Differential Non-Volatile Metabolomics in High- and Low-Alcohol Strong-Flavor Baijiu by Non-Targeted Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Chemicals and Materials
2.3. UHPLC-Q Exactive Plus Mass Analysis
2.3.1. Sample Preparation
2.3.2. Chromatographic Conditions
2.3.3. Mass Spectrometry Conditions
2.4. Multivariate Statistical Analysis and Network Visualization
3. Results and Discussion
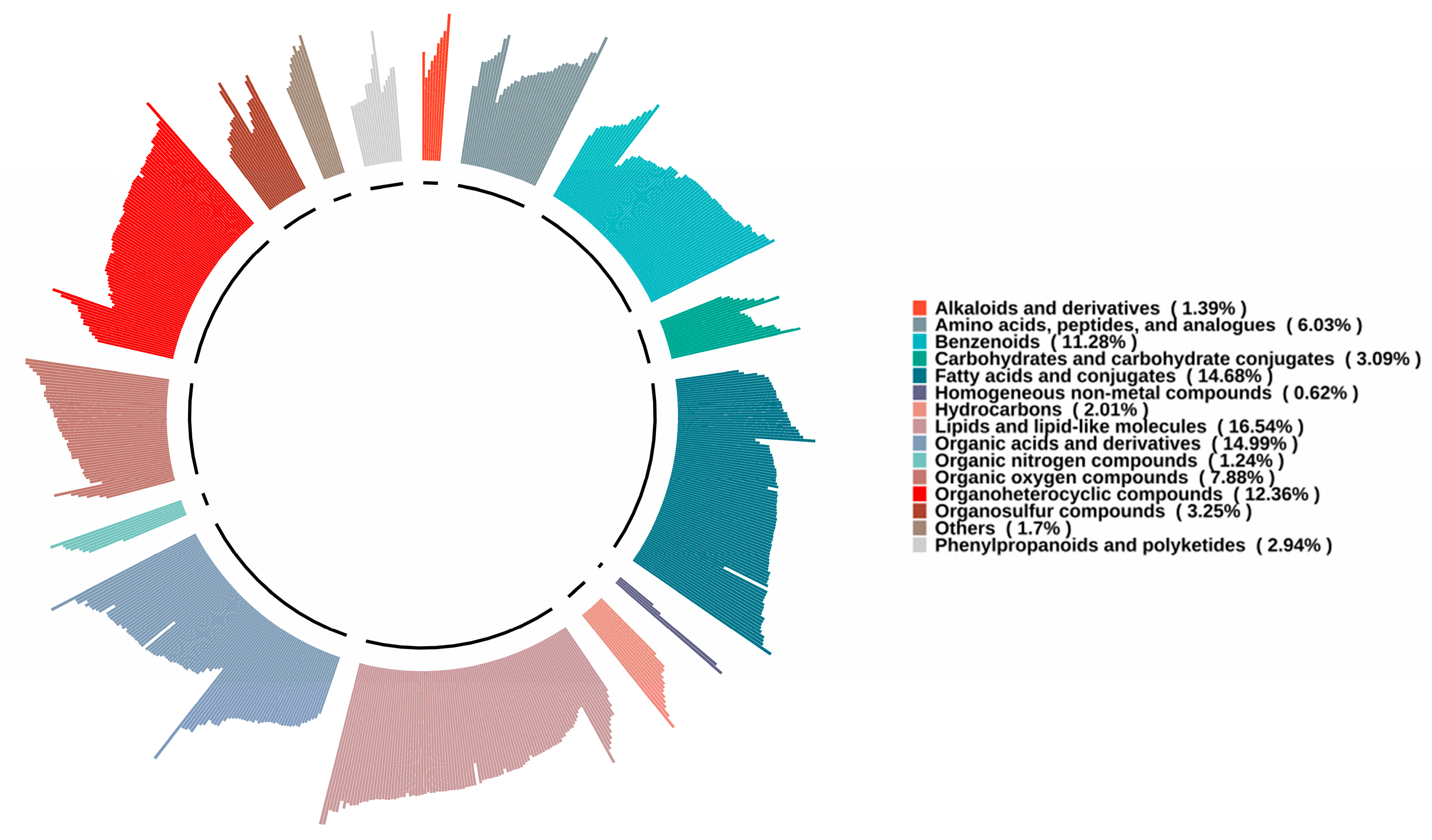
3.1. Analysis of Non-Volatile Metabolic Compounds in SFB
