The Structure, Assembly Processes of Microbial Communities and Their Effects on the Quality of Goat MEAT During Chilled Storage (4 °C)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Pretreatment
2.2. Determination of pH
2.3. Determination of Color Value
2.4. Determination of Mass Loss Rate
2.5. Determination of Myoglobin
2.6. Determination of Total Volatile Basic Nitrogen (TVB-N)
2.7. Determination of Total Plate Count (TPC)
2.8. DNA Extraction and Bacterial Community Analysis
2.9. Models of Microbial Community Assembly
2.10. Statistics Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
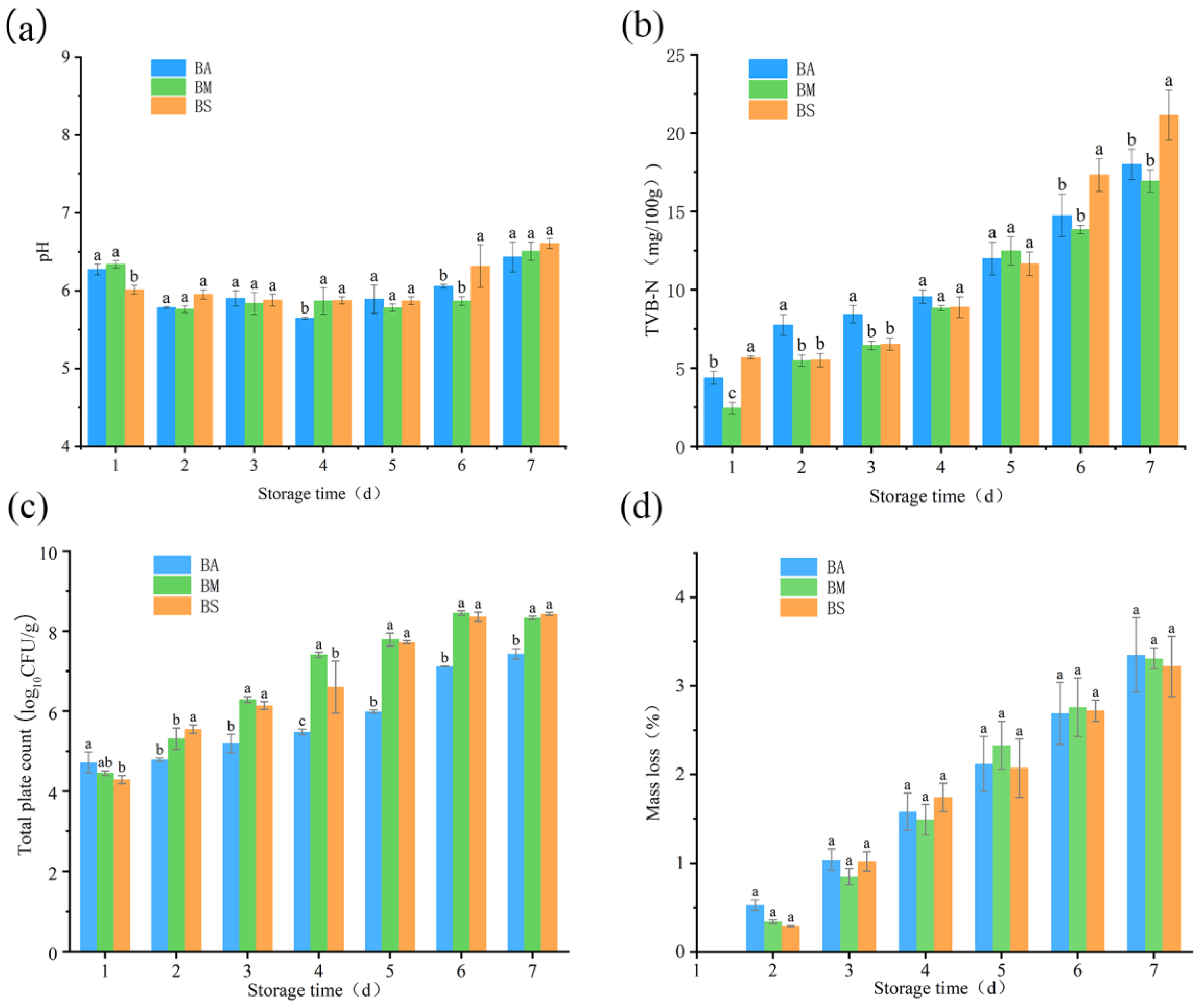
3.1. Quality Changes in Goat Meat During Chilled Storage
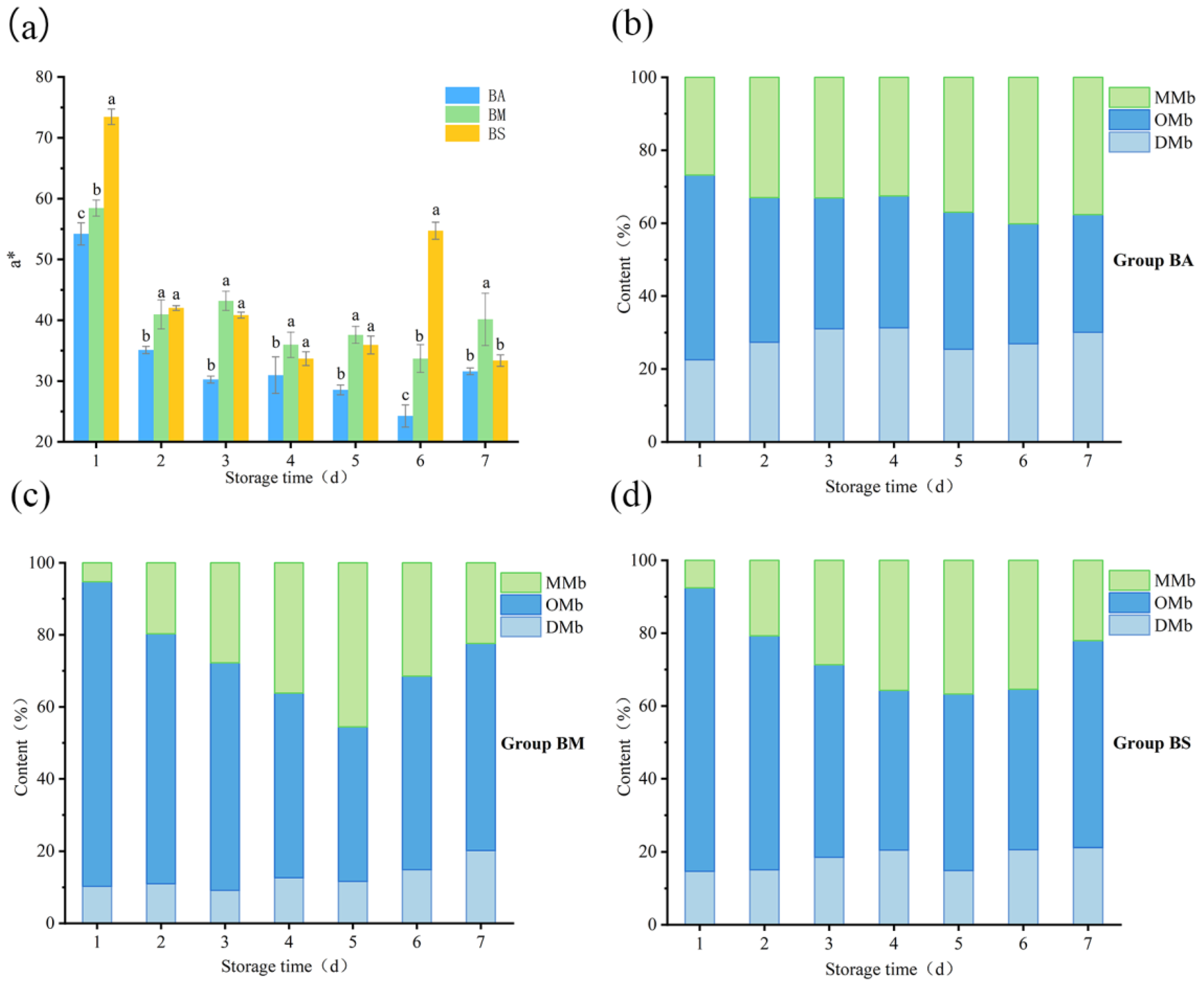
3.2. Red–Green Axis (a*) and Myoglobin Changes in Goat Meat During Chilled Storage
3.3. Microbial Richness and Diversity of Goat Meat During Chilled Storage
3.4. Analysis of Microbial Community Dynamics During Chilled Storage
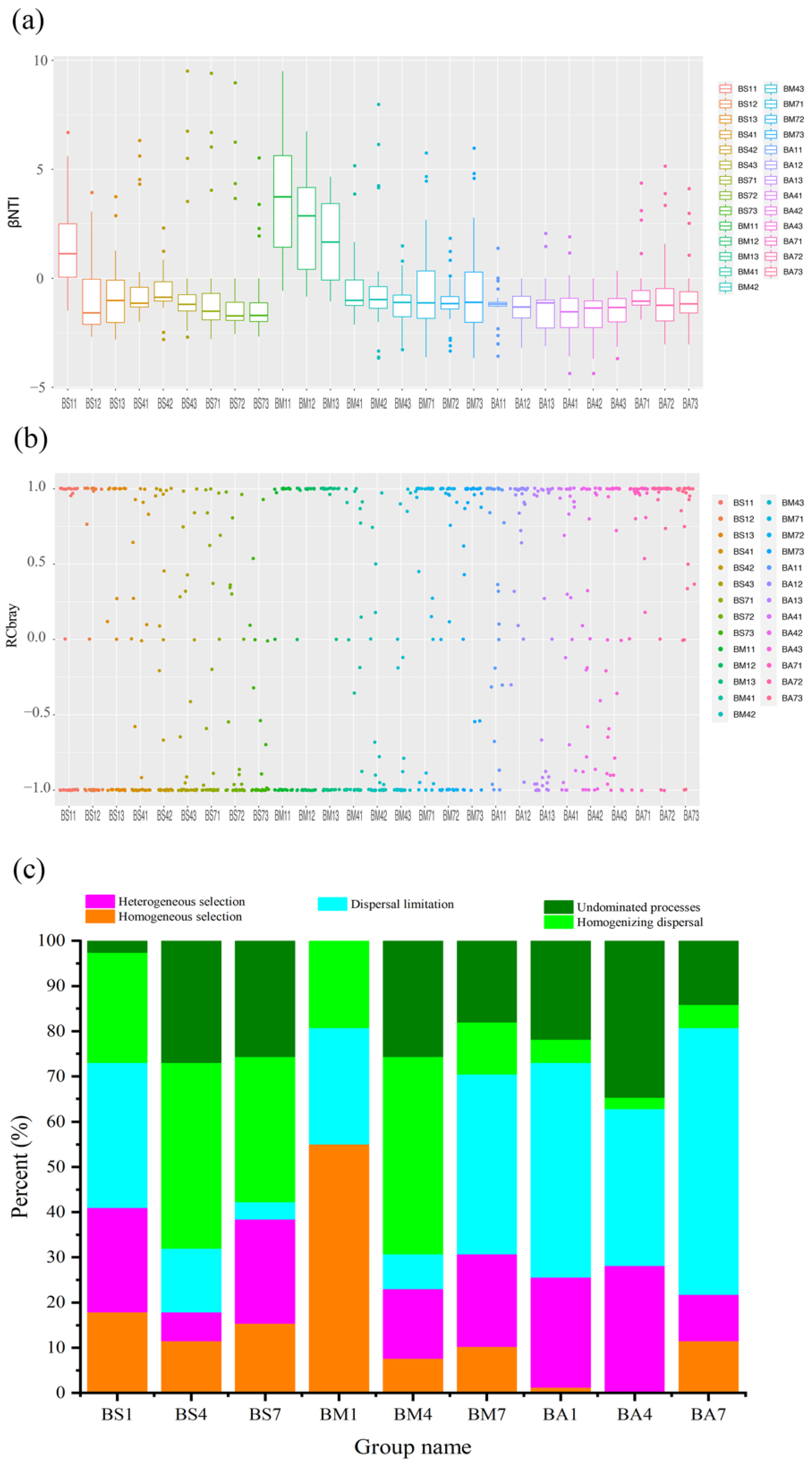
3.5. Ecological Assembly Processes of Bacterial Communities
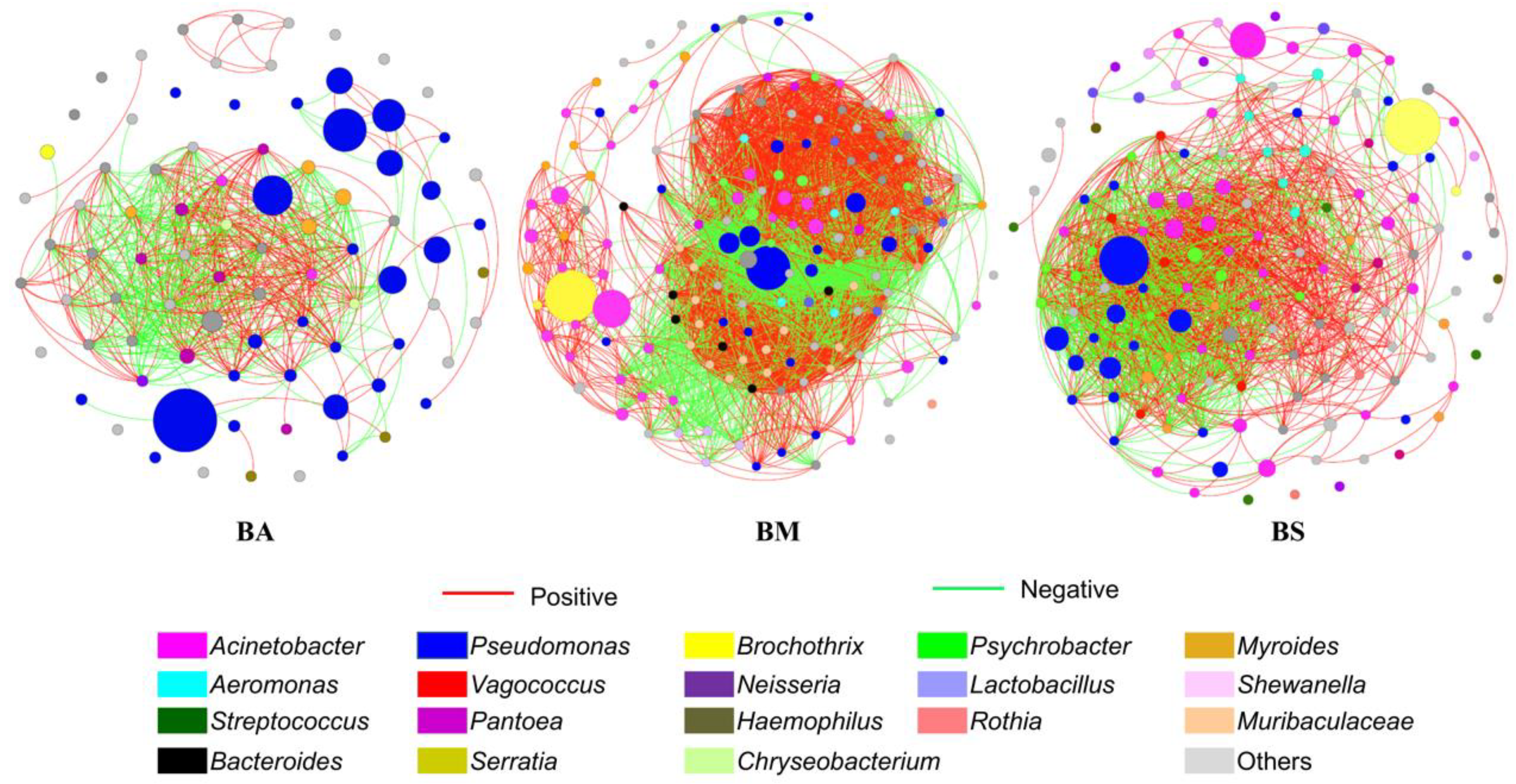
3.6. Co-Occurrence Networks Revealed Bacterial Interactions at Genus Level
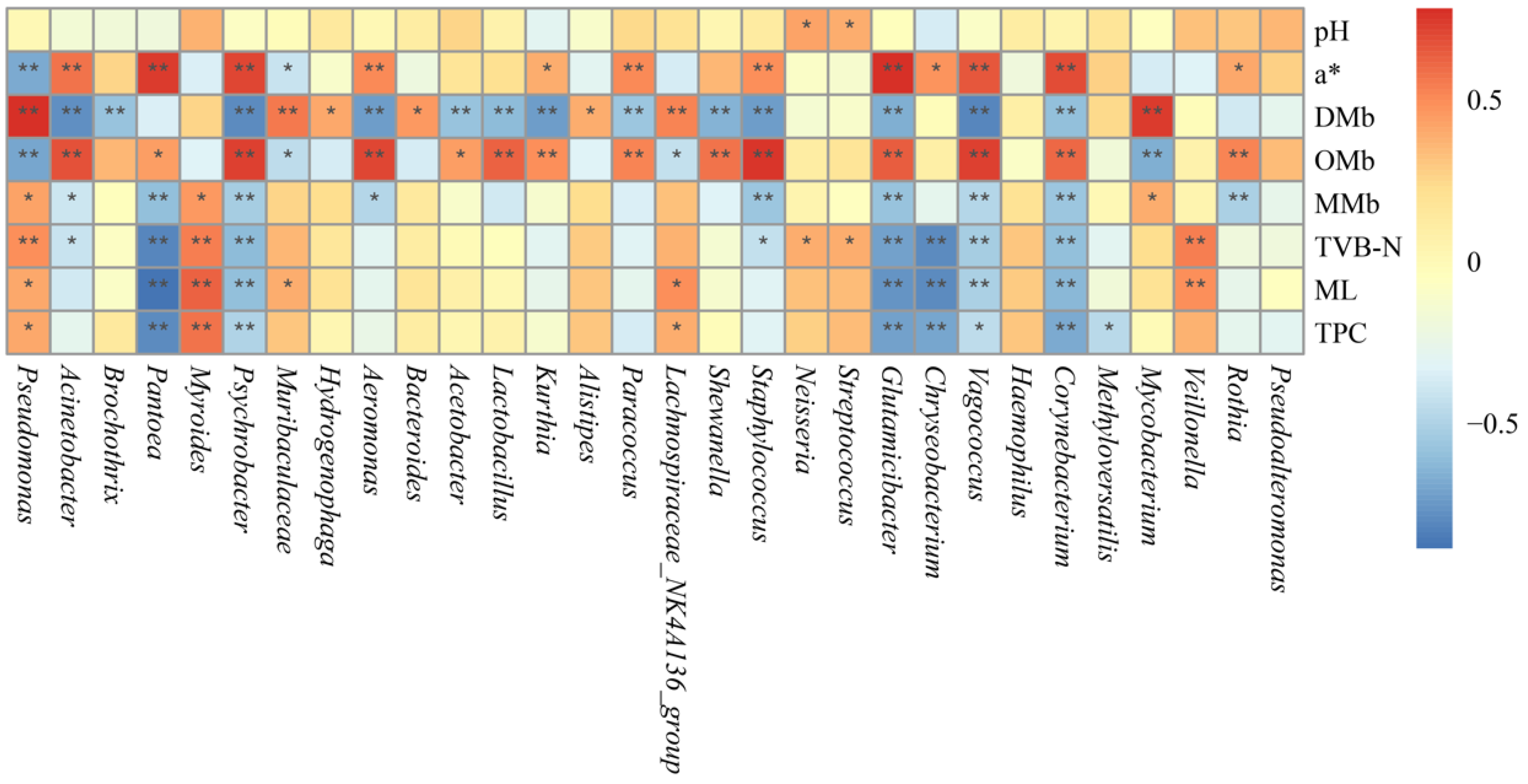
3.7. Analysis of the Relationship Between Bacterial Community and Physicochemical Indexes During Chilled Storage
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, J.H.; Kannan, G.; Eega, K.R.; Kouakou, B.; Getz, W.R. Nutritional and quality characteristics of meat from goats and lambs finished under identical dietary regime. Small Rumin. Res. 2008, 74, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toohey, E.S.; Hopkins, D.L. Eating quality of commercially processed hot boned sheep meat. Meat Sci. 2006, 72, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ercolini, D.; Ferrocino, I.; Nasi, A.; Ndagijimana, M.; Vernocchi, P.; La Storia, A.; Laghi, L.; Mauriello, G.; Guerzoni, M.E.; Villani, F. Monitoring of microbial metabolites and bacterial diversity in beef stored under different packaging conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7372–7381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekhit, A.E.