Abstract
The adsorption of heavy metals on allophane has been extensively studied due to the properties of allophane special. However, the difference in adsorption behaviors and mechanisms of a metal cation and metal anion on allophane remains uncertain. The present study aimed to investigate the removal of Pb(II) and Cr(VI) onto synthetic allophane under variable pH, initial Pb(II) and Cr(VI) concentrations, and contact time. The results showed that the maximum adsorption capacity of allophane for Pb(II) and Cr(VI) was 88 and 8 mg/g, respectively. Equilibrium adsorption for Pb(II) was achieved in <2 min, but it took >12 h for Cr(VI). The response to changes in pH indicated the occurrence of electrostatic adsorption occurred during Cr(VI) absorption. XPS analysis suggested that reactions between predominant surface functional groups of allophane (Al-O- and Si-O-) and Pb(II) occurred through the formation of P-O bonds. The uptake mechanism of Pb(II) was based on a chemical reaction rather than a physical adsorption process. Synthetic allophane holds great potential to effectively remove aqueous metal ions for special wastewater treatment applications.
1. Introduction
The world is hurtling toward a future with dwindling water resources, and water pollution is one of the most compelling global concerns [1,2,3,4]. Heavy-metal pollution in water, as one of the most common sources of water pollution, has become a serious environmental issue caused by anthropogenic activities and natural processes [5]. For example, lead (Pb) is generally released into the environment through metal mining industries of acid lead batteries, paper, glass, and polishing industries, which may cause anemia, neurological dysfunction, and kidney damage, and chromium (Cr) causes diseases such as liver damage, nephritis, and stomach distresses and is also the major cause of nasal mucous ulcer [6]. To reduce the heavy-metal pollution in water, numerous methods have been developed including removal through adsorption, phytoremediation, bioremediation, chemical precipitation, coagulation, membrane filtration, ion exchange, and redox processes [7,8,9]. Among them, adsorption has been deemed as a promising alternative for metal pollution due to its easy obtainment, simple production, and operation with relatively high efficiency and low cost [10]. In previous studies, various adsorbents (e.g., biochar, carbon nanotubes, activated carbon, and minerals) have been used to remove heavy metals [11]. Finding a cost-effective and highly efficient adsorbent is still necessary.
One such adsorbent that has not been sufficiently investigated is allophane [12]. Allophane (1-2SiO2·Al2O3·nH2O) is a short-range ordered clay mineral of ubiquitous occurrence in soils of volcanic origin, which has abundant surface functional groups (e.g., Al-O, Si-O, and Si-OH) and a large specific surface area (>300 m2/g) [13]. Natural allophane spherule consisted of an outer diameter of ~5 nm, a wall thickness of 0.7–1.0 nm, and a perforation of ~0.3 nm [14]. The functional groups (e.g., Al(OH)3, (OH)Si(AlO)3, and (HO)Al(OH2)) were exposed to outer, wall, and perforation, respectively [15]. The hollow nanosphere structure of allophane is fundamentally composed of an outer layer of a gibbsite-like sheet with SiO4 tetrahedral attached to its interior with defects or perforations in the wall structure with diameters of around 0.3 nm [16]. This layered structure offers abundant sites for the absorption processes. Conceptually, given the application, the uniform shape, size, and inherent acidity of synthetic allophane are considered better than the natural ones [17]. However, the sorption properties of synthetic allophane are barely utilized in the remediation of wastewater. Basic studies are needed to explore the qualitative and quantitative assessment of the metal ion removal efficiencies and the determination of adsorption capacities of critical metal ions by using synthetic allophanes for water clean-up [18].
The present aim of this paper is to examine and compare the co-precipitation and adsorption characteristics of different metal ions to reveal the adsorption mechanisms of the allophane concerning heavy metal cations and anions. Here, Pb and Cr are regarded as representatives of common metal cations and anions, as they were found mainly in cations (Pb2+) and anions (CrO42−) formed in the environment, respectively [19]. In this context, this study investigated the uptake of Pb(II) and Cr(VI) by synthesizing allophane at different conditions to figure out the adsorption mechanisms of the synthesized allophane. Specifically, synthetic allophane was used to remove Pb(II) and Cr(VI) in aqueous solution with varying pH, initial concentrations, and contact time. The results show that the maximum adsorption capacity of allophane for Pb(II) and Cr(VI) was 88 and 8 mg/g, respectively. The adsorption of Pb(II) is relatively high compared to other adsorbents, but the adsorption level of Cr(VI) is common. Furthermore, the equilibrium adsorption time for Pb(II) was much faster than Cr(VI). Interestingly, the Pb-adsorbed-synthetic allophane cracked and settled when adjusting pH to 7 due to the chemical reaction. The potential use of the synthetic allophane in heavy metal water processing technologies was also discussed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis
Allophane was synthesized based on the method reported by Ohashi et al. [16]. The fabrication processes are shown in Figure 1. Al source and Si source were AlCl3 and Na2SiO4, respectively. NaOH was added to Si solution for adjusting the alkalinity to favorable conditions for allophane synthesis. Both solutions were mixed rapidly with an atomic ratio of Al:Si of 4:3, then stirred for 1 hour at room temperature. After removing the by-product (NaCl) by centrifugation, the precursor was collected and hydro-thermalized at 95–100 ℃ for 48 h. Allophane was carried out through repeated washing with deionized water until pH is neutral. Allophane suspension was applied in this experiment.

