Chocolate Quality Assessment Based on Chemical Fingerprinting Using Near Infra-red and Machine Learning Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chocolate Samples
2.2. Participants for Sensory Sessions
2.3. Sensory Evaluation
2.4. pH, Total Soluble Solids (TSS) and Viscosity Measurements
2.5. Near infra-red Spectroscopy and Color Measurements
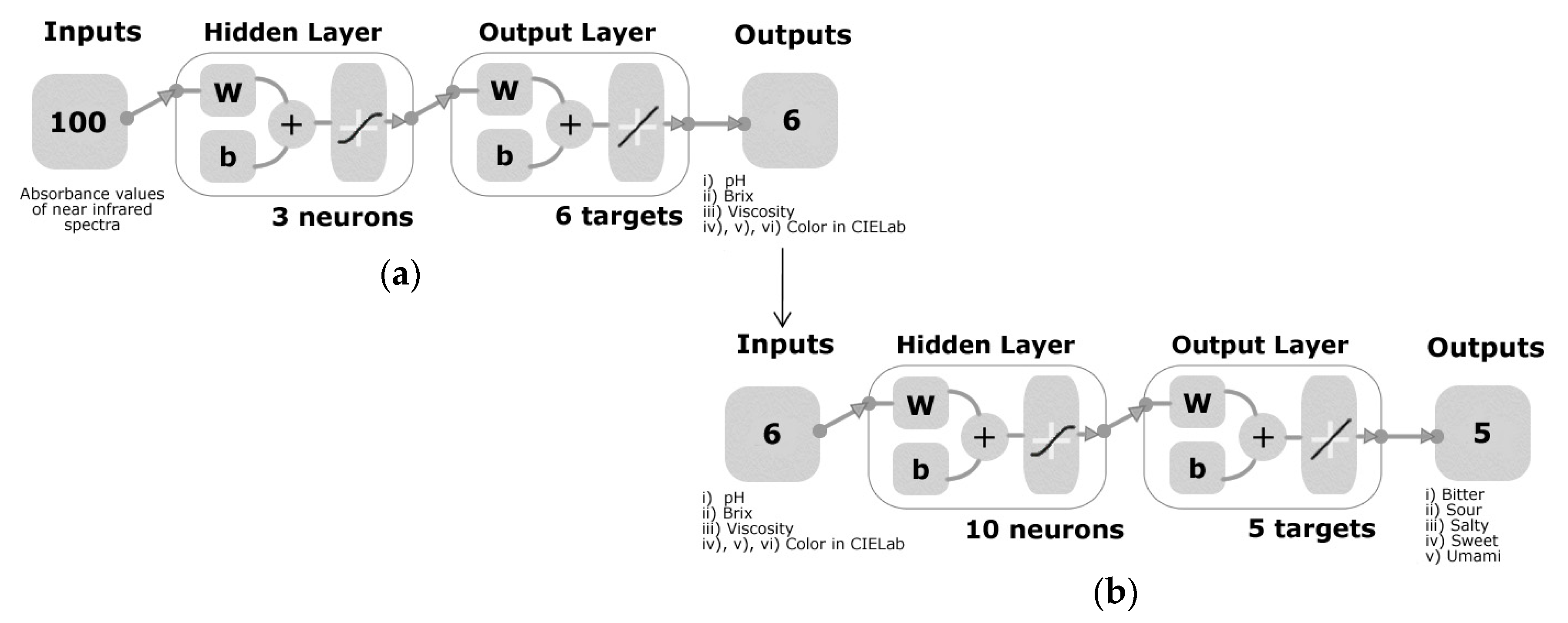
2.6. Statistical Analysis and Machine Learning Modeling
3. Results
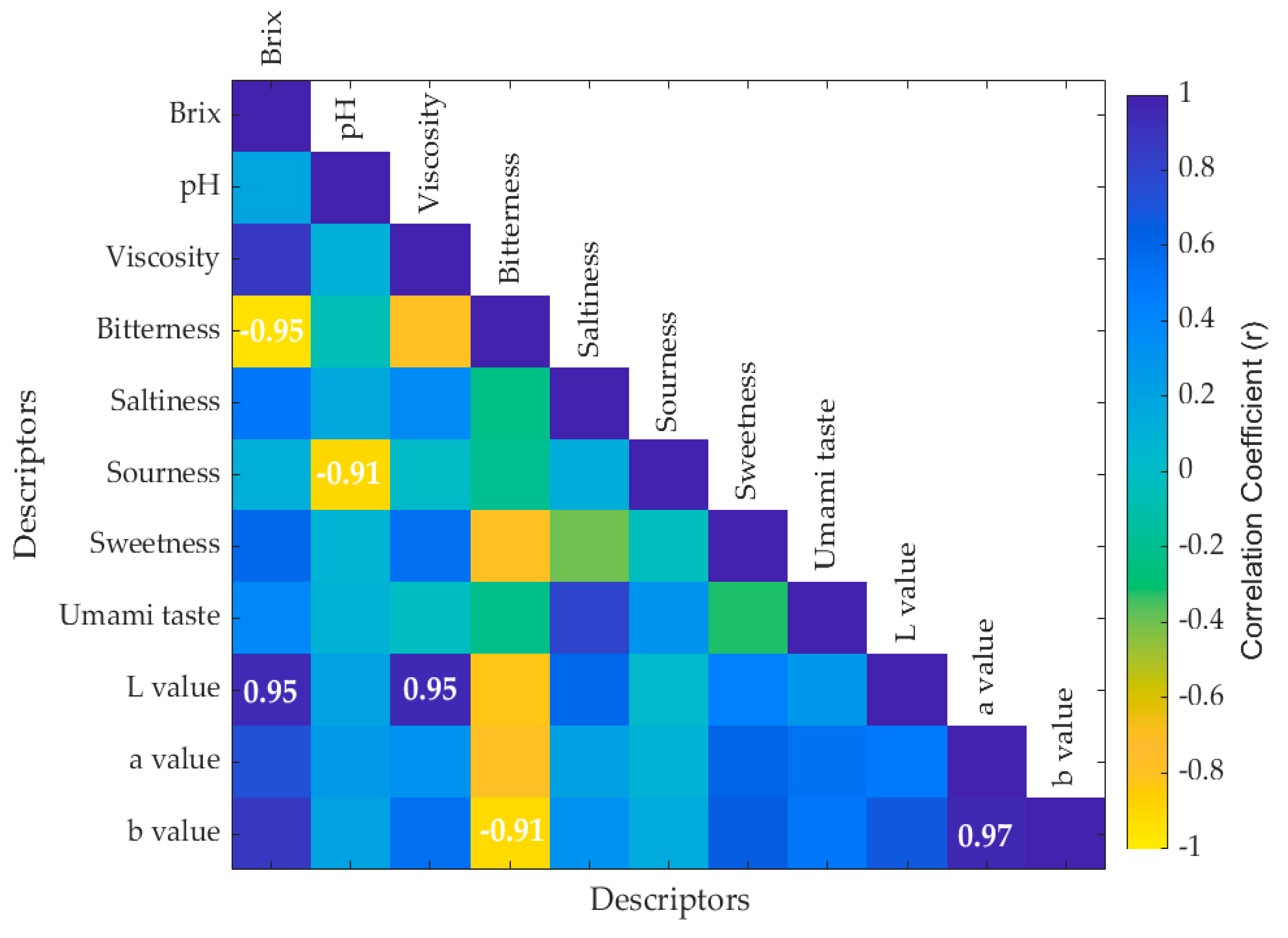
3.1. Sensory and Chemical Analysis
