Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) as a Tool for Investigating Self-Organized Ascending Bubble-Driven Flow Patterns in Champagne Glasses
Abstract
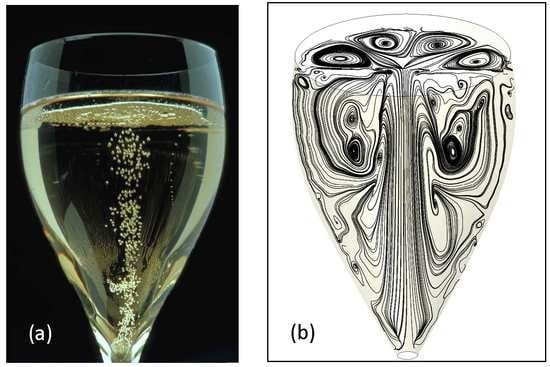
1. Introduction
2. Modeling the Glass and Physicochemical Parameters of Champagne
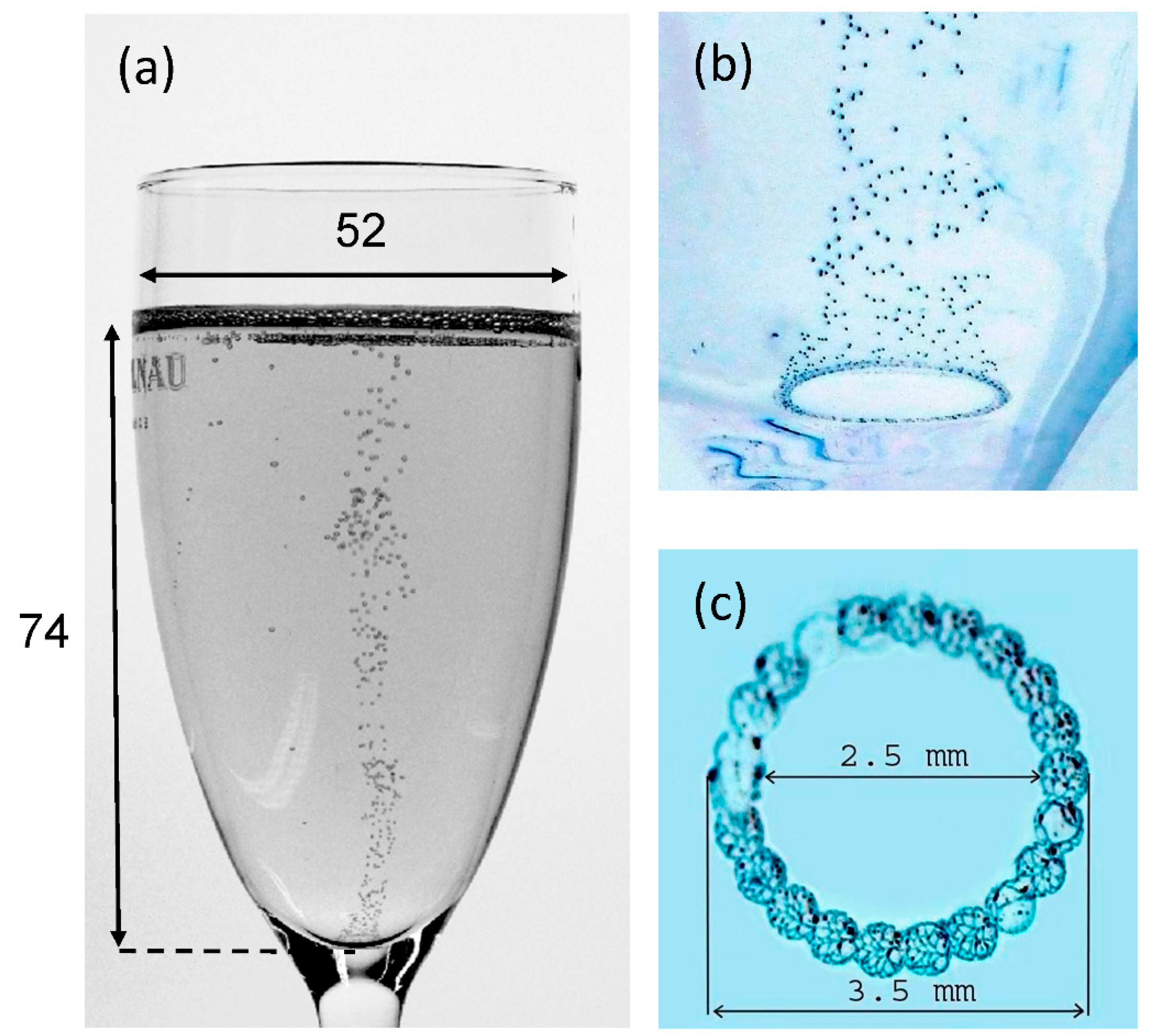
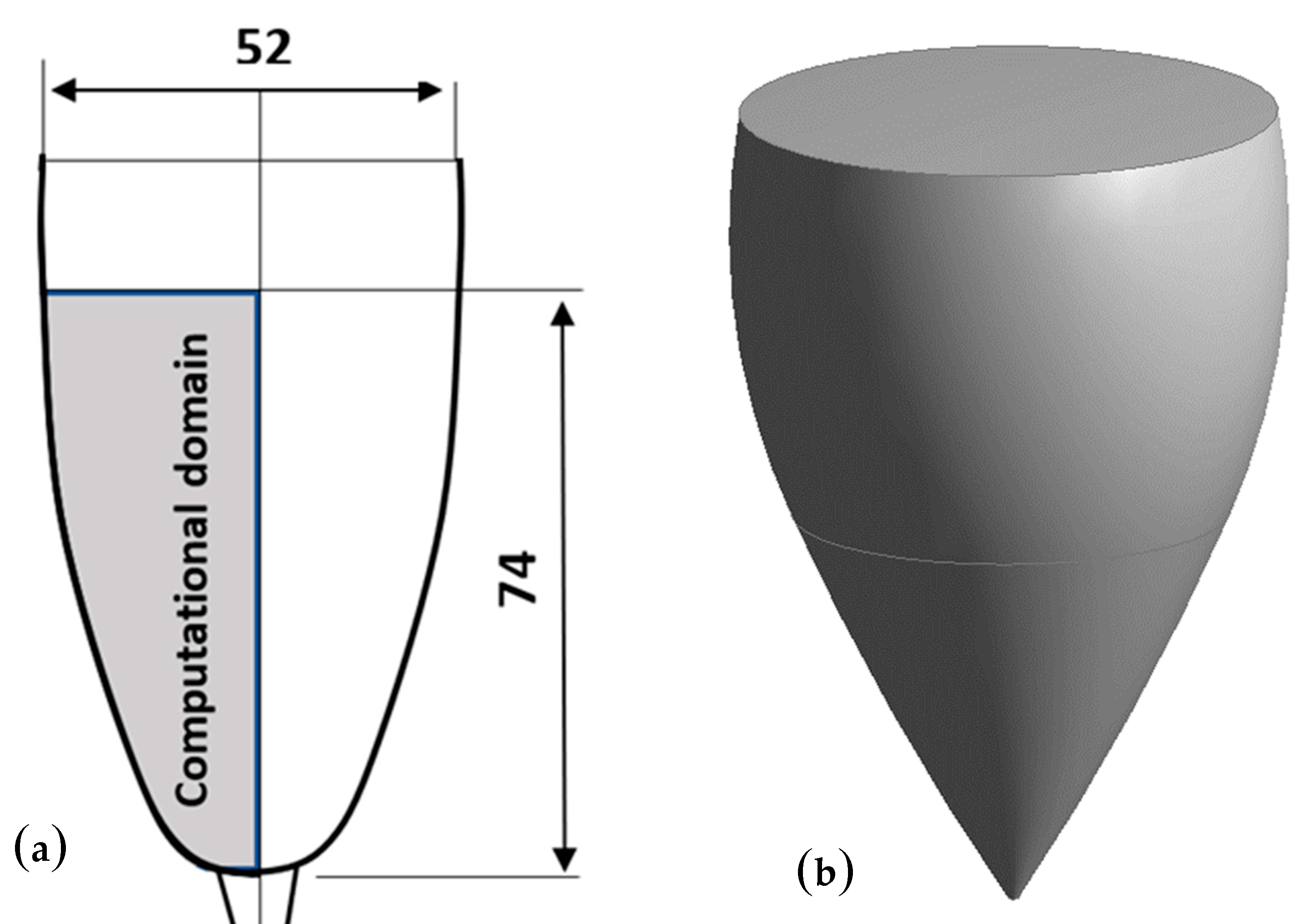
2.1. Modeling the Champagne Glass
2.2. Meshing of the Computational Domain
2.3. Physicochemical Parameters of Champagne and Gas-Phase CO2
3. Numerical Methods and Set-Up
3.1. Liquid-Phase Governing Equations
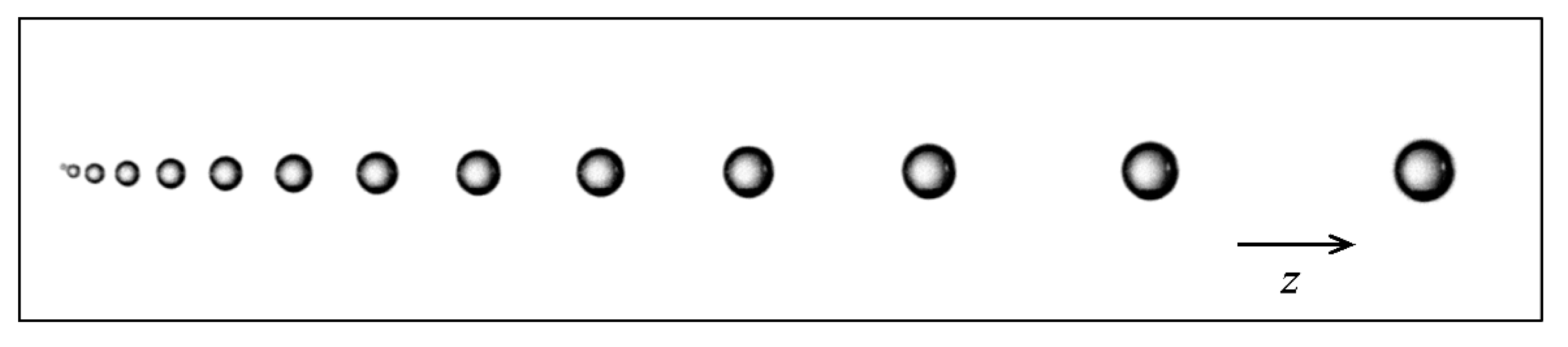
3.2. Discrete Phase Modeling
3.3. Boundary Conditions
4. Results and Discussion
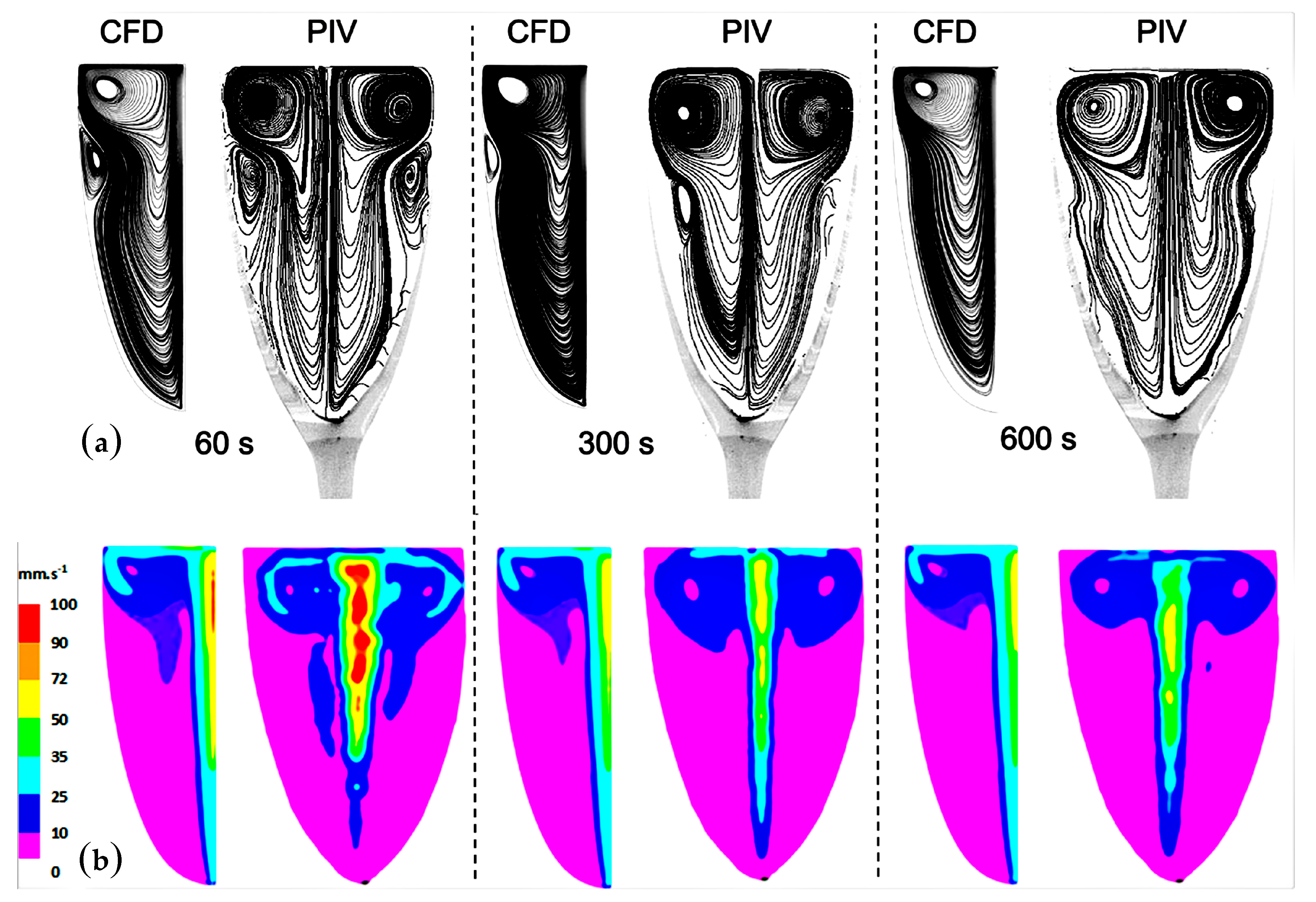
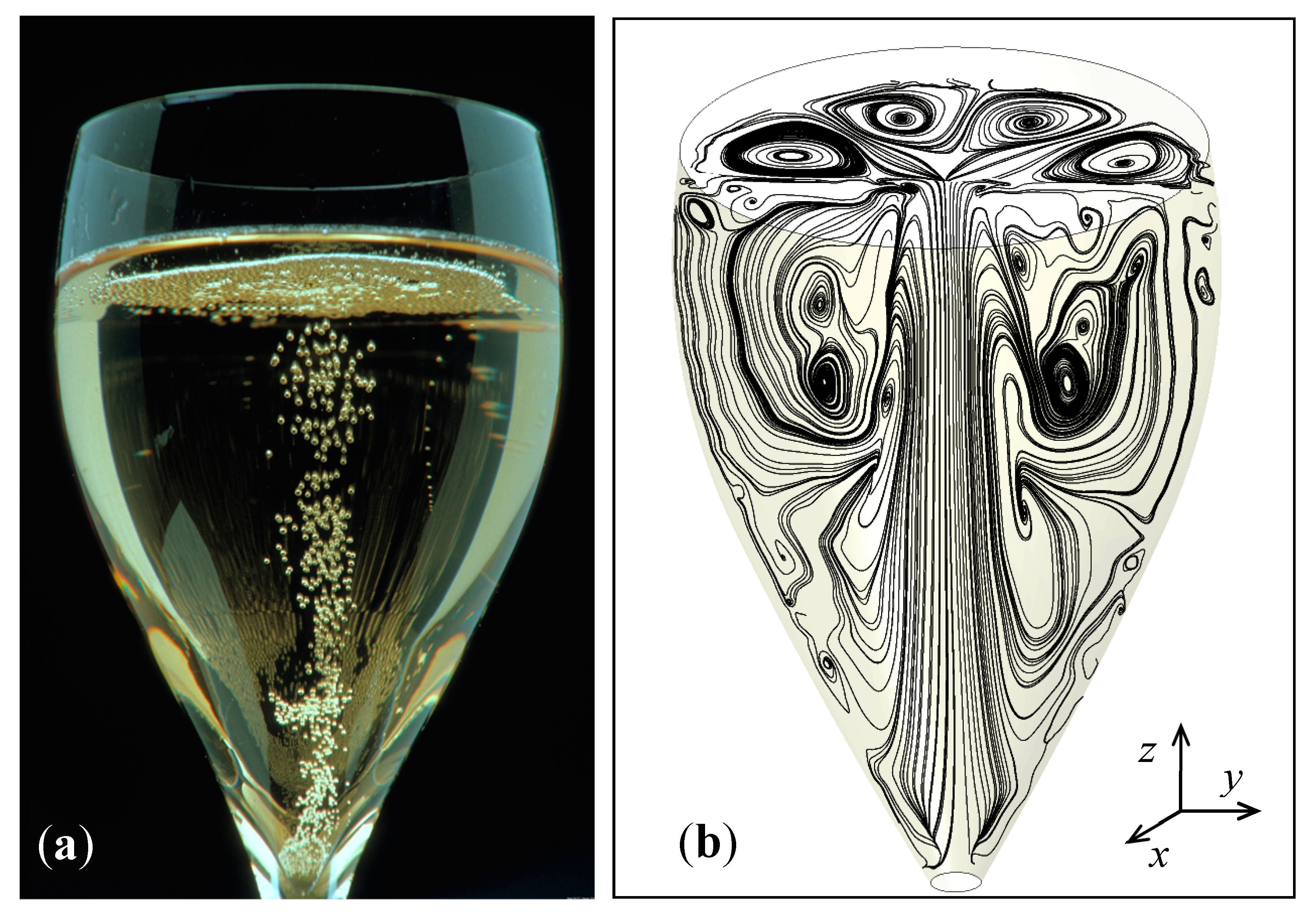
4.1. The Two-Dimensional (2D) Model
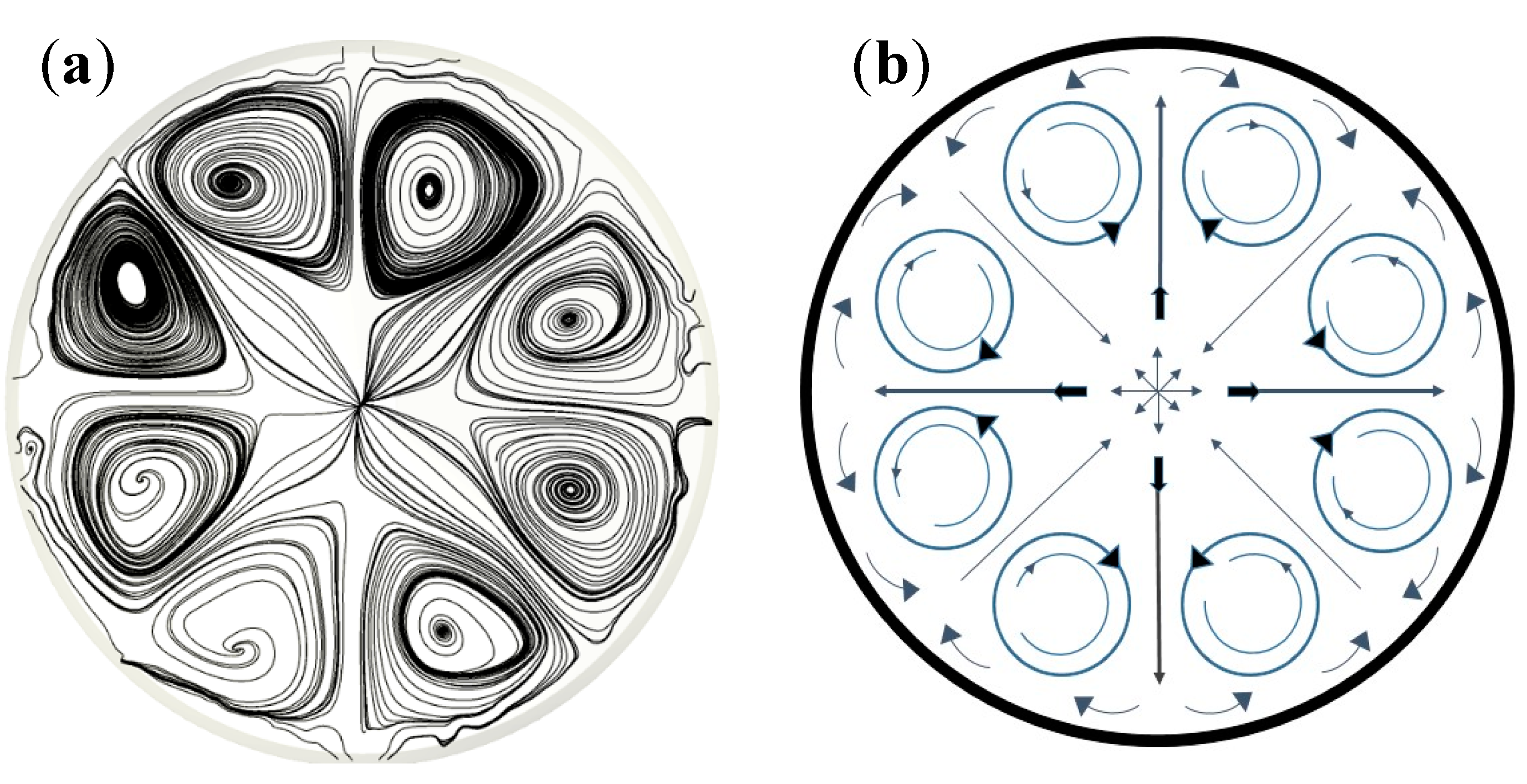
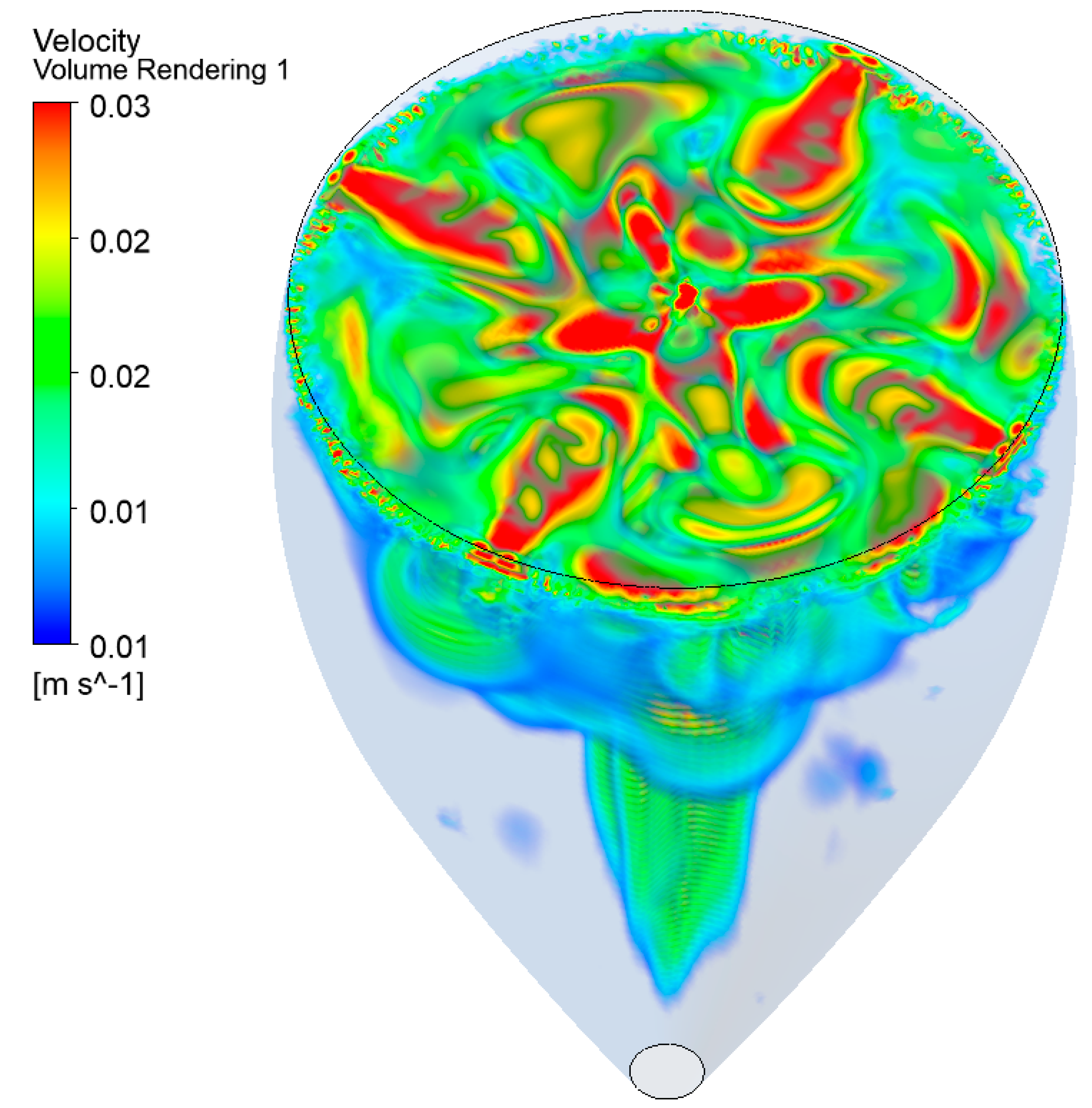
4.2. The Three-Dimensional (3D) Model
5. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liger-Belair, G.; Carvajal-Perez, D.; Cilindre, C.; Facque, J.; Brevot, M.; Litoux-Desrues, F.; Chaperon, V.; Geoffroy, R. Evidence for moderate losses of dissolved CO2 during aging on lees of a champagne prestige cuvee. J. Food Eng. 2018, 233, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liger-Belair, G.; Bourget, M.; Villaume, S.; Jeandet, P.; Pron, H.; Polidori, G. On the Losses of Dissolved CO2 During Champagne Serving. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 8768–8775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liger-Belair, G.; Parmentier, M.; Cilindre, C. More on the Losses of Dissolved CO2 during Champagne Serving: Toward a Multiparameter Modeling. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 11777–11786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liger-Belair, G.; Bourget, M.; Pron, H.; Polidori, G.; Cilindre, C. Monitoring Gaseous CO2 and Ethanol above Champagne Glasses: Flute versus Coupe, and the Role of Temperature. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liger-Belair, G.; Conreux, A.; Villaume, S.; Cilindre, C. Monitoring the losses of dissolved carbon dioxide from laser-etched champagne glasses. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liger-Belair, G. How Many Bubbles in Your Glass of Bubbly? J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 3156–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liger-Belair, G. Modeling the losses of dissolved carbon dioxide from laser-etched champagne glasses. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 3724–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polidori, G.; Jeandet, P.; Liger-Belair, G. Bubbles and Flow Patterns in Champagne. Am. Sci. 2009, 97, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilindre, C.; Conreux, A.; Liger-Belair, G. Simultaneous Monitoring of Gaseous CO2 and Ethanol above Champagne Glasses via Micro-gas Chromatography (μGC). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 7317–7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriaux, A.-L.; Vallon, R.; Parvitte, B.; Zeninari, V.; Liger-Belair, G.; Cilindre, C. Monitoring gas-phase CO2 in the headspace of champagne glasses through combined diode laser spectrometry and micro-gas chromatography analysis. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liger-Belair, G.; Religieux, J.-B.; Fohanno, S.; Vialatte, M.