Figure 1.
The scheme of the synthesis processes of allophane.
2.2. Characterization of Adsorbent
Physiochemical properties of the synthesized allophane, including allophane content, morphology, and surface reactivity towards polar compounds and surface functional groups were analyzed [7]. The content of allophane was determined by acid oxalate extraction and sodium pyrophosphate extraction methods [20]. The crystallinity of synthetic allophane was determined by the X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns, recording on a Bruker D8 Advance X-ray diffractometer using Cu Kα radiation. The morphology of allophane was shown by transmission electron microscopy (TEM, JEM-2100F, JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) analysis. Surface reactivity towards polar compounds of synthetic allophane was determined by water content of air-dried samples [21]. Surface functional groups of allophane were conducted by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (Nicolet 5700, FTIR spectrometer). The chemical information of the materials was analyzed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, K-Alpha, Al Ka radiation). Allophane suspension at a 1:500 (w/v) ratio was prepared, and the pH was adjusted by adding HCl and NaOH. It was used to measure the zeta potential of allophane in the pH range from 2 to 13 by Malvern Zetasizer Nano ZS.
2.3. Adsorption Experiments
The stock solutions of CrO42− and Pb2+ with a concentration of 2000 mg/L were prepared using K2CrO4 and PbCl2. These solutions were further diluted for the desired concentrations of Pb and Cr. Adsorption experiments were carried out in 50 mL centrifuge tubes, where allophane suspension and the solution containing either Pb or Cr at the concentrations under study were added at the ratio of 1:500 (w/v) [22]. Adsorption parameters considered included initial concentration of Pb and Cr, contact time, and solution pH (adjusting by adding either 1 M NaOH or 1 M HCl), which were varied from 5 to 1200 mg/L, 0 to 24 h, and 2 to 10, respectively. After adsorption, suspensions were filtered by using 0.45 µm membrane, and the concentration of residual Pb and Cr in the filtrate was measured by using a microwave plasma-atomic emission spectrometer (4200 MP-AES, Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA), setting 405 nm for Pb and 425 nm for Cr. All experiments were conducted in three replicates. The results obtained were calculated and fitted as described below.
The adsorbed heavy metal ions onto synthetic allophane and removal percentage (%) were calculated by Equations (1) and (2), respectively.
where is the concentration of adsorbed heavy metal ions (mg/g), and are the initial and equilibrium concentration of heavy metal ions in solution (mg/L), m is the dray mass of adsorbent (mg), and V is the volume of the adsorbent solution (mL).
The Langmuir and Freundlich models employed as empirical isotherm models were expressed as Equations (3) and (4), respectively.
where and were the same in Equation (1), is the maximum adsorption capacity of synthetic allophane (mg/g), is the empirical affinity Langmuir coefficient (L/mg), is the Freundlich adsorption affinity coefficient (L/kg), and n is the Freundlich linearity constant, depending on the character of the adsorbent.
Non-linear isotherms were assumed as Langmuir models, as the shape can be expressed by a dimensionless constant separation factor or equilibrium parameter (), and RL is defined as Equation (5) [23].
where (L/mg) is Langmuir model constant and (mg/L) is the largest initial concentration of metal solutions. indicate unfavorable, linear, favorable, and irreversible adsorption, respectively.
The pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order were employed to study the adsorption kinetics and expressed as Equations (6) and (7), respectively.
where and were the concentration of adsorbed heavy metal ion at equilibrium and at time , respectively (mg/g), was shaking time (h), and and were adsorption rate of the first order and second order, respectively.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterizations of Synthetic Allophane
In this study, the synthetic allophane yield was ca. 90% of total product with the Al/Si ratio of 0.77. TEM images of synthetic allophane were shown in Figure 2, which shows the hollow structure of allophane clearly. Specifically, allophane spherules coalesced to form nanoaggregates with the diameter of ca. 100 nm. Consequently, those nanoaggregates can form larger allophane aggregates with the diameter of hundreds of nanometer (Figure 2a,b). The single synthetic allophane appeared as a nano-spherule with an external diameter of ca. 20 nm and a shell of about 2 nm (Figure 2c). Additionally, there were many pores within aggregates resulting in porous structure of allophane aggregates (Figure 2b), which is also beneficial for the absorption. As shown in Figure 2d, the XRD patterns of synthetic allophane exhibited two broad peaks at ~3.4 Å and ~2.3 Å, which are typical peaks for short-range ordered aluminosilicates such as allophane [24]. The specific surface area (SSAs) of synthetic allophane was tested to be a high level of 354 m2/g, which is related to its core–shell structure and aggregation state. The FTIR spectra of synthetic allophane is shown in Figure 2e. Identifiable FTIR features for synthetic allophane correspond to OH stretching (at 3600–3000 cm−1), organic complex of organic impurities (at 1750–1470 cm−1), Si-O-(Al) or Si-O-(Si) bonding (at 1010 cm−1), Si-OH bonding (at 890 cm−1), and Al-O and Si-OH bonding (at 800–400 cm−1) [17,25].
