Unlocking the Functional Potential of Pecan Nut Cake: A Study on Bioactive Peptide Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Study of PNC Proteins and Derived Hydrolysates
2.2.1. Analysis of Protein and Amino Acid Composition in PNC
2.2.2. Preparation of PNCH by Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation
2.3. Determination of PNCH Bioactivity
2.3.1. Determination of Chemical Antioxidant Activity In Vitro
2.3.2. Determination of α-Glucosidase Inhibition Activity In Vitro
2.3.3. Animal Experimental Design
2.3.4. Serum and Liver Biochemical Index
2.3.5. Histological Analysis
2.4. Purification and Activity Identification
2.4.1. Identification of Peptide Sequences from PNCH
2.4.2. Peptide Sequence Analysis and Activity Prediction
2.4.3. Peptide Synthesis and Characterization
2.4.4. Protective Effects of Peptides on Oxidative Stress in Caco-2 Cells
2.4.5. In Silico Interaction Analysis of Peptides and Target Proteins
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
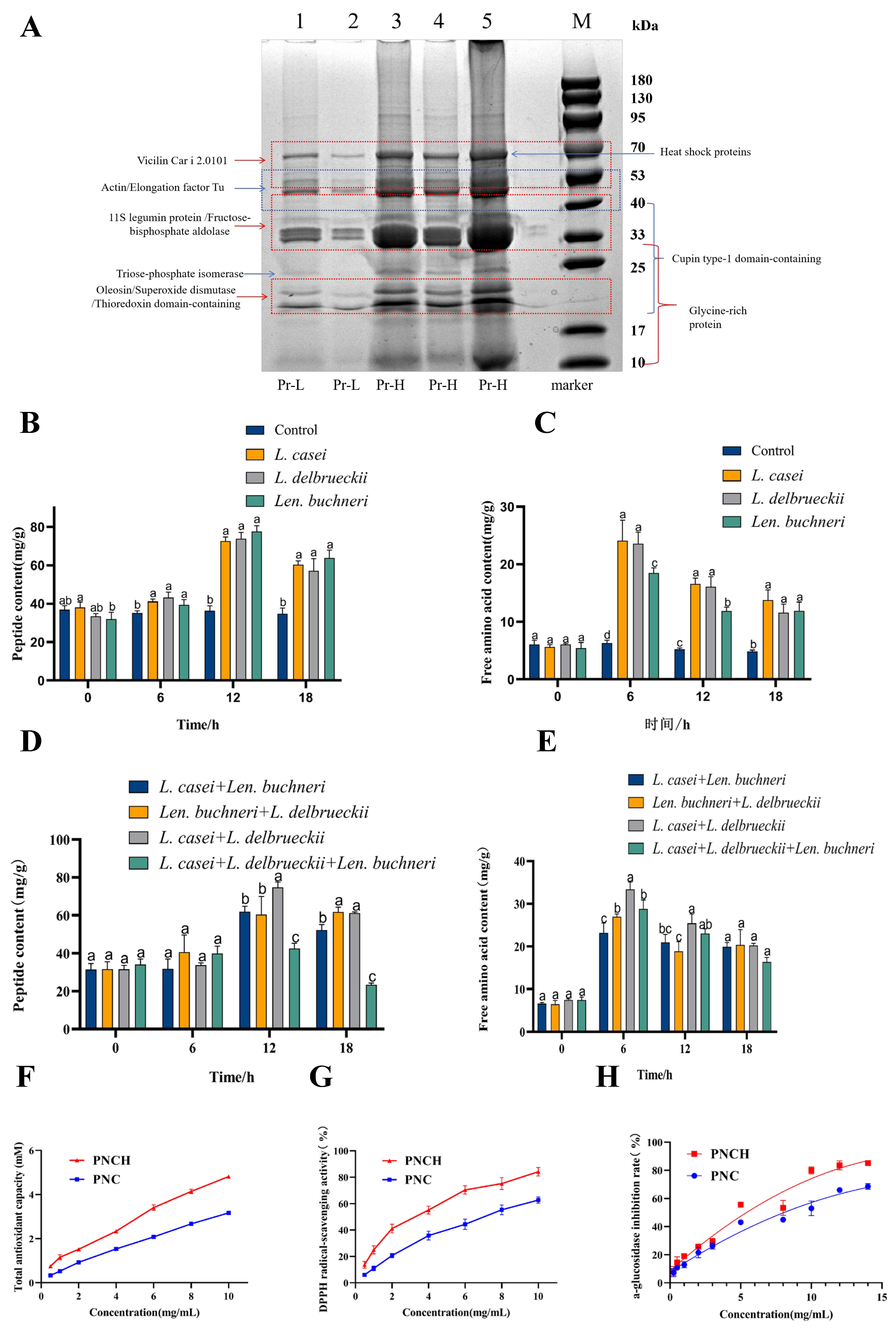
3.1. Protein and Amino Acid Composition of PNC
3.2. Strain-Specific and Synergistic Effects on Peptide and Amino Acid Production
3.3. Antioxidant Capacity and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity of PNCH
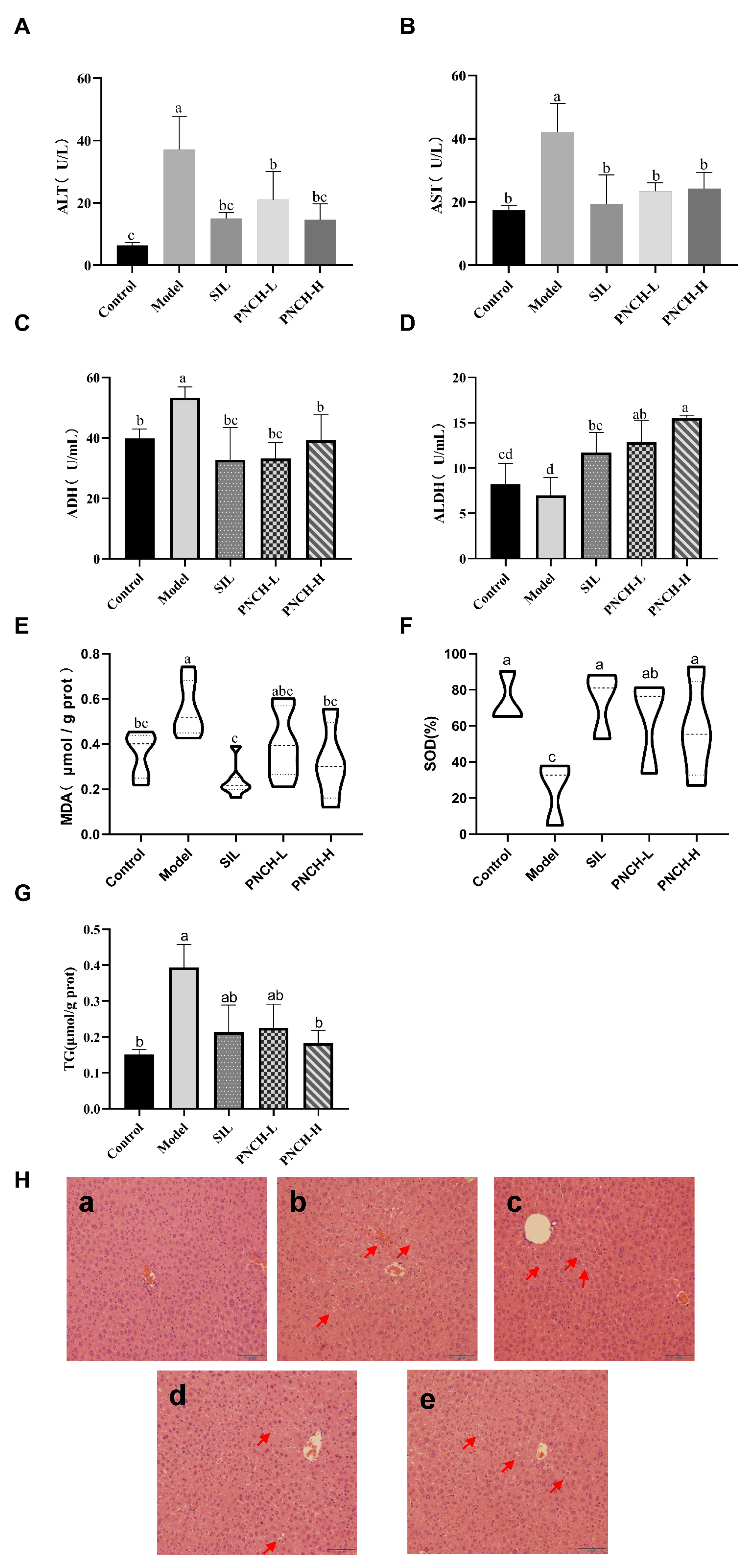
3.4. Evaluation of PNCH to Alleviate Acute Alcoholic Liver Injury in Mice
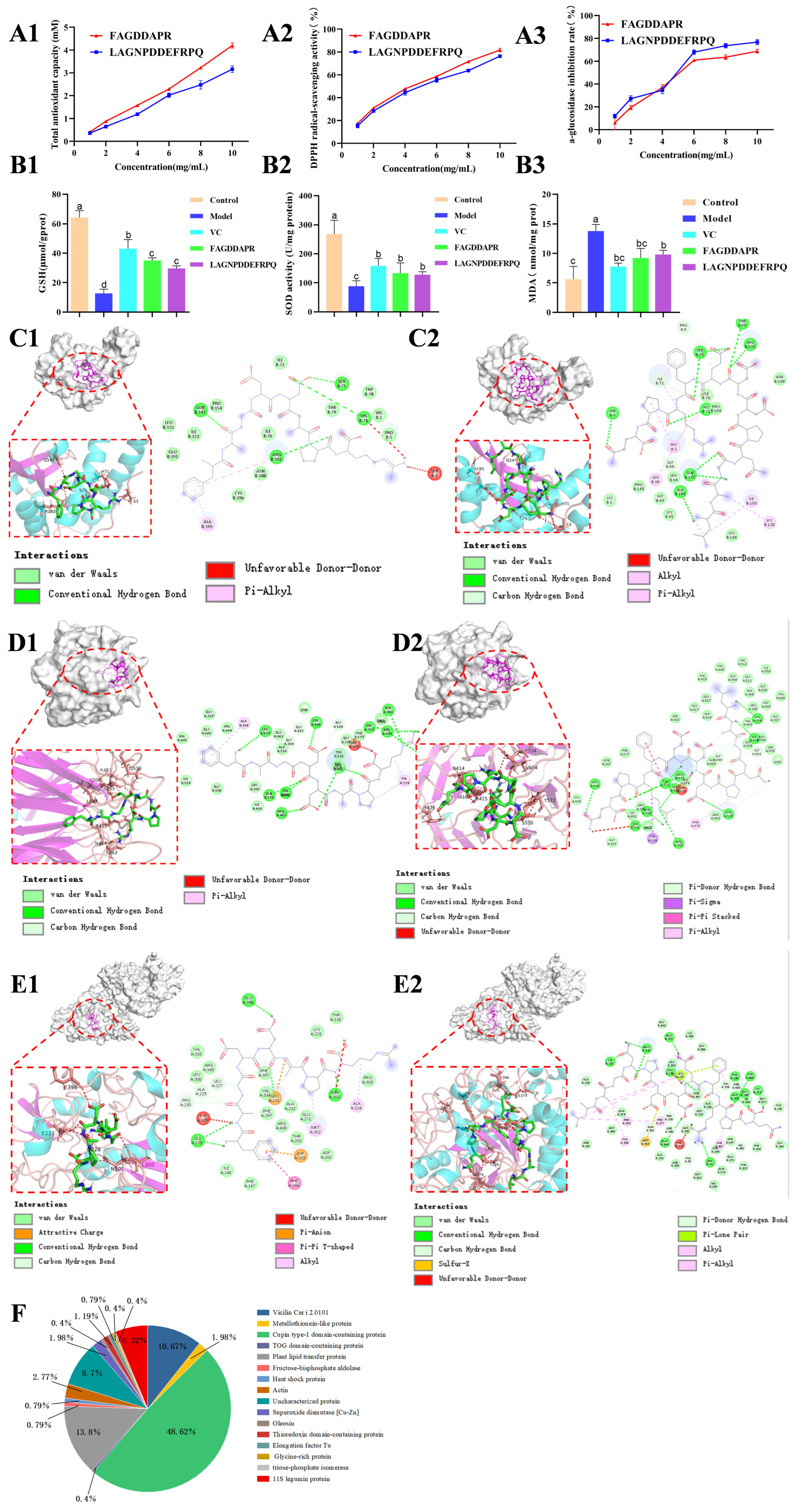
3.5. Peptide Sequence Identification and Its Activity Prediction
3.6. The Activity Validation of Peptides
3.7. Molecular Docking of Peptides with SOD
3.8. Molecular Docking of Peptides with Keap1
3.9. Molecular Docking of Peptides with Alpha-Glucosidase
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaur, S.P.; Sagar, N.A.; Rani, N. Alternative proteins: Innovations in sources, processing, and consumption. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2025, 9, 1641712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharehbeglou, P.; Sarabandi, K.; Akbarbaglu, Z. Insights into enzymatic hydrolysis: Exploring effects on antioxidant and functional properties of bioactive peptides from Chlorella proteins. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 16, 101129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres Fabbri, L.; Cavallero, A.; Vidotto, F.; Gabriele, M. Bioactive Peptides from Fermented Foods: Production Approaches, Sources, and Potential Health Benefits. Foods 2024, 13, 3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Shang, Y.; Li, S.; Xia, J.; Tian, Y.; Jia, Y.; Ma, A. Progress in the preparation, identification and biological activity of walnut peptides. J. Future Foods 2024, 4, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, M.; Chi, J.; Ma, J. Bioactive Peptides from Walnut Residue Protein. Molecules 2020, 25, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamila dos Santos, A.; Confortin, T.C.; Todero, I.; Rodrigues, A.S.; Ribeiro, S.R.; Sasso, S.R.; Canabarro, N.I.; Wagner, R.; Cichoski, A.J.; Mazutti, M.A.; et al. Use of compressed fluids in the recovery of pecan nut cake oil: Influence of extraction conditions on yield and extract quality. