Impulsivity, Emotional Intelligence, and Alcohol Consumption in Young People: A Mediation Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Instruments
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Preliminary Analyses
3.2. Mediation Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health 2018; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Observatorio Europeo de las Drogas y las Toxicomanías (EMCDDA). Informe Europeo Sobre Drogas 2018. Tendencias Y Novedades; Oficina de Publicaciones de la Unión Europea: Luxembourg, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rehm, J.; Mathers, C.; Popova, S.; Thavorncharoensap, M.; Teerawattananon, Y.; Patra, J. Global burden of disease and injury and economic cost attributable to alcohol use and alcohol-use disorders. Lancet 2009, 373, 2223–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adan, A.; Forero, D.A.; Navarro, J.F. Personality Traits Related to Binge Drinking: A Systematic Review. Front. Psychiatry 2017, 8, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luchetti, M.; Sutin, A.R.; Delitala, A.; Stephan, Y.; Fiorillo, E.; Marongiu, M.; Masala, M.; Schlessinger, D.; Terracciano, A. Personality traits and facets linked with self-reported alcohol consumption and biomarkers of liver health. Addict. Behav. 2018, 82, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezquita, L.; Camacho, L.; Ibáñez, M.I.; Villa, H.; Moya-Higueras, J.; Ortet, G. Five-Factor Model and alcohol outcomes: Mediating and moderating role of alcohol expectancies. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2015, 74, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, D.M.; Smith, G.; Olausson, P.; Mitchell, S.H.; Leeman, R.F.; O’Malley, S.S.; Sher, K. Understanding the construct of impulsivity and its relationship to alcohol use disorders. Addict. Biol. 2010, 15, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, Z.W.; Kaiser, A.J.; Lynam, D.R.; Charnigo, R.J.; Milich, R. Drinking motives as mediators of the impulsivity-substance use relation: Pathways for negative urgency, lack of premeditation, and sensation seeking. Addict. Behav. 2012, 37, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evren, C.; Dalbudak, E. Relationship of Personality Trait Impulsivity with Clinical Variables in Male Alcohol-Dependent Inpatients. Klin. Psikofarmakol. Bul. Istanb. 2009, 19, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- James, L.M.; Taylor, J. Impulsivity and negative emotionality associated with substance use problems and Cluster B personality in college students. Addict. Behav. 2007, 32, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKillop, J.; Mattson, R.E.; Anderson MacKillop, E.J.; Castelda, B.A.; Donovick, P.J. Multidimensional Assessment of Impulsivity in Undergraduate Hazardous Drinkers and Controls. J. Stud. Alcohol Drugs 2007, 68, 785–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magid, V.; MacLean, M.G.; Colder, C.R. Differentiating between sensation seeking and impulsivity through their mediated relations with alcohol use and problems. Addict. Behav. 2007, 32, 2046–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejuez, C.W.; Magidson, J.F.; Mitchell, S.H.; Sinha, R.; Stevens, M.C.; De Wit, H. Behavioral and biological indicators of impulsivity in the development of alcohol use, problems, and disorders. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2010, 34, 1334–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behavioral Expressions and Biosocial Bases of Sensation Seeking. Available online: https://www.cambridge.org/cn/academic/subjects/life-sciences/animal-behaviour/behavioral-expressions-and-biosocial-bases-sensation-seeking?format=HB&isbn=9780521432009 (accessed on 8 September 1994).
- Barratt, E.S. Impulsiveness subtraits: Arousal and information processing. In Motivation, Emotion and Personality; Spence, J.T., Izard, C.E., Eds.; North Holland Elsevier Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- The Psychology of Fear and Stress. Available online: https://books.google.com.hk/books?hl=zh-CN&lr=&id=nww5AAAAIAAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PR6&dq=The+Psychology+of+Fear+and+Stress%3B&ots=roCw7tXewX&sig=tW8zVJryaix7axpXZTo8dtSXU9A&redir_esc=y&hl=zh-CN&sourceid=cndr#v=onepage&q=The%20Psychology%20of%20Fear%20and%20Stress%3B&f=false (accessed on 8 January 1987).