-D.A.; Holman, B.W.B.; Giteru, S.G.; Hopkins, D.L. Total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) and its role in meat spoilage: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 280–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlapani, F.F.; Haroutounian, S.A.; Nychas, G.J.; Boziaris, I.S. Microbiological spoilage and volatiles production of gutted European sea bass stored under air and commercial modified atmosphere package at 2 °C. Food Microbiol. 2015, 50, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fegan, N.; Jenson, I. The role of meat in foodborne disease: Is there a coming revolution in risk assessment and management? Meat Sci. 2018, 144, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geeraerts, W.; Pothakos, V.; Vuyst, L.D.; Leroy, F. Diversity of the dominant bacterial species on sliced cooked pork products at expiration date in the Belgian retail. Food Microbiol. 2017, 65, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, D.L.; Xiong, X.; Wang, H.H.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Zou, Y.F. Characterization of the bacterial community of braised chicken, a specialty poultry product in China. Poult. Sci. 2018, 98, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Ding, T.; Liang, C.; Zheng, X.; Yang, W.; Hou, C. Dynamic changes of bacteria and screening of potential spoilage markers of lamb in aerobic and vacuum packaging. Food Microbiol. 2022, 104, 103996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamatsia, C.; Patsias, A.; Kontominas, M.; Savvaidis, I. Possible role of volatile amines as quality-indicating metabolites in modified atmosphere-packaged chicken fillets: Correlation with microbiological and sensory attributes. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1622–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, N.N.; Ravensdale, J.; Coorey, R.; Chandry, S.P.; Dykes, G.A. The predominance of psychrotrophic pseudomonads on aerobically stored chilled red meat. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1622–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casaburi, A.; Piombino, P.; Nychas, G.J.; Villani, F.; Ercolini, D. Bacterial populations and the volatilome associated to meat spoilage. Food Microbiol. 2015, 45, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Zhang, D.; Wen, X.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Zheng, X.; Fang, F.; Li, J.; Hou, C. Effects of chilling rate on the freshness and microbial community composition of lamb carcasses. LWT 2022, 153, 112559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansur, A.R.; Song, E.J.; Cho, Y.S.; Nam, Y.D.; Choi, Y.S.; Kim, D.O.; Seo, D.H.; Nam, T.G. Comparative evaluation of spoilage-related bacterial diversity and metabolite profiles in chilled beef stored under air and vacuum packaging. Food Microbiol. 2019, 77, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, J.; Li, R.; Ye, K. High-throughput sequencing analysis of the bacterial community for assessing the differences in extraction methods of bacteria separation from chilled pork. LWT 2020, 134, 110213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Xiang, X.; Sun, R.; Yang, T.; He, D.; Zhang, K.; Ni, Y.; Zhu, Y.G.; Adams, J.M.; et al. Spatial scale affects the relative role of stochasticity versus determinism in soil bacterial communities in wheat fields across the North China Plain. Microbiome 2018, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, B.; Ning, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, T.; Wu, L.; Li, T.; Liu, W.; Zhou, J.; Wen, X. Seasonal dynamics of the microbial community in two full-scale wastewater treatment plants: Diversity, composition, phylogenetic group based assembly and co-occurrence pattern. Water Res. 2021, 200, 117295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yao, J.; Chen, Z.; Ma, B.; Li, H.; Wancheng, P.; Liu, J.; Wang, D.; Duran, R. Biogeography, assembly