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2020, 161, 104820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, L.G.; Ribeiro, F.L.; Teixeira, G.L.; Molognoni, L.; Nascimento Dos Santos, J.; Larroza Nunes, I.; Mara Block, J. The potential of the pecan nut cake as an ingredient for the food industry. Food Res. Int. 2020, 127, 108718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.; He, X.; Cao, Y.; Woldemariam, K.Y.; Cai, M.; Wang, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Tang, W.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Sustainable microbial fermentation of plant Proteins: Potential, biological resources, fermentation mechanisms, applications and challenges in food industry. Food Biosci. 2025, 68, 106727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Guo, Y.; Ma, H. Production, bioactivities and bioavailability of bioactive peptides derived from walnut origin by-products: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 8032–8047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpoghelie, P.O.; Edo, G.I.; Ali, A.B.M.; Yousif, E.; Zainulabdeen, K.; Owheruo, J.O.; Isoje, E.F.; Igbuku, U.A.; Essaghah, A.E.A.; Makia, R.S.; et al. Lactic acid bacteria: Nature, characterization, mode of action, products and applications. Process Biochem. 2025, 152, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, H.; Li, Z. Immune regulation by fermented milk products: The role of the proteolytic system of lactic acid bacteria in the release of immunomodulatory peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 10498–10516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuva, B.; Gawai, K.M.; Singh, B.P.; Sarkar, P.; Hassan, M.Z.; Kovaleva, E.G.; Hati, S. Production, characterization and bio-functional properties of multi-functional peptides from fermented plant-based foods: A review. Food Biosci. 2025, 64, 105877. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Xiong, E.; Wang, W.; Scali, M.; Cresti, M. Universal sample preparation method integrating trichloroacetic acid/acetone precipitation with phenol extraction for crop proteomic analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gang, Y.; Eom, T.-Y.; Marasinghe, S.D.; Lee, Y.; Jo, E.; Oh, C. Optimising the DPPH Assay for Cell-Free Marine Microorganism Supernatants. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y. In vitro α-glucosidase inhibitory activity of isolated fractions from water extract of Qingzhuan dark tea. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Sun, S. Preparation and Identification of Peptides with α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity from Shiitake Mushroom (Lentinus edodes) Protein. Foods 2023, 12, 2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Hu, Q.; Shen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gao, L.; Xu, X.; Hao, G. Research Progress on Antioxidant Peptides from Fish By-Products: Purification, Identification, and Structure–Activity Relationship. Metabolites 2024, 14, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluko, R. Amino acids, peptides, and proteins as antioxidants for food preservation. In Handbook of Antioxidants for Food Preservation; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 105–140. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Li, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Song, K.; Meng, L. Antioxidant Function and Application of Plant-Derived Peptides. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Cheng, J.; Wu, H. Discovery of Food-Derived Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitory Peptides: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarbaglu, Z.; Mazloomi, N.; Karimzadeh, L.; Sarabandi, K.; Jafari, S.M.; Hesarinejad, M.A. Nutritional value, antibacterial activity, ACE and DPP IV inhibitory of red pomegranate seeds protein and peptides. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 10802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atma, Y.; Murray, B.S.; Sadeghpour, A.; Goycoolea, F.M. Encapsulation of short-chain bioactive peptides (BAPs) for gastrointestinal delivery: A review. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 3959–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; He, W.; Zhao, S.; Jiao, T.; Hu, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Zang, J. Advanced Insights into Walnut Protein: Structure, Physiochemical Properties and Applications. Foods 2023, 12, 3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescuma, M.; Hébert, E.M.; Rabesona, H.; Drouet, M.; Choiset, Y.; Haertlé, T.; Mozzi, F.; de Valdez, G.F.; Chobert, J.M. Proteolytic action of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus CRL 656 reduces antigenic response to bovine β-lactoglobulin. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sheng, L.; Lu, Y. Cu2−xSe@Bi2MoO6 nanozyme-based immunoassay for the colorimetric detection of walnut allergen in foods. Food Chem. 2025, 471, 142808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.; Zuo, L.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Tong, P.; Chen, H. Degradation of major allergens and allergenicity reduction of soybean meal through solid-state fermentation with microorganisms. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 1899–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, W.; Dong, M.; Rui, X. The Conformational Structural Change of Soy Glycinin via Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermentation Reduced Immunoglobulin E Reactivity. Foods 2021, 10, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Zuo, L.