Predicting the Bioconcentration Factor in Fish from Molecular Structures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Set and Data Curation
2.2. Theoretical Molecular Descriptors
2.3. Multiple Linear Regression and ANN
2.4. Classification
3. Results
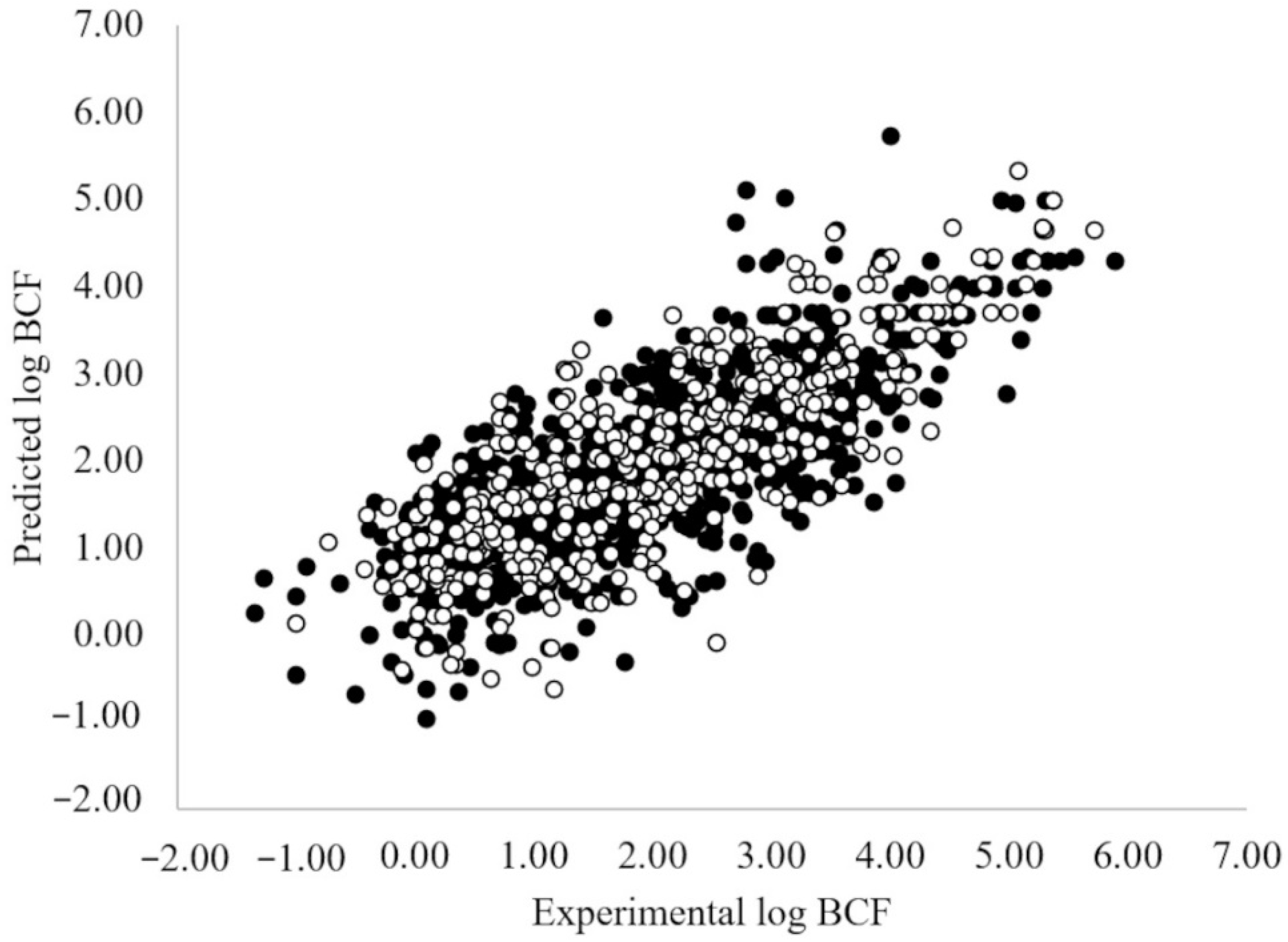
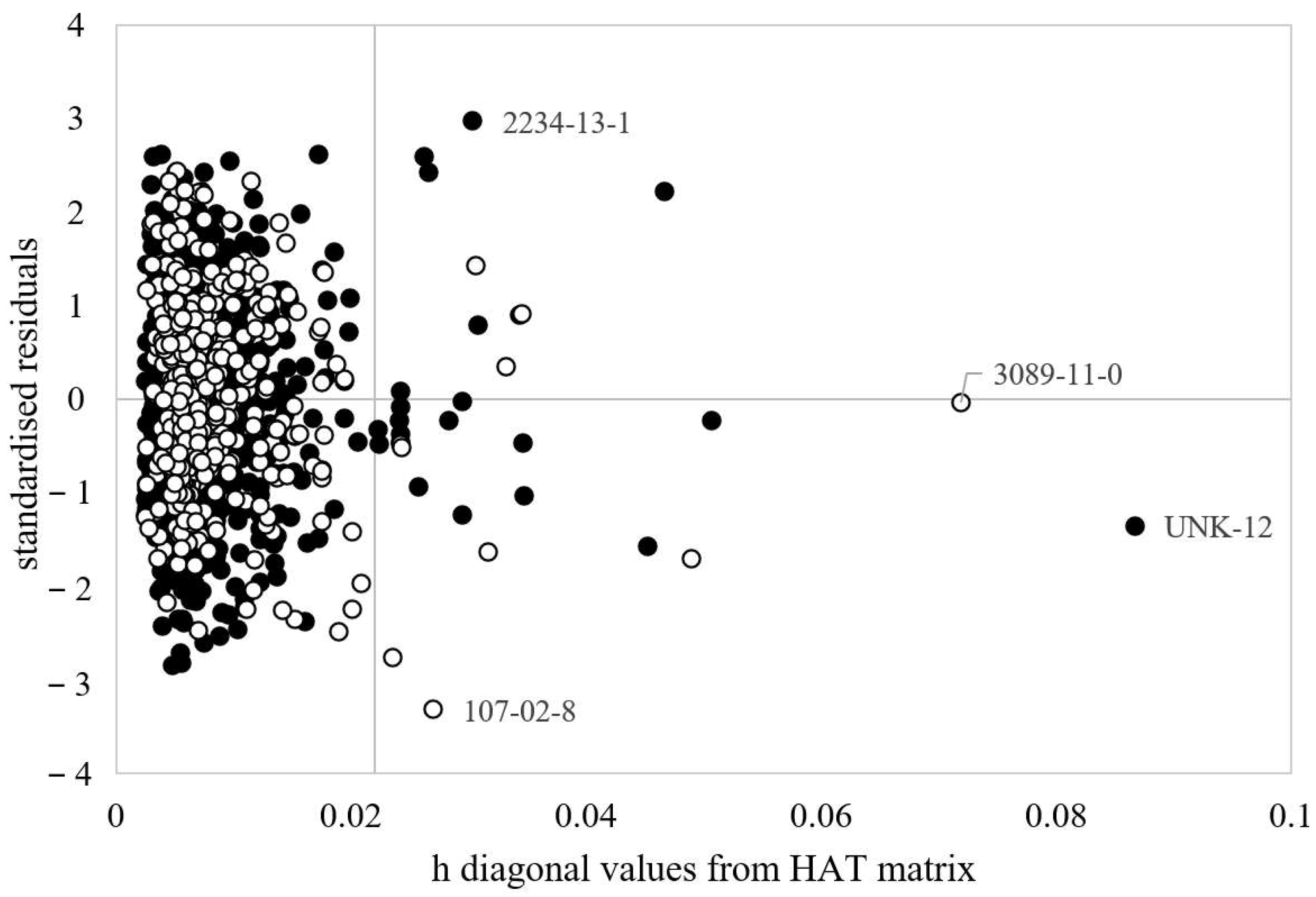
