Health Benefits and Molecular Mechanisms of Resveratrol: A Narrative Review
Abstract
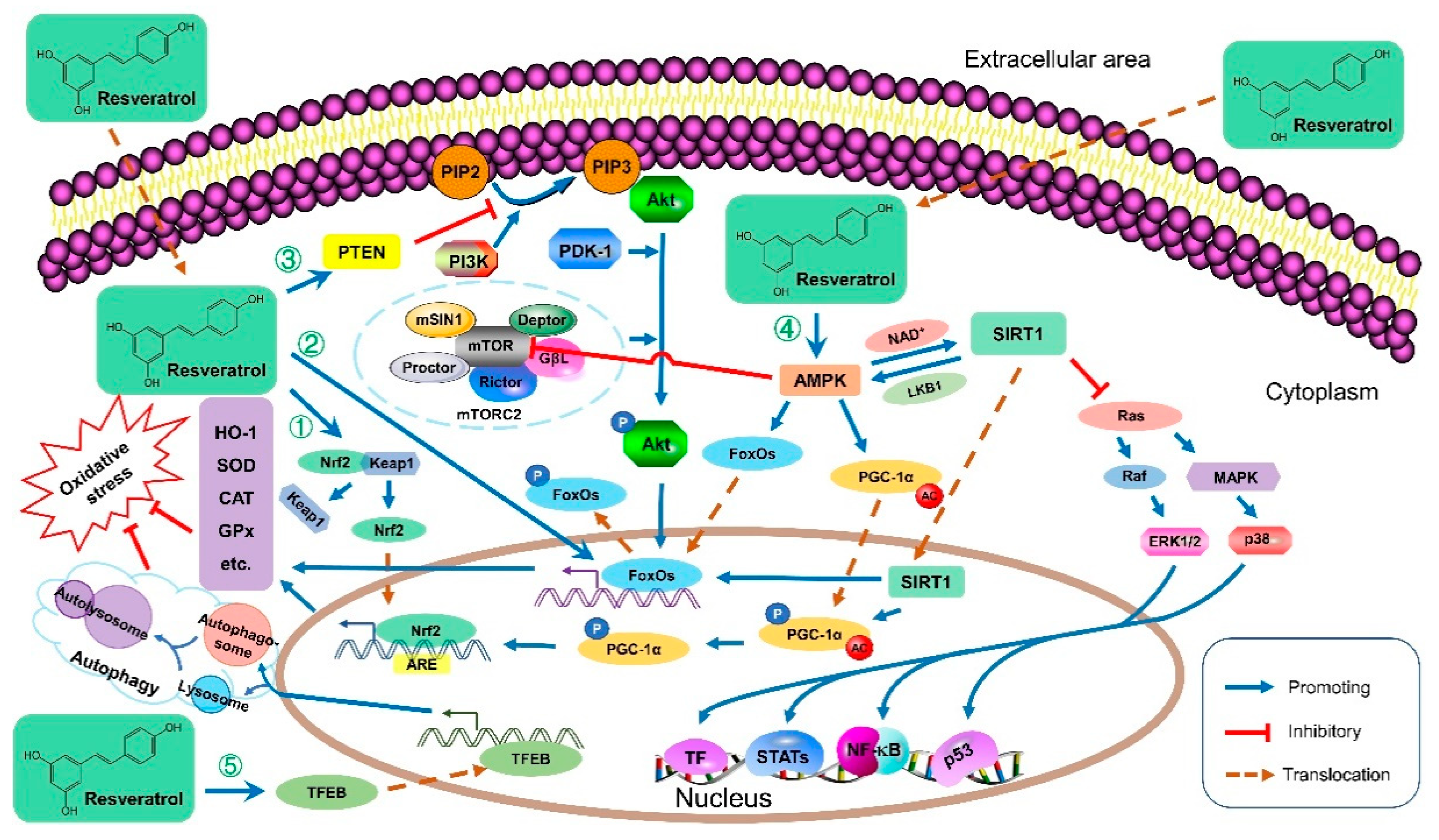
:1. Introduction
2. Observational Studies
3. Experimental Studies
3.1. Antioxidative Activities
3.2. Anti-Inflammatory Activities
3.3. Immunomodulating Effects
3.4. Cardiovascular Diseases
3.5. Cancers
3.6. Liver Diseases
3.7. Diabetes
3.8. Obesity
3.9. Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease
3.10. Sex-Dependent Effects of Resveratrol
| Study Type | Subject | Dose | Main Findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antioxidative activities | ||||
| In vitro | HepG2 cells | 0–100 μM | Dose-dependently increasing antioxidant effects by enhancing SIRT2’s activity to deacetylate Prx1 | [24] |
| In vitro | HepG2, C2C12, and HEK293 cells | 10, 25 μM | Activating AMPK to maintain the structural stability of FoxO1 | [25] |
| In vitro | MCF-7 cells | 1 nM, 0.02 μM, 0.1 μM, 0.5 μM, 1.5 μM | Upregulating PTEN (except at the highest dose, 1.5 μM), which decreased Akt phosphorylation, leading to an upregulation of antioxidant enzyme mRNA levels such as CAT and SOD | [26] |
| In vivo | Rats | 20 mg kg/b.w./day | Improving the antioxidant defense system by modulating antioxidant enzymes through downregulation of ERK activated by ROS | [27] |
| In vivo | Rats | 10 mg/kg b.w. | Reducing the ischemia-reperfusion injury-induced oxidative stress by inhibiting the activation of p38 MAPK pathway to increase antioxidants like GSH and scavenge free radicals | [28] |
| In vivo | Rats | 5, 10 mg/kg | Activating SIRT1 to scavenge ROS | [29] |
| In vivo | Mice | 15, 30, 60 mg/kg | Activating AMPK, SIRT1, and Nrf2 associated antioxidant defense pathways to improve systemic oxidative and nitrosative stress | [30] |
| In vivo | Sows | 300 mg/kg | Regulating antioxidant gene expression via Keap1/Nrf2 pathway and SIRT1 | [31] |
| In vitro | HUVECs | 10 μM | Inducing autophagy via the activation of TFEB | [32] |
| In vitro | HEK293 cells or HEK293T | 5 μg/mL | Inducing autophagy via the AMPK-mediated inhibition of mTOR signaling | [33] |
| Anti-inflammatory activities | ||||
| In vivo | Mice | 8 mg/kg/day | Inhibiting the activation of NALP3 inflammasome and inducing autophagy via SIRT1 upregulation | [34] |
| In vitro | J774 mouse macrophages, Mouse bone-marrow cells | 0.5–100 μM | Inhibiting the activation of NALP3 inflammasome | [35] |
| In vitro; In vivo | BEAS-2B cells, Mice | 25 μM, 20 mg/kg | Inducing NF-κB inhibition, decreasing IL-6 secretion, suppressing STAT3 activation, blocking ERK1/2 activation, and upregulating MyD88 Short | [36] |
| In vitro | RAW264.7 macrophages | 0–20 μM | Inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-1β, but also by inducing anti-inflammatory HO-1 | [38] |
| In vitro | RAW264.7 macrophages, MCF-7 cells | 10 μM | Suppressing IL-6 transcription, modulating the inflammatory responses as an ERα ligand mediated by SIRT1. | [39] |
| In vitro | Mouse C2C12 myoblasts | 20, 50, 100 μM | Inhibiting NF-κB signaling independent of SIRT1 | [40] |
| In vitro | RAW264.7 macrophages | 1, 5, 10, 20, 40 μM | Downregulating HMGB1 as well as suppressing NF-κB and JAK/STAT signaling pathways | [41] |
| In vitro | U937 monocytic cells | 15, 30, 50 μM | Inhibiting NF-κB and JAK/STAT signaling pathways | [42] |
| In vitro In vivo | NRK-52E, Rat | 100 μmol/mL, 0.23 μg/kg | Inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB signaling cascade | [43] |
| In vivo | Rats | 30, 10 and 3 mg/kg, | Inhibiting TLR4/NF-κBp65/MAPKs signaling cascade | [44] |
| In vitro | Primary chondrocytes and macrophages | 10, 25, 50, 100 μM | Interrupting an inflammatory amplification loop | [45] |
| Immunomodulating effects | ||||
| In vitro | A549 cells | 56.25, 112.5 μg/mL | Triggering an immune response to protect against non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae without developing resistance | [46] |
| In vitro | H1HeLa cells, Human nasal epithelia | 0–300 μM | Inhibiting human rhinoviruses-16 replication and normalized virus-induced IL-6, IL-8, and RANTES as well as the expression of ICAM-1 | [47] |
| In vitro | Rhabdosarcoma cells | 2.5–100 μg/mL | Preventing EV71 replication, reducing the virus-induced elevated IL-6 and TNF-α secretion via suppressing IKK/NF-κB signaling pathway | [48] |
| In vivo | Chickens | 200, 400, 800 mg/kg | Reducing immunocyte apoptosis in chickens receiving conventional vaccinations, and improving the growth of young chickens | [49] |
| In vivo | Piglets | 3, 10, 30 mg/kg/d | Maintaining the immune function and attenuating diarrhea and inflammation | [51] |
| In vitro | Atlantic salmon macrophages | 10, 30, 50 μM | Reducing bacterial and inflammatory biomarkers in LPS-challenged primary Atlantic salmon macrophages | [52] |
| In vivo | Mice | 30 mg/kg | Upregulating SIRT1 and reducing cytokines such as TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-6, and MCP-1 | [53] |
| In vivo | Mice | 30 mg/kg | Enhancing immune activity in immunosuppressive mice, showing a bidirectional regulatory effect on immunity | [54] |
| In vitro | Human CD4+ T cells | 10, 30, or 50 μM | Suppressing the AhR pathway, resulting in the reversal of imbalanced Th17/Treg | [56] |
| Cardiovascular diseases | ||||
| In vivo | Rhesus monkeys | 80 mg/day (1st year), 480 mg/day (2nd year) | Improving central arterial wall stiffening based on its antioxidative and anti-inflammation | [7] |
| In vivo | Rabbits | 2.5 mg/kg | Mitigating atrial fibrillation by upregulating PI3K/AKT/eNOS | [8] |
| In vitro | Peripheral blood mononuclear cells | 3–80 μM | Blocking atherosclerotic plaque progression by acting against pro-atherogenic oxysterol signaling in M1 and M2 macrophages | [57] |
| In vitro In vivo | THP-1 monocytes, Mice | 0, 25, 50, 100 μM (dose-dependent), 10 mg/kg/day | Ameliorating atherosclerosis partially through restoring intracellular GSH via AMPK-α activation, inhibiting monocyte differentiation, and reducing pro-inflammatory cytokine production | [59] |
| In vivo | Rats | 50 mg/L | Preventing the pathological progression of hypertension through Nrf2 activation | [60] |
| In vitro; In vivo | Rat aortic smooth muscle cells; Mice | 100 μmol/L, ~320 mg/kg | Lowering blood pressure by inducing oxidative activation of cGMP-dependent PKG1α | [61] |
| In vivo | Rats | 50 mg/kg/day | Preventing the activation of inflammasome via downregulating NF-κB p65 and p38 MAPK expression, and upregulating SIRT1 expression | [62] |
| In vivo | Mice | 20 mg/kg | Regulated the FERM-kinase and Nrf2 interaction, decreasing the expression of ICAM-1, and inhibiting monocyte adhesion | [63] |
| In vivo | Rats | 1.24 μg/d | Improving the cardiac and vascular autonomic function | [65] |
| In vitro | Human RBCs | 100 μM | Protecting the erythrocytes via interacting with hemoglobin and reducing heme-iron oxidation | [66] |
| Cancers | ||||
| In vitro | LNCaP cells | 5, 10, 20, 50 μM | Inducing the expression of COX-2, promoting ERK1/2 activation, and facilitating p53-dependent anti-proliferation gene expression | [14] |
| In vitro; In vivo | tBregs; Mice | 12.5 μM; 20, 50, 500 μg/mouse | Preventing breast cancer metastasis by promoting antitumor immune responses via blunting STAT3, leading to inhibited generation and function of tBregs as well as decreased production of TGF-β | [67] |
| In vivo | Mice | 150, 300 ppm | Inhibiting the formation and growth of colorectal cancer by downregulating oncogenic KRAS expression | [68] |
| In vitro; In vivo | NSCLC cells Mice | 25, 50, 100 μM, 30 mg/kg every 3 days | Preventing tumorigenesis and progression by interrupting glycolysis via inhibition of hexokinase II expression, which was mediated by downregulation of EGFR/Akt/ERK1/2 signaling pathway | [69] |
| In vitro | MCF-7 cells MVLN cells | Low: 0.1 and 1 μM; High: 10 and 25 μM; | Low concentrations: Increasing the growth of ERα+ cells High concentrations: Inhibiting the proliferation of eERα+ breast cancer | [75] |
