Influence of Adding Chinese Yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) Flour on Dough Rheology, Gluten Structure, Baking Performance, and Antioxidant Properties of Bread
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Dough Preparation and Laboratory Bread Making Method
2.3. Dough Properties
2.3.1. Farinograph and Extensibility
2.3.2. Texture Properties
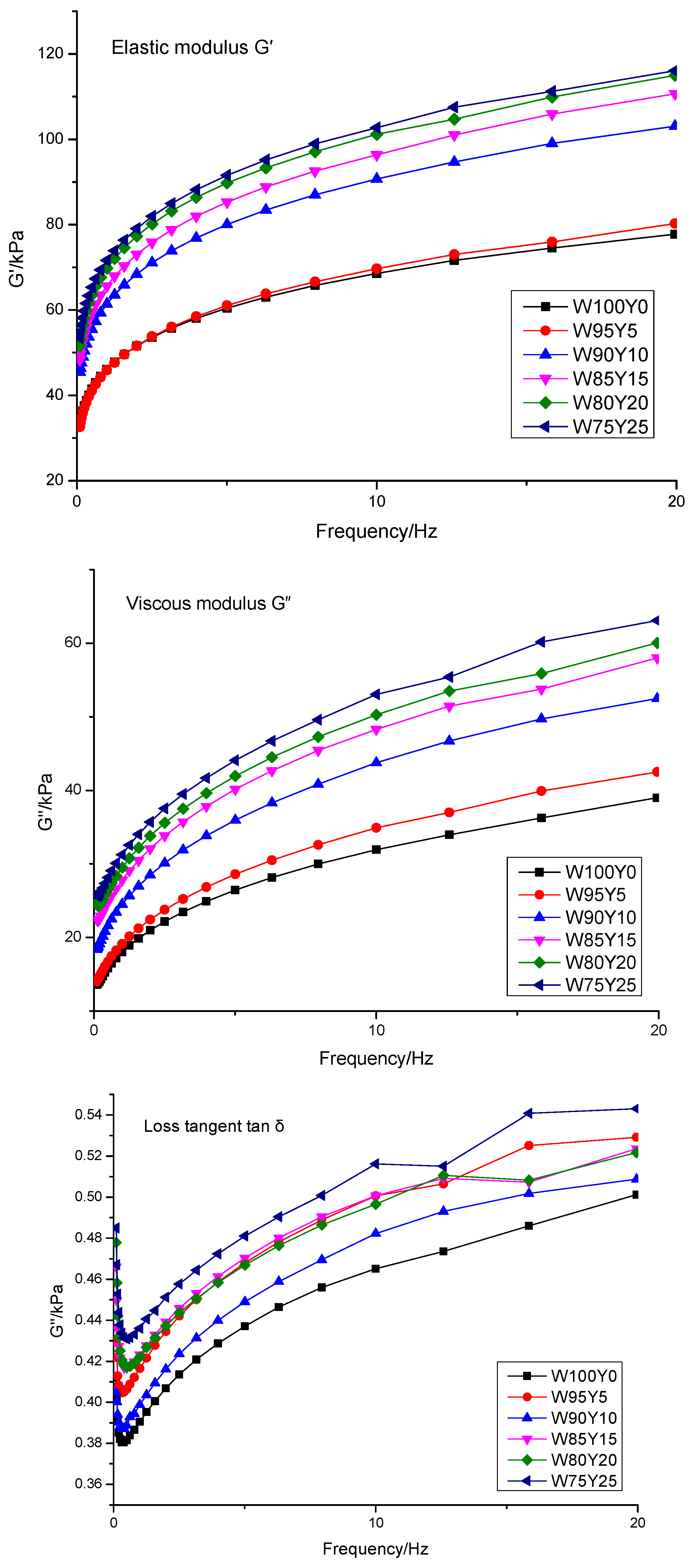
2.3.3. Rheological Analysis
2.3.4. Pasting Properties
2.4. Structure Analysis of Dough and Gluten
2.4.1. Drying of Dough and Gluten
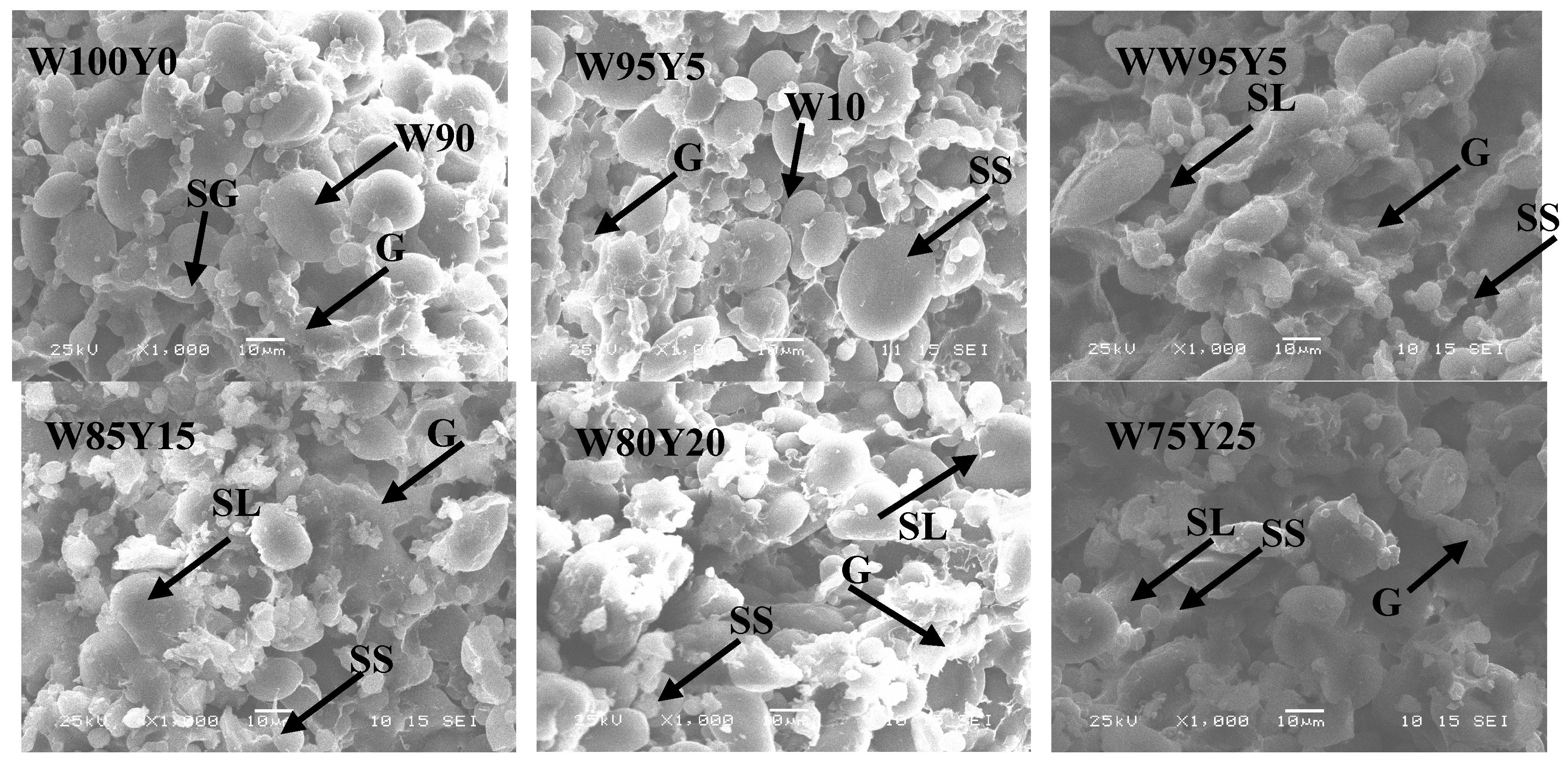
2.4.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
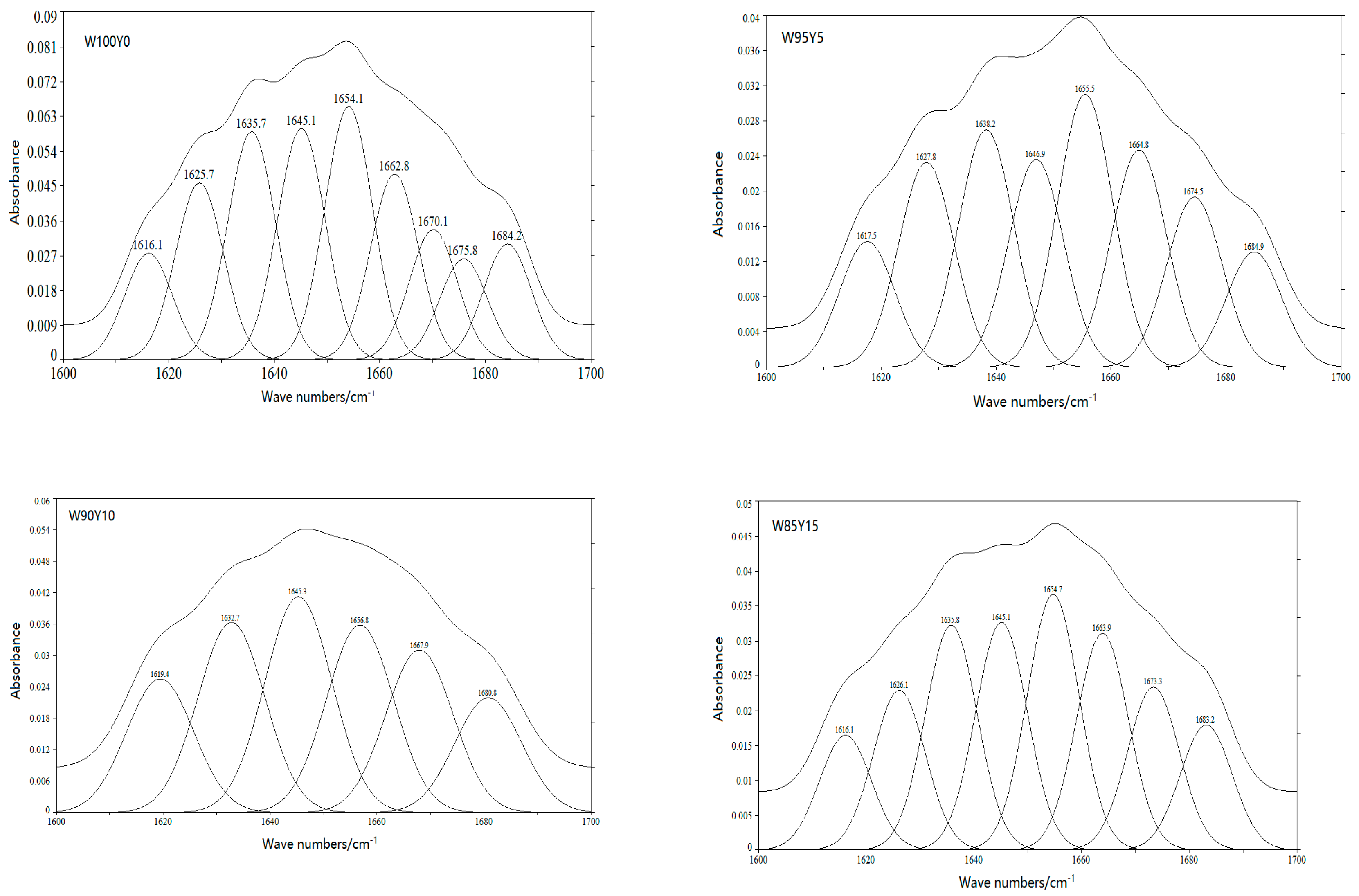
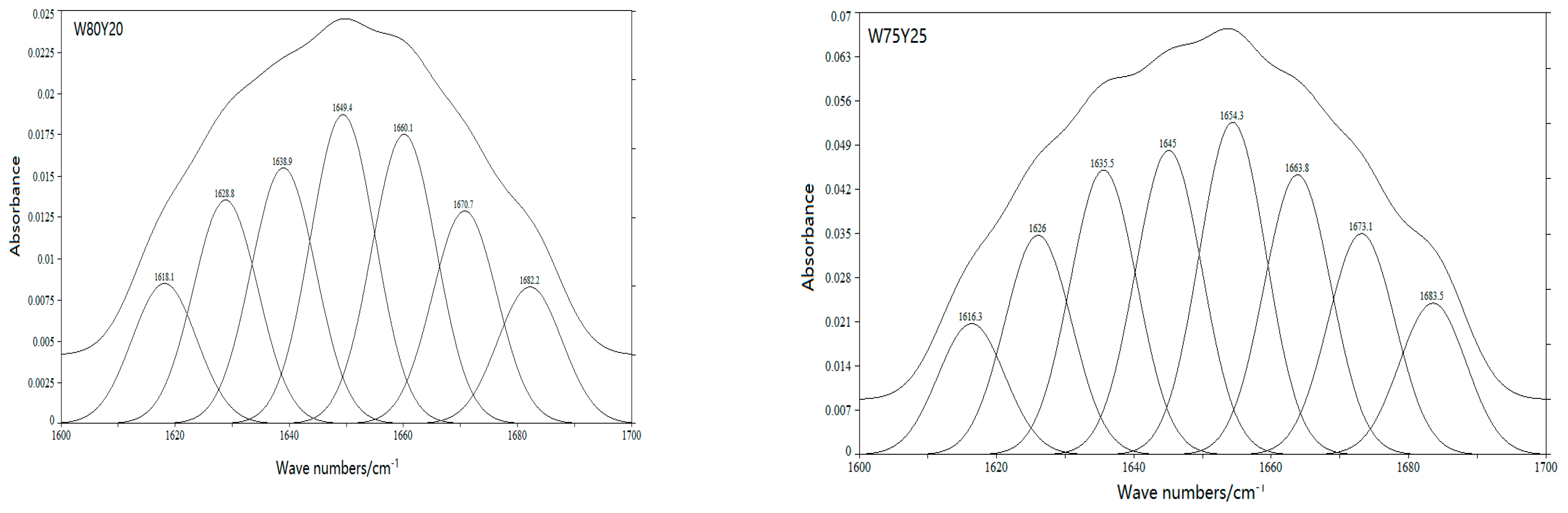
2.4.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.5. Evaluation of Bread Quality
2.5.1. Bread Image Analysis
2.5.2. Specific Volume (SV)
2.5.3. Crumb Texture
2.5.4. Antioxidant Property
2.5.5. Sensory Evaluation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Yam Flour Substitution on Pasting, Farinograph, Rheological, and Texture Properties of Dough
3.2. Effect of Yam Flour on the Secondary Structure of Gluten Protein
3.3. Effect of Yam Flour on Antioxidant Capacity of Bread
3.4. Digital Images of Dough and Gluten
3.5. Effect of Yam Flour on Bread Baking Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hsu, C.L.; Chen, W.; Weng, Y.M.; Tseng, C.Y. Chemical composition, physical properties, and antioxidant activities of yam flours as affected by different drying methods. Food Chem. 2003, 83, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinwande, B.A.; Abiodun, O.A.; Adeyemi, I.A. Effect of steaming on properties of yam flour. Nutr. Food Sci. 2013, 43, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.-H.; Huang, C.-C.; Yang, M.-Y.; Wang, C.-C.R. Textural and sensory properties of salted noodles containing purple yam flour. Food Res. Int. 2012, 47, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djeukeu, W.A.; Gouado, I.; Leng, M.S.; Vijaykrishnaraj, M.; Prabhasankar, P. Effect of dried yam flour (Dioscorea schimperiana) on cooking quality, digestibility profile and antioxidant potential of wheat based pasta. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2017, 11, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amandikwa, C.; Iwe, M.O.; Uzomah, A.; Olawuni, A.I. Physico-chemical properties of wheat-yam flour composite bread. Niger. Food J. 2015, 33, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.L.; Hurang, S.L.; Chen, W.; Weng, Y.M.; Tseng, C.Y. Qualities and antioxidant properties of bread as affected by the incorporation of yam flour in the formulation. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 39, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nindjin, C.; Amani, G.N.; Sindic, M. Effect of blend levels on composite wheat doughs performance made from yam and cassava native starches and bread quality. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eke-Ejiofor, J.; Deedam, J.N.; Beleya, E.A. Effect of Addition of Three Leaf Yam Flour on Dough Properties and Sensory Qualities of Bread. J. Food Res. 2015, 4, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.S.; Deng, J.S.; Chang, H.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Lee, M.M.; Hou, W.C.; Lee, C.Y.; Huang, S.S.; Huang, G.J. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of Taiwanese yam (Dioscorea japonica Thunb. var. pseudojaponica (Hayata) Yamam.) and its reference compounds. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.C.; Ferng, L.H.A.; Huang, P.Y. Quantitative analysis of allantoin and allantoic acid in yam tuber, mucilage, skin and bulbil of the Dioscorea species. Food Chem. 2006, 94, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lu, K.; Yu, J.; Copeland, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, S. Effect of purple yam flour substitution for wheat flour on in vitro starch digestibility of wheat bread. Food Chem. 2019, 284, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Ehmke, L.; Sharma, C.; Miller, R.; Faa, P.; Smith, G.; Li, Y. Physicochemical properties and gluten structures of hard wheat flour doughs as affected by salt. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Shu, Q.; Xia, L.; Li, Y.; Su, X.; Wang, F.; Xiong, X.; Wei, B. Comparative Analysis of Physicochemical Properties from Yam Flours of Six Varieties (in Chinese). Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, K.A.; Barry-Ryan, C.; Burke, R.; McCarthy, S.; Gallagher, E. Dough properties and baking characteristics of white bread, as affected by addition of raw, germinated and toasted pea flour. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 56, 102189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna Kumar, R.; Bejkar, M.; Du, S.; Serventi, L. Flax and wattle seed powders enhance volume and softness of gluten-free bread. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2019, 25, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozer, N.; Cicerelli, L.; Heiniö, R.-L.; Poutanen, K. Effect of wheat bran addition on in vitro starch digestibility, physico-mechanical and sensory properties of biscuits. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 60, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuhumury, H.C.D.; Small, D.M.; Day, L. The effect of sodium chloride on gluten network formation and rheology. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 60, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivam, A.S.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Perera, C.O.; Waterhouse, G.I.N. Application of FT-IR and Raman spectroscopy for the study of biopolymers in breads fortified with fibre and polyphenols. Food Res. Int. 2013, 50, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Tay, S.L.; Koh, A.H.S.; Zhou, W. Dough and bread made from high- and low-protein flours by vacuum mixing: Part 2. Yeast activity, dough proofing and bread quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 77, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrera-Rebollo, R.R.; Salgado-Cruz, M.d.l.P.; Chanona-Pérez, J.; Gutiérrez-López, G.F.; Alamilla-Beltrán, L.; Calderón-Domínguez, G. Evaluation of Image Analysis Tools for Characterization of Sweet Bread Crumb Structure. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2011, 5, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graça, C.; Fradinho, P.; Sousa, I.; Raymundo, A. Impact of Chlorella vulgaris on the rheology of wheat flour dough and bread texture. LWT 2018, 89, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, X.; Mao, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, T.; Qu, Z.; Miao, J.; Gao, W. Effects of drying processes on starch-related physicochemical properties, bioactive components and antioxidant properties of yam flours. Food Chem. 2017, 224, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, P. Purification and structural characterization of Chinese yam polysaccharide and its activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 117, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Sun, J. Physicochemical and sensory properties of steamed bread fortified with purple sweet potato flour. Food Biosci. 2019, 30, 100411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julianti, E.; Rusmarilin, H.; Ridwansyah; Yusraini, E. Functional and rheological properties of composite flour from sweet potato, maize, soybean and xanthan gum. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2017, 16, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pycia, K.; Jaworska, G.; Telega, J.; Sudoł, I.; Kuźniar, P. Effect of adding potato maltodextrins on baking properties of triticale flour and quality of bread. LWT 2018, 96, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-l.; Mu, T.-h.; Sun, H.-n.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.-w. Influence of potato flour on dough rheological properties and quality of steamed bread. J. Integr. Agr. 2016, 15, 2666–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Li, Y.; Ding, S.; Yang, J. Characterization of textural, rheological, thermal, microstructural, and water mobility in wheat flour dough and bread affected by trehalose. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belghith Fendri, L.; Chaari, F.; Maaloul, M.; Kallel, F.; Abdelkafi, L.; Ellouz Chaabouni, S.; Ghribi-Aydi, D. Wheat bread enrichment by pea and broad bean pods fibers: Effect on dough rheology and bread quality. LWT 2016, 73, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Guo, P.; Dong, S.; Li, H. Effect of wheat flour substitution with potato pulp on dough rheology, the quality of steamed bread and in vitro starch digestibility. LWT 2019, 111, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestra, F.; Cocci, E.; Pinnavaia, G.; Romani, S. Evaluation of antioxidant, rheological and sensorial properties of wheat flour dough and bread containing ginger powder. LWT 2011, 44, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Kun, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, G.; Xianfeng, D. Physicochemical properties of soya bean protein gel prepared by microbial transglutaminase in the presence of okara. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 2402–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Li, B.; Tian, J. Impact of Punicalagin on the Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Wheat Flour Dough. Foods 2019, 8, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, E.G.; Gomez, A.V.; Anon, M.C.; Puppo, M.C. Structural changes in gluten protein structure after addition of emulsifier. A Raman spectroscopy study. Spectrochim Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 79, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, H.; Kitts, D.D. Comparison of the antioxidative and cytotoxic properties of glucose-lysine and fructose-lysine Maillard reaction products. Food Res. Int. 2000, 33, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Ma, S.; Li, L.; Zheng, X.; Wang, X. Impact of wheat bran dietary fiber on gluten and gluten-starch microstructure formation in dough. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 95, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burešová, I.; Tokár, M.; Mareček, J.; Hřivna, L.; Faměra, O.; Šottníková, V. The comparison of the effect of added amaranth, buckwheat, chickpea, corn, millet and quinoa flour on rice dough rheological characteristics, textural and sensory quality of bread. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 75, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinma, C.E.; Anuonye, J.C.; Ocheme, O.B.; Abdullahi, S.; Oni, S.; Yakubu, C.M.; Azeez, S.O. Effect of acha and bambara nut sourdough flour addition on the quality of bread. LWT 2016, 70, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, M.J.; Kwak, H.S.; Kim, S.S. Characteristics of Bread Made of Various Substitution