-A.; Jeandet, P.; Polidori, G. Visualization of Mixing Flow Phenomena in Champagne Glasses under Various Glass-Shape and Engravement Conditions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liger-Belair, G.; Beaumont, F.; Vialatte, M.-A.; Jégou, S.; Jeandet, P.; Polidori, G. Use of laser tomography techniques to determine the kinetics and stability of the mixing flow patterns found in champagne glasses:Likely impact on champagne tasting. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 621, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polidori, G.; Beaumont, F.; Jeandet, P.; Liger-Belair, G. Ring vortex scenario in engraved champagne glasses. J. Vis. 2009, 12, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liger-Belair, G.; Cilindre, C.; Beaumont, F.; Jeandet, P.; Polidori, G. Evidence for ascending bubble driven flow patterns in champagne glasses, and their impact on gaseous CO2 and ethanol release under standard tasting conditions. Bubble Sci. Eng. Technol. 2012, 4, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, F.; Liger-Belair, G.; Polidori, G. Flow analysis from PIV in engraved champagne tasting glasses: Flute versus coupe. Exp. Fluids 2015, 56, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, F.; Liger-Belair, G.; Polidori, G. Instabilities and topological behavior of the flow inside champagne glasses. J. Flow Visual. Image Proces. 2015, 22, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, F.; Liger-Belair, G.; Polidori, G. Unsteady evolution of the two-phase flow in sparkling wine tasting and the subsequent role of glass shape. Exp. Fluids 2019, 60, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, F.; Liger-Belair, G.; Bailly, Y.; Polidori, G. A