Construction and Characterization of Emulsions Stabilized by Whey Protein Isolate-Naringin-Sodium Alginate Ternary Complex
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Ternary Complex
2.3. Turbidity Measurement of Ternary Complex
2.4. Fluorescence Spectroscopy Measurement of Ternary Complex
2.5. Preparation of Emulsion
2.6. Determination of Emulsion Oil Droplet Size and ζ-Potential
2.7. Optical Microscopy Observation
2.8. Micro-Rheological Characterization of Emulsions
2.9. Determination of Lipid Oxidation
2.10. Determination of Lutein Stability
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
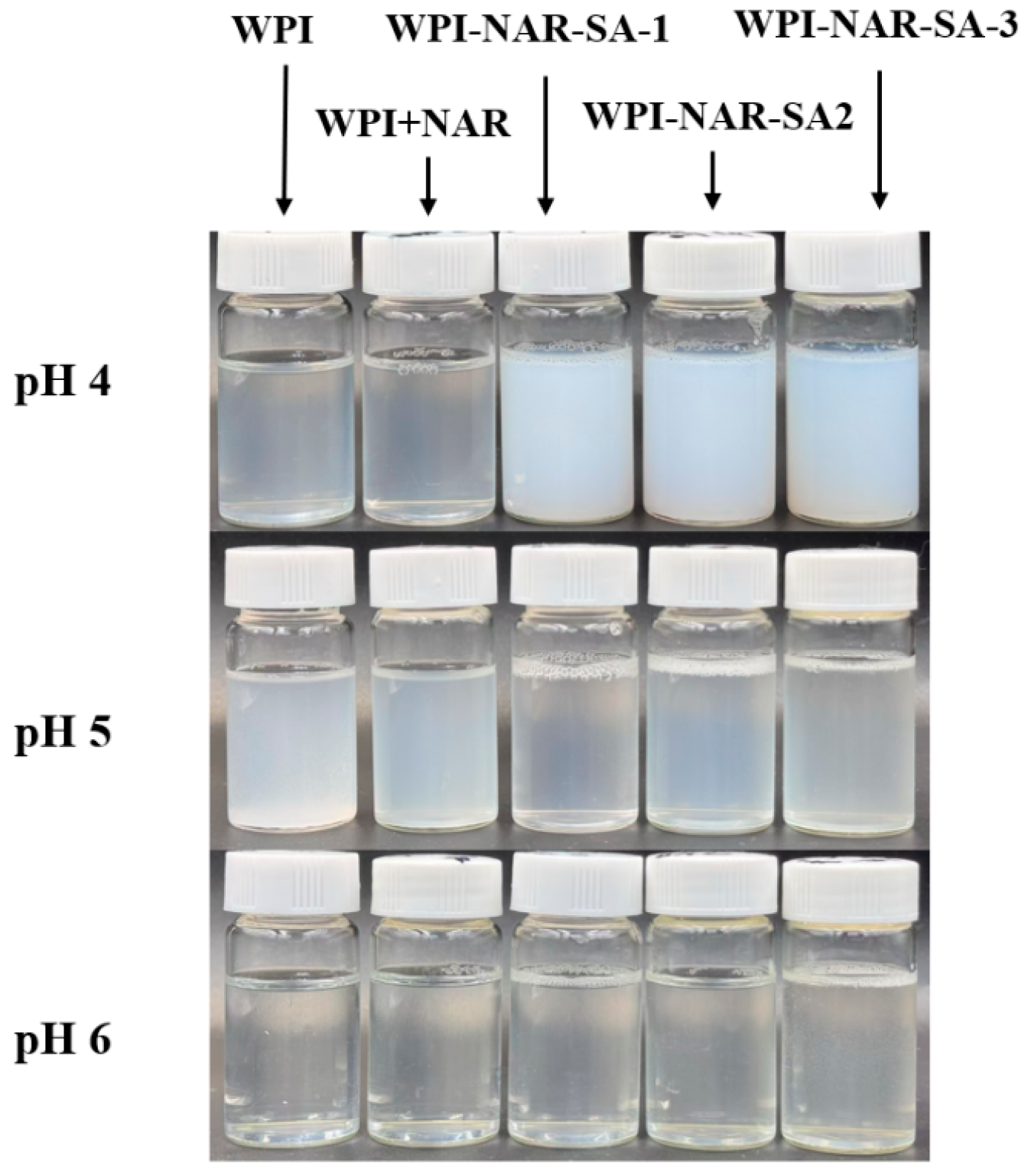
3.1. Turbidity of Ternary Complex
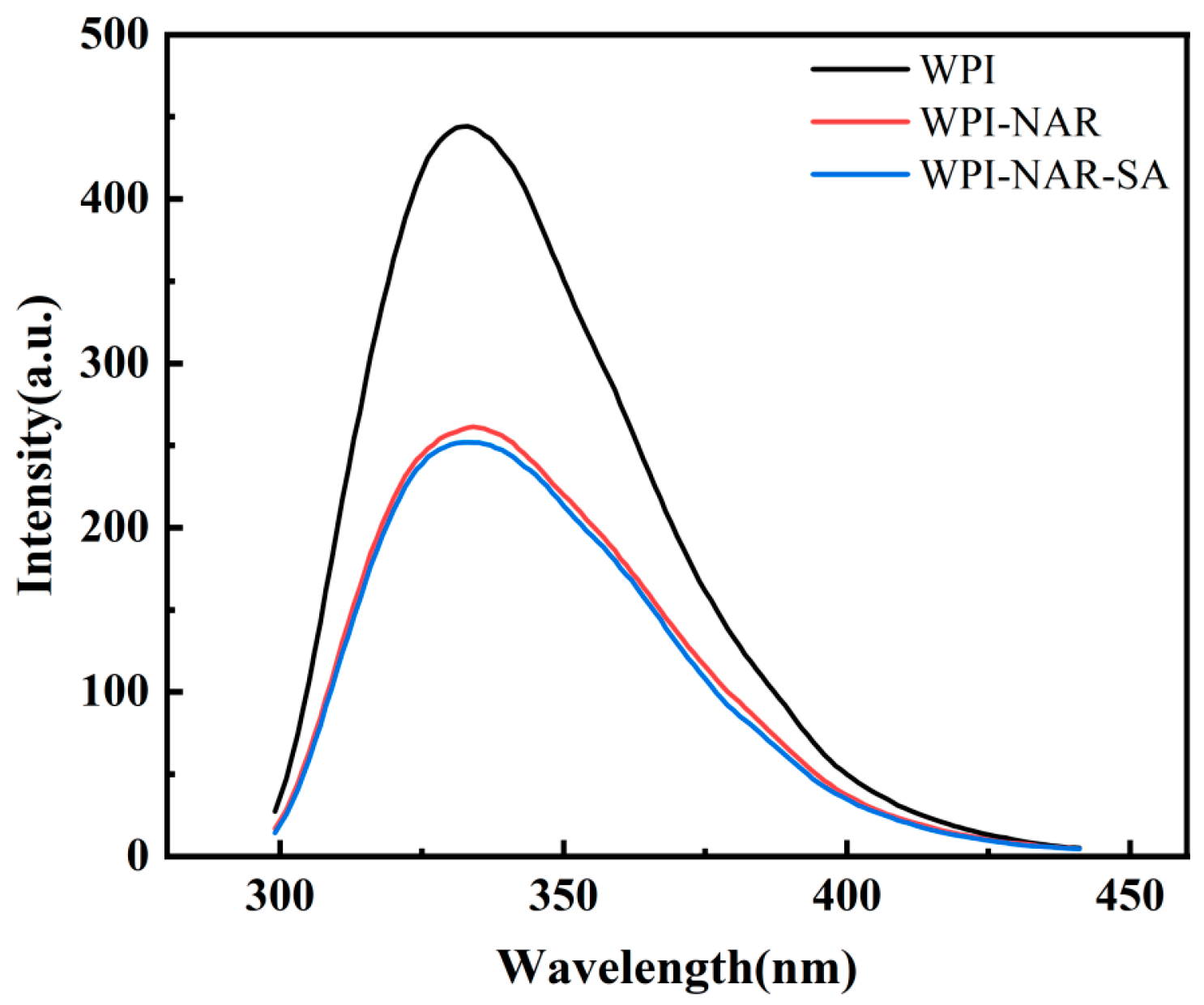
3.2. Fluorescence Spectra of Ternary Complex
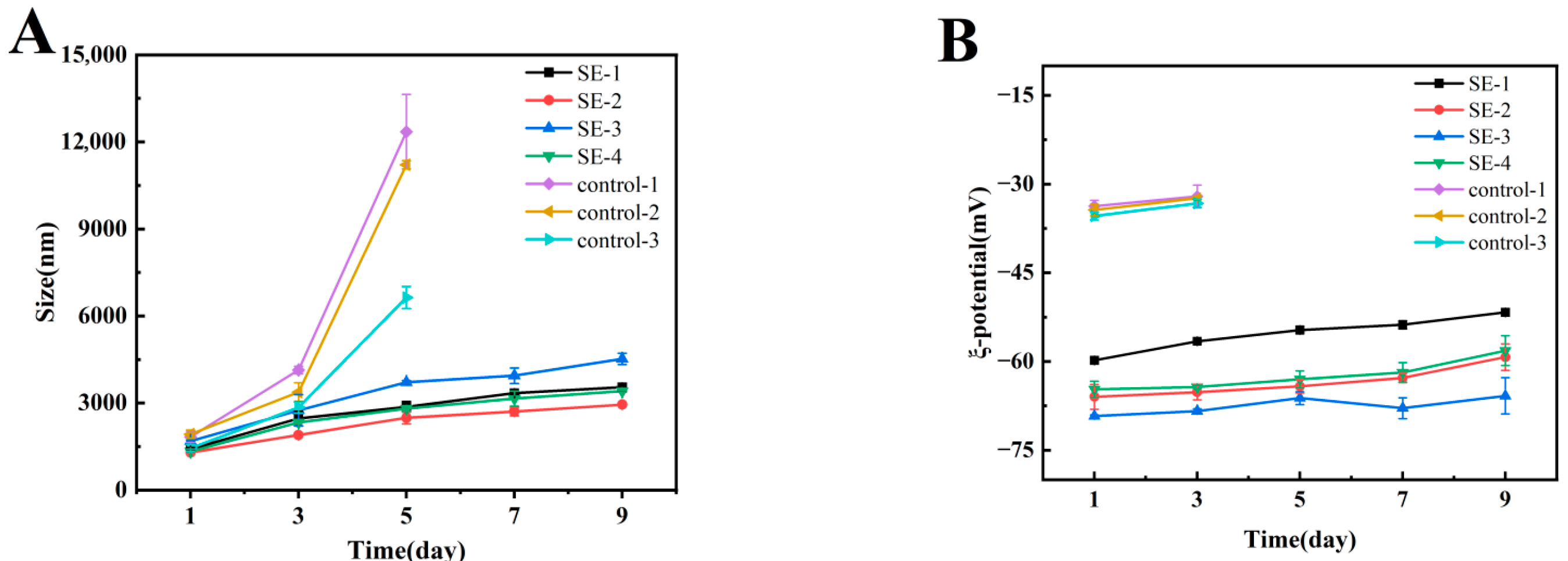
3.3. Droplet Size and ζ-Potential of Emulsion
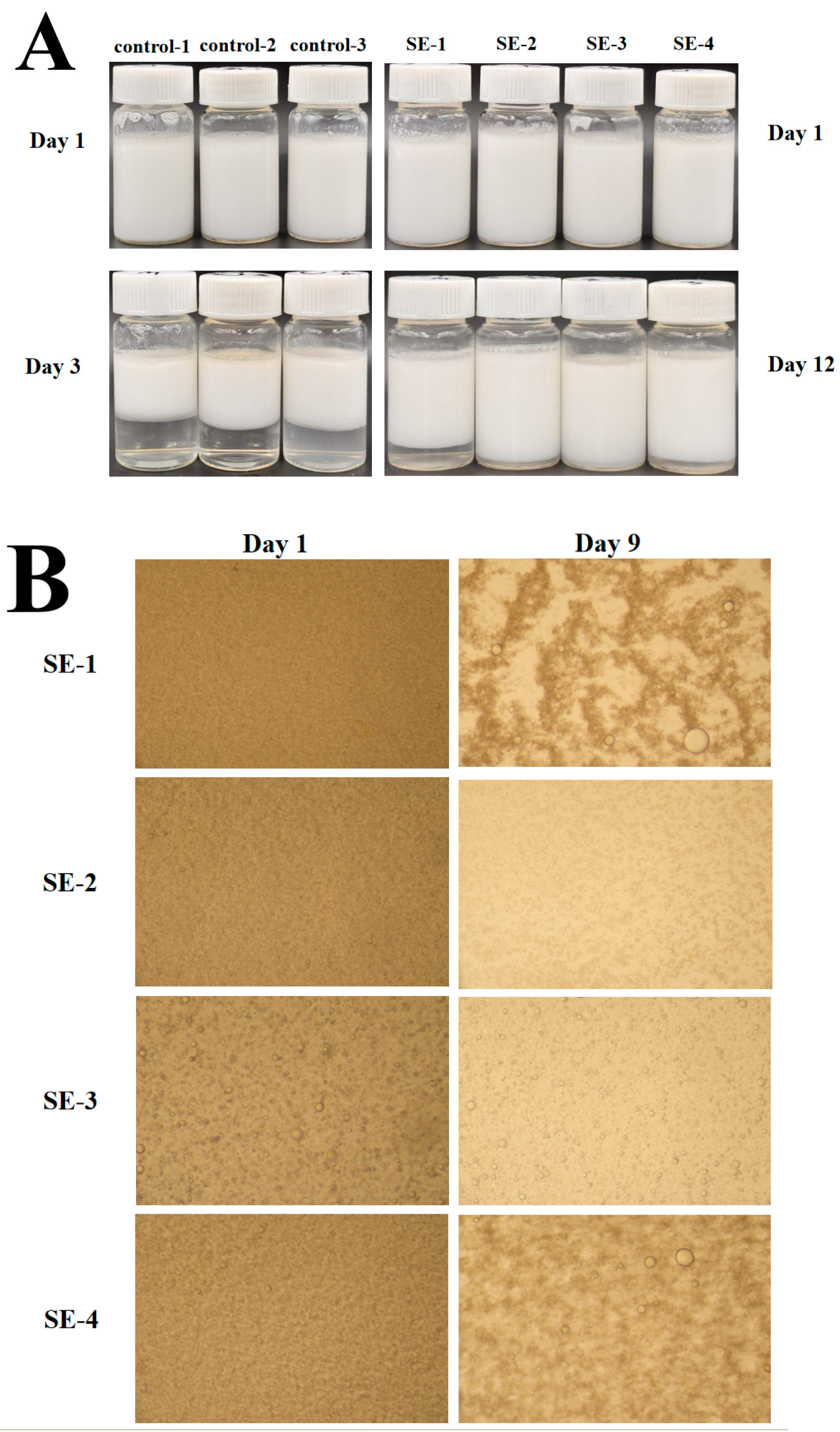
3.4. Appearance and Microscopic Observation of Emulsion
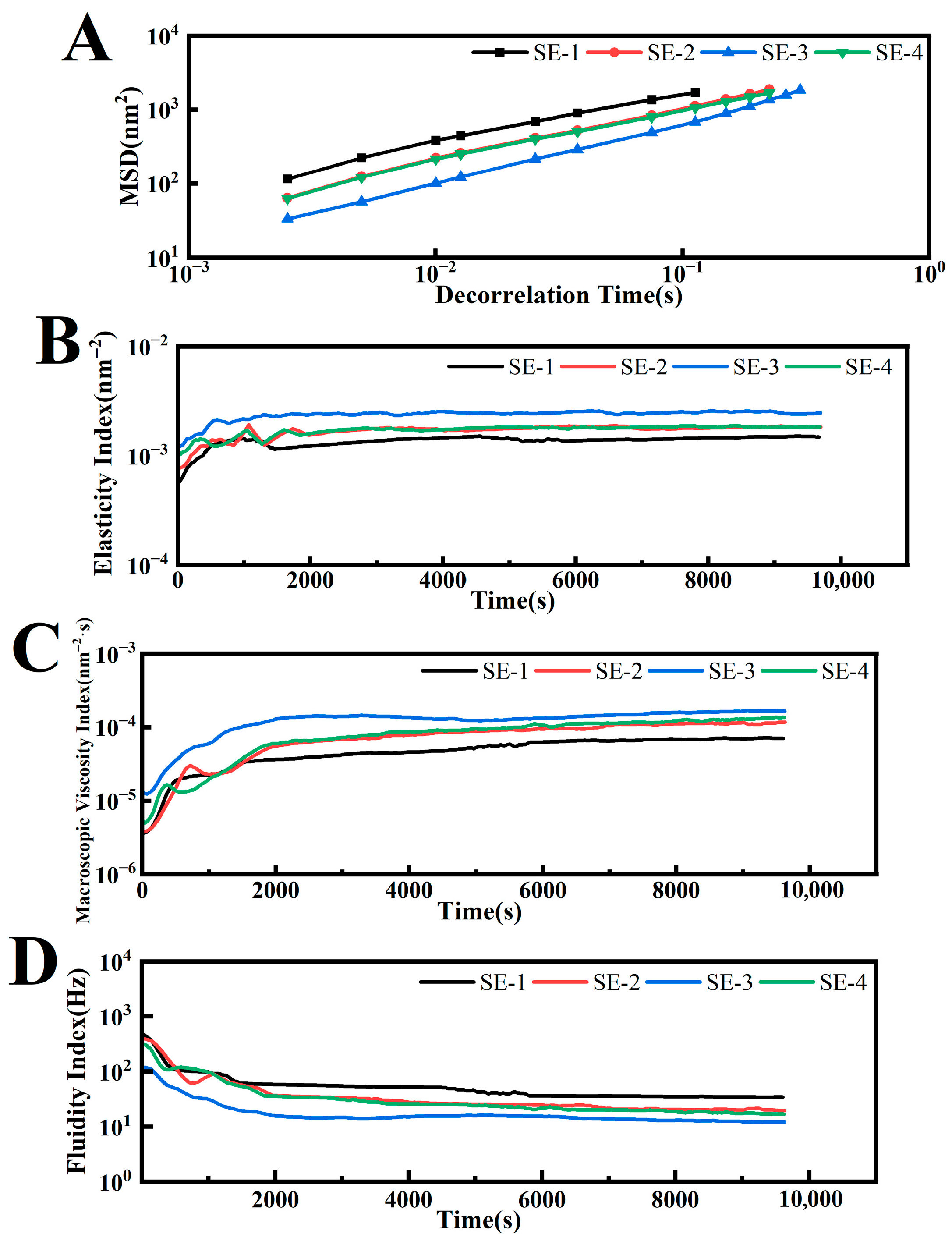
3.5. Microrheological Properties of Emulsion
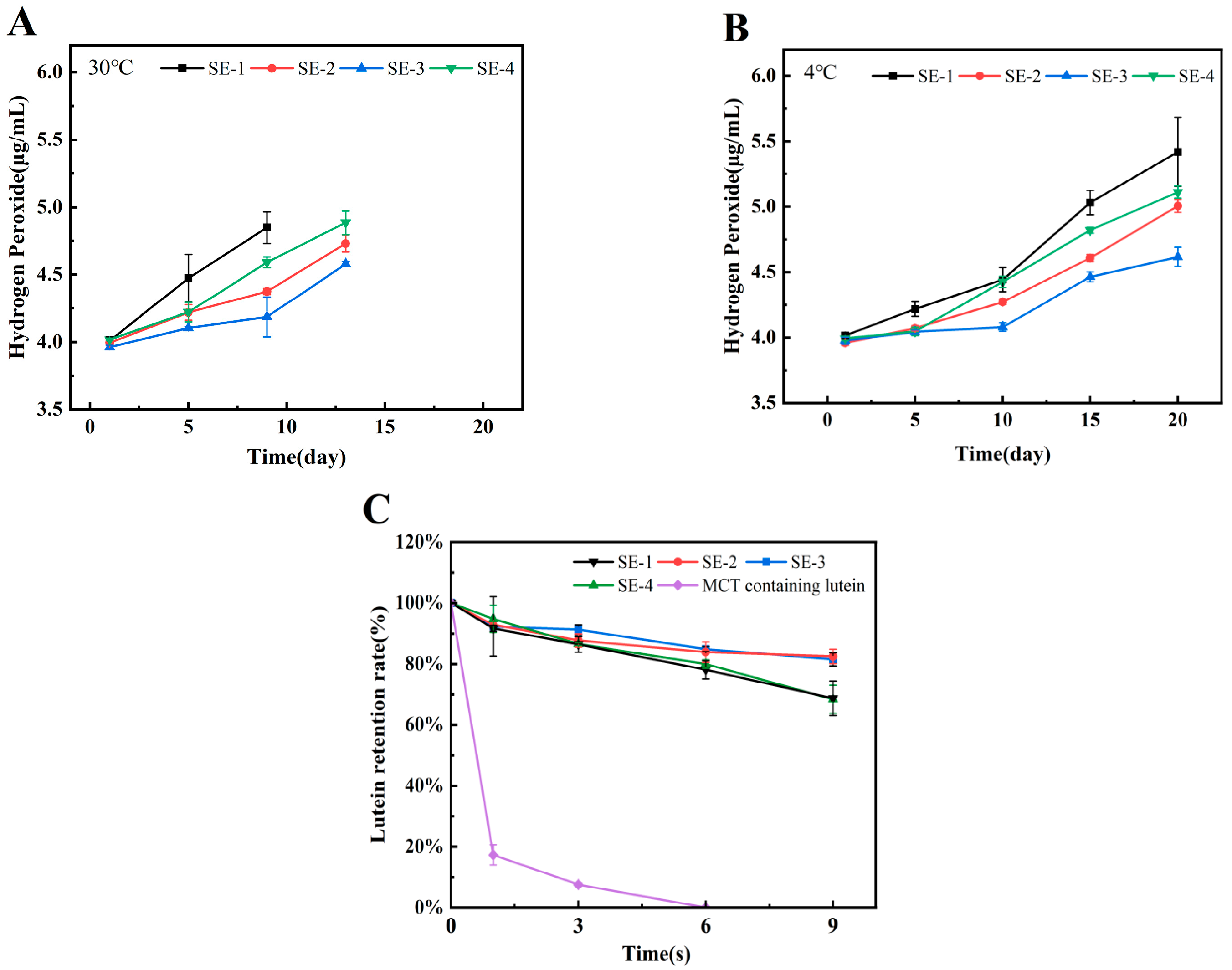
3.6. Oxidative Stability of Emulsion Lipids
3.7. Lutein Protection Ability of Emulsion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Falsafi, S.R.; Karaca, A.C.; Deng, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Askari, G.; Rostamabadi, H. Insights into whey protein-based carriers for targeted delivery and controlled release of bioactive components. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 133, 108002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, R.S.H.; Nickerson, M.T. Food proteins: A review on their emulsifying properties using a structure-function approach. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Tian, M.; Tan, C.; Ying, R.; Ahmad, M.; Hao, G.; Liao, Q. Thermal stability, antioxidant activity and bioavailability of pea protein-naringin Pickering emulsion for enhanced delivery applications. Food Res. Int. 2024, 188, 114393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Vardhanabhuti, B. Influence of the molecular weight of carboxymethylcellulose on properties and stability of whey protein-stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 3305–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fang, Y.; Al-Assaf, S.; Phillips, G.O.; Jiang, F. Complexation of bovine serum albumin and sugar beet pectin: Stabilising oil-in-water emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 388, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Huang, Q. Assembly of protein-polysaccharide complexes for delivery of bioactive ingredients: A perspective paper. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, W.; Deng, Y.; Cao, Y.; Xiao, J. Regulation of whey protein microparticle adsorption and interfacial film formation by polysaccharides for enhanced Pickering emulsion stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 162, 110879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnsilawat, T.; Pongsawatmanit, R.; McClements, D.J. Stabilization of model beverage cloud emulsions using protein-polysaccharide electrostatic complexes formed at the oil-water interface. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 5540–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ji, A.; Qiu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Yin, L. Covalent conjugation of bovine serum albumin and sugar beet pectin through Maillard reaction/laccase catalysis to improve the emulsifying properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 76, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.-N.; Zheng, H.; Chen, X.-X.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Xu, M.-F. Synergetic effects of whey protein isolate and naringin on physical and oxidative stability of oil-in-water emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, J. Oxidative stability and in vitro digestion of menhaden oil emulsions with whey protein: Effects of EGCG conjugation and interfacial cross-linking. Food Chem. 2018, 265, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Ma, C.; McClements, D.J.; Gao, Y. Development of polyphenol-protein-polysaccharide ternary complexes as emulsifiers for nutraceutical emulsions: Impact on formation, stability, and bioaccessibility of β-carotene emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Luo, S.; Ning, F.; Ye, J.; Liu, C. Preparation of protein-polyphenol-polysaccharide ternary complexes to regulate the interfacial structure of emulsions: Interfacial behavior and emulsion stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 157, 110434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Li, X.