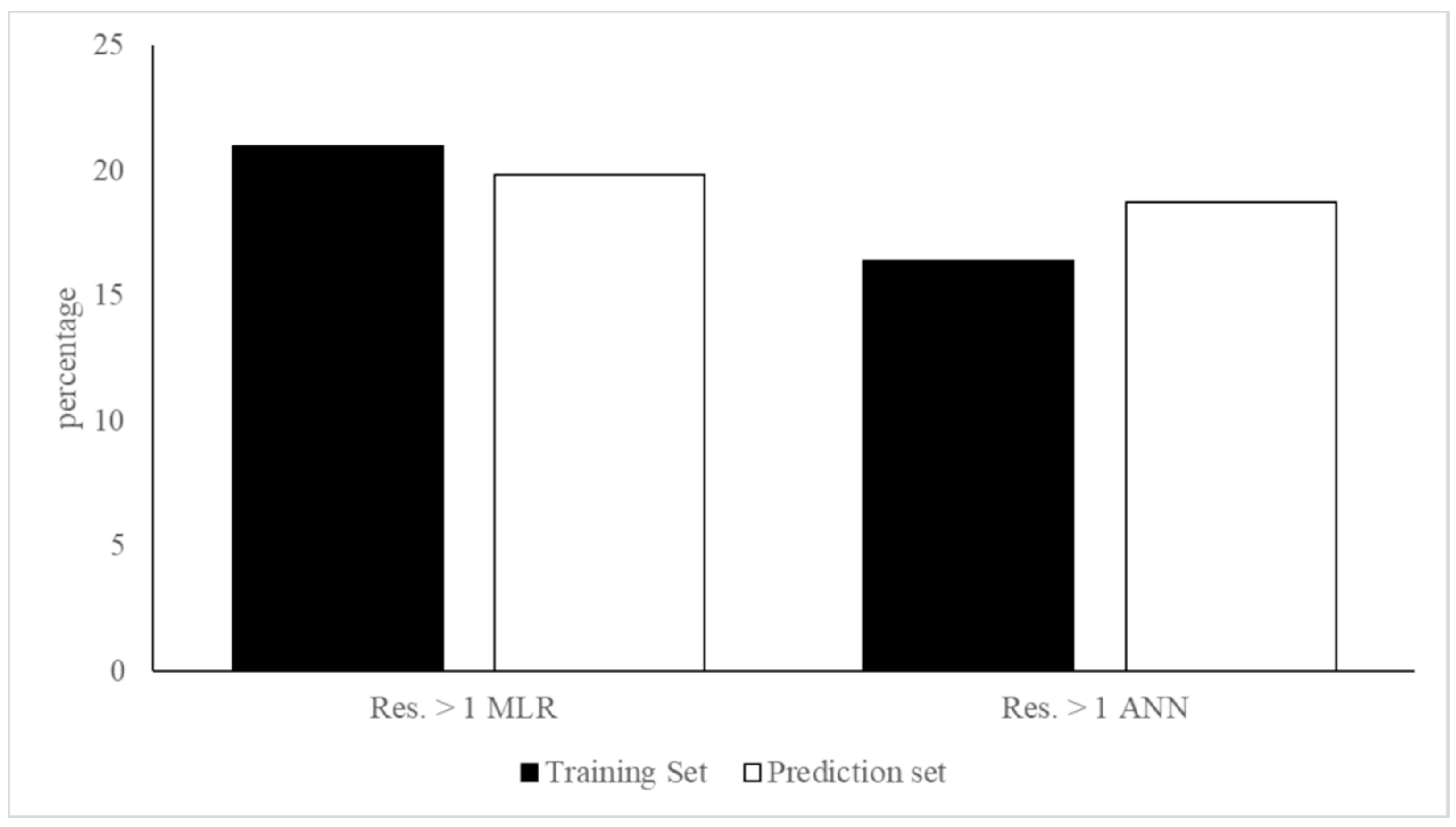
3.1. MLR-OLS Regression Models for Log BCF
3.2. ANN Regression Models for Log BCF
3.3. GA-LDA Classification Models for Log BCF
3.4. ANN Classification Model for Log BCF
3.5. Application of the Classification Models to the Not-B Dataset
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patinha Caldeira, C.; Farcal, R.; Moretti, C.; Mancini, L.; Rauscher, H.; Rasmussen, K.; Riego Sintes, J.; Sala, S. Safe and Sustainable by Design Chemicals and Materials Review of Safety and Sustainability Dimensions, Aspects, Methods, Indicators, and Tools, EUR 30991 EN; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2022; ISBN 978-92-76-47609-2.