- Gray, J.A. A. A Critique of Eysenck’s Theory of Personality. In A Model for Personality; Eysenck, H.J., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1981; pp. 246–276. [Google Scholar]
- Squillace, M.; Picón Janeiro, J.; Schmidt, V. El concepto de impulsividad y su ubicación en las teorías psicobiológicas de la personalidad. Rev. Neuropsicol. Latinoam. 2011, 3, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.H.; Hong, H.G.; Jeon, S.-M. Personality and alcohol use: The role of impulsivity. Addict. Behav. 2012, 37, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aluja, A.; Lucas, I.; Blanch, A.; Blanco, E. Personality and disinhibitory psychopathology in alcohol consumption: A study from the biological-factorial personality models of Eysenck, Gray and Zuckerman. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2019, 142, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Extremera Pacheco, N.; Fernández Berrocal, P. Inteligencia emocional percibida y diferencias individuales en el meta-conocimiento de los estados emocionales: Una revisión de los estudios con el TMMS. Ansiedad y estrés 2005, 11, 101–122. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, J.D.; Salovey, P. What is emotional intelligence? In Emotional Development and Emotional Intelligence: Educational Implications, 2nd ed.; Salovey, P., Sluyter, D.J., Eds.; Basic: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 3–31. [Google Scholar]
- Salovey, P.; Mayer, J.D.; Goldman, S.L.; Turvey, C.; Palfai, T.P. Emotional attention, clarity, and repair: Exploring emotional intelligence using the Trait Meta-Mood Scale. In Emotion, Disclosure, and Health; Pennebaker, J.W., Ed.; American Psychological Assn.: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; pp. 125–154. [Google Scholar]
- Claros, E.; Sharma, M. The relationship between emotional intelligence and abuse of alcohol, marijuana, and tobacco among college students. J. Alcohol Drug Educ. 2012, 56, 8–37. [Google Scholar]
- Trinidad, D.R.; Johnson, C.A. The association between emotional intelligence and early adolescent tobacco and alcohol use. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2002, 32, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehra, D.K.; Sharma, V.; Mush-taq, H.; Sharma, N.R.; Sharma, M.; Nehra, S. Emotional intelligence and self esteem in cannabis abusers. J. Indian Acad. Appl. Psychol. 2012, 38, 385–393. [Google Scholar]
