The “Grass-Fed” Milk Story: Understanding the Impact of Pasture Feeding on the Composition and Quality of Bovine Milk
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Nutritional Value of Milk
3. Milk Fat
4. Impact of Feeding System on the Lipid Fraction of Bovine Milk
5. Potential Methods for the Verification of Pasture or “Grass-Fed” Dairy Products
6. Milk Protein
7. Impact of Feeding System on Bovine Milk Proteins
8. Impact of Feeding System on the Micronutrients and Lactose content of Bovine Milk
9. Impact of Feeding System on the Sensory Characteristics and Volatile Organic Compounds of Bovine Milk
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Givens, D.I. The Role of Animal Nutrition in Improving the Nutritive Value of Animal-Derived Foods in Relation to Chronic Disease. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2007, 64, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, A.; Høstmark, A.T.; Harstad, O.M. Bovine Milk in Human Nutrition—A Review. Lipids Health Dis. 2007, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomet, P.; Piccand, V. Resource-Efficient Milk Production Which Cow Type Is Suitable? Lehr- und Forschungszentrum für Landwirtschaft Raumberg-Gumpenstein: Irdning, Austria, 2011; pp. 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Knaus, W. Perspectives on Pasture Versus Indoor Feeding of Dairy Cows. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, D.; Brennan, P.; Humphreys, J.; Ruane, E.; Shalloo, L. An Appraisal of Carbon Footprint of Milk from Commercial Grass-Based Dairy Farms in Ireland According to a Certified Life Cycle Assessment Methodology. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2014, 19, 1469–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado-Uria, C.; Hennessy, D.; Shalloo, L.; O’Connor, D.; Delaby, L. Relationships between Meteorological Data and Grass Growth over Time in the South of Ireland. Irish Geography 2013, 46, 175–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, P.; Roche, J.R.; Shalloo, L.; Horan, B. Optimising Financial Return from Grazing in Temperate Pastures. In Proceedings of the Satellite Workshop of the XXth International Grassland Congress, Cork, Ireland, July 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hurtado-Uria, C.; Hennessy, D.; Shalloo, L.; Schulte, R.P.; Delaby, L.; O’Connor, D. Evaluation of Three Grass Growth Models to Predict Grass Growth in Ireland. J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 151, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, D.; Moran, B.; Shalloo, L. A National Methodology to Quantify the Diet of Grazing Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 8595–8604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Callaghan, F.T.; Sugrue, I.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. Nutritional Aspects of Raw Milk: A Beneficial or Hazardous Food Choice. In Raw Milk; Nero, L.A., de Carvalho, A.F., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; Chapter 7; pp. 127–148. [Google Scholar]
- Schönfeldt, C.H.; Hall, N.G.; Smit, L.E. The Need for Country Specific Composition Data on Milk. Food Res. Int. 2012, 47, 207–209. [Google Scholar]
- White, L.S.; Bertrand, J.A.; Wade, M.R.; Washburn, S.P.; Green, J.T., Jr.; Jenkins, T.C. Comparison of Fatty Acid Content of Milk from Jersey and Holstein Cows Consuming Pasture or a Total Mixed Ration. J. Dairy Sci. 2001, 84, 2295–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewhurst, J.R.; Shingfield, K.J.; Lee, M.R.F.; Scollan, N.D. Increasing the Concentrations of Beneficial Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Milk Produced by Dairy Cows in High-Forage Systems. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2006, 131, 168–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, J.A. Functional Foods and Health Promotion. J. Nutr. 1999, 129, 1395S–1397S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riekerink, R.O.; Barkema, H.W.; Stryhn, H. The Effect of Season on Somatic Cell Count and the Incidence of Clinical Mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 1704–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kristensen, T.; Oudshoorn, F.; Munksgaard, L.; Søegaard, K. Effect of Time at Pasture Combined with Restricted Indoor Feeding on Production and Behaviour in Dairy Cows. Animal 2007, 1, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, F.T.; Hennessy, D.; McAuliffe, S.; Sheehan, D.; Kilcawley, K.; Dillon, P.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. The Effect of Cow Feeding System on the Composition and Quality of Milk and Dairy Products; Animal & Grassland Research and Innovation Centre: Teagasc, Ireland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gulati, A.; Galvin, N.; Lewis, E.; Hennessy, D.; O’Donovan, M.; McManus, J.J.; Fenelon, M.A.; Guinee, T.P. Outdoor Grazing of Dairy Cows on Pasture Versus Indoor Feeding on Total Mixed Ration: Effects on Gross Composition and Mineral Content of Milk During Lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 2710–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McManaman, J.L. Formation of Milk Lipids: A Molecular Perspective. Clin Lipidol. 2009, 4, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Callaghan, F.T.; Hennessy, D.; McAuliffe, S.; Kilcawley, K.N.; O’Donovan, M.; Dillon, P.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. Effect of Pasture Versus Indoor Feeding Systems on Raw Milk Composition and Quality over an Entire Lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 9424–9440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, M.; Mente, A.; Rangarajan, S.; Sheridan, P.; Mohan, V.; Iqbal, R.; Gupta, R.; Lear, S.; Wentzel-Viljoen, E.; Avezum, A.; et al. Association of Dairy Intake with Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality in 21 Countries from Five Continents (Pure): A Prospective Cohort Study. Lancet 2018, 392, 2288–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarche, B.; Givens, D.I.; Soedamah-Muthu, S.; Krauss, R.M.; Jakobsen, M.U.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.; Pan, A.; Després, J. Does Milk Consumption Contribute to Cardiometabolic Health and Overall Diet Quality? Can. J. Cardiol. 2016, 32, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soedamah-Muthu, S.S.; Ding, E.L.; Hu, F.B.; Geleijnse, J.M.; Engberink, M.F.; Al-Delaimy, W.K.; Willett, W.C. Milk and Dairy Consumption and Incidence of Cardiovascular Diseases and All-Cause Mortality: Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.Q.; Xu, J.Y.; Han, S.; Zhang, Z.L.; Zhao, Y.; Szeto, I.M. Dairy Consumption and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 24, 90–100. [Google Scholar]