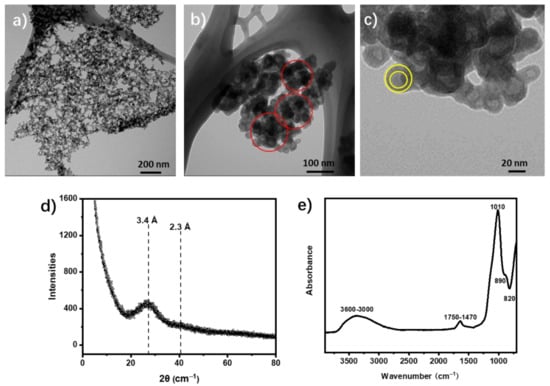
Figure 2.
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of synthetic allophane showing spherical (a,b) and hollow (c) morphology of allophane. PXRD pattern (d) and FTIR spectra (e) for synthetic allophane.
3.2. Adsorption Test
To investigate the absorption capacity of the synthetic allophane, Pb(II) and Cr(VI) as two typical heavy metal pollutants are used as targets. Different aqueous solutions with varying pH, initial concentrations, contact time, and electrolytes were tested.
3.2.1. Effect of Concentration
The initial concentrations of the Pb2+ and CrO42− solution had an obvious influence on the corresponding adsorptions. The dosage of the absorbent was 40 mg/L. The effect of initial concentrations of CrO42− and Pb2+ on the efficiency of adsorption is shown in Figure 3a,b. The Pb2+ adsorption capacities went up with increasing initial concentrations from 50 to 1200 mg/L. The increase in adsorption of Pb2+ was not significant as the initial concentration was higher than 800 mg/L, which was attributed to the increased competitive adsorption, for Pb2+ adsorption may be due to limited surface active sites of the adsorbent at high initial concentrations [26]. The maximum adsorption capacity reached 90.17 mg/g with a removal rate of 14.6%. The CrO42− adsorption capacities went up with increasing concentrations from 5 to 100 mg/L. The maximum adsorption capacity was 4.63 mg/g (removal percentage = 9.5%). The effect of adsorbent concentration of pollutions with a contact time of 24 h is shown in Figure 3c; the removal rate of the Pb(II) and Cr(VI) showed almost linear growth with the increase in absorbent dosage. The positive relationships between adsorbent dosage and removal rate of both Pb2+ and CrO42− could be explained by the adsorption site increasing according to the amount of adsorbent injected. [27]. Figure 3d shows the FTIR features for synthetic allophane after the adsorption, which indicates that the synthetic allophane is rarely changed in the chemical structure.
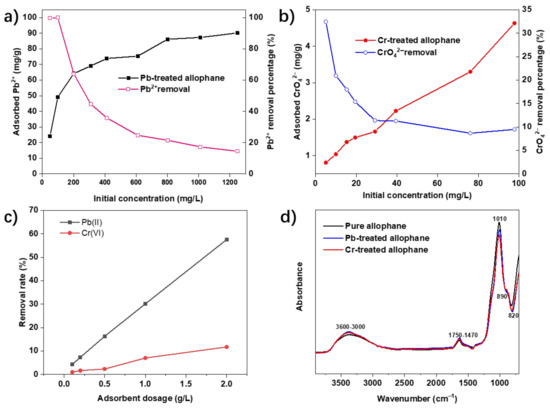
Figure 3.
Effects of initial concentration of Pb2+ and CrO42− onto synthetic allophane: (a) Contact time of 24 h, pH at 5; (b) Contact time of 24 h, pH at 2. (c) Effect of adsorbent concentration onto synthetic with an initial concentration of Pb(II) and Cr(VI): 200 mg/L and 10 mg/L, respectively; Pb(II) solution pH at 5, Cr(VI) solution pH at 2; and (d) FTIR spectra for synthetic allophanes before and after absorption.
3.2.2. Effect of Contact Time
The effect of contact time of CrO42− and Pb2+ on the efficiency of adsorption is shown in Figure 4. Similarly, adsorption rate was high for both Pb2+ and CrO42− during the initial contact time (10 mins), and then adsorption rate gradually decreased. During the initial contact time, abundant vacant adsorption sites of allophane were provided to react with CrO42− and Pb2+, resulting in the high adsorption rate. However, by increasing the contact time, the available sites were gradually reduced due to the increased occupation of the sites by adsorbed CrO42− and Pb2+. Notably, the ca. 91% of the equilibrium adsorption capacity for Pb2+ was achieved within 2 minutes, and then the adsorption capacity gradually slowed down and reached a rough equilibrium in 10 minutes. The equilibrium adsorption capacity for CrO42− was achieved after 12 h of shaking. The equilibrium adsorption was generally considered related to the progressive saturation of the surface active sites for the CrO42− and Pb2+ adsorption [26,28].
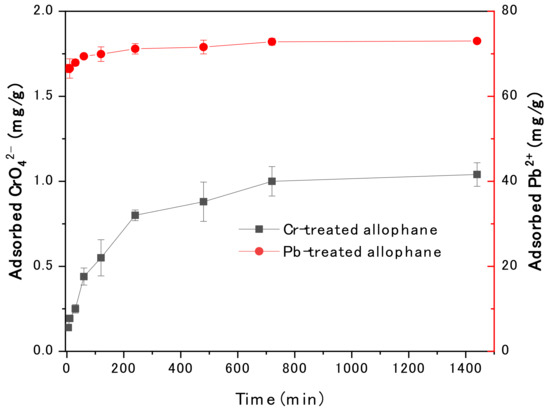
Figure 4.