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Tong, P.; Wu, Y.; Fan, Q.; Chen, H.; Yang, A. Characterization of the protein structure of soymilk fermented by Lactobacillus and evaluation of its potential allergenicity based on the sensitized-cell model. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Chen, C.; Xie, Q.; Gu, S.; Tao, S.; Xue, W. Pediococcus acidilactici Strain Alleviates Gluten-Induced Food Allergy and Regulates Gut Microbiota in Mice. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 845142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayeoba, T.A.; Ijabadeniyi, O.A. 9—Lactic acid bacteria for the generation of bioactive peptides. In Lactic Acid Bacteria as Cell Factories; Montet, D., Ray, R.C., De Carvalho Azevedo, V.A., Paramithiotis, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2023; pp. 165–182. [Google Scholar]
- Egbujor, M.C.; Olaniyan, O.T.; Emeruwa, C.N.; Saha, S.; Saso, L.; Tucci, P. An insight into role of amino acids as antioxidants via NRF2 activation. Amino Acids 2024, 56, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, G.; Shi, X.; Chen, L.; Kou, J.; Meng, J.; Chen, H. Antioxidant Peptides from Goat Milk Fermented by Lactobacillus casei L61: Preparation, Optimization, and Stability Evaluation in Simulated Gastrointestinal Fluid. Nutrients 2018, 10, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, V.B.C.; Huligere, S.S.; Shbeer, A.M.; Ageel, M.; Jayanthi, M.K.; Chandra, S.J.; Ramu, R. Probiotic Potential Lacticaseibacillus casei and Limosilactobacillus fermentum Strains Isolated from Dosa Batter Inhibit α-Glucosidase and α-Amylase Enzymes. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1195. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, M.; Bosman, B.W.; Tan, P.S. Comparison of proteolytic activities in various lactobacilli. J. Dairy Res. 1995, 62, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Ma, R.; Tang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S. Structural properties and antioxidant activities of soybean protein hydrolysates produced by Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus cell envelope proteinase. Food Chem. 2023, 410, 135392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, B.; Xing, M.; Cui, L.; Deng, Y.; Xu, Y.; Huang, M.; Zhang, S. Antioxidant, antihypertensive, and immunomodulatory activities of peptide fractions from fermented skim milk with Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus LB340. J. Dairy. Res. 2011, 78, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.-L.; Gong, Y.; Qi, Y.-J.; Shao, Z.-M.; Jiang, Y.-Z. Effects of dietary intervention on human diseases: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Li, X.