synchronized particle image velocimetry and infrared thermography technique applied to convective mass transfer in champagne glasses. Exp. Fluids 2016, 57, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, F.; Popa, C.V.; Liger-Belair, G.; Polidori, G. Temperature Dependence of Ascending Bubble-Driven Flow Patterns Found in Champagne Glasses as Determined through Numerical Modeling. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2013, 5, 156430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, F.; Popa, C.; Liger-Belair, G.; Polidori, G. Numerical modelling of bubble-driven flow patterns in champagne glasses. Int. J. Numer. Method. H. 2014, 24, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, F.; Liger-Belair, G.; Polidori, G. Three-dimensional modeling of complex swirling flows in champagne glasses: CFD and flow visualization. Acta Mech. 2018, 230, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benilov, E.S.; Cummins, C.; Lee, W. Why do bubbles in Guinness sink? Am. J. Phys. 2013, 81, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watamura, T.; Iwatsubo, F.; Sugiyama, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Yotsumoto, Y.; Shiono, T. Bubble cascade in Guinness beer is caused by gravity current instability. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liger-Belair, G.; Parmentier, M.; Jeandet, P. Modeling the Kinetics of Bubble Nucleation in Champagne and Carbonated Beverages. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 21145–21151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perret, A.; Bonhommeau, D.; Liger-Belair, G.; Cours, T.; Alijah, A. CO2 Diffusion in Champagne Wines: A Molecular Dynamics Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 1839–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonhommeau, D.; Perret, A.; Nuzillard, J.