processes and species coexistence patterns of microbial communities in metalloids-laden soils around mining and smelting sites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywicki, K. The determination of haem pigments in meat. Meat Sci. 1982, 7, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.228-2016; Determination of the Volatile Basic Nitrogen in Food of China Food Safety National Standard. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China. China Food and Drug Administration: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 4789.2-2016; Determination of the Total Number of Colonies in Food Microbiological Inspection of China Food Safety National Standard. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China. China Food and Drug Administration: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Ramanathan, R.; Mancini, R.A. Role of mitochondria in beef color: A review. Meat Muscle Biol. 2018, 2, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, C.; Fernandez, A.M. Effect of ageing time on suckling lamb meat quality resulting from different carcass chilling regimes. Meat Sci. 2014, 96, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Li, N.; Li, Z.; He, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, Z.; Kang, Z.; Ma, H. Shelf life of fresh chilled pork as affected by antimicrobial intervention with nisin, tea polyphenols, chitosan, and their combination. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 1047–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Li, S.; Zhong, G.; Liu, Y. Properties of novel chitosan incorporated with hexahydro-beta-acids edible films and its effect on shelf life of pork. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 2707-2016; Fresh (Frozen) Livestock and Poultry Products of China Food Safety National Standard. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China. China Food and Drug Administration: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB/T 9961-2008; Fresh and Frozen Carcasses of Mutton of China Food Safety National Standard. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Zhu, L.G.; Brewer, M.S. Effects of urea denatureation and pH on the ability of porcine myoglobin to undergo reduction. Meat Sci. 2003, 63, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, X.; Zhang, W.; Wen, P. Effects of storage methods on the microbial community and quality of Sichuan smoked bacon. LWT 2022, 158, 113115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, R.K.; Denny, J.E.; Namazzi, R.; Opoka, R.O.; Datta, D.; John, C.C.; Schmidt, N.W. Dynamic modulation of spleen germinal center reactions by gut bacteria during Plasmodium infection. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Qiao, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y. Tissue Type: A crucial factor influencing the fungal diversity and communities in sichuan pork bacon. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 655500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, S.; Jin, T.; Li, K.; Han, Z.; Li, Y. Microbiome analysis reveals the alterations in gut microbiota in different intestinal segments of Yimeng black goats. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 155, 104900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, B.E.; Button, J.E.; Santarelli, M.; Dutton, R.J. Cheese rind communities provide tractable systems for in situ and in vitro studies of microbial diversity. Cell. 2014, 158, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoops, J.; Ruyters, S.; Busschaert, P.; Spaepen, R.; Verreth, C.; Claes, J.; Lievens, B.; Van Campenhout, L. Bacterial community dynamics during cold storage of minced meat packaged under modified atmosphere and supplemented with different preservatives. Food Microbiol. 2015, 48, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, H. Advances in understanding the predominance, phenotypes, and mechanisms of bacteria related to meat spoilage. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 118, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doulgeraki, A.I.; Ercolini, D.; Villani, F.; Nychas, G.J. Spoilage microbiota associated to the storage of raw meat in different conditions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 157, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katiyo, W.; de Kock, H.L.; Coorey, R.; Buys, E.M. Sensory implications of chicken meat spoilage in relation to microbial and physicochemical characteristics during refrigerated storage. LWT 2020, 128, 109468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Qing, l.; Tang, W.; Ma, F.; Wang, H.; Xu, X.; Qiu, W. AprD is important for extracellular proteolytic activity, physicochemical properties and spoilage potential in meat-borne Pseudomonas fragi. Food Control 2021, 124, 107868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellissery, A.J.; Vinayamohan, P.G.; Amalaradjou, M.; Venkitanarayanan, K. Spoilage bacteria and meat quality. Meat Quality Anal. 2020, 307–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Konopka, A.E. Estimating and mapping ecological processes influencing microbial community assembly. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Chen, X.; Kennedy, D.W.; Murray, C.J.; Rockhold, M.L.; Konopka, A. Quantifying community assembly processes and identifying features that impose them. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yang, H.; Dai, X.; Gui, G.; Xiao, Y. Microbial community structure and drug resistance gene on water, ground and surface of slaughtering equipment in poultry slaughterhouse. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2018, 30, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Knelman, J.E.; Nemergut, D.R. Changes in community assembly may shift the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem function. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, E.B.; Stegen, J.C. Dispersal-Based Microbial Community Assembly Decreases Biogeochemical Function. Processes 2017, 5, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliveres, S.; van der Plas, F.; Manning, P.; Prati, D.; Gossner, M.M.; Renner, S.C.; Alt, F.; Arndt, H.; Baumgartner, V.; Binkenstein, J.; et al. Biodiversity at multiple trophic levels is needed for ecosystem multifunctionality. Nature 2016, 536, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.J.; Zeng, Y.H.; Zhu, J.M.; Cai, Z.H.; Zhou, J. The structure and assembly mechanisms of plastisphere microbial community in natural marine environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 421, 126780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Jiang, P.; Wang, P.; Pei, Y.; Huang, H.; Xiao, F.; Deng, G.J. Three-Component Cascade Synthesis of Carbazoles through [1s,6s] Sigmatropic Shift under Metal-Free Conditions. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 3121–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Samples | Chao1 | Coverage | OTUs | Pielou_e | Shannon | Simpson |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BA1 | 501.31 ± 211.37 a | 1.0000 a | 499 ± 211 a | 0.5317 ± 0.00 b | 4.72 ± 0.35 ab | 0.883 ± 0.003 b |
| BA4 | 348.96 ± 48.54 a | 1.0000 a | 345 ± 49 a | 0.4767 ± 0.01 c | 4.01 ± 0.20 c | 0.886 ± 0.010 b |
| BA7 | 342.99 ± 87.97 a | 1.0000 a | 342 ± 88 a | 0.5980 ± 0.04 a | 5.02 ± 0.52 a | 0.932 ± 0.016 a |
| BM1 | 543.72 ± 33.95 a | 0.9993 a | 537 ± 38 a | 0.7267 ± 0.01 a | 6.59 ± 0.15 a | 0.975 ± 0.003 a |
| BM4 | 215.64 ± 25.70 c | 1.0000 a | 207 ± 24 c | 0.5797 ± 0.02 b | 4.46 ± 0.28 c | 0.881 ± 0.021 b |
| BM7 | 371.08 ± 9.32 b | 1.0000 a | 365 ± 13 b | 0.5850 ± 0.03 b | 4.98 ± 0.23 b | 0.899 ± 0.025 b |
| BS1 | 443.70 ± 9.71 a | 0.9993 a | 439 ± 9 a | 0.7200 ± 0.01 a | 6.32 ± 0.08 a | 0.972 ± 0.003 a |
| BS4 | 274.42 ± 40.33 b | 0.9997 a | 266 ± 38 b | 0.6317 ± 0.02 b | 5.08 ± 0.26 b | 0.920 ± 0.022 b |
| BS7 | 231.51 ± 32.68 b | 1.0000 a | 227 ± 31 b | 0.6010 ± 0.04 b | 4.70 ± 0.42 b | 0.908 ± 0.024 b |
