Occurrence and Distribution of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) from Sele River, Southern Italy: Analysis of Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Organochlorine Pesticides in a Water–Sediment System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
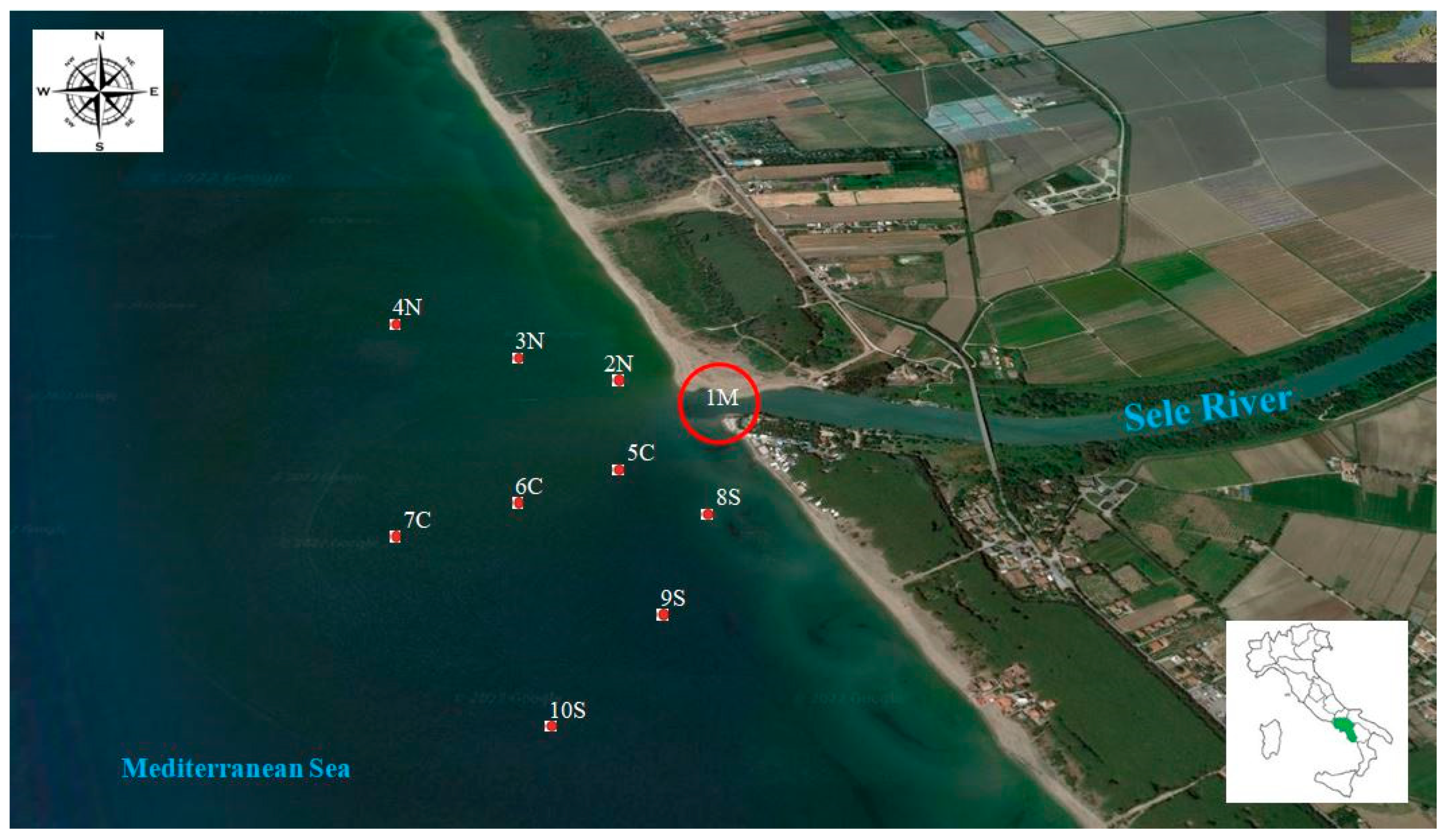
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Processing and Chemical Analysis
2.4. Quality Assurance and Quality Control
2.5. Analysis and Contaminants Load
2.6. Toxicity and Dioxin-like PCBs
2.7. Risk Assessment
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. PCBs Distribution in DP, SPM and Sediment Samples
3.2. OCPs Distribution in DP, SPM and Sediment Samples
3.3. Spatiotemporal Diffusion
3.4. Potential Sources of PCBs
3.5. Dioxin Toxicity Equivalency
3.6. Risk Assessment of PCBs and OCPs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Islam, M.S.; Ahmed, M.K.; Rakanuzzaman, M.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Islam, M.K. Heavy metal pollutionin surface water and sediment: A preliminary assessment of an urbanriver in a developing country. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, R.; Hu, B. Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments of the Bohai and Yellow Seas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Guo, C.S.; Luo, Y.; Lv, J.P.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H.X.; Wang, I.; Xu, J. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics, antibiotic resistence genes in the urban rivers in Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 213, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhoumi, B.; Beldean-Galea, M.S.; Al-Rawabdeh, A.M.; Roba, C.; Martonos, I.M.; Balc, R.; Kahlaoui, M.; Touil, S.; Tedetti, M.; Driss, M.R.; et al. Occurrence, distribution and ecological risk of trace metals and organic pollutants in surface sediments from a Southeastern European river (Someşu Mic River, Romania). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 660–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, N.H.; Minh, T.B.; Kajiwara, N.; Kunisue, T.; Iwata, H.; Viet, P.H.; Cam Tu, N.P.; Tuyen, B.C.; Tanabe, S. Pollution sources and occurrences of selected persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in sediments of the Mekong River delta, South Vietnam. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 1794–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montuori, P.; Triassi, M. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons loads into the Mediterranean Sea: Estimate of Sarno River inputs. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loqanathan, B.G.; Kannan, K. Global organochlorine contamination trends: An overview. Ambio 1994, 23, 187–191. [Google Scholar]
- Muir, D.; Sverko, E. Analytical methods for PCBs and organochlorine pesticides in environmental monitoring and surveillance: A critical appraisal. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 386, 769–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hou, H.; Zhou, Y.; Xue, N.; Li, H.; Li, L. Distribution and ecological risk of polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in surficial sediments from Haihe River and Haihe Estuary Area, China. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shi, Y.; Hu, J.; Yao, Z.; Fang, X.; Dong, Y. Determination of dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls in soil and moss from Fildes Peninsula, Antarctica. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimou, K.N.; Su, T.L.; Hires, R.I.; Miskewitz, R. Distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls in the Newark Bay Estuary. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Mo, L.; Kong, Y.; Lou, I. Occurrence and possible sources of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) along the Chao River, China. Chemosphere 2014, 114, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montuori, P.; Aurino, S.; Garzonio, F.; Triassi, M. Polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in Tiber River and Estuary: Occurrence, distribution and ecological risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 1001–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montory, M.; Ferrer, J.; Rivera, D.; Villouta, M.V.; Grimalt, J.O. First report on organochlorine pesticides in water in a highly productive agro-industrial basin of the Central Valley, Chile. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafilzadeh, F. Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water and sediments of the Soltan Abad River, Iran. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2015, 41, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Wang, L.; Lei, K.; Nan, B. Distribution and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water, suspended particulate matter and sediment from Daliao River estuary and the adjacent area, China. Chemosphere 2016, 149, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eremina, N.; Paschke, A.; Mazlova, E.A.; Schüürmann, G. Distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls, phthalic acid esters, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organochlorine substances in the Moscow River, Russia. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.Y.; Yu, M.; Luo, X.J.; Chen, S.J.; Mai, B.X. The factors controlling the partitioning of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polychlorinated biphenyls in the water-column of the Pearl River Estuary in South China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 62, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gutiérrez, A.I.; Jover, E.; Bodineau, L.; Albaigés, J.; Bayona, J.M. Organic contaminant loads into the Western Mediterranean Sea: Estimate of Ebro river inputs. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.F.; Wang, J.Z.; Ni, H.G.; Zeng, E.Y. Organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in riverine runoff of the Pearl River Delta, China: Assessment of mass loading, input source and environmental fate. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, G.; Alberico, I.; Aucelli, P.P.C.; Matano, F.; Rizzo, A.; Vilardo, G. Coastal subsidence detected by Synthetic Aperture Radar interferometry and its effects coupled with future sea-level rise: The case of the Sele Plain (Southern Italy). J. Flood Risk Manag. 2018, 11, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arienzo, M.; Bolinesi, F.; Aiello, G.; Barra, D.; Donadio, C.; Stanislao, C.; Trifuoggi, M. The environmental assessment of an estuarine transitional environment, southern Italy. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diodato, N.; Fagnano, M.; Alberico, I. Geospatial and visual modeling for exploring sediment source areas across the Sele river landscape, Italy. Ital. J. Agron. 2011, 6, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, S.; De Vivo, B.; Lima, A.; Cicchella, D. Geochemical background and baseline values of toxic elements in stream sediments of Campania region (Italy). J. Geochem. Explor. 2007, 93, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menghan, W.; Stefano, A.; Annamaria, L.; Claudia, C.; Antonio, C.; Wanjun, L.; Angela, D. Compositional analysis and pollution impact assessment: A case study in the Gulfs of Naples and Salerno. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 160, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, S.; De Vivo, B.; Lima, A.; Cicchella, D.; Civitillo, D.; Cosenza, A. Geochemical baselines and risk assessment of the Bagnoli brownfield site coastal sea sediments (Naples, Italy). J. Geochem. Explor. 2010, 105, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montuori, P.; De Rosa, E.; Di Duca, F.; De Simone, B.; Scippa, S.; Russo, I.; Triassi, M. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Dissolved Phase, Particulate Matter, and Sediment of the Sele River, Southern Italy: A Focus on Distribution, Risk Assessment, and Sources. Toxics 2022, 10, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montuori, P.; De Rosa, E.; Sarnacchiaro, P.; Di Duca, F.; Provvisiero, D.P.; Nardone, A.; Triassi, M. Polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in water and sediment from Volturno River, Southern Italy: Occurrence, distribution and risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montuori, P.; Cirillo, T.; Fasano, E.; Nardone, A.; Esposito, F.; Triassi, M. Spatial distribution and partitioning of polychlorinated biphenyl and organochlorine pesticide in water and sediment from Sarno River and Estuary, southern Italy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 5023–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP/MAP. Guidelines for River (Including Estuaries) Pollution Monitoring Programme for the Mediterranean Region; MAP Technical Reports Series No. 151; UNEP/MAP: Athens, Greece, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jolliffe, I.T. Principal Component Analysis, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Berg, M.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Denison, M.; De Vito, M.; Farland, W.; Feeley, M.; Fiedler, H.; Hakansson, H.; Hanberg, A.; Haws, L.; et al. The 2005 World Health Organization reevaluation of human and Mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 93, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, G.F. A review of chemical-based sediment quality assessment methodologies for the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 9751001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Water Quality: Guidelines, Standards and Health; IWA: London, UK, 2001.
- USEPA (US Environmental Protection Agency). Regional Screening Levels for Chemical Contaminants at Superfund Sites. Regional Screening Table. User’s Guide. 2012. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/risk/regional-screening-levels-rslsgeneric-tables (accessed on 2 August 2022).
