Quality Evaluation of Oviductus Ranae Based on PUFAs Using HPLC Fingerprint Techniques Combined with Chemometric Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Samples
2.2. Fatty Acid Extraction
2.3. HPLC Chromatography Analysis
2.4. Validation of the Method
2.5. Establishment of Chromatographic Fingerprint
2.6. Data Analysis
2.6.1. Hierarchical Clustering Analysis (HCA)
2.6.2. Principal component analysis (PCA)
2.6.3. Partial Least Squares Discrimination Analysis (PLS-DA)
3. Results and Discussion
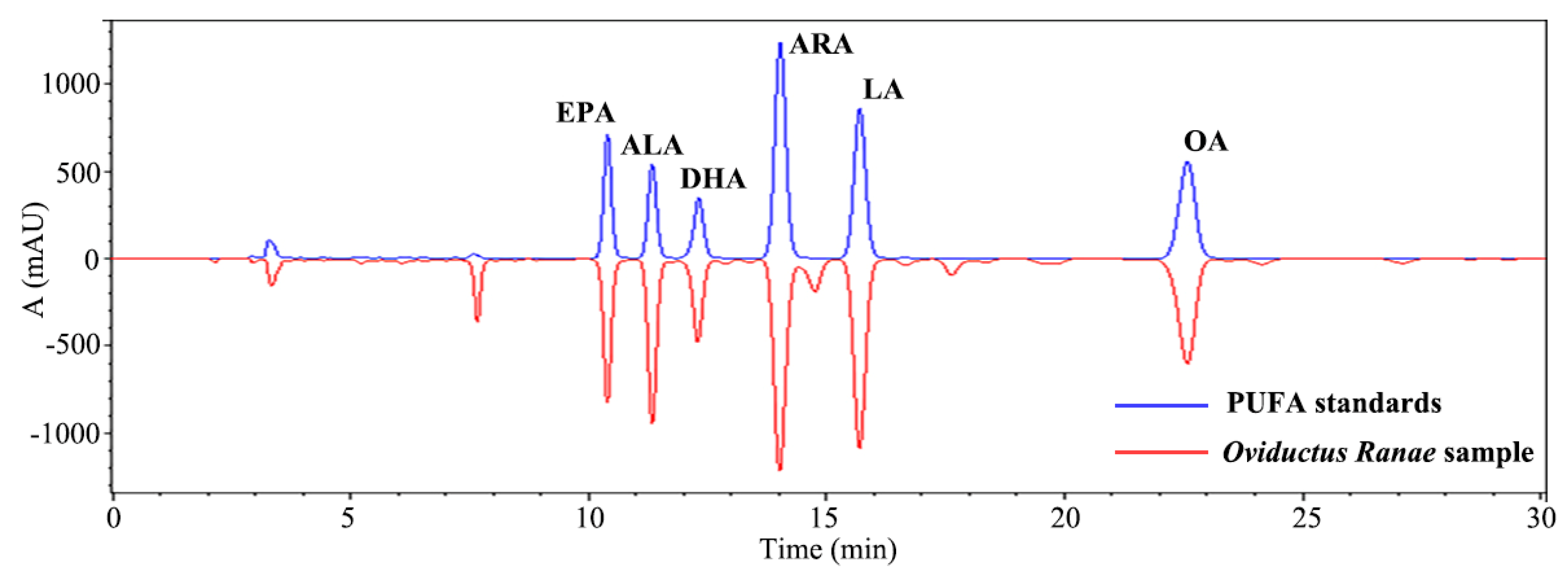
3.1. PUFA Standards Analysis
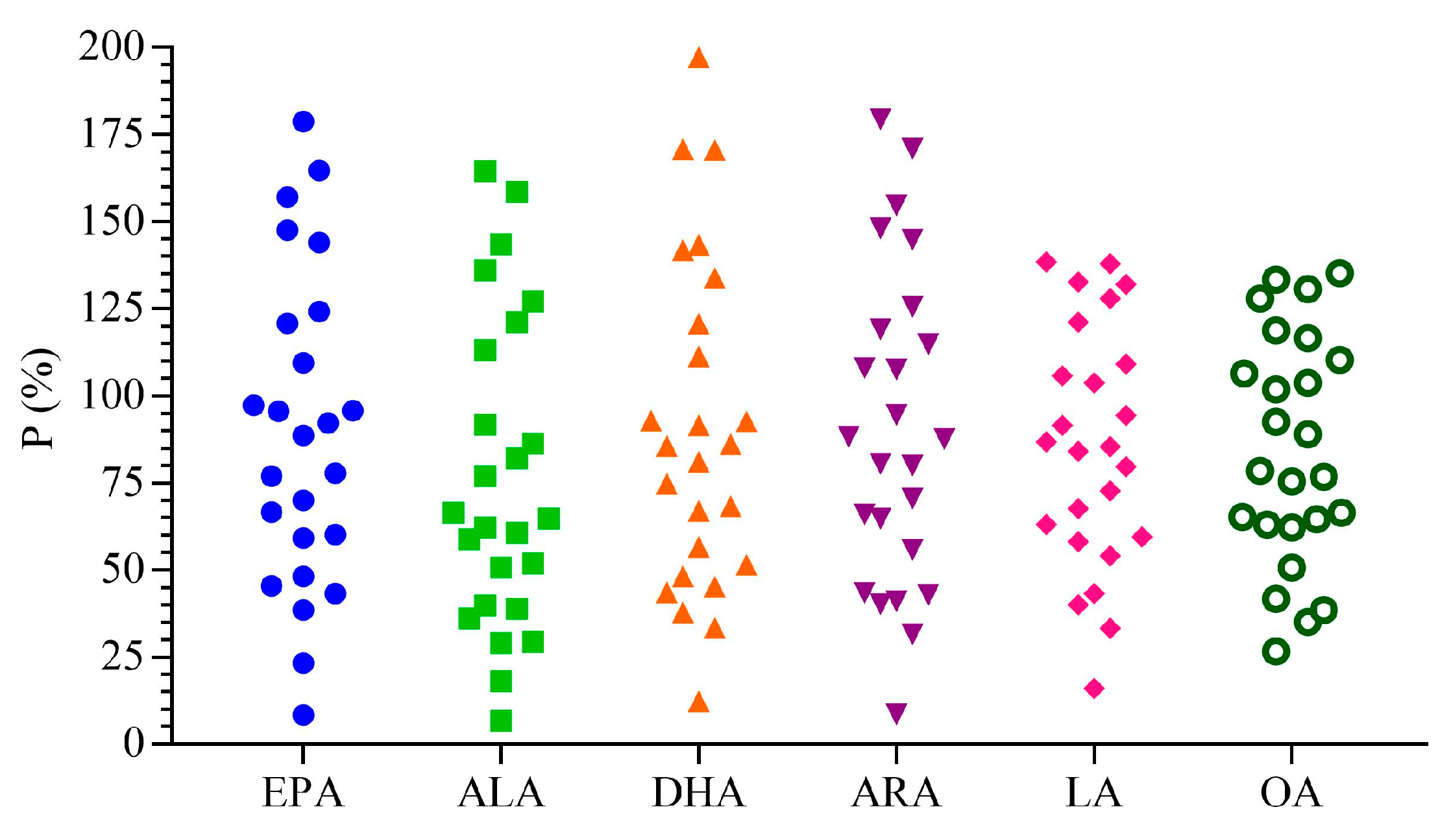
3.2. Methodology Validation
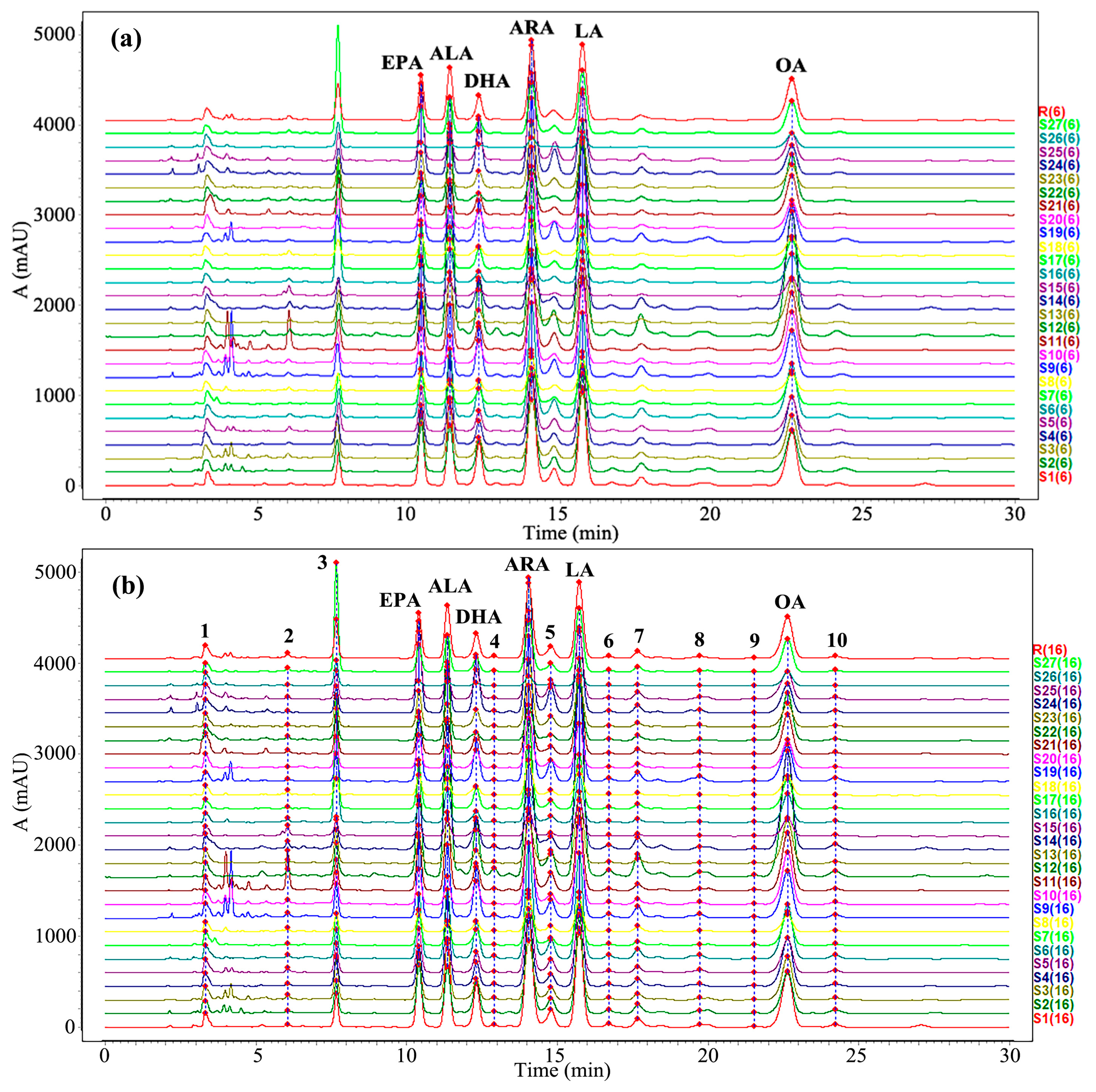
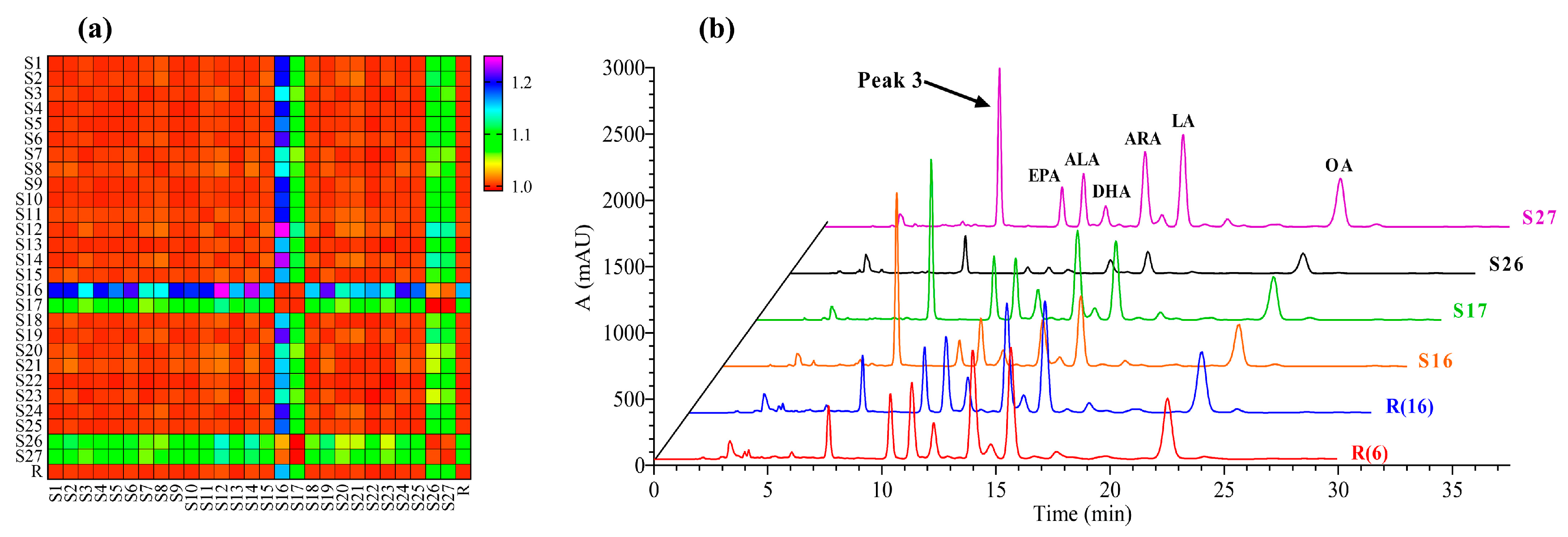
3.3. Fingerprint Analysis
3.4. Analysis of PUFAs in Oviductus Ranae
3.5. Chemometric Analysis
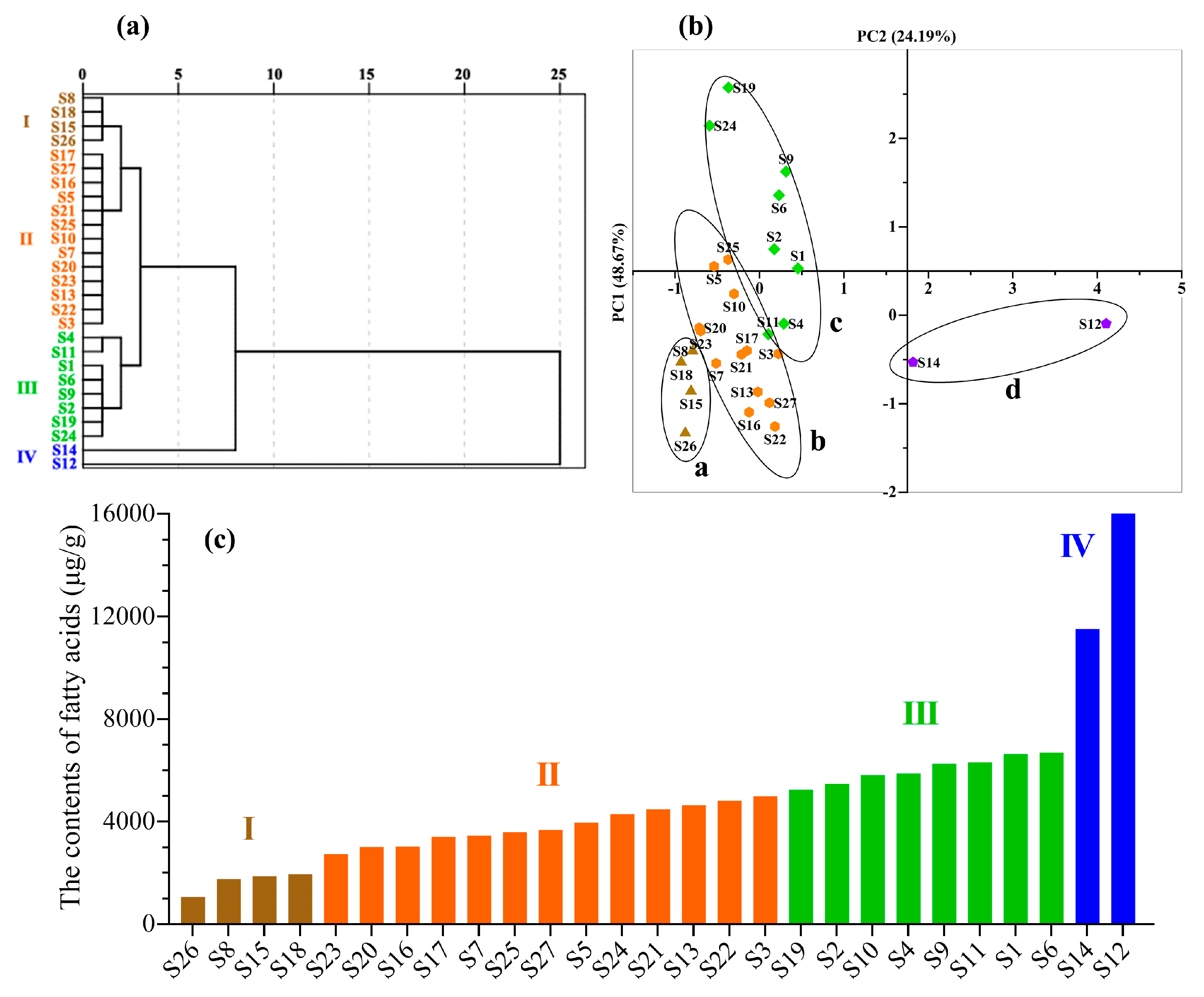
3.5.1. Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA)
3.5.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
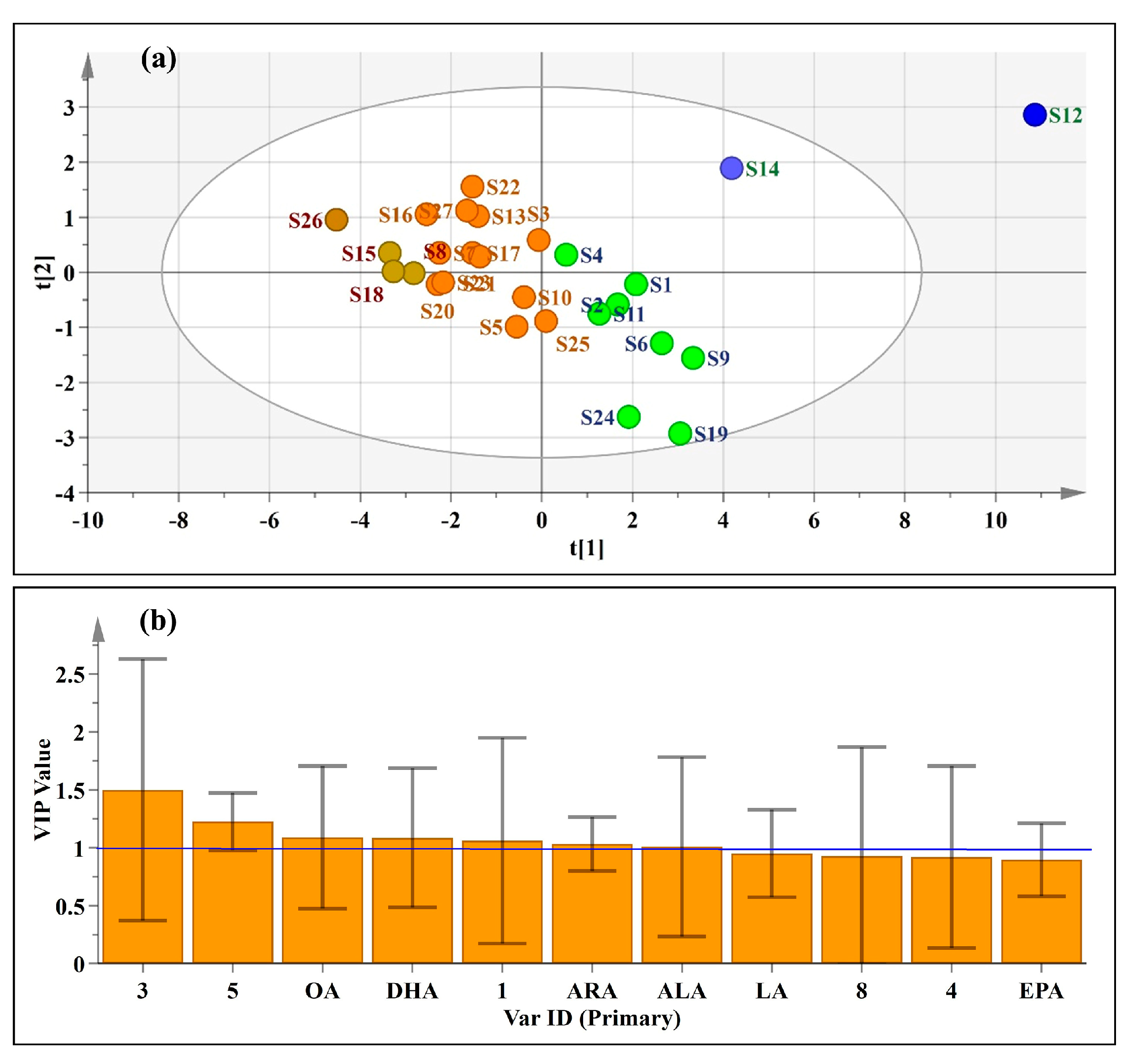
3.5.3. Partial Least Squares Discrimination Analysis (PLS-DA)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gan, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, S.; Guo, H.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. Protein-based fingerprint analysis for the identification of Ranae oviductus using RP-HPLC. Molecules 2019, 24, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.D.; Cui, H.; Xu, X.X.; Mao, L.P.; Zhou, H.L. Antioxidant and immunomodulatory activities of Oviductus ranae in mice. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 54, e17751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Lv, Z.; Jin, X.; Wang, Y. Simultaneous determination of six active components in Oviductus ranae via quantitative analysis of multicomponents by single marker. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2017, 2017, 9194847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.B.; Kong, D.J.; Wu, B.; Wang, S.H.; Wang, Y.S. Synthesis and evaluation of anti-inflammatory and antitussive activity of hydantion derivatives. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2012, 9, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, S.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qu, X. Evaluation of the merits of the new method of Oviductus ranae by HPLC-DAD. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2015, 38, 1218–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Wang, L.L.