Effects of contact time on the adsorption of Pb2+ and CrO42− onto synthetic allophane (initial concentration of CrO42− and Pb2+ were maintained at 10 and 200 mg/L, respectively; pH of CrO42− and Pb2+ were maintained at 2 and 5, respectively; the dosage of the absorbent was 40 mg/L).
3.2.3. Effect of pH and Zeta (ξ) Potential
As presented in Figure 5a, the pH of the solutions, ranging from 2 to 10, had different influences on the adsorption of Pb2+ and CrO42−. Adsorption capacity for CrO42− gradually decreased with an increase in pH value, and would not further decrease when pH was higher than 9, which is probably because the hydrogen ions in solution assisted in adsorption. It is a typical electrostatic adsorption phenomenon of negative ions. In contrast, an obvious increase in Pb2+ adsorption ability (from 54.67 to 97.83 mg/g) was observed when pH increases from 2 to 4. The absorption decreased from pH at 5, and then could not be recorded when the pH value was higher than 6 due to precipitation. This phenomenon only occurs during the adsorption of Pb2+ ions, combined with the characteristics of short adsorption time, we suspect that certain chemical reactions occurred between Pb ions and the synthetic allophane. At any pH level, allophane plays better adsorption performance on Pb(II) than Cr(VI), which may also be related to their hydration energy and hydrated ionic radius [29]. During the adsorption process, hydrated water surrounded by metal ions would be dissociated and become free water, entropy-generated and spontaneous [30]. Additionally, lower hydration energy results in easier adsorption. Hydration energy is ranked as: Pb(II) < Cr(VI), and hydrated radius of Pb2+ and CrO42− are 0.401 nm and 0.375 nm, respectively [31]. As a result, Pb(II) was more likely to be adsorbed onto allophane due to its easy appearance as free ions.

Figure 5.
(a) Effect of pH on the adsorption of Pb2+ and CrO42− onto synthetic allophane (fixed shaking time was 24 h; initial concentrations of CrO42− and Pb2+ were 100 and 800 mg/L, respectively; dosage of the absorbent was 40 mg/L). (b) Zeta (ξ) potential of synthetic allophane. (c) XPS of the synthetic allophane. (d) pH changes in the solution of CrO42− and Pb2+ by applying synthetic allophane, data from the experiment of effect of pH.
To figure out the difference between the two absorptions, the surface charge of the synthetic allophane was measured. Its surface charge status at different pH is shown in Figure 5b. The zeta (ξ) potential value of the adsorbent increased from pH 2 to pH 4, then started to decrease to pH 10. This curve was a classical backward S shape, which indicated structural shifts at pH < 4 and pH > 10, or shielding effect due to excessive ions in the suspension at pH > 10. Point of zero charge/isoelectric point (PZC/IEP), where the zeta potential crosses positive and negative surface charge, was found at pH 5.6. In other words, the synthetic allophane surface was positively charged at pH < 5.6, and negatively charged at pH > 5.6. Due to the presence of aluminol groups, allophanes could either acquire or lose protons in response to pH changes, and were more protonated at lower pH [32]. Combined with the pH adsorption diagram, we can find that there is a correlation between the adsorption of the two metal ions and the zeta potential. When the pH is less than 5.6, the zeta potential is positive, and the adsorption efficiency of Pb2+ is continuously increased. Low adsorption capacity for Pb2+ was observed at low pH because surface sites were positively charged, resulting in electrostatic repulsion between Si-OH2+ and Pb2+. The reaction on the surface is shown as follows: Si-OH + H+ → Si-OH2+. The effect of electrostatic repulsion and negative charge decreased with raising pH. Pb has also been reported to have a larger ionic radius (1.20 Å), which has a lower charge density and is easily affected by the protonation of the surface groups, resulting in a reduction in the adsorption sites [33]. Additionally, the increased H+, having a great affinity for many complexation and cation exchange sites, would induce competition for the adsorption Pb2+ sites. A slight decrease in Pb2+ adsorption ability was also observed when pH was higher than 5, which may be attributed to the occurrence of PbOH+ as pH was higher than ca. 5.5 [34], while the absorption of CrO4− was rarely affected by the change of the zeta potential. Then, the XPS was applied to test the elements and their conditions in the absorption. As shown in Figure 5c, there is no change in the overall structure and content of materials of the adsorbent before and after adsorption. The faint Cr peak was not found in the Cr-treated sample, which may relate to the small adsorption capacity on the one hand, and weak physical adsorption on the other hand. XPS spectra of the Pb level region was given in the inner part of Figure 5c; Pb–O bonding is involved, indicating peaks due to multiple oxidation states [35]. Active sites owned by allophane were Si-OH/Al-OH, -O-Si-O-/-O-Al-O-, and Al-O-/Si-O-. Adsorption occurs when the allophane-like oxygen ions on the surface of Pb-allophane bind to form a bond Si-O-Pb or Al-O-Pb. Pb, which acts as a Lewis acid, will receive a free electron pair of which acts as a base Lewis. The electron paired by O and Pb will form a coordinate covalent bond.