- Chen, C.; Zou, W.; Chen, S.; Zhang, K.; Ma, L. Ecological and health risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides in an urbanized river network of Shanghai, China. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yang, H.; Ge, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Han, D.; Cheng, J. Long-term study of heavy metal pollution in the northern Hangzhou Bay of China: Temporal and spatial distribution, contamination evaluation, and potential ecological risk. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 28, 10718–10733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srédlovà, K.; Cajthaml, T. Recent advances in PCB removal from historically contaminate environmental matrices. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.; Nizzetto, L.; Guo, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. DDTs and HCHs in sediment cores from the coastal East China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čonka, K.; Chovancová, J.; Stachová Sejáková, Z.; Dömötörová, M.; Fabišiková, A.; Drobná, B.; Kočan, A. PCDDs, PCDFs, PCBs and OCPs in sediments from selected areas in the Slovak Republic. Chemosphere 2014, 98, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, J.H.; Malik, R.N.; Li, J.; Chaemfa, C.; Zhang, G.; Jones, K.C. Status, distribution and ecological risk of organochlorines (OCs) in the surface sediments from the Ravi River, Pakistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, B.; Sarkar, S.K.; Mukherjee, N. Organochlorine pesticide residues in sediments of a tropical mangrove estuary, India: Implications for monitoring. Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, A.O.; Khairy, M.; Aukaily, I. Persistent organochlorine pesticide and PCB residues in surface sediments of Lake Qarun, a protected area of Egypt. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 2467–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, N.Q.; Que, M.X.; Li, Y.F.; Liu, L.Y.; Wang, X.N.; Xu, D.D.; Sverko, E.D.; Ma, J.M. Polychlorinated biphenyls in Chinese surface soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 41, 3871–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Li, W.; Shi, G.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y. Relationships between PAHs and PCBs, and quantitative source apportionment of PAHs toxicity in sediments from Fenhe reservoir and watershed. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 248–249, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; He, M.; Yang, Z.; Lin, C.; Quan, X.; Wang, H. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water, suspended particulate matter and sediment from Daliao River watershed, China. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Feng, J.; Niu, J.; Shen, Z. Release of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from Yangtze River sediment cores during periods of simulated resuspension. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 155, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Jia, H.; Liu, X.; Sun, Y.; Yang, M.; Hong, W.; Li, Y.F. Historical contamination and ecological risk of organochlorine pesticides in sediment core in northeastern Chinese river. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 93, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doong, R.; Lee, S.; Lee, C.; Sun, Y.; Wu, S. Characterization and composition of heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants in water and estuarine sediments from Gao-ping River, Taiwan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 57, 846–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.S.; Khaled, A.; Nemr, A.E. Assessment of pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments of the Egyptian Mediterranean coast. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2013, 39, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Kong, D.; Li, L.; Zou, C.; Chen, F.; Li, M.; Cao, T.; Yu, C.; Song, J.; Jia, W.; et al. Distribution and sources of DDT and its metabolites in porewater and sediment from a typical tropical bay in the South China Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Hernandez, C.M.; Mesa-Albernas, M.; Tolosa, I. Organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in sediments from the Gulf of Batabano, Cuba. Chemosphere 2013, 94, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuranchie-Mensah, H.; Atiemo, S.M.; Palm, L.M.; Blankson-Arthur, S.; Tutu, A.O.; Fosu, P. Determination of organochlorine pesticide residue in sediment and water from the Densu river basin, Ghana. Chemosphere 2011, 86, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aries, E.; Anderson, D.R.; Fisher, R. PCDD/F and Dioxin-like PCB emissions from iron ore sintering plants in the UK. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 1470–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibamoto, T.; Yasuhara, A.; Katami, T. Dioxin formation from waste incineration. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioia, R.; Nizzetto, L.; Lohmann, R. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in air and seawater of the Atlantic Ocean: Sources, trends and processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 1416–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totten, L.A.; Gigliotti, C.L.; VanRy, D.A. Atmospheric concentrations and deposition of polychorinated biphenyls to the Hudson River Estuary. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 2568–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Chen, J.; Shen, Z.; Liu, H.; Che, Y. Seasonal and spatial distributions and possible sources of polychlorinated biphenyls in surface sediments of Yangtze Estuary, China. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Hu, X.; Zhang, H.; He, S.; Lv, S. Distributions and sources of petroleum, aliphatic hydrocarbons and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediments from Bohai Bay and its adjacent river, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 90, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz, R.; Grimalt, J.O.; Fernández, P. Toxicity assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from European high mountain lakes. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, M.M.; Wu, J.H.; Wang, K.B. Potential health risk assessment of HFRs, PCBs, and OCPs in the Yellow River basin. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 275, 116648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinc, B.; Çelebi, A.; Avaz, G.; Canlı, O.; Güzel, B.; Eren, B.; Yetis, U. Spatial distribution and source identification of persistent organic pollutants in the sediments of the Yeşilırmak River and coastal area in the Black Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sampling Location | ΣPCBs | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site Number Identificatin | Site | Sampling Point | DP (ng L−1) | SPM (ng L−1) (ng g−1 Dry wt) | SED (ng g−1 Dry wt) | ||||||
| Apr | Jul | Nov | Feb | Apr | Jul | Nov | Feb | Apr | |||
| 1 (river water) | Sele River Source | 40°28′55″ N 14°56′33″ E | 6.80 | 12.1 | 7.01 | 4.20 | 14.0 (1758.6) | 9.21 (1026.2) | 26.0 (2622.7) | 35.1 (1895.3) | 79.3 |
| 2 (sea water) | River Mouth at 500 mt North | 40°29′04″ N 14°56′14″ E | 5.71 | 6.70 | 6.56 | 4.68 | 2.11 (223.2) | 2.85 (1236.0) | 10.7 (402.2) | 22.2 (179.0) | 51.2 |
| 3 (sea water) | River Mouth at 500 mt Central | 40°29′12″ N 14°55′56″ E | 6.51 | 7.29 | 6.84 | 4.76 | 4.2 (1126.7) | 5.04 (2514.3) | 8.81 (2589.2) | 6.85 (1674.7) | 36.4 |
| 4 (sea water) | River Mouth at 500 mt South | 40°29′20″ N 14°55′38″ E | 8.72 | 10.2 | 7.77 | 5.02 | 7.00 (952.1) | 6.18 (2698.2) | 24.9 (589.5) | 30.6 (212.5) | 62.1 |
| 5 (sea water) | River Mouth at 1000 mt North | 40°28′55″ N 14°56′12″ E | 6.21 | 6.66 | 6.32 | 3.94 | 1.52 (118.0) | 1.17 (263.1) | 6.50 (374.3) | 8.08 (125.3) | 34.2 |
| 6 (sea water) | River Mouth at 1000 mt Central | 40°28′55″ N 14°55′50″ E | 6.35 | 5.90 | 6.71 | 3.74 | 2.90 (1569.3) | 2.52 (1524.0) | 3.40 (1348.7) | 2.66 (910.3) | 12.3 |
| 7 (sea water) | River Mouth at 1000 mt South | 40°28′55″ N 14°55′28″ E | 6.90 | 8.20 | 6.74 | 4.73 | 4.10 (460.5) | 3.10 (325.3) | 15.3 (548.6) | 11.5 (84.2) | 35.4 |
| 8 (sea water) | River Mouth at 1500 mt North | 40°28′47″ N 14°56′16″ E | 4.90 | 5.55 | 4.84 | 2.41 | 1.10 (106.9) | 0.35 (36.4) | 2.18 (774.0) | 3.76 (1048.6) | 19.2 |
| 9 (sea water) | River Mouth at 1500 mt Central | 40°28′39″ N 14°55′56″ E | 5.30 | 5.89 | 5.00 | 1.98 | 3.22 (582.2) | 1.00 (614.3) | 1.50 (486.1) | 1.78 (547.2) | 5.0 |
| 10 (sea water) | River Mouth at 1500 mt South | 40°28′30″ N 14°55′38″ E | 7.00 | 7.22 | 4.32 | 3.16 | 4.21 (1986.5) | 2.12 (156.1) | 4.10 (120.3) | 7.54 (1486.4) | 10.1 |
