Rapid HPLC Method for Determination of Isomaltulose in the Presence of Glucose, Sucrose, and Maltodextrins in Dietary Supplements
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Methods for Saccharides Determination
1.2. Methods for Isomaltulose Determination
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Optimized Separation Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mobile Phase of Acetonitrile-Water (Isocratic Elution)
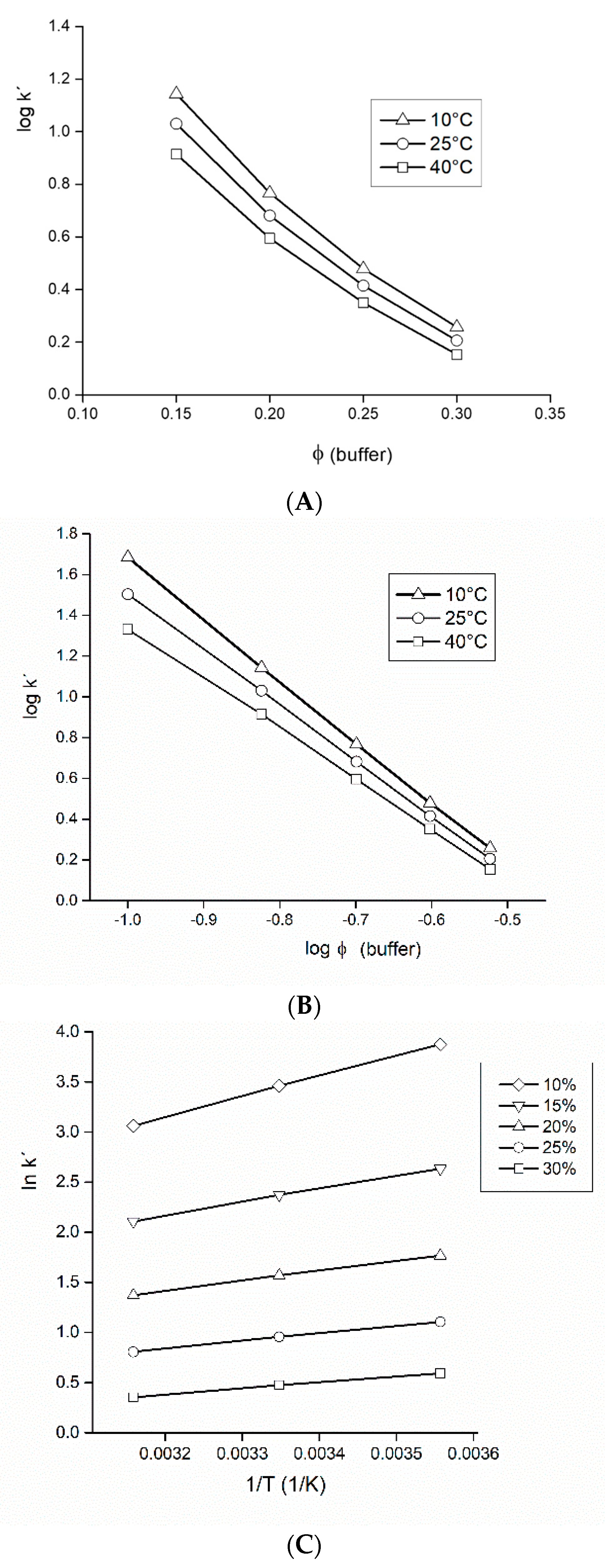
3.2. Mobile Phase of Acetonitrile-Formate Buffer (Isocratic Elution)
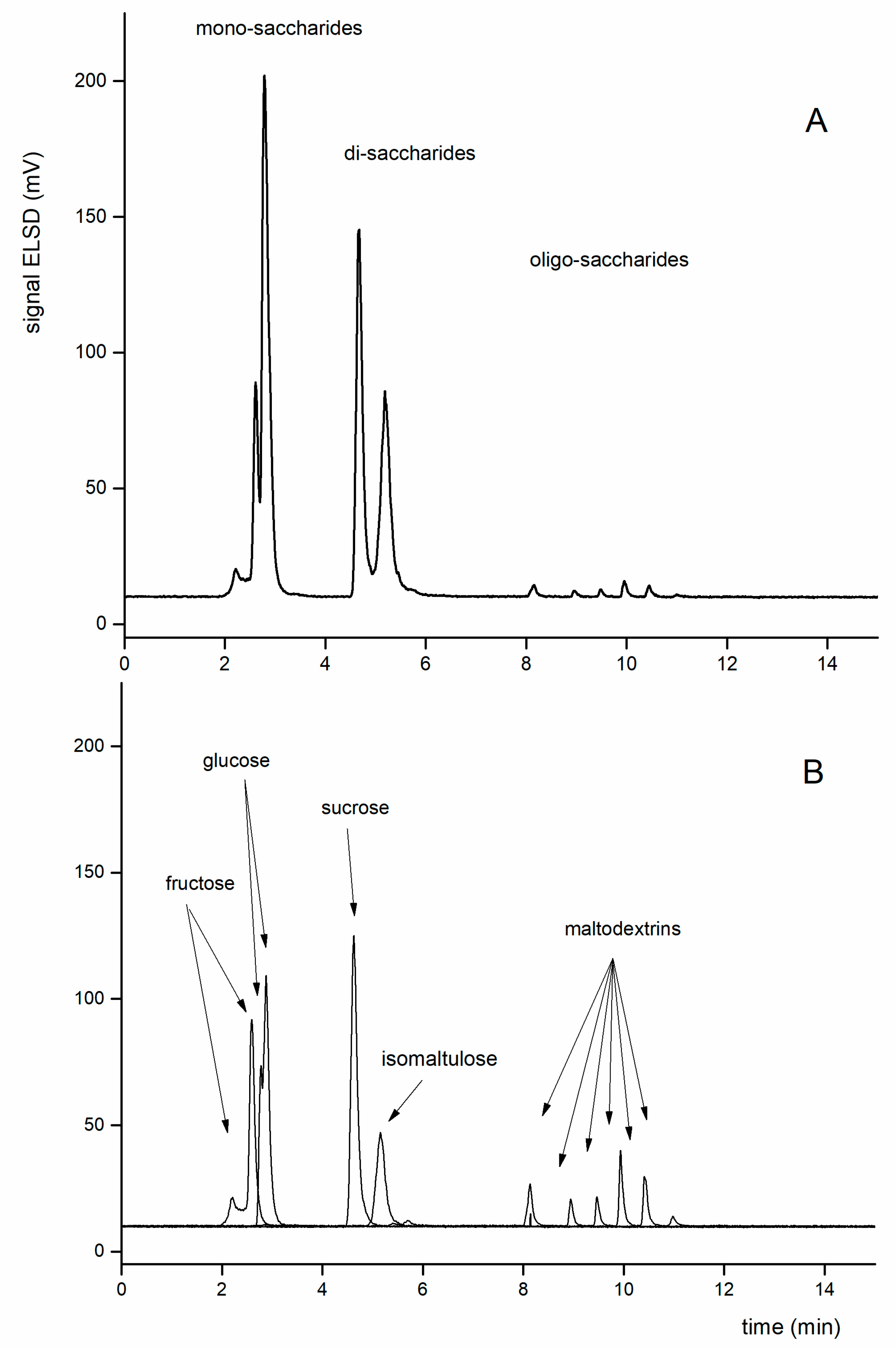
3.3. Sample Analysis
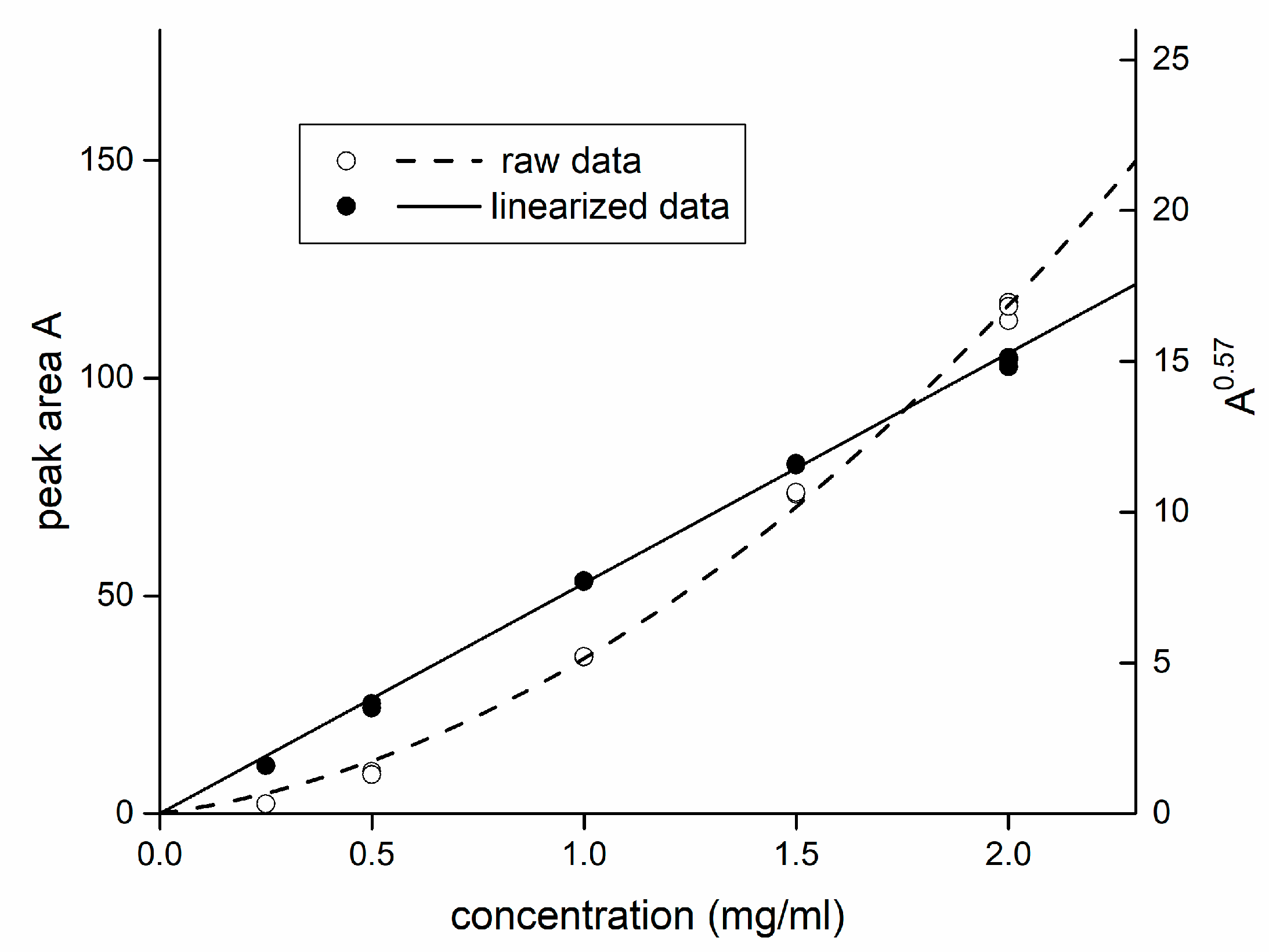
3.3.1. Calibration
3.3.2. The Method Validation
3.3.3. Sample Preparation
3.3.4. Determination of Isomaltulose in Samples
3.3.5. Beverages
3.3.6. Dietary Supplements for Exercise and Athletic Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mu, W.M.; Li, W.J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, B. Current studies on sucrose isomerase and biological isomaltulose production using sucrose isomerase. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 6569–6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, Z.-P.; Sheng, J.; Zheng, Y.; Ji, X.-F.; Zhou, H.-X.; Liu, X.-Y.; Chi, Z.-M. High and efficient isomaltulose production using an engineered Yarrowia lipolytica strain. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, Z.P.; Ji, X.F.; Sheng, J. Display of a sucrose isomerase on the cell surface of Yarrowia lipolytica for synthesis of isomaltulose from sugar cane by-products. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lina, B.A.R.; Jonker, D.; Kozianowski, G. Isomaltulose (Palatinose): A review of biological and toxicological studies. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2002, 40, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawale, P.D.; Shendurse, A.M.; Mohan, M.S.; Patil, G.R. Isomaltulose (Palatinose)—An emerging carbohydrate. Food Biosci. 