-Y.; Li, Q.-M.; Pan, L.-H.; Luo, J.-P.; Zha, X.-Q. Development of chondroitin sulfate-modified quinoa protein isolate-dihydromyricetin composite nanoparticles: Focus on naringenin delivery, cell cytoprotective ability and anti-inflammatory effects. Food Chem. 2025, 493, 145761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archut, A.; Klost, M.; Drusch, S.; Kastner, H. Complex coacervation of pea protein and pectin: Contribution of different protein fractions to turbidity. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 134, 108032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Shao, G.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Zhu, D.; Li, Y.; et al. pH-induced conformational changes and interfacial dilatational rheology of soy protein isolated/soy hull polysaccharide complex and its effects on emulsion stabilization. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 109, 106075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Bai, L.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, B.; Geng, S. Characterization of Okra Seed Protein/Rutin Covalent Complex and Its Application in Nanoemulsions. Foods 2025, 14, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Ma, Y.; Wang, C.; Ma, H.; Geng, S. Oil/water interface behavior of hesperidin methylchalcone and its application in nano-emulsions. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, C.; Sanchez, C.; Desobry-Banon, S.; Hardy, J. Structure and technofunctional properties of protein-polysaccharide complexes: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1998, 38, 689–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xue, F.; Adhikari, B. Recent advances in plant protein modification: Spotlight on hemp protein. Sustain. Food Technol. 2024, 2, 893–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, C.; Turgeon, S.L. Protein/polysaccharide complexes and coacervates in food systems. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 167, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Chen, B.; Rao, J. Pea protein isolate-high methoxyl pectin soluble complexes for improving pea protein functionality: Effect of pH, biopolymer ratio and concentrations. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 80, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisaidoobe, A.B.; Chung, S.J. Intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence in the detection and analysis of proteins: A focus on Förster resonance energy transfer techniques. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 22518–22538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Jafari, S.M. Improving emulsion formation, stability and performance using mixed emulsifiers: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 251, 55–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Szeto, I.M.