- Lovegrovem, A.J.; Givens, D.I. Dairy Food Products: Good or Bad for Cardiometabolic Disease? Nutr. Res. Rev. 2016, 29, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.P. Assessing the Overall Impact of the Dairy Sector. In Achieving Sustainable Production of Milk Volume 2; Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 325–348. [Google Scholar]
- Pimpin, L.; Wu, J.H.Y.; Haskelberg, H.; del Gobbo, L.; Mozaffarian, D. Is Butter Back? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Butter Consumption and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes, and Total Mortality. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordan, R.; Tsoupras, A.; Mitra, B.; Zabetakis, I. Dairy Fats and Cardiovascular Disease: Do We Really Need to Be Concerned? Foods 2018, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, W.J. Health Effects of Vegan Diets. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 1627S–1633S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beto, J.A. The Role of Calcium in Human Aging. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2015, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clarys, P.; Deliens, T.; Huybrechts, I.; Deriemaeker, P.; Vanaelst, B.; de Keyzer, W.; Hebbelinck, M.; Mullie, P. Comparison of Nutritional Quality of the Vegan, Vegetarian, Semi-Vegetarian, Pesco-Vegetarian and Omnivorous Diet. Nutrients 2014, 6, 1318–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storhaug, L.C.; Fosse, S.K.; Fadnes, L.T. Country, Regional, and Global Estimates for Lactose Malabsorption in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, J.D. Altering Milk Composition by Feeding. J. Dairy Sci. 1989, 72, 2801–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.E.P. Feeding for Milk Composition. In Proceedings of the VI International Congress on Bovine Medicine; Spanish Association of Specialists in Bovine Medicine (ANEMBE): Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ceballos, S.L.; Morales, E.R.; Adarve, G.d.; Castro, J.D.; Martínez, L.P.; Sampelayo, M.R.S. Composition of Goat and Cow Milk Produced under Similar Conditions and Analyzed by Identical Methodology. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2009, 22, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacGibbon, H.A.K.; Taylor, M.W. Advanced Dairy Chemistry, Volume 2: Lipids; Fox, P.F., McSweeney, P.L.H., Eds.; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Santin, A.J.I.; Silva, K.C.C.; Cucco, D.C. Milk Fatty Acids Profile and the Impact on Human Health. Dairy Vet. Sci. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belitz, D.H.; Grosch, W.; Schieberle, P. Springer Food Chemistry 4th Revised and Extended Edition. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 79, 655–681. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, B.M. Chemical Composition of Milk and Milk Products. In Handbook of Food Chemistry; Cheung, P.C.K., Mehta, B.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 511–553. [Google Scholar]
- Jandal, J.M. Some Factors Affecting Lipase Activity in Goat Milk. Small Ruminant Res. 1995, 16, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudry, C.; Thewis, A. Bovine Colostrum as a Natural Growth Factor. Bull. Univ. Agric. Sci. Vet. Med. Cluj-Napoca Animal Sci. Biotechnol. 2009, 66, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Park, W.Y.; Juárez, M.; Ramos, M.; Haenlein, G.F.W. Physico-Chemical Characteristics of Goat and Sheep Milk. Small Ruminant Res. 2007, 68, 88–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccio, P. The Proteins of the Milk Fat Globule Membrane in the Balance. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.W. Minor Species Milk. In Handbook of Milk of Non-Bovine Mammals; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 393–406. [Google Scholar]
- Séverin, S.; Wenshui, X. Milk Biologically Active Components as Nutraceuticals: Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 45, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lock, L.A.; Shingfield, K.J. Optimising Milk Composition. BSAP Occas. Public. 2004, 29, 107–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Månsson, H.L. Fatty Acids in Bovine Milk Fat. Food Nutr. Res. 2008, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, T.F. The Benefits of Pasture-Based Dairy. Irish Food 2019, 1, 34–35. [Google Scholar]
- Tina, N.S.; Ellen, M.S.; Mogens, V.; Kris, S. Effect of Silage Type and Concentrate Level on Conjugated Linoleic Acids, Trans-C18:1 Isomers and Fat Content in Milk from Dairy Cows. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 2006, 46, 699–712. [Google Scholar]
- Bauman, E.D.; Perfield, J.W.; Lock, A.L. Effect of Trans Fatty Acids on Milk Fat and Their Impact on Human Health. In Proceedings of the Southwest Nutrition Conference, Tempe, AZ, USA, 26–27 February 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Palmquist, D.L. Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Metabolism, Health, and Nutrition and for Modified Animal Product Foods. Profess. Anim. Sci. 2009, 25, 207–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitsberg, V.L. Invited Review: Bovine Milk Fat Globule Membrane as a Potential Nutraceutical. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 2289–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Xu, X.; He, C.; Li, L. Lipase-Catalyzed Modification of Lard to Produce Human Milk Fat Substitutes. Food Chem. 2003, 80, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straarup, M.E.; Lauritzen, L.; Jan Faerk, H.C.; Michaelsen, K.F. The Stereospecific Triacylglycerol Structures and Fatty Acid Profiles of Human Milk and Infant Formulas. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2006, 42, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bauman, E.D.; Griinari, J.M. Nutritional Regulation of Milk Fat Synthesis. Ann. Rev. Nutr. 2003, 23, 203–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmquist, L.D.; Beaulieu, D.A.; Barbano, D.M. Feed and Animal Factors Influencing Milk Fat Composition 1. J. Dairy Sci. 1993, 76, 1753–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmquist, D.L. Milk Fat: Origin of Fatty Acids and Influence of Nutritional Factors Thereon. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry Volume 2 Lipids; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 43–92. [Google Scholar]
