Diabetogenic and Obesogenic Effects of Cadmium in Db/Db Mice and Rats at a Clinically Relevant Level of Exposure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Cd Dosing
2.3. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
2.4. Body and Fat Pad Weight
2.5. Determination of Metabolic Indicators in Serum
2.6. Morphometric Analyses of Pancretic Islets
2.7. Determination of Cd Content in the Renal Cortex
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cadmium Accumulation in Renal Cortex
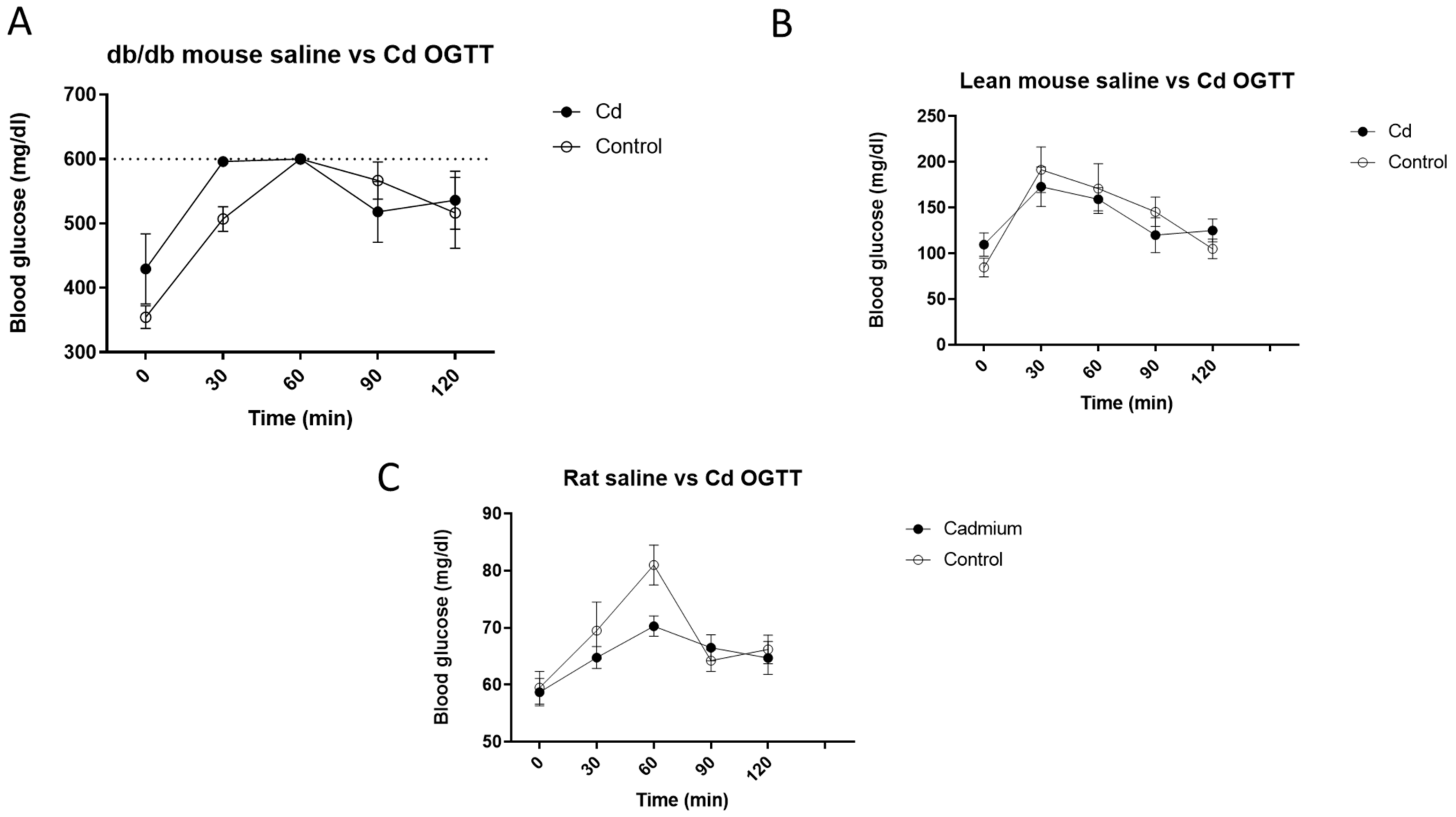
3.2. Cd and Oral Glucose Tolerance Tests
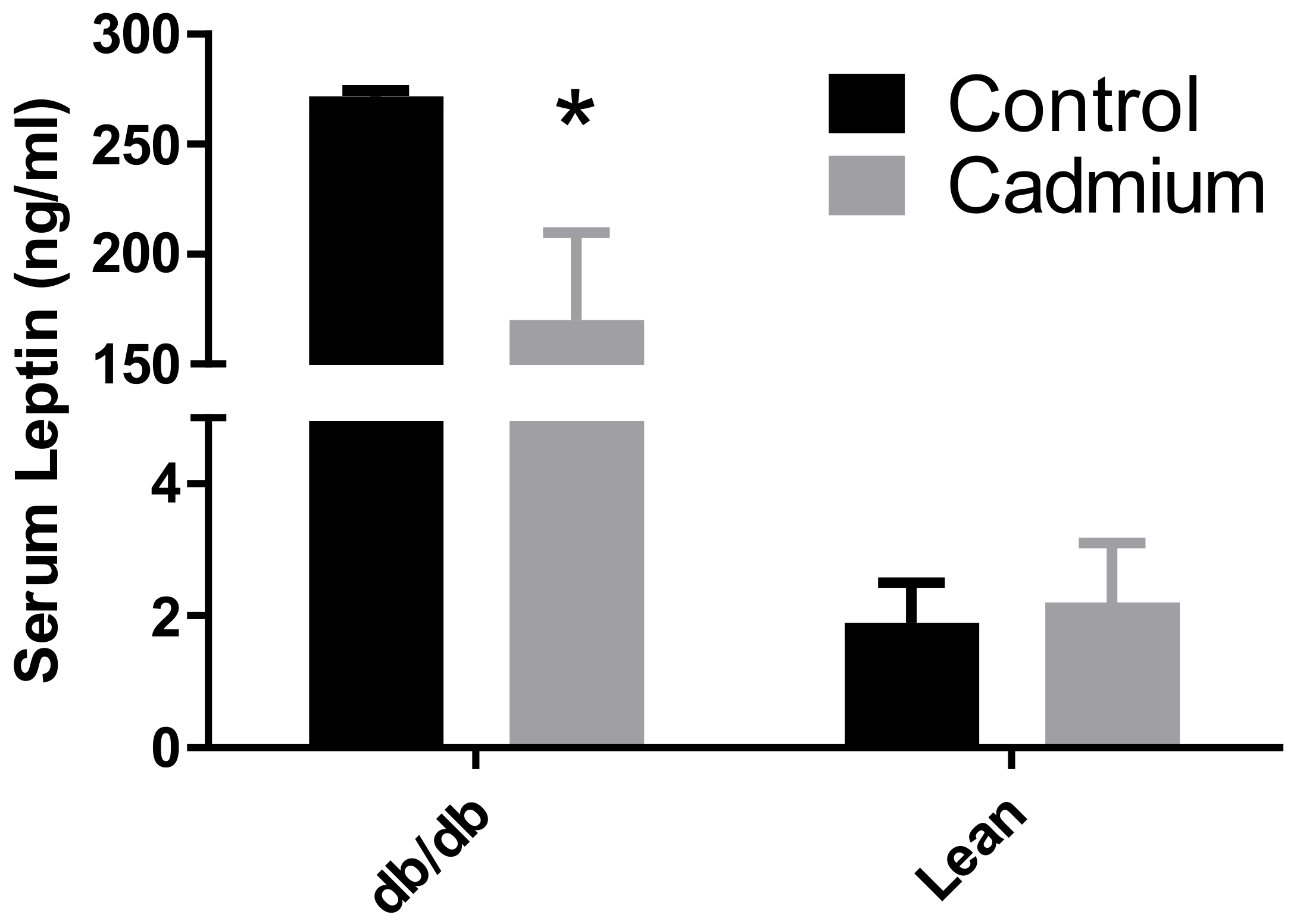
3.3. Cd Effects on Mediators of Metabolism Found in Blood
3.4. Cd and Pancreatic Islet Morphology
3.5. Cd Post-Exposure Effects on Individual Bodyweight Changes over Time
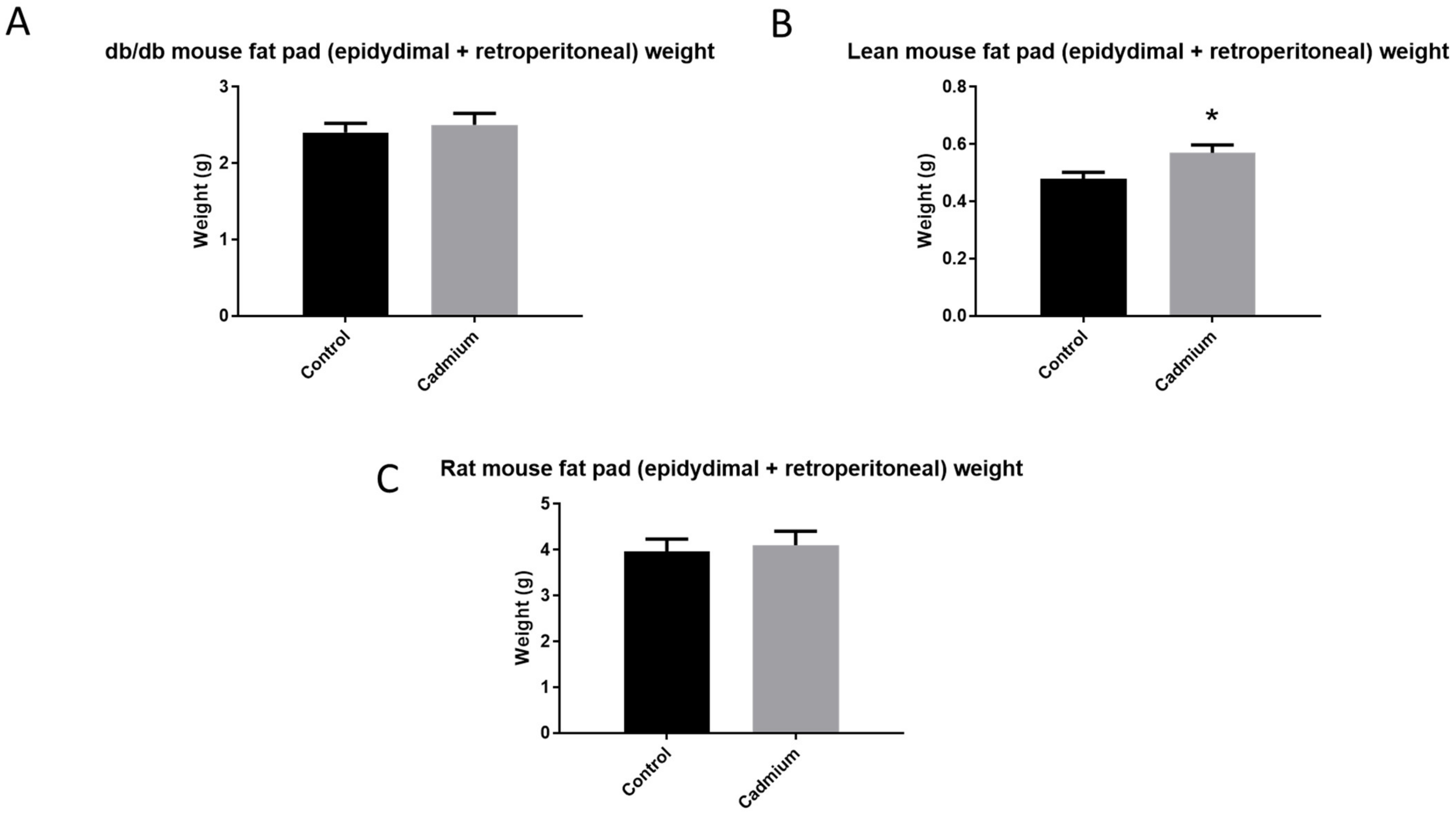
3.6. Cd Effects on Epidydimal and Retroperitoneal Fat Pad Weight
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jarup, L.; Berglund, M.; Elinder, C.G.; Nordberg, G.; Vahter, M. Health effects of cadmium exposure—A review of the literature and a risk estimate. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 1998, 24, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Friberg, L. Cadmium and the kidney. Environ. Health Perspect. 1984, 54, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uetani, M.; Kobayashi, E.; Suwazono, Y.; Honda, R.; Nishijo, M.; Nakagawa, H.; Kido, T.; Nogawa, K. Tissue cadmium (Cd) concentrations of people living in a Cd polluted area, Japan. Biometals 2006, 19, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satarug, S. Dietary Cadmium Intake and Its Effects on Kidneys. Toxics 2018, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolachi, N.F.; Kazi, T.G.; Afridi, H.I.; Kazi, N.; Khan, S.; Kandhro, G.A.; Shah, A.Q.; Baig, J.A.; Wadhwa, S.K.; Shah, F.; et al. Status of Toxic Metals in Biological Samples of Diabetic Mothers and Their Neonates. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2010, 143, 196–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, G.G.; Il’yasova, D.; Ivanova, A. Urinary cadmium, impaired fasting glucose, and diabetes in the NHANES III. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 468–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satarug, S. Long-term exposure to cadmium in food and cigarette smoke, liver effects and hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr. Drug Metab. 2012, 13, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menke, A.; Guallar, E.; Cowie, C.C. Metals in Urine and Diabetes in U.S. Adults. Diabetes 2016, 65, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.R.; Prozialeck, W.C. Cadmium, diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 238, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, R.R.; Early, J.L.; Nonavinakere, V.K.; Mallory, Z. Effect of cadmium on blood glucose level in the rat. Toxicol. Lett. 1990, 54, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, R.; Olsen, A.; Nguyen, J.; Wong, W.; El Muayed, M.; Edwards, J. Pancreatic Islets Accumulate Cadmium in a Rodent Model of Cadmium-Induced Hyperglycemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentki, M.; Nolan, C.J. Islet beta cell failure in type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Invest. 2006, 116, 1802–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Muayed, M.; Raja, M.R.; Zhang, X.; MacRenaris, K.W.; Bhatt, S.; Chen, X.; Urbanek, M.; O’Halloran, T.V.; Lowe, W.L., Jr. Accumulation of cadmium in insulin-producing beta cells. Islets 2012, 4, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.J.; Chen, L.; Jin, T.Y.; Nordberg, M.; Chang, X.L. Estimation of benchmark dose for pancreatic damage in cadmium-exposed smelters. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 97, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.C.; Park, S.Y.; Hah, B.G.; Choi, G.