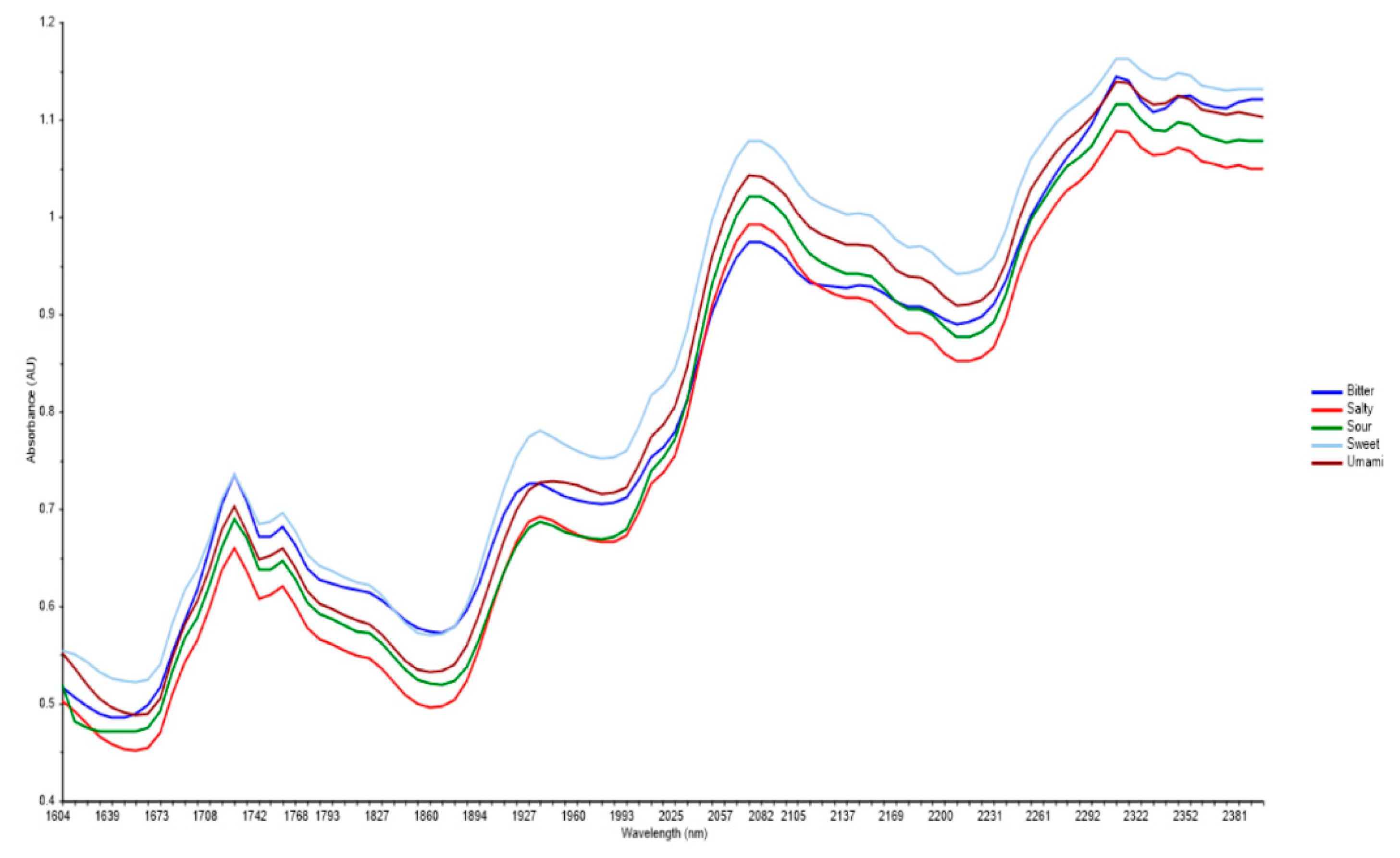
3.2. Near Infra-Red Spectroscopy
3.3. Multivariate Data Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cocoa Beans: From Tree to Factory. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/9781444301588.ch2 (accessed on 20 September 2019).
