Effects of Ultrasound Treatment on Emulsifying Properties of Pea Protein Isolates Obtained from Four Different Pea Flour Varieties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
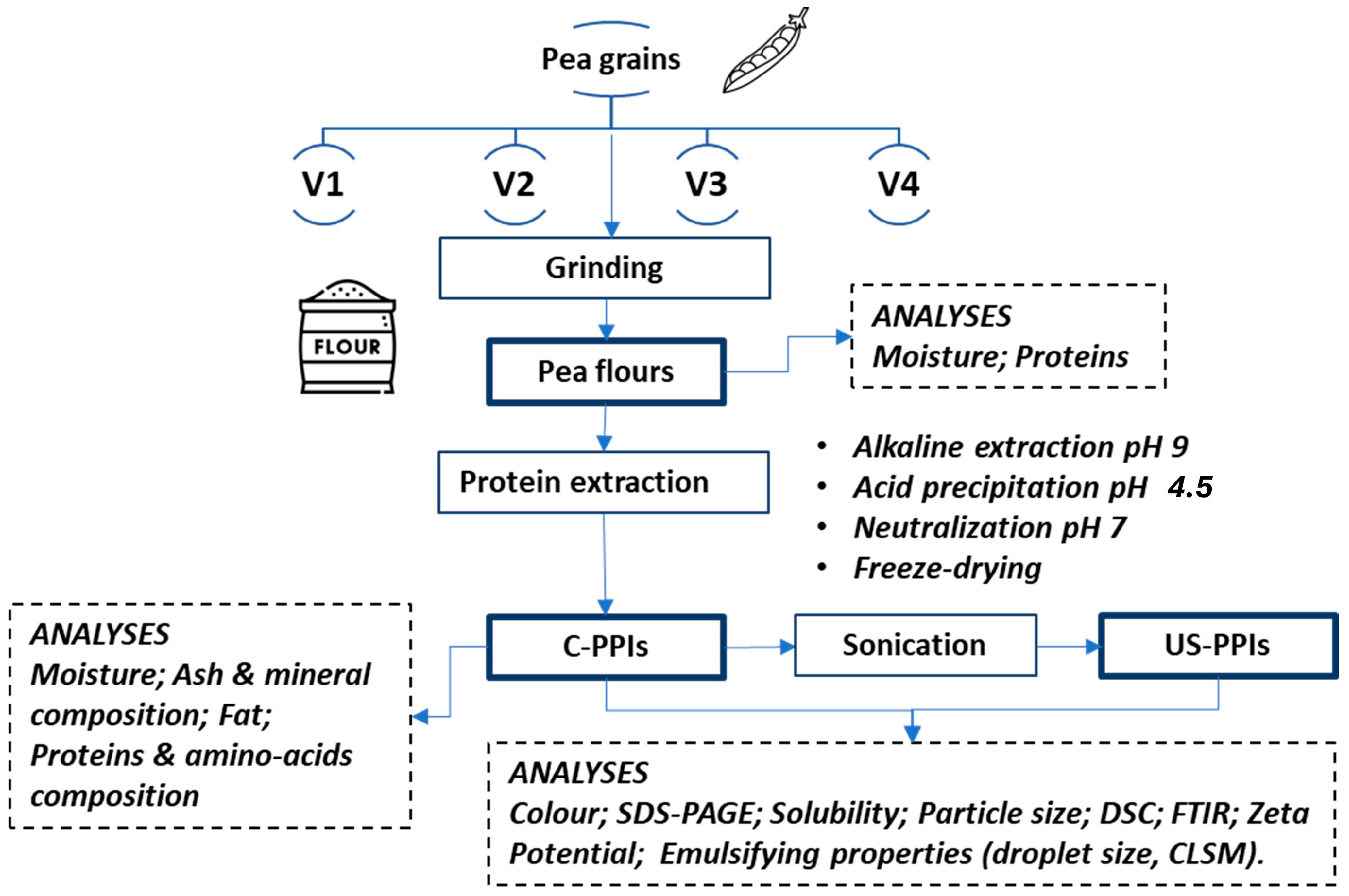
2.1. Material
2.2. Extraction Protocol
2.3. Ultrasound Treatment
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.4.1. Protein, Moisture, Ash, and Fat Content
2.4.2. Amino Acids Composition
2.4.3. Mineral Composition
2.4.4. Color Measurement
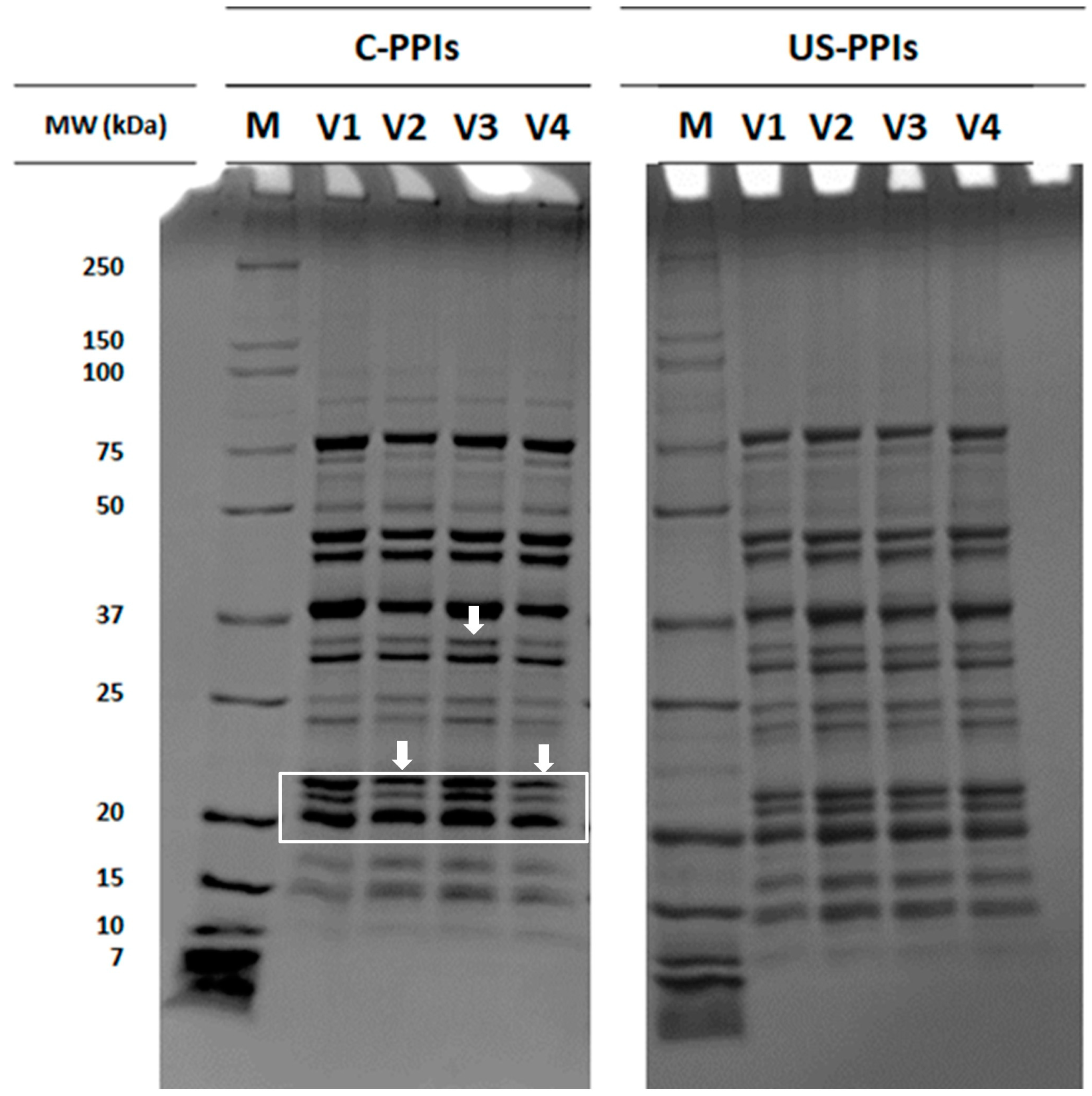
2.4.5. SDS-PAGE
2.4.6. Solubility
2.4.7. Particle Size Analysis
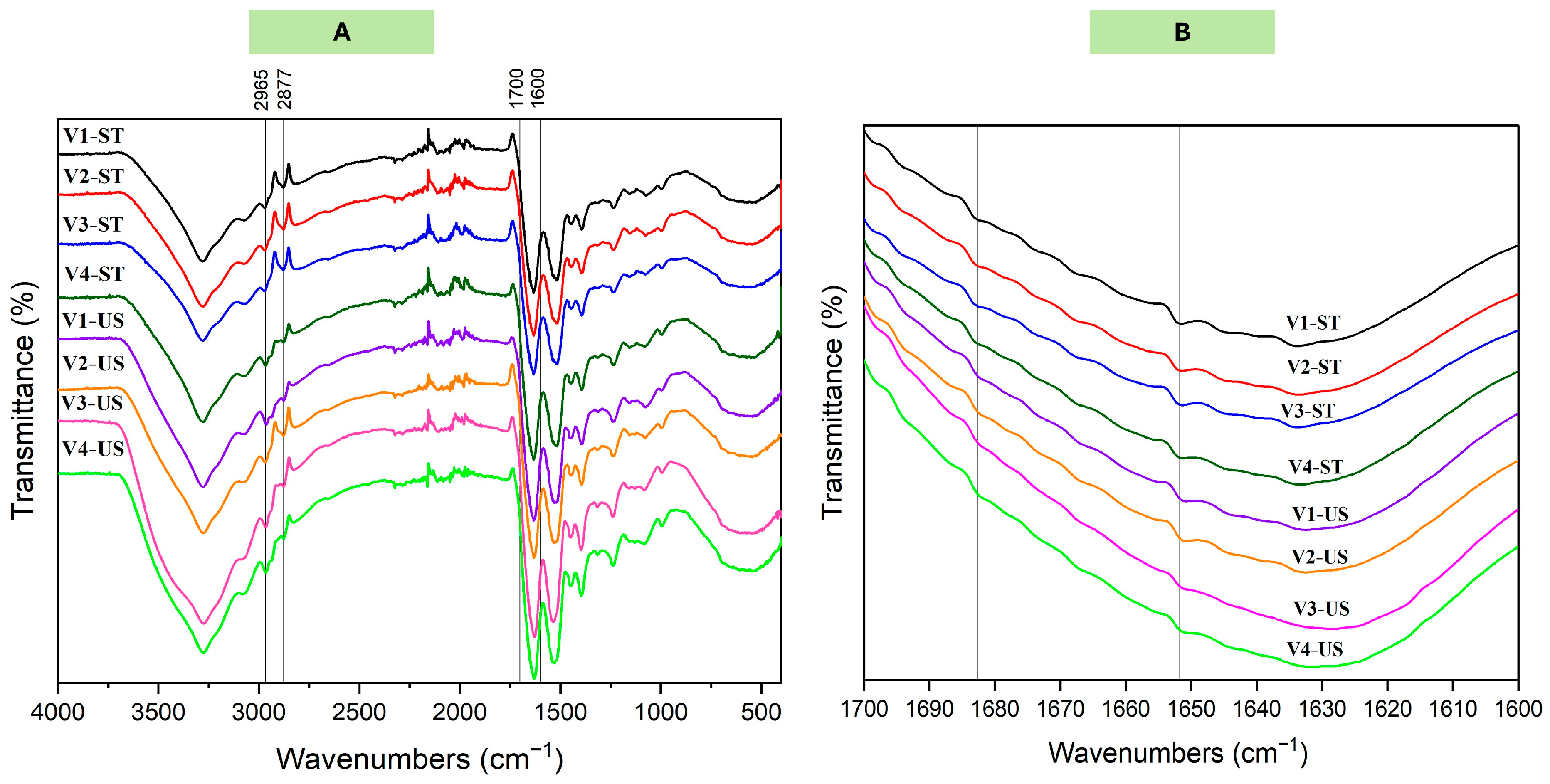
2.4.8. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.4.9. Zeta-Potential
2.5. Emulsifying Properties
2.5.1. Emulsion’s Droplet Size and ζ-Potential
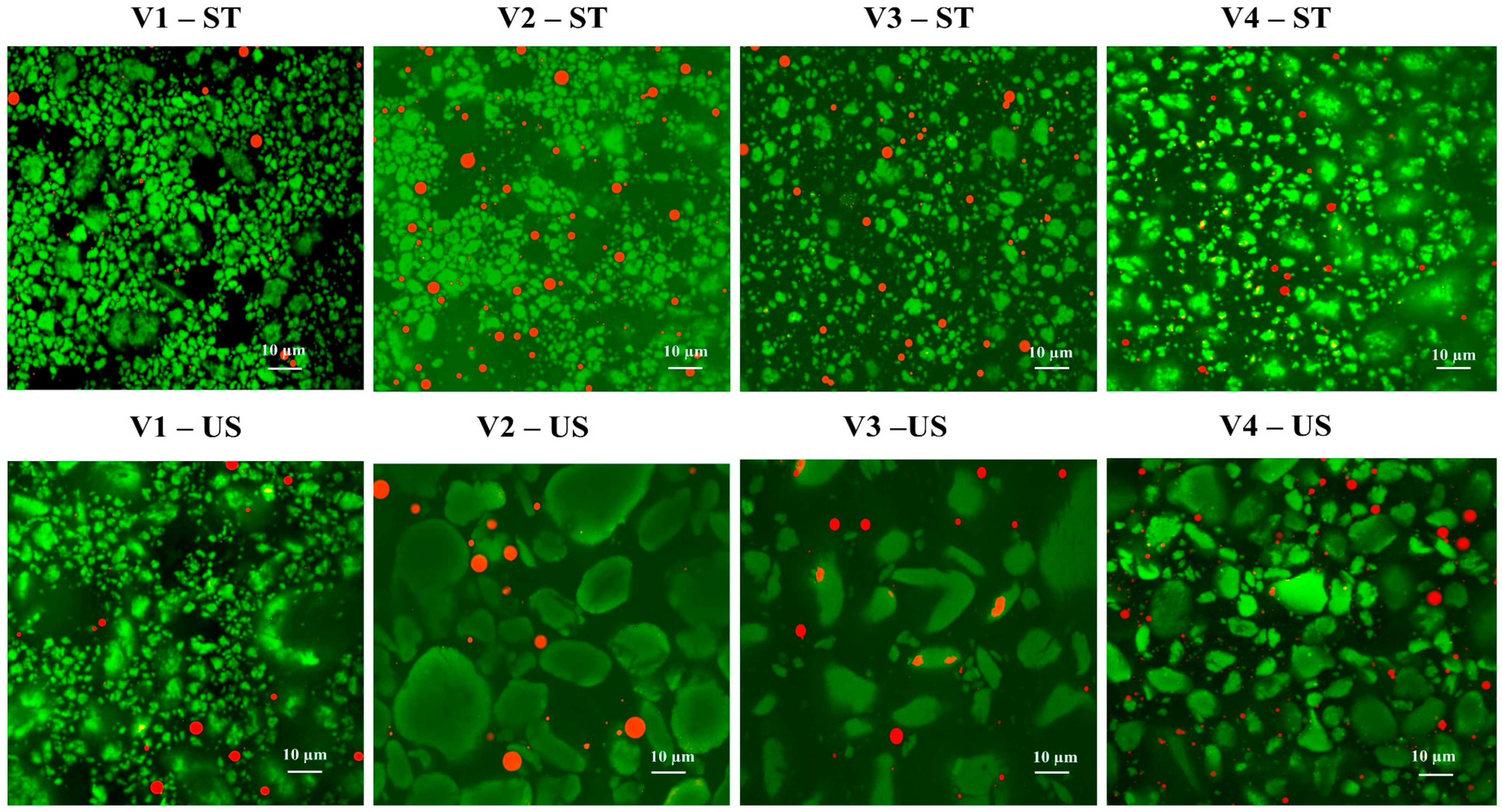
2.5.2. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Variety on Protein Recovery, Proximate Analysis, and Mineral Composition
3.2. Effect of Ultrasound Treatment and Variety on Protein Quality and Functionality
3.2.1. Protein Molecular Weight Distribution and Amino Acid Profile
3.2.2. Colorimetry
3.2.3. Particle Size
3.2.4. Secondary Structure
3.3. Emulsifying Properties
3.3.1. Microstructure of Protein Particles and Emulsions
3.3.2. Droplet Size and Zeta-Potential
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akharume, F.U.; Aluko, R.E.; Adedeji, A.A. Modification of Plant Proteins for Improved Functionality: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 198–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.X.; He, J.F.; Zhang, Y.C.; Bing, D.J. Composition, Physicochemical Properties of Pea Protein and Its Application in Functional Foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2593–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevkani, K.; Singh, N.; Chen, Y.; Kaur, A.; Yu, L. Pulse Proteins: Secondary Structure, Functionality and Applications. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 2787–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Wang, L.H.; Wen, Q.H.; He, F.; Xu, F.Y.; Chen, B.R.; Zeng, X.A. Combination of Pulsed Electric Field and PH Shifting Improves the Solubility, Emulsifying, Foaming of Commercial Soy Protein Isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 134, 108049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakemond, C.M.M.; De Jongh, H.H.J.; Hessing, M.; Gruppen, H.; Voragen, A.G.J. Soy Glycinin: Influence of PH and Ionic Strength on Solubility and Molecular Structure at Ambient Temperatures. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1985–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, S.Y.J.; Srv, A.; Chiang, J.H.; Henry, C.J. Plant Proteins for Future Foods: A Roadmap. Foods 2021, 10, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadidi, M.; Aghababaei, F.; McClements, D.J. Enhanced Alkaline Extraction Techniques for Isolating and Modifying Plant-Based Proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145, 109132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Shen, P.; Lan, Y.; Cui, L.; Ohm, J.B.; Chen, B.; Rao, J. Effect of Alkaline Extraction PH on Structure Properties, Solubility, and Beany Flavor of Yellow Pea Protein Isolate. Food Res. Int. 2020, 131, 109045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernès, L.; Abert-Vian, M.; El Maâtaoui, M.; Tao, Y.; Bornard, I.; Chemat, F. Application of Ultrasound for Green Extraction of Proteins from Spirulina. Mechanism, Optimization, Modeling, and Industrial Prospects. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 54, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, A.; Ahmed, E.; Ismaiel, A.; Ashokkumar, M.; Xu, X.; Pan, S.; Hu, H. Ultrasonic Emulsification: An Overview on the Preparation of Different Emulsifiers-Stabilized Emulsions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 105, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parniakov, O.; Apicella, E.; Koubaa, M.; Barba, F.J.; Grimi, N.; Lebovka, N.; Pataro, G.; Ferrari, G.; Vorobiev, E. Ultrasound-Assisted Green Solvent Extraction of High-Added Value Compounds from Microalgae Nannochloropsis spp. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 198, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Taha, A.; Hu, H.; Lu, Q.; Pan, S. Effects of Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction on the Physicochemical Properties of Different Walnut Proteins. Molecules 2019, 24, 4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Lamsal, B.P. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction and Modification of Plant-Based Proteins: Impact on Physicochemical, Functional, and Nutritional Properties. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 1457–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, S.U.; Tiwari, B.K.; Álvarez, C.; O’Donnell, C.P. Ultrasound Applications for the Extraction, Identification and Delivery of Food Proteins and Bioactive Peptides. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 46, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, G.; Poojary, M.M.; O’Donnell, C.; Lund, M.N.; Garcia-Vaquero, M.; Tiwari, B.K. Ultrasound-Assisted Processing of Chlorella Vulgaris for Enhanced Protein Extraction. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 1709–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, R.; Zaragoza, J.; Purpura, M.; Iametti, S.; Marengo, M.; Tinsley, G.M.; Anzalone, A.J.; Oliver, J.M.; Fiore, W.; Biffi, A.; et al. Probiotic Administration Increases Amino Acid Absorption from Plant Protein: A Placebo-Controlled, Randomized, Double-Blind, Multicenter, Crossover Study. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaktan, H.; Uzun, S.; Uzun, O.; Yasar Ciftci, C. Change in Chemical Composition and Morphological Traits of Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) Genotypes Grown Under Natural Conditions. Gesunde Pflanz. 2023, 75, 1385–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, N.D.; Cakli, S.; Szymczak, M.; Shen, C.; Matak, K.E.; Jaczynski, J. Nutrification and Fat Reduction of Deep-Fried Protein Isolates. Food Chem. 2024, 437, 137833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. SDS-Page Laemmli Method. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, L.G.L.; Queiroz, L.S.; Petersen, H.O.; Marie, R.; Silva, N.F.N.; Mohammadifar, M.A.; de Sá Peixoto Júnior, P.P.; Delaplace, G.; de Carvalho, A.F.; Casanova, F. High-Intensity Ultrasound Treatment on Casein: Pea Mixed Systems: Effect on Gelling Properties. Food Chem. 2023, 422, 136178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Li, X.; Taha, A.; Wei, Y.; Hu, T.; Fatamorgana, P.B.