- Knutsen, M.T.; Olsen, H.G.; Tafintseva, V.; Svendsen, M.; Kohler, A.; Kent, M.P.; Lien, S. Unravelling Genetic Variation Underlying De Novo-Synthesis of Bovine Milk Fatty Acids. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, F.T.; Vázquez-Fresno, R.; Serra-Cayuela, A.; Dong, E.; Mandal, R.; Hennessy, D.; McAuliffe, S.; Dillon, P.; Wishart, S.D.; Stanton, C.; et al. Pasture Feeding Changes the Bovine Rumen and Milk Metabolome. Metabolites 2018, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Cortés, P.; Juárez, M.; de la Fuente, M.A. Milk Fatty Acids and Potential Health Benefits: An Updated Vision. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 81, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgersma, A.S.; Tamminga, E.G. Modifying Milk Composition through Forage. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2006, 131, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, T.; Yan, S.; Shi, B.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X. Influence of Pasture or Total Mixed Ration on Fatty Acid Composition and Expression of Lipogenic Genes of Longissimus Thoracis and Subcutaneous Adipose Tissues in Albas White Cashmere Goats. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 18, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, B.; Fedele, V.; Ferlay, A.; Grolier, P.; Rock, E.; Gruffat, D.; Chilliard, Y. Effects of Grass-Based Diets on the Content of Micronutrients and Fatty Acids in Bovine and Caprine Dairy Products; vdf Hochschulverlag AG an der ETH Zurich: Zürich, Switzerland, 2004; pp. 876–886. [Google Scholar]
- Schwendel, H.B.; Wester, T.J.; Morel, P.C.H.; Tavendale, M.H.; Deadman, C.; Shadbolt, N.M.; Otter, D.E. Invited Review: Organic and Conventionally Produced Milk—An Evaluation of Factors Influencing Milk Composition. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 721–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, R.; Kang, R.; Meng, J.; Ao, C. Milk Fatty Acids Profiles and Milk Production from Dairy Cows Fed Different Forage Quality Diets. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 2, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilliard, Y.; Glasser, F.; Ferlay, A.; Bernard, L.; Rouel, J.; Doreau, M. Diet, Rumen Biohydrogenation and Nutritional Quality of Cow and Goat Milk Fat. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2007, 109, 828–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanbergue, E.; Peyraud, J.L.; Ferlay, A.; Miranda, G.; Martin, P.; Hurtaud, C. Effects of Feeding Level, Type of Forage and Milking Time on Milk Lipolytic System in Dairy Cows. Livestock Sci. 2018, 217, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rego, A.O.; Cabrita, A.R.J.; Rosa, H.J.D.; Alves, S.P.; Duarte, V.; Fonseca, A.J.M.; Vouzela, C.F.M.; Pires, F.R.; Bessa, R.J.B. Changes in Milk Production and Milk Fatty Acid Composition of Cows Switched from Pasture to a Total Mixed Ration Diet and Back to Pasture. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 15, 6–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KouřimsKá, L.; LegaroVá, V.; PanoVsKá, Z.; PáneK, J. Quality of Cows’ Milk from Organic and Conventional Farming. Czech, J. Food Sci. 2014, 32, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kučević, D.; Trivunović, S.; Bogdanović, V.; Čobanović, K.; Janković, D.; Stanojević, D. Composition of Raw Milk from Conventional and Organic Dairy Farming. Biotechnol. Anim. Husbandry 2016, 32, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdela, N. Sub-Acute Ruminal Acidosis (Sara) and Its Consequence in Dairy Cattle: A Review of Past and Recent Research at Global Prospective. Achiev. Life Sci. 2016, 10, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleen, L.J.; Hooijer, G.A.; Rehage, J.; Noordhuizen, J.P.T.M. Subacute Ruminal Acidosis (Sara): A Review. J. Vet. Med. Ser. A 2003, 50, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smid, C.A.; Weary, D.M.; Costa, J.H.C.; von Keyserlingk, M.A.G. Dairy Cow Preference for Different Types of Outdoor Access. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 1448–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, B.; Hennessy, D. Scientific Appraisal of the Irish Grass-Based Milk Production System as a Sustainable Source of Premium Quality Milk and Dairy Products. Irish J. Agric. Food Res. 2017, 56, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donovan, M.; Lewis, E.; O’Kiely, P. Requirements of Future Grass-Based Ruminant Production Systems in Ireland. IJAFR 2011, 50, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Olmos, G.; Boyle, L.; Hanlon, A.; Patton, J.; Murphy, J.J.; Mee, J.F. Hoof Disorders, Locomotion Ability and Lying Times of Cubicle-Housed Compared to Pasture-Based Dairy Cows. Livestock Sci. 2009, 125, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskell, J.M.; Rennie, L.J.; Bowell, V.A.; Bell, M.J.; Lawrence, A.B. Housing System, Milk Production, and Zero-Grazing Effects on Lameness and Leg Injury in Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 4259–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Washburn, P.S.; White, S.L.; Green, J.T.; Benson, G.A. Reproduction, Mastitis, and Body Condition of Seasonally Calved Holstein and Jersey Cows in Confinement or Pasture Systems. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, F.B.; Deighton, M.H.; O’Loughlin, B.M.; Mulligan, F.J.; Boland, T.M.; O’Donovan, M.; Lewis, E. Effects of a Perennial Ryegrass Diet or Total Mixed Ration Diet Offered to Spring-Calving Holstein-Friesian Dairy Cows on Methane Emissions, Dry Matter Intake, and Milk Production. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 1941–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, D.; Shalloo, L.; Patton, J.; Buckley, F.; Grainger, C.; Wallace, M. Evaluation of the Effect of Accounting Method, Ipcc, V. Lca, on Grass-Based and Confinement Dairy Systems’ Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Animal 2012, 6, 1512–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, F.T.; Faulkner, H.; McAuliffe, S.; O’Sullivan, M.G.; Hennessy, D.; Dillon, P.; Kilcawley, K.N.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P. Quality Characteristics, Chemical Composition, and Sensory Properties of Butter from Cows on Pasture Versus Indoor Feeding Systems. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 9441–9460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moate, J.P.; Chalupa, W.; Boston, R.C.; Lean, I.J. Milk Fatty Acids. I. Variation in the Concentration of Individual Fatty Acids in Bovine Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 4730–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benbrook, M.C.; Davis, D.R.; Heins, B.J.; Latif, M.A.; Leifert, C.; Peterman, L.; Butler, G.; Faergeman, O.; Abel-Caines, S.; Baranski, M. Enhancing the Fatty Acid Profile of Milk through Forage-Based Rations, with Nutrition Modeling of Diet Outcomes. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 681–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, R.T.; Anand, G.R.; Satter, L.D.; Pariza, M.W. Conjugated Linoleic Acid Content of Milk from Cows Fed Different Diets1. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 2146–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, A.; Agabriel, C.; Sibra, C.; Journal, C.; Martin, B.; Chilliard, Y. Tanker Milk Variability in Fatty Acids According to Farm Feeding and Husbandry Practices in a French Semi-Mountain Area. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2008, 88, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, A.; Martin, B.; Pradel, P.; Coulon, J.B.; Chilliard, Y. Influence of Grass-Based Diets on Milk Fatty Acid Composition and Milk Lipolytic System in Tarentaise and Montbéliarde Cow Breeds. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 4026–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, A.; Cajarville, C.; Repetto, J.L. Short Communication: Intake, Milk Production, and Milk Fatty Acid Profile of Dairy Cows Fed Diets Combining Fresh Forage with a Total Mixed Ration. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 1938–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croissant, E.A.; Washburn, S.P.; Dean, L.L.; Drake, M.A. Chemical Properties and Consumer Perception of Fluid Milk from Conventional and Pasture-Based Production Systems. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 4942–4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, F.T.; Mannion, D.T.; Hennessy, D.; McAuliffe, S.; O’Sullivan, M.G.; Leeuwendaal, N.; Beresford, T.P.; Dillon, P.; Kilcawley, K.N.; Sheehan, J.J.; et al. Effect of Pasture Versus Indoor Feeding Systems on Quality Characteristics, Nutritional Composition, and Sensory and Volatile Properties of Full-Fat Cheddar Cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 6053–6073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Or-Rashid, M.M.; Odongo, N.E.; Subedi, B.; Karki, P.; McBride, B.W. Fatty Acid Composition of Yak (Bos Grunniens) Cheese Including Conjugated Linoleic Acid and Trans-18:1 Fatty Acids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1654–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segato, S.; Galaverna, G.; Contiero, B.; Berzaghi, P.; Caligiani, A.; Marseglia, A.; Cozzi, G. Identification of Lipid Biomarkers to Discriminate between the Different Production Systems for Asiago Pdo Cheese. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 9887–9892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prema, D.; Pilfold, J.L.; Krauchi, J.; Church, J.S.; Donkor, K.K.; Cinel, B. Rapid Determination of Total Conjugated Linoleic Acid Content in Select Canadian Cheeses by 1h Nmr Spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 9915–9921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chion, R.; Andrea; Tabacco, E.; Giaccone, D.; Peiretti, P.G.; Battelli, G.; Borreani, G. Variation of Fatty Acid and Terpene Profiles in Mountain Milk and Toma Piemontese Cheese as Affected by Diet Composition in Different Seasons. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couvreur, S.; Hurtaud, C.; Lopez, C.; Delaby, L.; Peyraud, J.L. The Linear Relationship between the Proportion of Fresh Grass in the Cow Diet, Milk Fatty Acid Composition, and Butter Properties. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 1956–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallia, S.; Piccinali, P.; Rehberger, B.; Badertscher, R.; Escher, F.; Schlichtherle-Cerny, H. Determination of Storage Stability of Butter Enriched with Unsaturated Fatty Acids/Conjugated Linoleic Acids (Ufa/Cla) Using Instrumental and Sensory Methods. Int. Dairy J. 2008, 18, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villeneuve, P.M.; Lebeuf, Y.; Gervais, R.; Tremblay, G.F.; Vuillemard, J.C.; Fortin, J.; Chouinard, P.Y. Milk Volatile Organic Compounds and Fatty Acid Profile in Cows Fed Timothy as Hay, Pasture, or Silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 7181–7194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargo, F.; Delahoy, J.E.; Schroeder, G.F.; Baumgard, L.H.; Muller, L.D. Supplementing Total Mixed Rations with Pasture Increase the Content of Conjugated Linoleic Acid in Milk. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2006, 131, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, L.R.; Bayard, C.C.; Fabien, R.J. Evaluation of Sequential Methods for the Determination of Butterfat Fatty Acid Composition with Emphasis Ontrans-18:1 Acids. Application to the Study of Seasonal Variations in French Butters. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1995, 72, 1471–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryhänen, L.E.; Tallavaara, K.; Griinari, J.M.; Jaakkola, S.; Mantere-Alhonen, S.; Shingfield, K.J. Production of Conjugated Linoleic Acid Enriched Milk and Dairy Products from Cows Receiving Grass Silage Supplemented with a Cereal-Based Concentrate Containing Rapeseed Oil. Int. Dairy J. 2005, 15, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallia, S.; Escher, F.; Dubois, S.; Schieberle, P.; Schlichtherle-Cerny, H. Characterization and Quantification of Odor-Active Compounds in Unsaturated Fatty Acid/Conjugated Linoleic Acid (Ufa/Cla)-Enriched Butter and in Conventional Butter During Storage and Induced Oxidation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 7464–7472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, G.; Masucci, F.; Napolitano, F.; Braghieri, A.; Romano, R.; Manzo, N.; di Francia, A. Fatty Acid and Sensory Profiles of Caciocavallo Cheese as Affected by Management System. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 1918–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppa, M.; Ferlay, A.; Monsallier, F.; Verdier-Metz, I.; Pradel, P.; Didienne, R.; Farruggia, A.; Montel, M.C.; Martin, B. Milk Fatty Acid Composition and Cheese Texture and Appearance from Cows Fed Hay or Different Grazing Systems on Upland Pastures. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 1132–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, L.; Edmond, R.; Jean-François, C.; Isabelle, V.; Patrick, B.; Jean-Baptiste, C. Respective Effects of Milk Composition and the Cheese-Making Process on Cheese Compositional Variability in Components of Nutritional Interest. Lait 2006, 86, 21–41. [Google Scholar]