- Afoakwa, E.; Paterson, A.; Fowler, M. Factors influencing rheological and textural qualities in chocolate—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glicerina, V.; Balestra, F.; Dalla Rosa, M.; Romani, S. Rheological, textural and calorimetric modifications of dark chocolate during process. J. Food Eng. 2013, 119, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servais, C.; Ranc, H.; Roberts, I. Determination of chocolate viscosity. J. Texture Stud. 2003, 34, 467–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consumer Insight into the Monosodium Glutamate. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/book/10.1002/9781444301588 (accessed on 20 September 2019).
- Wendin, K.; Allesen-Holm, B.H.; Bredie, W.L. Do facial reactions add new dimensions to measuring sensory responses to basic tastes? Food Qual. Prefer. 2011, 22, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consumer Insight into the Monosodium Glutamate. Available online: https://scholar.google.com.hk/scholar?hl=zh-CN&as_sdt=0%2C5&as_ylo=2015&q=Consumer+insight+into+the+monosodium+glutamate&btnG= (accessed on 20 September 2019).
- Hashimoto, J.; Lima, J.; Celeghini, R.M.S.; Nogueira, A.; Efraim, P.; Poppi, R.; Pallone, J.A.L. Quality Control of Commercial Cocoa Beans (Theobroma cacao L.) by Near-infrared Spectroscopy. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, C. Near Infrared Spectroscopy: Fundamentals, practical aspects and analytical applications. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2003, 14, 198–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Infrared Spectroscopy for Food Quality Analysis and Control. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez Viejo, C.; Fuentes, S.; Torrico, D.; Howell, K.; Dunshea, F.R. Assessment of beer quality based on foamability and chemical composition using computer vision algorithms, near infrared spectroscopy and machine learning algorithms. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M. Prediction of total soluble solids and ph in banana using near infrared spectroscopy. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2018, 13, 254. [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza, F.; Cichy, K.; Sprague, C.; Goffnett, A.; Lu, R.; Kelly, J. Prediction of canned black bean texture (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) from intact dry seeds using visible/near infrared spectroscopy and hyperspectral imaging data. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewe, V.; Navarro-Cerrillo, R.M.; García-Olmo, J.; Riccioli, C.; Sánchez-Cuesta, R. Discriminant analysis of Mediterranean pine nuts (Pinus pinea L.) from Chilean plantations by near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS). Food Control 2017, 73, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krähmer, A.; Engel, A.; Kadow, D.; Ali, N.; Umaharan, P.; Kroh, L.; Schulz, H. Fast and neat—Determination of biochemical quality parameters in cocoa using near infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2015, 181, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Costa Filho, P.A. Rapid determination of sucrose in chocolate mass using near infrared spectroscopy. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 631, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, A.M.C.; Franklin, J.G.; Grant, A.; Griffiths, N.M.; Shepherd, R.; Fenwick, G.R. Prediction of chocolate quality from near-infrared spectroscopic measurements of the raw cocoa beans. Vib. Spectrosc. 1991, 2, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, S.; Gonzalez Viejo, C.; Torrico, D.; Dunshea, F. Development of a Biosensory Computer Application to Assess Physiological and Emotional Responses from Sensory Panelists. Sensors 2018, 18, 2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homayouni Rad, A.; Roudbaneh, M.; Aref Hosseyni, S. Filled chocolate supplemented with Lactobacillus paracasei. Int. Res. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2014, 8, 2026–2031. [Google Scholar]
