Soybean-Enriched Snacks Based on African Rice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Rice and Soybeans
2.2. Production of Soybean-Enriched Extruded Rice Snacks
2.3. Protein Characterization
2.4. Physical Properties of the Products
2.5. E-Sensing: Electronic Nose and Electronic Tongue
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
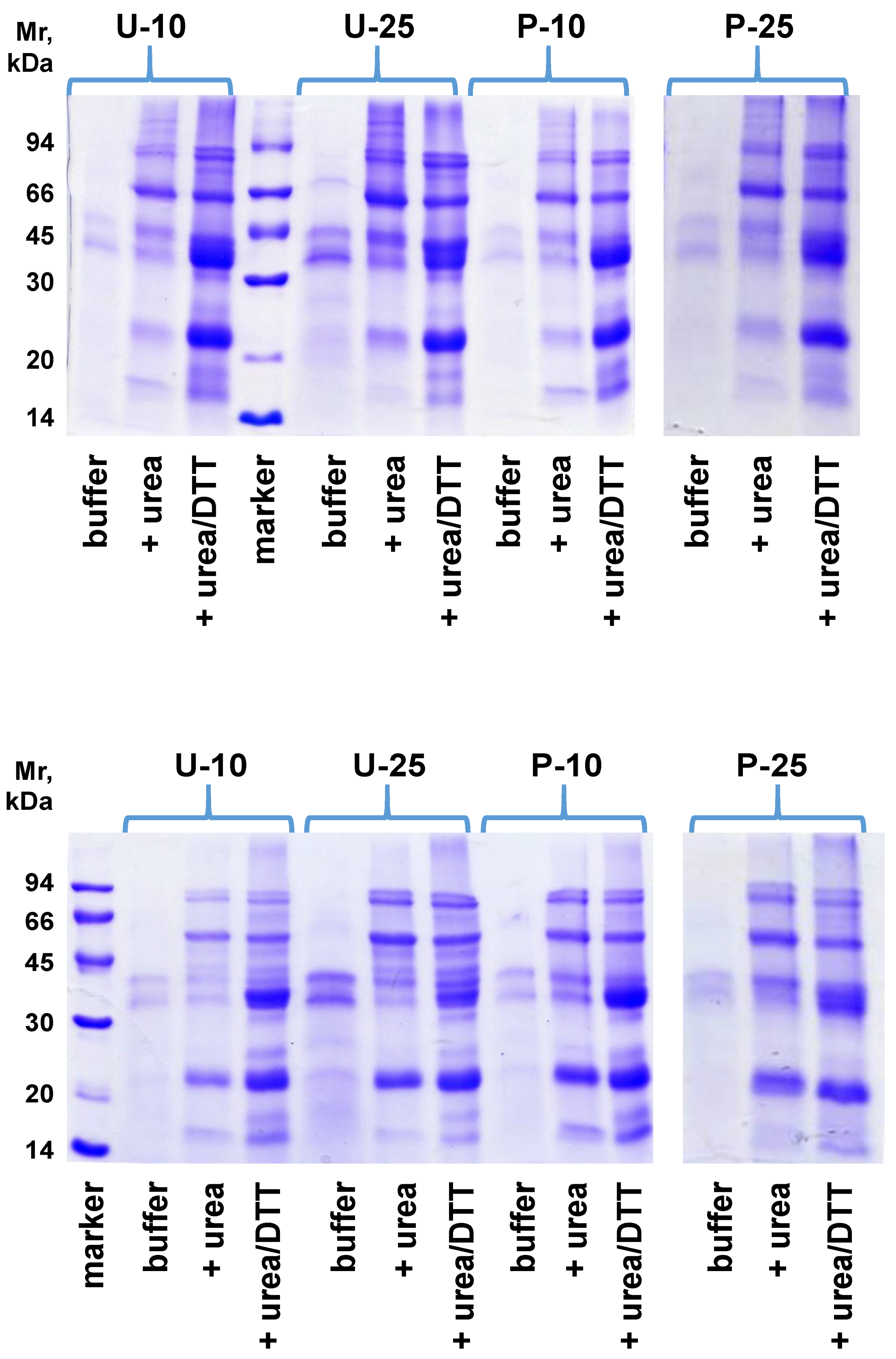
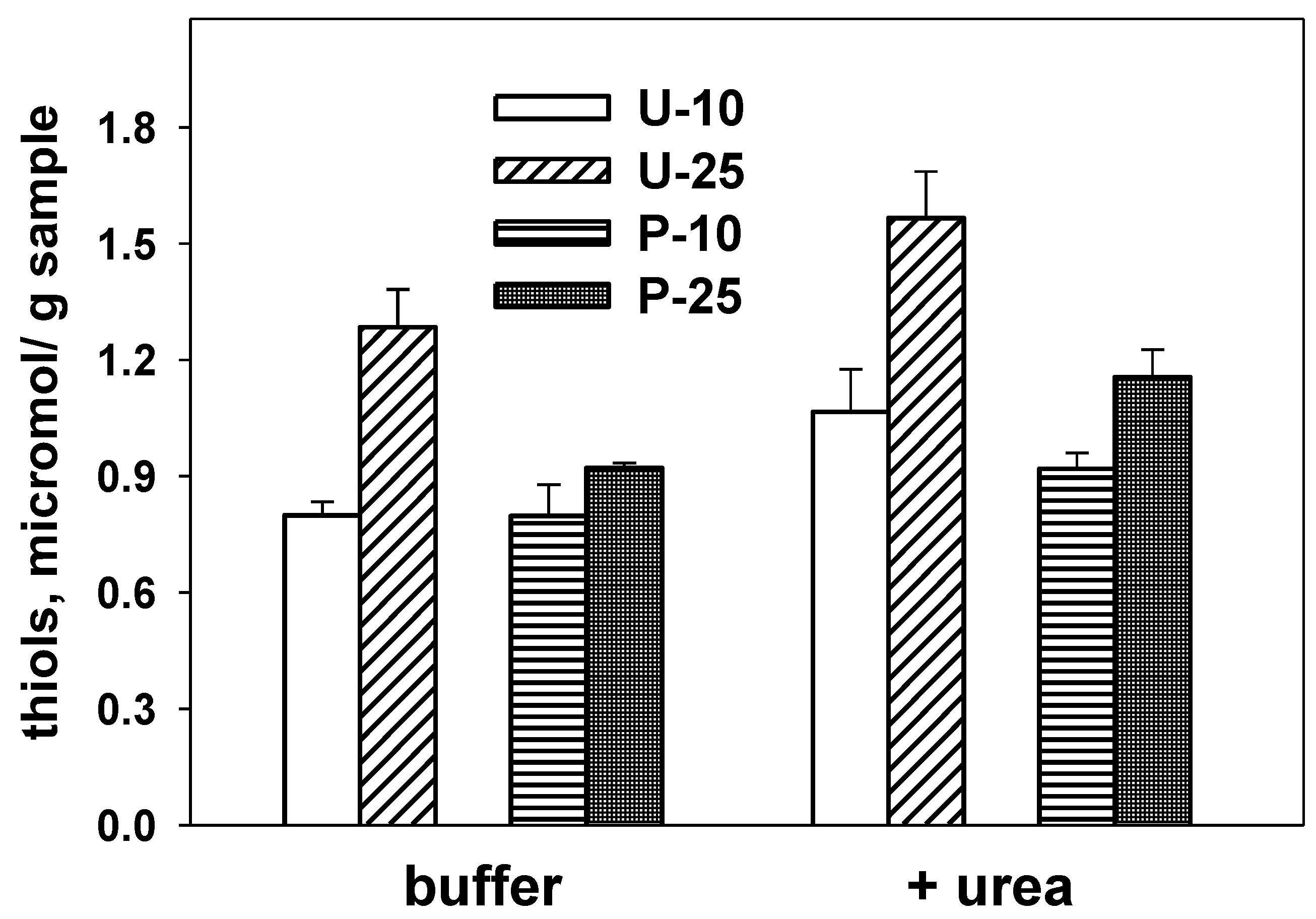
3.1. Overall Protein Organization
3.2. Physical Properties
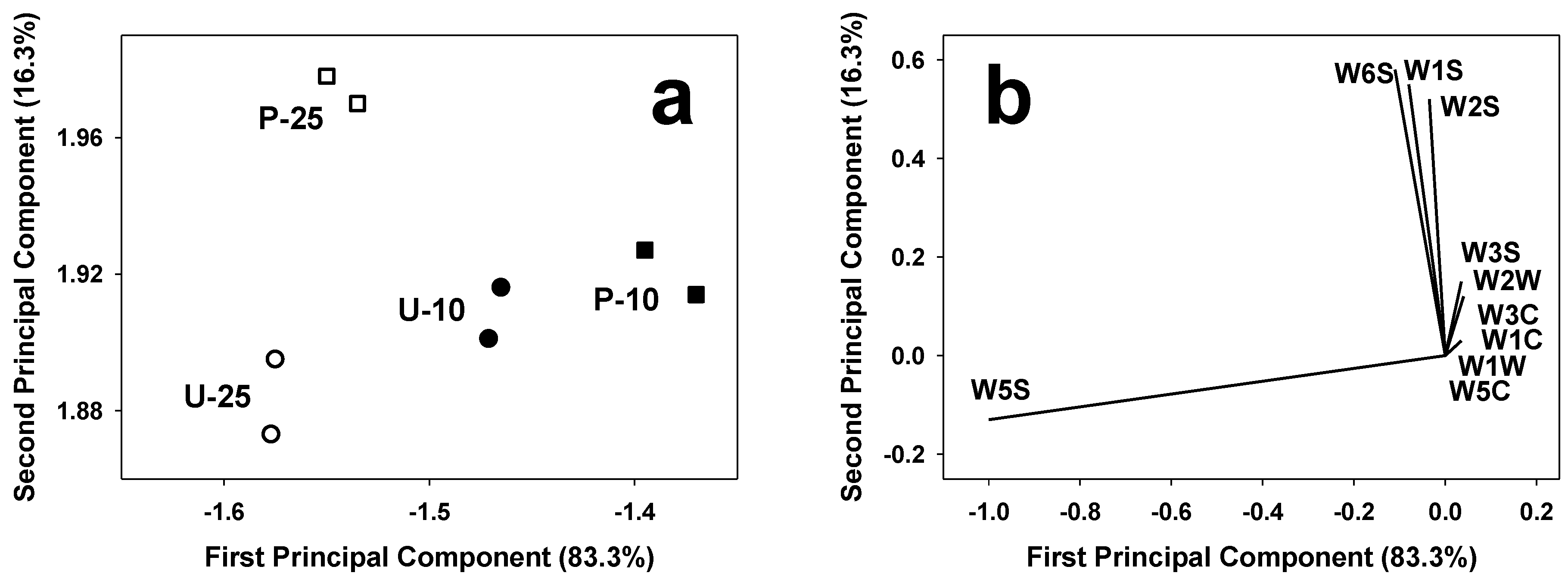
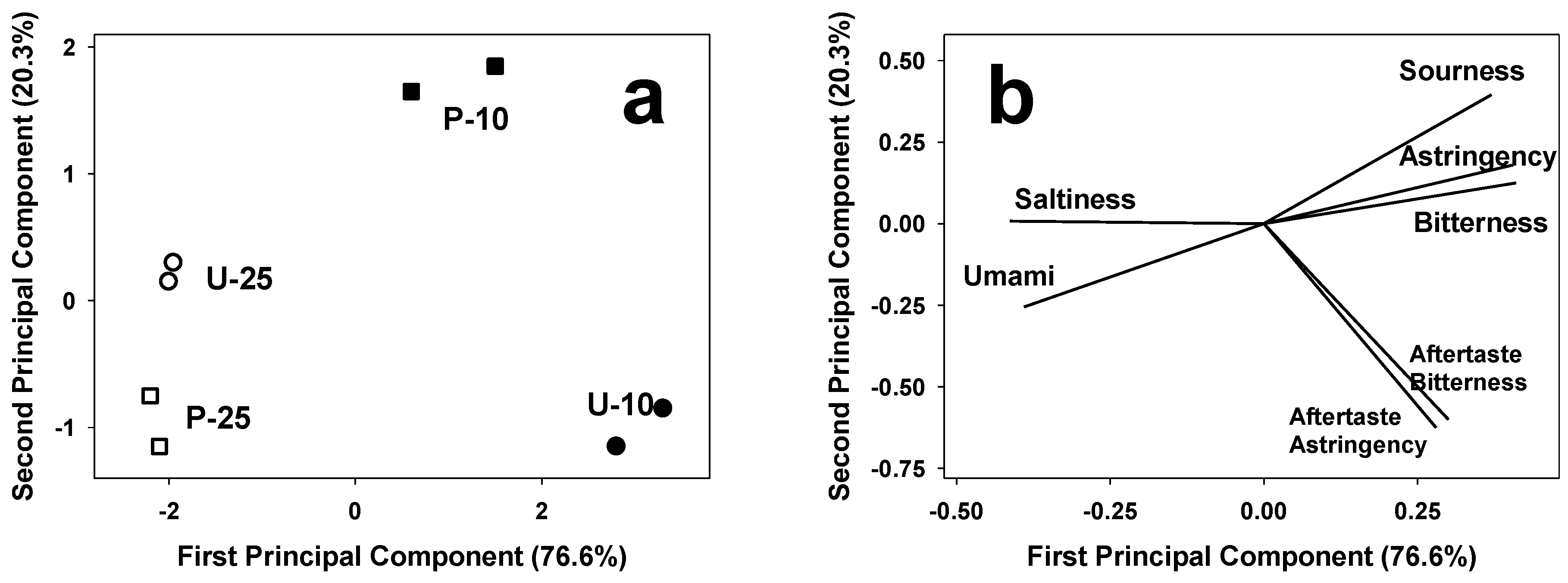
3.3. E-Sensing
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Omwamba, M.; Mahungu, S.M. Development of a protein-rich ready-to-eat extruded snack from a composite blend of rice, sorghum and soybean flour. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 5, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, M.A.; Derbyshire, E.; Tiwari, B.K.; Brennan, C.S. Ready-to-eat snack products: The role of extrusion technology in developing consumer acceptable and nutritious snacks. Int. J. Food Sci. Techol. 2013, 48, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetteh Anang, B.; Adjetey, S.N.A.; Abiriwe, S.A. Consumer preferences for rice quality characteristics and the effects on price in the Tamale metropolis, Northern region, Ghana. Int. J. AgriSci. 2011, 1, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Kadan, R.S.; Bryant, R.J.; Pepperman, A.B. Functional properties of extruded rice flours. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 1669–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayin, J.; Chandi, G.K.; Manful, J.; Seetharaman, K. Classification of rice based on statistical analysis of pasting properties and apparent amylose content: The case of Oryza glaberrima accessions from Africa. Cereal Chem. 2015, 92, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diako, C.; Sakyi-Dawson, E.; Bediako-Amoa, B.; Saalia, F.K.; Manful, J.T. Consumer perceptions, knowledge and preferences for aromatic rice types in Ghana. Nat. Sci. 2010, 8, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Tomlins, K.I.; Manful, J.T.; Larwer, P.; Hammond, L. Urban consumer preferences and sensory evaluation of locally produced and imported rice in West Africa. Food Qual. Prefer. 