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.T.; Wang, Z.H. Isolation and identification of two steroid compounds from Oviductus ranae. Nat. Prod. Res. 2010, 24, 1518–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, S.; Yu, J.; Yan, Z.; Zhou, H. Traditional uses, bioactive constituents, biological functions, and safety properties of Oviductus ranae as functional foods in China. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 4739450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X. Effect of Oviductus ranae on reducing serum lipid and ability of anti-anoxia and anti-fatigue. Food Res. Dev. 2012, 33, 201–203. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, C.Y.; Yang, P.; Wang, Y.S.; Qiao, L.; Chen, B.; Wang, S.H.; Xu, Y.; Lu, H.B. Synthesis, evaluation of analgesic and gastric ulcerogenic activities and the metabolites in rat plasma of hydantoin ibuprofen conjugates. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2013, 10, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, F.; Guo, H.; Wang, S.; Ni, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bao, H.; Wang, Y. Antitussive and anti-inflammatory dual-active agents developed from natural product lead compound 1-methylhydantoin. Molecules 2019, 24, 2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Jia, X.; Weng, L.; Dong, J. The nutrition health care function and its product development progress of Oviductus ranae. Asia-Pac. Tradit. Med. 2018, 14, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, S.H.; Luo, Y.; Yang, H.L.; Hu, X.Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Qu, X.B. Separation of steroidal constituents of Oviductus Ranae by one-step method high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2015, 38, 1494–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Study on the Quality Evalutation and the Active Components Derivatives of Oviductus ranae. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Ni, S.; Wang, S.; Gan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, H.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. Environmental Influences on Quality Features of Oviductus ranae in Changbai Mountains. 2019; Under Review. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, L.; Chan, H.; Kuo, P.; Hung, H.; Li, Y.; Kuo, C.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Kuo, D.; Sun, I.; et al. A feasible and practical 1H NMR analytical method for the quality control and quantification of bioactive principles in Lycii Fructus. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwyer, J.T.; Coates, P.M.; Smith, M.J. Dietary supplements: Regulatory challenges and research resources. Nutrients 2018, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fibigr, J.; Šatínský, D.; Solich, P. Current trends in the analysis and quality control of food supplements based on plant extracts. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1036, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fascella, G.; D’Angiolillo, F.; Mammano, M.M.; Amenta, M.; Romeo, F.V.; Rapisarda, P.; Ballistreri, G. Bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity of four rose hip species from spontaneous Sicilian flora. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinli, S.; Zhang, S.; Duan, H.; Shi, S.; Guo, J. Antidepressant effects of petroleum ether extracts from Ranae oviductus. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formul. 2013, 19, 271–274. [Google Scholar]
- You, J.; Zhang, R.; Guo, J.; Liu, Y.; Shi, S.; Hou, W.; Shi, J. Antidepressive effects of petroleum ether extract from Ranae oviductus and its possible mechanism. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2013, 44, 2717–2721. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Qin, J.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Bi, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, W. Determination of α-linolenic acid, linoleic acid and oleic acid in Oviductus ranae by HPLC. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formul. 2013, 19, 82–85. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W. Comparison of the fatty acid in Oviductus Ranae and Forest Frog’s trunk. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2008, 28, 888–890. [Google Scholar]
- Chikwanha, O.C.; Vahmani, P.; Muchenje, V.; Dugan, M.E.R.; Mapiye, C. Nutritional enhancement of sheep meat fatty acid profile for human health and wellbeing. Food Res. Int. 2018, 104, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacks, F.M.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Wu, J.H.Y.; Appel, L.J.; Creager, M.A.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Miller, M.; Rimm, E.B.; Rudel, L.L.; Robinson, J.G.; et al. American Heart, A. Dietary fats and cardiovascular disease a presidential advisory from the american heart association. Circulation 2017, 136, e1–e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Alcalá, L.M.; Calvo, M.V.; Fontecha, J.; Alonso, L. Alterations in the fatty acid composition in infant formulas and ω3-PUFA enriched UHT milk during storage. Foods 2019, 8, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahidi, F.; Ambigaipalan, P. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and their health benefits. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 345–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.D. Dietary n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: Epidemiologic evidence. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2018, 135, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yary, T.; Voutilainen, S.; Tuomainen, T.P.; Ruusunen, A.; Nurmi, T.; Virtanen, J.K. Omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids, serum zinc, delta-5- and delta-6-desaturase activities and incident metabolic syndrome. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2017, 30, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, J.; Qu, Y.; Li, S.; Shen, G.; Chen, A.; Luo, Q.; Liu, X.; Wu, H.; Li, M.; Pu, B.; et al. Application of HPLC fingerprint based on acid amide components in Chinese prickly ash (Zanthoxylum). Ind. Crops. Prod. 2018, 119, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.W.; Lv, Z.Y.; Cui, Q.Y.; Jin, X.Q.; Wang, Y.S. HPLC fingerprint combined with quantitation of main effective components and chemometrics as an efficient method for quality evaluation of Oviductus ranae. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2017, 12, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, P. Chromatographic fingerprint analysis of yohimbe bark and related dietary supplements using UHPLC/UV/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 61, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, S.; Xie, M.; Nie, S.; Liu, W.; Li, C.; Gong, X.; Wang, Y. Quality control and original discrimination of Ganoderma lucidum based on high-performance liquid chromatographic fingerprints and combined chemometrics methods. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 623, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichelli, A.; Pertesana, G.P. High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of chlorophylls, pheophytins and carotenoids in virgin olive oils: Chemometric approach to variety classification. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1046, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Gong, X.; Wang, Z.; Pan, C.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, X.; Liu, W. Multiple fingerprint profiles and chemometrics analysis of polysaccharides from Sarcandra glabra. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulukcu, E.; Cebi, N.; Sagdic, O. Chemical fingerprinting of seeds of some salvia species in Turkey by using GC-MS and FTIR. Foods 2019, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, A.; Jangir, J.; Anu-Appaiah, K.A. Chemical characterization complemented with chemometrics for the botanical origin identification of unifloral and multifloral honeys from India. Food Res. Int. 2018, 107, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Delgado, R.; Eugenia