Ratios of Bran Pulverized by Hammer Mill or Jet Mill. Foods 2020, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packkia-Doss, P.P.; Chevallier, S.; Pare, A.; Le-Bail, A. Effect of supplementation of wheat bran on dough aeration and final bread volume. J. Food Eng. 2019, 252, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

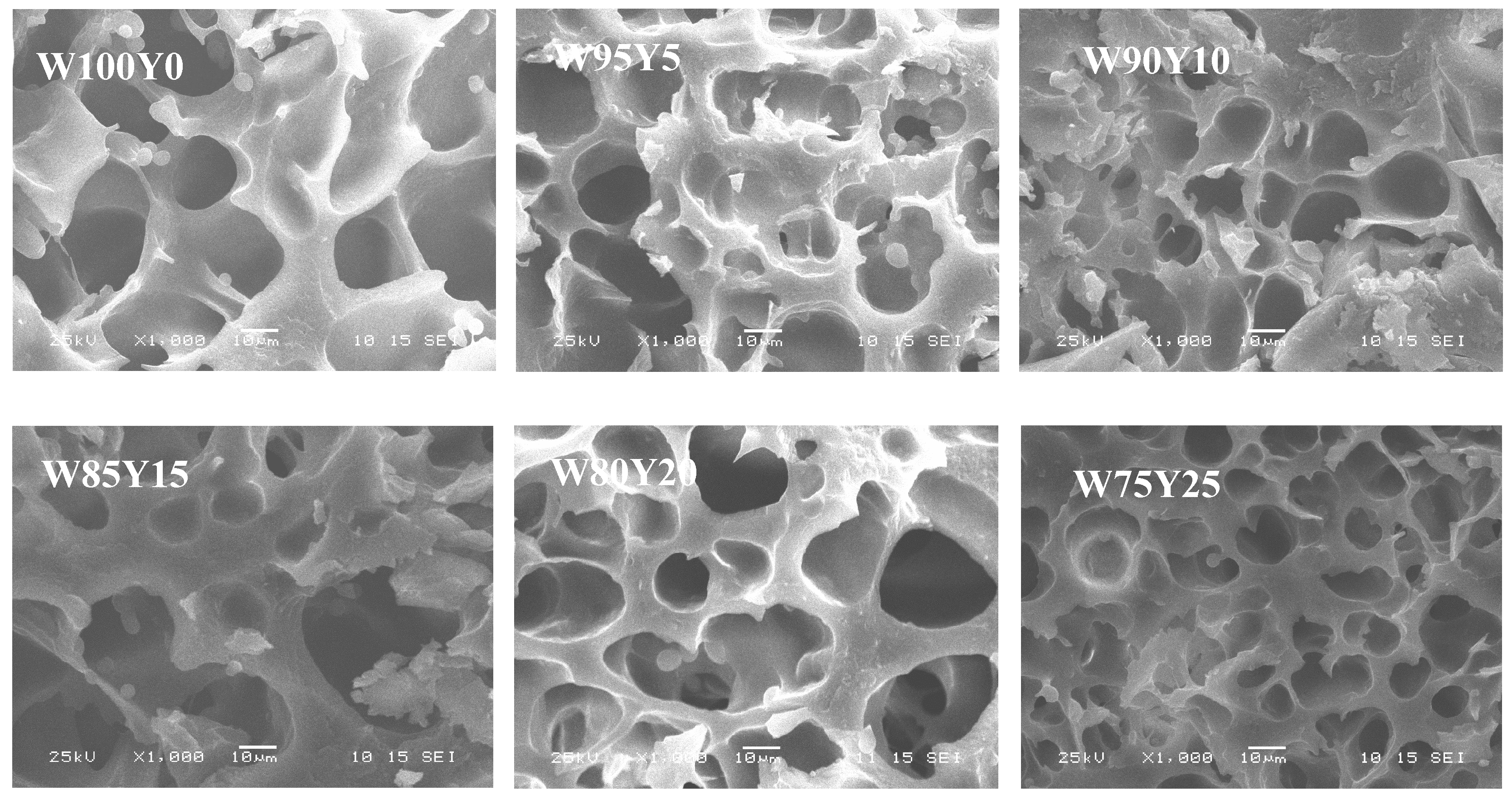
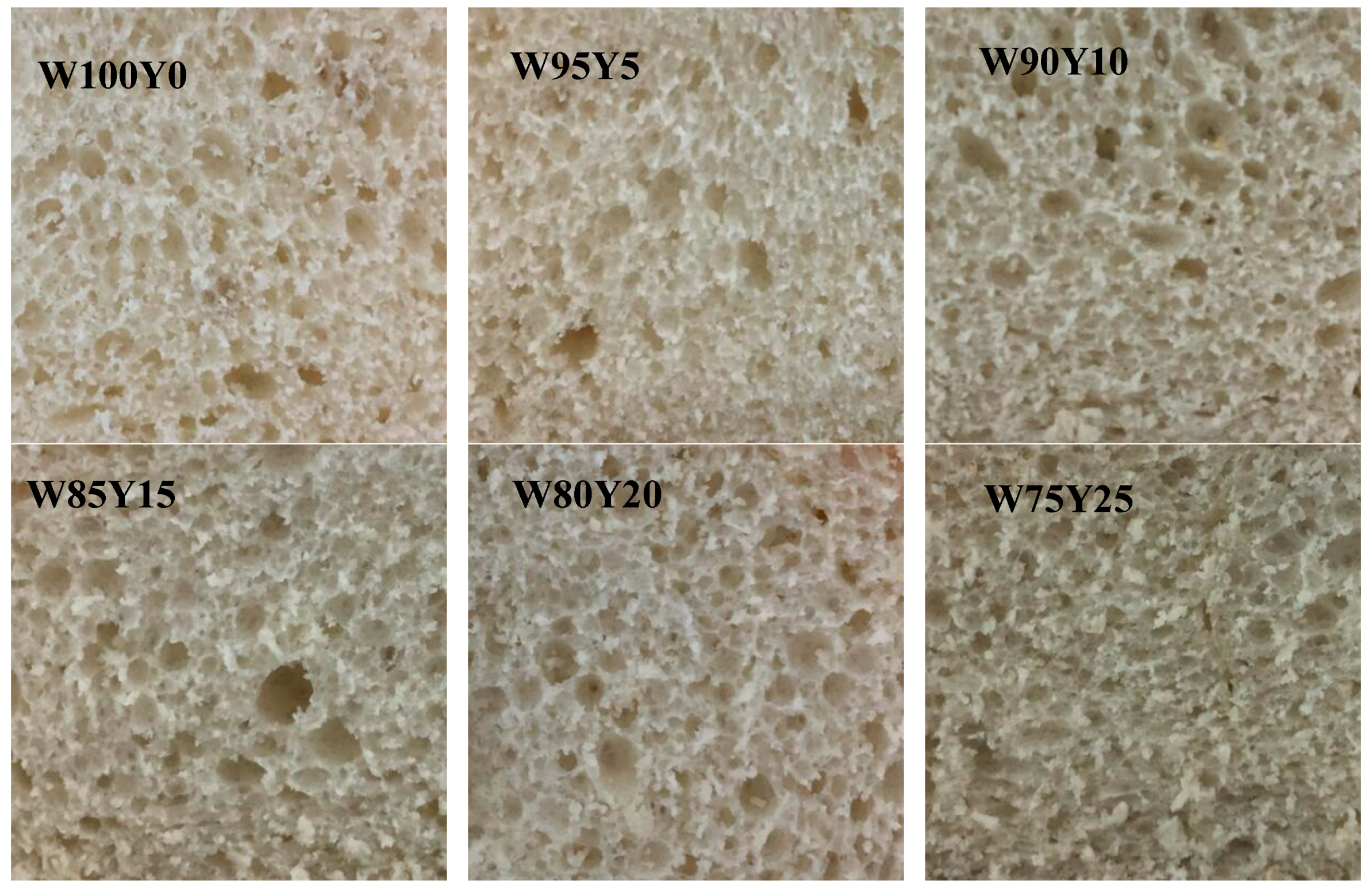
| Item | W100Y0 | W95Y5 | W90Y10 | W85Y15 | W80Y20 | W75Y25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pasting temperature (°C) | 69.10 ± 0.05b | 70.02 ± 0.88ab | 69.97 ± 0.88ab | 69.42 ± 0.51b | 70.02 ± 0.80ab | 71.12 ± 1.0a |
| Peak time (min) | 6.60 ± 0.07a | 5.93 ± 0.07b | 5.58 ± 0.08c | 5.38 ± 0.04d | 5.31 ± 0.03d | 5.02 ± 0.02e |
| Peak viscosity (cP) | 2275 ± 52.92a | 1441 ± 6.66b | 1271 ± 18.33c | 1285 ± 7.00c | 1232 ± 2.31d | 1285 ± 9.54c |
| Trough viscosity (cP) | 1540 ± 52.92a | 629 ± 9.45b | 440 ± 13.53c | 391 ± 13.23d | 355 ± 1.73d | 350 ± 5.51d |
| Final viscosity (cP) | 2737 ± 54.60a | 1488 ± 9.02b | 1068 ± 12.17c | 911 ± 23.12d | 791 ± 10.02e | 745 ± 25.51e |
| Setback (cP) | 1198 ± 15.56a | 859 ± 17.44b | 628 ± 5.00c | 520 ± 10.69d | 436 ± 9.61e | 395 ± 20.30f |
| Breakdown (cP) | 736 ± 43.50e | 811 ± 7.51d | 831 ± 25.51c | 894 ± 9.17b | 877 ± 0.58b | 935 ± 8.08a |
| Water absorption (%) | 63.4 ± 0.00d | 63.6 ± 0.06c | 64.5 ± 0.10b | 65.4 ± 0.06a | 65.5 ± 0.10a | 65.4 ± 0.10a |
| Dough development time (min) | 2.9 ± 0.06a | 2.2 ± 0.06b | 1.9 ± 0.10c | 1.7 ± 0.00d | 1.7 ± 0.06d | 1.7 ± 0.06d |
| Dough stability (min) | 18.1 ± 0.20a | 15.3 ± 0.35b | 15.0 ± 0.20b | 1.5 ± 0.06c | 1.5 ± 0.10c | 1.5 ± 0.06c |
| Degree of softening (FU) | 22 ± 0.58e | 35 ± 1.53d | 44 ± 2.52c | 86 ± 2.65a | 76 ± 3.06b | 88 ± 2.00a |
| Area under the curve (energy, cm2) | 114 ± 4.58a | 82 ± 3.06c | 93 ± 4.00b | 68 ± 1.00d | 66 ± 4.16d | 58 ± 2.52e |
| Extensibility (mm) | 108 ± 5.03a | 89 ± 5.69b | 105 ± 6.11a | 83 ± 3.78bc | 80 ± 4.51bc | 76 ± 2.00c |
| Resistance to extension (EU) | 878 ± 20.52a | 843 ± 25.36a | 831 ± 30.62a | 736 ± 31.90b | 713 ± 22.05b | 634 ± 44.96c |
