Heavy Metal Contamination in Sediments from Wetlands Invaded by Spartina alterniflora in the Yellow River Delta
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Areas and Sampling
2.2. Sample Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ecological Risk Assessment Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Levels of Heavy Metals in Sediments
| Region | Type/Species | Co | Ni | As | Cd | Pb | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YRD, China | S. alterniflora | 9–16 | 14–28 | 3–14 | 0.08–0.24 | 18–37 | This study |
| YRD, China | Phragmites australis | 9–11 | 28–31 | 15–33 | 0.26–0.77 | 21–40 | [9] |
| YRD, China | not mentioned | 24–30 | 7-9 | 0.09–0.12 | 20–21 | [13] | |
| Shandong Peninsula | marine sediment | 7–16 | 0.05–0.13 | 24–45 | [15] | ||
| YRD, China | Tamarix Chinensis | 36 | 31 | 0.68 | 21 | [26] | |
| Luoyuan wetland, China | S. Alterniflora, tideland | 22–26 | 39–46 | 7–15 | 0.06–0.23 | 16–26 | [27] |
| Kerala, India | sediment in fishing zones | 17–30 | 20–70 | 1.1–2.3 | 29–74 | [28] | |
| Yangtze River estuary, China | marine sediment | 18–56 | 0.01–0.16 | 9–37 | [29] | ||
| Bohai Bay, China | S. alterniflora | 8.21 | 48.12 | [30] | |||
| YRD, China | soil | 5–12 | 0.08–0.28 | 13–39 | [31] | ||
| YRD, China | mud flat & S. heteroptera et al. | 7.9 | 16.2 | [32] | |||
| YRD, China | mud flat, thin reed, S. heteroptera et al. | 11–36 | 4–13 | 0.02–0.84 | 4–26 | [33] | |
| YRD, China | not mentioned | 18-45 | 6-17 | 0.05–0.57 | 14–33 | [34] | |
| Pearl River Estuary, China | mangrove sediment | 29 | 0.96 | 43 | [35] | ||
| Alexandria Coast, Egypt | marine sediment | 33 | 0.3 | 33 | [36] |
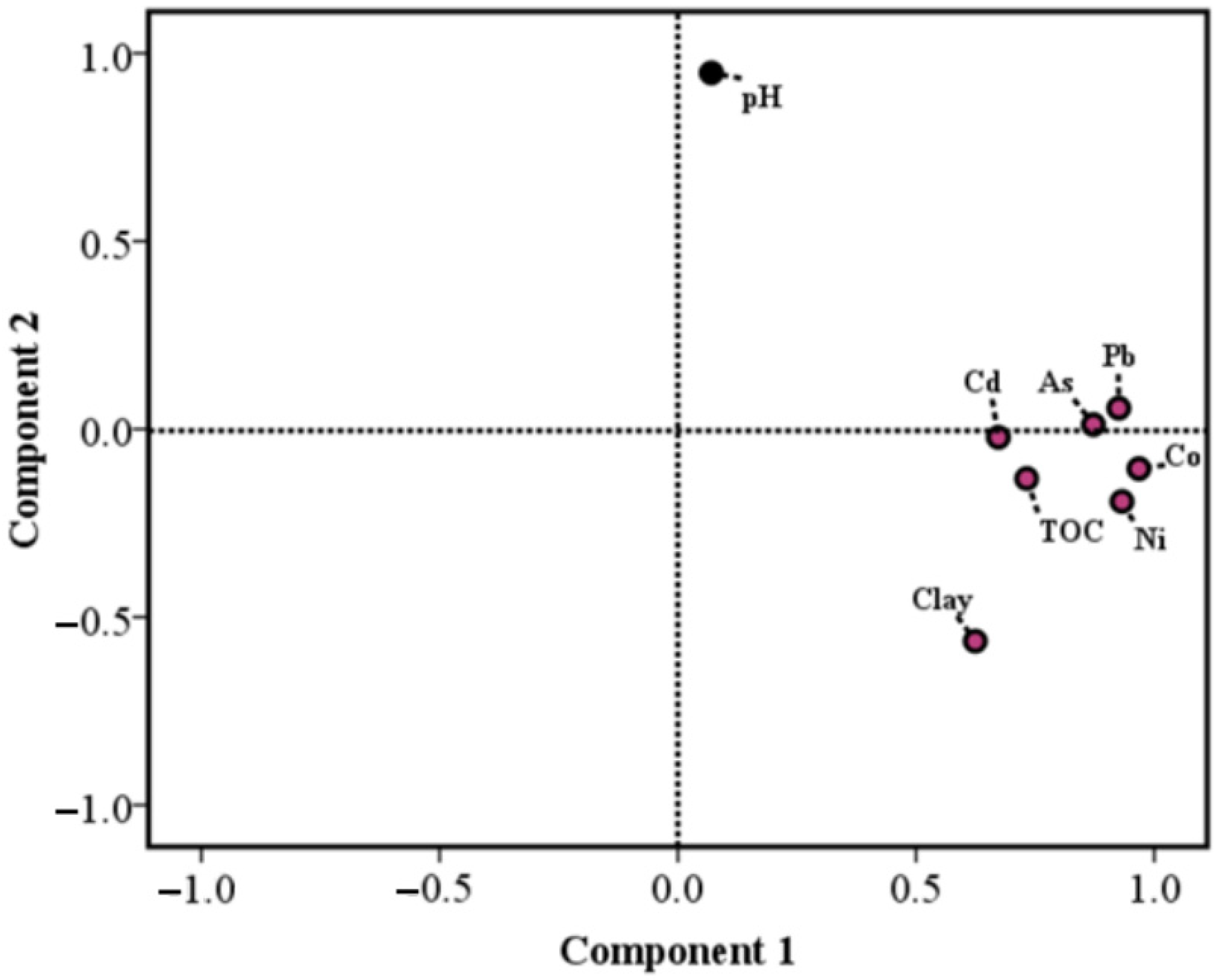
3.2. Correlation between Heavy Metals and Sediment Properties
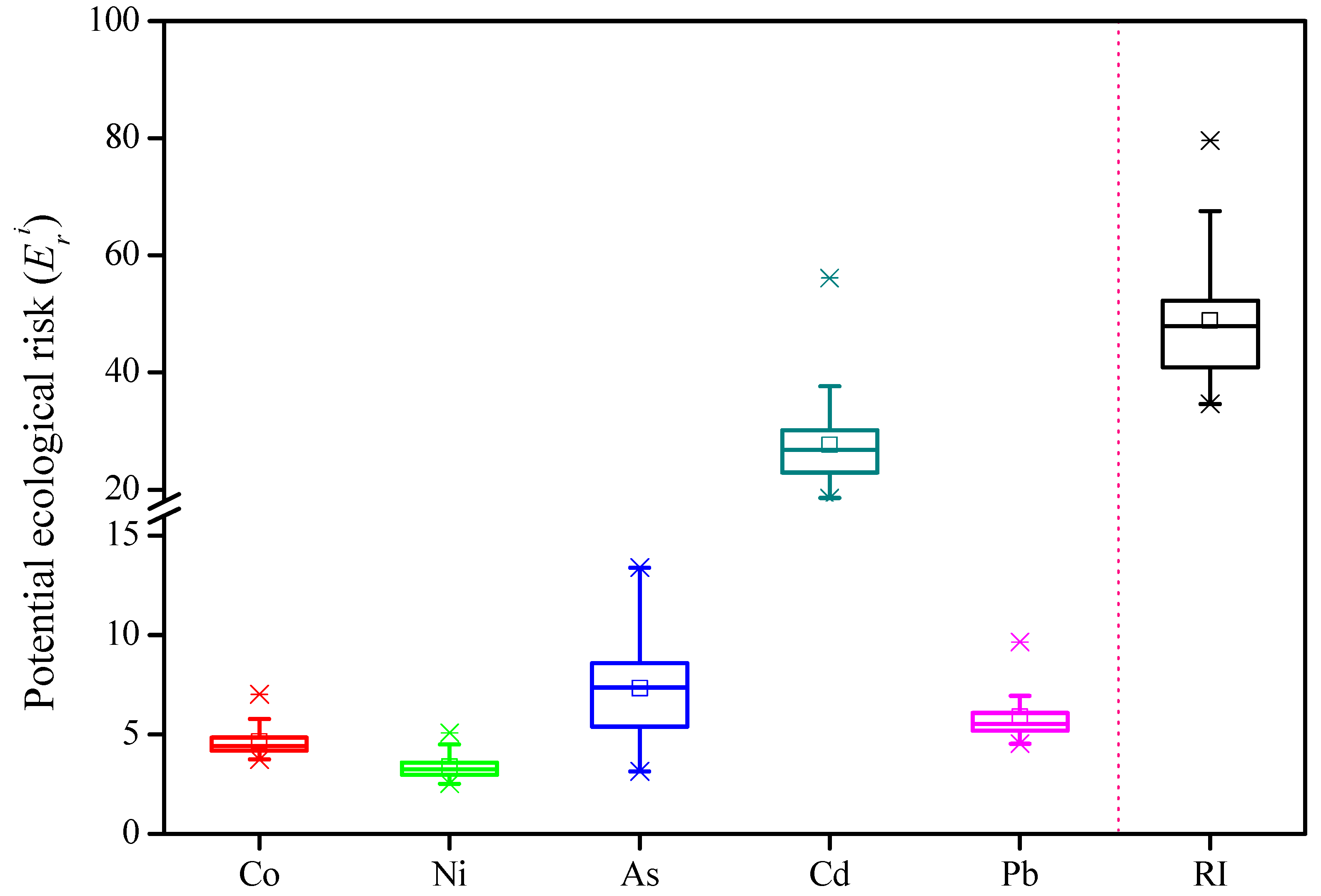
3.3. Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Liu, G.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, H.; Lam, P.K.S. Heavy metals (As, Hg and V) and stable isotope ratios (δ13C and δ15N) in fish from Yellow River Estuary. China Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, M.; Liu, G.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y. Levels of metals in fish tissues of Liza haematocheila and Lateolabrax japonicus from the Yellow River Delta of China and risk assessment for consumers. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 157, 111286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Liu, Y.; Shan, B.; Xu, J.; Yu, W.; Sun, D.; Zhang, Z. Heavy metal concentrations and associated health risks in edible tissues of marine nekton from the outer Pearl River Estuary, South China Sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 2108–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varol, M.; Sünbül, M.R. Environmental contaminants in fish species from a large dam reservoir and their potential risks to human health. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaliwal, S.S.; Singh, J.; Taneja, P.K.; Mandal, A. Remediation techniques for removal of heavy metals from the soil contaminated through different sources: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 1319–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, K.; Anthony, J.; Muthuramalingam, S. Heavy metal pollutants and their spatial distribution in surface sediments from Thondi Coast, Palk Bay, South India. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2021, 33, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandkumar, A.; Nagarajan, R.; Prabakaran, K.; Bing, C.H.; Rajaram, R. Human health risk assessment and bioaccumulation of trace metals in fish species collected from the Miri coast, Sarawak, Borneo. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 655–663. [Google Scholar]
- Burger, J.; Gochfeld, M. 2011. Mercury and selenium levels in 19 species of saltwater fish from New Jersey as a function of species, size, and season. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1418–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nie, M.; Xian, N.; Fu, X.; Chen, X.; Li, B. The interactive effects of petroleum-hydrocarbon spillage and plant rhizosphere on concentrations and distribution of heavy metals in sediments in the Yellow River Delta, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girones, L.; Oliva, A.L.; Negrin, V.; Macrovecchio, J.; Arias, A.H. Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in coastal wetlands: A review of their occurrence, toxic effects, and biogeochemical cycling. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Sun, Y.; Yu, S.; Chen, Y.; Peng, J. Heavy metal and organic contaminants in mangrove ecosystems of China: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 11938–11950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M.; Pryor, R.; Wilking, L. Fate and effects of anthropogenic chemicals in mangrove ecosystems: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2328–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, J.; Shi, L.; Xie, F.; Li, X. Spatial variations of arsenic and heavy metal pollutants before and after the water-sediment regulation in the wetland sediments of the Yellow River Estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Bai, J.; Zhao, Q.; Jia, J.; Wen, X. Heavy metals pollution in soil profile from seasonal-flooding riparian wetlands in a Chinese delta: Levels, distributions and toxic risks. Phys. Chem. Earth 2017, 97, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, G.; Liu, J.; Pei, S.; Gao, M.; Kong, X. Transport pathway and depocenter of anthropogenic heavy metals off the Shandong Penisula, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 180, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Song, J.; Yuan, H.; Li, X.; Li, N.; Duan, L.; Yu, Y. Petroleum hydrocarbons and their effects on fishery species in the Bohai Sea, North China. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ke, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhou, D.; Zhu, L.; Bai, J. Mapping coastal wetlands in the Yellow River Delta, China during 2008-2019: Impacts of valid observations, harmonic regression, and critical months. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 7880–7906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, A.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, P. Monitoring the invasion of smooth cordgrass Spartina alterniflora within the modern Yellow River Delta using remote sensing. J. Coast. Res. 2019, sp90, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, C.; Chen, L.; Liu, C.; Yan, L.; Li, B. Effects of smooth cordgrass Spartina alterniflora invasion on macrobenthic fauna in the Yellow River Delta. Wetlands 2022, 42, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, W.; Sun, T.; Jin, Y. Potential ecological risk of heavy metal contamination in sediments and macrobenthos in coastal wetlands induced by freshwater releases: A case study in the Yellow River Delta, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 103, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, X.; Du, Z.; Xiang, L.; Wang, W. Assessment of heavy metal contamination and wetland management in a newly created coastal natural reserve, China. J. Coast. Res. 2015, 32, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in soils of the Rhine River. Geojournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, X.; Dai, J.; Yu, C.; Ren, T.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Gao, H.; Zeng, X.; Ren, W.; Wang, Z.; et al. Soil geochemical reference value of 17 cities in Shandong Province. Shandong Land Resour. 2019, 35, 36–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, L.; Lin, X.; Yan, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, C. Spatial distribution, control factors and sources of heavy metal in the surface sediments of Fudu Estuary, East Liaodong Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 156, 111279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Bai, J.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, J. Spatial and seasonal distribution and risk assessments for metals in a Tamarix Chinensis wetland, China. Wetlands 2016, 30 (Suppl. 