Muñoz-Pérez, M.; Arce, L. Detection of adulteration in extra virgin olive oils by using UV-IMS and chemometric analysis. Food Control 2018, 85, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahena, F.; Zaidul, I.S.M.; Jinap, S.; Yazid, A.M.; Khatib, A.; Norulaini, N.A.N. Fatty acid compositions of fish oil extracted from different parts of Indian mackerel (Rastrelliger kanagurta) using various techniques of supercritical CO2 extraction. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Yang, J. 2.27-Common clustering algorithms. In Comprehensive Chemometrics; Brown, S.D., Tauler, R., Walczak, B., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 577–618. [Google Scholar]
- Granato, D.; Santos, J.S.; Escher, G.B.; Ferreira, B.L.; Maggio, R.M. Use of principal component analysis (PCA) and hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) for multivariate association between bioactive compounds and functional properties in foods: A critical perspective. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 72, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; Shao, C.; Li, C.; Liu, S.; Peng, X.; Xu, Y. Chemical fingerprint analysis for the quality evaluation of deepure instant Pu-erh tea by HPLC combined with chemometrics. Food Anal. Meth. 2016, 9, 3298–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, A.; Centonze, C.; Grasso, M.E.; Latronico, M.F.; Mastrangelo, P.F.; Sparascio, F.; Fanizzi, F.P.; Maffia, M. A comparative study of phenols in apulian Italian wines. Foods 2017, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasenaki, M.E.; Drakopoulou, S.K.; Aalizadeh, R.; Thomaidis, N.S. Targeted and untargeted metabolomics as an enhanced tool for the detection of pomegranate juice adulteration. Foods 2019, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.; Hwang, G.; Kim, K.M.; Ahn, H.; Park, W.; Van Den Berg, F.; Hong, Y.; Lee, C. Metabolomic studies on geographical grapes and their wines using 1H NMR analysis coupled with multivariate statistics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, L.; Yuan, D.; Liang, Y.; Xie, P.; Zhao, Y. Quality control and discrimination of Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae and Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae Viride based on high-performance liquid chromatographic fingerprints and multivariate statistical analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 588, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragusa, A.; Centonze, C.; Grasso, M.E.; Latronico, M.F.; Mastrangelo, P.F.; Fanizzi, F.P.; Maffia, M. Composition and statistical analysis of biophenols