evaluate the hydrogeological behaviour of oxygen barriers made of silty materials. Can. Geotech. J. 2007, 44, 245–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabambi, A.K.; Bussière, B.; Demers, I. Hydrogeological Behaviour of Covers with Capillary Barrier Effects Made of Mining Materials. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2017, 35, 1199–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molson, J.; Aubertin, M.; Bussière, B.; Benzaazoua, M. Geochemical transport modelling of drainage from experimental mine tailings cells covered by capillary barriers. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagenais, A.M.; Aubertin, M.; Bussiere, B.; Cyr, J. Performance of the Lorraine mine site cover to limit oxygen migration. In Transactions—Society for Mining Metallurgy and Exploration Incorporated; SME: Englewood, CO, USA, 2005; Volume 318. [Google Scholar]
- Larochelle, C.G.; Bussiere, B.; Pabst, T. Acid-Generating Waste Rocks as Capillary Break Layers in Covers with Capillary Barrier Effects for Mine Site Reclamation. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagenais, A.-M.; Aubertin, M.; Bussière, B.; Martin, V. Large scale applications of covers with capillary barrier effects to control the production of acid mine drainage. Proc. Post-Min. 2005, 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ouangrawa, M.; Aubertin, M.; Molson, J.W.; Bussière, B.; Zagury, G.J. Preventing Acid Mine Drainage with an Elevated Water Table: Long-Term Column Experiments and Parameter Analysis. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 213, 437–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouangrawa, M.; Molson, J.; Aubertin, M.; Bussière, B.; Zagury, G.J. Reactive transport modelling of mine tailings columns with capillarity-induced high water saturation for preventing sulfide oxidation. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 1312–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouangrawa, M.; Molson, J.; Aubertin, M.; Zagury, G.; Bussière, B. The effect of water table elevation on acid mine drainage from reactive tailings: A laboratory and numerical modeling study. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Acid Rock Drainage (ICARD), St. Louis, MO, USA, 26–30 March 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mbonimpa, M.; Aubertin, M.; Aachib, M.; Bussière, B. Diffusion and consumption of oxygen in unsaturated cover materials. Can. Geotech. J. 2003, 40, 916–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussière, B.; Maqsoud, A.; Aubertin, M.; Martschuk, J.; Mcmullen, J.; Julien, M. Performance of the oxygen limiting cover at the LTA site, Malartic, Quebec. CIM Bull. 2006, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Dagenais, A.M.; Aubertin, M.; Bussière, B. Parametric study on the water content profiles and oxidation rates in nearly saturated tailings above the water table. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Acid Rock Drainage, St. Louis, MO, USA, 26–30 March 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Khire, M.V.; Benson, C.H.; Bosscher, P.J. Capillary Barriers: Design Variables and Water Balance. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. 2000, 126, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobchuk, B.; Nichol, C.; Wilson, G.W.; Aubertin, M. Evaluation of a single-layer desulphurized tailings cover. Can. Geotech. J. 2013, 50, 777–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagenais, A.M. Techniques de Controle du Drainage Minier Acide Basees Sur les Effets Capillaires; Ecole Polytechnique: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kleinmann, R. At-source control of acid mine drainage. Mine Water Environ. 1990, 9, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, P.R.; Crundwell, F.K. The kinetics of the oxidation of pyrite by ferric ions and dissolved oxygen: An electrochemical study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, T.; Molson, J.; Aubertin, M.; Bussiere, B. Reactive transport modelling of the hydro-geochemical behaviour of partially oxidized acid-generating mine tailings with a monolayer cover. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 78, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorakhki, M.H.; Bareither, C.A.; Gorakhki, M.H.; Bareither, C.A. Sustainable reuse of mine tailings and waste rock as water-balance covers. Minerals 2017, 7, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylona, E.; Xenidis, A.; Paspaliaris, I. Inhibition of acid generation from sulphidic wastes by the addition of small amounts of limestone. Miner. Eng. 2000, 13, 1161–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demers, I.; Bouda, M.; Mbonimpa, M.; Benzaazoua, M.; Bois, D.; Gagnon, M. Valorization of acid mine drainage treatment sludge as remediation component to control acid generation from mine wastes, part 2: Field experimentation. Miner. Eng. 2015, 76, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakkou, R.; Benzaazoua, M.; Bussiere, B. Laboratory Evaluation of the Use of Alkaline Phosphate Wastes for the Control of Acidic Mine Drainage. Mine Water Environ. 2009, 28, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demers, I.; Benzaazoua, M.; Mbonimpa, M.; Bouda, M.; Bois, D.; Gagnon, M. Valorisation of acid mine drainage treatment sludge as remediation component to control acid generation from mine wastes, part 1: Material characterization and laboratory kinetic testing. Miner. Eng. 2015, 76, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Tabelin, C.B.; Jeon, S.; Li, X.; Seno, K.; Ito, M.; Hiroyoshi, N. A review of recent strategies for acid mine drainage prevention and mine tailings recycling. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzaazoua, M.; Marion, P.; Picquet, I.; Bussière, B. The use of pastefill as a solidification and stabilization process for the control of acid mine drainage. Miner. Eng. 2004, 17, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahna, J.S.; Song, H.; Yim, G.J.; Sang, W.J.; Kim, J.G. An engineered cover system for mine tailings using a hardpan layer: A solidification/stabilization method for layer and field performance evaluation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 197, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzaazoua, M.; Fall, M.; Belem, T. A contribution to understanding the hardening process of cemented pastefill. Miner. Eng. 2004, 17, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzaazoua, M.; Bussière, B.; Demers, I.; Aubertin, M.; Fried, é.; Blier, A. Integrated mine tailings management by combining environmental desulphurization and cemented paste backfill: Application to mine Doyon, Quebec, Canada. Miner. Eng. 2008, 21, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komnitsas, K.; Zaharaki, D. Geopolymerisation: A review and prospects for the minerals industry. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 1261–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Torgal, F.; Castro-Gomes, J.; Jalali, S. Alkali-activated binders: A review Part 1. Historical background, terminology, reaction mechanisms and hydration products. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 1305–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Yanful, E.K. A review of binders used in cemented paste tailings for underground and surface disposal practices. Cheminform 2013, 131, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.L.; Zhang, L.Y.; Huang, J.B.; Shi, H.S. Detoxification and solidification of heavy metal of chromium using fly ash-based geopolymer with chemical agents. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 151, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkkinen, M.; Kujala, K.; Gehör, S. Decision support framework for solid waste management based on sustainability criteria: A case study of tailings pond cover systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 263, 117583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, V.K.B.; Raj, S.K.; Sairam, M.D.; Kasyap, A.; Kumar, V.G.; Padmapriya, R.; Baalamurugan, J.; Sonawane, P.D. Geopolymer green technology. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Processing and Fabrication of Advanced Materials (PFAM), Chennai, India, 7–9 December 2021; pp. 1003–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Kefeni, K.K.; Msagati, T.A.M.; Mamba, B.E.B. Acid mine drainage: Prevention, treatment options, and resource recovery: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 151, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alakangas, L.; Andersson, E.; Mueller, S. Neutralization/prevention of acid rock drainage using mixtures of alkaline by-products and sulfidic mine wastes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 7907–7916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Jorda, M.P.; Garrido, F.; Garcia-Gonzalez, M.T. Effect of the addition of industrial by-products on Cu, Zn, Pb and As leachability in a mine sediment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 213–214, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doye, I.; Duchesne, J. Neutralisation of acid mine drainage with alkaline industrial residues: Laboratory investigation using batch-leaching tests. Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 1197–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertocchi, A.F.; Ghiani, M.; Peretti, R.; Zucca, A. Red mud and fly ash for remediation of mine sites contaminated with As, Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 134, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Lopez, R.; Nieto, J.M.; de Almodovar, G.R. Immobilization of toxic elements in mine residues derived from mining activities in the Iberian Pyrite Belt (SW Spain): Laboratory experiments. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 1919–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olds, W.; Weber, P.; Pizey, M. Alkalinity producing caps for minimisation of acid mine drainage generation in waste rock dumps. In Proceedings of the AusIMM New Zealand Branch Annual Conference, Nelson, New Zealand, 25–28 August 2013; pp. 253–262. [Google Scholar]
- Smart, R.; Miller, S.D.; Stewart, W.S.; Rusdinar, Y.; Schumann, R.E.; Kawashima, N.; Li, J. In situ calcite formation in limestone-saturated water leaching of acid rock waste. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3392–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Abreu, A.T.; de Faria, E.M.; Guimaraes, J.A.C.; Leite, A.D.; de Lena, J.C. Laboratory evaluation of the use of alkaline covers to prevent acid mine drainage. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2012, 36, 787–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Dong, X. At-Source control methods for acid mine drainage from tailing impoundments. China Min. Mag. 2015, 24, 6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Germain, D.; Tassé, N.; Cyr, J. Rehabilitation of Mine Tailings by Simultaneous Prevention of Oxidation and Treatment of Acid Effluents Using a Wood-Waste Cover. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Acid Rock Drainage, Cairns, Australian, 14–17 July 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cabral, A.; Racine, I.; Burnotte, F.; Lefebvre, G. Diffusion of oxygen through a pulp and paper residue barrier: Reply. Can. Geotech. J. 2001, 38, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, W.G.; Belzile, N.; Wiseman, M.E.; Winterhalder, K. Composted organic wastes as anaerobic reducing covers for long term abandonment of acid-generating tailing. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Mining and Reclamation (ASMR), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 24–29 April 1994; pp. 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nason, P.; Jia, Y.; Maurice, C.; Alakangas, L.; Öhlander, B. Biodegradation of Biosolids Under Aerobic Conditions: Implications for Cover Materials for Sulfide Mine Tailings Remediation. Mine Water Environ. 2016, 35, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeta, I.; Ptacek, C.J.; Blowes, D.W.; Jambor, J.L. The potential for metal release by reductive dissolution of weathered mine tailings. J. Contam. Hydrol. 1995, 17, 239–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Si, M.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Lin, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhu, F.; Tian, S.; Zhao, Q. Recent Advances and Future Prospects on the Tailing Covering Technology for Oxidation Prevention of Sulfide Tailings. Toxics 2023, 11, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010011
Si M, Chen Y, Li C, Lin Y, Huang J, Zhu F, Tian S, Zhao Q. Recent Advances and Future Prospects on the Tailing Covering Technology for Oxidation Prevention of Sulfide Tailings. Toxics. 2023; 11(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleSi, Meiyan, Yunjian Chen, Chen Li, Yichao Lin, Jianhong Huang, Feng Zhu, Senlin Tian, and Qun Zhao. 2023. "Recent Advances and Future Prospects on the Tailing Covering Technology for Oxidation Prevention of Sulfide Tailings" Toxics 11, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010011
APA StyleSi, M., Chen, Y., Li, C., Lin, Y., Huang, J., Zhu, F., Tian, S., & Zhao, Q. (2023). Recent Advances and Future Prospects on the Tailing Covering Technology for Oxidation Prevention of Sulfide Tailings. Toxics, 11(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11010011