Combined Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria Inoculants Were More Beneficial than Single Agents for Plant Growth and Cd Phytoextraction of Brassica juncea L. during Field Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Bacterial Suspensions
2.2. Field Layout and Experimental Design
2.3. Determination of Cd Contents in Plant Samples and Soil Samples
2.4. Calculation of Plant Cd Extraction and Soil Cd Removal
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of PGPB Inoculants on Plant Growth
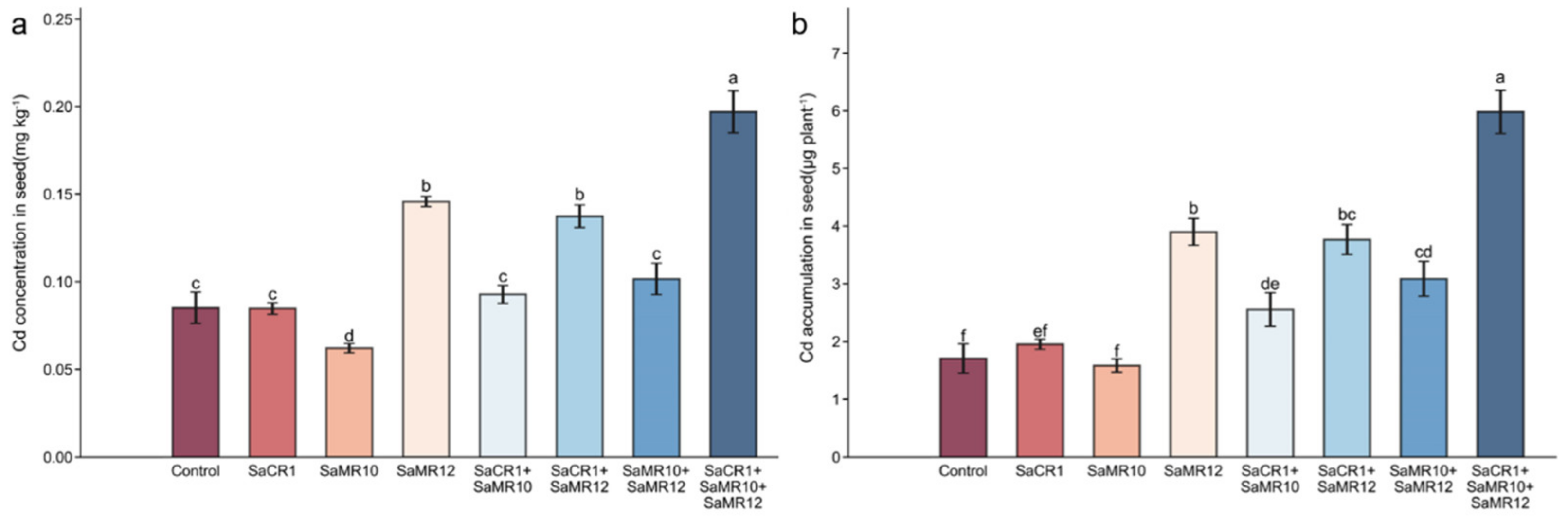
3.2. Effects of PGPB Inoculants on Seed Yield, Seed Cd Uptake, and Accumulation
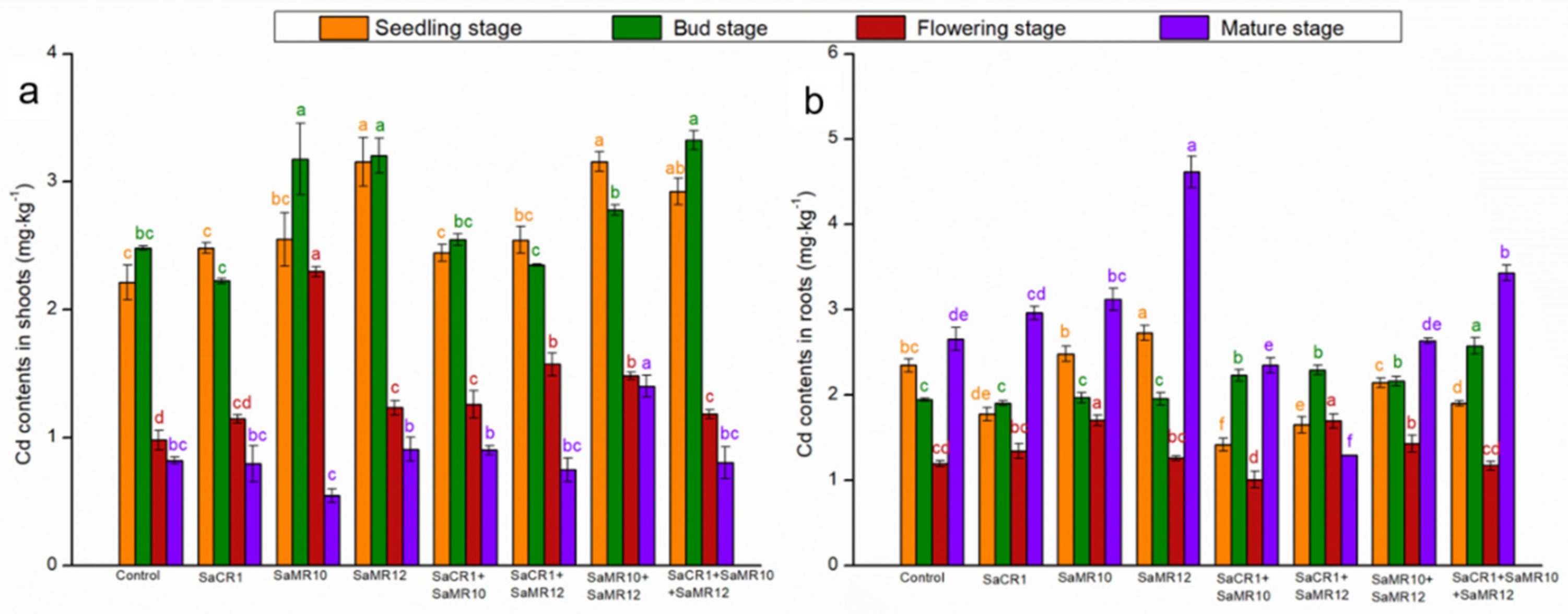
3.3. Effects of PGPB Inoculants on Plant Cd Uptake and Accumulation
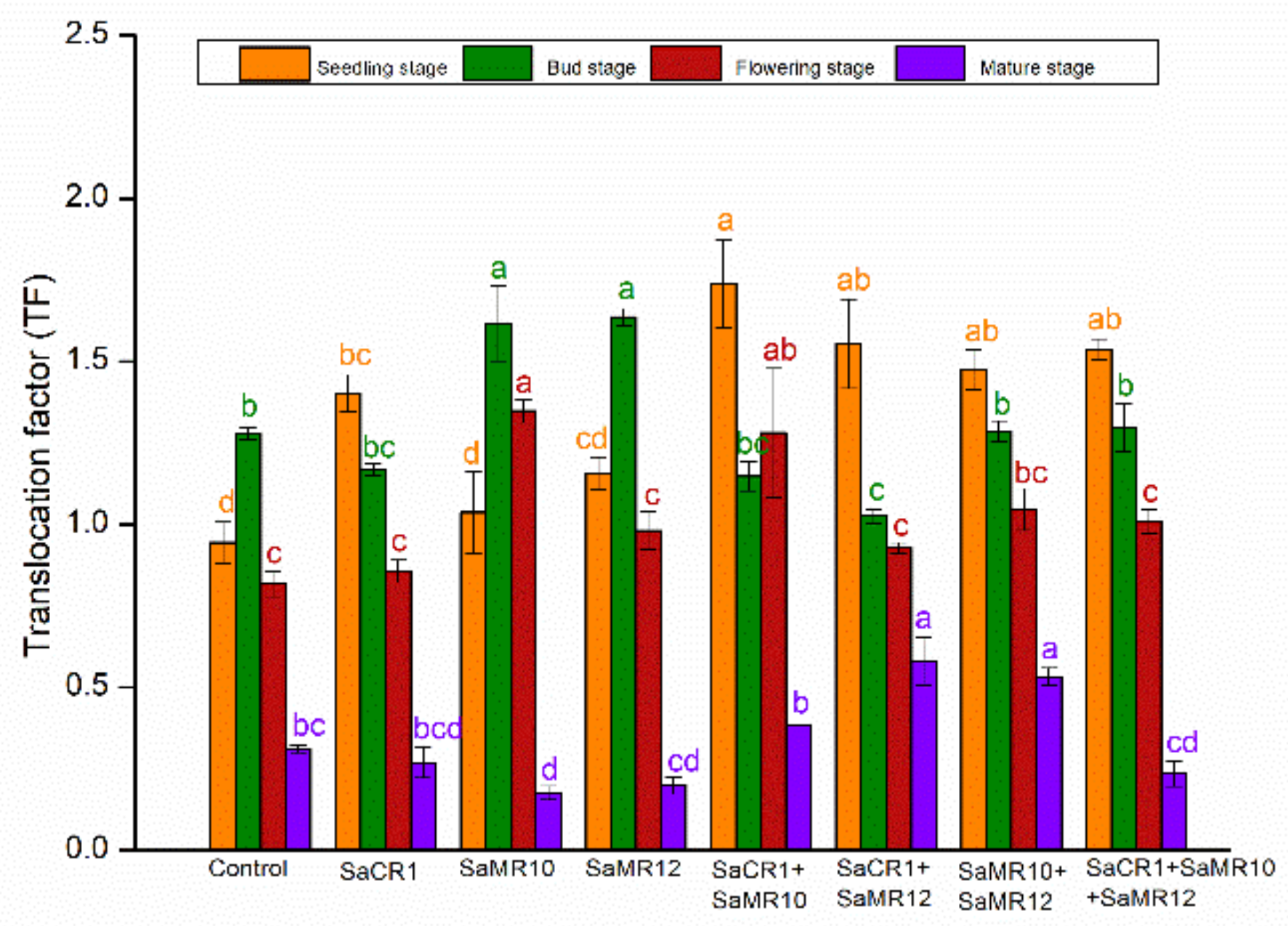
3.4. Effects of PGPB Inoculants on Cd Translocation Factor
3.5. Effects of PGPB Inoculants on Plant Cd Extraction and Soil Cd Removal
4. Discussion
4.1. PGPB Combined Inoculants Were More Beneficial to Plant Growth
4.2. PGPB Combined Inoculants Were More Pronounced for Cd Phytoremediation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Rehman, M.Z.U.; Rinklebe, J.; Tsang, D.C.; Bashir, A.; Maqbool, A.; Tack, F.; Ok, Y.S. Cadmium phytoremediation potential of Brassica crop species: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 1175–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cojocaru, P.; Gusiatin, Z.M.; Cretescu, I. Phytoextraction of Cd and Zn as single or mixed pollutants from soil by rape (Brassica napus). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 10693–10701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seth, C.S.; Chaturvedi, P.K.; Misra, V. The role of phytochelatins and antioxidants in tolerance to Cd accumulation in Brassica juncea L. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 71, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Shi, Y.; Chen, X.; Huang, B. Screening of Cd-safe genotypes of Chinese cabbage in field condition and Cd accumulation in relation to organic acids in two typical genotypes under long-term Cd stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 16590–16599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinadasa, N.; Collins, D.; Holford, P.; Milham, P.J.; Conroy, J.P. Reactions to cadmium stress in a cadmium-tolerant variety of cabbage (Brassica oleracea L.): Is cadmium tolerance necessarily desirable in food crops? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 23, 5296–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozdova, I.; Alekseeva-Popova, N.; Dorofeyev, V.; Bech, J.; Belyaeva, A.; Roca, N. A comparative study of the accumulation of trace elements in Brassicaceae plant species with phytoremediation potential. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 108, 104377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-León, E.; Ruiz, J.M.; Albacete, A.; Blasco, B. Tolerance to cadmium toxicity and phytoremediation potential of three Brassica rapa CAX1a TILLING mutants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 189, 109961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Habib, M.; Kakavand, S.N.; Zahid, Z.; Zahra, N.; Sharif, R.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Phytoremediation of Cadmium: Physiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Mechanisms. Biology 2020, 9, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ge, C.F.; Xu, S.A.; Wu, Y.J.; Sahito, Z.A.; Ma, L.Y.; Pan, F.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, L.; Feng, Y.; et al. The endophytic bacterium Sphingomonas SaMR12 alleviates Cd stress in oilseed rape through regulation of the GSH-AsA cycle and antioxidative enzymes. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Luo, S.; Wu, Y.; Ye, J.; Wang, Q.; Xu, X.; Pan, F.; Khan, K.Y.; Feng, Y.; Yang, X. The effects of the endophytic bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens Sasm05 and IAA on the plant growth and cadmium uptake of Sedum alfredii Hance. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, X.; Xu, M.; Wei, Q.; Tang, M.; Guan, L.; Lou, L.; Xu, X.; Hu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Z.; et al. Promotion of growth and phytoextraction of cadmium and lead in Solanum nigrum L. mediated by plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 205, 111333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.F.; Vivanco, J.M.; Shen, Q.R. The unseen rhizosphere root-soil-microbe interactions for crop production. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2017, 37, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, W.; Liu, L.; Jin, X.; Duan, C.; Cui, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, D.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Y.; Fang, L. Co-inoculation effect of plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria and rhizobium on EDDS assisted phytoremediation of Cu contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visioli, G.; Vamerali, T.; Mattarozzi, M.; Dramis, L.; Sanangelantoni, A.M. Combined endophytic inoculants enhance nickel phytoextraction from serpentine soil in the hyperaccumulator Noccaea caerulescens. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Andrade, F.M.; Pereira, T.D.A.; Souza, T.P.; Guimarães, P.H.S.; Martins, A.D.; Schwan, R.; Pasqual, M.; Dória, J. Beneficial effects of inoculation of growth-promoting bacteria in strawberry. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 223–225, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, L.; Xu, S.; Fu, Y.; Hou, D.; Feng, Y.; Yang, X. Cadmium phytoextraction through Brassica juncea L. under different consortia of plant growth-promoting bacteria from different ecological niches. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 237, 113541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ma, L.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Pan, F.; Huang, L.; Yang, X.; Feng, Y. Inoculation of plant growth promoting bacteria from hyperaccumulator facilitated non-host root development and provided promising agents for elevated phytoremediation efficiency. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.Y.; Wu, Y.J.; Wang, Q.; Feng, Y. The endophytic bacterium relieved healthy risk of pakchoi intercropped with hyperaccumulator in the cadmium polluted greenhouse vegetable field. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; Glick, B.R. The role of plant growth-promoting bacteria in metal phytoremediation. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2017, 71, 97–132. [Google Scholar]
- Kurniawan, S.B.; Ramli, N.N.; Said, N.S.M.; Alias, J.; Imron, M.F.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Othman, A.R.; Purwanti, I.F.; Abu Hasan, H. Practical limitations of bioaugmentation in treating heavy metal contaminated soil and role of plant growth promoting bacteria in phytoremediation as a promising alternative approach. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.X.; Zhang, R.R.; Dai, J.X.; Lin, Z.T.; Li, Y.P.; Herzberg, M.; Zhang, J.L.; Al-Wathnani, H.; Zhang, C.K.; Feng, R.W.; et al. Potential of cadmium resistant Burkholderia contaminans strain ZCC in promoting growth of soybeans in the presence of cadmium. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 211, 111914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajmal, A.W.; Yasmin, H.; Hassan, M.N.; Khan, N.; Jan, B.L.; Mumtaz, S. Heavy metal-resistant plant growth-promoting Citrobacter werkmanii strain WWN1 and Enterobacter cloacae strain JWM6 enhance wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) growth by modulating physiological attributes and some key antioxidants under multi-metal stress. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 815704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Wang, W.; Hou, J. Plant performance of enhancing licorice with dual inoculating dark septate endophytes and Trichoderma viride mediated via effects on root development. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.M.; Guo, S.J.; Tian, W.; Chen, Y.; Han, H.; Chen, E.; Li, B.L.; Li, Y.Y.; Chen, Z.J. Effects of plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB) inoculation on the growth, antioxidant activity, Cu uptake, and bacterial community structure of rape (Brassica napus L.) grown in Cu-contaminated agricultural soil. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Ma, L.; Liu, Q.; Vestergård, M.; Topalovic, O.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, L.; Yang, X.; Feng, Y. The plant-growth promoting bacteria promote cadmium uptake by inducing a hormonal crosstalk and lateral root formation in a hyperaccumulator plant Sedum alfredii. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 395, 122661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vejan, P.; Abdullah, R.; Khadiran, T.; Ismail, S.; Nasrulhaq Boyce, A. Role of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in agricultural sustainability—A review. Molecules 2016, 21, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Du, W.; Ai, F.; Yin, Y.; Ji, R.; Guo, H. Microbial communities in the rhizosphere of different willow genotypes affect phytoremediation potential in Cd contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 145224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyasundar, P.G.S.A.; Ali, A.; Azeem, M.; Li, Y.; Guo, D.; Sikdar, A.; Abdelrahman, H.; Kwon, E.; Antoniadis, V.; Mani, V.M.; et al. Green remediation of toxic metals contaminated mining soil using bacterial consortium and Brassica juncea. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 116789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 2762-2017; National Food Safety Standard Limit of Pollutants in Food. National Health and Family Planning Commission and China Food and Drug Administration: Beijing, China, 2017. (In Chinese)
- Stratford, J.P.; Hutchings, T.R.; De Leij, F.A. Intrinsic activation: The relationship between biomass inorganic content and porosity formation during pyrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 159, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Song, Y.; Bian, Y.; Ji, R.; Wang, F.; Gu, C.; Yang, X.; Jiang, X. Sustainable synthesis of nanoporous carbons from agricultural waste and their application for solid-phase microextraction of chlorinated organic pollutants. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 15915–15922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Genus Affiliation | 16S rDNA Accession No. | ACC Deaminase Activity | IAA Production | Siderophore Production | Phosphate Solubilization | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SaCR1 | Cupriavidus | JQ806419 | − | + | + | + |