- Vollmer, M.; Möllmann, K.-P.; Karstädt, D. More experiments with microwave ovens. Phys. Educ. 2004, 39, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Conesa, A.; Manera, F.C.; Brotons, J.M.; Fernandez-Zapata, J.C.; Simón, I.; Simón-Grao, S.; Alfosea-Simón, M.; Nicolás, J.M.; Valverde, J.M.; García-Sanchez, F. Changes in the content of chlorophylls and carotenoids in the rind of Fino 49 lemons during maturation and their relationship with parameters from the CIELAB color space. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 243, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, D.A.; Ciurczak, E.W. Handbook of Near-Infrared Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Erdem, Ö.; Gültekin Özgüven, M.; Berktaş, I.; Erşan, S.; Tuna, H.E.; Karadağ, A.; Özçelik, B.; Güneş, G.; Cutting, S.M. Development of a novel synbiotic dark chocolate enriched with Bacillus indicus HU36, maltodextrin and lemon fiber: Optimization by response surface methodology. Lebensm. Wiss. Technol. 2014, 56, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moros, J.; Iñón, F.A.; Garrigues, S.; de la Guardia, M. Near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy and neural networks for measuring nutritional parameters in chocolate samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 584, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, R.; Magrí, A.D.; Magrí, A.L.; Marini, D.; Marini, F. Chemical authentication of extra virgin olive oil varieties by supervised chemometric procedures. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Li, X. Discriminating varieties of waxberry using near infrared spectra. J. Infrared Millim. Waves Chin. Ed. 2006, 25, 192. [Google Scholar]
- Ibarz, A.; Pagán, J.; Panadés, R.; Garza, S. Photochemical destruction of color compounds in fruit juices. J. Food Eng. 2005, 69, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.-T.; Ou, L.-C.; Luo, M.R.; Hutchings, J.B. Optimisation of food expectations using product colour and appearance. Food Qual. Prefer. 2012, 23, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, H.; He, Y. Theory and application of near infrared reflectance spectroscopy in determination of food quality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, A.H.; He, Y.; Pereira, A.G. Non-destructive measurement of acidity, soluble solids and firmness of Satsuma mandarin using Vis/NIR-spectroscopy techniques. J. Food Eng. 2006, 77, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Zhang, G.; Kokot, S. Simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of maltol, ethyl maltol, vanillin and ethyl vanillin in foods by multivariate calibration and artificial neural networks. Food Chem. 2005, 89, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geesink, G.; Schreutelkamp, F.; Frankhuizen, R.; Vedder, H.; Faber, N.; Kranen, R.; Gerritzen, M. Prediction of pork quality attributes from near infrared reflectance spectra. Meat Sci. 2003, 65, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aske, N.; Kallevik, H.; Sjöblom, J. Determination of saturate, aromatic, resin, and asphaltenic (SARA) components in crude oils by means of infrared and near-infrared spectroscopy. Energy Fuels 2001, 15, 1304–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M.; Coello, J.; Iturriaga, H.; Maspoch, S.; Pages, J. Calibration in non-linear near infrared reflectance spectroscopy: A comparison of several methods. Anal. Chim. Acta 1999, 384, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, UK, 2016; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Beale, M.H.; Hagan, M.T.; Demuth, H.B. Neural Network Toolbox™ User’s Guide; The MathWorks, Inc.: Natick, MA, USA. Available online: www. mathworks.com (accessed on 20 September 2019).