-M.; Cilindre, C.; Cours, T.; Alijah, A.; Liger-Belair, G. Unveiling the Interplay Between Diffusing CO2 and Ethanol Molecules in Champagne Wines by Classical Molecular Dynamics and 13C NMR Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 4232–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, E.; Finn, J.R.; Apte, S. A numerical scheme for Euler-Lagrange simulation of bubbly flows in complex systems. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2010, 67, 1865–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groll, R.; Tropea, C.; Jakirlic, S. Comparative study of Euler/Euler and Euler/Lagrange approaches simulating evaporation in a turbulent gas-liquid flow. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2009, 59, 873–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.R.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, J.; Van, S.H. A volume-of-fluid method for incompressible free surface flows. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2009, 61, 1331–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annaland, M.V.S.; Deen, N.G.; Kuipers, J. Numerical simulation of gas bubbles behaviour using a three-dimensional volume of fluid method. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 2999–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabha, S.S.; Buwa, V.V. Volume-of-fluid (VOF) simulations of rise of single/multiple bubbles in sheared liquids. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikseresht, A.H.; Alishahi, M.M.; Emdad, H. Complete flow field computation around an ACV (air-cushion vehicle) using 3D VOF with Lagrangian propagation in computational domain. Comput. Struct. 2008, 86, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnaashari, A.; Akhtari, A.A.; Dehghani, A.A.; Bonakdari, H. Experimental and numerical investigation of the flow field in the gradual transition of rectangular to trapezoidal open channels. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2016, 10, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, A.; Kia, S.H. Numerical investigation of turbulent open channel flow with semi-cylindrical rough beds. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2014, 18, 2252–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.-P.; Zitney, S.E.; Shahnam, M.; Syamlal, M.; Rogers, W.A. Modelling coal gasification with CFD and discrete phase method. J. Energy Inst. 2006, 79, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, E.; Lihavainen, H.; Hyvärinen, A.-P.; Riipinen, I.; Wilck, M.; Stratmann, F.; Kulmala, M. Nucleation Simulations Using the Fluid Dynamics Software FLUENT with the Fine Particle Model FPM. J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 12448–12455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liger-Belair, G. Effervescence in champagne and sparkling wines: From grape harvest to bubble rise. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2017, 226, 3–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafer, N.E.; Zare, R.N. Through a Beer Glass Darkly. Phys. Today 1991, 44, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z. Fizzics of Bubble Growth in Beer and Champagne. Elements 2008, 4, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liger-Belair, G.; Jeandet, P. More on the Surface State of Expanding Champagne Bubbles Rising at Intermediate Reynolds and High Peclet Numbers. Langmuir 2003, 19, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duineveld, P. Bouncing and Coalescence of Bubble Pairs Rising at High Reynolds Number in Pure Water or Aqueous Surfactant Solutions. Flow Turbul. Combust. 1997, 58, 409–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liger-Belair, G. Nucléation, ascension et éclatement d’une bulle de champagne. Ann. Phys. 2006, 31, 1–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Manica, R.; Liu, Q.; Klaseboer, E.; Xu, Z. Coalescence or Bounce? How Surfactant Adsorption in Milliseconds Affects Bubble Collision. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 5662–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Q.; Luo, Z.; Hou, Q.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Zou, Z. Numerical Study of Inclusion Removal in Steel Continuous Casting Mold Considering Interactions Between Bubbles and Inclusions. ISIJ Int. 2018, 58, 2062–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, F.; Liger-Belair, G.; Polidori, G. Unveiling self-organized two-dimensional (2D) convective cells in champagne glasses. J. Food Eng. 2016, 188, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, L.; Gondret, P. Redressement d’un écoulement alternatif. J. Phys. II 1992, 2, 2115–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, N.; Trinh, E.H. Steady streaming in an oscillatory inviscid flow. Phys. Fluids 2001, 13, 1956–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, M. Steady streaming around a circular cylinder in an oscillatory flow. Ocean Eng. 2009, 36, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Champagne | Gas-Phase CO2 | |