in Apulian Italian EVOOs. Foods 2017, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragusa, A.; Centonze, C.; Grasso, M.E.; Latronico, M.F.; Mastrangelo, P.F.; Sparascio, F.; Maffia, M. HPLC analysis of phenols in negroamaro and primitivo red wines from Salento. Foods 2019, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wu, Z.; Yang, K.; Ding, H.; Wu, Y. Quantitative analysis combined with chromatographic fingerprint for comprehensive evaluation of Danhong injection using HPLC-DAD. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 76, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Tang, L.; Wu, H.; Zhou, G.; Wang, T.; Kou, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, Z. Chemometric analyses for the characterization of raw and processed seeds of Descurainia sophia (L.) based on HPLC fingerprints. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 111, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| No. | Origin | Collection Date |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | Jilin, Jilin | December 2016 |
| S2 | Jilin, Jilin | December 2016 |
| S3 | Jilin, Jilin | December 2016 |
| S4 | Jilin, Jilin | December 2016 |
| S5 | Jilin, Jilin | December 2016 |
| S6 | Jilin, Jilin | November 2015 |
| S7 | Jilin, Jilin | November 2015 |
| S8 | Jilin, Jilin | December 2016 |
| S9 | Baishan, Jilin | December 2016 |
| S10 | Baishan, Jilin | November 2015 |
| S11 | Baishan, Jilin | December 2016 |
| S12 | Baishan, Jilin | December 2016 |
| S13 | Baishan, Jilin | December 2016 |
| S14 | Baishan, Jilin | November 2015 |
| S15 | Baishan, Jilin | December 2016 |
| S16 | Baishan, Jilin | December 2016 |
| S17 | Baishan, Jilin | December 2016 |
| S18 | Tonghua, Jilin | December 2016 |
| S19 | Tonghua, Jilin | January 2016 |
| S20 | Tonghua, Jilin | December 2016 |
| S21 | Tonghua, Jilin | December 2016 |
| S22 | Tonghua, Jilin | December 2016 |
| S23 | Yanbian, Jilin | March 2016 |
| S24 | Yanbian, Jilin | March 2016 |
| S25 | Yanbian, Jilin | December 2016 |
| S26 | Yanbian, Jilin | December 2016 |
| S27 | Yanbian, Jilin | March 2016 |
| Compounds | Regression Equation | R2 | Linearity Range (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| EPA | y = 11198x + 94.40 | 0.9999 | 14.59–116.74 |
| ALA | y = 6244x + 91.95 | 0.9999 | 21.76–174.07 |
| DHA | y = 14151x + 34.20 | 1.0000 | 7.20–57.57 |
| ARA | y = 10379x + 505.69 | 0.9996 | 38.34–306.73 |
| LA | y = 4221x + 522.27 | 0.9994 | 68.35–546.82 |
| OA | y = 817x + 866.82 | 0.9982 | 303.56–2428.48 |
| Peak No. | Precision RSD | Repeatability RSD | Stability RSD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retention Time | Peak Area | Retention Time | Peak Area | Retention Time | Peak Area | |