- Kun, B.; Demetrovics, Z. Emotional intelligence and addictions: A systematic review. Subst Use Misuse 2010, 45, 1131–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resurrección, D.M.; Salguero, J.M.; Ruiz-Aranda, D. Emotional intelligence and psychological maladjustment in adolescence: A systematic review. J. Adolesc. 2014, 37, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, H.; Schutte, N.S. Low emotional intelligence as a predictor of substance-use problems. J. Drug Educ. 2003, 33, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Aranda, D.; Fernandez-Berrocal, P.; Cabello, R.; Extremera, N. Inteligencia Emocional Percibida Y Consumo De Tabaco Y Alcohol En Adolescentes. Ansiedad y Estrés 2006, 12, 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Coccaro, E.F.; Zagaja, C.; Chen, P.; Jacobson, K. Relationships between perceived emotional intelligence, aggression, and impulsivity in a population-based adult sample. Psychiatry Res. 2016, 246, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limonero, J.T.; Gómez, M.J.; Fernández, J.; Tomás-Sábado, J. Influencia de la inteligencia emocional percibida y la impulsividad en el abuso de cánnabis en jóvenes. Ansiedad y estrés 2013, 19, 223–234. [Google Scholar]
- Patton, J.H.; Stanford, M.S.; Barratt, E.S. Factor structure of the Barratt impulsiveness scale. J. Clin Psychol 1995, 51, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oquendo, M.A.; Baca-García, E.; Graver, R.; Morales, M.; Montalvan, V.; Mann, J. Spanish adaptation of the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale (BIS-11). Eur. J. psychiatry 2001, 15, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Torrubia, R.; Ávila, C.; Moltó, J.; Caseras, X. The Sensitivity to Punishment and Sensitivity to Reward Questionnaire (SPSRQ) as a measure of Gray’s anxiety and impulsivity dimensions. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2001, 31, 837–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, C.S.; White, T.L. Behavioral Inhibition, Behavioral Activation, and Affective Responses to Impending Reward and Punishment: The BIS/BAS Scales. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1994, 67, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caseras, X.; Àvila, C.; Torrubia, R. The measurement of individual differences in Behavioural Inhibition and Behavioural Activation Systems: A comparison of personality scales. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2003, 34, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Berrocal, P.; Extremera, N.; Ramos, N. Validity and reliability of the spanish modified version of the trait meta-mood scale. Psychol. Rep. 2004, 94, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.F. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process. Analysis. A Regression-Based Approach, 2nd ed.; Guilford Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Adan, A.; Navarro, J.F.; Forero, D.A. Personality profile of binge drinking in university students is modulated by sex. A study using the Alternative Five Factor Model. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2016, 165, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Loredo, V.; Fernández-Hermida, J.R.; de La Torre-Luque, A.; Fernández-Artamendi, S. Polydrug use trajectories and differences in impulsivity among adolescents. Int. J. Clin. Health Psychol. 2018, 18, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charfi, N.; Smaoui, N.; Turki, M.; Maâlej, M.B.; Omri, S.; Ben, J.T.; Zouari, N.; Zouari, L.; Maâlej, M. Alcohol use in adolescents and its association with sensation seeking and impulsivity: A survey in the city of Sfax, Tunisia. Rev. Epidemiol Sante Publique 2019, 67, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.; Settles, R.; Collins, B.; Gunn, R.; Smith, G.T. The role of negative urgency and expectancies in problem drinking and disordered eating: Testing a model of comorbidity in pathological and at-risk samples. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2012, 26, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Smith, G.T. Binge eating, problem drinking, and pathological gambling: Linking behavior to shared traits and social learning. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2008, 44, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteside, S.P.; Lynam, D.R. Understanding the role of impulsivity and externalizing psychopathology in alcohol abuse: Application of the UPPS Impulsive Behavior Scale. Personal. Disord. Theory Res. Treat. 2009, 11, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, E.J.; Saklofske, D.H.; Egan, V. Personality, well-being and health correlates of trait emotional intelligence. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2005, 38, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canto, J.; Fernández-Berrocal, P.; Guerrero, F.; Extremera, N. Función protectora de las habilidades emocionales en las adicciones. In Psicología Social y Problemas Sociales; Biblioteca Nueva: Madrid, Spain, 2005; pp. 583–590. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández, B.; Jorge, V.; Bejar, E. Función protectora de las habilidades emocionales en la prevención del consumo de tabaco y alcohol: Una propuesta de intervención. Psicooncología 2009, 6, 243–256. [Google Scholar]