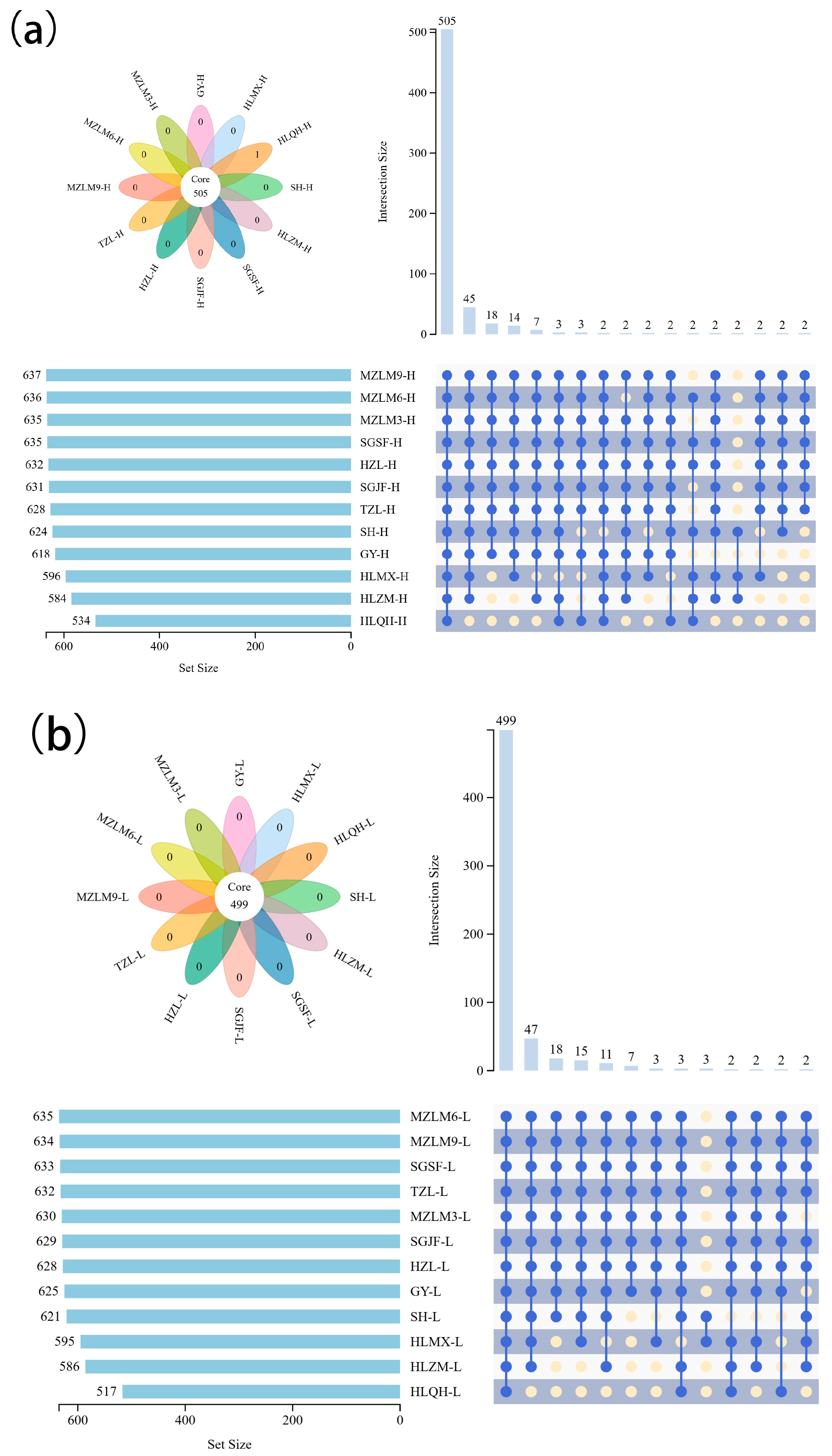
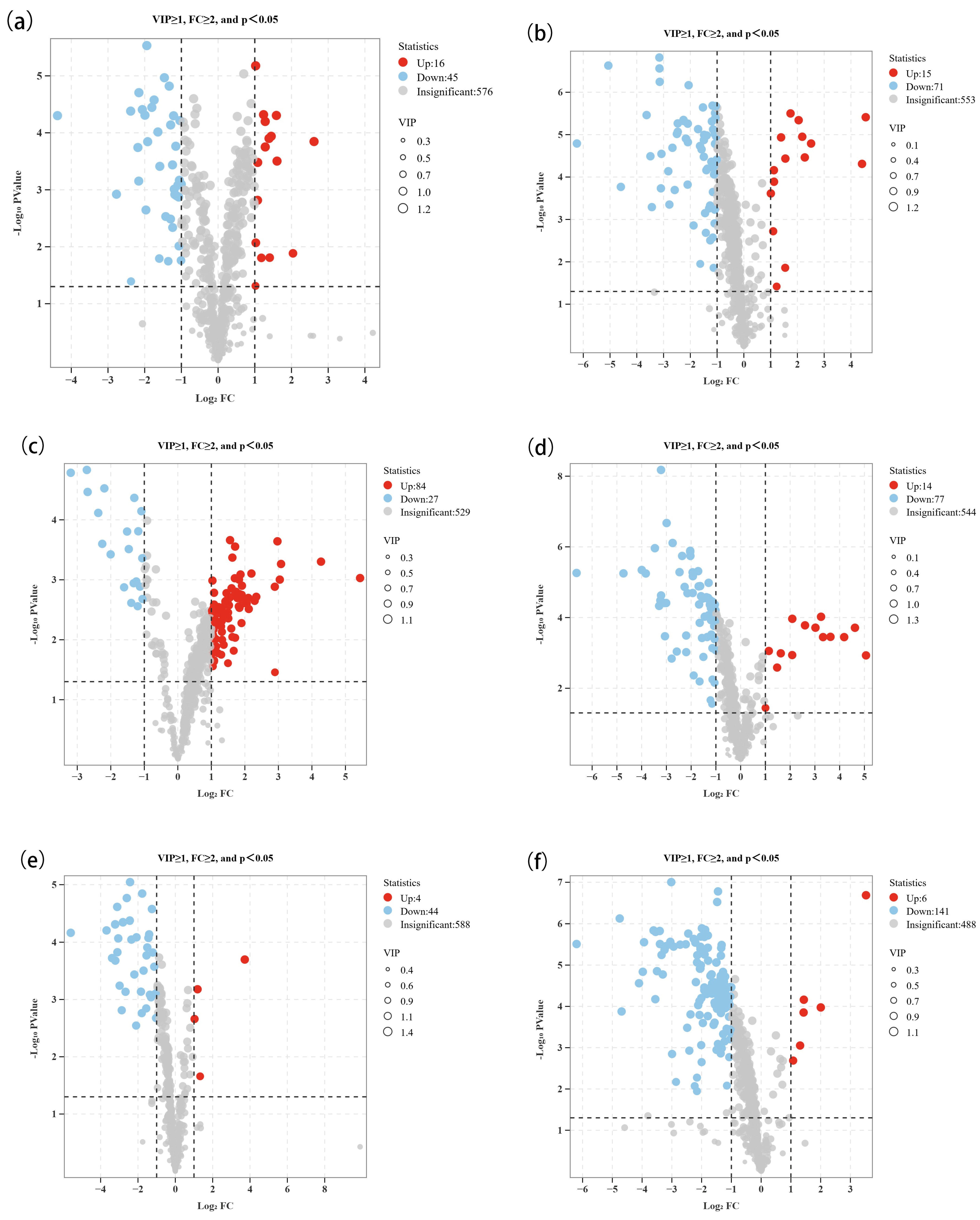
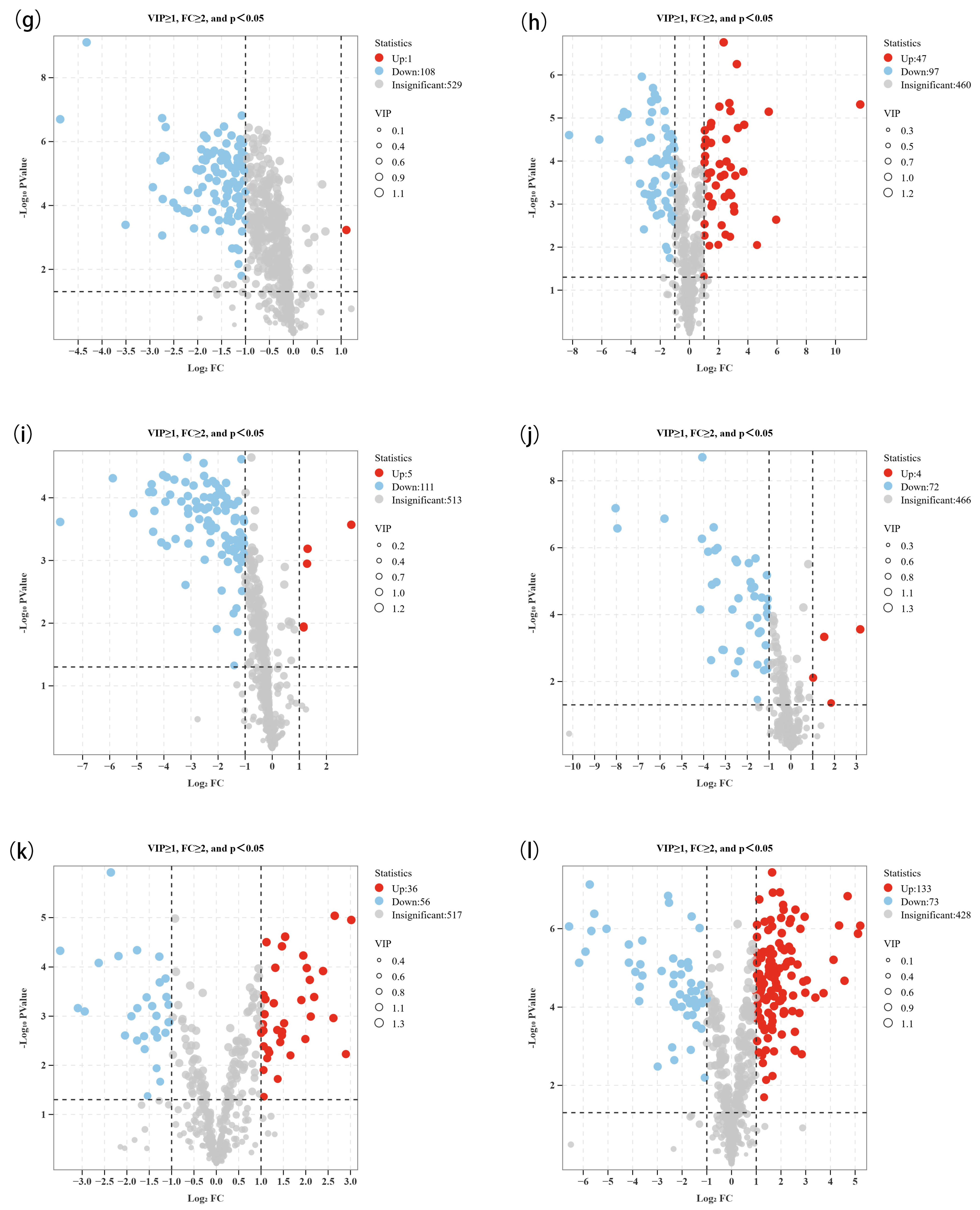
3.2. Screening of Non-Volatile Differential Metabolites Between High- and Low-Alcohol SFB
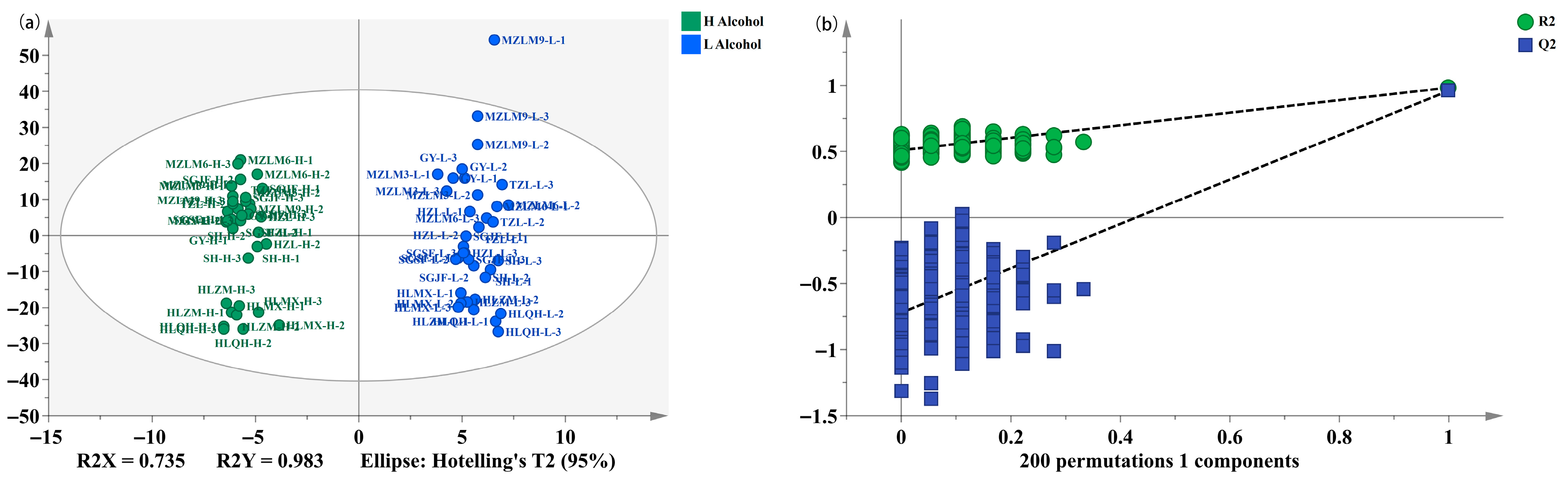
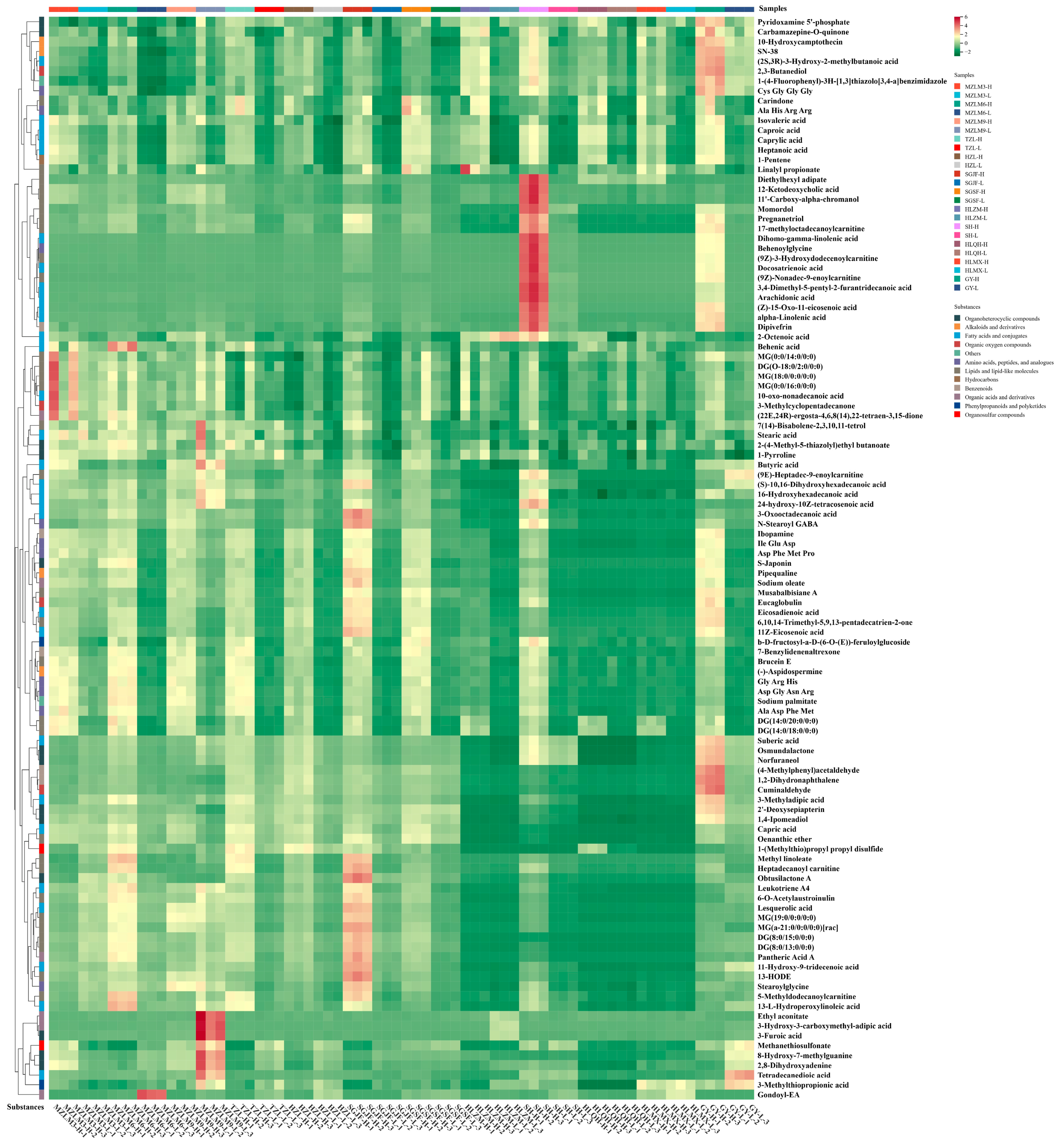
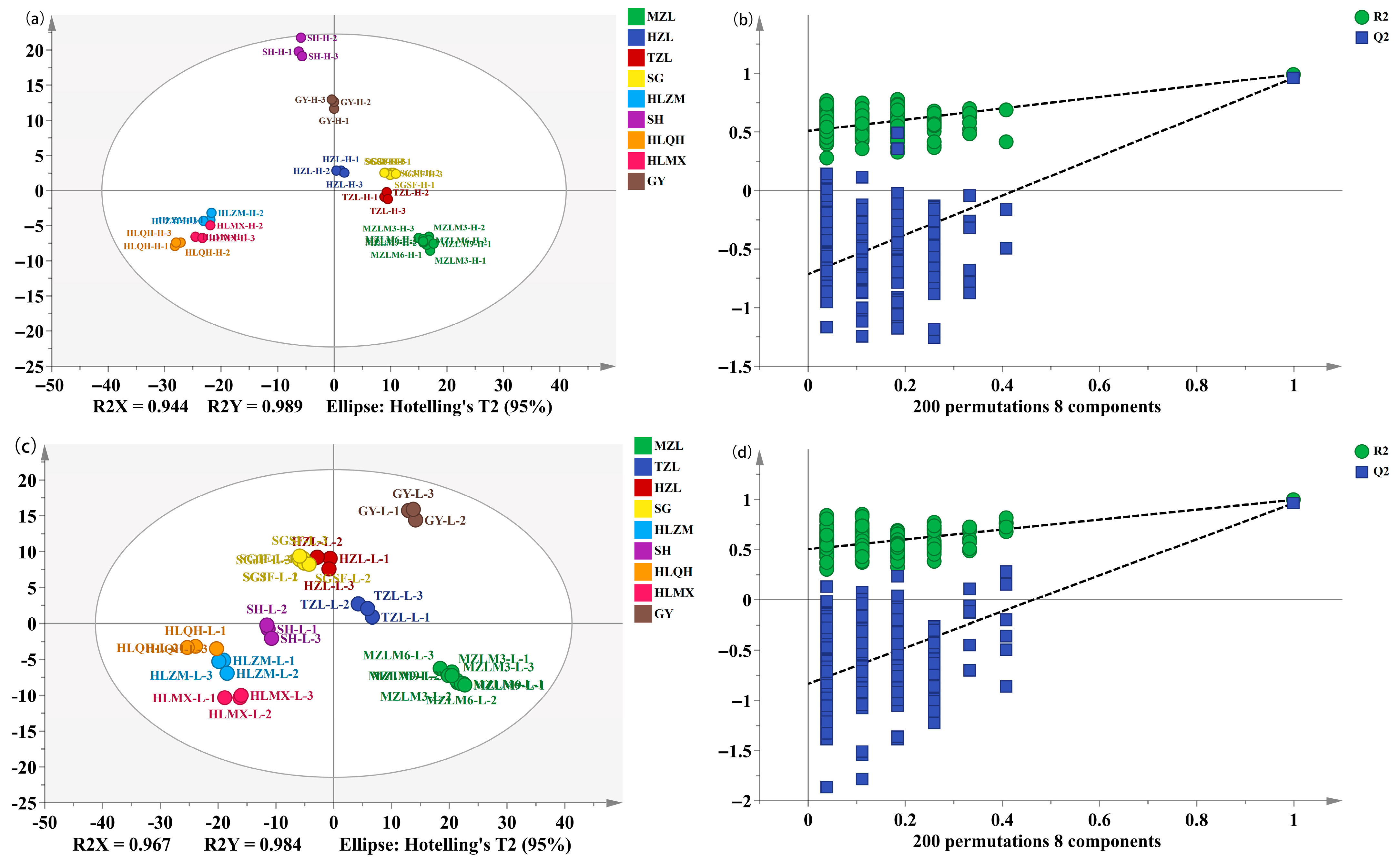
3.3. Comparison and Differential Metabolic Analysis of High- and Low-Alcohol SFB
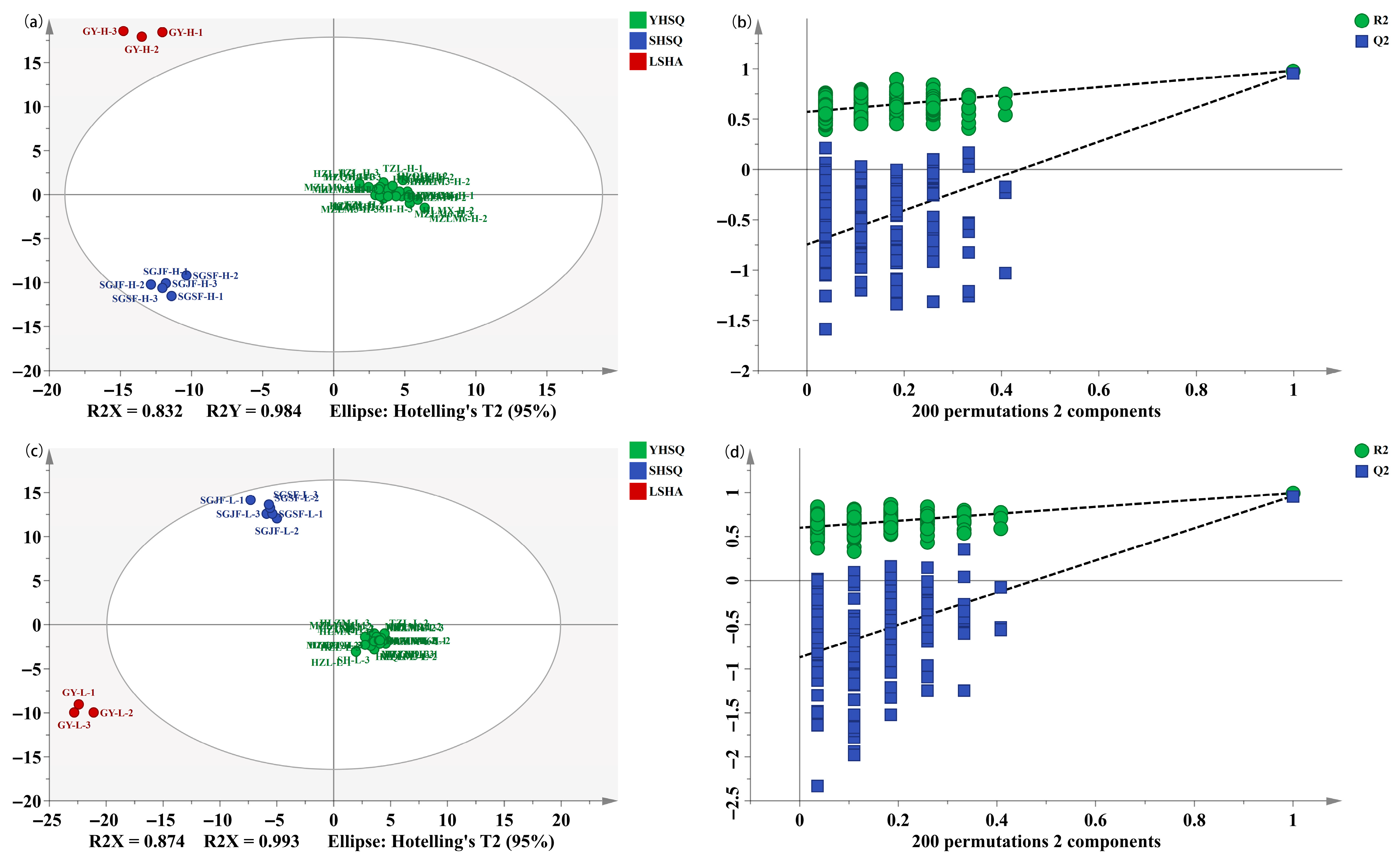
3.4. Discrimination of the Different Categories of Strong-Flavor Baijiu
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, G.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, Y. Mystery Behind Chinese Liquor Fermentation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 63, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.X.; Zhao, D.R.; Sun, B.G. Research Progress on the Profile of Trace Components in Baijiu. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 1666–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Du, Y.; Zheng, J.; Qiao, Z.; Luo, H.; Zou, W. Production of caproic acid by Rummeliibacillus suwonensis 3B-1 Isolated from the Pit Mud of Strong-Flavor Baijiu. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 358, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Bureau of Statistics. Available online: https://data.stats.gov.cn/easyquery.htm?cn=A01&zb=A020909&sj=202511 (accessed on 9 December 2025).