| Name | Group Name | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| BA | BM | BS | |
| Number of nodes | 85 | 165 | 144 |
| Number of edges | 193 | 1283 | 218 |
| Positive (%) | 58.86 | 59.49 | 63.01 |
| Negative (%) | 41.14 | 40.51 | 36.99 |
| Average degree | 4.541 | 15.552 | 3.028 |
| Average path length | 1.260 | 1.570 | 2.784 |
| Network diameter | 2.841 | 5.445 | 6.616 |
| Clustering coefficient | 0.866 | 0.743 | 0.567 |
| Graph density | 0.054 | 0.095 | 0.021 |
| Centralization betweenness | 0.0059 | 0.0066 | 0.0252 |
| Centralization degree | 0.148 | 0.143 | 0.091 |
| Connectance | 0.054 | 0.095 | 0.021 |
| Modularity | 0.486 | 0.505 | 0.625 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, L.; Cui, L.; Lapu, M.; Bai, T.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Liu, D.; Liu, M.; Wang, X. The Structure, Assembly Processes of Microbial Communities and Their Effects on the Quality of Goat MEAT During Chilled Storage (4 °C). Foods 2025, 14, 1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091653
Xiao L, Cui L, Lapu M, Bai T, Wang J, Guo X, Liu D, Liu M, Wang X. The Structure, Assembly Processes of Microbial Communities and Their Effects on the Quality of Goat MEAT During Chilled Storage (4 °C). Foods. 2025; 14(9):1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091653
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Longquan, Lin Cui, Molazi Lapu, Ting Bai, Juan Wang, Xiaoying Guo, Dayu Liu, Mingxue Liu, and Xinhui Wang. 2025. "The Structure, Assembly Processes of Microbial Communities and Their Effects on the Quality of Goat MEAT During Chilled Storage (4 °C)" Foods 14, no. 9: 1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091653
APA StyleXiao, L., Cui, L., Lapu, M., Bai, T., Wang, J., Guo, X., Liu, D., Liu, M., & Wang, X. (2025). The Structure, Assembly Processes of Microbial Communities and Their Effects on the Quality of Goat MEAT During Chilled Storage (4 °C). Foods, 14(9), 1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091653