- Yan, L.; Bai, Y.; Yang, B.; Chen, N.; Tan, Z.A.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A. Extending absorption of near-infrared wavelength range for high efficiency CIGS solar cell via adjusting energy band. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2018, 18, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quelal Vásconez, M.; Pérez Esteve, É.; Arnau Bonachera, A.; Barat, J.; Talens, P. Rapid fraud detection of cocoa powder with carob flour using near infrared spectroscopy. Food Control 2018, 92, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajka, T.; Riddellova, K.; Tomaniova, M.; Hajslova, J. Recognition of beer brand based on multivariate analysis of volatile fingerprint. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 4195–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Sun, H.; Ni, Z.; Yan, G. Rapid determination of oil quantity in intact rapeseeds using near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Food Process Eng. 2018, 41, e12594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, W.F. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy The Giant is Running Strong. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 42A–53A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Bitterness | Saltiness | Sourness | Sweetness | Umami | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bitter | 10.16 ± 3.62 a | 2.25 ± 2.91 c,d | 2.35 ± 3.40 b,c | 4.31 ± 3.34 c | 3.28 ± 4.13 c | |
| Salty | 3.15 ± 3.90 b | 13.37 ± 2.25 a | 4.17 ± 4.39 b | 5.12 ± 3.69 c | 6.40 ± 4.70 a,b | |
| Sour | 2.17 ± 2.85 b,c | 3.93 ± 3.82 c | 9.54 ± 4.29 a | 9.00 ± 3.61 b | 4.79 ± 3.77 b,c | |
| Sweet | 0.99 ± 2.35 c | 1.84 ± 2.48 d | 1.15 ± 2.05 c | 11.95 ± 3.39 a | 2.56 ± 3.22 c | |
| Umami | 2.82 ± 4.07 b,c | 7.02 ± 3.17 b | 3.31 ± 3.67 b,c | 7.85 ± 4.45 b | 7.43 ± 5.25 a | |
| Sample | pH | Brix | Viscosity (cP) | L Value | a Value | b Value |
| Bitter | 6.40 ± 0.07 c | 3.90 ± 0.34 d | 13680 ± 2319 d | 40.73 | 12.19 | 4.37 |
| Salty | 6.56 ± 0.07 b | 6.27 ± 0.89 a | 23443 ± 618 a | 65.21 | 20.47 | 23.05 |