| EPA | 0.29% | 1.90% | 1.37% | 0.73% | 0.75% | 0.64% |
| ALA | 0.35% | 2.16% | 1.04% | 2.18% | 0.86% | 0.74% |
| DHA | 0.38% | 3.01% | 0.57% | 3.62% | 0.90% | 0.92% |
| ARA | 0.48% | 2.90% | 1.12% | 3.28% | 1.08% | 0.85% |
| LA | 0.51% | 1.79% | 1.03% | 0.73% | 1.15% | 0.21% |
| OA | 0.65% | 1.91% | 1.86% | 1.51% | 1.35% | 0.25% |
| No | EPA (μg/g) | ALA (μg/g) | DHA (μg/g) | ARA (μg/g) | LA (μg/g) | OA (μg/g) | Total PUFAs (μg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 214.09 ± 6.68 | 465.34 ± 19.06 | 115.22 ± 2.45 | 471.10 ± 10.03 | 1085.30 ± 33.89 | 4289.44 ± 91.30 | 6640.49 ± 207.35 |
| S2 | 142.43 ± 5.83 | 253.48 ± 5.39 | 95.69 ± 3.31 | 460.82 ± 15.96 | 1120.31 ± 45.88 | 3408.23 ± 118.06 | 5480.96 ± 224.45 |
| S3 | 124.53 ± 2.65 | 332.17 ± 11.51 | 57.82 ± 0.86 | 255.86 ± 3.79 | 725.47 ± 15.44 | 3494.53 ± 51.71 | 4990.39 ± 106.21 |
| S4 | 115.29 ± 2.45 | 482.87 ± 16.73 | 62.64 ± 0.93 | 300.60 ± 4.45 | 1028.25 ± 21.88 | 3901.76 ± 57.74 | 5891.39 ± 125.39 |
| S5 | 126.43 ± 2.69 | 152.58 ± 5.29 | 54.68 ± 0.81 | 342.29 ± 5.07 | 713.37 ± 15.18 | 2577.81 ± 38.15 | 3967.16 ± 84.44 |
| S6 | 187.37 ± 6.49 | 373.22 ± 5.52 | 96.78 ± 3.44 | 491.98 ± 17.48 | 1169.85 ± 40.52 | 4380.19 ± 155.67 | 6699.38 ± 232.07 |
| S7 | 86.57 ± 3.00 | 106.14 ± 1.57 | 45.18 ± 1.61 | 206.08 ± 7.32 | 493.37 ± 17.09 | 2524.24 ± 89.71 | 3461.58 ± 119.91 |
| S8 | 59.09 ± 0.87 | 52.98 ± 1.88 | 29.38 ± 0.90 | 130.51 ± 4.00 | 340.31 ± 5.04 | 1153.14 ± 35.34 | 1765.41 ± 26.13 |
| S9 | 232.37 ± 3.44 | 399.19 ± 14.19 | 133.14 ± 4.08 | 543.52 ± 16.66 | 1125.50 ± 16.66 | 3827.95 ± 117.30 | 6261.68 ± 92.66 |
| S10 | 101.23 ± 1.50 | 148.88 ± 5.29 | 62.68 ± 1.92 | 399.61 ± 12.25 | 897.53 ± 13.28 | 4203.24 ± 128.80 | 5813.18 ± 86.03 |
| S11 | 161.58 ± 5.74 | 421.28 ± 12.91 | 75.14 ± 2.13 | 343.60 ± 9.74 | 880.00 ± 31.27 | 4442.21 ± 125.96 | 6323.82 ± 224.74 |
| S12 | 345.16 ± 12.27 | 1602.63 ± 49.11 | 143.55 ± 4.07 | 729.40 ± 20.68 | 2807.28 ± 99.77 | 11109.46 ± 315.01 | 16737.47 ± 594.83 |
| S13 | 77.00 ± 2.74 | 240.83 ± 7.38 | 34.85 ± 0.99 | 177.32 ± 5.03 | 776.62 ± 27.60 | 3344.39 ± 94.83 | 4651.01 ± 165.29 |
| S14 | 157.19 ± 4.82 | 702.42 ± 19.92 | 90.36 ± 2.11 | 378.98 ± 8.83 | 1958.06 ± 60.00 | 8232.10 ± 191.83 | 11519.11 ± 352.98 |
| S15 | 30.26 ± 0.93 | 85.19 ± 2.42 | 22.63 ± 0.53 | 100.18 ± 2.33 | 367.33 ± 11.26 | 1266.76 ± 29.52 | 1872.34 ± 57.37 |
| S16 | 50.02 ± 1.42 | 177.98 ± 4.15 | 32.49 ± 1.41 | 127.79 ± 5.53 | 505.00 ± 14.32 | 2145.41 ± 92.90 | 3038.70 ± 86.16 |