- Radkowska, I.; Herbut, E. The Effect of Housing System of Simmental Cows on Processing Suitability of Milk and Quality of Dairy Products. Anim. Sci. Pap. Rep. 2017, 35, 147–158. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, G.C.C.; Silva, S.P.M.; Prates, J.A.M.; Bessa, R.J.B.; Rosa, H.J.D.; Rego, O.A. Physicochemical Traits and Sensory Quality of Commercial Butter Produced in the Azores. Int. Dairy J. 2019, 88, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuano, E.; van der Veer, G.; Boerrigter-Eenling, R.; Elgersma, A.; jan Rademaker; Sterian, A.; van Ruth, S.M. Verification of Fresh Grass Feeding, Pasture Grazing and Organic Farming by Cows Farm Milk Fatty Acid Profile. Food Chem. 2014, 164, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewhurst, J.R.; Scollan, N.D.; Youell, S.J.; Tweed, J.K.S.; Humphreys, M.O. Influence of Species, Cutting Date and Cutting Interval on the Fatty Acid Composition of Grasses. Grass Forage Sci. 2001, 56, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurousseau, B.; Bauchart, D.; Calichon, E.; Micol, D.; Priolo, A. Effect of Grass or Concentrate Feeding Systems and Rate of Growth on Triglyceride and Phospholipid and Their Fatty Acids in the M. Longissimus Thoracis of Lambs. Meat Sci. 2004, 66, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, F.T.; Mannion, D.; Apopei, D.; McCarthy, A.N.; Hogan, A.S.; Kilcawley, N.K.; Egan, M. Influence of Supplemental Feed Choice for Pasture-Based Cows on the Fatty Acid and Volatile Profile of Milk. Foods 2019, 8, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundekilde, U.K.; Larsen, B.L.; Bertram, C.H. Nmr-Based Milk Metabolomics. Metabolites 2013, 3, 204–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.F. Milk Proteins: General and Historical Aspects. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry—1 Proteins: Part A/Part B; Fox, P.F., McSweeney, P.L.H., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Schlimme, E.; Meisel, H. Bioactive Peptides Derived from Milk Proteins. Structural, Physiological and Analytical Aspects. Food/Nahrung 1995, 39, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steijns, J. Milk Ingredients as Nutraceuticals. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2001, 54, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, E.; Chand, R. Antihypertensive and Antimicrobial Bioactive Peptides from Milk Proteins. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 227, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, K.D.; Katie, W. Bioactive Proteins and Peptides from Food Sources. Applications of Bioprocesses Used in Isolation and Recovery. Curr. Pharm. Design 2003, 9, 1309–1323. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, S.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C. Milk Intelligence: Mining Milk for Bioactive Substances Associated with Human Health. Int. Dairy J. 2011, 21, 377–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, F.Z.; Bhat, H. Milk and Dairy Products as Functional Foods: A Review. Int. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, H.; Pihlanto, A. Bioactive Peptides: Production and Functionality. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 945–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Agamy, E.I. The Challenge of Cow Milk Protein Allergy. Small Ruminant Res. 2007, 68, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auldist, J.M.; Marett, L.C.; Greenwood, J.S.; Wright, M.M.; Hannah, M.; Jacobs, J.L.; Wales, W.J. Milk Production Responses to Different Strategies for Feeding Supplements to Grazing Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 657–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, C.T.; McGuire, M.A. Major Advances in Nutrition: Impact on Milk Composition. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.D.; Marcondes, M.I.; Rennó, L.N.; de Barros, L.V.; Cabral, C.H.A.; Martins, L.S.; Marquez, D.E.C.; Saldarriaga, F.V.; Villadiego, F.A.C.; Cardozo, M.A.; et al. Estimation of Daily Milk Yield of Nellore Cows Grazing Tropical Pastures. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2018, 50, 1771–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanbergue, E.; Delaby, L.; Peyraud, J.L.; Colette, S.; Gallard, Y.; Hurtaud, C. Effects of Breed, Feeding System, and Lactation Stage on Milk Fat Characteristics and Spontaneous Lipolysis in Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 4623–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanigan, D.M.; Crompton, L.A.; Bequette, B.J.; Mills, J.A.N.; France, J. Modelling Mammary Metabolism in the Dairy Cow to Predict Milk Constituent Yield, with Emphasis on Amino Acid Metabolism and Milk Protein Production: Model Evaluation. J. Theor. Biol. 2002, 217, 311–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanigan, D.M.; Crompton, L.A.; Metcalf, J.A.; France, J. Modelling Mammary Metabolism in the Dairy Cow to Predict Milk Constituent Yield, with Emphasis on Amino Acid Metabolism and Milk Protein Production: Model Construction. J. Theor. Biol. 2001, 213, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, M.R.; Chandler, P.T.; Park, C.S. Limiting Amino Acids for Milk Protein Synthesis by Bovine Mammary Cells in Culture1. J. Dairy Sci. 1978, 61, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bionaz, M.; Hurley, W.; Loor, J. Milk Protein Synthesis in the Lactating Mammary Gland: Insights from Transcriptomics Analyses. In Milk Protein; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 285–324. [Google Scholar]