- Huang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, S.; Shen, C.; Shi, B. Effects of Metals Released in Strong-Flavor Baijiu on the Evolution of Aroma Compounds During Storage. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 1904–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, D. Uncover the Flavor Code of Strong-Aroma Baijiu: Research Progress on the Revelation of Aroma Compounds in Strong-Aroma Baijiu by Means of Modern Separation Technology and Molecular Sensory Evaluation. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 109, 104499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.M.; Mu, Y.C.; Lv, X.X.; Chen, N.; Chen, L.; Wen, T.Z.; Su, W. Analysis of Fermentation Characteristics in Fermented Grains Across Seven Rounds of Sauce-Flavored Baijiu: Microbial Communities Structure, Physicochemical Parameters, Volatile and Non-Volatile Flavor Compounds. Food Chem. X 2025, 25, 102228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Ma, R. Rutian Cross-Modal Interactions Caused by Nonvolatile Compounds Derived from Fermentation, Distillation and Aging to Harmonize Flavor. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2023, 64, 6686–6713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wu, M.; Lai, J.; Zong, E.; Zheng, J.; Xu, Y.; Sun, B. Butyrogenic and Caprogenic Bacteria from Pit Mud of Strong-Aroma Baijiu Engage in Mutualistic Cross-Feeding and Promoting Caproic Acid Biosynthesis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2025, 443, 111434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Dai, X.R.; Jia, Y.T.; Ye, S.T.; Shen, C.H.; Liu, M.; Lin, F.; Sun, X.T.; Xiong, Y.F.; Deng, B. Association Between Baijiu Chemistry and Taste Change: Constituents, Sensory Properties, and Analytical Approaches. Food Chem. X 2024, 437, 137826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.A.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.F.; Zhang, N.; Zheng, F.P. A Review on Flavor of Baijiu and Other World-Renowned Distilled Liquors. Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 100870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Chen, J.; Shi, W.; Shi, J.; Ma, T.; Wang, X. Can Nonvolatile Tastants be Smelled during Food Oral Processing? Chem. Senses 2023, 48, bjad028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Zheng, F.; Chen, T.; Liu, X.; Hu, C.; Ma, M.; Lu, X.; Xu, G. Untargeted and Quantitative Analyses of amine and Phenol Compounds in Baijiu via Chemical Isotope labeling. Explor. Foods Foodomics 2023, 1, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Mao, Z.; Penttinen, P.; Zhang, F.; Dong, L.; Song, C.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Fu, X.; Zhang, S.; et al. Chemical Isotope Labeling Liquid Chromatograph-Mass Spectrometer: A Powerful Tool for Analyzing Non-Volatile Organic Acids in Baijiu. Foods 2025, 14, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Y.; Pan, S.; Chen, X.; Wu, T. Identifying Distinct Markers in Two Sorghum Varieties for Baijiu Fermentation Using Untargeted Metabolomics and Molecular Network Approaches. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, D.; Mao, S.; Yang, Y.; Tian, J.; Chen, C.; Tu, H.; Ye, X.; Yang, F. Phenolic Metabolites Changes During Baijiu Fermentation Through Non-Targeted Metabonomic. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Song, X.; Zhu, L.; Li, Q.; Zheng, F.; Geng, X.; Li, L.; Wu, J.; Li, H.; Sun, B. A Flavoromics Strategy for the Differentiation of Different Types of Baijiu According to the Non-Volatile Organic Acids. Food Chem. X 2021, 374, 131641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.H.; Yang, Y.B.; Song, F.H.; Xiang, P.; Yang, F.; Tu, H.B. Decoding Baijiu Flavor Complexity: Integrating Dynamic Sensory Analysis, High-Resolution Metabolomics, and Advanced Mass Spectrometry. Food Res. Int. 2025, 221, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S.; Qing, Y.; Zhang, D. Multi-Omics Technology-Based Flavor Formation Mechanisms and Intelligent Quality Control Research in Strong-Flavor Baijiu. Int. J. Biol. Life Sci. 2025, 11, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Qiu, S.; Xu, X.; Chen, R.; Ye, C. Research Progress on the Detection and Analysis of Non-Volatile Flavor Components in Baijiu. China Brew. 2023, 42, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.; Du, H.; Jia, W.; Xu, Y. Compositional Differences and Similarities Between Typical Chinese Baijiu and Western Liquor as Revealed by Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics. Metabolites 2019, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, J.N.; Li, H.X.; Ma, Y.; Pu, Z.E.; Li, L.; Huang, L.B.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.Q.; Jiang, G.F.; et al. Based on Electronic Nose and Multi-omics, Investigate the Dynamic Changes of Volatile and Non-Volatile Organic Compounds in Waxy Wheat Baijiu from Different Years. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 101864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Yang, X.; Guo, Q.; Li, B.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, L. Microbial Communities and Flavor Compounds During the Fermentation of Traditional Hong Qu Glutinous Rice Wine. Foods 2022, 11, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.L.; Ni, B.; Yang, J.G.; Qin, Y. Nitrogenous Compounds and Chinese Baijiu: A Review. J. Inst. Brew. 2022, 128, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Jia, W. Extracellular Proteolytic Enzyme-mediated Amino Exposure and β-oxidation Drive the Raspberry Aroma and Creamy Flavor Formation. Food Chem. 2023, 424, 136442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Yang, F.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Wang, T.; Lu, X.; Lu, J.; Hu, C.; Tu, H.; et al. High-Sensitivity Profiling of Dipeptides in Sauce-Flavor Baijiu Daqu by Chemical Derivatization and Ultrahigh-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chang, R.