Health Risk Assessment Based on Source Identification of Heavy Metal(loid)s: A Case Study of Surface Water in the Lijiang River, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Collection and Analyses of Water Samples
2.3. Assessment Method
2.3.1. Evaluation of Surface Water Quality Based on Heavy Metal(loid)s
2.3.2. Human Health Risk Assessment
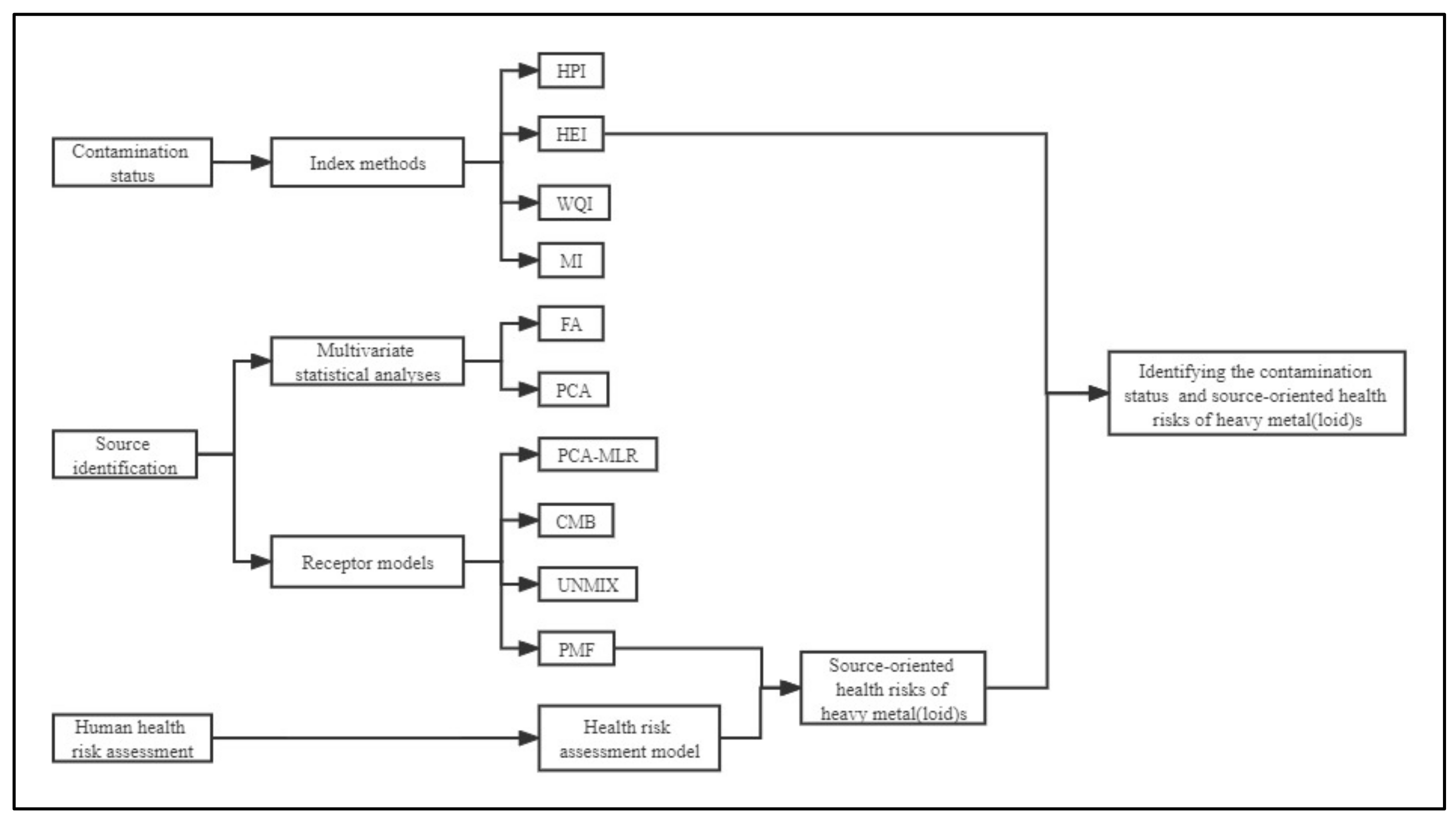
2.3.3. Pollution Sources of Heavy Metal(loid)s
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Analysis of Heavy Metal(loid)s Concentrations in Surface Water in the Study Area
3.2. Time Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Metal(loid)s Concentrations in Surface Water in the Study Area
3.3. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Heavy Metal(loid)s Concentrations in Surface Water in the Study Area
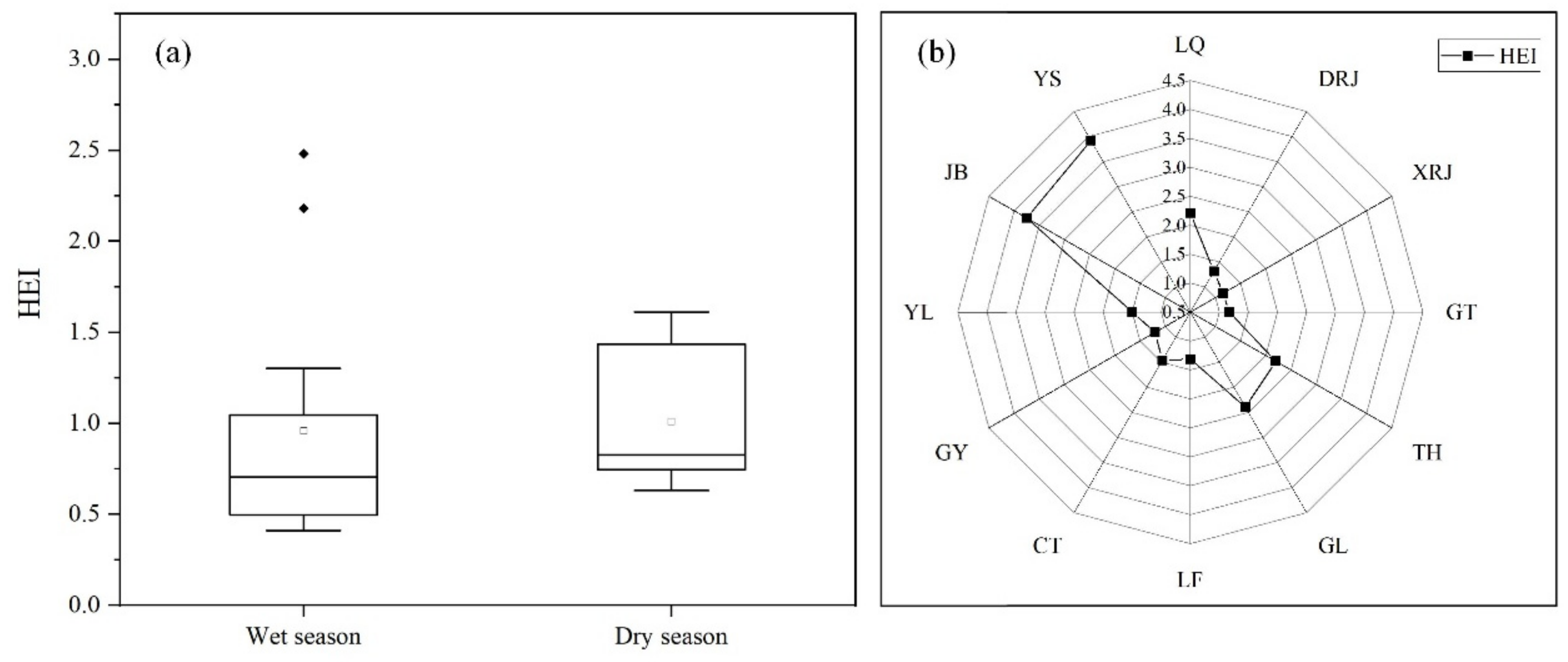
3.4. Surface Water Quality
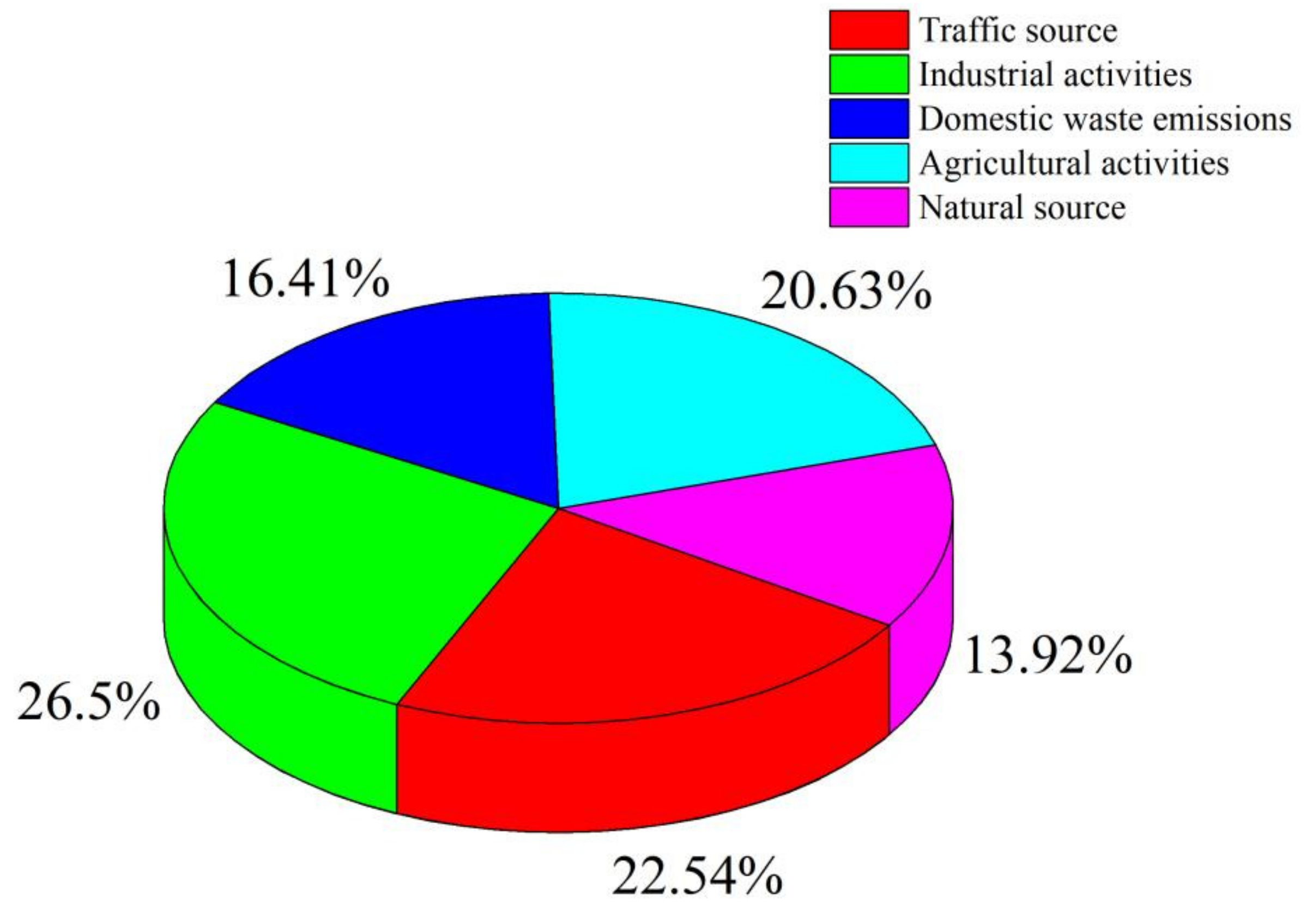
3.5. Pollution Sources of Heavy Metal(loid)s in Surface Water in the Study Area
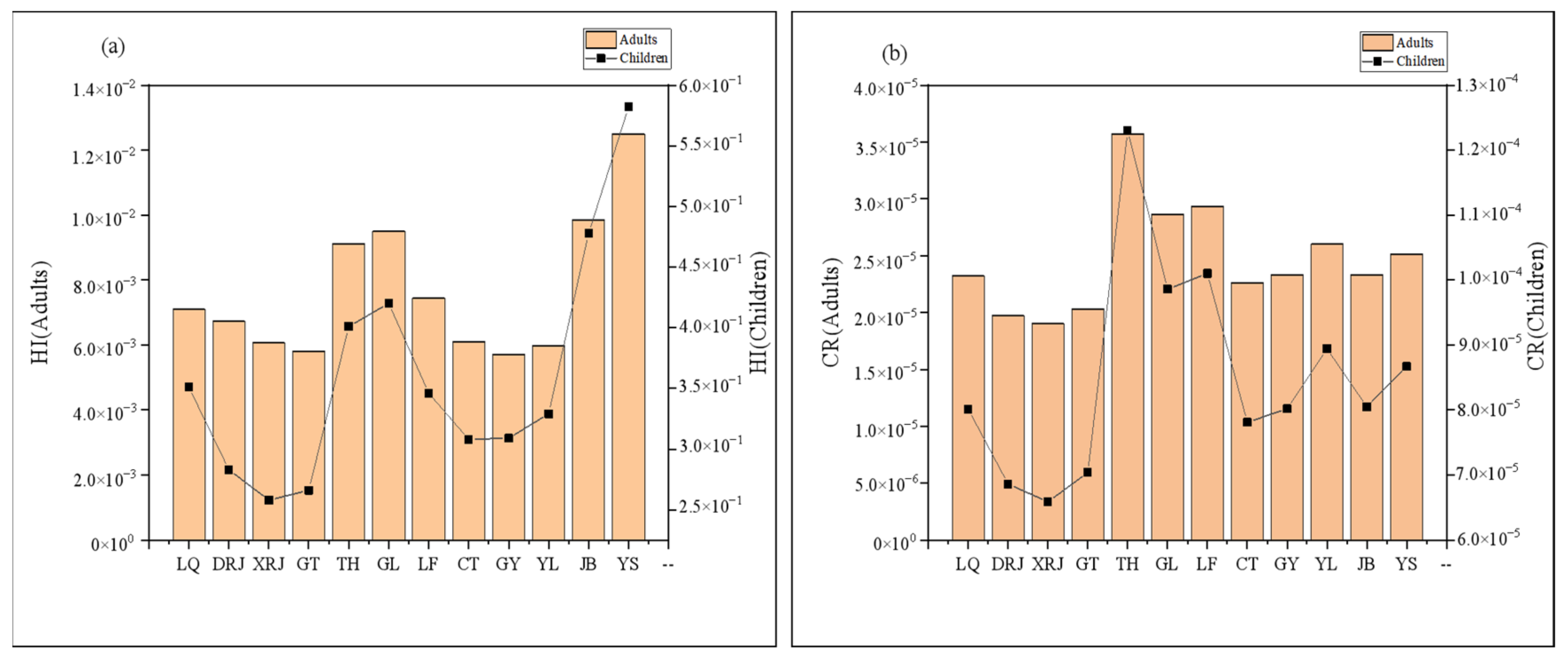
3.6. Human Health Risk Assessment
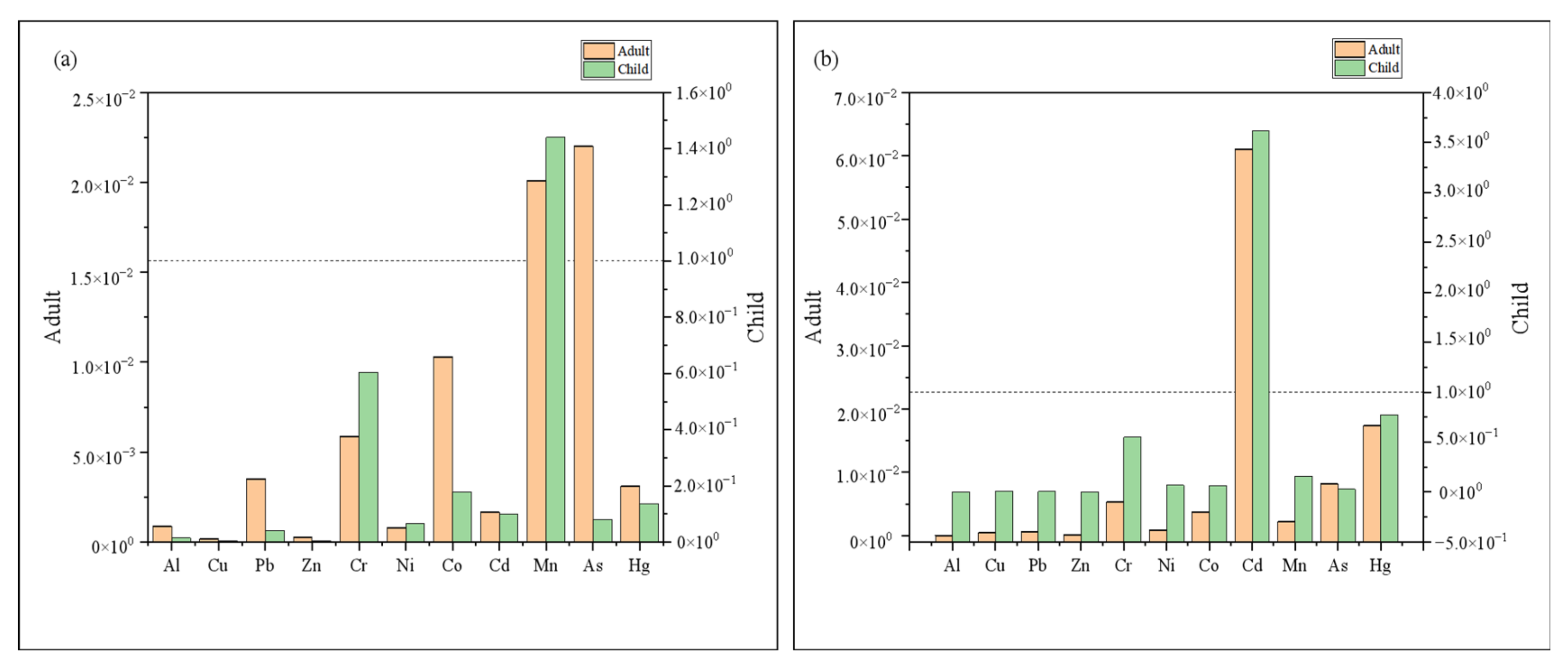
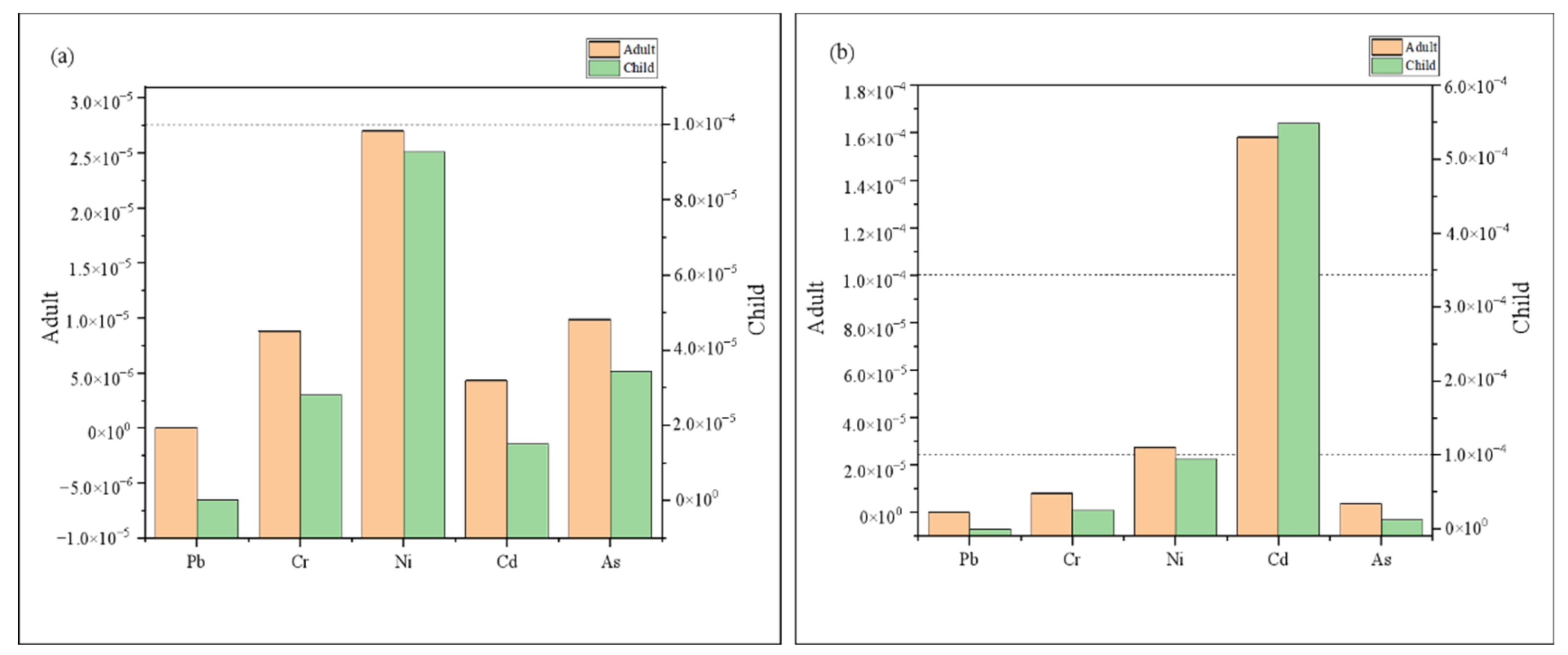
3.6.1. Human Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal(loid)s
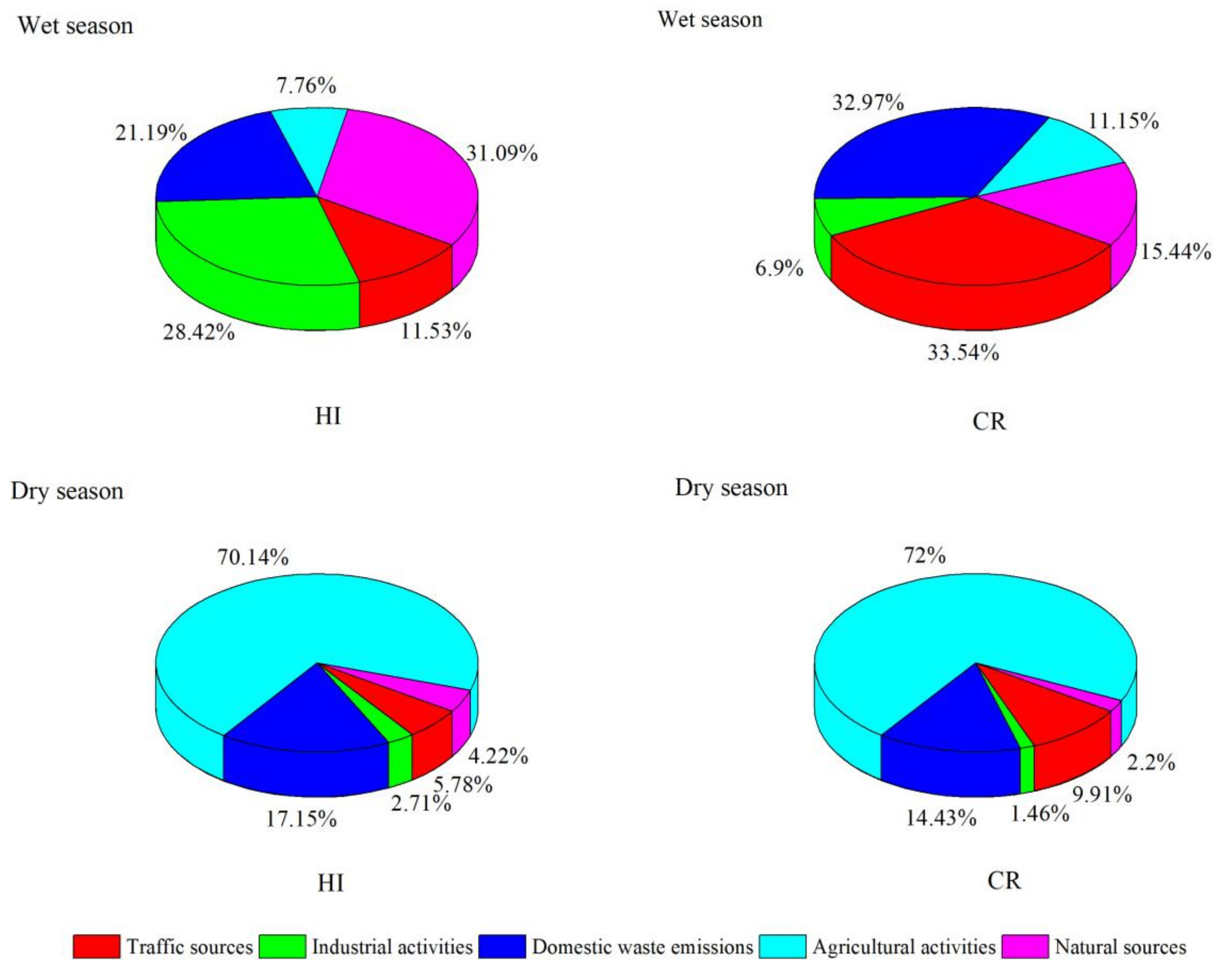
3.6.2. Source-Oriented Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal(loid)s
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wijesiri, B.; Liu, A.; He, B.B.; Yang, B.; Zhao, X.; Ayoko, G.; Goonetilleke, A. Behaviour of metals in an urban river and the pollution of estuarine environment. Water Res. 2019, 164, 114911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.H.; Xu, C.B.; Wang, J.H.; Xiang, Y.; Ren, M.; Qie, H.T.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yao, R.H.; Li, L.; Lin, A.J. Health risk assessment based on source identification of heavy metals: A case study of Beiyun River, China. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2021, 213, 112046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Abuduwaili, J.; Jiang, F.Q. Heavy metal contamination, sources, and pollution assessment of surface water in the Tianshan Mountains of China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.F.; Duan, J.M.