In addition to the surface potential, pH changes of allophane suspension during adsorption were also recorded to determine H+/OH− release. As shown in Figure 5d, at the initial lower pH, OH− was released from allophane, then the H+ was released after the pH go to a high level. This phenomenon proves that the adsorbent itself has the function of a slow-release agent that releases anions and cations. With the addition of two salts, the pH of the solutions changed because PbCl2 presented acidic and K2CrO4 presented alkaline at the initial stage. The two intersections between dash line and metal solutions indicated that the solution pH did not change at initial pH 4.5 and 8.5 for Pb(II) solution Cr(VI) solution, respectively. When the initial pH was ranged from 2 to 6, the pH of Pb(II) solution after allophane application was stably at ca. 4, Similarly, when the initial pH was ranged from 7 to 10, the pH of Cr(VI) solution after allophane application was stably at ca. 8.5. However, the pH of the Pb-allophane solution suddenly loses its stability after the pH is over 6, which is due to the broken structure of the allophane. This implied there are at least two different adsorption mechanisms for both metals crossing the zeta potential. Combined with the zeta potential diagram, we can find that there is a correlation between the adsorption of the pH changing in the two solutions. The pH of the Cr-allophane solution equals 4 when the initial pH was 2, which means that the Zeta potential of the allophone is at the highest positive value. That is the reason why Cr adsorption from the initial pH equal to 2 is the highest amount of adsorption. The Cr absorption was almost stopped when initial pH was higher than 6; this is because the allophane became negative. This phenomenon also indicates that the adsorption of Cr is an electrostatic physical adsorption.
There is a conjecture about the breakage of Pb-allophane with pH adjustment after adsorption. As known, allophane generally dissolves to some extent in alkaline environments. At a lower pH (≤11.0), the preferential dissolution of polymerized silicates mainly occurred, but the amounts of dissolved Si and dissolved Al were small. The chemical composition and fundamental structure of the hollow spherules were barely affected [13]. The occupation of the O bonding after Pb absorption may reduce the stability of the original structure, which speeds up the disruption of the hollow spherules. This phenomenon is not necessarily a bad one in the application process. As known, only when the adsorbent is evenly dispersed in the solution can its adsorption effect improve. However, the nano-adsorbents with better dispersion should be separated from the solution by means of add magnetism or high-speed centrifugation [36]. Here, we can naturally separate the Pb-absorbed allophane from the solution by only adjusting the pH, which is easier to implement in the application process. The desorption experiments of the two ions were also conducted. After several treatments of desorption, the allophane disintegrated as shown in Figure 5a due to the instability of core–shell structure. Fortunately, the cost of mass production is low. Both harmless disposal and metal ion recovery can be achieved during disintegration and desorption.
3.3. Adsorption Behaviors
The adsorption isotherm and kinetics models were carried also carried out to provide a better understanding of the potential mechanisms behind adsorption behaviors on synthetic allophane.
3.3.1. Adsorption Isotherm
The isotherm fitting results were shown in Figure 6 and Table 1. The regression coefficients (R2) of Langmuir and Freundlich models for CrO42− adsorption rates were 0.920 and 0.959, respectively, while for Pb2+ adsorption rates were 0.770 and 0.942, respectively. This result showed that the adsorption process of both CrO42− and Pb2+ onto synthetic allophane could be better described by the Freundlich model, indicating a heterogeneous adsorption process. Using Freundlich models, 1/n represented the exponent of non-linearity. It described the degree of curvature of fitting line and adsorption intensity. The value of n was 1.56 for CrO42− and 9.40 for Pb2−, resulting in a more curved isotherm for Pb2+ than the isotherm for CrO42−. The values of for Pb2+ and CrO42− were 34.91 and 0.24, respectively. The isotherm type was constant partition, and the initial isotherm was linear, indicating constant partition. The great value indicated synthetic allophane had much greater adsorption capacity for Pb2+ than CrO42−. The values of in Langmuir models were found to be 0.03 to 0.32 for the removal of Pb(II), and 0.53 to 0.967 for the removal of Cr(VI), respectively. This implied that the Pb(II) and Cr(VI) adsorption on allophane were both favorable adsorption processes.
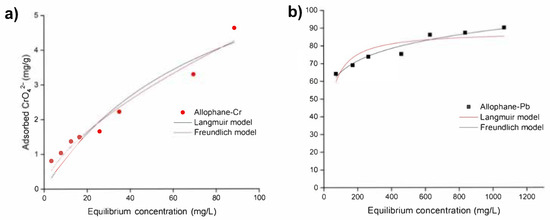
Figure 6.
(a) Isotherm of CrO42− adsorption onto synthetic allophane. (b) Isotherm of Pb2+ adsorption onto synthetic allophane. The dosage of the absorbent was 40 mg/L.

Table 1.
Isotherm parameters of CrO42− and Pb2+ onto synthetic allophane derived from Langmuir and Freundlich models.
3.3.2. Adsorption Kinetics
The kinetic fitting results for the absorption were shown in Figure 7 and Table 2. The pseudo-second order model could give a better simulation for both CrO42− and Pb2+ adsorption onto synthetic allophane due to higher R2. The value of R2 for Pb2+ adsorption in pseudo-second order model was 0.650 due to rapid absorption in a short period of time. The equilibrium adsorption capacities were similar to the experimental results that improved the reliability of pseudo-second order model. The adsorption rate constant for CrO42− and Pb2+ was 1.09 and 23.24 h−1, respectively, indicating that the adsorption of Pb2+ was about 21 times faster than CrO42−.