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, Q.; Shen, C.; Lan, Y.; Cao, X.; Mao, J. Conversion of Baijiu Distillers’ Grains to Functional Peptides: Process Optimization and Antioxidant Activity Evaluation. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 108, 105722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atique, R.; Saeed, H.A.; Ijaz, A.; Talib, A.; Shah, R.R.; Haidar, A.; Naveed, A.; Sharif, J.; Nadeem, A.; Latif, M.; et al. Microbial Food Fermentation: An Extraordinary Approach to Improve Food Quality Employing Beneficial Microbes. Food Biomacromol. 2025, 2, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Jing, S.; Song, X.; Zhu, L.; Zheng, F.; Sun, B. Reconstitution of the Flavor Signature of Laobaigan-Type Baijiu Based on the Natural Concentrations of Its Odor-Active Compounds and Nonvolatile Organic Acids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 70, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hua, J. Regulation and Mechanisms of L-Lactic Acid and D-Lactic Acid Production in Baijiu Brewing: Insights for Flavor Optimization and Industrial Application. Fermentation 2025, 11, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Y.; Wen-lai, F.; Yan, X. Characterization of Non-Volatile Organic Acids in Baijius (Chinese liquors) Based on BSTFA Derivatization Coupled with GC-MS. Food Ferment. Ind. 2017, 43, 192–197. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Pan, S.; Xu, X.; Yuan, F. Influences of Non-Volatile Components on the Aroma of Strong-Aroma Baijiu by Gas Chromatography-Olfactometry and Recombination-Omission Test. Foods 2025, 14, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Q.; Lang, L.; Linghu, K.; Wei, C.; Lin, L.; Kilmartin, P.A.; Zhang, C. Non-Volatile Compounds as Aroma Modulators in Jiangxiang-Flavor Baijiu: Regional Flavor Differentiation and Synergistic Interactions with Volatile Aromas. Food Chem. X 2025, 490, 145015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Qi, J.; Zhao, W.; Gu, J.; Guo, W.; Li, Y. Screening of Specific Quantitative Peptides of Beef by LC–MS/MS Coupled with OPLS-DA. Food Chem. X 2022, 387, 132932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Ji, W.; Ding, L. Untargeted GC-MS Metabolomics Combined with Multivariate Statistical Analysis as An Effective Method for Discriminating the Geographical Origin of Shrimp Paste. Food Anal. Methods 2023, 17, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Lee, G.; Seong, G.U.; Jo, D.M.; Kim, Y.M.; Cho, J.S.; Lim, J.H.; Park, K.J. Investigation of Potential Quality Indicators for Raw Laver (Pyropia spp.) Standardization: A Collaborative Approach Between Traditional Assessment and Analytical Chemistry. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1676911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.L.J.; Tropsha, A.; Winkler, D.A. Beware of R2: Simple, Unambiguous Assessment of the Prediction Accuracy of QSAR and QSPR Models. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Ao, R.; Huang, H.; Hong, J.; Zhao, D.; et al. “Key Factor” for Baijiu Quality: Research Progress on Acid Substances in Baijiu. Foods 2022, 11, 2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Sun, B.G. Effect of Fermentation Processing on the Flavor of Baijiu. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5425–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Gao, L.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, B.; Liu, M.; Sun, B.; Li, H. Effect of Temperature on Microbial Communities and Flavor Compounds During the Fermentation of Light-Flavor Baijiu. Food Sci. 2025, 46, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.B.; Zhang, P.P.; Tang, Y.Y.; Huang, R.N.; Han, S.N.; Hou, J.G.; Pan, C.M. Combined Metagenomics and Metabolomics to Analyse the Fermentation Process of Taorong-Type Baijiu and Its Response Mechanism with Amino Acids. Food Chem. X 2025, 30, 102987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.N.; Jing, S.; Wang, X.L.; Zheng, F.P.; Li, H.H.; Sun, B.G.; Li, Z.X. Evaluation of the Perceptual Interaction Among Ester Odorants and Nonvolatile Organic Acids in Baijiu by GC-MS, GC-O, Odor Threshold, and Sensory Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 13987–13995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Fan, W.; Nie, Y.; Xu, Y. The Formation and Structural Characteristics of Melanoidins from Fermenting and Distilled Grains of Chinese Liquor (Baijiu). Food Chem. 2023, 410, 135372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyereko, Y.G.; Wireko-Manu, F.D.; Alemawor, F.; Adzanyo, M.; Patarata, L. Effects of Production Methods on Flavour Characteristics of Nonalcoholic Wine. J. Food Qual. 2021, 2021, 3014793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Tu, Y.; Luo, C.; Li, C.; Ni, B.; Liu, G. Fermentation Process Optimization, Analysis of Volatile Flavor Components and Non-volatile Metabolites of Litchi Fruit Wine. China Brew. 2025, 44, 76–85. [Google Scholar]
- Hedger, P.; Parr, W.; Sáenz-Navajas, M.P.; Rodrigues, H. Sensory Differentiation of Old World Wines from New World Wines: Has this Become More Challenging? Food Rev. Int. 2024, 196, 115098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, Y.; Mäkinen, M.; Jänis, J. Analysis of Volatile and Nonvolatile Constituents in Gin by Direct-Infusion Ultrahigh-Resolution ESI/APPI FT-ICR Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 7082–7089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Wang, N.; Guo, X.G.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Chang, D.; Li, J.X.; Gao, H.B. Analysis of Non-volatile Organic Acids Based on Silanization Combined with Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry and Chemometrics: A Robust Strategy to Discriminate Geographical Origin of Sauce-Flavor Baijiu. J. Chromatogr. A 2025, 1760, 466320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yangming, H.; Górska-Horczyczak, E.; Wierzbicka, A.; Jeleń, H.H. Rapid Analysis of Baijiu Volatile Compounds Fingerprint for their Aroma and Regional Origin Authenticity Assessment. Food Chem. 2021, 337, 128002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Lin, L.; Zheng, C.; Liu, X.; Cui, W.; Li, X.; Lyu, X.; Zhang, C. Using in Situ Untargeted Flavoromics Analysis to Unravel the Empty Cup Aroma of Jiangxiang-Type Baijiu: A Novel Strategy for Geographical Origin Traceability. Food Chem. 2024, 438, 137932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.X.; Xue, H.T.