2017, 18, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyam, S.; Ramadas, A.; Chang, S.K. Isomaltulose: Recent evidence for health benefits. J. Funct. Food 2018, 48, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.; Park, H.R.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, K.S. Oral administration of palatinose vs sucrose improves hyperglycemia in normal C57BL/6J mice. Nutr. Res. 2018, 59, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davila, L.A.; Bermudez, V.; Aparicio, D.; Cespedes, V.; Escobar, M.C.; Duran-Aguero, S.; Cisternas, S.; Costa, J.D.; Rojas-Gomez, D.; Reyna, N.; et al. Effect of Oral Nutritional Supplements with Sucromalt and Isomaltulose versus Standard Formula on Glycaemic Index, Entero-Insular Axis Peptides and Subjective Appetite in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomised Cross-Over Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1147. [Google Scholar]
- Martinussen, C.; Bojsen-Moller, K.N.; Dirksen, C.; Svane, M.S.; Kristiansen, V.B.; Hartmann, B.; Holst, J.J.; Madsbad, S. Augmented GLP-1 Secretion as Seen After Gastric Bypass May Be Obtained by Delaying Carbohydrate Digestion. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 3233–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquelme, A.; Cruces, C.; Segovia, A.; Maury, E.; Valenzuela-Melgarejo, F.J. Effect of Isomaltulose Consumption during the Pregnancy in New Born Rats. (Preliminary Results). Placenta 2019, 83, E96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo-Gallego, R.; Pérez-Calahorra, S.; Lamiquiz-Moneo, I.; Marco-Benedí, V.; Bea, A.M.; Fumanal, A.J.; Prieto-Martín, A.; Laclaustra, M.; Cenarro, A.; Civeira, F. Effect of an alcohol-free beer enriched with isomaltulose and a resistant dextrin on insulin resistance in diabetic patients with overweight or obesity. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 287, e93–e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, T.; Sugiyama, Y.; Okumura, J.; Fujii, N.; Kenny, G.P.; Nishiyasu, T.; Inoue, Y.; Kondo, N.; Sasagawa, K.; Enoki, Y.; et al. Effects of isomaltulose ingestion on postexercise hydration state and heat loss responses in young men. Exp. Physiol. 2019, 104, 1494–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, L.D.; Stevenson, E.J.; Rollo, I.; Russell, M. The influence of a 12% carbohydrate-electrolyte beverage on self-paced soccer-specific exercise performance. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2017, 20, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyashita, M.; Hamada, Y.; Fujihira, K.; Namura, S.; Sakazaki, M.; Miyasaka, K.; Nagai, Y. The effects of isomaltulose ingestion on gastric parameters and cycling performance in young men. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2019, 17, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuren, J. Food Labeling: Health Claims; Dietary Noncariogenic Carbohydrate Sweeteners and Dental Caries. Fed. Regist. 2008, 73, 30299–30301. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA. Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to the sugar replacers. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2076. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA. Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to intense sweeteners. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2229. [Google Scholar]
- Yatka, R.J.; Richey, L.C.; Meyers, M.A.; Reed, M.A. Chewing Gum Containing Hydrogenated Isomaltulose; (Wm Wrigley Jr Co., Chicago, IL 60611, USA). PCT International Patent Application WO 95/08926 A1, 1 May 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann. Babydream, Früchte Tee. Available online: https://www.rossmann.de/de/baby-und-kind-babydream-fruechte-tee/p/4305615541297 (accessed on 1 December 2019).
- HeavenLabs. Mana. Available online: https://drinkmana.com/ (accessed on 10 June 2020).
