Tracing of Listeria monocytogenes Contamination Routes in Fermented Sausage Production Chain by Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis Typing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Analyses
2.2. Molecular Confirmation of L. monocytogenes Strains
2.3. Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis (PFGE) Typing of L. monocytogenes Strains
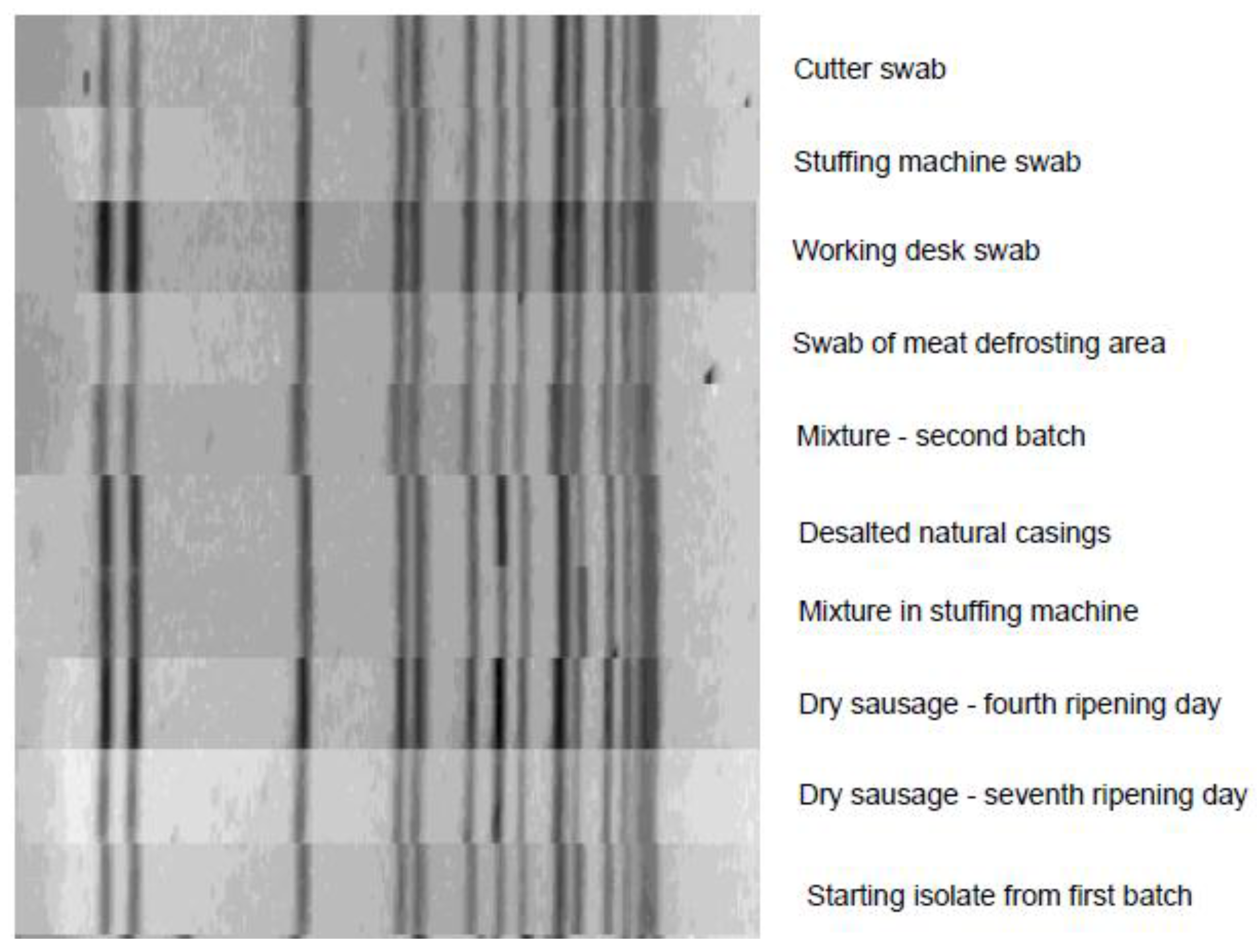
3. Results and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vrdoljak, J.; Dobranić, V.; Filipović, I.; Zdolec, N. Microbiological quality of soft, semi-hard and hard cheeses during the shelf-life. Mac. Vet. Rev. 2016, 39, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjerdal, T.; Gefferth, A.; Spajik, M.; Estanga, E.G.; de Cecare, A.; Vitali, S.; Pasquali, F.; Bovo, F.; Manfreda, G.; Mancusi, R.; et al. The STARTEC decision support tool for better tradeoffs between food safety, quality, nutrition, and costs in production of advanced ready-to-eat foods. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 6353510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagerlund, A.; Møretrø, T.; Heir, E.; Briandet, R.; Langsrud, S. Cleaning and disinfection of biofilms composed of Listeria monocytogenes and background microbiota from meat processing surfaces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01046-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriques, A.R.; Fraqueza, M.J. Biofilm-forming ability and biocide susceptibility of Listeria monocytogenes strains isolated from the ready-to-eat meat-based food products food chain. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 81, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdolec, N. Fermented Meat Products: Health Aspects; CRC Press; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zdolec, N.; Kozačinski, L.; Hadžiosmanović, M.; Cvrtila, Ž.; Filipović, I. Inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes growth in dry fermented sausages. Vet. Arhiv 2007, 77, 507–514. [Google Scholar]