| Max-extensible resistance (EU) | 944 ± 46.52a | 858 ± 28.10b | 844 ± 23.90b | 737 ± 15.52c | 733 ± 14.53c | 658 ± 31.97d |
| Extensible rate | 8.16 ± 0.35bc | 9.53 ± 0.57a | 7.90 ± 0.18c | 8.91 ± 0.25ab | 8.90 ± 0.64ab | 8.35 ± 0.48bc |
| Max-extensible rate | 8.77 ± 0.38ab | 9.69 ± 0.30a | 8.04 ± 0.68b | 8.93 ± 0.58ab | 9.15 ± 0.69a | 8.67 ± 0.60ab |
| Sample | Hardness (g) | Adhesiveness (g·s) | Chewiness (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| W100Y0 | 4891.46 ± 282.38c | 5129.16 ± 398.46d | 3932.19 ± 226.28c |
| W95Y5 | 3919.22 ± 157.88d | 5328.83 ± 242.85d | 3121.39 ± 193.17d |
| W90Y10 | 5084.16 ± 121.99c | 5016.86 ± 301.85d | 4031.96 ± 144.53c |
| W85Y15 | 5712.79 ± 475.73b | 5709.71 ± 86.72c | 4543.46 ± 318.80b |
| W80Y20 | 6722.81 ± 334.47a | 7440.66 ± 351.81a | 5551.42 ± 239.90a |
| W75Y25 | 5537.48 ± 178.36b | 6356.22 ± 246.05b | 4622.98 ± 189.89b |
| Sample | Relative Proportion (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-Helix | β-Sheet | β-Turn | Random Coil | |
| W100Y0 | 32.24 | 41.02 | 6.61 | 15.13 |
| W95Y5 | 30.98 | 28.75 | 24.97 | 15.30 |
| W90Y10 | 18.67 | 32.34 | 27.61 | 21.48 |
| W85Y15 | 31.75 | 41.98 | 10.96 | 15.31 |
| W80Y20 | 38.18 | 31.93 | 13.57 | 16.32 |
| W75Y25 | 31.82 | 40.88 | 11.49 | 15.81 |
| Sample | Total Phenolics Content (mg GE/g) | Polysaccharides Content (mg/g) | Total Flavonoids Content (mg RE/g) | Allantoin Content (mg/g) | IC50Value (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W100Y0 | 0.467 ± 0.002d | 21.18 ± 0.14f | 0.162 ± 0.004e | 0.05 ± 0.011f | 124.14 ± 1.62a |
| W95Y5 | 0.470 ± 0.002cd | 22.45 ± 0.06e | 0.268 ± 0.006d | 0.279 ± 0.006e | 130.09 ± 1.44a |
| W90Y10 | 0.471 ± 0.002cd | 25.04 ± 0.11d | 0.378 ± 0.008c | 0.459 ± 0.066d | 117.36 ± 0.82b |
| W85Y15 | 0.480 ± 0.003b | 27.65 ± 0.04c | 0.475 ± 0.003b | 0.781 ± 0.012c | 113.37 ± 0.47c |
| W80Y20 | 0.481 ± 0.002b | 29.67 ± 0.09b | 0.525 ± 0.015a | 0.894 ± 0.004b | 102.98 ± 0.95d |
| W75Y25 | 0.491 ± 0.002a | 31.52 ± 0.07a | 0.516 ± 0.009a | 1.063 ± 0.001a | 101.36 ± 0.95d |
| Sample | Fractal Dimension | Hardness (g) | Springiness | Cohesiveness | Chewiness (g) | Specific Volume (mL/g) | Overall Acceptability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W100Y0 | 1.71 ± 0.01c | 472.32 ± 29.31de | 0.639 ± 0.035a | 0.567 ± 0.008a | 170.90 ± 10.09b | 4.47 ± 0.02a | 98.0 ± 0.67a |