2005, 16, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asante, M.D.; Asante, B.O.; Acheampong, G.K.; Offei, S.K.; Gracen, V.; Adu-Dapaah, H.; Danquah, Y.E. Farmer and consumer preferences for rice in the Ashanti region of Ghana: Implications for rice breeding in West Africa. J. Plant Breed. Crop Sci. 2013, 5, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinlschmidt, P.; Sussmann, D.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U.; Eisner, P. Enzymatic treatment of soy protein isolates: Effects on the potential allergenicity, techno functionality, and sensory properties. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 4, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.P.; Vij, S.; Hati, S. Functional significance of bioactive peptides derived from soybean. Peptides 2014, 54, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanovski, B.; Seetharaman, K.; Duizer, L.M. Development of soy-based bread with acceptable sensory properties. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, S71–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marengo, M.; Bonomi, F.; Marti, A.; Pagani, M.A.; Elkhalifa, A.E.O.; Iametti, S. Molecular features of fermented and sprouted sorghum flours relate to their suitability as components of enriched gluten-free pasta. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye-binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iametti, S.; Marengo, M.; Miriani, M.; Pagani, M.A.; Marti, A.; Bonomi, F. Integrating the information from proteomic approaches: A “thiolomics” approach to assess the role of thiols in protein-based networks. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbiroli, A.; Bonomi, F.; Casiraghi, M.C.; Iametti, S.; Pagani, M.A.; Marti, A. Process conditions affect starch structure and its interactions with proteins in rice pasta. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1865–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, R.G. Reporting of objective color measurements. HortScience 1992, 27, 1254–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Benedetti, S.; Buratti, S.; Spinardi, A.; Mannino, S.; Mignani, I. Electronic nose as a non-destructive tool to characterise peach cultivars and to monitor their ripening stage during shelf-life. Postharvest Biol. Tech. 2008, 47, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratti, S.; Ballabio, D.; Giovanelli, G.; Zuluanga Dominguez, C.M.; Moles, A.; Benedetti, S.; Sinelli, N. Monitoring of alcoholic fermentation using near infrared and mid infrared spectroscopies combined with electronic nose and electronic tongue. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 697, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Habara, M.; Ikezazki, H.; Chen, R.; Naito, Y.; Toko, K. Advanced taste sensors based on artificial lipids with global selectivity to basic taste qualities and high correlation to sensory scores. Sensors 2010, 10, 3411–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroni, A.V.; Iametti, S.; Bonomi, F.; Arendt, E.K.; Dal Bello, F. Solubility of proteins from non-gluten cereals: A comparative study on combinations of solubilising agents. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Chavez, F.; Calderon de la Barca, A.M.; Islas-Rubio, A.R.; Marti, A.; Marengo, M.; Pagani, M.A.; Bonomi, F.; Iametti, S. Molecular rearrangements in extrusion processes for the production of amaranth-enriched, gluten-free rice pasta. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, A.; Barbiroli, A.; Marengo, M.; Fongaro, L.; Iametti, S.; Pagani, M.A. Structuring and texturing gluten-free pasta: Egg albumen or whey proteins? Eur. Food Res. Techol. 