- Kerksick, C.; Wilborn, C.; Roberts, M.; Smith-Ryan, A.; Kleiner, S.; Jäger, R.; Collins, R.; Cooke, M.; Davis, J.; Galvan, E.; et al. ISSN exercise & sports nutrition review update: Research & recommendations. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2018, 15, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganzera, M.; Stuppner, H. Evaporative Light Scattering Detection (ELSD) for the Analysis of Natural Products. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2005, 1, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M. Evaporative light scattering detection: Trends in its analytical uses. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 388, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez-Sillero, I.; Cárdenas, S.; Valcárcel, M. Comparison of two evaporative universal detectors for the determination of sugars in food samples by liquid chromatography. Microchem. J. 2013, 110, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazourek, J. Monitoring of mutarotation of monosaccharides by hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 974–981. [Google Scholar]
- Pazourek, J. Fast separation and determination of free myo-inositol by hydrophilic liquid chromatography. Carbohydr. Res. 2014, 391, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pazourek, J. Rapid HPLC method for monitoring of lactulose production with a high yield. Carbohydr. Res. 2019, 484, 107773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spáčil, Z.; Folbrová, J.; Megoulas, N.; Solich, P.; Koupparis, M. Simultaneous liquid chromatographic determination of metals and organic compounds in pharmaceutical and food-supplement formulations using evaporative light scattering detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 583, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raessler, M. Sample preparation and current applications of liquid chromatography for the determination of non-structural carbohydrates in plants. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 1833–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasik, P. Chemical and Functional Properties of Food Saccharides; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 15th ed.; AOAC: Arlington, VA, USA, 1990; Volume 1, p. 684. [Google Scholar]
- Prošek, M.; Simonovska, B.; Golc-Wondra, A.; Vovk, I.; Andrensek, S.; Micovic, E.; Golob, T. Use of HPTLC for quantitative evaluation of inulin in food products. JPC J. Planar Chromatogr. Mod. TLC 2003, 16, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojvodic, A.; Komes, D.; Belscak-Cvitanovic, A.; Busic, A.; Vovk, I.; Santek, B. Carbohydrate monomer profiling of waste plant biomass using HPTLC and HPLC-PDA. New Biotechnol. 2016, 33, S88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár-Perl, I.; Horvath, K. Simultaneous quantitation of mono-, di- and trisaccharides as their TMS ether oxime derivatives by GC-MS. 1. In model solutions. Chromatographia 1997, 45, 321–327. [Google Scholar]