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Guan, J.L.; Beecham, S.; Mulcahy, D. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment in the Wei River in China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Saluja, R.; Joshi, V.; Garg, J.K. Heavy metal pollution in surface water of the Upper Ganga River, India: Human health risk assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.A.; Volesky, B.; Mucci, A. A review of the biochemistry of heavy metal biosorption by brown algae. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4311–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurowski, K.; Kondratowicz-Pietruszka, E.; Krośniak, M. The Toxicological Safety Assessment of Heavy Metal Impurities (As, Pb, and Cd) in Mint Tea Infusions (Mentha piperita L.) Available in Polish Markets. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, Y.; Nogawa, K.; Nishijo, M.; Sakurai, M.; Ishizaki, M.; Morikawa, Y.; Kido, T.; Nakagawa, H.; Suwazono, Y. Relationship between cancer mortality and environmental cadmium exposure in the general Japanese population in cadmium non-polluted areas. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 223, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, D.R.; Meng, X.H.; Wen, X.H.; Wu, J.; Yu, H.J.; Wu, M. Contamination characteristics, source identification, and source-specific health risks of heavy metal (loid)s in groundwater of an arid oasis region in Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorer, O.S.; Ceylan, H.; Dogru, M. Assessment of some trace heavy metals and radioactivity concentration in water of Bendimahi River Basin (Van, Turkey). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 147, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wu, J.K.; Abuduwaili, J. Climate and environmental changes over the past 150 years inferred from the sediments of Chaiwopu Lake, central Tianshan Mountains, northwest China. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2013, 102, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.V.; Nithila, P.; Reddy, S.J. Estimation of heavy metals in drinking water and development of heavy metal pollution index. J. Environ. Sci. Health A. 1996, 31, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz, M.F.; Kilic, S.; Yalcin, F.; Kilic, M.; Yalcin, M.G. Evaluation of heavy metal risk potential in Bogacayi River water (Antalya, Turkey). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herojeet, R.; Rishi, M.S.; Kishore, N. Integrated approach of heavy metal pollution indices and complexity quantification using chemometric models in the Sirsa Basin, Nalagarh valley, Himachal Pradesh, India. Chin. J. Geochem. 2015, 34, 620–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaouzas, I.; Kapetanaki, N.; Mentzafou, A.; Kanellopoulos, T.D.; Skoulikidis, N. Heavy metal contamination status in Greek surface waters: A review with application and evaluation of pollution indices. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goher, M.E.; Hassan, A.M.; Abdel-Moniem, I.A.; Fahmy, A.H.; El-sayed, S.M. Evaluation of surface water quality and heavy metal indices of Ismailia Canal, Nile River, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquatic Res. 2014, 40, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Xu, P.P.; Qian, H. Groundwater quality assessment using improved water quality index (WQI) and human health risk (HHR) evaluation in a semi-arid region of northwest China. Expos. Health. 2020, 12, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addey, C.I.; Ayoola, N.O.; Omobolaji, A.A.; Tolulope, O.E. Heavy metals pollution index of surface water from Commodore channel, Lagos, Nigeria. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Tech. 2018, 12, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojekunle, O.Z.; Ojekunle, O.V.; Adeyemi, A.A.; Taiwo, A.G.; Sangowusi, O.R.; Taiwo, A.M.; Adekitan, A.A. Evaluation of surface water quality indices and ecological risk assessment for heavy metals in scrap yard neighbourhood. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, M.; Akter, A.; Islam, S.; Dey, S.C.; Choudhury, T.R.; Fatema, K.J.; Begum, B.A. Assessment of contamination level, pollution risk and source apportionment of heavy metals in the Halda River water, Bangladesh. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.P.; Wu, R.; Cui, J.L.; Gan, S.C.; Pan, J.C.; Guo, P.R. Improvement of water quality in the Pearl River Estuary, China: A long-term (2008–2017) case study of temporal-spatial variation, source identification and ecological risk of heavy metals in surface water of Guangzhou. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 21084–21097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, B.T.; Nguyen, V.N.; Truong, H.T.T.; Do, D.D.; Nguyen, T.X.; Nguyen, D.T.P.; Nguyen, M.H.; Dong, H.P.; Le, A.H.; Bach, Q.V. Assessment and source quantification of heavy metal (loid) s in surface water using multivariate analyses from the Saigon River, Vietnam. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 19383–19397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, K.K.; Bristy, M.S.; Alam, N.; Baki, M.A.; Shojib, F.H.; Quraishi, S.B.; Khan, M.F. Ecological risk and source apportionment of heavy metals in surface water and sediments on Saint Martin’s Island in the Bay of Bengal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 31827–31840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanotti, C.; Rotiroti, M.; Fumagalli, L.; Stefania, G.A.; Canonaco, F.; Stefenelli, G.; Prevot, A.S.H.; Leoni, B.; Bonomi, T. Groundwater and surface water quality characterization through positive matrix factorization combined with GIS approach. Water Res. 2019, 159, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.Y.; Gong, D.D.; Zhao, W.H.; Lin, L.; Yang, W.J.; Guo, W.J.; Tang, X.Q.; Li, Q.Y. Spatial-temporal distribution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in surface water of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 134883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Singh, A.K. Human health risk assessment via drinking water pathway due to metal contamination in the groundwater of Subarnarekha River Basin, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, A.; Toriman, M.E.; Juahir, H.; Zain, S.M.; Habir, N.L.A.; Retnam, A.; Kamaruddin, M.K.A.; Umar, R.; Azid, A. Spatial assessment and source identification of heavy metals pollution in surface water using several chemometric techniques. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 106, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.Q.