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Kwon, T.H.; Kim, E.K.; Lachaal, M.; Jung, C.Y.; Lee, W. Cadmium induces impaired glucose tolerance in rat by down-regulating GLUT4 expression in adipocytes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 413, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajanna, B.; Hobson, M.; Reese, J.; Sample, E.; Chapatwala, K.D. Chronic hepatic and renal toxicity by cadmium in rats. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 1984, 7, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapatwala, K.D.; Boykin, M.; Butts, A.; Rajanna, B. Effect of intraperitoneally injected cadmium on renal and hepatic gluconeogenic enzymes in rats. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 1982, 5, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Wang, N.; Chen, Y.; Chen, C.; Han, B.; Zhu, C.; Chen, Y.; Xia, F.; Cang, Z.; Lu, M.; et al. Blood cadmium in Chinese adults and its relationships with diabetes and obesity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 18714–18723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, M.; Slone, D.; Jick, H.; Shapiro, S.; Lewis, G.P. Cadmium content of cigarettes. Lancet 1969, 294, 1329–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.K.; Zopey, M.; Friedman, T.C. Metabolic effects of smoking cessation. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellmann, L.; Nascimento, A.R.; Tibirica, E.; Bousquet, P. Murine models for pharmacological studies of the metabolic syndrome. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 137, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.M.; Mantzoros, C.S. 20 years of leptin: From the discovery of the leptin gene to leptin in our therapeutic armamentarium. Metabolism 2015, 64, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, K.P.; Dickie, M.M.; Coleman, D.L. Diabetes, a new mutation in the mouse. Science 1966, 153, 1127–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.M.; Zhu, L.F.; Zhong, R.; Grant, D.; Goyer, R.A.; Cherian, M.G. Nephrotoxicity in rats following liver transplantation from cadmium-exposed rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1993, 123, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y.; Wideman, R.D.; Asadi, A.; Yang, G.K.; Baker, R.; Webber, T.; Zhang, T.; Wang, R.; Ao, Z.; Warnock, G.L.; et al. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide is expressed in pancreatic islet alpha-cells and promotes insulin secretion. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 1966–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prozialeck, W.C.; Edwards, J.R. Early biomarkers of cadmium exposure and nephrotoxicity. Biometals 2010, 23, 793–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prozialeck, W.C.; Lamar, P.C.; Edwards, J.R. Effects of sub-chronic Cd exposure on levels of copper, selenium, zinc, iron and other essential metals in rat renal cortex. Toxicol. Rep. 2016, 3, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lane, E.A.; Canty, M.J.; More, S.J. Cadmium exposure and consequence for the health and productivity of farmed ruminants. Res. Vet. Sci. 2015, 101, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chandrasekera, P.C.; Pippin, J.J. Leptin- and leptin receptor-deficient rodent models: Relevance for human type 2 diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2014, 10, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigle, D.S.; Duell, P.B.; Connor, W.E.; Steiner, R.A.; Soules, M.R.; Kuijper, J.L. Effect of fasting, refeeding, and dietary fat restriction on plasma leptin levels. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ali, Y.; Lim, C.Y.; Hong, W.; Pang, Z.P.; Han, W. Insulin-stimulated leptin secretion requires calcium and PI3K/Akt activation. Biochem. J. 2014, 458, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakami, T.; Nishiyama, K.; Kadota, Y.; Sato, M.; Inoue, M.; Suzuki, S. Cadmium modulates adipocyte functions in metallothionein-null mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 272, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasenko, S.; Bradford, E.M.; Piasek, M.; Henson, M.C.; Varnai, V.M.; Jurasovic, J.; Kusec, V. Metals in human placenta: Focus on the effects of cadmium on steroid hormones and leptin. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2010, 30, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kryfti, M.; Dimakou, K.; Toumbis, M.; Daniil, Z.; Hatzoglou, C.; Gourgoulianis, K.I. Effects of smoking cessation on serum leptin and adiponectin levels. Tob. Induc. Dis. 2015, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.; Ackerman, C. A Review of Diabetes Mellitus and Exposure to the Environmental Toxicant Cadmium with an Emphasis on Likely Mechanisms of Action. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2016, 12, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurata, Y.; Katsuta, O.; Doi, T.; Kawasuso, T.; Hiratsuka, H.; Tsuchitani, M.; Umemura, T. Chronic cadmium treatment induces islet B cell injury in ovariectomized cynomolgus monkeys. Jpn. J. Vet. Res. 2003, 50, 175–183. [Google Scholar]
- Padilla, M.A.; Elobeid, M.; Ruden, D.M.; Allison, D.B. An examination of the association of selected toxic metals with total and central obesity indices: NHANES 99-02. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 3332–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Yin, X.M.; Wang, Y. The association between amount of cigarettes smoked and overweight, central obesity among Chinese adults in Nanjing, China. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 16, 240–247. [Google Scholar]
- Bielohuby, M.; Popp, S.; Bidlingmaier, M. A guide for measurement of circulating metabolic hormones in rodents: Pitfalls during the pre-analytical phase. Mol. Metab. 2012, 1, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Boron | Cadmium | Calcium | Copper | Iron | Magnesium | Manganese | Molybdenum | Phosphorus | Potassium | Sodium | Zinc * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control lean mouse | 12.8 ± 6.5 | a 0.82 ± 0.33 | 121 ± 44 | 5.62 ± 1.0 | 81.5 ± 10 | 255 ± 19 | 2.02 ± 0.24 | 0.88 ± 0.3 | 4373 ± 279 | 5271 ± 433 | 1290 ± 150 | 41.0 ± 5.9 |