|---|---|---|
|
Density ρ (kg m−3) | 9.98 × 102 | 1.79 |
|
Dynamic viscosity η (kg m−1 s−1) | 1.56 × 10−3 | 1.37 × 10−5 |
|
Surface tension γ (mN m−1) | 46.8 | / |
| Dissolved CO2 concentration [CO2]ini (g L−1) | 7.4 | / |
|
CO2 diffusion coefficient D (m2 s−1) | ≈1.4 × 10−9 | / |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beaumont, F.; Liger-Belair, G.; Polidori, G. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) as a Tool for Investigating Self-Organized Ascending Bubble-Driven Flow Patterns in Champagne Glasses. Foods 2020, 9, 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9080972
Beaumont F, Liger-Belair G, Polidori G. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) as a Tool for Investigating Self-Organized Ascending Bubble-Driven Flow Patterns in Champagne Glasses. Foods. 2020; 9(8):972. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9080972
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeaumont, Fabien, Gérard Liger-Belair, and Guillaume Polidori. 2020. "Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) as a Tool for Investigating Self-Organized Ascending Bubble-Driven Flow Patterns in Champagne Glasses" Foods 9, no. 8: 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9080972
APA StyleBeaumont, F., Liger-Belair, G., & Polidori, G. (2020). Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) as a Tool for Investigating Self-Organized Ascending Bubble-Driven Flow Patterns in Champagne Glasses. Foods, 9(8), 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9080972