- Onetti, G.S.; Shaver, R.D.; McGuire, M.A.; Palmquist, D.L.; Grummer, R.R. Effect of Supplemental Tallow on Performance of Dairy Cows Fed Diets with Different Corn Silage:Alfalfa Silage Ratios. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuuren, V.M.A.; van der Koelen, C.J.; Bruin, J.V. Ryegrass Versus Corn Starch or Beet Pulp Fiber Diet Effects on Digestion and Intestinal Amino Acids in Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 1993, 76, 2692–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schären, M.; Jostmeier, S.; Ruesink, S.; Hüther, L.; Frahm, J.; Bulang, M.; Meyer, U.; Rehage, J.; Isselstein, J.; Breves, G.; et al. The Effects of a Ration Change from a Total Mixed Ration to Pasture on Health and Production of Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 1183–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.R.; Thomson, N.A. Effect of Pasture Species on Milk Yield and Milk Composition. In Proceedings of the Conference-New Zealand Grassland Association, Oamaru, New Zeland, 1996; pp. 151–156. [Google Scholar]
- Schwendel, H.B.; Wester, T.J.; Morel, P.C.H.; Fong, B.; Tavendale, M.H.; Deadman, C.; Shadbolt, N.M.; Otter, D.E. Pasture Feeding Conventional Cows Removes Differences between Organic and Conventionally Produced Milk. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, J.D.; Beever, D.E.; Haines, M.J.; Cammell, S.B.; Evans, R.T.; Dhanoa, M.S.; Austin, A.R. Yield and Composition of Milk from Friesian Cows Grazing Either Perennial Ryegrass or White Clover in Early Lactation. J. Dairy Res. 1985, 52, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandison, S.A.; Manning, D.J.; Thomson, D.J.; Anderson, M. Chemical Composition, Rennet Coagulation Properties and Flavour of Milks from Cows Grazing Ryegrass or White Clover. J. Dairy Res. 1985, 52, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barłowska, J.; Litwińczuk, Z.; Brodziak, A.; Chabuz, W. Effect of the Production Season on Nutritional Value and Technological Suitability of Milk Obtained from Intensive (Tmr) and Traditional Feeding System of Cows. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2012, 1, 1205–1220. [Google Scholar]
- Szwajkowska, M.; Wolanciuk, A.; Barłowska, J.; Krol, J.; Litwińczuk, Z. Bovine Milk Proteins as the Source of Bioactive Peptides Influencing the Consumers’ Immune System—A Review. Anim. Sci. Pap. Rep. 2011, 29, 269–280. [Google Scholar]
- Król, J.; Brodziak, A.; Litwińczuk, Z.; Szwajkowska, M. Whey Protein Utilization in Health Promotion. Żywienie Człowieka i Metabolizm 2011, 38, 36–45. [Google Scholar]
- Król, J.; Litwińczuk, Z.; Litwińczuk, A.; Brodziak, A. Content of Protein and Its Fractions in Milk of Simmental Cows with Regard to Rearing Technology. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2008, 8, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Coppa, M.; Martin, B.; Pradel, P.; Leotta, B.; Priolo, A.; Vasta, V. Effect of a Hay-Based Diet or Different Upland Grazing Systems on Milk Volatile Compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 4947–4954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendall, J.G. Aroma Compounds of Fresh Milk from New Zealand Cows Fed Different Diets. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4825–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller, S.; Mathew, C.; Wilson, G.F. Pasture Protein and Soluble Carbohydrate Levels in Spring Dairy Pasture and Associations with Cow Performance; New Zealand Society of Animal Production: Auckland, New Zealand, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Kolver, E.S. Nutritional Limitations to Increased Production on Pasture-Based Systems. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2003, 62, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, R.V.; Neil, P.G. Milk Production and Ruminal Metabolites from Cows Offered Two Pasture Diets Supplemented with Non-Structural Carbohydrate. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 1997, 40, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, F.; Santiago, C.; Jiménez-Calderón, J.D.; Martínez-Fernández, A. Capacity of Milk Composition to Identify the Feeding System Used to Feed Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Res. 2017, 84, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, E.K.; Budge, S.; Rose, M.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V.; MacLaren, L.; Green-Johnson, J.; Fredeen, A.H. Effect of Feeding Fresh Forage and Marine Algae on the Fatty Acid Composition and Oxidation of Milk and Butter. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 2797–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargo, F.; Muller, L.D.; Delahoy, J.E.; Cassidy, T.W. Performance of High Producing Dairy Cows with Three Different Feeding Systems Combining Pasture and Total Mixed Rations. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 2948–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, F.G.; Delahoy, J.E.; Vidaurreta, I.; Bargo, F.; Gagliostro, G.A.; Muller, L.D. Milk Fatty Acid Composition of Cows Fed a Total Mixed Ration or Pasture Plus Concentrates Replacing Corn with Fat. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 3237–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, H.J.; Klusmeyer, T.H.; Cameron, M.R. Microbial Protein Synthesis and Flows of Nitrogen Fractions to the Duodenum of Dairy Cows1. J. Dairy Sci. 1992, 75, 2304–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagorska, J.; Ciprovica, I. The Chemical Composition of Organic and Conventional Milk in Latvia. In Proceedings of the 3rd Baltic conference on food science and technology, Jelgava, Latvia, 17–18 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Stockdale, C.R. Effect of Diet on the Energy Required to Improve Milk Protein Content in Dairy Cows; Australian Society of Animal Production: Sidney, Australia, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Cannas, A.; Pes, A.; Mancuso, R.; Vodret, B.; Nudda, A. Effect of Dietary Energy and Protein Concentration on the Concentration of Milk Urea Nitrogen in Dairy Ewes1. J. Dairy Sci. 1998, 81, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, F.C.; Morris, S.T.; Hodgson, J.; Fathalla, M. Seasonal Changes of Herbage Quality within a New Zealand Beef Cattle Finishing Pasture. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 2005, 48, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller, S. An Evaluation of Major Nutrients in Dairy Pasture in New Zealand and Their Effects on Milk Production and Herd Reproductive Performance. Ph.D. Thesis, Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Westwood, T.C.; Lean, I.J.; Kellaway, R.C. Indications and Implications for Testing of Milk Urea in Dairy Cattle: A Quantitative Review. Part 1. Dietary Protein Sources and Metabolism. N. Z. Vet. J. 1998, 46, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westwood, T.C.; Lean, I.J. Nutrition and Lameness in Pasture-Fed Dairy Cattle; New Zealand Society of Animal Production: Auckland, New Zealand, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Colmenero, O.J.J.; Broderick, G.A. Effect of Dietary Crude Protein Concentration on Milk Production and Nitrogen Utilization in Lactating Dairy Cows1. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 1704–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, G.A. Effects of Varying Dietary Protein and Energy Levels on the Production of Lactating Dairy Cows1. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 1370–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, A.L.; Muller, L.D.; Varga, G.A.; Hillard, P.J. Ruminal Digestion and Duodenal Nutrient Flows in Dairy Cows Consuming Grass as Pasture, Hay, or Silage. J. Dairy Sci. 1994, 77, 3034–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitani, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Ueda, K.; Kondo, S. Discrimination of “Grazing Milk” Using Milk Fatty Acid Profile in the Grassland Dairy Area in Hokkaido. Anim. Sci. J. 2016, 87, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargo, F.; Muller, L.D.; Kolver, E.S.; Delahoy, J.E. Invited Review: Production and Digestion of Supplemented Dairy Cows on Pasture. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleixo, C.P.; Nóbrega, J.A. Direct Determination of Iron and Selenium in Bovine Milk by Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Food Chem. 2003, 83, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agabriel, C.; Cornu, A.; Journal, C.; Sibra, C.; Grolier, P.; Martin, B. Tanker Milk Variability According to Farm Feeding Practices: Vitamins a and E, Carotenoids, Color, and Terpenoids. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 4884–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, H.; O’Callaghan, T.F.; McAuliffe, S.; Hennessy, D.; Stanton, C.; O’Sullivan, M.G.; Kerry, J.P.; Kilcawley, K.N. Effect of Different Forage Types on the Volatile and Sensory Properties of Bovine Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 1034–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, N.B.; Kristensen, T.; Nebel, C.; Dalsgaard, T.K.; Hellgren, L.I.; Young, J.F.; Larsen, M.K. Content and Distribution of Phytanic Acid Diastereomers in Organic Milk as Affected by Feed Composition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salado, E.E.; Bretschneider, G.; Cuatrin, A.; Descalzo, A.M.; Gagliostro, G.A. Productive Response of Dairy Cows Fed with Different Levels of Totally Mixed Ration and Pasture. Agric. Sci. 2018, 9, 824–851. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Nozière, P.; Graulet, B.; Lucas, A.; Martin, B.; Grolier, P.; Doreau, M. Carotenoids for Ruminants: From Forages to Dairy Products. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2006, 131, 418–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prache, S.; Priolo, A.; Tournadre, H.; Jailler, R.; Dubroeucq, H.; Micol, D.; Martin, B. Traceability of Grass-Feeding by Quantifying the Signature of Carotenoid Pigments in Herbivores Meat, Milk and Cheese. In Multi-fonction Grasslands: Quality Forages, Animal Products and Landscapes; British Grassland Society: Kenilworth, UK, 2002; pp. 592–593. [Google Scholar]
- Duplessis, M.; Pellerin, D.; Robichaud, R.; Fadul-Pacheco, L.; Girard, C.L. Impact of Diet Management and Composition on Vitamin B12 Concentration in Milk of Holstein Cows. Animal 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, A.N.; Rybicka, I.; Poulsen, H.D.; Larsen, L.B.; Andersen, K.K.; Larsen, M.K. Seasonal Variation in Content of Riboflavin and Major Minerals in Bulk Milk from Three Danish Dairies. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 42, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christophe, B.; Solange, B.; Agnès, H.; Jean-Baptiste, C. Relationships between Flavour and Chemical Composition of Abondance Cheese Derived from Different Types of Pastures. Lait 2001, 81, 757–773. [Google Scholar]
- Calsamiglia, S.; Busquet, M.; Cardozo, P.W.; Castillejos, L.; Ferret, A. Invited Review: Essential Oils as Modifiers of Rumen Microbial Fermentation. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 2580–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de la Fuente, M.A. Changes in the Mineral Balance of Milk Submitted to Technological Treatments. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1998, 9, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, A. Minerals and Trace Elements in Milk. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Kinsella, J.E., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992; pp. 209–252. [Google Scholar]
- Gaucheron, F. The Minerals of Milk. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 2005, 45, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Crespo, F.; Miranda, M.; López-Alonso, M. Essential Trace and Toxic Element Concentrations in Organic and Conventional Milk in Nw Spain. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 55, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Bermúdez, R.; López-Alonso, M.; Miranda, M.; Fouz, R.; Orjales, I.; Herrero-Latorre, C. Chemometric Authentication of the Organic Status of Milk on the Basis of Trace Element Content. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabryszuk, M.; Słoniewski, K.; Sakowski, T. Macro- and Microelements in Milk and Hair of Cows from Conventional Vs. Organic Farms. Anim. Sci. Papers Rep. 2008, 26, 199–209. [Google Scholar]
- Argamentería, A.; Vicente, F.; Martínez-Fernández, A.; Cueto, M.A.; de la Roza-Delgado, B. Influence of Partial Total Mixed Rations Amount on the Grass Voluntary Intake by Dairy Cows; Sociedad Española para el Estudio de los Pastos (SEEP): Madrid, Spain, 2006; pp. 161–163. [Google Scholar]
- Morales-Almaraz, E.; Vicente, F.; Soldado, A.; Martínez-Fernández, A.; de la Roza-Delgado, B. Effect of Different Grazing Times on Milk Fatty Acid Composition; Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences: Uppsala: Sweden, 2008; pp. 412–414. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Ortega, M.; Morales-Almaráz, E.; Martínez-Fernández, A.; de la Roza-Delgado, B.; Vicente, F. Milk Production and Composition of Day and Night Grazing of Cows Fed a Total Mixed Ration; Mecke Druck und Verlag: Duderstadt, Germany, 2010; pp. 601–603. [Google Scholar]