| Sour | 5.42 ± 0.01 d | 5.64 ± 0.28 c | 19360 ± 444 b | 53.57 | 22.55 | 23.95 |
| Sweet | 6.91 ± 0.40 a | 6.20 ± 0.19 a,b | 23600 ± 664 a | 60.94 | 23.49 | 26.02 |
| Umami | 6.90 ± 0.05 a | 5.82 ± 0.58 b,c | 16747 ± 674 c | 53.19 | 30.40 | 32.30 |
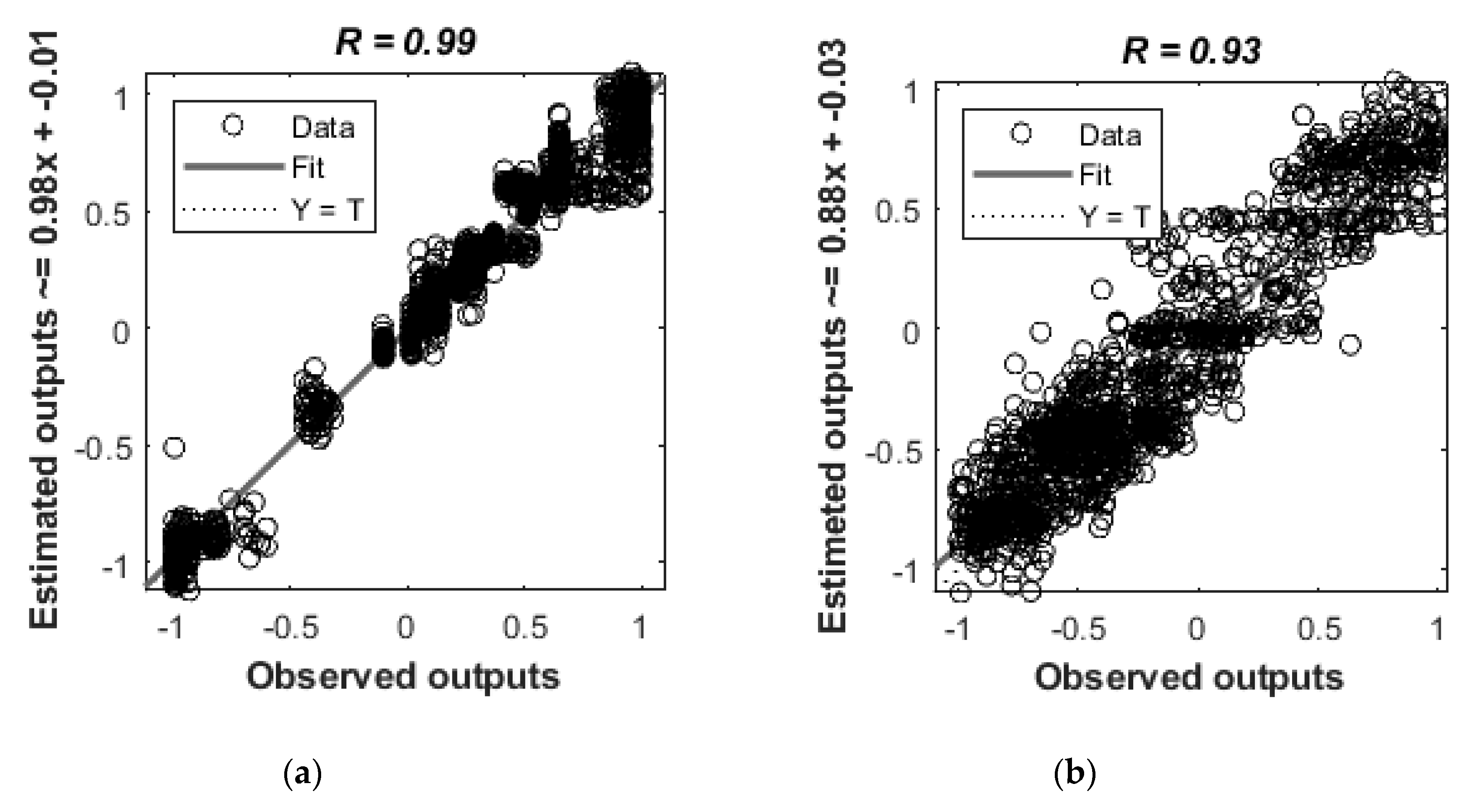
| Stage | Samples | R | Performance (MSE) | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | ||||
| Training | 84 | 0.99 | 0.001 | 0.98 |
| Validation | 18 | 0.99 | 0.01 | 0.99 |
| Testing | 18 | 0.99 | 0.01 | 0.97 |
| Overall | 120 | 0.99 | 0.01 | 0.98 |
| Model 2 | ||||
| Training | 84 | 0.94 | 0.05 | 0.88 |
| Validation | 18 | 0.93 | 0.05 | 0.91 |
| Testing | 18 | 0.93 | 0.05 | 0.86 |
| Overall | 120 | 0.93 | 0.04 | 0.88 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gunaratne, T.M.; Gonzalez Viejo, C.; Gunaratne, N.M.; Torrico, D.D.; Dunshea, F.R.; Fuentes, S. Chocolate Quality Assessment Based on Chemical Fingerprinting Using Near Infra-red and Machine Learning Modeling. Foods 2019, 8, 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8100426
Gunaratne TM, Gonzalez Viejo C, Gunaratne NM, Torrico DD, Dunshea FR, Fuentes S. Chocolate Quality Assessment Based on Chemical Fingerprinting Using Near Infra-red and Machine Learning Modeling. Foods. 2019; 8(10):426. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8100426
Chicago/Turabian StyleGunaratne, Thejani M., Claudia Gonzalez Viejo, Nadeesha M. Gunaratne, Damir D. Torrico, Frank R. Dunshea, and Sigfredo Fuentes. 2019. "Chocolate Quality Assessment Based on Chemical Fingerprinting Using Near Infra-red and Machine Learning Modeling" Foods 8, no. 10: 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8100426
APA StyleGunaratne, T. M., Gonzalez Viejo, C., Gunaratne, N. M., Torrico, D. D., Dunshea, F. R., & Fuentes, S. (2019). Chocolate Quality Assessment Based on Chemical Fingerprinting Using Near Infra-red and Machine Learning Modeling. Foods, 8(10), 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8100426








