Effects of Dark Chocolate Intake on Brain Electrical Oscillations in Healthy People
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Baseline EEG Recording
2.2. Experimental Maneuver
2.3. Statistical Mnalysis
3. Results
3.1. Acute Effect of Dark Chocolate Intake
3.2. Acute Effect of Low-Calorie Milk Intake
3.3. Subchronic Effect of Seven-Day Dark Chocolate Intake
3.4. Acute Effect on a Subchronic Effect of Dark Chocolate Intake
3.5. Modifications of Mean Frequency
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalaria, R.N.; Maestre, G.E.; Arizaga, R.; Friedland, R.P.; Galasko, D.; Hall, K.; Luchsinger, J.A.; Ogunniyi, A.; Perry, E.K.; Potocnik, F.; et al. Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia in developing countries: Prevalence, management, and risk factors. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 812–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsell, L.; Malouf, R.; Morris, J.; Kurinczuk, J.J.; Marlow, N. Prognostic factors for poor cognitive development in children born very preterm or with very low birth weight: A systematic review. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, 1162–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehagia, A.A. A neurological perspective on the enhancement debate: Lessons learned from Parkinson’s disease. J. Psychopharmacol. 2016, 30, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magrone, T.; Russo, M.A.; Jirillo, E. Cocoa and dark chocolate polyphenols: From biology to clinical applications. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desideri, G.; Kwik-Uribe, C.; Grassi, D.; Necozione, S.; Ghiadoni, L.; Mastroiacovo, D.; Raffaele, A.; Ferri, L.; Bocale, R.; Lechiara, M.C.; et al. Benefits in cognitive function, blood pressure, and insulin resistance through cocoa flavanol cognition and aging (CoCoA) study. Hypertension 2012, 60, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brickman, A.M.; Khan, U.A.; Provenzano, F.A.; Yeung, L.K.; Suzuki, W.; Schroeter, H. Enhancing dentate gyrus function with dietary flavanols improves cognition in older adults. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 1798–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socci, V.; Tempesta, D.; Desideri, G.; De Gennaro, L.; Ferrara, M. Enhancing human cognition with cocoa flavonoids. Front. Nutr. 2017, 16, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, E.R.; Karmel, B.Z.; Corning, W.C.; Easton, P.; Brown, D.; Ahn, H. Neurometrics. Science 1977, 196, 1393–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thatcher, R.W.; North, D.M.; Biver, C.J. Intelligence and EEG phase reset: A two compartmental model of phase shift and lock. Neuroimage 2008, 42, 1639–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thatcher, R.W.; Palmero-Soler, E.; North, D.M.; Biver, C.J. Intelligence and EEG measuresof information flow: Efficiency and homeostatic neuroplasticity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, J.L.; Valdés, P.; Biscay, R.; Virues, T.; Szava, S.; Bosch, J. A global scale factor in brain topography. Int. J. Neurosci. 1994, 76, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camfield, P.; Camfield, C.; Pohlmann-Eden, B. Transition from pediatric to adult epilepsy care: A difficult process marked by medical and social crisis. Epilepsy Curr. 2012, 12, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, S.T.; Head, K.; Morris, P.G.; Macdonald, I.A. The effect of flavanol-rich cocoa on the fMRI response to a cognitive task in healthy young people. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2006, 47 (Suppl. 2), S215–S220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decroix, L.; Tonoli, C.; Soares, D.D.; Tagougui, S.; Heyman, E.; Meeusen, R. Acute cocoa flavanol improves cerebral oxygenation without enhancing executive function at rest or after exercise. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholey, A.B.; French, S.J.; Morris, P.J.; Kennedy, D.O.; Milne, A.L.; Haskell, C.F. Consumption of cocoa flavanols results in improvements in mood and cognitive performance during sustained mental effort. J. Psychopharmacol. 2010, 24, 1505–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, D.T.; Williams, C.M.; Butler, L.T. Consumption of cocoa flavanols results in an improvement in visual and cognitive functions. Physiol. Behav. 2011, 103, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pase, M.P.; Scholey, A.B.; Pipingas, A.; Kras, M.; Nolidin, K.; Gibbs, A. Cocoa polyphenols enhance positive mood states but not cognitive performance: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J. Psychopharmacol. 2013, 27, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi, D.; Lippi, C.; Necozione, S.; Desideri, G.; Ferri, C. Short-term administration of dark chocolate is followed by a significant increase in insulin sensitivity and a decrease in blood pressure in healthy persons. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datla, K.P.; Christidou, M.; Widmer, W.W.; Rooprai, H.K.; Dexter, D.T. Tissue distribution and neuroprotective effects of citrus flavonoid tangeretin in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroreport 2001, 12, 3871–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernell, M.; Swinton, C.; Lukowiak, K. Epicatechin, a component of dark chocolate, enhances memory formation if applied during the memory consolidation period. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2016, 9, 1205772–1205774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicvaric, A.; Bulat, T.; Bormann, D.; Yang, J.; Auer, B.; Milenkovic, I. Sustained consumption of cocoa-based dark chocolate enhances seizure-like events in the mouse hippocampus. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 1532–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, O.; Gelfand, J.; Kounios, J.; Lisman, J.E. Oscillations in the alpha band (9–12 Hz) increase with memory load during retention in a short-term memory task. Cereb. Cortex 2002, 12, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poch, C.; Valdivia, M.; Capilla, A.; Hinojosa, J.A.; Campo, P. Suppression of no-longer relevant information in working memory: An alpha-power related mechanism? Biol. Psychol. 2018, 135, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mierau, A.; Klimesch, W.; Lefebvre, J. State-dependent alpha peak frequency shifts: Experimental evidence, potential mechanisms and functional implications. Neuroscience 2017, 360, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
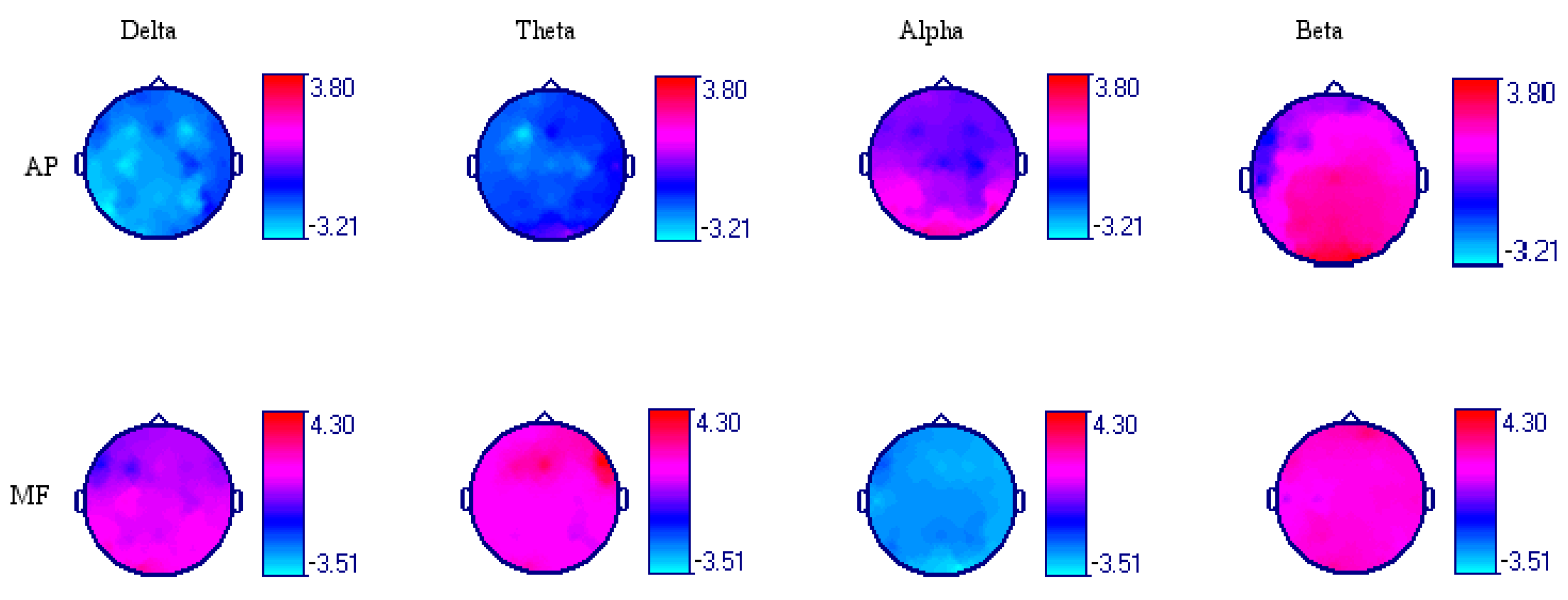
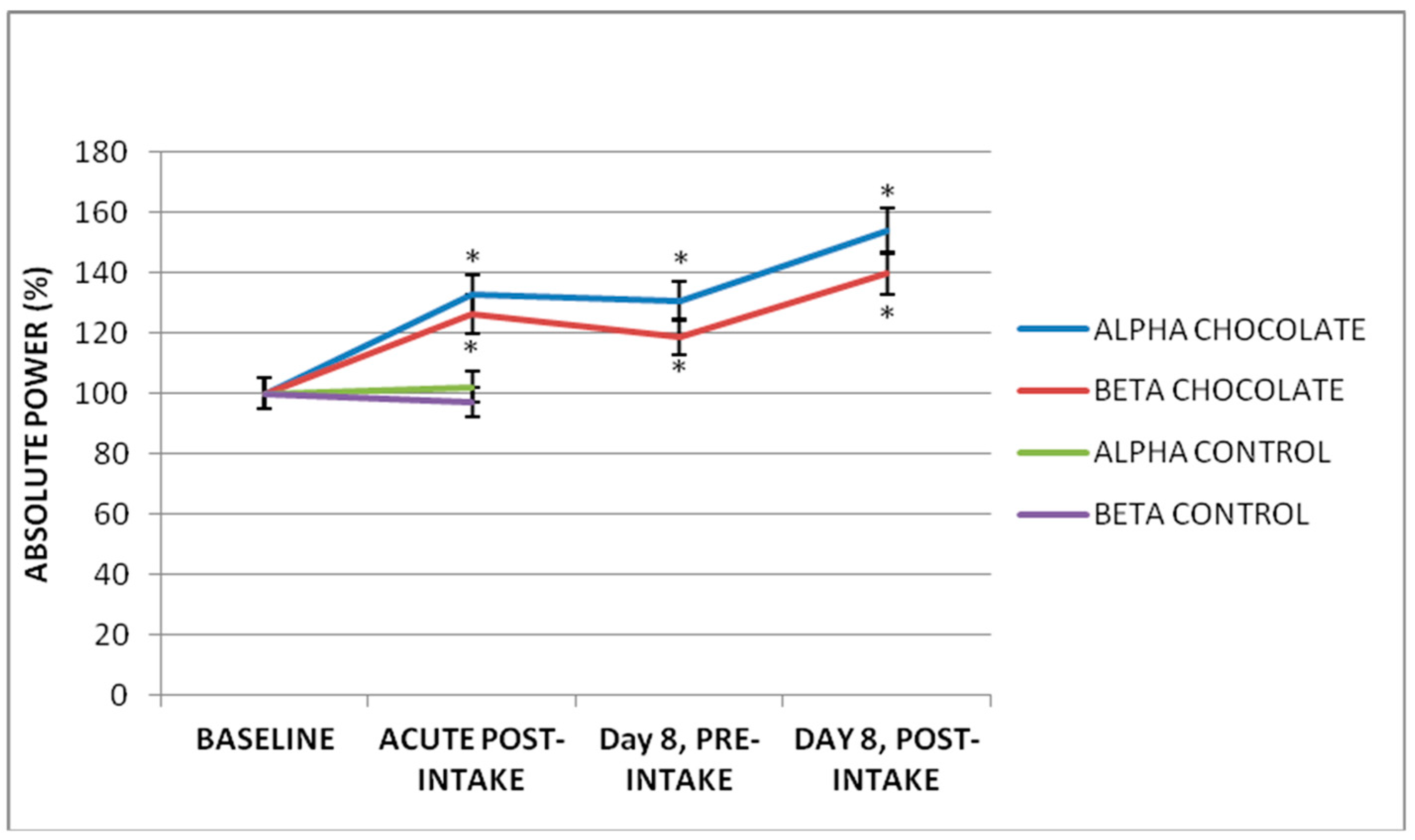
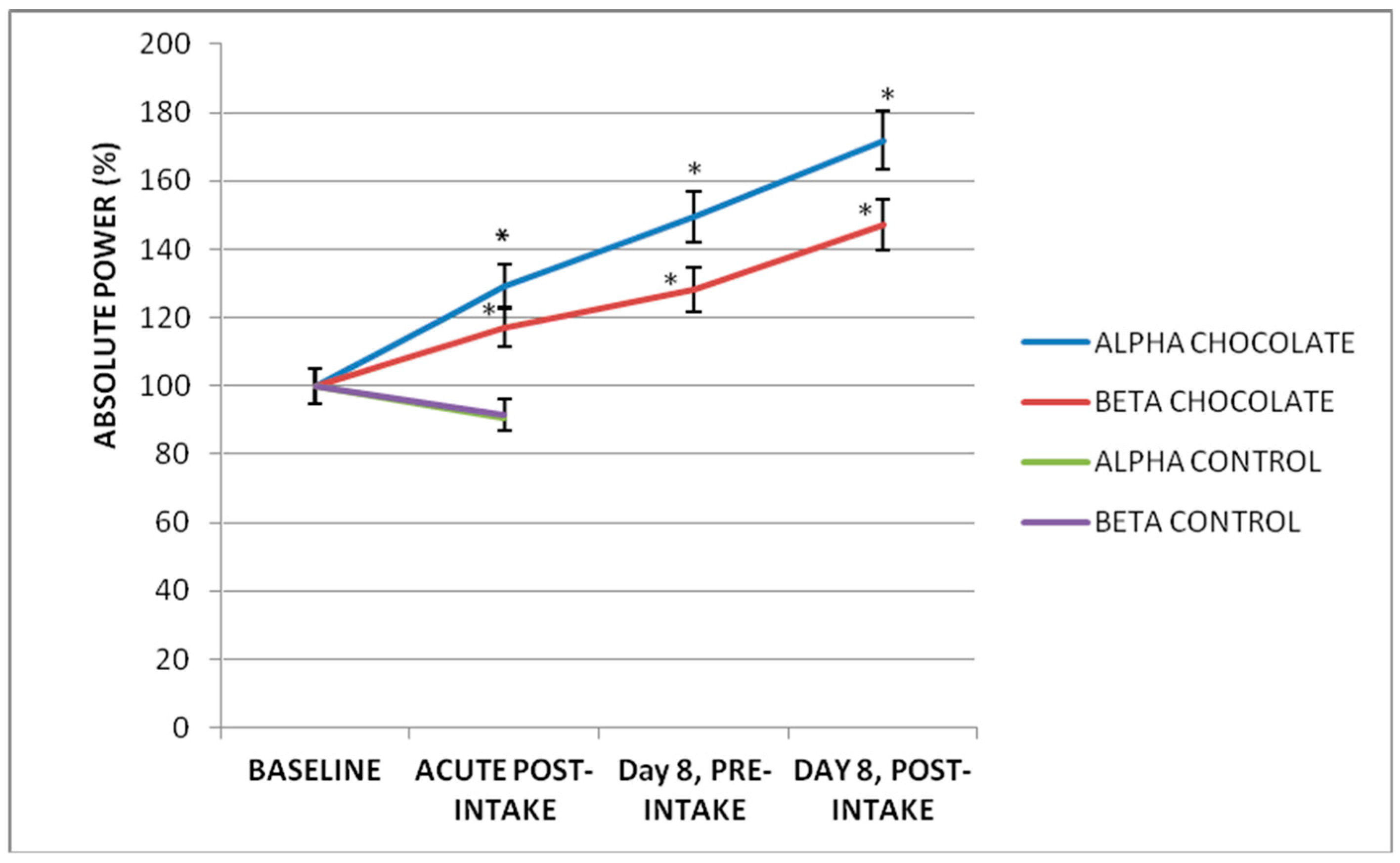
| Leads | AP Delta | AP Theta | AP Alpha | AP Beta |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fp1-AVR | −1.566 | −1.906 * | 0.332 | 0.352 |
| Fp2-AVR | −2.073 * | −1.409 | −0.122 | 0.042 |
| F3-AVR | −2.795 * | −3.035 * | −0.349 | 0.128 |
| F4-AVR | −2.905 * | −1.323 | −0.521 | 1.681 |
| C3-AVR | −2.994 * | −2.108 * | 0.295 | 2.027 * |