- García del Castillo, J.A.G. Del Editorial: Evaluation of drug use in perspective/La evaluación del consumo de drogas en perspectiva. Health Addict. Salud y Drog. 2011, 11, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Trinidad, D.R.; Unger, J.B.; Chou, C.-P.; Anderson Johnson, C. The protective association of emotional intelligence with psychosocial smoking risk factors for adolescents. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2004, 36, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, L. The validity of self-reported drug use in survey research: An overview and critique of research methods. NIDA Res. Monogr 1997, 167, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lintonen, T.; Ahlström, S.; Metso, L. The reliability of self-reported drinking in adolescence. Alcohol Alcohol. 2004, 39, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Females | Males | Overall | t | gl | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | M | SD | |||||
| Alcohol Frequency | 46.39 | 42.25 | 57.85 | 54.84 | 48.33 | 44.76 | −1.592 | 80.184 | 0.115 | |
| Amount of Alcohol | 3.35 | 1.53 | 3.86 | 2.06 | 3.43 | 1.64 | −1.911 | 78.966 | 0.060 | |
| SSS-V | Thrill and Adventure Seeking | 5.52 | 2.96 | 6.94 | 2.74 | 5.76 | 2.97 | −3.568 | 382 | 0.000 ** |
| Experience Seeking | 6.34 | 1.76 | 6.55 | 1.99 | 6.37 | 1.80 | −0.893 | 382 | 0.373 | |
| Disinhibition | 4.35 | 2.08 | 5.74 | 2.59 | 4.58 | 2.23 | −4.073 | 81.603 | 0.000 ** | |
| Boredom Susceptibility | 3.57 | 1.96 | 3.60 | 1.93 | 3.57 | 1.96 | −0.122 | 382 | 0.903 | |
| BIS-11 | Cognitive | 13.97 | 4.11 | 15.51 | 4.79 | 14.23 | 4.27 | −2.672 | 382 | 0.008 ** |
| Motor | 15.51 | 6.23 | 15.57 | 6.13 | 15.52 | 6.21 | −0.065 | 382 | 0.948 | |
| Non-planning | 14.27 | 5.93 | 16.54 | 7.09 | 14.65 | 6.20 | −2.714 | 382 | 0.007 ** | |
| SPSRQ | Sensitivity to Punishment | 11.32 | 4.92 | 10.23 | 5.43 | 11.14 | 5.02 | 1.602 | 382 | 0.11 |
| Sensitivity to Reward | 9.58 | 4.16 | 11.32 | 4.33 | 9.87 | 4.23 | −3.065 | 382 | 0.002 ** | |
| TMMS-24 | Emotional Attention | 29.18 | 5.24 | 28.54 | 5.00 | 29.07 | 5.20 | 0.9 | 382 | 0.369 |
| Emotional Clarity | 28.83 | 5.39 | 29.25 | 4.99 | 28.90 | 5.32 | −0.569 | 382 | 0.57 | |