| S17 | 124.29 ± 3.52 | 225.99 ± 5.27 | 58.18 ± 2.52 | 254.30 ± 11.01 | 573.60 ± 16.26 | 2186.20 ± 94.67 | 3422.57 ± 97.05 |
| S18 | 56.38 ± 1.60 | 86.10 ± 2.01 | 30.58 ± 1.32 | 136.73 ± 5.92 | 282.63 ± 8.01 | 1371.83 ± 59.40 | 1964.25 ± 55.70 |
| S19 | 204.33 ± 4.76 | 190.00 ± 8.23 | 115.27 ± 4.32 | 640.97 ± 24.04 | 1174.22 ± 27.36 | 2921.16 ± 109.57 | 5245.95 ± 122.24 |
| S20 | 91.16 ± 2.12 | 114.00 ± 4.94 | 50.49 ± 1.89 | 224.45 ± 8.42 | 459.50 ± 10.71 | 2071.03 ± 77.68 | 3010.64 ± 70.16 |
| S21 | 119.93 ± 2.79 | 182.93 ± 7.92 | 61.78 ± 2.32 | 278.98 ± 10.46 | 801.59 ± 18.68 | 3039.26 ± 114.00 | 4484.46 ± 104.50 |
| S22 | 62.61 ± 2.71 | 355.43 ± 13.33 | 25.50 ± 0.47 | 138.36 ± 2.54 | 617.66 ± 26.75 | 3624.21 ± 66.43 | 4823.76 ± 208.87 |
| S23 | 100.14 ± 4.34 | 117.11 ± 4.39 | 46.09 ± 0.84 | 280.98 ± 5.15 | 535.16 ± 23.17 | 1666.96 ± 30.56 | 2746.45 ± 118.92 |
| S24 | 260.79 ± 9.78 | 269.35 ± 4.94 | 154.45 ± 4.82 | 570.49 ± 17.81 | 925.92 ± 34.73 | 2120.20 ± 66.20 | 4301.20 ± 161.34 |
| S25 | 191.92 ± 7.20 | 172.66 ± 3.16 | 81.40 ± 2.54 | 365.47 ± 11.41 | 736.09 ± 27.61 | 2043.51 ± 63.81 | 3591.06 ± 134.70 |
| S26 | 10.88 ± 0.20 | 19.81 ± 0.62 | 8.31 ± 0.34 | 27.07 ± 1.11 | 136.43 ± 2.50 | 878.52 ± 35.98 | 1081.01 ± 19.82 |
| S27 | 78.25 ± 1.43 | 194.87 ± 6.08 | 38.27 ± 1.57 | 209.59 ± 8.58 | 676.80 ± 12.41 | 2478.02 ± 101.48 | 3675.80 ± 67.38 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, H.; Gan, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Ni, S.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. Quality Evaluation of Oviductus Ranae Based on PUFAs Using HPLC Fingerprint Techniques Combined with Chemometric Methods. Foods 2019, 8, 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8080322
Guo H, Gan Y, Liu M, Wang S, Ni S, Zhou Y, Xiao Y, Wang Z, Wang Y. Quality Evaluation of Oviductus Ranae Based on PUFAs Using HPLC Fingerprint Techniques Combined with Chemometric Methods. Foods. 2019; 8(8):322. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8080322
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Hongye, Yuanshuai Gan, Min Liu, Shihan Wang, Shuling Ni, Yan Zhou, Yao Xiao, Zhihan Wang, and Yongsheng Wang. 2019. "Quality Evaluation of Oviductus Ranae Based on PUFAs Using HPLC Fingerprint Techniques Combined with Chemometric Methods" Foods 8, no. 8: 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8080322
APA StyleGuo, H., Gan, Y., Liu, M., Wang, S., Ni, S., Zhou, Y., Xiao, Y., Wang, Z., & Wang, Y. (2019). Quality Evaluation of Oviductus Ranae Based on PUFAs Using HPLC Fingerprint Techniques Combined with Chemometric Methods. Foods, 8(8), 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8080322