- Kamenik, J. Hurdle technologies in fermented meat production. In Fermented Meat Products: Health Aspects; Zdolec, N., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 95–126. [Google Scholar]
- Kurpas, M.; Wieczorek, K.; Osek, J. Ready-to-eat meat products as a source of Listeria monocytogenes. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 61, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henri, C.; Félix, B.; Guillier, L.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Michelon, D.; Mariet, J.-F.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Mistou, M.-Y.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Roussel, S. Population genetic structure of Listeria monocytogenes strains determined by pulsed-field gel 2 electrophoresis and multilocus sequence typing. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 5720–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleta, S.; Hammerl, J.A.; Dieckmann, R.; Malorny, B.; Borowiak, M.; Halbedel, S.; Prager, R.; Trost, E.; Flieger, A.; Wilking, H.; et al. Molecular tracing to find source of protracted invasive listeriosis outbreak, Southern Germany, 2012–2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1680–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, A.K.; Björkman, J.T.; Ethelberg, S.; Kiil, K.; Kemp, M.; Nielsen, E.M. Molecular typing and epidemiology of human listeriosis cases, Denmark, 2002–2012. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PulseNet, PFGE Protocols. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/pulsenet/pdf/listeria-pfge-protocol-508c.pdf (accessed on 3 October 2018).