1), 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Du, Y.; Gao, S.; Ingels, J.; Wang, D. Heavy metal accumulation reflecting natural sedimentary processes and anthropogenic activities in two contrasting coastal wetland ecosystems, eastern China. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 1093–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibinimol, P.A.; Sujatha, C.H. Distribution and geochemical speciation of sediment bound heavy metals in the specific zones of central kerala, india. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100358. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, C.; Huang, X.; Zhao, L.; Yin, D. Distribution and source of heavy metals in the sediments of the coastal east china sea: Geochemical controls and typhoon impact. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 113936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, M.; Shi, F.; Li, R.; Shen, X. Heavy metal contamination and ecological risk in Spartina alterniflora marsh in intertidal sediments of Bohai Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 84, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zou, S.; Ye, S.; Xie, Z. Spatial distribution of heavy metals and their potential sources in the soil of Yellow River Delta: A traditional oil field in China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 42, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; He, J.; Fu, G.; Shen, Q.; Zhao, C.; Cao, M. Distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals of surface sediments in intertidal flats of the Yellow River Delta, China. Res. Environ. Sci. 2020, 33, 1488–1496. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Zhao, G.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Y. Comparison of arsenic and heavy metals contamination between existing wetlands and wetlands created by river diversion in the Yellow River Estuary, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 1677–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Q.; Lou, G.; Huang, W.; Li, X. Assessment and potential sources of metals in the surface sediments of the Yellow River Delta, Eastern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 17446–17454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, D.; Peng, Y.; Wang, A. Pollution and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in sediment of coastal wetland of the pearl river estuary. Trop. Geo 2011, 31, 353–356. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Khaled, A.; Ahdy, H.H.H.; Hamed, E.S.A.E.; Ahmed, H.O.; Razek, F.A.A.; Fahmy, M.A.; Elmasry, E. Spatial distribution and potential risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment along Alexandria coast, Mediterranean Sea, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2020, 46, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Du, Y.; Wang, D.; Gao, S.; Gao, W. Distribution patterns and pollution assessment of heavy metals in the Spartina alterniflora salt-marsh wetland of Rudong, Jiangsu Province. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 2401–2410. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xia, W.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, C.; Liu, M. Distribution of soil factors across the habitat gradient of Spartina alterniflora and Suaeda sala communities. J. Nanjing Forest. Univ. 2021, 45, 37–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Jin, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, D.; Li, H.; Yang, C.; Huang, Y. Contamination of heavy metals in sediments from an estuarine bay, South China: Comparison with previous data and ecological risk assessment. Processes 2022, 10, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, G.; Liu, Y.; Shan, B.; Wang, L.; Sun, D.; Huang, Y. Heavy metal distribution in surface sediments of the Coastal Pearl Bay, South China Sea. Processes 2022, 10, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sampling Region | Co | Ni | As | Cd | Pb | pH | TOC (‰) | Clay (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (n = 16) | minimum | 8.5 | 13.9 | 3.8 | 0.08 | 17.6 | 6.8 | 4.6 | 1.0 |
| maximum | 16.0 | 27.9 | 13.8 | 0.24 | 37.5 | 7.9 | 55.0 | 42.5 | |
| mean | 11.6 | 20.7 | 9.4 | 0.13 | 24.4 | 7.3 | 31.7 | 17.4 | |
| median | 11.2 | 20.8 | 9.2 | 0.12 | 23.1 | 7.7 | 42.4 | 17.0 | |
| standard deviation | 3.1 | 5.7 | 4.1 | 0.07 | 8.4 | 0.3 | 21.1 | 12.9 | |
| B (n = 12) | minimum | 9.1 | 14.5 | 6.3 | 0.09 | 19.9 | 7.0 | 4.2 | 5.4 |
| maximum | 11.2 | 19.8 | 8.8 | 0.15 | 26.9 | 8.0 | 7.5 | 20.6 | |
| mean | 9.9 | 17.7 | 7.5 | 0.12 | 22.5 | 7.5 | 5.5 | 13.0 | |
| median | 9.7 | 17.8 | 7.6 | 0.12 | 22.2 | 7.5 | 5.4 | 11.6 | |
| standard deviation | 0.9 | 2.2 | 1.0 | 0.02 | 2.91 | 0.4 | 1.2 | 4.5 | |
| C (n = 9) | minimum | 9.2 | 14.6 | 3.2 | 0.08 | 19.7 | 7.3 | 0.7 | 11.5 |
| maximum | 10.8 | 19.1 | 5.6 | 0.14 | 21.7 | 7.6 | 19.6 | 22.6 | |
| mean | 9.7 | 16.1 | 4.3 | 0.10 | 20.5 | 7.5 | 12.0 | 15.2 | |
| median | 9.6 | 15.8 | 4.0 | 0.10 | 20.4 | 7.5 | 11.9 | 14.9 | |
| standard deviation | 0.7 | 1.9 | 1.0 | 0.02 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 1.2 | 4.7 | |
| K (n = 6) | minimum | 7.5 | 11.2 | 5.3 | 0.07 | 14.7 | 6.7 | 4.1 | 0.9 |
| maximum | 7.9 | 15.5 | 5.8 | 0.08 | 15.1 | 7.8 | 5.6 | 7.3 | |
| mean | 7.7 | 13.8 | 5.6 | 0.07 | 14.9 | 6.7 | 4.9 | 4.6 | |
| median | 7.7 | 14.3 | 5.6 | 0.07 | 14.9 | 7.0 | 5.0 | 5.2 | |