- Schenk, J.; Nagy, G.; Pohl, N.L.B.; Leghissa, A.; Smuts, J.; Schug, K.A. Identification and deconvolution of carbohydrates with gas chromatography-vacuum ultraviolet spectroscopy. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1513, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mhanna, N.M.; Huebner, H.; Buchholz, R. Analysis of the Sugar Content in Food Products by Using Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry and Enzymatic Methods. Foods 2018, 7, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, P. The analysis of fluorophore-labeled carbohydrates by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Mol. Biotechnol. 1996, 5, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vochyanová, B.; Opekar, F.; Tůma, P.; Štulik, K. Rapid determinations of saccharides in high-energy drinks by short-capillary electrophoresis with contactless conductivity detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 1549–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Nagai, E.; Asada, Y.; Kinoshita, M.; Suzuki, S. A rapid and highly sensitive microchip electrophoresis of mono- and mucin-type oligosaccharides labeled with 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 1499–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mopper, K.; Dawson, R.; Liebezeit, G.; Hansen, H.P. Borate Complex Ion-Exchange Chromatography with Fluorimetric Detection for Determination of Saccharides. Anal. Chem. 1980, 52, 2018–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wach, W.; Fornefett, I.; Buttersack, C.; Buchholz, K. Chromatographic separation of saccharide mixtures on zeolites. Food Bioprod. Process. 2019, 114, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ispiryan, L.; Zannini, E.; Arendt, E.K. Characterization of the FODMAP-profile in cereal-product ingredients. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 92, 102916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyassin, M.; Campbell, G.M.; O’Neill, H.M.; Bedford, M.R. Simultaneous determination of cereal monosaccharides, xylo- and arabinoxylo-oligosaccharides and uronic acids using HPAEC-PAD. Food Chem. 2020, 315, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, J.L.; González-Castro, M.J.; Alba, I.N.; García, C.D. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of mono- and oligosaccharides in vegetables with evaporative light-scattering detection and refractive index detection. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 1998, 36, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grembecka, M.; Lebiedzińska, A.; Szefer, P. Simultaneous separation and determination of erythritol, xylitol, sorbitol, mannitol, maltitol, fructose, glucose, sucrose and maltose in food products by high performance liquid chromatography coupled to charged aerosol detector. Microchem. J. 2014, 117, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Sun, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, S. Simultaneous separation and determination of fructose, sorbitol, glucose and sucrose in fruits by HPLC–ELSD. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.K.; Kleiber, T.; Zydlik, Z.; Rutkowski, K.; Wozniak, A.; Swierczynski, S.; Bednarski, W.; Kesy, J.; Marczak, L.; Seo, J.H.; et al. A Comparison of Selected Biochemical and Physical Characteristics and Yielding of Fruits in Apple Cultivars (Malus domestica Borkh.). Agronomy 2020, 10, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokrzywnicka, M.; Koncki, R. Disaccharides Determination: A Review of Analytical Methods. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2018, 48, 186–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, A.; Matsunaga, A.; Mizukami, E. Determination of Palatinose in Food by High-Performance Liquid-Chromatography with a Polarized Photometric Detector. J. Food Hyg. Soc. Jpn. 1992, 33, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, T.; Toda, C.; Nagano, H.; Ishihara, H. Determination of oligosaccharides in foods for specified health use by HPLC. J. Food Hyg. Soc. Jpn. 1996, 37, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Véronèse, T.; Bouchu, A.; Perlot, P. Rapid method for trehalulose production and its purification by preparative high-performance liquid chromatography. Biotechnol. Tech. 1999, 13, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annaratone, C.; De Roeck, A.; Hertog, M.L.A.T.M.; Nicolaï, B.M. Hydrophilic interaction chromatography and evaporative light scattering detection for the determination of polar analytes in Belgian endive. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wach, W.; Buttersack, C.; Buchholz, K. Chromatography of mono- and disaccharides on granulated pellets of hydrophobic zeolites. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1576, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitsch, J.; Weghuber, J. Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography Coupled with Charged Aerosol Detection for Simultaneous Quantitation of Carbohydrates, Polyols and Ions in Food and Beverages. Molecules 2019, 24, 4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazourek, J. Determination of glucosamine and monitoring of its mutarotation by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography with evaporative light scattering detector. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2018, 32, 4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemström, P.; Irgum, K. Hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2006, 29, 1784–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, A.J.; Shukla, M.; Shukla, A.K.; Zieske, L.R.; Yuen, S.W.; Ferguson, M.A.J.; Mehlert, A.; Pauly, M.; Orlando, R. Hydrophilic-interaction chromatography of complex carbohydrates. J. Chromatogr. A 1994, 676, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euerby, M.R.; Hulse, J.; Petersson, P.; Vazhentsev, A.; Kassam, K. Retention modelling in hydrophilic interaction chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 9135–9152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soare, A.C.; Galaon, T.; Moldoveanu, S.; David, V. The influence of column temperature on the extrapolated values of the retention factor in reversed-phase liquid chromatography for water as mobile phase. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2019, 64, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Gaiki, S. Retention and selectivity of stationary phases for hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 5920–5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpert, A.J. Effect of salts on retention in hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1538, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, A.J. Electrostatic repulsion hydrophilic interaction chromatography for isocratic separation of charged solutes and selective isolation of phosphopeptides. Anal. Chem 2008, 80, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatapanis, A.E.; Fiamegos, Y.C.; Stalikas, C.D. Study of the Behavior of Water-Soluble Vitamins in HILIC on a Diol Column. Chromatographia 2010, 71, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Food and Drug Administration—Federal Register. International Conference on Harmonisation; Guideline on the Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology; Availability. Docket No. 96D–0030 ed. Fed. Regist. 1997, 62, 22463–27467. [Google Scholar]
- EU_Parliament_and_Council. Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 on the provision of food information to consumers. Off. J. Eur Union 2011, 304, 18–63. [Google Scholar]
- Crha, T.; Pazourek, J. Rapid Determination of Isomaltulose in Food Supplements by HPLC with ELSD. In Proceedings of the 19th International Nutrition & Diagnostics Conference (INDC 2019), Prague, Czech Republic, 15–18 October 2019; Horna, A., Ed.; RADANAL, Ltd.: Prague, Czech Republic, 2019. [Google Scholar]
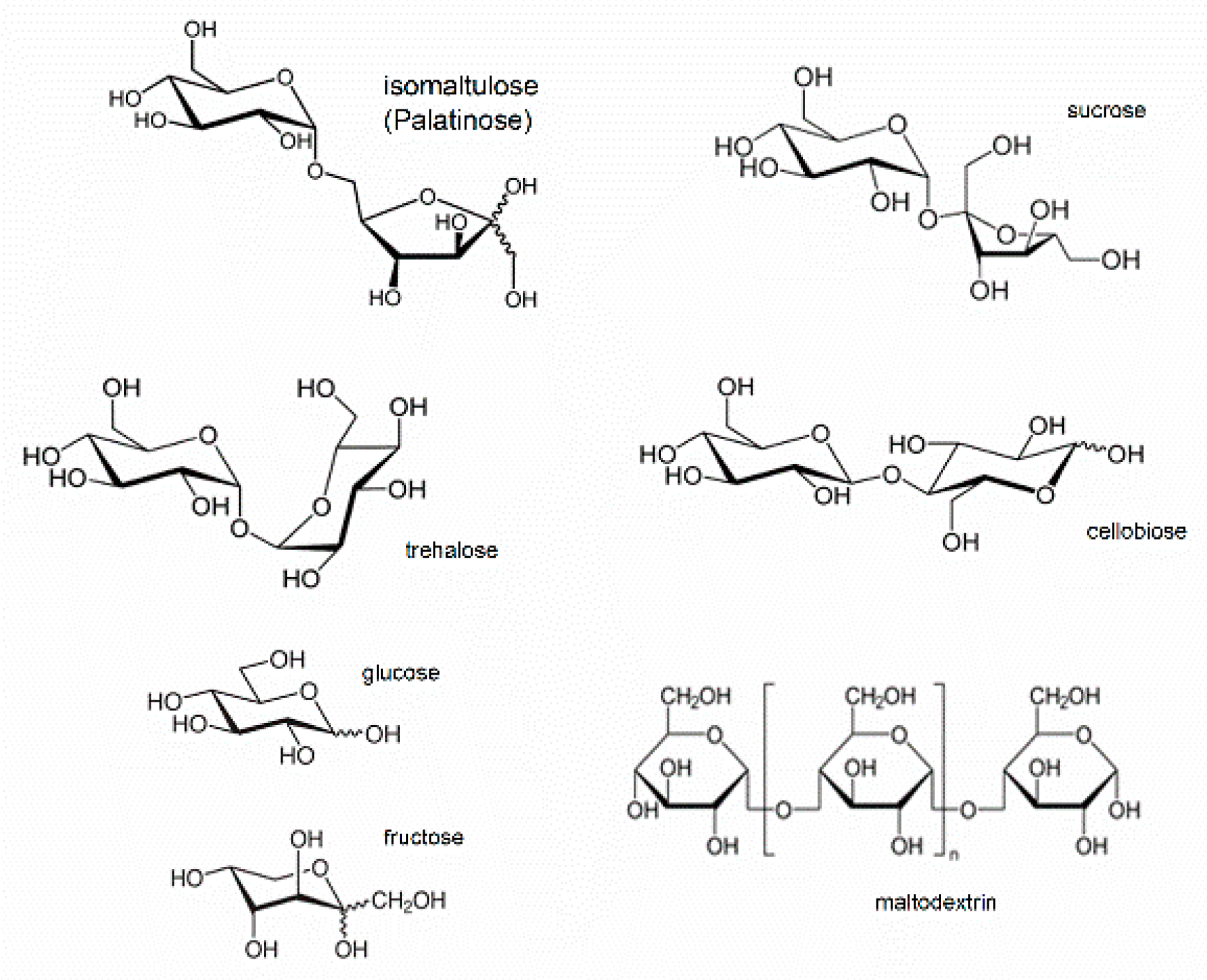
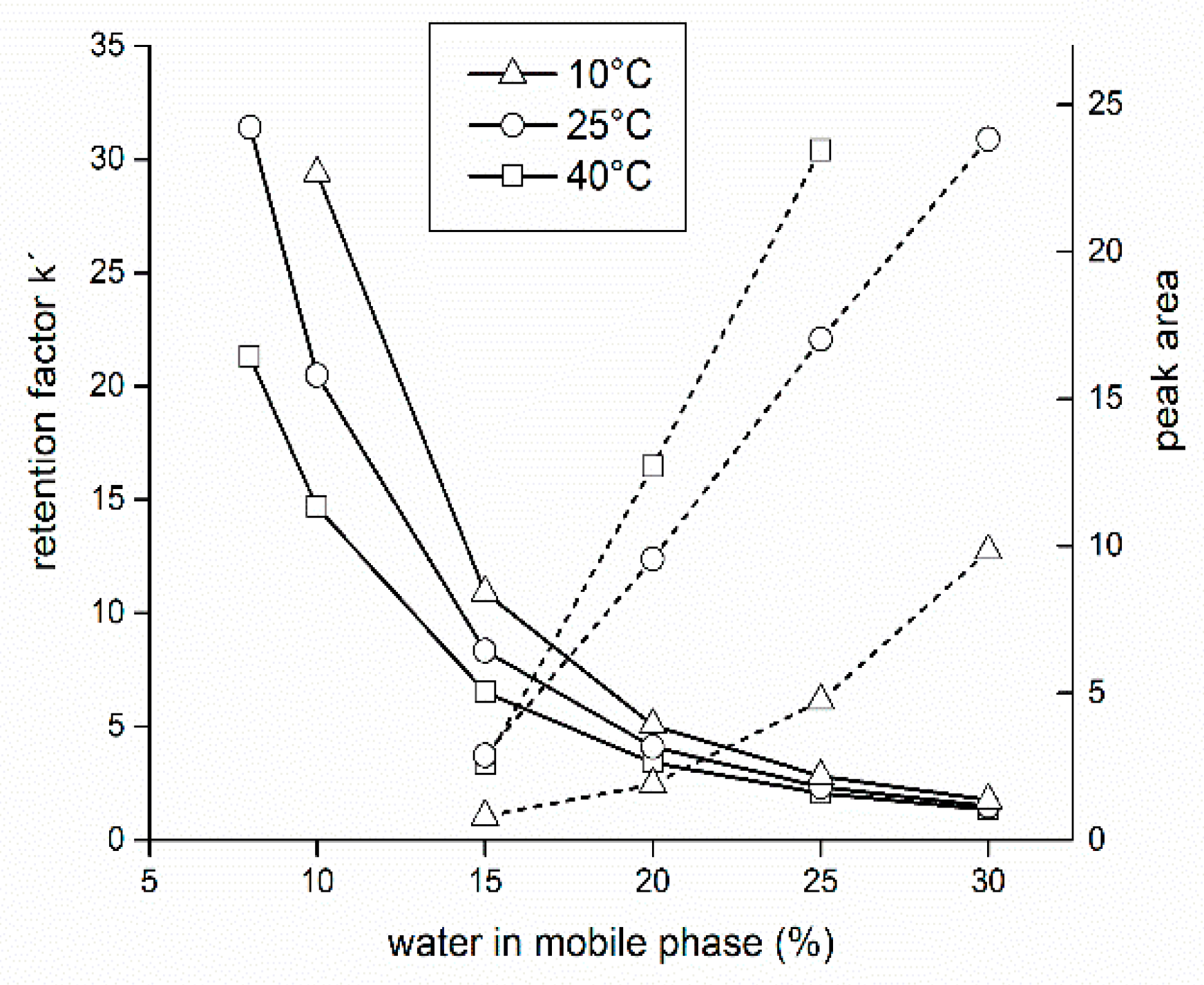
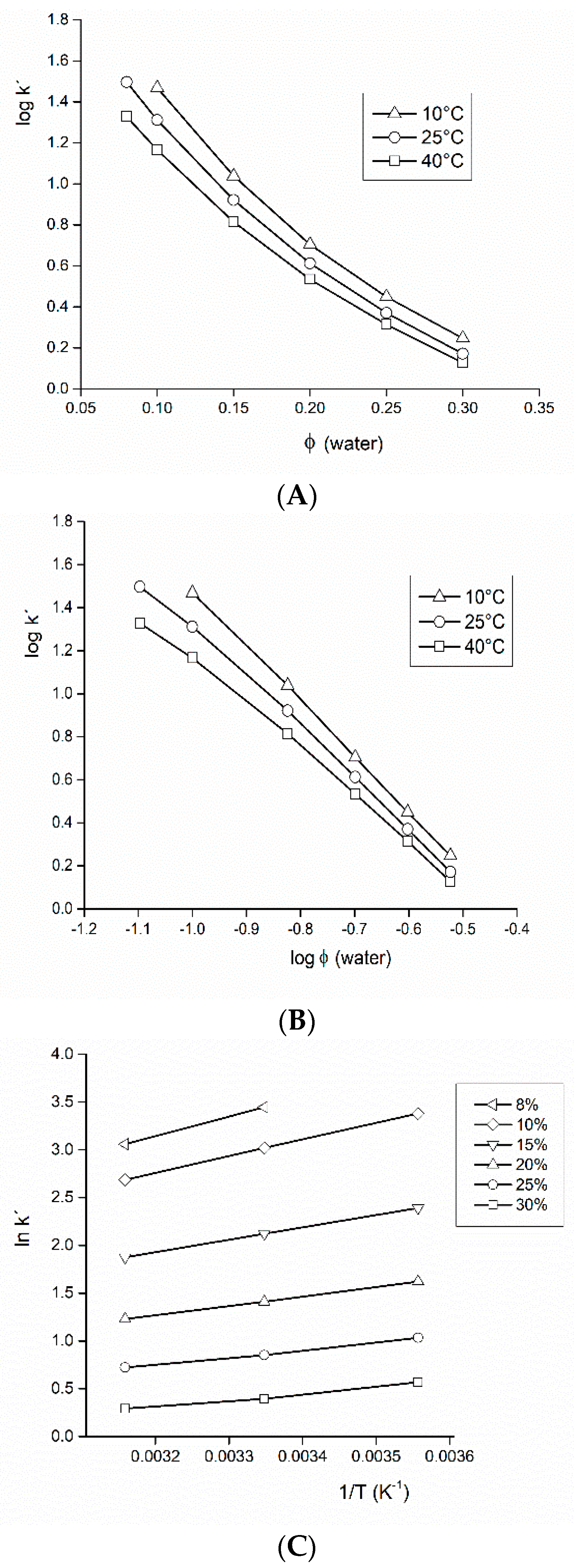
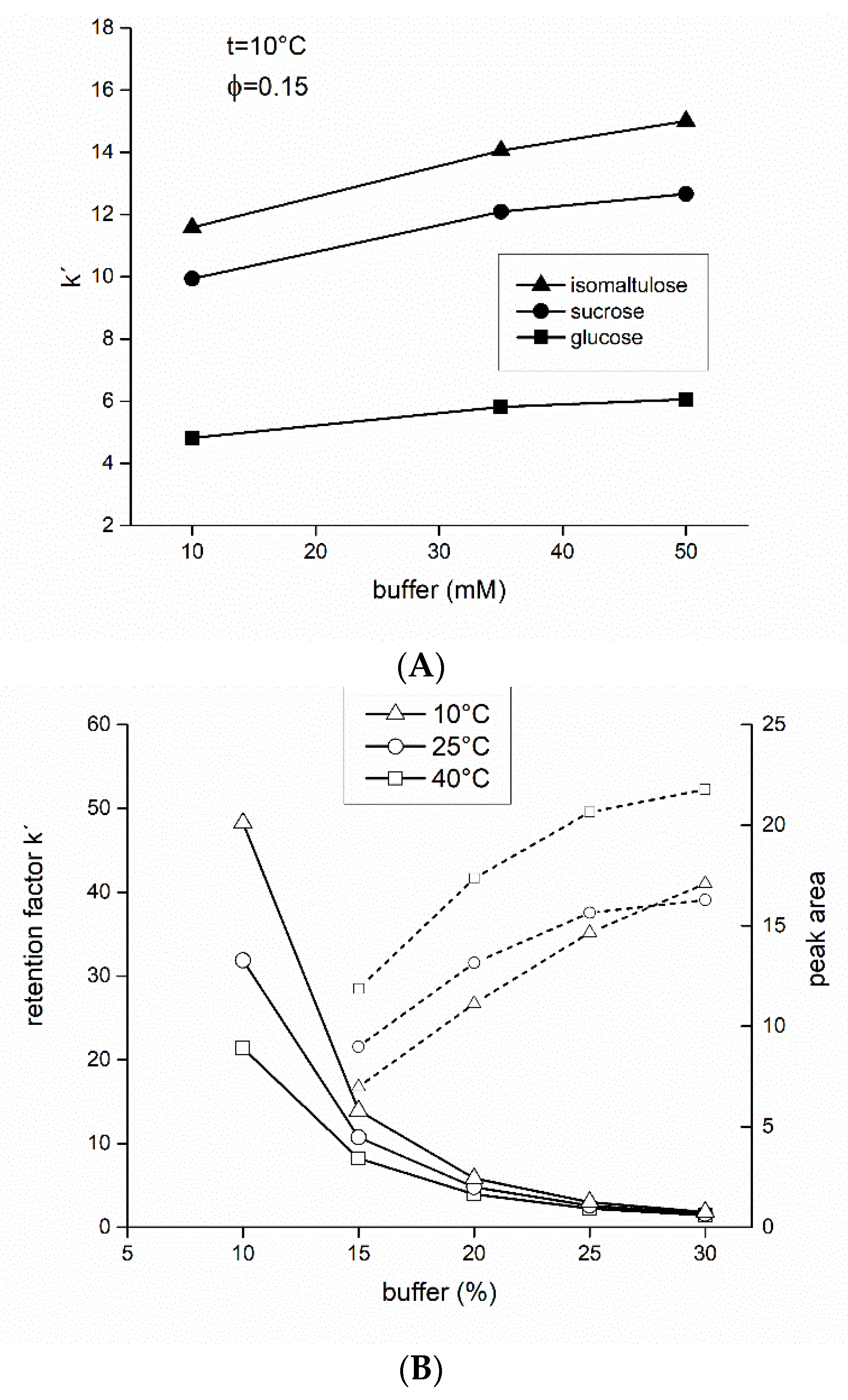

| Type of Sample | Commercial Name, Flavor | Producer, Package Type | Isomaltulose (or Sugars) Declared | Isomaltulose Determined |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beverages | ||||
| instant tee (granulate) | Babydream Früchte-Tee | Rossmann container 190 g | 93.9% | 92.8% |
| complete-nutrition food (drink) *** | Mana non-flavored drink | Heaven labs box 330 mL | 2.2% (sugars) | 2.1% |
| Dietary Supplements for Exercise and Athletic Performance | ||||