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, R.J.; Guo, J.; Zhang, W.; Yu, K.F. Distribution, speciation, environmental risk, and source identification of heavy metals in surface sediments from the karst aquatic environment of the Lijiang River, Southwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 9122–9133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Shahab, A.; Xi, B.D.; Chang, Q.X.; You, S.H.; Li, J.Y.; Sun, X.J.; Huang, H.W.; Li, X.K. Heavy metal pollution, ecological risk, spatial distribution, and source identification in sediments of the Lijiang River, China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.M.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.L.; Leng, B.; Huang, W.Y.; Chen, Z.H. Concentration, distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediments from Lijiang River, South China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Tox. 2013, 90, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.G.; Yu, Z.D.; Liu, G.Z.; Chen, R.Z.; Peng, G.Y. Genetoxicity of water samples from the scenic Lijang river in the Guilin area, China, evaluated by Tradescantia bioassays. Mutat. Res. Fund. Mol. Mech. Mut. 1999, 426, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurowski, K.; Buszewski, B.; Piekoszewski, W. Bioanalytics in quantitive (bio) imaging/mapping of metallic elements in biological samples. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2015, 45, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurowski, K.; Buszewski, B.; Piekoszewski, W. The analytical calibration in (bio) imaging/mapping of the metallic elements in biological samples-definitions, nomenclature and strategies: State of the art. Talanta. 2015, 131, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardaway, C.J.; Sneddon, J.; Sneddon, E.J.; Kiran, B.; Lambert, B.J.; McCray, T.C.; Bowser, D.Q.; Douvris, C. Study of selected metal concentrations in sediments by inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry from a metropolitan and more pristine bayou in Southwest Louisiana, United States. Microchem. J. 2016, 100, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Jin, Z.J.; Li, Q. Changes in land use and their effects on soil properties in Huixian karst wetland system. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edet, A.E.; Offiong, O.E. Evaluation of water quality pollution indices for heavy metal contamination monitoring. A study case from Akpabuyo-Odukpani area, Lower Cross River Basin (southeastern Nigeria). Geojournal 2002, 57, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamasi, G.; Cini, R. Heavy metals in drinking waters from Mount Amiata (Tuscany, Italy). Possible risks from arsenic for public health in the Province of Siena. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 327, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 3838–2002. Environmental quality standards for surface water. Available online: https://www.docin.com/p-2686407728.html (accessed on 28 April 2002).
- Wu, Z.S.; Ma, T.T.; Lai, X.J.; Li, K.Y. Concentration, distribution, and assessment of dissolved heavy metals in rivers of Lake Chaohu Basin, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 300, 113744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Wu, H.H.; Wei, W.X.; Xu, C.B.; Tan, X.; Wen, Y.; Lin, A. Health risk assessment of heavy metal (loid) s in the farmland of megalopolis in China by using APCS-MLR and PMF receptor models: Taking Huairou District of Beijing as an example. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund Volume 1: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A); Office of Superfund Remediation and Technology Innovation: Washington, DC, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Cheng, S.Q.; Li, H.F.; Fu, K.; Xu, Y. Groundwater pollution source identification and apportionment using PMF and PCA-APCA-MLR receptor models in a typical mixed land-use area in Southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayembe, J.M.; Sivalingam, P.; Salgado, C.D.; Maliani, J.; Ngelinkoto, P.; Otamonga, J.P.; Mulaji, C.K.; Mubedi, J.I.; Pote, J. Assessment of water quality and time accumulation of heavy metals in the sediments of tropical urban rivers: Case of Bumbu River and Kokolo Canal, Kinshasa City, Democratic Republic of the Congo. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 147, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241548151 (accessed on 27 June 2011).