| In vitro | KPL-1, MCF-7, MKL-F cells | Low (KPL-1, ≤22 μM; MCF-7, ≤4 μM); High: ≥44 μM | Low concentrations: Causing cell proliferation ER+ cells High concentrations: Suppressing cell growth | [76] |
| In vitro In vivo | Apc10.1 cells; Mice; Humans | 0.001–1 μM; 0.7, 14.3 mg/kg diet; 5 mg, 1 g | Lower doses of resveratrol: Showing superior efficacy than high doses due to the pro-oxidant activity and AMPK signaling upregulation | [79] |
| In vitro | A2780, OVCAR-3, SKOV-3 cells | 10, 50, 100 μM | Decreasing the efficiency of ovarian cancer cells adhering to peritoneal mesothelium by downregulating the production of α5β1 integrins and upregulating the release of soluble hyaluronic acid | [70] |
| In vitro | Hela cells | 0.1, 1, 10 μM, 10, 20, 50, 100 μM | Inhibiting the expression of PLSCR1, leading to the growth inhibition of HeLa cells | [71] |
| In vitro | HepG2 cells | 25, 50, 100, 200 μM | Inhibiting proliferation and inducing apoptosis by activating caspase-3 and caspase-9, upregulating the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, and inducing p53 expression | [72] |
| In vitro | SGC7901 and BGC823 cells | 5, 10, 25, 50, 100, 200, and 400 μM | Inhibiting the invasion and migration of human gastric cancer cells by blocking the MALAT1-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition | [73] |
| Liver diseases | ||||
| In vivo | Mice | 0.2% of diet | Improving HFD-induced fatty liver by downregulating adipose differentiation-related proteins and increasing the numbers of CD68+ Kupffer cells | [9] |
| In vivo | Rats | 10 mg/kg | Attenuating hepatic fibrosis by restoring the architecture and normalizing collagen deposition, mainly due to its antioxidative activities and downregulation of α-SMA | [80] |
| In vivo | Rats | 50, 100 mg/kg | Alleviating NAFLD by upregulating LDLR and SRB1 gene expressions | [83] |
| In vivo | Rats | 250 mg/kg/day | Downregulating HIF-1α expression and mitochondrial ROS production | [85] |
| In vitro; In vivo | HepG2 cells; Mice | 45 μmol 10, 30, 100 mg/kg | Restoring the morphology and function of alcohol-injured liver through inducing autophagy | [86] |
| In vivo | Rats | 10 mg/kg | Mitigating liver cirrhosis by improving the homing of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells | [87] |
| Diabetes | ||||
| In vivo | Rats | 20 mg/kg | Increasing insulin action and glucose utilization due to visfatin expression restoration, SIRT1 activation, and glucose transporter modulation | [89] |
| In vivo | Mice | 50 mg/kg | Increasing glucose uptake to improve insulin resistance in the muscle by decreasing DAG accumulation and PKC-θ translocation, and preventing lipolysis under the condition of adipose hypoxia | [90] |
| In vivo | Rats | 147.6 mg/kg/day | Preventing the offspring’s glucose intolerance and islet dysfunction | [91] |
| In vivo | Mice | 0.3% diet | Reducing blood glucose levels, plasma lipids, and free fatty acids, inhibiting the expression of inflammatory mediators both in the aorta and in the blood, by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway | [92] |
| In vivo | Mice | 50 mg/kg | Preventing ROS-mediated mitochondrial fission via AMPK-dependent upregulation of Drp1 phosphorylation, and blocking the activation of NALP3 inflammasome via inhibition of ERS | [93] |
| Obesity | ||||
| In vivo | Zebrafish | 40 mg/kg/day | Inhibiting transcriptional regulators such as EP300 | [95] |
| In vivo | Mice | 0.06% diet | Decreasing the body weight and fat mass, reducing leptin and lipids in plasma, modulating metabolism of glucose and insulin, and restoring immune dysfunction by activating PI3K/SIRT1 and Nrf2 signaling pathway | [96] |
| In vitro; In vivo | 3T3-L1 cells; Mice | 0.03 to 100 μM; 1, 10, 30 mg/kg | In vitro: low concentrations of resveratrol (1-10 μM) suppressed adipogenic differentiation in pre-adipocytes, downregulated the expression of PPAR-γ and perilipin protein in differentiated adipocytes, and inhibiting TNF-α-induced lipolysis in mature adipocytes In vivo: Dose-dependently decreasing weight gain and lipid deposition in the liver and adipose tissue | [97] |
| In vitro | RAW 264.7 macrophage cells | 25 μM | Enhancing the catecholamine production, accompanying by suppressing the pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages, and activating anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages in white adipose tissue | [98] |
| In vivo | Mice | 0.2% diet | Promoting white adipose browning and thermogenesis in the male descendants, and these health benefits persisted and prevented obesity in their future life | [99] |
| In vitro; In vivo | L6 myogenic cell line; Rats | 1, 5, 10, 25 or 50 μM; 0.4% diet | In vitro: Improving mitochondrial function and reducing oxidative stress through the PKA/LKB1/AMPK pathway; In vivo: Preventing muscle loss and myofiber size decrease, improving grip strength, and abolishing excessive fat accumulation | [100] |
| In vivo | Mice | 0.06% diet | Improving obesity-related complications by restoring plasma thyroid hormone levels, and attenuating oxidative stress in the heart | [101] |
| In vitro | Human sperm | 2.6, 6, 15, 30, 50, 100 μmol/L | Improving obesity-related complications by restoring reproductive dysfunction like infertility | [102] |
| Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease | ||||
| In vivo | Rats | 20 mg/kg/day | Ameliorating ERS by downregulating the gene expression of CHOP and GRP78, inhibiting caspase-3 activity, and ameliorating oxidative damage via suppressing xanthine oxidase activity and protein carbonyl formation as well as activating glutathione peroxidase and Nrf2 signaling pathway | [10] |
| In vitro | CL2006 cells | 100 μM | Inhibiting the aggregation of Aβ by modulating specific proteins such as UBL/XBP-1 involved in proteostasis | [103] |
| In vivo | Mice | 16 mg/kg/day | Preventing memory loss by decreasing elevated levels of mitochondrial complex IV protein in the mouse brain via the activation of SIRT1 and AMPK pathways | [104] |
| In vivo | Mice | 100 mg/kg/day | Preventing memory loss via the activation of SIRT1 and AMPK pathways | [105] |
| In vitro; In vivo | SH-SY5Y cells; Mice | 50 μM; 50 mg/kg | Elevating miR-214 expression, leading to decreased mRNA expression of α-synuclein | [106] |
| Sex-dependent effects of resveratrol | ||||
| In vivo | Rats | 2.5 mg/kg/day | Superior improvements of MI in females in terms of IVSDs, ESV, EF, FS, and IVRT, among which IVRT is purely sex-dependent | [109] |
| In vivo | Rats | 50 mg/L in drinking water | Increasing the relaxations to estrogen in aortae, more potent in males, probably due to resveratrol’s promoting nitric oxide and/or suppressing superoxide effects | [110] |
| In vitro; In vivo | MESC2.10 and SN4741 cells; Mice | 20 mg/kg; 10 μM | Increasing DAT in the striatum in females but not in males; Upregulating DAT in the dopaminergic cells by inducing its gene transcription | [111] |
| In vivo | Mice | 100 mg/kg | Adverse effects in females but not in males, regarding weight loss, stool consistency, and discomfort | [112] |
4. Clinical Trials