| Energy gel | Enduro snack green apple | Nutrend tube 75 g | 37.0% (sugars) | 30.1% |
| Energy gel | Enduro snack apricot | Nutrend tube 75 g | 37.0% (sugars) | 32.0% |
| Energy drink (powder) | Energy drink orange | Penco container 900 g | 20.0% | 19.0% (Figure 8A) |
| Energy drink (powder) | Energy drink orange | Penco bag 30 g | 20.0% | 21.4% |
| Gel | Vitargo gel black currant | Energikakan bag 45 g | 18.9% | 19.4% (Figure 8B) |
| Gel | Vitargo gel watermelon | Energikakan bag 45 g | 18.9% | 19.3% |
| Gel | Energy gel long trail raspberry | Penco tube 70 g | 10.0% | 10.5% (Figure 8C) |
| Gel | Energy gel long trail orange | Penco tube 70 g | 10.0% | 10.9% |
| Gel | Energy gel long trail lemon | Penco bag 35 g | 10.0% | 9.8% |
| Gel | Energy gel long trail orange | Penco bag 35 g | 10.0% | 9.6% |
| Gel | Energy gel long trail pink grapefruit | Penco bag 35 g | 10.0% | 9.9% |
| Gel *** | Express Energy Gel | Extrifit capped bag 80 g | 5.0% | 5.3% |
| Gel | IsoGel Smart Snack juicy orange | Amix capped bag 70 mL | 42% (sugars) | 2.4% |
| Gel | IsoGel Smart Snack green apple | Amix capped bag 70 mL | 42% (sugars) | 2.2% |
| Gel | IsoGel Energy Shock juicy orange | Amix capped bag 70 mL | 46.6% (sugars) | 2.5% |
| Gel | IsoGel Energy Shocklemon lime | Amix capped bag 70 mL | 46.6% (sugars) | 2.4% |
| Gel | Rock’s! energy gel lemon lime | Amix bag 32 g | 46.6% (sugars) | 2.0% |
| Gel | Enervit Sport gel, orange | Vitamin Center bag 25 mL | 1.0% | 0.9% (Figure 8D) |
| Calibration Range | 0.25–2.0 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Accuracy/Recovery (0.25–2.0 mg/mL) | 97.7–103.8% |
| Repeatability (retention time) | 0.2% |
| Repeatability (peak area) | 1.1% |
| Intermediate precision (peak area) | 2.4% |
| Limit of detection, LOD (S/N = 3) | 20 mg/L |
| Limit of quantification, LOQ | 66 mg/L |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crha, T.; Pazourek, J. Rapid HPLC Method for Determination of Isomaltulose in the Presence of Glucose, Sucrose, and Maltodextrins in Dietary Supplements. Foods 2020, 9, 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9091164
Crha T, Pazourek J. Rapid HPLC Method for Determination of Isomaltulose in the Presence of Glucose, Sucrose, and Maltodextrins in Dietary Supplements. Foods. 2020; 9(9):1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9091164
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrha, Tomáš, and Jiří Pazourek. 2020. "Rapid HPLC Method for Determination of Isomaltulose in the Presence of Glucose, Sucrose, and Maltodextrins in Dietary Supplements" Foods 9, no. 9: 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9091164
APA StyleCrha, T., & Pazourek, J. (2020). Rapid HPLC Method for Determination of Isomaltulose in the Presence of Glucose, Sucrose, and Maltodextrins in Dietary Supplements. Foods, 9(9), 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9091164