- Wang, Q.; Chen, Q.Y.; Yan, D.; Xin, S.G. Distribution, ecological risk, and source analysis of heavy metals in sediments of Taizihe River, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giersz, J.; Bartosiak, M.; Jankowski, K. Sensitive determination of Hg together with Mn, Fe, Cu by combined photochemical vapor generation and pneumatic nebulization in the programmable temperature spray chamber and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. Talanta 2017, 167, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, L.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Cheng, Z.X.; Su, L.M. Pollution characteristics, spatial distributions, and source apportionment of heavy metals in cultivated soil in Lanzhou, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrabadi, T. An Index Approach to Metallic Pollution in River Waters. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2015, 9, 385–394. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, R.I.S.; Sampaio, C.F.; Nadal, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L.; Segura-Munoz, S.I. Metal concentrations in surface water and sediments from Pardo River, Brazil: Human health risks. Environ. Res. 2014, 133, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, M.; Bakar, M.A.; Rashed-Un-Nabi, M.; Senapathi, V.; Chung, S.Y.; Islam, M.S. Monitoring and assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface water and sediment of the Old Brahmaputra River, Bangladesh. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Pei, N.C.; Sun, Y.X.; Li, J.L.; Li, X.P.; Yu, S.; Xu, X.R.; Hu, Y.X.; Mai, B.X. Halogenated organic pollutants in sediments and organisms from mangrove wetlands of the Jiulong River Estuary, South China. Environ. Res. 2019, 171, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.W.; Xiao, H.; Wang, D.Q.; Xin, B.D.; Sun, X.J.; Li, J.Y.; Li, X.K. Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in the water of Lijiang River Basin. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 1714–1723. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondol, M.N.; Chamon, A.S.; Faiz, B.; Elahi, S.F. Seasonal variation of heavy metal concentrations in Water and plant samples around Tejgaon industrial Area of Bangladesh. J. Bangladesh Acad. Sci. 2011, 35, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.Q.; Ren, B.; Li, Y.Z.; Niu, Y.D.; Ding, X.H.; Yao, X.; Bian, H.L. Trends and sources of dissolved heavy metal pollution in water of rivers and lakes in China. Environ. Chem. 2020, 8, 2044–2054. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Liu, X.M.; Zhu, M.Z.; Zhao, K.L.; Wu, J.J.; Xu, J.M.; Huang, P.M. Identification of trace element sources and associated risk assessment in vegetable soils of the urban-rural transitional area of Hangzhou, China. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 151, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Qi, S.H.; Wu, C.X.; Ke, Y.P.; Chen, J.; Chen, W.; Gong, X.Y. Preliminary assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface water and sediments from Honghu Lake, East Central China. Front. Earth Sci. 2012, 6, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, I.; Singh, U.K.; Singh, R.P.; Kumari, D.; Jha, P.K.; Mehta, P. Characterization of heavy metal pollution in an anthropogenically and geologically influenced semi-arid region of east India and assessment of ecological and human health risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, K.S.; Park, H.; Ha, E.; Hong, Y.C.; Ha, M.; Park, H.; Kim, B.N.; Lee, B.E.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, K.Y.; et al. Performance IQ in children is associated with blood cadmium concentration in early pregnancy. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2015, 30, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.Y.; Zhang, Q.F. Risk assessment and seasonal variations of dissolved trace elements and heavy metals in the Upper Han River, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quazi, S.; Sarkar, D.; Datta, R. Human health risk from arsenical pesticide contaminated soils: A long-term greenhouse study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.S.; Bi, C.J.; Jia, J.P.; Deng, L.; Chen, Z.L. Impact of intensive land use on heavy metal concentrations and ecological risks in an urbanized river network of Shanghai. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 116, 106501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