-Y.; Yan, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, J.; Evivie, S.E.; Li, B.; Duan, S. Evaluating the binding mechanism, structural changes and stability of ternary complexes formed by the interaction of folic acid with whey protein concentrate-80 and L-ascorbyl 6-palmitate. Food Chem. 2024, 457, 139924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, E.F.; Morell, P.; Nicoletti, V.R.; Quiles, A.; Hernando, I. Protein- and polysaccharide-based particles used for Pickering emulsion stabilisation. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 119, 106839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Xie, C.; Ashokkumar, M.; Dunshea, F.R.; Suleria, H.A. Incorporation of brown seaweed (Ecklonia radiata) polyphenol crude extracts in whey protein isolate-sodium alginate emulsion delivery systems. Food Chem. 2025, 493, 146011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.S. Pickering emulsions for food and drinks. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 27, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; He, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhao, X. Oil density and viscosity affect emulsion stability and destabilization mechanism. J. Food Eng. 2024, 366, 111864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomuso, L.B.; Corredig, M.; Akoh, C.C. Effect of emulsifier on oxidation properties of fish oil-based structured lipid emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2957–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Xin, Y.; Wu, B.; Jiang, X.; Wu, X.; Hou, P.; Qi, J.; Zhang, J. Pickering emulsions stabilized by ternary complexes involving curcumin-modified zein and polysaccharides with different charge amounts for encapsulating β-carotene. Food Chem. 2024, 433, 137338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, G.K.; Chen, T.