- European Chemicals Agency. Guidance on Information Requirements and Chemical Safety Assessment: QSARs and Grouping of Chemicals; European Chemicals Agency: Helsinki, Finland, 2017; Volume 3, ISBN 9789292447601.
- Arnot, J.A.; Gobas, F.A.P.C. A Review of Bioconcentration Factor (BCF) and Bioaccumulation Factor (BAF) Assessments for Organic Chemicals in Aquatic Organisms. Environ. Rev. 2006, 14, 257–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnot, J.A.; Meylan, W.; Tunkel, J.; Howard, P.H.; Mackay, D.; Bonnell, M.; Boethling, R.S. A Quantitative Structure—Activity Relationship for Predicting Metabolic Biotransformation Rates for Organic Chemicals in Fish. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, E.; van der Wal, L.; Arnot, J.A.; Gramatica, P. Metabolic biotransformation half-lives in fish: QSAR modeling and consensus analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnot, J.A.; Brown, T.N.; Wania, F. Estimating Screening-Level Organic Chemical Half-Lives in Humans. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, E.; Arnot, J.A.; Sangion, A.; Gramatica, P. In Silico Approaches for the Prediction of In Vivo Biotransformation Rates. Chall. Adv. Comput. Chem. Phys. 2017, 24, 425–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gissi, A.; Nicolotti, O.; Carotti, A.; Gadaleta, D.; Lombardo, A.; Benfenati, E. Integration of QSAR models for bioconcentration suitable for REACH. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 456–457, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gissi, A.; Lombardo, A.; Roncaglioni, A.; Gadaleta, D.; Mangiatordi, G.F.; Nicolotti, O.; Benfenati, E. Evaluation and Comparison of Benchmark QSAR Models to Predict a Relevant REACH Endpoint: The Bioconcentration Factor (BCF). Environ. Res. 2015, 137, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisoni, F.; Consonni, V.; Villa, S.; Vighi, M.; Todeschini, R. QSAR Models for Bioconcentration: Is the Increase in the Complexity Justified by More Accurate Predictions? Chemosphere 2015, 127, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Chemicals Agency. The Use of Alternatives to Testing on Animals for the REACH Regulation—Fourth Report under Article 117(3) of the REACH Regulation; European Chemicals Agency: Helsinki, Finland, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Pavan, M.; Worth, A.; Netzeva, T.I. Review of QSAR Models for Bioconcentration; European Commission Joint Research Centre: Ispra, Italy, 2006; 142p. [Google Scholar]
- Mackay, D. Correlation of Bioconcentration Factors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1982, 16, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, M.G.; Stehly, G.R.; Hayton, W.L. Pharmacokinetic Modeling in Aquatic Animals I. Models and Concepts. Aquat. Toxicol. 1990, 18, 61–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southworth, G.R.; Keffer, C.C.; Beauchamp, J.J. Potential and Realized Bioconcentration. A Comparison of Observed and Predicted Bioconcentration of Azaarenes in the Fathead Minnow (Pimephales promelas). Environ. Sci. Technol. 1980, 14, 1529–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bintein, S.; Devillers, J.; Karcher, W. Nonlinear Dependence of Fish Bioconcentration on N-Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 1993, 1, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, S.D.; Mekenyan, O.G.; Walker, J.D. Non-Linear Modeling of Bioconcentration Using Partition Coefficients for Narcotic Chemicals. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2002, 13, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nendza, M. QSARs of Bioconcentration—Validity Assessment of Log P/Log BCF Correlations. In Bioaccumulation in Aquatic Systems; Nagel, R., Loskill, R., Eds.; VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Connell, D.W.; Hawker, D.W. Use of Polynomial Expressions to Describe the Bioconcentration of Hydrophobic Chemicals by Fish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1988, 16, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramatica, P.; Papa, E. QSAR Modeling of Bioconcentration Factor by Theoretical Molecular Descriptors. QSAR Comb. Sci. 2003, 22, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, E.; Dearden, J.C.; Gramatica, P. Linear QSAR Regression Models for the Prediction of Bioconcentration Factors by Physicochemical Properties and Structural Theoretical Molecular Descriptors. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Boriani, E.; Chana, A.; Roncaglioni, A.; Benfenati, E. A New Hybrid System of QSAR Models for Predicting Bioconcentration Factors (BCF). Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1701–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, S.; Roy, K. Modeling Bioconcentration Factor (BCF) Using Mechanistically Interpretable Descriptors Computed from Open Source Tool “PaDEL-Descriptor”. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 2955–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunghini, F.; Marcou, G.; Azam, P.; Patoux, R.; Enrici, M.H.; Bonachera, F.; Horvath, D.; Varnek, A. QSPR Models for Bioconcentration Factor (BCF): Are They Able to Predict Data of Industrial Interest? SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2019, 30, 507–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piir, G.; Sild, S.; Roncaglioni, A.; Benfenati, E.; Maran, U. QSAR Model for the Prediction of Bio-Concentration Factor Using Aqueous Solubility and Descriptors Considering Various Electronic Effects. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2010, 21, 711–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piir, G.; Sild, S.; Maran, U. Classifying Bio-Concentration Factor with Random Forest Algorithm, Influence of the Bio-Accumulative vs. Non-Bio-Accumulative Compound Ratio to Modelling Result, and Applicability Domain for Random Forest Model. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2014, 25, 967–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, T.H.; Gallidabino, M.D.; MacRae, J.R.; Owen, S.F.; Bury, N.R.; Barron, L.P. Prediction of Bioconcentration Factors in Fish and Invertebrates Using Machine Learning. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearden, J.C.; Shinnawei, N.M. Improved Prediction of Fish Bioconcentration Factor of Hydrophobic Chemicals. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2004, 15, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Yoshida, K. Development of QSAR Models for Prediction of Fish Bioconcentration Factors Using Physicochemical Properties and Molecular Descriptors with Machine Learning Algorithms. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 63, 101285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Environmental Protection Agency. Estimation Programs Interface SuiteTM for Microsoft® Windows 2012; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/tsca-screening-tools/epi-suitetm-estimation-program-interface#:~:text=Citing%20EPI%20Suite%E2%84%A2&text=US%20EPA.,%2C%20Washington%2C%20DC%2C%20USA (accessed on 25 September 2022).
- Benfenati, E.; Manganaro, A.; Gini, G. VEGA-QSAR: AI inside a Platform for Predictive Toxicology. CEUR Workshop Proc. 2013, 1107, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Mansouri, K.; Grulke, C.M.; Judson, R.S.; Williams, A.J. OPERA Models for Predicting Physicochemical Properties and Environmental Fate Endpoints. J. Cheminform. 2018, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruusmann, V.; Sild, S.; Maran, U. QSAR DataBank Repository: Open and Linked Qualitative and Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship Models. J. Cheminform. 2015, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcou, G.; Horvath, D.; Bonachera, F.; Varnek, A. ISIDA Predictor. 2019. Available online: http://infochim.u-strasbg.fr/ (accessed on 25 September 2022).