| Cadmium lean mouse | 7.73 ± 1.1 | 45.4 ± 3.6 | 91.1 ± 3.0 | 5.72 ± 0.52 | 74.2 ± 7.6 | 260 ± 13 | 2.14 ± 0.05 | 0.68 ± 0.04 | 4338 ± 239 | 5246 ± 411 | 1305 ± 143 | 45.0 ± 2.6 |
| Control db/db mouse | 4.28 ± 0.61 | a 0.4 ± 0.04 | 81.2 ± 2.7 | 5.1 ± 0.17 | 68.2 ± 5.6 | 243 ± 8.4 | 1.81 ± 0.03 | 0.74 ± 0.02 | 3938 ± 100 | 4797 ± 277 | 1080 ± 111 | 32 ± 0.41 |
| Cadmium db/db mouse | 4.88 ± 1.0 | 46.3 ± 5.7 | 91.9 ± 16 | 5.87 ± 0.43 | 82.2 ± 7.5 | 246 ± 7.1 | 1.96 ± 0.08 | 0.80 ± 0.07 | 3983 ± 125 | 4944 ± 385 | 1157 ± 140 | 46.7 ± 4.8 |
| Control rat | 2.22 ± 0.38 | a 0.26 ± 0.07 | 89.5 ± 4.8 | a 7.42 ± 0.21 | 51.6 ± 4.4 | 212 ± 5.8 | 0.95 ± 0.03 | 0.38 ± 0.05 | 3281 ± 83 | 3691 ± 172 | 1026 ± 38 | 31.1 ± 2.1 |
| Cadmium rat | 2.59 ± 0.66 | 71.24 ± 2.9 | 83.7 ± 7.3 | 22.8 ± 1.8 | 53.6 ± 7.2 | 194 ± 3.7 | 0.92 ± 0.02 | 0.52 ± 0.12 | 3059 ± 57 | 3425 ± 89 | 1100 ± 58 | 42.3 ± 2.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, J.; Patel, A.; Gensburg, A.; Bokhari, R.; Lamar, P.; Edwards, J. Diabetogenic and Obesogenic Effects of Cadmium in Db/Db Mice and Rats at a Clinically Relevant Level of Exposure. Toxics 2022, 10, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10030107
Nguyen J, Patel A, Gensburg A, Bokhari R, Lamar P, Edwards J. Diabetogenic and Obesogenic Effects of Cadmium in Db/Db Mice and Rats at a Clinically Relevant Level of Exposure. Toxics. 2022; 10(3):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10030107
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Jessica, Arjun Patel, Andrew Gensburg, Rehman Bokhari, Peter Lamar, and Joshua Edwards. 2022. "Diabetogenic and Obesogenic Effects of Cadmium in Db/Db Mice and Rats at a Clinically Relevant Level of Exposure" Toxics 10, no. 3: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10030107
APA StyleNguyen, J., Patel, A., Gensburg, A., Bokhari, R., Lamar, P., & Edwards, J. (2022). Diabetogenic and Obesogenic Effects of Cadmium in Db/Db Mice and Rats at a Clinically Relevant Level of Exposure. Toxics, 10(3), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10030107