| SaMR10 | Burkholdria | HQ730964 | + | + | + | + |
| SaMR12 | Sphingomonas | JN573357 | − | + | + | + |
| Treatments | Cd Extraction by Straw (mg·plot−1) | Cd Extraction Rates by Straw (%) | Cd Extraction by Seeds (mg·plot−1) | Cd Extraction Rates by Seeds (%) | Soil Cd Removal (mg·plot−1) | Soil Cd Removal Rates (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 87.50 ± 4.42 c | 1.43 | 5.72 ± 0.84 f | 0.09 | 1196.29 ± 89.51 b | 19.61 |
| SaCR1 | 94.31 ± 17.72 bc | 1.55 | 6.54 ± 0.29 ef | 0.11 | 1983.93 ± 411.81 ab | 32.52 |
| SaMR10 | 65.05 ± 7.38 c | 1.07 | 5.31 ± 0.38 f | 0.09 | 1578.86 ± 115.23 ab | 25.88 |
| SaMR12 | 108.03 ± 10.55 bc | 1.77 | 13.05 ± 0.78 b | 0.21 | 1843.53 ± 293.25 ab | 30.22 |
| SaCR1 + SaMR10 | 107.73 ± 3.19 bc | 1.77 | 8.56 ± 0.98 de | 0.14 | 2044.72 ± 168.71 a | 33.52 |
| SaCR1 + SaMR12 | 105.89 ± 8.88 bc | 1.74 | 12.61 ± 0.87 bc | 0.21 | 1820.83 ± 163.36 ab | 29.85 |
| SaMR10 + SaMR12 | 223.45 ± 23.09 a | 3.66 | 10.34 ± 1.00 cd | 0.17 | 1434.56 ± 149.60 ab | 23.52 |
| SaCR1 + SaMR10 + SaMR12 | 135.23 ± 21.58 b | 2.22 | 20.03 ± 1.26 a | 0.33 | 1920.34 ± 295.75 ab | 31.48 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Xu, S.; Wen, Z.; Liu, Q.; Huang, L.; Shao, G.; Feng, Y.; Yang, X. Combined Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria Inoculants Were More Beneficial than Single Agents for Plant Growth and Cd Phytoextraction of Brassica juncea L. during Field Application. Toxics 2022, 10, 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10070396
Wang Q, Xu S, Wen Z, Liu Q, Huang L, Shao G, Feng Y, Yang X. Combined Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria Inoculants Were More Beneficial than Single Agents for Plant Growth and Cd Phytoextraction of Brassica juncea L. during Field Application. Toxics. 2022; 10(7):396. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10070396
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qiong, Shun’an Xu, Zheyu Wen, Qizhen Liu, Lukuan Huang, Guosheng Shao, Ying Feng, and Xiaoe Yang. 2022. "Combined Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria Inoculants Were More Beneficial than Single Agents for Plant Growth and Cd Phytoextraction of Brassica juncea L. during Field Application" Toxics 10, no. 7: 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10070396
APA StyleWang, Q., Xu, S., Wen, Z., Liu, Q., Huang, L., Shao, G., Feng, Y., & Yang, X. (2022). Combined Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria Inoculants Were More Beneficial than Single Agents for Plant Growth and Cd Phytoextraction of Brassica juncea L. during Field Application. Toxics, 10(7), 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10070396