-S.; Philip, T. Quantitative analysis of lutein esters in marigold flowers (Tagetes erecta) by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Food Sci. 1986, 51, 1093–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ahmed, F.; Bernstein, P.S. Studies on the singlet oxygen scavenging mechanism of human macular pigment. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 504, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, L. Fabrication of resveratrol-loaded whey protein-dextran colloidal complex for the stabilization and delivery of β-carotene emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9481–9489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| SE-1 | SE-2 | SE-3 | SE-4 | Control-1 | Control-2 | Control-3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPI (Whey Protein Isolate, %) | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.695 | 0.92 | 1.37 |
| SA (Sodium Alginate, %) | 0.225 | 0.45 | 0.9 | 0.45 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| NAR (Naringin, %) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Sodium azide (%) | 0.005 | ||||||
| MCT (Medium Chain Triglycerides, %) | 5 | ||||||
| pH Treatment | WPI | WPI-NAR | WPI-NAR-SA-1 | WPI-NAR-SA-2 | WPI-NAR-SA-3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 4 | 57.2 d ± 0.53 | 51.3 d ± 2.01 | 1298.67 a ± 8.96 | 982.67 b ± 17.10 | 734.67 c ± 7.10 |
| pH 5 | 299 a ± 1.00 | 193 b ± 3.46 | 32.57 e ± 0.32 | 92.6 c ± 1.35 | 86.77 d ±0.9 |
| pH 6 | 11.67 d ± 0.29 | 11.6 d ± 0.20 | 12.87 c ± 0.32 | 14.23 b ± 0.21 | 41.87 a ± 0.67 |
| Parameter | SE-1 | SE-2 | SE-3 | SE-4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLB (solid–liquid balance) | 0.68 | 0.72 | 0.81 | 0.71 |
| EI (elasticity index; nm−2) | 1.51 × 10−3 | 1.84 × 10−3 | 2.42 × 10−3 | 1.82 × 10−3 |
| MVI(macroscopic viscosity Index; nm−2·s) | 7.47 × 10−5 | 1.22 × 10−4 | 1.73 × 10−4 | 1.43 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Wei, M.; Liu, G.; Liu, B. Construction and Characterization of Emulsions Stabilized by Whey Protein Isolate-Naringin-Sodium Alginate Ternary Complex. Foods 2026, 15, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010019
Chen S, Wei M, Liu G, Liu B. Construction and Characterization of Emulsions Stabilized by Whey Protein Isolate-Naringin-Sodium Alginate Ternary Complex. Foods. 2026; 15(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Si, Mengmeng Wei, Guoyang Liu, and Benguo Liu. 2026. "Construction and Characterization of Emulsions Stabilized by Whey Protein Isolate-Naringin-Sodium Alginate Ternary Complex" Foods 15, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010019
APA StyleChen, S., Wei, M., Liu, G., & Liu, B. (2026). Construction and Characterization of Emulsions Stabilized by Whey Protein Isolate-Naringin-Sodium Alginate Ternary Complex. Foods, 15(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods15010019