- Piantoni, P.; Lock, A.L.; Allen, M.S. Palmitic Acid Increased Yields of Milk and Milk Fat and Nutrient Digestibility across Production Level of Lactating Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 7143–7154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yayota, M.; Tsukamoto, M.; Yamada, Y.; Ohtani, S. Milk Composition and Flavor under Different Feeding Systems: A Survey of Dairy Farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 5174–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, A.M.; Drake, S.; Bodyfelt, F.; Clark, S.; Costello, M. History of Sensory Analysis. In The Sensory Evaluation of Dairy Products; Clark, S., Costello, M., Drake, M., Bodyfelt, F., Eds.; Springer US: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hedegaard, V.R.; Kristensen, D.; Nielsen, J.H.; Frøst, M.B.; Østdal, H.; Hermansen, J.E.; Kröger-Ohlsen, M.; Skibsted, L.H. Comparison of Descriptive Sensory Analysis and Chemical Analysis for Oxidative Changes in Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kilcawley, N.K.; Faulkner, H.; Clarke, H.J.; O’Sullivan, M.G.; Kerry, J.P. Factors Influencing the Flavour of Bovine Milk and Cheese from Grass Based Versus Non-Grass Based Milk Production Systems. Foods 2018, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilcawley, K.N. Cheese Flavour. In Fundamentals of Cheese Science; Fox, P.F., Guinee, T.P., Cogan, T.M., McSweeney, P.L.H., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 443–474. [Google Scholar]
- Aprea, E.; Biasioli, F.; Carlin, S.; Endrizzi, I.; Gasperi, F. Investigation of Volatile Compounds in Two Raspberry Cultivars by Two Headspace Techniques: Solid-Phase Microextraction/Gas Chromatography−Mass Spectrometry (Spme/Gc−Ms) and Proton-Transfer Reaction−Mass Spectrometry (Ptr−Ms). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 4011–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Landaverde, A.P.; Torres, J.A.; Qian, M.C. Quantification of Trace Volatile Sulfur Compounds in Milk by Solid-Phase Microextraction and Gas Chromatography–Pulsed Flame Photometric Detection. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 2919–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, M.M.; de la Hoz, L. Flavour of Heated Milks. A Review. Int. Dairy J. 1992, 2, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbach, G. Effect of Feed on Flavor in Dairy Foods. J. Dairy Sci. 1990, 73, 3639–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpino, S.; Acree, T.E.; Barbano, D.M.; Licitra, G.; Siebert, K.J. Chemometric Analysis of Ragusano Cheese Flavor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpino, S.; Mallia, S.; la Terra, S.; Melilli, C.; Licitra, G.; Acree, T.E.; Barbano, D.M.; van Soest, P.J. Composition and Aroma Compounds of Ragusano Cheese: Native Pasture and Total Mixed Rations. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 816–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
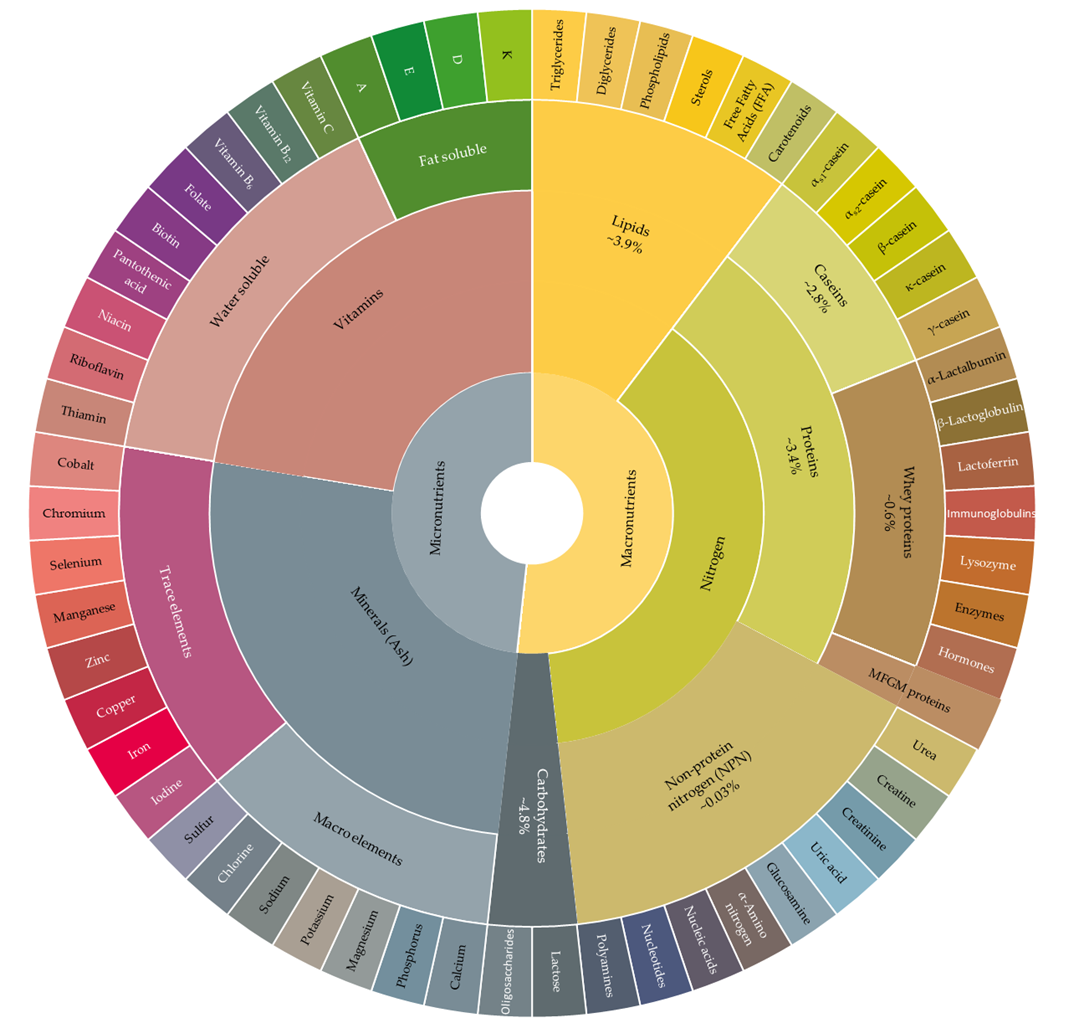
| Component | Concentration | Unit | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Macronutrients | ||||
| Lipids | Fat | 3.42–5.27 | % | [18,20,35] |
| Triglycerides | ~98 | % of total lipids | [36] | |
| Long chain FA (C ≥ 16) | 50–70 | % of total FA in fat globule | [34,37] | |
| Short and medium chain FA (4 ≤ C ≤ 8; 10 ≤ C ≤ 14) | 30–50 | |||
| Nitrogen | Protein | 2.82–4.49 | % | [18,20,35] |
| Caseins | 2.32–3.52 | % | [18,20] | |
| αs1-Casein | 1.1 | [38,39] | ||
| αs2-Casein | 0.3 | |||
| β-Casein | 0.9 | |||
| κ-Casein | 0.3 | |||
| Whey proteins | 0.83–3.52 | [20,40] | ||
| β-Lactoglobulin | 0.32 | [35,39] | ||
| α-Lactalbumin | 0.12 | |||
| Serum albumin | 0.04 | |||
| Lactoferrin | 0.02–0.3 | g/L | [41,42] | |
| IgA | 0.04–0.06 | |||
| IgM | 0.03–0.06 | |||
| IgG | 0.59 | |||
| Lysozyme | 0.0014–0.007 | |||
| MFGM proteins | 1–2 | % of total proteins | [43] | |
| Non-protein nitrogen (NPN) | 0.03–0.2 | % | [20,42] | |
| Urea | 0.654 | mg N/L | [42,44] | |
| Creatinine | 0.019 | |||
| Creatine | 0.355 | |||
| Uric acid | 0.155 | % | ||
| α-amino N | 2.20 | μg/mL | ||
| Carbohydrate | Lactose | 0.46–0.53 | g/L | [2,18,20] |
| Micronutrients | ||||
| Macro elements | Calcium (Ca) | 113.58–150.4 | mg/100 g | [18,35,39,42] |
| Phosphorus (P) | 87.04–109.6 | |||
| Potasium (K) | 143–152 | |||
| Magnesium (Mg) | 9.40–15 | |||
| Sodium (Na) | 48–58 | |||
| Chlorine (Cl) | 100 | |||
| Sulphur (S) | 32 | |||
| Trace elements | Iodine (I) | 0.021 | ||
| Ferrous (Fe) | 0.022–0.166 | |||
| Copper (Cu) | 0.003–0.06 | |||
| Zinc (Zn) | 0.408–0.532 | |||
| Manganese (Mn) | 0.002–0.02 | |||
| Selenium (Se) | 0.001–0.96 | |||
| Cobalt (Co) | 0.002–0.023 | |||
| Fat Soluble Vitamins | Vitamin A (retinol) | 0.4 | mg/L | [38,39,42] |
| Vitamin D (calciferol) | 0.001 | |||
| Vitamin E (tocopherol) | 1.0 | |||
| Vitamin K (phylloquinone) | 0.004–0.018 | |||
| Water Soluble Vitamins | Thiamin | 40 | ||
| Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) | 190 | |||
| Niacin | 0.08 | |||
| Vitamin B12 | 0.357 | |||
| Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) | 0.6 | |||
| Folic acid | 0.05–5 | |||
| Pantothenic acid | 3.5 | |||
| Biotin | 0.03–2 | |||
| Vitamin C | 20 | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alothman, M.; Hogan, S.A.; Hennessy, D.; Dillon, P.; Kilcawley, K.N.; O’Donovan, M.; Tobin, J.; Fenelon, M.A.; O’Callaghan, T.F. The “Grass-Fed” Milk Story: Understanding the Impact of Pasture Feeding on the Composition and Quality of Bovine Milk. Foods 2019, 8, 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8080350
Alothman M, Hogan SA, Hennessy D, Dillon P, Kilcawley KN, O’Donovan M, Tobin J, Fenelon MA, O’Callaghan TF. The “Grass-Fed” Milk Story: Understanding the Impact of Pasture Feeding on the Composition and Quality of Bovine Milk. Foods. 2019; 8(8):350. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8080350
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlothman, Mohammad, Sean A. Hogan, Deirdre Hennessy, Pat Dillon, Kieran N. Kilcawley, Michael O’Donovan, John Tobin, Mark A. Fenelon, and Tom F. O’Callaghan. 2019. "The “Grass-Fed” Milk Story: Understanding the Impact of Pasture Feeding on the Composition and Quality of Bovine Milk" Foods 8, no. 8: 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8080350
APA StyleAlothman, M., Hogan, S. A., Hennessy, D., Dillon, P., Kilcawley, K. N., O’Donovan, M., Tobin, J., Fenelon, M. A., & O’Callaghan, T. F. (2019). The “Grass-Fed” Milk Story: Understanding the Impact of Pasture Feeding on the Composition and Quality of Bovine Milk. Foods, 8(8), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8080350