| standard deviation | 0.2 | 1.8 | 0.2 | <0.01 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 5.9 | 3.9 |
| Co | Ni | As | Cd | Pb | pH | TOC | Clay | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co | 1 | |||||||
| Ni | 0.934 ** | 1 | ||||||
| As | 0.802 ** | 0.830 ** | 1 | |||||
| Cd | 0.576 ** | 0.651 ** | 0.594 ** | 1 | ||||
| Pb | 0.912 ** | 0.803 ** | 0.735 ** | 0.559 ** | 1 | |||
| pH | −0.029 | −0.133 | −0.021 | −0.048 | 0.125 | 1 | ||
| TOC | 0.728 ** | 0.635 ** | 0.602 * | 0.213 | 0.624 ** | −0.034 | 1 | |
| Clay | 0.661 ** | 0.640 ** | 0.386 * | 0.353 * | 0.596 ** | −0.331 * | 0.522 ** | 1 |
| Principle Component | Initial Eigenvalues | Element | Sum of Squared Loadings | Factor Loading | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | % Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % Variance | Cumulative % | PC1 | PC2 | ||
| 1 | 4.908 | 61.352 | 61.352 | Co | 4.908 | 61.352 | 61.352 | 0.967 | −0.105 |
| 2 | 1.181 | 14.763 | 76.116 | Ni | 1.181 | 14.763 | 76.116 | 0.932 | −0.192 |
| 3 | 0.829 | 10.365 | 86.481 | As | 0.872 | 0.012 | |||
| 4 | 0.503 | 6.288 | 92.769 | Cd | 0.673 | −0.022 | |||
| 5 | 0.259 | 3.243 | 96.012 | Pb | 0.925 | 0.056 | |||
| 6 | 0.165 | 2.057 | 98.069 | pH | 0.070 | 0.948 | |||
| 7 | 0.129 | 1.608 | 99.677 | TOC | 0.732 | −0.132 | |||
| 8 | 0.026 | 0.323 | 100.000 | Clay | 0.624 | −0.564 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Yu, W.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Wu, T.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Shang, S.; et al. Heavy Metal Contamination in Sediments from Wetlands Invaded by Spartina alterniflora in the Yellow River Delta. Toxics 2022, 10, 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10070374
Zhang Z, Zhang T, Yu W, Xu J, Li J, Wu T, Liu S, Wang H, Wang Y, Shang S, et al. Heavy Metal Contamination in Sediments from Wetlands Invaded by Spartina alterniflora in the Yellow River Delta. Toxics. 2022; 10(7):374. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10070374
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zaiwang, Tongrui Zhang, Wenhao Yu, Jikun Xu, Jialiang Li, Tao Wu, Suzhe Liu, Haiyang Wang, Yuxia Wang, Shuai Shang, and et al. 2022. "Heavy Metal Contamination in Sediments from Wetlands Invaded by Spartina alterniflora in the Yellow River Delta" Toxics 10, no. 7: 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10070374
APA StyleZhang, Z., Zhang, T., Yu, W., Xu, J., Li, J., Wu, T., Liu, S., Wang, H., Wang, Y., Shang, S., & Lin, A. (2022). Heavy Metal Contamination in Sediments from Wetlands Invaded by Spartina alterniflora in the Yellow River Delta. Toxics, 10(7), 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10070374