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, F.; Ma, Q.Y.; Sun, J.F.; Liu, Y.Q.; Tang, Y.W.; Wang, W.X. Geographical Identification of Chinese Wine Based on Chemometrics Combined with Mineral Elements, Volatile Components and Untargeted Metabonomics. Food Chem.-X 2024, 22, 101412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliya; Liu, S.; Zhang, D.N.; Cao, Y.F.; Sun, J.Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y. Research on the Evaluation of Baijiu Flavor Quality Based on Intelligent Sensory Technology Combined with Machine Learning. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Name | Alcohol Content (%vol) | Origin | No. | Name | Alcohol Content (%vol) | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MZLM3-H | 52 | Yanghe, Suqian | 2 | MZLM3-L | 45 | Yanghe, Suqian |
| 3 | MZLM6-H | 52 | Yanghe, Suqian | 4 | MZLM6-L | 40.8 | Yanghe, Suqian |
| 5 | MZLM9-H | 52 | Yanghe, Suqian | 6 | MZLM9-L | 45 | Yanghe, Suqian |
| 7 | TZL-H | 52 | Yanghe, Suqian | 8 | TZL-L | 42 | Yanghe, Suqian |
| 9 | HZL-H | 52 | Yanghe, Suqian | 10 | HZL-L | 42 | Yanghe, Suqian |
| 11 | SGJF-H | 52 | Sihong, Suqian | 12 | SGJF-L | 41.8 | Sihong, Suqian |
| 13 | SGSF-H | 52 | Sihong, Suqian | 14 | SGSF-L | 42 | Sihong, Suqian |
| 15 | HLZM-H | 52 | Yanghe, Suqian | 16 | HLZM-L | 42 | Yanghe, Suqian |
| 17 | SH-H | 50.8 | Yanghe, Suqian | 18 | SH-L | 40.8 | Yanghe, Suqian |
| 19 | HLQH-H | 52 | Yanghe, Suqian | 20 | HLQH-L | 42 | Yanghe, Suqian |
| 21 | HLMX-H | 52 | Yanghe, Suqian | 22 | HLMX-L | 42 | Yanghe, Suqian |
| 23 | GY-H | 52 | Lianshui, Huai’an | 24 | GY-L | 42 | Lianshui, Huai’an |
| Class | Number | Component Name | CAS | Formula | Observed m/z | Rt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lipids and lipid-like molecules | 1 | Musabalbisiane A | 143183-61-3 | C23H28O12 | 495.15 | 7.18 |
| 2 | 6,10,14-Trimethyl-5,9,13-pentadecatrien-2-one | 762-29-8 | C18H30O | 263.24 | 7.99 | |
| 3 | Pregnanetriol | 27178-64-9 | C21H36O3 | 337.27 | 7.28 | |
| 4 | (9Z)-Nonadec-9-enoylcarnitine | C26H49NO4 | 440.37 | 7.16 | ||
| 5 | Oenanthic ether | 106-30-9 | C9H18O2 | 159.14 | 6.36 | |
| 6 | MG (0:0/14:0/0:0) | 3443-83-2 | C17H34O4 | 325.23 | 6.75 | |
| 7 | Diethylhexyl adipate | 103-23-1 | C22H42O4 | 371.32 | 7.68 | |
| 8 | Momordol | 189156-42-1 | C26H48O5 | 458.38 | 6.93 | |
| 9 | Brucein E | C20H28O9 | 413.18 | 7.36 | ||
| 10 | Linalyl propionate | 144-39-8 | C13H22O2 | 228.2 | 7.22 | |
| 11 | DG(O-18:0/2:0/0:0) | C23H46O4 | 404.37 | 7.44 | ||
| 12 | 17-methyloctadecanoylcarnitine | C26H51NO4 | 442.39 | 7.28 | ||
| 13 | MG(a-21:0/0:0/0:0) [rac] | C24H48O4 | 418.39 | 7.11 | ||
| 14 | (9Z)-3-Hydroxydodecenoylcarnitine | C19H35NO5 | 375.29 | 7.62 | ||
| 15 | 5-Methyldodecanoylcarnitine | C20H39NO4 | 358.29 | 6.24 | ||
| 16 | (9E)-Heptadec-9-enoylcarnitine | C24H45NO4 | 412.34 | 7.24 | ||
| 17 | MG (19:0/0:0/0:0) | C22H44O4 | 390.36 | 6.67 | ||
| 18 | DG (8:0/13:0/0:0) | C24H46O5 | 437.32 | 6.83 | ||
| 19 | 12-Ketodeoxycholic acid | 5130-29-0 | C24H38O4 | 391.28 | 7.64 | |
| 20 | DG (14:0/20:0/0:0) | C37H72O5 | 619.53 | 13.27 | ||
| 21 | DG (14:0/18:0/0:0) | C35H68O5 | 591.5 | 11.71 | ||
| 22 | 6-O-Acetylaustroinulin | 75207-46-4 | C22H36O4 | 382.29 | 6.69 | |
| 23 | Heptadecanoyl carnitine | 106182-29-0 | C24H47NO4 | 414.36 | 7.05 | |
| 24 | 11′-Carboxy-alpha-chromanol | C26H42O4 | 436.34 | 7.64 | ||
| 25 | 7(14)-Bisabolene-2,3,10,11-tetrol | 122470-42-2 | C15H28O4 | 290.23 | 6.28 | |
| 26 | Carindone | 38045-62-4 | C31H44O6 | 530.35 | 6.65 | |
| 27 | DG (8:0/15:0/0:0) | C26H50O5 | 460.4 | 7.05 | ||
| 28 | MG (18:0/0:0/0:0) | 22610-61-3 | C21H42O4 | 381.3 | 7.44 | |
| 29 | MG (0:0/16:0/0:0) | 23470-00-0 | C19H38O4 | 353.27 | 7.07 | |
| 30 | S-Japonin | 36031-35-3 | C19H28O3S | 381.17 | 7.46 | |
| 31 | Eucaglobulin | 241130-84-7 | C23H30O12 | 497.17 | 7.46 | |
| 32 | Cuminaldehyde | 122-03-2 | C10H12O | 149.1 | 6.2 | |
| Organic acid and derivatives | 33 | Sodium oleate | C18H33NaO2 | 349.24 | 7.46 | |
| 34 | Ethyl aconitate | 1321-30-8 | C8H10O6 | 203.06 | 4.61 | |
| 35 | 3-Hydroxy-3-carboxymethyl-adipic acid | C8H12O7 | 243.05 | 4.61 | ||
| 36 | Gondoyl-EA | C22H43NO2 | 371.36 | 6.85 | ||
| 37 | Pantheric Acid A | C22H40O3 | 353.3 | 6.97 | ||
| 38 | (22E,24R)-ergosta-4,6,8(14),22-tetraen-3,15-dione | C28H38O2 | 407.29 | 7.44 | ||
| 39 | (9Z,11E,13S)-13-hydroxyoctadeca-9,11-dienoic acid | 29623-28-7 | C18H32O3 | 297.24 | 6.57 | |
| Fatty acids and conjugates | 40 | 3-Methylthiopropionic acid | 646-01-5 | C4H8O2S | 165.02 | 0.98 |
| 41 | Tetradecanedioic acid | 821-38-5 | C14H26O4 | 303.18 | 5.68 | |
| 42 | 16-Hydroxyhexadecanoic acid | 506-13-8 | C16H32O3 | 271.23 | 6.93 | |
| 43 | Methyl linoleate | 112-63-0 | C19H34O2 | 339.25 | 6.60 | |
| 44 | (Z)-15-Oxo-11-eicosenoic acid | 182145-55-7 | C20H36O3 | 323.26 | 6.97 | |
| 45 | 13 L-Hydroperoxylinoleic acid | 33964-75-9 | C18H32O4 | 311.22 | 6.24 | |
| 46 | Stearic acid | 57-11-4 | C18H36O2 | 283.26 | 7.87 | |
| 47 | Docosatrienoic acid | 28845-86-5 | C22H38O2 | 352.32 | 7.62 | |
| 48 | 11Z-Eicosenoic acid | 5561-99-9 | C20H38O2 | 311.29 | 8.42 | |
| 49 | 3-Methyladipic acid | 3058-01-3 | C7H12O4 | 183.06 | 5.44 | |
| 50 | Butyric acid | 107-92-6 | C4H8O2 | 89.06 | 5.79 | |
| 51 | Leukotriene A4 | 72059-45-1 | C20H30O3 | 319.23 | 7.05 | |
| 52 | 24-hydroxy-10Z-tetracosenoic acid | C24H46O3 | 400.38 | 7.87 | ||
| 53 | 3-Oxooctadecanoic acid | C18H34O3 | 299.26 | 6.83 | ||
| 54 | Arachidonic acid | 506-32-1 | C20H32O2 | 305.25 | 7.38 | |