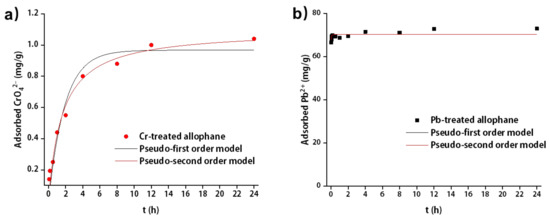
Figure 7.
Kinetics of (a) CrO42− and (b) Pb2+ adsorption onto synthetic allophane. The dosage of the absorbent was 40 mg/L.

Table 2.
Kinetic parameters of CrO42− and Pb2+ onto synthetic allophane derived from pseudo-first order model and pseudo-second order model.
3.4. Compare with Different Clay Materials
Many clay minerals (e.g., kaolinite, montmorillonite, and illite clays) have the ability to adsorb heavy metals. We compared the adsorption capacities of different adsorbents for Pb(II) and Cr(III/VI) and presented them in Table 3 and Table 4. Synthetic allophane possesses higher adsorption capacity onto Pb(II) than other clays. It is expected that the synthetic allophane have excellent potential for the removal of heavy metal cations (especially for Pb) without any modifications as they are low-cost and easily obtainable materials. However, its removal capacity for anions should be further improved.

Table 3.
Adsorption capacity of various clay materials towards Pb(II).

Table 4.
Adsorption capacity of various clay materials towards Cr(III/VI).
4. Conclusions
The findings of the current study have offered an insight into the adsorption behaviors of heavy metal anion CrO42− and cation Pb2+ on the synthetic allophane and the mechanisms behind them. The results emphasize that the adsorptions were dominated by heterogonous surfaces, and the maximum adsorption capacity of Pb2+ was 10 times greater than that for metal anion CrO42−. The ca. 91% of the equilibrium adsorption capacity for Pb2+ was achieved within 2 minutes, which is much faster than the equilibrium adsorption capacity for CrO42− (after 12 h of shaking). The adjustment of pH has an important effect on both adsorptions. As a result, the electrostatic attraction played important role in CrO42− adsorption, while a complex chemical reaction of Pb2+ adsorption occurred with the formation of P-O band. Further study of these mutual effects in the adsorption process on synthetic allophane is needed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.X. (Yan Xia); methodology, Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.X. (Yan Xia); writing—review and editing, Y.X. (Ying Xu); visualization, Y.X. (Ying Xu); supervision, Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 52000161. The 68th batch of China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, grant number 2020M682356. The CRSRI Open Research Program, grant number CKWV2021892/KY. Authors acknowledge Marta Camps-Arbestain for providing a lot of help during the entire research.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fang, Q.; Li, T.; Chen, Z.; Lin, H.; Wang, P.; Liu, F. Full Biomass-Derived Solar Stills for Robust and Stable Evaporation To Collect Clean Water from Various Water-Bearing Media. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 10672–10679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Hou, H.; Zuo, J.; Cui, F.; Liu, D.; Wang, W. A mechanically durable, sustained corrosion-resistant photothermal nanofiber membrane for highly efficient solar distillation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 22296–22306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Tang, C.; Ma, J.; Liu, D.; Qi, D.; You, S.; Cui, F.; Wei, Y.; Wang, W. Low-Tortuosity Water Microchannels Boosting Energy Utilization for High Water Flux Solar Distillation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 5150–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, H.; Wang, J.; Sheng, X.; Yan, J.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Y. Removal of Polystyrene Microplastics from Aqueous Solution Using the Metal–Organic Framework Material of ZIF-67. Toxics 2022, 10, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, F.; He, J.; Xu, H.; Cui, F.; Wang, W. Robust phosphate capture over inorganic adsorbents derived from lanthanum metal organic frameworks. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 326, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baby, R.; Saifullah, B.; Hussein, M.Z. Carbon Nanomaterials for the Treatment of Heavy Metal-Contaminated Water and Environmental Remediation. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva-Yumi, J.; Escudey, M.; Gacitua, M.; Pizarro, C. Kinetics, adsorption and desorption of Cd(II) and Cu(II) on natural allophane: Effect of iron oxide coating. Geoderma 2018, 319, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Luo, X.-B.; Ding, L.; Luo, S.-L. Application of nanotechnology in the removal of heavy metal from water. In Nanomaterials for the Removal of Pollutants and Resource Reutilization; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 83–147. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Wu, T.; Hsu, P.C.; Xie, J.; Zhao, J.; Liu, K.; Sun, J.; Xu, J.; Tang, J.; Ye, Z.; et al. Direct/Alternating Current Electrochemical Method for Removing and Recovering Heavy Metal from Water Using Graphene Oxide Electrode. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 6431–6437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; You, S.; Gong, X.; Qi, D.; Chandran, B.K.; Bi, L.; Cui, F.; Chen, X. Bioinspired Nanosucker Array for Enhancing Bioelectricity Generation in Microbial Fuel Cells. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keng, P.-S.; Lee, S.-L.; Ha, S.-T.; Hung, Y.-T.; Ong, S.-T. Removal of hazardous heavy metals from aqueous environment by low-cost adsorption materials. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2014, 12, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liao, P.; Peng, S.; Liang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Dang, Z.; Shi, Z. Molecular fractionation and sub-nanoscale distribution of dissolved organic matter on allophane. Environ. Sci.-Nano 2019, 6, 2037–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Du, P.; Yuan, P.; Zhong, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Deng, L. Changes in the structure and porosity of hollow spherical allophane under alkaline conditions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 166, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theng, B.K.; Yuan, G. Nanoparticles in the soil environment. Elements 2008, 4, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyoda, F.; Hayashi, S.; Arakawa, S.; John, B.; Okamoto, M.; Hayashi, H.; Yuan, G. Synthesis and adsorption characteristics of hollow spherical allophane nano-particles. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 56, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, F.; Wada, S.-I.; Suzuki, M.; Maeda, M.; Tomura, S. Synthetic allophane from highconcentration solutions: Nanoengineering of the porous solid. Clay Miner. 2002, 37, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-T.; Lowe, D.J.; Churchman, G.J.; Schipper, L.A.; Cursons, R.; Zhang, H.; Chen, T.-Y.; Cooper, A. DNA adsorption by nanocrystalline allophane spherules and nanoaggregates, and implications for carbon sequestration in Andisols. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 120, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldermann, A.; Grießbacher, A.; Baldermann, C.; Purgstaller, B.; Letofsky-Papst, I.; Kaufhold, S.; Dietzel, M. Removal of Barium, Cobalt, Strontium, and Zinc from Solution by Natural and Synthetic Allophane Adsorbents. Geosciences 2018, 8, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishikiori, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Kubota, S.; Tanaka, N.; Fujii, T. Removal of detergents and fats from waste water using allophane. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 47, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parfitt, R.; Henmi, T. Comparison of an oxalate-extraction methon and an infrared spectroscopic method for determining allophane in soll clays. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1982, 28, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parfitt, R.; Whitton, J.; Theng, B. Surface reactivity of A horizons towards polar compounds estimated from water adsorption and water content. Soil Res. 2001, 39, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Mei, T.; Wang, G.; Guo, A.; Dai, G.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Investigation on enhancing effects of Au nanoparticles on solar steam generation in graphene oxide nanofluids. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 114, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.W.; Chakravorti, R.K. Pore and solid diffusion models for fixed-bed adsorbers. AIChE J. 1974, 20, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B.; Yang, H.; Wu, S.; Tian, Y.; Guo, X.; Xu, C.; Kuang, W.; Yan, J.; Cen, K.; Bo, Z.; et al. Multifunctional solar bamboo straw: Multiscale 3D membrane for self-sustained solar-thermal water desalination and purification and thermoelectric waste heat recovery and storage. Carbon 2021, 171, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opiso, E.; Sato, T.; Yoneda, T. Adsorption and co-precipitation behavior of arsenate, chromate, selenate and boric acid with synthetic allophane-like materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Chang, N. Phosphate adsorption on hydroxyl–iron–lanthanum doped activated carbon fiber. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 215, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasi, A.; Omidi, M.; Khodadadian, M.; Khamutian, R.; Gholivand, M.B. Lead(II) and cadmium(II) removal from aqueous solution using processed walnut shell: Kinetic and equilibrium study. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2012, 94, 660–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Feng, X.; Dai, Z.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Xu, J. Adsorption characteristics of Cu(II) from aqueous solution onto biochar derived from swine manure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 7035–7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, B.E.; Ayranci, E. Effective Ionic Radii and Hydration Volumes for Evaluation of Solution Properties and Ionic Adsorption. J. Solut. Chem. 1999, 28, 163–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, W.; Xiong, L.; Xu, N.; Ni, J. Influence of pH, ionic strength and humic acid on competitive adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cr(III) onto titanate nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 215, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy Choudhury, P.; Majumdar, S.; Sahoo, G.C.; Saha, S.; Mondal, P. High pressure ultrafiltration CuO/hydroxyethyl cellulose composite ceramic membrane for separation of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) from contaminated water. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 336, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashizume, H.; Theng, B.K. Adenine, adenosine, ribose and 5′-AMP adsorption to allophane. Clays Clay Miner. 2007, 55, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abollino, O.; Aceto, M.; Malandrino, M.; Sarzanini, C.; Mentasti, E. Adsorption of heavy metals on Na-montmorillonite. Effect of pH and organic substances. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1619–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, R.A.; Shimp, N.F. Effect of pH on exchange-adsorption or precipitation of lead from landfill leachates by clay minerals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1976, 10, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahara, O. Model of cation adsorption on allophanic andisols I. Theory and algorithm. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2000, 46, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.G.; Wu, P.; Liu, G.J.; He, X.F.; Qi, B.Y.; Zeng, G.F.; Wang, W.; Sun, Y.H.; Cui, F.Y. Ultrahigh adsorption capacity of anionic dyes with sharp selectivity through the cationic charged hybrid nanofibrous membranes. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, K.G.; Gupta, S.S. Adsorptive accumulation of Cd(II), Co(II), Cu(II), Pb(II) and Ni(II) ions from water onto kaolinite: Influence of acid activation. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2009, 27, 47–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, A.; Tuzen, M.; Citak, D.; Soylak, M. Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies of adsorption of Pb(II) from aqueous solution onto Turkish kaolinite clay. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.-Q.; Wang, Q.-P.; Jin, X.-Y.; Chen, Z.-l. Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution using modified and unmodified kaolinite clay. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiew, C.S.C.; Yeoh, H.K.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Krishnaiah, K.; Poh, P.E.; Tey, B.T.; Chan, E.S. Halloysite/alginate nanocomposite beads: Kinetics, equilibrium and mechanism for lead adsorption. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 119, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sdiri, A.; Higashi, T.; Hatta, T.; Jamoussi, F.; Tase, N. Evaluating the adsorptive capacity of montmorillonitic and calcareous clays on the removal of several heavy metals in aqueous systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaari, I.; Fakhfakh, E.; Chakroun, S.; Bouzid, J.; Boujelben, N.; Feki, M.; Rocha, F.; Jamoussi, F. Lead removal from aqueous solutions by a Tunisian smectitic clay. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhu, P.; Cai, M.; Hu, H.; Fu, Q. Comparative adsorption of Pb(II), Cu(II) and Cd(II) on chitosan saturated montmorillonite: Kinetic, thermodynamic and equilibrium studies. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 143, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etci, Ö.; Bektaş, N.; Öncel, M.S. Single and binary adsorption of lead and cadmium ions from aqueous solution using the clay mineral beidellite. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 61, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdes, D.; Duran, C.; Senturk, H.B. Adsorptive removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions from aqueous solutions by using Turkish illitic clay. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 3082–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lu, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Pan, C.; Zhang, R.; Li, J.; Xiang, W. Structural Incorporation of Manganese into Goethite and Its Enhancement of Pb(II) Adsorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4719–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Korashy, S.A.; Elwakeel, K.Z.; El-Hafeiz, A.A. Fabrication of bentonite/thiourea-formaldehyde composite material for Pb(II), Mn(VII) and Cr(VI) sorption: A combined basic study and industrial application. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anna, B.; Kleopas, M.; Constantine, S.; Anestis, F.; Maria, B. Adsorption of Cd(II), Cu(II), Ni(II) and Pb(II) onto natural bentonite: Study in mono- and multi-metal systems. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 5435–5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatas, M. Removal of Pb(II) from water by natural zeolitic tuff: Kinetics and thermodynamics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 199–200, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Du, M.; Zhu, H.; Bao, S.; Yang, T.; Zou, M. Structure regulation of silica nanotubes and their adsorption behaviors for heavy metal ions: pH effect, kinetics, isotherms and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futalan, C.M.; Kan, C.-C.; Dalida, M.L.; Hsien, K.-J.; Pascua, C.; Wan, M.-W. Comparative and competitive adsorption of copper, lead, and nickel using chitosan immobilized on bentonite. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Pan, Z.; Wang, Y. Enhanced adsorption of cationic Pb(II) and anionic Cr(VI) ions in aqueous solution by amino-modified nano-sized illite-smectite clay. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 11126–11139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, W. Evaluating the adsorption of Shanghai silty clay to Cd(II), Pb(II), As(V), and Cr(VI): Kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Jalajamony, S.; Sreekumari, S.S. Adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by amine and carboxylate functionalised bentonites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 65–66, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinhua, W.; Xiang, Z.; Bing, Z.; Yafei, Z.; Rui, Z.; Jindun, L.; Rongfeng, C. Rapid adsorption of Cr(VI) on modified halloysite nanotubes. Desalination 2010, 259, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Duan, Y.; Wang, F.; Gao, P.; Jia, H.; Ma, C.; Wang, C. Silane-modified halloysite/Fe3O4 nanocomposites: Simultaneous removal of Cr(VI) and Sb(V) and positive effects of Cr(VI) on Sb(V) adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 311, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zhang, Q.; Dai, Y.; Zhu, N.; Dang, Z.; Li, P.; Wu, J.; Wang, X. Adsorption of Cu(II), Cd(II) and Cr(III) ions from aqueous solutions on humic acid modified Ca-montmorillonite. Geoderma 2011, 164, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Luo, H. Adsorption of hexavalent chromium onto montmorillonite modified with hydroxyaluminum and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brum, M.C.; Capitaneo, J.L.; Oliveira, J.F. Removal of hexavalent chromium from water by adsorption onto surfactant modified montmorillonite. Miner. Eng. 2010, 23, 270–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhana Krishna Kumar, A.; Ramachandran, R.; Kalidhasan, S.; Rajesh, V.; Rajesh, N. Potential application of dodecylamine modified sodium montmorillonite as an effective adsorbent for hexavalent chromium. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 211–212, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, S.; Ding, D.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Lei, Z.; Feng, C.; Zhang, Z. Effective adsorption of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution using natural Akadama clay. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 395, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajouyed, O.; Hurel, C.; Marmier, N. Evaluation of the Adsorption of Hexavalent Chromium on Kaolinite and Illite. J. Environ. Prot. 2011, 2, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arfaoui, S.; Frini-Srasra, N.; Srasra, E. Modelling of the adsorption of the chromium ion by modified clays. Desalination 2008, 222, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Zavala, M.Á.; Romero-Santana, H.; Monárrez-Cordero, B.E. Removal of Cr(VI) from water by adsorption using low cost clay-perlite-iron membranes. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocaoba, S. Adsorption of Cd(II), Cr(III) and Mn(II) on natural sepiolite. Desalination 2009, 244, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).