| C4-AVR | −1.378 | −2.196 * | −0.791 | 2.110 * |
| P3-AVR | −2.172 * | −1.431 | 1.407 | 2.494 * |
| P4-AVR | −2.776 * | −1.204 | 0.058 | 2.191 * |
| O1-AVR | −2.680 * | −0.395 | 2.557 * | 3.356 * |
| O2-AVR | −1.796 * | 0.318 | 2.061 * | 3.800 * |
| F7-AVR | −1.499 | −1.809 * | −0.168 | −1.000 |
| F8-AVR | −1.559 | −1.273 | −0.177 | 0.66 |
| T3-AVR | −2.817 * | −1.967 * | 0.443 | −0.915 |
| T4-AVR | −1.509 | −0.397 | 0.076 | 1.741 * |
| T5-AVR | −3.213 * | −1.541 | 1.768 * | 1.381 |
| T6-AVR | −0.878 | −1.222 | 2.134 * | 2.088 * |
| FZ-AVR | −1.577 | −0.878 | 0.000 | 1.663 |
| CZ-AVR | −2.354 * | −2.154 * | −0.595 | 2.528 * |
| PZ-AVR | −2.607 * | −1.851 * | 0.312 | 2.493 * |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santiago-Rodríguez, E.; Estrada-Zaldívar, B.; Zaldívar-Uribe, E. Effects of Dark Chocolate Intake on Brain Electrical Oscillations in Healthy People. Foods 2018, 7, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods7110187
Santiago-Rodríguez E, Estrada-Zaldívar B, Zaldívar-Uribe E. Effects of Dark Chocolate Intake on Brain Electrical Oscillations in Healthy People. Foods. 2018; 7(11):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods7110187
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantiago-Rodríguez, Efraín, Brenda Estrada-Zaldívar, and Elba Zaldívar-Uribe. 2018. "Effects of Dark Chocolate Intake on Brain Electrical Oscillations in Healthy People" Foods 7, no. 11: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods7110187
APA StyleSantiago-Rodríguez, E., Estrada-Zaldívar, B., & Zaldívar-Uribe, E. (2018). Effects of Dark Chocolate Intake on Brain Electrical Oscillations in Healthy People. Foods, 7(11), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods7110187