| W95Y5 | 1.72 ± 0.01c | 422.87 ± 15.41e | 0.618 ± 0.012ab | 0.541 ± 0.019b | 141.53 ± 12.37c | 4.26 ± 0.06b | 96.7 ± 1.64a |
| W90Y10 | 1.74 ± 0.01b | 486.52 ± 23.30cd | 0.590 ± 0.020bc | 0.521 ± 0.010bc | 149.41 ± 9.75c | 4.06 ± 0.04c | 92.2 ± 1.26b |
| W85Y15 | 1.75 ± 0.00b | 530.83 ± 33.63bc | 0.580 ± 0.005c | 0.505 ± 0.011c | 155.38 ± 10.24bc | 3.97 ± 0.01d | 89.1 ± 1.84c |
| W80Y20 | 1.76 ± 0.00b | 575.94 ± 20.40b | 0.582 ± 0.015c | 0.510 ± 0.019c | 171.22 ± 13.18b | 3.89 ± 0.06d | 80.8 ± 3.38d |
| W75Y25 | 1.80 ± 0.01a | 789.20 ± 49.57a | 0.586 ± 0.004bc | 0.476 ± 0.010d | 220.04 ± 12.24a | 3.80 ± 0.07e | 76.1 ± 2.23e |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.-M.; Li, Y.; Zou, J.-H.; Guo, S.-Y.; Wang, F.; Yu, P.; Su, X.-J. Influence of Adding Chinese Yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) Flour on Dough Rheology, Gluten Structure, Baking Performance, and Antioxidant Properties of Bread. Foods 2020, 9, 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9030256
Li Q-M, Li Y, Zou J-H, Guo S-Y, Wang F, Yu P, Su X-J. Influence of Adding Chinese Yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) Flour on Dough Rheology, Gluten Structure, Baking Performance, and Antioxidant Properties of Bread. Foods. 2020; 9(3):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9030256
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qing-Ming, Yan Li, Jin-Hao Zou, Shi-Yin Guo, Feng Wang, Peng Yu, and Xiao-Jun Su. 2020. "Influence of Adding Chinese Yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) Flour on Dough Rheology, Gluten Structure, Baking Performance, and Antioxidant Properties of Bread" Foods 9, no. 3: 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9030256
APA StyleLi, Q.-M., Li, Y., Zou, J.-H., Guo, S.-Y., Wang, F., Yu, P., & Su, X.-J. (2020). Influence of Adding Chinese Yam (Dioscorea opposita Thunb.) Flour on Dough Rheology, Gluten Structure, Baking Performance, and Antioxidant Properties of Bread. Foods, 9(3), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9030256