| Emotional Repair | 29.16 | 5.82 | 30.17 | 4.53 | 29.33 | 5.63 | −1.560 | 111.846 | 0.122 | |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alcohol Frecuency | - | |||||||||||||
| 2 | Amount of alcohol | 0.260 ** | |||||||||||||
| 3 | Thrill and Adventure Seeking | 0.162 ** | 0.129 * | ||||||||||||
| 4 | Experience Seeking | 0.180 ** | 0.172 ** | 0.376 ** | |||||||||||
| 5 | Disinhibition | 0.312 ** | 0.262 ** | 0.356 ** | 0.492 ** | ||||||||||
| 6 | Boredom Susceptibility | 0.070 | 0.095 | 0.195 ** | 0.181 ** | 0.290 ** | |||||||||
| 7 | Cognitive | 0.085 | 0.087 | 0.076 | 0.272 ** | 0.315 ** | 0.229 ** | ||||||||
| 8 | Motor | 0.117 * | 0.114 * | 0.119 * | 0.259 ** | 0.313 ** | 0.314 ** | 0.493 ** | |||||||
| 9 | No planning | 0.147 ** | 0.142 ** | 0.226 ** | 0.291 ** | 0.301 ** | 0.331 ** | 0.392 ** | 0.356 ** | ||||||
| 10 | Sensitivity to Punishment | −0.086 | −0.082 | −0.126 * | −0.151 ** | −0.045 | −0.034 | 0.051 | −0.084 | −0.112 * | |||||
| 11 | Sensitivity to Reward | 0.186 ** | 0.131 ** | 0.189 ** | 0.237 ** | 0.508 ** | 0.353 ** | 0.289 ** | 0.388 ** | 0.183 ** | 0.008 | ||||
| 12 | Emotional Attention | −0.101 * | −0.042 | −0.037 | −0.001 | 0.009 | −0.059 | 0.035 | 0.014 | −0.028 | 0.238 ** | 0.064 | |||
| 13 | Emotional Clarity | 0.029 | 0.010 | 0.023 | −0.105 * | −0.182 ** | −0.219 ** | −0.208 ** | −0.182 ** | −0.083 | −0.319 ** | −0.183 ** | 0.116 * | ||
| 14 | Emotional Repair | −0.012 | −0.043 | 0.250 ** | 0.053 | 0.030 | −0.102 * | −0.056 | 0.011 | 0.012 | −0.339 ** | −0.025 | 0.017 | 0.274 ** | |
| 15 | Age | −0.059 | 0.056 | 0.003 | 0.097 | 0.065 | −0.056 | −0.006 | −0.034 | −0.050 | −0.050 | −0.038 | 0.005 | 0.125 * | −0.023 |
| Alcohol Frequency | ||||||||||||
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | |||||||||
| R | 0.363 | 0.363 | 0.343 | 0.344 | ||||||||
| R2 | 0.132 | 0.132 | 0.118 | 0.118 | ||||||||
| F-value | 4.692 ** | 4.320 ** | 16.939 ** | 12.685 ** | ||||||||
| Predictor variables | Emotional Attention | Emotional Clarity | DIS | Emotional Attention | Emotional Clarity | DIS | Emotional Attention | Emotional Clarity | DIS | Emotional Attention | Emotional Clarity | DIS |
| Beta | −0.114 | 0.11 | 0.273 | −0.114 | 0.11 | 0.273 | −0.116 | 0.102 | 0.331 | −0.116 | 0.102 | 0.329 |
| t | −2.209 * | 1.959 * | 4.199 ** | −2.202 * | 1.953 * | 4.123 ** | −2.398 * | 2.077 * | 6.758 ** | −2.378 * | 2.049 * | 6.489 ** |
| Amount of Alcohol | ||||||||||||
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | |||||||||