| 55 | Behenic acid | 112-85-6 | C22H44O2 | 358.37 | 6.24 | |
| 56 | 3,4-Dimethyl-5-pentyl-2-furantridecanoic acid | 57818-43-6 | C24H42O3 | 396.35 | 7.38 | |
| 57 | Capric acid | 334-48-5 | C10H20O2 | 173.15 | 6.52 | |
| 58 | (S)-10,16-Dihydroxyhexadecanoic acid | 69232-67-3 | C16H32O4 | 306.26 | 6.34 | |
| 59 | Isovaleric acid | 503-74-2 | C5H10O2 | 103.08 | 6.16 | |
| 60 | Lesquerolic acid | 4103-20-2 | C20H38O3 | 327.29 | 6.67 | |
| 61 | 11-Hydroxy-9-tridecenoic acid | 105798-56-9 | C13H24O3 | 229.18 | 6.48 | |
| 62 | alpha-Linolenic acid | 463-40-1 | C18H30O2 | 279.23 | 6.97 | |
| 63 | 2-Octenoic acid | 1577-96-4 | C8H14O2 | 143.11 | 5.48 | |
| 64 | Caproic acid | 142-62-1 | C6H12O2 | 117.09 | 6.2 | |
| 65 | Suberic acid | 505-48-6 | C8H14O4 | 175.1 | 5.59 | |
| 66 | Eicosadienoic acid | 5598-38-9 | C20H36O2 | 309.28 | 7.99 | |
| 67 | 10-oxo-nonadecanoic acid | 820-42-8 | C19H36O3 | 313.27 | 7.07 | |
| 68 | Dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid | 1783-84-2 | C20H34O2 | 307.26 | 7.62 | |
| 69 | Heptanoic acid | 111-14-8 | C7H14O2 | 131.11 | 6.2 | |
| 70 | (2S,3R)-3-Hydroxy-2-methylbutanoic acid | 71526-30-2 | C5H10O3 | 141.05 | 4.77 | |
| 71 | Caprylic acid | 124-07-2 | C8H16O2 | 145.12 | 6.2 | |
| Organoheterocyclic compounds | 72 | 3-Furoic acid | 488-93-7 | C5H4O3 | 111.01 | 4.62 |
| 73 | 1-Pyrroline | 5724-81-2 | C4H7N | 70.07 | 1.11 | |
| 74 | 2-(4-Methyl-5-thiazolyl) ethyl butanoate | C10H15NO2S | 214.09 | 5.75 | ||
| 75 | Carbamazepine-O-quinone | 1135202-29-7 | C15H10N2O3 | 289.06 | 4.77 | |
| 76 | 1,4-Ipomeadiol | 53011-73-7 | C9H14O3 | 171.1 | 6.18 | |
| 77 | Pyridoxamine 5′-phosphate | 529-96-4 | C8H13N2O5P | 249.06 | 5.63 | |
| 78 | Obtusilactone A | 56522-15-7 | C19H32O3 | 309.24 | 7.01 | |
| 79 | 2,8-Dihydroxyadenine | 30377-37-8 | C5H5N5O2 | 185.08 | 4.24 | |
| 80 | 8-Hydroxy-7-methylguanine | 1688-85-3 | C6H7N5O2 | 199.09 | 4.83 | |
| 81 | 2′-Deoxysepiapterin | 1797-87-1 | C9H11N5O2 | 239.13 | 6.18 | |
| 82 | Norfuraneol | 19322-27-1 | C5H6O3 | 115.04 | 5.59 | |
| 83 | Osmundalactone | 69308-39-0 | C6H8O3 | 129.05 | 5.59 | |
| Benzenoids | 84 | 7-Benzylidenenaltrexone | C27H27NO4 | 428.19 | 7.36 | |
| 85 | 1,2-Dihydronaphthalene | 447-53-0 | C10H10 | 131.09 | 6.2 | |
| 86 | (4-Methylphenyl) acetaldehyde | 104-09-6 | C9H10O | 135.08 | 6.2 | |
| 87 | Dipivefrin | 52365-63-6 | C19H29NO5 | 369.24 | 7.07 | |
| 88 | Ibopamine | 66195-31-1 | C17H25NO4 | 325.21 | 7.18 | |
| Organic oxygen compounds | 89 | 3-Methylcyclopentadecanone | 541-91-3 | C16H30O | 239.24 | 7.07 |
| 90 | 2,3-Butanediol | 513-85-9 | C4H10O2 | 91.08 | 4.77 | |
| Amino acids, peptides, and analogs | 91 | Asp Phe Met Pro | C23H32N4O7S | 553.2 | 7.46 | |
| 92 | Ala Asp Phe Met | C21H30N4O7S | 527.18 | 7.36 | ||
| 93 | Asp Gly Asn Arg | C16H28N8O8 | 459.2 | 7.36 | ||
| 94 | Cys Gly Gly Gly | C9H16N4O5S | 147.05 | 4.75 | ||
| 95 | Gly Arg His | C14H24N8O4 | 369.2 | 7.36 | ||
| 96 | Ala His Arg Arg | C21H38N12O5 | 556.34 | 6.65 | ||
| 97 | Stearoylglycine | 6333-54-6 | C20H39NO3 | 342.3 | 6.59 | |
| 98 | Ile Glu Asp | C15H25N3O8 | 393.2 | 7.18 | ||
| 99 | N-Stearoyl GABA | 52558-71-1 | C22H43NO3 | 370.33 | 6.99 | |
| 100 | Behenoylglycine | 14246-59-4 | C24H47NO3 | 398.36 | 7.62 | |
| Organosulfur compounds | 101 | 1-(Methylthio)propyl propyl disulfide | 126876-22-0 | C7H16S3 | 195.03 | 4.29 |
| 102 | Methanethiosulfonate | 44059-82-7 | CH4O2S2 | 110.96 | 0.78 | |
| Phenylpropanoids and polyketides | 103 | b-D-fructosyl-a-D-(6-O-(E))-feruloylglucoside | C21H28O12 | 471.15 | 7.38 | |
| Hydrocarbons | 104 | 1-Pentene | 109-67-1 | C5H10 | 71.09 | 6.18 |
| Alkaloids and derivatives | 105 | Pipequaline | 77472-98-1 | C22H24N2 | 339.18 | 7.44 |
| 106 | 10-Hydroxycamptothecin | 64439-81-2 | C20H16N2O5 | 183.06 | 4.75 | |
| 107 | (−)-Aspidospermine | 466-49-9 | C22H30N2O2 | 377.22 | 7.36 | |
| 108 | SN-38 | 86639-52-3 | C22H20N2O5 | 197.08 | 4.75 | |
| Others | 109 | Sodium palmitate | 408-35-5 | C16H31NaO2 | 323.22 | 7.36 |
| 110 | 1-(4-Fluorophenyl)-3H-[1,3] thiazolo [3,4-a] benzimidazole | 136994-91-7 | C15H11FN2S | 293.05 | 4.75 |
| Comparison Group Information | Different Compounds Number | Up-Regulated Compounds Number | Down-Regulated Compounds Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| MZLM3-H/MZLM3-L | 61 | 16 | 45 |
| MZLM6-H/MZLM6-L | 86 | 15 | 71 |
| MZLM9-H/MZLM9-L | 111 | 84 | 27 |
| TZL-H/TZL-L | 91 | 14 | 77 |
| HZL-H/HZL-L | 48 | 4 | 44 |
| SGJF-H/SGJF-L | 147 | 6 | 141 |
| SGSF-H/SGSF-L | 109 | 1 | 108 |
| HLZM-H/HLZM-L | 144 | 47 | 97 |
| SH-H/SH-L | 116 | 5 | 111 |
| HLQH-H/HLQH-L | 76 | 4 | 72 |
| HLMX-H/HLMX-L | 92 | 36 | 56 |
| GY-H/GY-L | 206 | 133 | 73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Fan, Y.; Qiu, C.; Chen, P.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, X.; Jiang, S.; Liu, D.; Cao, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y. Differential Non-Volatile Metabolomics in High- and Low-Alcohol Strong-Flavor Baijiu by Non-Targeted Approach. Foods 2026, 15, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010037
Fan Y, Qiu C, Chen P, Zhao Y, Feng X, Jiang S, Liu D, Cao Y, Liu S, Liu Y. Differential Non-Volatile Metabolomics in High- and Low-Alcohol Strong-Flavor Baijiu by Non-Targeted Approach. Foods. 2026; 15(1):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010037
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Yuxia, Chenxi Qiu, Panpan Chen, Yajiao Zhao, Xiaoxiao Feng, Shui Jiang, Dengyong Liu, Yufa Cao, Shi Liu, and Yuan Liu. 2026. "Differential Non-Volatile Metabolomics in High- and Low-Alcohol Strong-Flavor Baijiu by Non-Targeted Approach" Foods 15, no. 1: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010037
APA StyleFan, Y., Qiu, C., Chen, P., Zhao, Y., Feng, X., Jiang, S., Liu, D., Cao, Y., Liu, S., & Liu, Y. (2026). Differential Non-Volatile Metabolomics in High- and Low-Alcohol Strong-Flavor Baijiu by Non-Targeted Approach. Foods, 15(1), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010037