| Sampling Location | ΣOCPs | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site Number Identification | Site | Sampling Point | DP (ng L−1) | SPM (ng L−1) (ng g−1 Dry wt) | SED (ng g−1 Dry wt) | ||||||
| Apr | Jul | Nov | Feb | Apr | Jul | Nov | Feb | Apr | |||
| 1 (river water) | Sele River Source | 40°48′54.03″ N 14°36′45.36″ E | 4.01 | 5.71 | 3.75 | 1.95 | 2.08 (198.5) | 1.56 (154.1) | 3.98 (243.0) | 4.82 (201.4) | 15.2 |
| 2 (sea water) | River Mouth at 500 mt North | 40°46′42.73″ N 14°34′00.48″ E | 1.70 | 2.98 | 2.12 | 1.10 | 1.06 (70.2 | 0.55 (284.1) | 1.22 (51.8) | 1.80 (174.3) | 1.39 |
| 3 (sea water) | River Mouth at 500 mt Central | 40°46′00.34″ N 14°33′10.68″ E | 2.03 | 2.01 | 1.98 | 0.80 | 1.20 (185.4) | 0.50 (154.2) | 1.26 (274.6) | 1.86 (119.4) | 1.54 |
| 4 (sea water) | River Mouth at 500 mt South | 40°43′42.62″ N 14°28′07.89″ E | 3.24 | 4.38 | 2.18 | 1.82 | 1.48 (150.2) | 0.68 (298.4) | 1.54 (97.5) | 2.20 (241.2) | 3.85 |
| 5 (sea water) | River Mouth at 1000 mt North | 40°43′40.11″ N 14°28′06.45″ E | 1.00 | 2.00 | 1.78 | 0.75 | 1.00 (94.1) | 0.48 (102.3) | 0.98 (95.4) | 1.03 (100.1) | 1.20 |
| 6 (sea water) | River Mouth at 1000 mt Central | 40°43′42.46″ N 14°28′05.03″ E | 0.98 | 1.32 | 1.20 | 0.49 | 1.10 (254.3) | 0.32 (36.8) | 0.99 (198.4) | 1.23 (155.2) | 1.32 |
| 7 (sea water) | River Mouth at 1000 mt South | 40°43′45.09″ N 14°28′05.17″ E | 2.12 | 2.85 | 1.60 | 1.10 | 1.24 (110.4) | 0.38 (89.2) | 1.26 (114.7) | 1.30 (10.2) | 2.84 |
| 8 (sea water) | River Mouth at 1500 mt North | 40°43′35.68″ N 14°28′02.94″ E | 0.84 | 1.20 | 0.90 | 0.70 | 0.50 (71.4) | 0.39 (96.8) | 0.84 (195.7) | 1.00 (180.3) | 1.21 |
| 9 (sea water) | River Mouth at 1500 mt Central | 40°43′42.25″ N 14°27′59.97″ E | 0.84 | 0.90 | 0.81 | 0.36 | 0.47 (112.2) | 0.05 (65.3) | 0.91 (117.8) | 0.89 (148.3) | 1.10 |
| 10 (sea water) | River Mouth at 1500 mt South | 40°43′49.26″ N 14°27′59.82″ E | 1.45 | 1.85 | 0.73 | 0.79 | 0.60 (196.5) | 0.10 (52.7) | 0.74 (17.4) | 0.89 (185.6) | 1.02 |
| TEL | Percentage over the TEL | PEL | Percentage over the PEL | ERL | Percentage over the ERL | ERM | Percentage over the ERM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCBs | ||||||||
| Total PCBs | 21.6 | 40 | 189 | 0 | 22.7 | 40 | 180 | 0 |
| OCPs | ||||||||
| γ-HCH (lindane) | 0.32 | 0 | 0.99 | 0 | - | - | ||
| Dieldrin | 0.72 | 0 | 4.3 | 0 | 0.02 | 50 | 8 | 0 |
| 4,4-DDD | 1.22 | 20 | 7.81 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 20 | 0 |
| 4,4-DDE | 2.07 | 0 | 374 | 0 | 2.2 | 0 | 27 | 0 |
| 4,4-DDT | 1.19 | 10 | 4.77 | 0 | 1 | 10 | 7 | 0 |
| Total DDT | 3.89 | 0 | 51.7 | 0 | 1.58 | 10 | 46.1 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Rosa, E.; Montuori, P.; Triassi, M.; Masucci, A.; Nardone, A. Occurrence and Distribution of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) from Sele River, Southern Italy: Analysis of Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Organochlorine Pesticides in a Water–Sediment System. Toxics 2022, 10, 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10110662
De Rosa E, Montuori P, Triassi M, Masucci A, Nardone A. Occurrence and Distribution of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) from Sele River, Southern Italy: Analysis of Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Organochlorine Pesticides in a Water–Sediment System. Toxics. 2022; 10(11):662. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10110662
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Rosa, Elvira, Paolo Montuori, Maria Triassi, Armando Masucci, and Antonio Nardone. 2022. "Occurrence and Distribution of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) from Sele River, Southern Italy: Analysis of Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Organochlorine Pesticides in a Water–Sediment System" Toxics 10, no. 11: 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10110662
APA StyleDe Rosa, E., Montuori, P., Triassi, M., Masucci, A., & Nardone, A. (2022). Occurrence and Distribution of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) from Sele River, Southern Italy: Analysis of Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Organochlorine Pesticides in a Water–Sediment System. Toxics, 10(11), 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10110662