| R | 0.301 | 0.306 | 0.262 | 0.268 | ||||||||
| R2 | 0.091 | 0.093 | 0.069 | 0.072 | ||||||||
| F-value | 3.077 ** | 2.931 ** | 28.173 ** | 14.797 ** | ||||||||
| Predictor variables | DIS | DIS | DIS | DIS | ||||||||
| Beta | 0.229 | 0.217 | 0.267 | 0.248 | ||||||||
| t | 3.446 ** | 3.213 ** | 5.308 ** | 4.887 ** | ||||||||
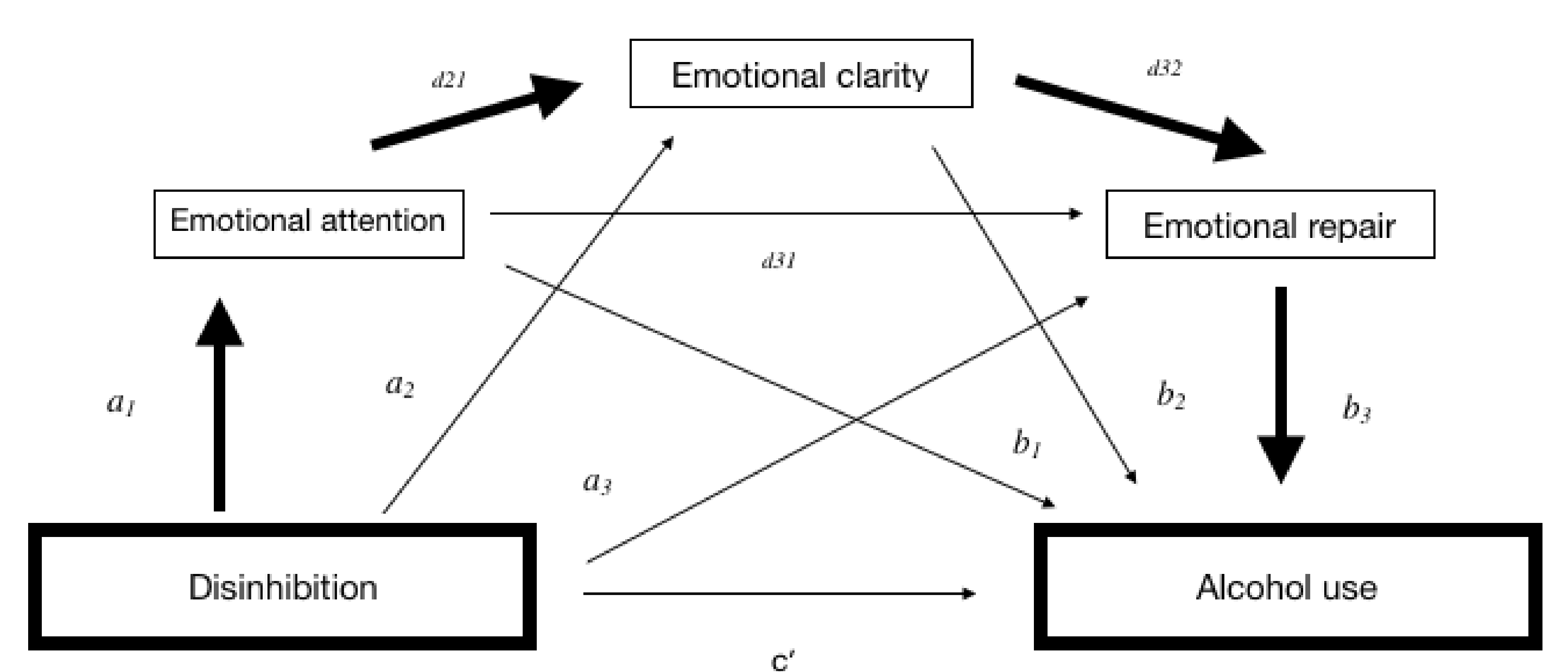
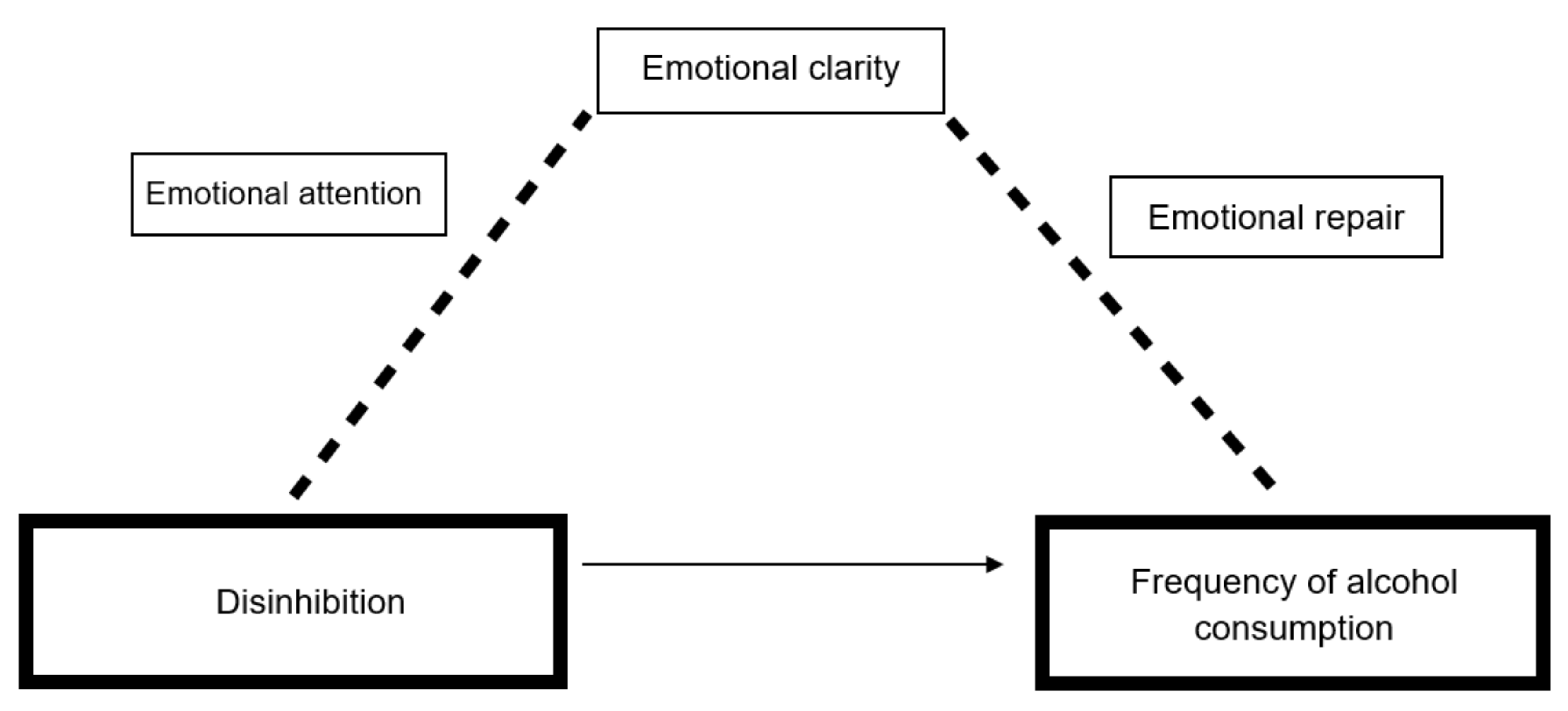
| Path | Coefficient | SE | BootLLCI | BootULCI | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total effect (c) | 6.255 | 0.9762 | 4.336 | 8.175 | 6.408 | 0.000 |
| Direct effect (c′) | 6.738 | 0.987 | 4.796 | 8.680 | 6.822 | 0.000 |
| a1 | 0.0215 | 0.1193 | −0.2131 | 0.256 | 0.1798 | 0.857 |
| a2 | −0.4368 | 0.1194 | −0.6716 | −0.202 | −36.576 | 0.000 |
| a3 | 0.2089 | 0.1263 | −0.0394 | 0.4573 | 1.654 | 0.098 |
| b1 | −1.009 | 0.4179 | −1.831 | −0.1882 | −2.416 | 0.016 |
| b2 | 0.9897 | 0.4328 | 0.1387 | 1.841 | 2.287 | 0.022 |
| b3 | −0.4153 | 0.3997 | −1.201 | 0.3706 | −1.039 | 0.299 |
| d21 | 0.1204 | 0.0512 | 0.0197 | 0.2211 | 2.351 | 0.019 |
| d31 | −0.0188 | 0.0536 | −0.1242 | 0.0867 | −0.35 | 0.726 |
| d32 | 0.3078 | 0.0533 | 0.2031 | 0.4126 | 5.779 | 0.000 |
| Indirect effects | Effect | SE | BootLLCI | BootULCI | ||
| Total indirect effect | −0.4825 | 0.2643 | −1.048 | −0.0021 | ||
| Ind2: a2b2 | −0.4323 | 0.2293 | −0.9312 | −0.0417 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Merchán-Clavellino, A.; Salguero-Alcañiz, M.P.; Guil, R.; Alameda-Bailén, J.R. Impulsivity, Emotional Intelligence, and Alcohol Consumption in Young People: A Mediation Analysis. Foods 2020, 9, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010071
Merchán-Clavellino A, Salguero-Alcañiz MP, Guil R, Alameda-Bailén JR. Impulsivity, Emotional Intelligence, and Alcohol Consumption in Young People: A Mediation Analysis. Foods. 2020; 9(1):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010071
Chicago/Turabian StyleMerchán-Clavellino, Ana, María Pilar Salguero-Alcañiz, Rocío Guil, and Jose Ramón Alameda-Bailén. 2020. "Impulsivity, Emotional Intelligence, and Alcohol Consumption in Young People: A Mediation Analysis" Foods 9, no. 1: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010071
APA StyleMerchán-Clavellino, A., Salguero-Alcañiz, M. P., Guil, R., & Alameda-Bailén, J. R. (2020). Impulsivity, Emotional Intelligence, and Alcohol Consumption in Young People: A Mediation Analysis. Foods, 9(1), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010071