- Jankuloski, D.; Sekulovski, P.; Prodanov, R.; Musliu, Z.H.; Dimzovska, B.S. Listeria monocytogenes contamination of the environment and surfaces of the equipment in the meat processing facilities in Republic of Macedonia. Mac. Vet. Rev. 2017, 30, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Nastasijevic, I.; Milanov, D.; Velebit, B.; Djordjevic, V.; Swift, C.; Painset, A.; Lakicevic, B. Tracking of Listeria monocytogenes in meat establishment using Whole Genome Sequencing as a food safety management tool: A proof of concept. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 257, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ray, A.J.; Hammons, S.R.; Oliver, H.F. Persistent and transient Listeria monocytogenes strains from retail deli environments vary in their ability to adhere and form biofilms and rarely have inlA premature stop codons. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2005, 12, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Félix, B.; Danan, C.; Van Walle, I.; Lailler, R.; Texier, T.; Lombard, B.; Brisabois, A.; Roussel, S. Building a molecular Listeria monocytogenes database to centralize and share PFGE typing data from food, environmental and animal strains throughout Europe. J. Microbiol. Methods 2014, 104, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popova, G.; Jankuloski, D.; Félix, B.; Boskovska, K.; Stojanovska-Dimzovska, B.; Tasic, V.; Blagoevska, K. Pulsed-Field-Gel-Elecrophoresis used for typing of extended-spectrum-β-lactamases-producing Escherichia coli isolated from infant’s respiratory and digestive system. Mac. Vet. Rev. 2018, 41, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Véghová, A.; Minarovičová, J.; Koreňová, J.; Drahovská, H.; Kaclíková, E. Prevalence and tracing of persistent Listeria monocytogenes strains in meat processing facility production chain. J. Food Saf. 2017, 37, e12315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, D.; NicAogáin, K.; Luque-Sastre, L.; McManamon, O.; Hunt, K.; Alvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Scollard, J.; Schmalenberger, A.; Fanning, S.; O’Byrne, C.; et al. A 3-year multi-food study of the presence and persistence of Listeria monocytogenes in 54 small food businesses in Ireland. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 249, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, D.; Alvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Jordan, K. Monitoring occurrence and persistence of Listeria monocytogenes in foods and food processing environments in the Republic of Ireland. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Samples | L. monocytogenes Presence |
|---|---|
| Fresh beef | Negative |
| Fresh pork | Negative |
| Frozen beef | Negative |
| Fat tissue | Negative |
| Swab of mixing machine | Negative |
| Salted natural swine casings | Negative |
| * Cutter swab | Positive |
| * Stuffing machine swab | Positive |
| * Working desk swab | Positive |
| * Swab of meat defrosting area | Positive |
| * Mixture—second batch | Positive |
| * Desalted natural casings | Positive |
| * Mixture in stuffing machine | Positive |
| * Dry sausage—fourth ripening day | Positive |
| * Dry sausage—seventh ripening day | Positive |
| Parameter | Days of Fermentation | Days of Storage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 4 | 7 | 14 | 14 | 30 | |
| pH | 5.37 | 5.12 | 5.15 | 5.23 | 5.33 | 5.43 |
| aw | 0.976 | 0.952 | 0.868 | 0.827 | 0.790 | 0.780 |
| Salt (%) | 2.5 | 2.56 | 3.05 | 3.75 | 3.42 | 3.30 |
| L. monocytogenes (cfu/g) | 600 | 200 | <100 | <100 | <100 | <100 |
| L. monocytogenes (25 g) | Positive | Positive | Positive | Negative | Negative | Negative |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pažin, V.; Jankuloski, D.; Kozačinski, L.; Dobranić, V.; Njari, B.; Cvrtila, Ž.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Zdolec, N. Tracing of Listeria monocytogenes Contamination Routes in Fermented Sausage Production Chain by Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis Typing. Foods 2018, 7, 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods7120198
Pažin V, Jankuloski D, Kozačinski L, Dobranić V, Njari B, Cvrtila Ž, Lorenzo JM, Zdolec N. Tracing of Listeria monocytogenes Contamination Routes in Fermented Sausage Production Chain by Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis Typing. Foods. 2018; 7(12):198. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods7120198
Chicago/Turabian StylePažin, Valerij, Dean Jankuloski, Lidija Kozačinski, Vesna Dobranić, Bela Njari, Željka Cvrtila, José Manuel Lorenzo, and Nevijo Zdolec. 2018. "Tracing of Listeria monocytogenes Contamination Routes in Fermented Sausage Production Chain by Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis Typing" Foods 7, no. 12: 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods7120198
APA StylePažin, V., Jankuloski, D., Kozačinski, L., Dobranić, V., Njari, B., Cvrtila, Ž., Lorenzo, J. M., & Zdolec, N. (2018). Tracing of Listeria monocytogenes Contamination Routes in Fermented Sausage Production Chain by Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis Typing. Foods, 7(12), 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods7120198