- OECD. Principles for the Validation, for Regulatory Purposes, of (Quantitative) Structure-Activity Relationship Models; OECD: Paris, France, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Guidance Document on the Validation of (Quantitative) Structure-Activity Relationships [(Q)SAR] Models; OECD: Paris, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, C.W. PaDEL-descriptor: A Software to Calculate Molecular Descriptors and Fingerprints. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 1466–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, E.; Villa, F.; Gramatica, P. Statistically Validated QSARs, Based on Theoretical Descriptors, for Modeling Aquatic Toxicity of Organic Chemicals in Pimephales promelas (Fathead Minnow) J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2005, 45, 1256–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobas, F.A.P.C.; De Wolf, W.; Burkhard, L.P.; Verbruggen, E.; Plotzke, K. Revisiting Bioaccumulation Criteria for POPs and PBT Assessments. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2009, 5, 624–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wijk, D.; Chénier, R.; Henry, T.; Hernando, M.D.; Schulte, C. Integrated Approach to PBT and POP Prioritization and Risk Assessment. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2009, 5, 697–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rücker, C.; Rücker, G.; Meringer, M. Y-Randomization and Its Variants in QSPR/QSAR. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2007, 47, 2345–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambure, P.; Halder, A.K.; González Díaz, H.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S. QSAR-Co: An Open Source Software for Developing Robust Multitasking or Multitarget Classification-Based QSAR Models. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59, 2538–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthold, M.R.; Cebron, N.; Dill, F.; Di Fatta, G.; Gabriel, T.R.; Georg, F.; Meinl, T.; Ohl, P.; Sieb, C.; Wiswedel, B. KNIME: The Konstanz Information Miner. In Proceedings of the 4th International Industrial Simulation Conference ISC’2006, Palermo, Italy, 5–7 June 2006; pp. 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Riedmiller, M.; Braun, H. A direct adaptive method for faster backpropagation learning: The RPROP algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, Francisco, CA, USA, 28 March–1 April 1993; Volume 16, pp. 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consonni, V.; Todeschini, R.; Ballabio, D.; Grisoni, F. On the Misleading Use of QF3 for QSAR Model Comparison. Mol. Inform. 2019, 38, 1800029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambure, P.; Bhat, J.; Puzyn, T.; Roy, K. Identifying Natural Compounds as Multi-Target-Directed Ligands against Alzheimer’s Disease: An in Silico Approach. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2019, 37, 1282–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Kar, S.; Ambure, P. On a Simple Approach for Determining Applicability Domain of QSAR Models. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2015, 145, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathea, M.; Klingspohn, W.; Baumann, K. Chemoinformatic Classification Methods and Their Applicability Domain. Mol. Inform. 2016, 35, 160–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todeschini, R.; Consonni, V. Molecular Descriptors for Chemoinformatics; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2009; ISBN 9783527628773. [Google Scholar]
- Gramatica, P.; Corradi, M.; Consonni, V. Modelling and Prediction of Soil Sorption Coefficients of Non-Ionic Organic Pesticides by Molecular Descriptors. Chemosphere 2000, 41, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassenaar, P.N.H.; Verbruggen, E.M.J.; Cieraad, E.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Vijver, M.G. Variability in Fish Bioconcentration Factors: Influences of Study Design and Consequences for Regulation. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Training | B | Not-B | Prediction | B | Not-B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | 88 | 12 | B | 90 | 10 |
| not-B | 15 | 85 | not-B | 23 | 77 |
| Split | Ac % | P % | Sn % | Sp % | AUC | AUCcv test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDA | Training | 87 | 88 | 88 | 85 | 0.92 | 0.89 |
| Prediction | 84 | 80 | 90 | 77 | 0.90 | - |
| Training | B | Not-B | Prediction | B | Not-B | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANN | B | 90 | 10 | B | 89 | 11 |
| not-B | 11 | 89 | not-B | 23 | 77 |
| Split | Ac % | P % | Sn % | Sp % | AUC | AUCcv test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANN | Training | 90 | 91 | 90 | 89 | 0.95 | 0.92 |
| Prediction | 83 | 80 | 89 | 77 | 0.88 | - |
| LDA | ANN | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of correct predictions (%) | 730 (76%) | 750 (78%) |
| Number of common misclassifications (%) | 179 (17%) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bertato, L.; Chirico, N.; Papa, E. Predicting the Bioconcentration Factor in Fish from Molecular Structures. Toxics 2022, 10, 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100581
Bertato L, Chirico N, Papa E. Predicting the Bioconcentration Factor in Fish from Molecular Structures. Toxics. 2022; 10(10):581. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100581
Chicago/Turabian StyleBertato, Linda, Nicola Chirico, and Ester Papa. 2022. "Predicting the Bioconcentration Factor in Fish from Molecular Structures" Toxics 10, no. 10: 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100581
APA StyleBertato, L., Chirico, N., & Papa, E. (2022). Predicting the Bioconcentration Factor in Fish from Molecular Structures. Toxics, 10(10), 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10100581