-G.; Zhao, M. Chapter Five—Bioactive peptides as a novel strategy to prevent alcoholic liver injury. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Toldrá, F., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 243–274. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.K.; Yates, E.; Lilly, K.; Dhanda, A.D. Oxidative stress in alcohol-related liver disease. World J. Hepatol. 2020, 12, 332–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alssema, M.; Ruijgrok, C.; Blaak, E.E.; Egli, L.; Dussort, P.; Vinoy, S.; Dekker, J.M.; Denise Robertson, M. Effects of alpha-glucosidase-inhibiting drugs on acute postprandial glucose and insulin responses: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Diabetes 2021, 11, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Kong, D.; Ai, D.; Xu, A.; Yu, W.; Peng, Z.; Peng, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, R.; et al. Insulin resistance enhances binge ethanol-induced liver injury through promoting oxidative stress and up-regulation CYP2E1. Life Sci. 2022, 303, 120681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avilés-Gaxiola, S.; García-Aguiar, I.; Jiménez-Ortega, L.A.; Gutiérrez-Grijalva, E.P.; Heredia, J.B. Bioactive Plant Peptides: Physicochemical Features, Structure-Function Insights and Mechanism of Action. Molecules 2025, 30, 3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Xie, T.; Wu, Q.; Hu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Luo, F. Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitory Peptides: Sources, Preparations, Identifications, and Action Mechanisms. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Hernández, D.; Juárez-González, V.R.; Bustamante, V.H.; Martínez-Martínez, L.L.; Ramírez, V.; Balleza, D.; Quintero-Hernández, V. Conformational Flexibility and Net Charge are Key Determinants for the Antimicrobial Activity of Peptide Uy234 Against Multidrug-resistant Bacteria. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2024, 30, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agoni, C.; Fernandez-Diaz, R.; Timmons, P.B.; Adelfio, A.; Gomez, H.; Shields, D.C. Molecular Modelling in Bioactive Peptide Discovery and Characterisation. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Tan, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Hui, S.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, W. Mechanistic Insights and Potential Therapeutic Implications of NRF2 in Diabetic Encephalopathy. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 61, 8253–8278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisman, E.; Duarte, P.; Dauden, E.; Cuadrado, A.; Rodríguez-Franco, M.I.; López, M.G.; León, R. KEAP1-NRF2 protein-protein interaction inhibitors: Design, pharmacological properties and therapeutic potential. Med. Res. Rev. 2023, 43, 237–287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liang, J.; He, M.; Jiang, B.; Liu, J.; Wu, J.; Li, P.; Du, B. Pueraria lobata-derived peptides hold promise as a novel antioxidant source by mitigating ethanol-induced oxidative stress in HepG2 cells through regulating the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway. Food Chem. 2025, 490, 145014. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Y.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Fan, L. In Vitro Inhibitory Effects of Polyphenols from Flos sophorae immaturus on α-Glucosidase: Action Mechanism, Isothermal Titration Calorimetry and Molecular Docking Analysis. Foods 2023, 12, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesiltas, B.; García-Moreno, P.J.; Gregersen, S.; Olsen, T.H.; Jones, N.C.; Hoffmann, S.V.; Marcatili, P.; Overgaard, M.T.; Hansen, E.B.; Jacobsen, C. Antioxidant peptides derived from potato, seaweed, microbial and spinach proteins: Oxidative stability of 5% fish oil-in-water emulsions. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Liu, C.; Bordoni, L.; Petracci, I.; Wu, D.; Fang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Gabbianelli, R.; Min, W. Advances on the Antioxidant Peptides from Nuts: A Narrow Review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, X.; Wei, L.; Cui, H.; Wei, Q.; Cai, J.; Zhao, Z.; Dong, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Rapid screening of the novel bioactive peptides with notable α-glucosidase inhibitory activity by UF-LC-MS/MS combined with three-AI-tool from black beans. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 130982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Hu, S.; Yu, J.; Gong, N.; Li, F.; Gao, X. Identification and characterization of novel α-glucosidase inhibitory peptides from sweet potato protein through heating combined with high hydrostatic pressure-assisted enzymatic hydrolysis. Food Chem. 2025, 493, 145877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Deng, F.; Deng, Z. Oxidative Stress: Signaling Pathways, Biological Functions, and Disease. MedComm 2025, 6, e70268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Liang, Q.; Zhao, B.; Chen, X.; Song, X. Functional Peptides from Yak Milk Casein: Biological Activities and Structural Characteristics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Name | Retention Time [min] | Area [mV.s] | Content [mg/g] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aspartic acid | 8.379 | 356.264 | 0.932 |
| Threonine | 10.185 | 307.785 | 0.747 |
| Serine | 11.211 | 210.056 | 0.39 |
| Glutamic acid | 13.429 | 591.654 | 1.41 |
| Glycine | 19.652 | 196.309 | 0.231 |
| Alanine | 20.94 | 292.439 | 0.418 |
| Cysteine | 22.583 | 132.629 | 0.713 |
| Valine | 23.203 | 106.165 | 0.23 |
| Methionine | 24.993 | 316.762 | 0.676 |
| Isoleucine | 26.693 | 221.234 | 0.588 |