2014, 238, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iametti, S.; Bonomi, F.; Pagani, M.A.; Zardi, M.; Cecchini, C.; D’Egidio, M.G. Properties of the protein and carbohydrate fractions in immature wheat kernels. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 10239–10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, L.L., Jr.; Hyatt, E.M.; Starr, R.G., Jr. Measuring consumer response to food products. Food Qual. Prefer. 2003, 14, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obatolu, A.V.; Omueti, O.O.; Adebowale, E.A. Qualities of extruded puffed snacks from maize/soybean mixture. J. Food Process Eng. 2006, 29, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagci, S.; Gögüs, F. Development of extruded snack from food by-products: A response surface analysis. J. Food Process Eng. 2009, 32, 565–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyakul, S.; Jangchud, K.; Jangchud, A.; Wuttijumnong, P.; Winger, R. Effect of extrusion conditions on physical and chemical properties of high protein glutinous rice-based snack. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 42, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.; Hardacre, A. Development of an extruded snack product from the legume Vicia faba minor. Procedia Food Sci. 2011, 1, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mildner-Szkudlarz, S.; Jeleń, H.H.; Zawirska-Wojtasiak, R. The use of electronic and human nose for monitoring rapeseed oil autoxidation. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2008, 110, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sareepuang, K.; Siriamornpun, S.; Wiset, L.; Meeso, N. Effect of soaking temperature on physical, chemical and cooking properties of parboiled fragrant rice. World J. Agric. Sci. 2008, 4, 409–415. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, H.; Panchal, R.; Pradhan, P.; Pasha, T.Y. Electronic tongue: A new taste sensor. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2010, 5, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- King, J.M.; Chin, S.M.; Svendsen, L.K.; Reitmeier, C.A.; Johnson, L.A.; Fehr, W.R. Processing of lipoxygenase-free soybeans and evaluation in foods. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2001, 78, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Color | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | a* | b* | Hardness, N | Expansion Ratio | |
| U-10 | 87.37 ± 0.51 a | −0.63 ± 0.06 a | 15.14 ± 0.24 a | 3.8 ± 0.74 a | 3.6 ± 0.14 a |
| U-25 | 84.10 ± 0.21 b | 0.11 ± 0.02 b | 19.72 ± 0.29 b | 5.9 ± 0.83 b | 3.3 ± 0.24 b |
| P-10 | 82.61 ± 0.56 c | 0.31 ± 0.06 c | 19.31 ± 0.35 b | 5.9 ± 0.62 b | 3.1 ± 0.34 b |
| P-25 | 81.74 ± 0.92 d | 0.62 ± 0.11 d | 21.25 ± 0.63 c | 8.8 ± 0.92 c | 2.4 ± 0.44 c |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marengo, M.; Akoto, H.F.; Zanoletti, M.; Carpen, A.; Buratti, S.; Benedetti, S.; Barbiroli, A.; Johnson, P.-N.T.; Sakyi-Dawson, E.O.; Saalia, F.K.; et al. Soybean-Enriched Snacks Based on African Rice. Foods 2016, 5, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods5020038
Marengo M, Akoto HF, Zanoletti M, Carpen A, Buratti S, Benedetti S, Barbiroli A, Johnson P-NT, Sakyi-Dawson EO, Saalia FK, et al. Soybean-Enriched Snacks Based on African Rice. Foods. 2016; 5(2):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods5020038
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarengo, Mauro, Hannah F. Akoto, Miriam Zanoletti, Aristodemo Carpen, Simona Buratti, Simona Benedetti, Alberto Barbiroli, Paa-Nii T. Johnson, Esther O. Sakyi-Dawson, Firibu K. Saalia, and et al. 2016. "Soybean-Enriched Snacks Based on African Rice" Foods 5, no. 2: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods5020038
APA StyleMarengo, M., Akoto, H. F., Zanoletti, M., Carpen, A., Buratti, S., Benedetti, S., Barbiroli, A., Johnson, P.-N. T., Sakyi-Dawson, E. O., Saalia, F. K., Bonomi, F., Pagani, M. A., Manful, J., & Iametti, S. (2016). Soybean-Enriched Snacks Based on African Rice. Foods, 5(2), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods5020038