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Gan, R.-Y.; Xu, D.-P.; Li, H.-B. Dietary sources and bioactivities of melatonin. Nutrients 2017, 9, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, C.-N.; Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, Q.; Tang, G.-Y.; Li, H.-B. Fruits for prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Nutrients 2017, 9, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weiskirchen, S.; Weiskirchen, R. Resveratrol: How much wine do you have to drink to stay healthy? Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jang, M.; Cai, L.; Udeani, G.O.; Slowing, K.V.; Thomas, C.F.; Beecher, C.W.; Fong, H.H.; Farnsworth, N.R.; Kinghorn, A.D.; Mehta, R.G.; et al. Cancer chemopreventive activity of resveratrol, a natural product derived from grapes. Science 1997, 275, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Yngve, A.; Lagergren, J.; Lu, Y. A dietary pattern rich in lignans, quercetin and resveratrol decreases the risk of oesophageal cancer. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 2002–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zamora-Ros, R.; Urpi-Sarda, M.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Arós, F.; Fitó, M.; Lapetra, J.; Estruch, R.; Andres-Lacueva, C. High urinary levels of resveratrol metabolites are associated with a reduction in the prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors in high-risk patients. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 65, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattison, J.A.; Wang, M.; Bernier, M.; Zhang, J.; Park, S.; Maudsley, S.; An, S.S.; Santhanam, L.; Martin, B.; Faulkner, S.; et al. Resveratrol prevents high fat/sucrose diet-induced central arterial wall inflammation and stiffening in nonhuman primates. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chong, E.; Chang, S.; Hsiao, Y.; Singhal, R.; Liu, S.; Leha, T.; Lin, W.; Hsu, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Resveratrol, a red wine antioxidant, reduces atrial fibrillation susceptibility in the failing heart by PI3K/AKT/eNOS signaling pathway activation. Heart Rhythm 2015, 12, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, K.; Iwaya, K.; Kinoshita, M.; Fujiwara, Y.; Akao, M.; Sonoda, M.; Thiruppathi, S.; Suzuki, T.; Hiroi, S.; Seki, S.; et al. Resveratrol increases CD68+ Kupffer cells colocalized with adipose differentiation-related protein and ameliorates high-fat-diet-induced fatty liver in mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 1155–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaballah, H.H.; Zakaria, S.S.; Elbatsh, M.M.; Tahoon, N.M. Modulatory effects of resveratrol on endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated apoptosis and oxido-inflammatory markers in a rat model of rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 251, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Sheng, Z.; Xie, J.; Li, R.; Chen, L.; Li, G.; Wang, L.; Xu, B. Reduced HMGB 1-mediated pathway and oxidative stress in resveratrol-treated diabetic mice: A possible mechanism of cardioprotection of resveratrol in diabetes mellitus. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moussa, C.; Hebron, M.; Huang, X.; Ahn, J.; Rissman, R.A.; Aisen, P.S.; Turner, R.S. Resveratrol regulates neuro-inflammation and induces adaptive immunity in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sung, M.M.; Kim, T.T.; Denou, E.; Soltys, C.M.; Hamza, S.M.; Byrne, N.J.; Masson, G.; Park, H.; Wishart, D.S.; Madsen, K.L.; et al. Improved glucose homeostasis in obese mice treated with resveratrol is associated with alterations in the gut microbiome. Diabetes 2017, 66, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, T.M.; Chin, Y.T.; Ho, Y.; Chen, Y.R.; Yang, Y.N.; Yang, Y.C.; Shih, Y.J.; Lin, T.I.; Lin, H.Y.; Davis, P.J. Resveratrol induces sumoylated COX-2-dependent anti-proliferation in human prostate cancer LNCaP cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 112, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huhn, S.; Beyer, F.; Zhang, R.; Lampe, L.; Grothe, J.; Kratzsch, J.; Willenberg, A.; Breitfeld, J.; Kovacs, P.; Stumvoll, M.; et al. Effects of resveratrol on memory performance, hippocampus connectivity and microstructure in older adults—A randomized controlled trial. Neuroimage 2018, 174, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ornstrup, M.J.; Harslof, T.; Kjaer, T.N.; Langdahl, B.L.; Pedersen, S.B. Resveratrol increases bone mineral density and bone alkaline phosphatase in obese men: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. J. Clin. Endocr. Metab. 2014, 99, 4720–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levi, F.; Pasche, C.; Lucchini, F.; Ghidoni, R.; Ferraroni, M.; La Vecchia, C. Resveratrol and breast cancer risk. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2005, 14, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabassa, M.; Zamora-Ros, R.; Urpi-Sarda, M.; Bandinelli, S.; Ferrucci, L.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Cherubini, A. Association of habitual dietary resveratrol exposure with the development of frailty in older age: The Invecchiare in Chianti study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 1534–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sohrab, G.; Hosseinpour-Niazi, S.; Hejazi, J.; Yuzbashian, E.; Mirmiran, P.; Azizi, F. Dietary polyphenols and metabolic syndrome among Iranian adults. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 64, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaud, S.; de Lorgeril, M. Wine, alcohol, platelets, and the French paradox for coronary heart disease. Lancet 1992, 339, 1523–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tresserra-Rimbau, A.; Rimm, E.B.; Medina-Remon, A.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; de la Torre, R.; Corella, D.; Salas-Salvado, J.; Gomez-Gracia, E.; Lapetra, J.; Aros, F.; et al. Inverse association between habitual polyphenol intake and incidence of cardiovascular events in the PREDIMED study. Nutr. Metab. Carbiovasc. Dis. 2014, 24, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tresserra-Rimbau, A.; Rimm, E.B.; Medina-Remon, A.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Lopez-Sabater, M.C.; Covas, M.I.; Corella, D.; Salas-Salvado, J.; Gomez-Gracia, E.; Lapetra, J.; et al. Polyphenol intake and mortality risk: A re-analysis of the PREDIMED trial. BMC Med. 2014, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, G.P.; Zhu, Y.P.; Zhang, Y.P.; Lang, J.M.; Chen, Y.P.; Ling, W.P. Estimated daily flavonoid and stilbene intake from fruits, vegetables, and nuts and associations with lipid profiles in Chinese adults. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2013, 113, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yuan, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J. Resveratrol exerts antioxidant effects by activating SIRT2 to deacetylate Prx1. Biochemistry US 2017, 56, 6325–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, H.; Park, S.; Kim, M.; Yang, W.K.; Im, D.U.; Yang, K.R.; Hong, J.; Choe, W.; Kang, I.; Kim, S.S.; et al. AMP-activated protein kinase mediates the antioxidant effects of resveratrol through regulation of the transcription factor FoxO1. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 4421–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingles, M.; Gambini, J.; Miguel, M.G.; Bonet-Costa, V.; Abdelaziz, K.M.; El Alami, M.; Vina, J.; Borras, C. PTEN mediates the antioxidant effect of resveratrol at nutritionally relevant concentrations. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 580852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.K.; Vinayak, M. Resveratrol alleviates inflammatory hyperalgesia by modulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), antioxidant enzymes and ERK activation. Inflamm. Res. 2017, 66, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Lv, R.; Wang, L.; Hou, H.; Liu, H.; Shao, S. Resveratrol, an antioxidant, protects spinal cord injury in rats by suppressing MAPK pathway. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Feng, L.; Xing, Y.; Wang, Y.; Du, L.; Xu, C.; Cao, J.; Wang, Q.; Fan, S.; Liu, Q.; et al. Radioprotective and antioxidant effect of resveratrol in hippocampus by activating Sirt1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 5928–5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Zlia, G.; Chen, L.; Ding, Y.; Lian, J.; Hong, G.; Lu, Z. Resveratrol protects mice from paraquat-induced lung injury: The important role of SIRT1 and NRF2 antioxidant pathways. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 1833–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Guo, T.; Li, G.; Sun, S.; He, S.; Cheng, B.; Shi, B.; Shan, A. Dietary resveratrol improves antioxidant status of sows and piglets and regulates antioxidant gene expression in placenta by Keap1-Nrf2 pathway and Sirt1. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, J.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hou, P.; Zeng, X.; Yi, L.; Mi, M. Resveratrol attenuates endothelial oxidative injury by inducing autophagy via the activation of transcription factor EB. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 16, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kundu, M.; Viollet, B.; Guan, K. AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.J.; Lim, Y. Resveratrol ameliorates hepatic metaflammation and inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Metabolism 2014, 63, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misawa, T.; Saitoh, T.; Kozaki, T.; Park, S.; Takahama, M.; Akira, S. Resveratrol inhibits the acetylated alpha-tubulin-mediated assembly of the NLRP3-inflammasome. Int. Immunol. 2015, 27, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, C.S.; Matsuyama, S.; Lee, B.; Li, J. Resveratrol suppresses NTHi-induced inflammation via upregulation of the negative regulator MyD88 short. Sci. Rep. UK 2016, 6, 34445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.H.; Fu, Y.C.; Wu, M.J. Does resveratrol play a role in decreasing the inflammation associated with contrast induced nephropathy in rat model? J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Son, Y.; Chung, H.; Pae, H. Differential effects of resveratrol and its natural analogs, piceatannol and 3,5,4′-trans-trimethoxystilbene, on anti-inflammatory heme oxigenase-1 expression in RAW264.7 macrophages. Biofactors 2014, 40, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwachukwu, J.C.; Srinivasan, S.; Bruno, N.E.; Parent, A.A.; Hughes, T.S.; Pollock, J.A.; Gjyshi, O.; Cavett, V.; Nowak, J.; Garcia-Ordonez, R.D.; et al. Resveratrol modulates the inflammatory response via an estrogen receptor-signal integration network. ELife 2014, 3, e2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, A.; Ebrahimi, S.S.S.; Golestani, A.; Meshkani, R. Resveratrol ameliorates palmitate-induced inflammation in skeletal muscle cells by attenuating oxidative stress and JNK/NF-κB pathway in a SIRT1-independent mechanism. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 2654–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Wang, Y.; Dong, L.; Li, M.; Cai, W. Anti-inflammatory effect of resveratrol through the suppression of NF-κB and JAK/STAT signaling pathways. Acta Bioch. Bioph. Sin. 2015, 47, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinheiro, D.; de Oliveira, A.; Coutinho, L.G.; Fontes, F.L.; de Medeiros, O.R.; Oliveira, T.T.; Faustino, A.; Lira, D.S.V.; de Melo, C.J.; Lajus, T.; et al. Resveratrol decreases the expression of genes involved in inflammation through transcriptional regulation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 130, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, L.; Jia, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Rong, R. Resveratrol alleviates inflammatory responses and oxidative stress in rat kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury and H2O2-induced NRK-52E Cells via the Nrf2/TLR4/NF-κB Pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 1677–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Hu, Z.; Fu, Q.; Song, X.; Cui, Q.; Jia, R.; Zou, Y.; He, C.; Li, L.; Yin, Z. Resveratrol mitigates lipopolysaccharide-mediated acute inflammation in rats by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κBp65/MAPKs signaling cascade. Sci. Rep. UK 2017, 7, 45006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limagne, E.; Lancon, A.; Delmas, D.; Cherkaoui-Malki, M.; Latruffe, N. Resveratrol interferes with IL1β-induced pro-inflammatory paracrine interaction between primary chondrocytes and macrophages. Nutrients 2016, 8, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Euba, B.; Lopez-Lopez, N.; Rodriguez-Arce, I.; Fernandez-Calvet, A.; Barberan, M.; Caturla, N.; Marti, S.; Diez-Martinez, R.; Garmendia, J. Resveratrol therapeutics combines both antimicrobial and immunomodulatory properties against respiratory infection by nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastromarino, P.; Capobianco, D.; Cannata, F.; Nardis, C.; Mattia, E.; De Leo, A.; Restignoli, R.; Francioso, A.; Mosca, L. Resveratrol inhibits rhinovirus replication and expression of inflammatory mediators in nasal epithelia. Antivir. Res. 2015, 123, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Gu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Shi, M.; Ji, Y.; Sun, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, J.; et al. Resveratrol inhibits enterovirus 71 replication and pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion in rhabdosarcoma cells through blocking IKKs/NF-κB signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e1168792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Tian, Y.; Yan, F.; Kang, X.; Han, R.; Sun, G.; Zhang, H. Modulation of growth and immunity by dietary supplementation with resveratrol in young chickens receiving conventional vaccinations. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2014, 75, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zang, N.; Zhou, N.; Li, W.; Xie, X.; Deng, Y.; Ren, L.; Long, X.; Li, S.; Zhou, L.; et al. Resveratrol inhibits the TRIF-dependent pathway by upregulating sterile α and armadillo motif protein, contributing to anti-inflammatory effects after respiratory syncytial virus infection. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 4229–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, Q.; Fu, Q.; Zhao, X.; Song, X.; Yu, J.; Yang, Y.; Sun, K.; Bai, L.; Tian, Y.; Chen, S.; et al. Protective effects and immunomodulation on piglets infected with rotavirus following resveratrol supplementation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e1926922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, N.C.; Christian, S.L.; Taylor, R.G.; Santander, J.; Rise, M.L. Immune modulatory properties of 6-gingerol and resveratrol in Atlantic salmon macrophages. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 95, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Chen, C.; Liu, H.; Lee, T.; Shieh, S. Resveratrol pretreatment attenuates concanavalin A-induced hepatitis through reverse of aberration in the immune response and regenerative capacity in aged mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lai, X.; Pei, Q.; Song, X.; Zhou, X.; Yin, Z.; Jia, R.; Zou, Y.; Li, L.; Yue, G.; Liang, X.; et al. The enhancement of immune function and activation of NF-κB by resveratrol-treatment in immunosuppressive mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 33, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburton, A.; Vasieva, O.; Quinn, P.; Stewart, J.P.; Quinn, J.P. Statistical analysis of human microarray data shows that dietary intervention with n-3 fatty acids, flavonoids and resveratrol enriches for immune response and disease pathways. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 119, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, N.H.; Fu, X.; Zi, F.M.; Song, Y.; Wang, S.; Cheng, J. The potential therapeutic benefit of resveratrol on Th17/Treg imbalance in immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 73, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttari, B.; Profumo, E.; Segoni, L.; D’Arcangelo, D.; Rossi, S.; Facchiano, F.; Saso, L.; Businaro, R.; Iuliano, L.; Rigano, R. Resveratrol counteracts inflammation in human M1 and M2 macrophages upon challenge with 7-oxo-cholesterol: Potential therapeutic implications in atherosclerosis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 257543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliemann, L.; Schmidt, J.F.; Olesen, J.; Bienso, R.S.; Peronard, S.L.; Grandjean, S.U.; Mortensen, S.P.; Nyberg, M.; Bangsbo, J.; Pilegaard, H.; et al. Resveratrol blunts the positive effects of exercise training on cardiovascular health in aged men. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 5047–5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasamsetti, S.B.; Karnewar, S.; Gopoju, R.; Gollavilli, P.N.; Narra, S.R.; Kumar, J.M.; Kotamraju, S. Resveratrol attenuates monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation and associated inflammation via modulation of intracellular GSH homeostasis: Relevance in atherosclerosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 96, 392–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javkhedkar, A.A.; Quiroz, Y.; Rodriguez-Iturbe, B.; Vaziri, N.D.; Lokhandwala, M.F.; Banday, A.A. Resveratrol restored Nrf2 function, reduced renal inflammation, and mitigated hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am. J. Physiol. Reg. I. 2015, 308, R840–R846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prysyazhna, O.; Wolhuter, K.; Switzer, C.; Santos, C.; Yang, X.; Lynham, S.; Shah, A.M.; Eaton, P.; Burgoyne, J.R. Blood pressure-lowering by the antioxidant resveratrol is counterintuitively mediated by oxidation of cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Circulation 2019, 140, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.Y.; Hu, M.M.; Xin, Y.F.; Gang, C. Resveratrol alleviates vascular inflammatory injury by inhibiting inflammasome activation in rats with hypercholesterolemia and vitamin D2 treatment. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 64, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, Y.; Park, J.; Choi, W.; Ju Son, D.; Sung Kim, Y.; Kim, M.; Yoon, B.; Pyee, J.; Tae Hong, J.; Go, Y.; et al. Antiatherogenic effect of resveratrol attributed to decreased expression of ICAM-1 (intercellular adhesion molecule-1). Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernandez-Castillejo, S.; Macia, A.; Motilva, M.J.; Catalan, U.; Sola, R. Endothelial cells deconjugate resveratrol metabolites to free resveratrol: A possible role in tissue factor modulation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1800715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillenburg, D.R.; Mostarda, C.; Moraes-Silva, I.C.; Ferreira, D.; Goncalves Bos, D.D.S.; Machado Duarte, A.A.; Irigoyen, M.C.; Rigatto, K. Resveratrol and grape juice differentially ameliorate cardiovascular autonomic modulation in L-NAME-treated rats. Auton. Neurosci. Basic 2013, 179, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tellone, E.; De Rosa, M.C.; Pirolli, D.; Russo, A.; Giardina, B.; Galtieri, A.; Ficarra, S. Molecular interactions of hemoglobin with resveratrol: Potential protective antioxidant role and metabolic adaptations of the erythrocyte. Biol. Chem. 2014, 395, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee-Chang, C.; Bodogai, M.; Martin-Montalvo, A.; Wejksza, K.; Sanghvi, M.; Moaddel, R.; de Cabo, R.; Biragyn, A. Inhibition of breast cancer metastasis by resveratrol-mediated inactivation of tumor-evoked regulatory B cells. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 4141–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saud, S.M.; Li, W.; Morris, N.L.; Matter, M.S.; Colburn, N.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Young, M.R. Resveratrol prevents tumorigenesis in mouse model of Kras activated sporadic colorectal cancer by suppressing oncogenic Kras expression. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Ma, X.; Li, N.; Liu, H.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yang, C.; Liu, Y.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, S.; et al. Resveratrol inhibits Hexokinases II mediated glycolysis in non-small cell lung cancer via targeting Akt signaling pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 349, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikula-Pietrasik, J.; Sosinska, P.; Ksiazek, K. Resveratrol inhibits ovarian cancer cell adhesion to peritoneal mesothelium in vitro by modulating the production of α5β1 integrins and hyaluronic acid. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 134, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yuan, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Resveratrol significantly inhibits the occurrence and development of cervical cancer by regulating phospholipid scramblase 1. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 120, 1527–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, X.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, X.; He, Q. Potentiation of resveratrol-induced apoptosis by matrine in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 2803–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Xie, Q.; Chen, Z.; Ni, H.; Xia, L.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, Z.; Chen, P. Resveratrol suppresses the invasion and migration of human gastric cancer cells via inhibition of MALAT1-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pezzuto, J.M. Resveratrol: Twenty years of growth, development and controversy. Biomol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basly, J.P.; Marre-Fournier, F.; Bail, J.C.L.; Habrioux, G.; Chulia, A.J. Estrogenic/antiestrogenic and scavenging properties of (E)- and (Z)- resveratrol. Life Sci. 2000, 66, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Kiyozuka, Y.; Uemura, Y.; Senzaki, H.; Shikata, N.; Hioki, K.; Tsubura, A. Resveratrol inhibits human breast cancer cell growth and may mitigate the effect of linoleic acid, a potent breast cancer cell stimulator. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. Suppl. 2001, 127, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkerd, E.; Dowsett, M. Sex hormones and breast cancer risk and prognosis. Breast 2013, 22, S38–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, F. Phytoestrogens in Functional Foods, 1st ed.; CRC Pres: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 210–211. ISBN 9780429113802. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.; Scott, E.; Kholghi, A.; Andreadi, C.; Rufini, A.; Karmokar, A.; Britton, R.G.; Horner-Glister, E.; Greaves, P.; Jawad, D.; et al. Cancer chemoprevention: Evidence of a nonlinear dose response for the protective effects of resveratrol in humans and mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 298ra117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, R. Resveratrol mitigate structural changes and hepatic stellate cell activation in N ′-nitrosodimethylamine-induced liver fibrosis via restraining oxidative damage. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 221, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, R. Proteomic approach to identify molecular signatures during experimental hepatic fibrosis and resveratrol supplementation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanriverdi, G.; Kaya-Dagistanli, F.; Ayla, S.; Demirci, S.; Eser, M.; Unal, Z.S.; Cengiz, M.; Oktar, H. Resveratrol can prevent CCl4-induced liver injury by inhibiting Notch signaling pathway. Histol. Histopathol. 2016, 31, 769–784. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xin, P.; Han, H.; Gao, D.; Cui, W.; Yang, X.; Ying, C.; Sun, X.; Hao, L. Alleviative effects of resveratrol on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease are associated with up regulation of hepatic low density lipoprotein receptor and scavenger receptor class B type I gene expressions in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 52, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Hai, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, H.; Li, K.; Weng, X. Resveratrol modulates autophagy and NF-κB activity in a murine model for treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 63, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Xu, M.; Bai, J.; Wu, S. Resveratrol improves alcoholic fatty liver disease by downregulating HIF-1α expression and mitochondrial ROS production. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e1834268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, L.; Yang, F.; Fang, Z.; Hu, C. Resveratrol ameliorates alcoholic fatty liver by inducing autophagy. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2016, 44, 1207–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajinejad, M.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Omidi, A.; Mortezaee, K.; Nekoonam, S.; Mahmoudi, R.; Kashani, I.R. Resveratrol pretreatment enhanced homing of SDF-1-preconditioned bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model of liver cirrhosis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 2939–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; An, R. Resveratrol and sildenafil synergistically improve diabetes-associated erectile dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Life Sci. 2015, 135, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencoglu, H.; Tuzcu, M.; Hayirli, A.; Sahin, K. Protective effects of resveratrol against streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats by modulation of visfatin/sirtuin-1 pathway and glucose transporters. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 66, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, A.; Feng, X.; Hou, T.; Liu, K.; Liu, B.; Zhang, N. Metformin and resveratrol ameliorate muscle insulin resistance through preventing lipolysis and inflammation in hypoxic adipose tissue. Cell. Signal. 2016, 28, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brawerman, G.M.; Kereliuk, S.M.; Brar, N.; Cole, L.K.; Seshadri, N.; Pereira, T.J.; Xiang, B.; Hunt, K.L.; Fonseca, M.A.; Hatch, G.M.; et al. Maternal resveratrol administration protects against gestational diabetes-induced glucose intolerance and islet dysfunction in the rat offspring. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 4175–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Liu, B.; Wang, K.; Zhou, S.; Li, W.; Xu, Y. Resveratrol ameliorates diabetic vascular inflammation and macrophage infiltration in db/db mice by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2014, 11, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Liu, K.; Huang, F.; Liu, B. Metformin and resveratrol inhibit Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission and prevent ER stress-associated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the adipose tissue of diabetic mice. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 434, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Gao, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Cui, B. Resveratrol ameliorates diabetic nephropathy in rats through negative regulation of the p38 MAPK/TGF-beta1 pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 3223–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nishimura, Y.; Sasagawa, S.; Ariyoshi, M.; Ichikawa, S.; Shimada, Y.; Kawaguchi, K.; Kawase, R.; Yamamoto, R.; Uehara, T.; Yanai, T.; et al. Systems pharmacology of adiposity reveals inhibition of EP300 as a common therapeutic mechanism of caloric restriction and resveratrol for obesity. Front. Pharmcol. 2015, 6, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Sun, J.; Li, L.; Zheng, J.; Shi, Y.; Le, G. Regulatory effects of resveratrol on glucose metabolism and T-lymphocyte subsets in the development of high-fat diet-induced obesity in C57BL/6 mice. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1452–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Lin, K.; Peng, K.; Day, Y.; Hung, L. Resveratrol exerts anti-obesity effects in high-fat diet obese mice and displays differential dosage effects on cytotoxicity, differentiation, and lipolysis in 3T3-L1 cells. Endocr. J. 2016, 63, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parmar, A.; Mula, R.V.R.; Azhar, Y.; Shashidharamurthy, R.; Rayalam, S. Resveratrol increases catecholamine synthesis in macrophages: Implications on obesity. FASEB J. 2016, S1, 301. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, T.; Chen, D.; Yang, Q.; Wang, B.; Zhu, M.; Nathanielsz, P.W.; Du, M. Resveratrol supplementation of high-fat diet-fed pregnant mice promotes brown and beige adipocyte development and prevents obesity in male offspring. J. Physiol. London 2017, 595, 1547–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Chen, K.; Lang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, P.; Ran, L.; Zhou, M.; Zheng, J.; Yi, L.; et al. Resveratrol prevents sarcopenic obesity by reversing mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress via the PKA/LKB1/AMPK pathway. Aging 2019, 11, 2217–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheserek, M.J.; Wu, G.; Li, L.; Li, L.; Karangwa, E.; Shi, Y.; Le, G. Cardioprotective effects of lipoic acid, quercetin and resveratrol on oxidative stress related to thyroid hormone alterations in long-term obesity. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 33, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Jing, X.; Wu, X.; Yan, M. Protective effect of resveratrol on spermatozoa function in male infertility induced by excess weight and obesity. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 4659–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Regitz, C.; Fitzenberger, E.; Mahn, F.L.; Dussling, L.M.; Wenzel, U. Resveratrol reduces amyloid-beta (Aβ1-42)-induced paralysis through targeting proteostasis in an Alzheimer model of Caenorhabditis elegans. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porquet, D.; Grinan-Ferre, C.; Ferrer, I.; Camins, A.; Sanfeliu, C.; Del Valle, J.; Pallas, M. Neuroprotective role of trans-resveratrol in a murine model of familial Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 42, 1209–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corpas, R.; Grinan-Ferre, C.; Rodriguez-Farre, E.; Pallas, M.; Sanfeliu, C. Resveratrol induces brain resilience against Alzheimer neurodegeneration through proteostasis enhancement. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 1502–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, G.; Zheng, D. MicroRNA-214 participates in the neuroprotective effect of resveratrol via inhibiting alpha-synuclein expression in MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease mouse. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 74, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E. Estrogen signaling and cardiovascular disease. Circ. Res. 2011, 109, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosca, L.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Wenger, N.K. Sex/gender differences in cardiovascular disease prevention: What a difference a decade makes. Circulation 2011, 124, 2145–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Louis, X.L.; Raj, P.; Chan, L.; Zieroth, S.; Netticadan, T.; Wigle, J.T. Are the cardioprotective effects of the phytoestrogen resveratrol sex-dependent? Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 97, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soylemez, S.; Gurdal, H.; Sepici, A.; Akar, F. The effect of long-term resveratrol treatment on relaxation to estrogen in aortae from male and female rats: Role of nitric oxide and superoxide. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2008, 49, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Liberto, V.; Makela, J.; Korhonen, L.; Olivieri, M.; Tselykh, T.; Malkia, A.; Do Thi, H.; Belluardo, N.; Lindholm, D.; Mudo, G. Involvement of estrogen receptors in the resveratrol-mediated increase in dopamine transporter in human dopaminergic neurons and in striatum of female mice. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagnerova, A.; Babickova, J.; Liptak, R.; Vlkova, B.; Celec, P.; Gardlik, R. Sex differences in the effect of resveratrol on DSS-induced colitis in mice. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2017, 2017, 8051870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolidou, C.; Adamopoulos, K.; Iliadis, S.; Kourtidou-Papadeli, C. Alterations of antioxidant status in asymptomatic hypercholesterolemic individuals after resveratrol intake. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 67, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansur, A.P.; Roggerio, A.; Goes, M.F.S.; Avakian, S.D.; Leal, D.P.; Maranhao, R.C.; Strunz, C.M.C. Serum concentrations and gene expression of sirtuin 1 in healthy and slightly overweight subjects after caloric restriction or resveratrol supplementation: A randomized trial. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 227, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tome-Carneiro, J.; Gonzalvez, M.; Larrosa, M.; Garcia-Almagro, F.J.; Aviles-Plaza, F.; Parra, S.; Yanez-Gascon, M.J.; Ruiz-Ros, J.A.; Garcia-Conesa, M.T.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A.; et al. Consumption of a grape extract supplement containing resveratrol decreases oxidized LDL and ApoB in patients undergoing primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: A triple-blind, 6-month follow-up, placebo-controlled, randomized trial. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, S.; Gambino, R.; Ponzo, V.; Cioffi, I.; Goitre, I.; Evangelista, A.; Ciccone, G.; Cassader, M.; Procopio, M. Effects of resveratrol on bone health in type 2 diabetic patients. A double-blind randomized-controlled trial. Nutr. Diabetes 2018, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asghari, S.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Somi, M.; Ghavami, S.; Rafraf, M. Comparison of calorie-restricted diet and resveratrol supplementation on anthropometric indices, metabolic parameters, and serum sirtuin-1 levels in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled clinical trial. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2018, 37, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, R.S.; Thomas, R.G.; Craft, S.; van Dyck, C.H.; Mintzer, J.; Reynolds, B.A.; Brewer, J.B.; Rissman, R.A.; Raman, R.; Aisen, P.S. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of resveratrol for Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2015, 85, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantartzis, K.; Fritsche, L.; Bombrich, M.; Machann, J.; Schick, F.; Staiger, H.; Kunz, I.; Schoop, R.; Lehn-Stefan, A.; Heni, M.; et al. Effects of resveratrol supplementation on liver fat content in overweight and insulin-resistant subjects: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 1793–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, M.M.; Vestergaard, P.F.; Clasen, B.F.; Radko, Y.; Christensen, L.P.; Stodkilde-Jorgensen, H.; Moller, N.; Jessen, N.; Pedersen, S.B.; Jorgensen, J.O.L. High-dose resveratrol supplementation in obese men an investigator-initiated, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial of substrate metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and body composition. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thazhath, S.S.; Wu, T.; Bound, M.J.; Checklin, H.L.; Standfield, S.; Jones, K.L.; Horowitz, M.; Rayner, C.K. Administration of resveratrol for 5 wk has no effect on glucagon-like peptide 1 secretion, gastric emptying, or glycemic control in type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Made, S.M.; Plat, J.; Mensink, R.P. Trans.-resveratrol supplementation and endothelial function during the fasting and postprandial phase: A randomized placebo-controlled trial in overweight and slightly obese participants. Nutrients 2017, 9, 5966. [Google Scholar]
- McDermott, M.M.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; Guralnik, J.M.; Tian, L.; Sufit, R.; Zhao, L.; Criqui, M.H.; Kibbe, M.R.; Stein, J.H.; Lloyd-Jones, D.; et al. Effect of resveratrol on walking performance in older people with peripheral artery disease The RESTORE randomized clinical trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2017, 2, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, W.; Qin, W.; Zhang, K.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Chen, Y.; Kliethermes, B.; Sauter, E.R. Trans.-resveratrol alters mammary promoter hypermethylation in women at increased risk for breast cancer. Nutr. Cancer 2012, 64, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Population/Country | Study Name/Type | Sample Size (Valid Data) | Dose and Schedule | Main Findings: Resveratrol vs. Measurements/Risk Factors/Biomarkers | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Swiss/Switzerland | Case-control | N = 971 (all female; case, 369; control, 602) | Tertiles: T1: 0.0–73.0 μg/day T2: 73.1–160.7 μg/day T3: >160.7 μg/day (food-frequency questionnaire, FFQ, on weekly frequency, 2 years prior) | Favorable: Inversely associated with breast cancer risk (OR (95% CI): T2 vs. T1, 0.64 (0.44–0.93); T3 vs. T1, 0.55 (0.39–0.76)) | [17] |
| Iranian (Tehranian)/Iran | Cross-sectional study, part of the TLG study | N = 2618 (male, 1162; female, 1456) | Quartiles: Q1: 0.014 mg/day Q2: 0.015–0.027 mg/day Q3: 0.028–0.053 mg/day Q4: 0.054 mg/day (FFQ on a daily frequency, 1 year prior) | Null: Significantly associated with WC, TG, HDL, BG, and MS Unfavorable: The top quantile of intake (0.054 mg/day and more) was positively associated with high BP (HR = 1.52; 95% CI: 1.02–2.27) | [19] |
| Spanish/Spain | Cross-sectional study, part of the PREDIMED study | N = 1000 (male, 479; female, 521) | Quintiles: Q1: 0.48 mg/day Q2: 1.04 mg/day Q3: 2.04 mg/day Q4: 5.75 mg/day (FFQ, 1 year prior) | Favorable: Significantly decreased CVD risk factors (FBG (95% CI: −1.033 to −0.033); TG (95% CI: −1.998 to −0.029); and heart rate (95% CI: −0.467 to −0.087)). Null: Resveratrol intake was not significantly associated with TC, HDL, LDL and BP | [6] |
| Spanish/Spain | Cross-sectional study, part of the PREDIMED study | N = 7172 (male, 3249; female, 3923) | Quintiles: Q1: 0.48 mg/d Q2: 1.04 mg/d Q3: 2.04 mg/day Q4: 5.75 mg/day (FFQ, 1 year prior) | Favorable: High dose intake (5.75 mg/d) significantly reduced all-cause mortality by 52% (HR = 0.48; 95% CI: 0.25–0.91) Null: No significant CVD risk reduction (HR = 0.77; 95% CI: 0.35–1.72) | [21,22] |
| Swedish/Sweden | Case-control study | N = 1400 (case, 594 including (OAC, 181; OSCC, 158; JAC, 255)) (control, 806) | Control: 0.1 mg/day OAC: 0.07 mg/day OSCC: 0.11 mg/day JAC: 0.09 mg/day (FFQ, 20 years prior) | Favorable: In a significantly negative association with the risk of 3 subtypes of esophageal cancer (OAC (95% CI: 0.12–0.49); OSCC (95% CI: 0.15–0.65), and JAC (95% CI: 0.28–0.84)) | [5] |
| Italian/Italy | Cohort study, “Aging in the Chianti Region” | N = 529 (male, 236; female, 293) | Tertiles: T1: 0.1 mg/day T2: 0.1–1.1 mg/day T3: >1.1 mg/day (FFQ) | Favorable: Inversely associated with the risk of frailty syndrome during the first 3-year follow-up (T3 vs. T1: OR = 0.11; 95% CI: 0.03–0.45) Null: No substantial association with (i) risk of frailty syndrome in 6-, or 9-year follow-up; (ii) inflammatory biomarkers including IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, and CRP; (iii) CVD, cancer or all-cause mortality | [18] |
| Chinese/China | Cross-sectional study, | N = 1393 (male, 446; female, 947) | Mean: 0.15 mg/d (FFQ, 1 year prior) | Null: Not significantly associated with CVD risk factors including BP, BG, lipid profiles (TC, TG, HDL, and LDL), and carotid IMT | [23] |
| Population | Targeting Diseases | Study Type | Sample Size (Valid Data) | Resveratrol Dose and Duration | Main Findings: Resveratrol vs. Measurements/Risk Factors/Biomarkers | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy and slightly overweight | CVD—atherosclerosis | Randomized, parallel | N = 48 (male, 24; female, 24) | Resveratrol supplement, 500 mg/day (30 days) | Favorable: Increased serum SIRT1 concentrations from 1.06 ± 0.71 to 5.75 ± 2.98 ng/mL, p < 0.0001 Null: Did not influence the various metabolic parameters (BW, BMI, WC, HR, BP, HDL, LDL, TG, BG, estradiol, estrone, insulin, hsCRP, and TAC) Unfavorable: Increased TC, ApoB, and HOMA-IR score | [114] |