| Leucine | 27.42 | 129.101 | 0.31 |
| Tyrosine | 29.841 | 82.201 | 0.286 |
| Phenylalanine | 30.716 | 90.616 | 0.263 |
| Histidine | 35.505 | 83.632 | 0.233 |
| Lysine | 36.845 | 139.955 | 0.373 |
| Arginine | 45.029 | 111.59 | 0.316 |
| Total | 3368.392 | 8.117 | |
| Receptor Protein | SOD | Keap1 | α-Glucosidase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polypeptide | FAGDDAPR | LAGNPDDEFRPQ | FAGDDAPR | LAGNPDDEFRPQ | FAGDDAPR | LAGNPDDEFRPQ | ||||||
| Molecular docking binding energy (kcal/mol) | −5.8 | −5.6 | −9.8 | −9.4 | −7.9 | −5.8 | ||||||
| Mode of action | Hydrogen bond | Hydrophobic interaction | Hydrogen bond | Hydrophobic interaction | Hydrogen bond | Hydrophobic interaction | Hydrogen bond | Hydrophobic interaction | Hydrogen bond | Hydrophobic interaction | Hydrogen bond | Hydrophobic interaction |
| Hydrogen-bonding residues and hydrophobic residues of the receptor protein | Ser-3, His-71, Ser-75, Gln-147, Arg-192 | Pro-5, Ile-76, Glu-191, Ala-195 | Ser-3, His-71, Ser-75, Gln-147, Arg-192, Ala-195 | Leu-38, Ile-72, Ile-76, Pro-154 | Ser-363, Asn-414, Arg-415, Arg-483, Ser-508, Gln-530, Ser-555, Leu-557 | Tyr-334, Ala-366, Tyr-535 | Tyr-334, Asn-414, Arg-415, Ile-416, His-436, Ser-555, Tyr-572, Val-604 | Tyr-334, Tyr-525, Phe-577 | Gly-228, Glu-231, Leu-300, Asn-301, Glu-396 | Phe-147, Thr-203, Ala-224, Leu-227, Met-302, Tyr-389, Phe-397 | Phe-62, Thr-226, Gly-228, Glu-231, Asp-274, Asp-275, Asp-333, Glu-377, Tyr-389, Ile-377, Glu-396 | Phe-147, Phe-166, Lys-225, Tyr-235, Pro-277, Phe-297, Asn-301, Pro-303, Tyr-308, Val-334, Val-335, Phe-397 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Long, T.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Kong, W.; Zhu, Y.; Tao, M.; Luo, H.; Cui, L.; Sun, M.; Wu, Z.; et al. Unlocking the Functional Potential of Pecan Nut Cake: A Study on Bioactive Peptide Production. Foods 2026, 15, 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15020323
Long T, Xu Y, Li Z, Kong W, Zhu Y, Tao M, Luo H, Cui L, Sun M, Wu Z, et al. Unlocking the Functional Potential of Pecan Nut Cake: A Study on Bioactive Peptide Production. Foods. 2026; 15(2):323. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15020323
Chicago/Turabian StyleLong, Tianjing, Yingjie Xu, Ziang Li, Weimei Kong, Yibo Zhu, Mingxuan Tao, Haibo Luo, Li Cui, Mingjun Sun, Zhen Wu, and et al. 2026. "Unlocking the Functional Potential of Pecan Nut Cake: A Study on Bioactive Peptide Production" Foods 15, no. 2: 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15020323
APA StyleLong, T., Xu, Y., Li, Z., Kong, W., Zhu, Y., Tao, M., Luo, H., Cui, L., Sun, M., Wu, Z., Zeng, X., Pan, D., & Guo, Y. (2026). Unlocking the Functional Potential of Pecan Nut Cake: A Study on Bioactive Peptide Production. Foods, 15(2), 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15020323