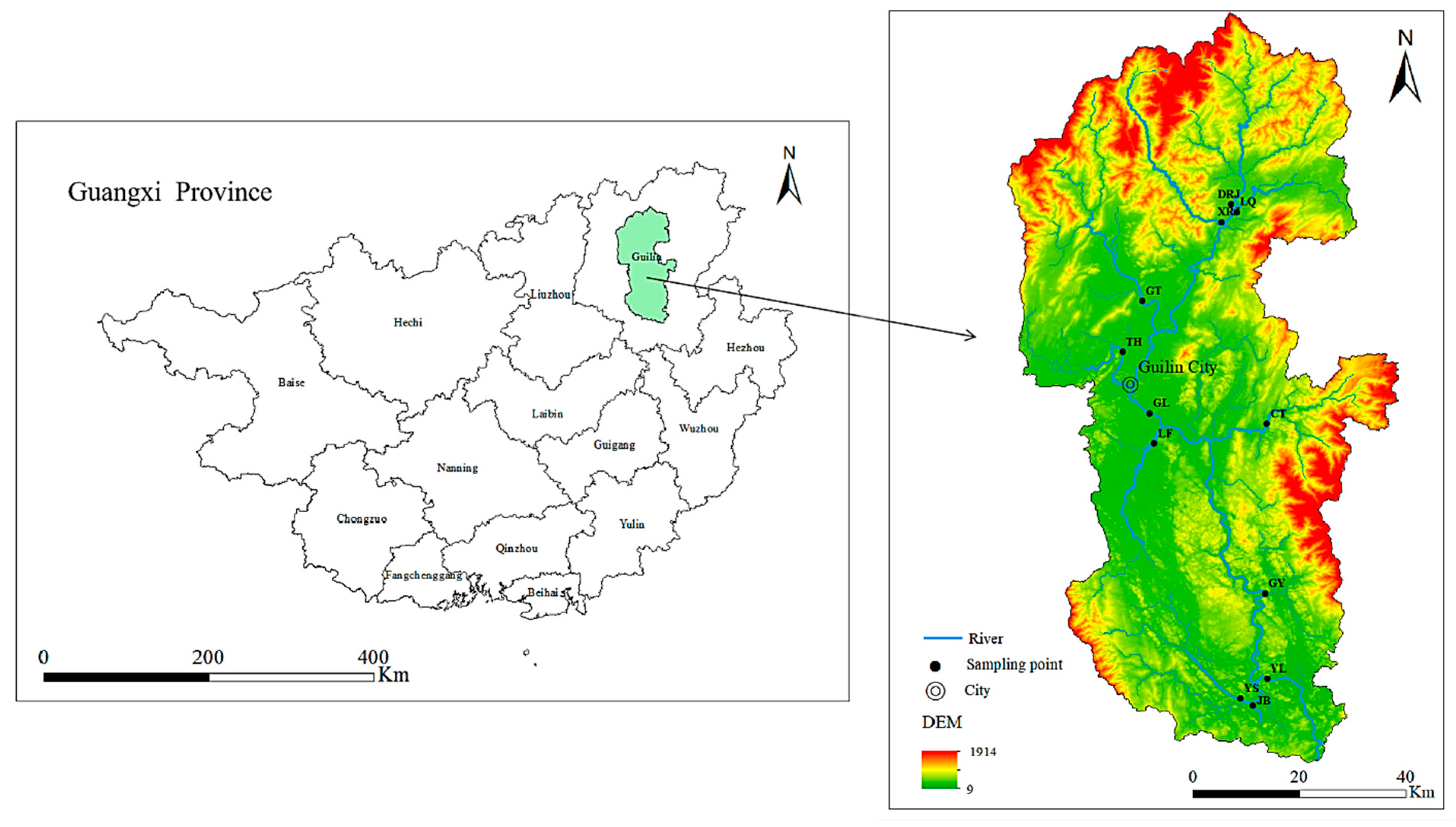


| Areas | Sampling Points | Abbreviations |
|---|---|---|
| Upstream area | Lingqu | LQ |
| Darong River | DRJ | |
| Xiaorong River | XRJ | |
| Midstream area | Gantang River | GT |
| Taohua River | TH | |
| Guilin Section | GL | |
| Liangfeng River | LF | |
| Chaotian River | CT | |
| Downstream area | Guangyan | GY |
| Yangshuo Section | YS | |
| Yulong River | YL | |
| Jinbao River | JB |
| Season | pH | T/°C | TDS/mg·L−1 | DO/mg·L−1 | EC/µs·cm−1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wet season | Max | 8.22 | 21.35 | 180.40 | 10.30 | 357.30 |
| Min | 6.85 | 14.88 | 18.51 | 6.03 | 36.67 | |
| Mean | 7.66 | 19.43 | 92.42 | 8.95 | 183.62 | |
| Dry season | Max | 8.73 | 17.15 | 144.70 | 14.01 | 419.20 |
| Min | 7.42 | 14.76 | 75.40 | 7.27 | 41.40 | |
| Mean | 8.13 | 16.01 | 109.23 | 10.53 | 233.93 |
| Elements | Al | Cu | Pb | Zn | Cr | Ni | Co | Cd | Mn | As | Hg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wet season | Mean | 69.73 | 0.50 | 0.39 | 6.45 | 1.10 | 1.30 | 0.26 | ND | 33.53 | 0.56 | ND |
| CV | 1.03 | 0.68 | 1.58 | 1.41 | 0.46 | 0.75 | 0.66 | - | 0.96 | 0.47 | - | |
| Dry season | Mean | 3.91 | 1.42 | ND | 1.53 | 1.00 | 1.31 | 0.09 | 2.20 | 3.70 | 0.16 | 0.39 |
| CV | 1.05 | 0.78 | - | 1.59 | 0.60 | 0.78 | 0.74 | 0.05 | 2.50 | 1.39 | 0.83 | |
| National Class II surface water environmental quality standard | - | 1000 | 10 | 1000 | 50 | - | - | 5 | - | 50 | 0.05 | |
| Standard (WHO) | 200 | 2000 | 10 | - | 50 | 20 | - | 3 | 400 | 10 | 6 | |
| River | Bogacayi, Turkey | Sirsa River, India | Haraz River, Iran | Pardo River, Brazil | Old Brahmaputra River, Bangladesh | Lake Chaohu Basin, China | Lijiang River, China |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | - | - | - | - | 6870 | - | 36.82 |
| Cu | 0.92 | 27.0 | 13.25 | 5.05 | 120 | 1.63 | 0.96 |
| Pb | 0.48 | 17.9 | 4.40 | 2.54 | 110 | 0.41 | 0.20 |
| Zn | - | 96.3 | 52.75 | 12.45 | 10 | 233.39 | 3.99 |
| Cr | 3.20 | 35.5 | - | 0.52 | 10 | 1.15 | 1.05 |
| Ni | 3.47 | 64.8 | - | 5.70 | 440 | 2.35 | 1.30 |
| Co | ND | - | - | - | 200 | - | 0.17 |
| Cd | 0.23 | 2.6 | 2.65 | 0.05 | 1 | 0.02 | 1.10 |
| Mn | 0.62 | 313.9 | 116 | 36.4 | 1440 | 38.85 | 18.61 |
| As | 0.43 | 5.5 | 55.35 | 2.14 | - | 1.50 | 0.36 |
| Hg | ND | - | - | ND | 1 | - | 0.20 |
| Reference | [13] | [14] | [48] | [49] | [50] | [39] | Present study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Xin, C.; Yu, S.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, W.; Fu, R. Health Risk Assessment Based on Source Identification of Heavy Metal(loid)s: A Case Study of Surface Water in the Lijiang River, China. Toxics 2022, 10, 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10120726
Wang Y, Xin C, Yu S, Xie Y, Zhang W, Fu R. Health Risk Assessment Based on Source Identification of Heavy Metal(loid)s: A Case Study of Surface Water in the Lijiang River, China. Toxics. 2022; 10(12):726. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10120726
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yu, Cunlin Xin, Shi Yu, Yincai Xie, Wanjun Zhang, and Rongjie Fu. 2022. "Health Risk Assessment Based on Source Identification of Heavy Metal(loid)s: A Case Study of Surface Water in the Lijiang River, China" Toxics 10, no. 12: 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10120726
APA StyleWang, Y., Xin, C., Yu, S., Xie, Y., Zhang, W., & Fu, R. (2022). Health Risk Assessment Based on Source Identification of Heavy Metal(loid)s: A Case Study of Surface Water in the Lijiang River, China. Toxics, 10(12), 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10120726