| Asymptomatic hypercholesterolemics (AHCs) and normohypercholemics (NC) | CVD—atherogenesis | Randomized, placebo-controlled | N = 40 (male, 21; female, 19) | Resveratrol supplement, 150 mg/day (4 weeks) | Favorable: Increased TAC (mean value increased to 136.7% after consumption, p = 0.035) in healthy NC individuals and facilitated an increase in vitamin E (7.18 μmol/l, i.e., 35.72%) in AHC Null: No differences found in TC, TG, HDL, LDL, TAC (in AHC), and vitamin E (in NC) | [113] |
| Overweight and slightly obese volunteers | CVD—endothelial function | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | N = 45 (male, 25; female, 20) | Trans-resveratrol supplement,150 mg/day (4 weeks) | Null: Did not improve endothelial function (FMD, arterial stiffness, and other endothelial activation markers), inflammation (IL-6 and TNF-α), glucose and lipid metabolism (BG, insulin, and serum TG) | [122] |
| 65 years or older with peripheral artery disease (PAD) | CVD—PAD | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | N = 66 (male, 45; female, 21) | Trans-resveratrol supplement,125 and 500 mg/day (6 months) | Favorable: 125 mg/day improved the outcome of 6-min walk test results statistically significant (95% CI: −5.7 to 39.5) but not clinically meaningful Null: 500 mg/day showed no significant improvement | [123] |
| Patients in primary cardiovascular disease prevention | CVD—atherogenesis | Triple-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled | N = 75 (male, 34; female, 41) | Resveratrol-enriched grape extract, 350 mg/day (6 months) | Favorable: Decreased LDL-C (−4.5%, p = 0.04), ApoB (−9.8%, p = 0.014), oxidized LDL (−20%, p = 0.001), and oxidized LDL/ApoB (−12.5%, p = 0.000); increased ratio non-HDL-C/ApoB (8.5%, p = 0.046) Null: No clinically significant effects on hepatic, thyroid, and renal function (GGT, AST, ALP, bilirubin and albumin; TSH, T4; CPK, creatinine, and urate) | [115] |
| Healthy aged men | CVD | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | N = 27 (male) | Trans-resveratrol supplement, 250 mg/day (8 weeks) | Null: No effects on SIRT1 protein concentrations or cardiovascular parameters (BG, TC, and HDL), and VCAM-1 Unfavorable: Abolished the exercise training-induced improvement in maximal oxygen uptake, BP, and lipids (LDL, TC/HDL ratio, and TG) | [58] |
| Women at increased breast cancer risk | Cancer—breast cancer | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | N = 39 (male) | Trans-resveratrol supplement, 10 or 100 mg/day (12 weeks) | Favorable: Decreased the methylation of RASSF-1α (p = 0.047) Null: Did not significantly alter PGE2 | [124] |
| Patients with type-2 diabetes | Type 2 diabetes | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | N = 192 (male, 126; female, 66) | Resveratrol supplement, 40 and 500 mg/day (6 months) | Favorable: Prevented bone density loss (500 mg/d) (whole-body BMD (0.01 vs. −0.03 g/cm2, p = 0.001), whole-body BMC (4.04 vs. −58.8 g, p < 0.001), whole-body T-score (0.15 vs. −0.26), and serum phosphorus (0.07 vs. −0.01 μmol/L, p = 0.002)); decreased CRP (not significantly) Null: BW, BMI, WC, BP, FBG, HbA1c, insulin, HOMA-IR, C-peptide, FFAs, ALT, AST, GGT, uric acid, IL-6, and adiponectin Unfavorable: Slightly increased TC and TG (500 mg/d) | [116] |
| Patients with diet-controlled type-2 diabetes | Type 2 diabetes | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | N = 14 (male) | Resveratrol capsules, 1000 mg/day (5 weeks) | Favorable: Modestly decreased FBG and HbA1c Null: No significant effects on GLP-1 secretion, gastric emptying, glycemic control (HbA1c, BG), energy intake, and BW | [121] |
| Obese men | Obesity | Randomized, placebo-controlled | N = 24 (male) | Trans-resveratrol tablets, 500 mg/day (4 weeks) | Null: Did not improve insulin sensitivity, BP, BG, insulin, HOMA-IR, HbA1c, lipids (TC, HDL-C, LDL-C and TG), liver and skeletal muscle lipid content, or inflammatory biomarkers (IL-6, TNF-α, and MCP1) and some metabolic markers Unfavorable: Insignificantly deteriorated insulin sensitivity | [120] |
| Overweight/obese with insulin-resistance subjects | Obesity | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | N = 108 (male, 54; female, 54) | Resveratrol supplement, 150 mg/day (12 weeks) | Null: Did not significantly impact liver fat content or cardiometabolic risk biomarkers (FBG, HbA1c, BP, TC, HDL, LDL, TG, AST, ALT, GGT, hsCRP, and IL-6) | [119] |
| Overweight/obese with NAFLD | Obesity—NAFLD | Randomized, placebo-controlled | N = 75 (male, 52; female, 23) | Resveratrol capsules, 600 mg/day (12 weeks) | Favorable: Significantly reduced BW (95% CI: −1.61 to −0.38) and BMI (95% CI: −0.54 to −0.12) Null: Did not significantly change ALT, AST, and lipid profiles (TG, TC, LDL-C, HDL-C), hepatic steatosis grade (ALT and AST), serum glycemic parameters (FBG, insulin, and HbA1c), and SIRT1 levels | [117] |
| Obese men | Obesity—bone health | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | N = 66 (male) | Trans-resveratrol tablets, 1000 or 150 mg/day, (16 weeks) | Favorable: Dose-dependently benefited bone by stimulating formation or mineralization as significantly increased BAP (R = 0.471, p < 0.001), and BMD (BAP and lumbar spine volumetric BMD were positively correlated: R = 0.281, p = 0.027) | [16] |
| Individuals with mild/moderate Alzheimer disease (AD) | Aging—AD | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | N = 119 (male, 51; female, 68) | Resveratrol supplement, 500–2000 mg/day (52 weeks) | Uncertain: Resveratrol and its major metabolites were detectable in plasma and CSF, suggesting CNS effects; CSF Aβ40 and plasma Aβ40 levels declined less than those in the placebo group; brain volume loss was more compared to placebo Null: No effects on plasma Aβ42, CSF Aβ42, CSF tau, CSF phospho-tau 181, hippocampal volume, entorhinal cortex thickness, MMSE, CDR, ADAS-cog, NPI, or glucose and insulin metabolism Unfavorable: The most common adverse events were nausea and diarrhea, but similar to placebo | [118] |
| Elderly participants | Aging—memory | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | N = 53 (male, 25; female, 28) | Resveratrol pills, 200 mg/day, (26 weeks) | Favorable: Non-significant trend for stable performance in a pattern recognition task Null: No significant changes in CVLT performance, HbA1c levels, hippocampus volume, microstructure, and functional connectivity Unfavorable: Increased serum cholesterol, weight, body fat, FBG, and inflammatory markers; decreased physical activity and neurotrophic factors Adverse events: Two dropouts (a sudden decrease in eyesight and a skin rash), and others (case no.): Diarrhea (n = 3), skin changes (n = 3), stomach aches (n = 1), dizziness (n = 1), improved mood changes (n = 1), loss of hair (n = 1) | [15] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, C.-N.; Gan, R.-Y.; Li, H.-B. Health Benefits and Molecular Mechanisms of Resveratrol: A Narrative Review. Foods 2020, 9, 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9030340
Meng X, Zhou J, Zhao C-N, Gan R-Y, Li H-B. Health Benefits and Molecular Mechanisms of Resveratrol: A Narrative Review. Foods. 2020; 9(3):340. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9030340
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Xiao, Jing Zhou, Cai-Ning Zhao, Ren-You Gan, and Hua-Bin Li. 2020. "Health Benefits and Molecular Mechanisms of Resveratrol: A Narrative Review" Foods 9, no. 3: 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9030340
APA StyleMeng, X., Zhou, J., Zhao, C.-N., Gan, R.-Y., & Li, H.-B. (2020). Health Benefits and Molecular Mechanisms of Resveratrol: A Narrative Review. Foods, 9(3), 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9030340