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, F.; Xu, X.; Pan, S.; et al. Effect of High Intensity Ultrasound on the Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Soy Protein Isolates Produced by Different Denaturation Methods. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, L.S.; Casanova, F.; Feyissa, A.H.; Jessen, F.; Ajalloueian, F.; Perrone, I.T.; de Carvalho, A.F.; Mohammadifar, M.A.; Jacobsen, C.; Yesiltas, B. Physical and Oxidative Stability of Low-Fat Fish Oil-in-Water Emulsions Stabilized with Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Protein Concentrate. Foods 2021, 10, 2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha, A.; Hu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Bakry, A.M.; Khalifa, I.; Pan, S.; Hu, H. Effect of Different Oils and Ultrasound Emulsification Conditions on the Physicochemical Properties of Emulsions Stabilized by Soy Protein Isolate. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 49, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altay, I.; Queiroz, L.S.; Silva, N.F.N.; Feyissa, A.H.; Casanova, F.; Sloth, J.J.; Mohammadifar, M.A. Effect of Moderate Electric Fields on the Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Cheese Emulsions. Gels 2023, 9, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunyemi, A.M.; Otegbayo, B.O.; Fagbenro, J.A. Effects of NPK and Biochar Fertilized Soil on the Proximate Composition and Mineral Evaluation of Maize Flour. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 2308–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanger, C.; Engel, J.; Kulozik, U. Influence of Extraction Conditions on the Conformational Alteration of Pea Protein Extracted from Pea Flour. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 107, 105949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Du, Z.; Wu, X.; Li, Y. Modulating Molecular Interactions in Pea Protein to Improve Its Functional Properties. J. Agric. Food Res. 2022, 8, 100313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liang, J.; Wang, R.; Chen, Y.; Ma, W.; Qi, B.; Zhang, M. Effects of Ultrasound on the Structure and Physical Properties of Black Bean Protein Isolates. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konieczny, D.; Stone, A.K.; Nosworthy, M.G.; House, J.D.; Korber, D.R.; Nickerson, M.T.; Tanaka, T. Nutritional Properties of Pea Protein-Enriched Flour Treated with Different Proteases to Varying Degrees of Hydrolysis. Cereal Chem. 2020, 97, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye, J.; Zare, F.; Pletch, A. Pulse Proteins: Processing, Characterization, Functional Properties and Applications in Food and Feed. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 414–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherfurd, S.M.; Fanning, A.C.; Miller, B.J.; Moughan, P.J. Protein Digestibility-Corrected Amino Acid Scores and Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Scores Differentially Describe Protein Quality in Growing Male Rats. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.; Zeitoun, A.; Hamad, G.; Zeitoun, M.A.M.; Taha, A.; Korma, S.A.; Esatbeyoglu, T. Lignocellulosic Biomasses from Agricultural Wastes Improved the Quality and Physicochemical Properties of Frying Oils. Foods 2022, 11, 3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, N.A.; Riar, C.S.; Singh, S. Physicochemical, Molecular and Thermal Properties of High-Intensity Ultrasound (HIUS) Treated Protein Isolates from Album (Chenopodium album) Seed. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 96, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Xiong, Y.L. Ultrasound-Induced Structural Modification and Thermal Properties of Oat Protein. LWT 2021, 149, 111861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, J.J.; Murray, B.A.; Flynn, C.; Norton, I.T. The Effect of Ultrasound Treatment on the Structural, Physical and Emulsifying Properties of Animal and Vegetable Proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 53, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Okagu, O.D.; Yagoub, A.E.G.A.; Udenigwe, C.C. Effects of Sonication on the in Vitro Digestibility and Structural Properties of Buckwheat Protein Isolates. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 70, 105348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebi, N.; Durak, M.Z.; Toker, O.S.; Sagdic, O.; Arici, M. An Evaluation of Fourier Transforms Infrared Spectroscopy Method for the Classification and Discrimination of Bovine, Porcine and Fish Gelatins. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, F.; Mohammadifar, M.A.; Jahromi, M.; Petersen, H.O.; Sloth, J.J.; Eybye, K.L.; Kobbelgaard, S.; Jakobsen, G.; Jessen, F. Physico-Chemical, Structural and Techno-Functional Properties of Gelatin from Saithe (Pollachius virens) Skin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 918–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greulich, O.; Duedahl-Olesen, L.; Mikkelsen, M.S.; Smedsgaard, J.; Bang-Berthelsen, C.H. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Tracking of Fermentation of Oat and Pea Bases for Yoghurt-Type Products. Fermentation 2024, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadat, A.; Joye, I.J. Peak Fitting Applied to Fourier Transform Infrared and Raman Spectroscopic Analysis of Proteins. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhou, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Jiang, L.; Liu, T.; Yu, D. Effect of High Intensity Ultrasound on the Structure and Solubility of Soy Protein Isolate-Pectin Complex. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 80, 105808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhu, W.; Yi, J.; Liu, N.; Cao, Y.; Lu, J.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Effects of Sonication on the Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Walnut Protein Isolate. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Dai, H.; Ma, L.; Fu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Guo, T.; Zhu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Properties of Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Food-Grade Gelatin Nanoparticles: Influence of the Nanoparticles Concentration. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 196, 111294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D. Food Emulsions: Principles, Practices, and Techniques, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; ISBN 0-8493-2023-2. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Fu, L.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Xue, S.-W.; Wang, P.; Xu, X.-L.; Bai, Y.-H. Use of High-Intensity Ultrasound to Improve Emulsifying Properties of Chicken Myofibrillar Protein and Enhance the Rheological Properties and Stability of the Emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Rao, J. Food-Grade Nanoemulsions: Formulation, Fabrication, Properties, Performance, Biological Fate, and Potential Toxicity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 285–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Bai, Y.; Li, B.; Xu, W. Effect of High Intensity Ultrasound on Physicochemical, Interfacial and Gel Properties of Chickpea Protein Isolate. LWT 2020, 129, 109563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, J.; Arellano, M.; Pichot, R.; Norton, I. The Effect of Ultrasound Treatment on the Structural, Physical and Emulsifying Properties of Dairy Proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 42, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variety | PPI | Flour | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture (% w/w) | Ash (% w/w) | Fat (% w/w) | Proteins (% w/w) | Proteins (% w/w) | Proteins Recovery from Flour (%) | |
| V1 | 5.77 ± 0.03 d | 2.83 ± 0.04 a | 1.81 ± 0.01 a | 88.39 ± 1.7 a | 23.90 ± 0.02 c | 52.85 ± 2.3 a |
| V2 | 7.13 ± 0.02 a | 2.57 ± 0.13 b | 0.98 ± 0.00 c | 91.67 ± 0.9 a | 25.24 ± 0.14 a | 42.61 ± 2.4 c |
| V3 | 6.50 ± 0.02 c | 2.27 ± 0.03 c | 1.55 ± 0.02 b | 91.91 ± 1.3 a | 23.94 ± 0.09 c | 46.10 ± 0.6 b |
| V4 | 6.63 ± 0.02 b | 2.78 ± 0.04 a | 1.83 ± 0.02 a | 91.24 ± 1.1 a | 24.44 ± 0.24 b | 51.20 ± 2.1 a |
| ELEMENT | V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MACROELEMENTS (g/kg) | Ca | 1.86 ± 0.03 | 1.47 ± 0.01 | 1.21 ± 0.02 | 1.69 ± 0.00 |
| K | 2.80 ± 0.04 | 2.57 ± 0.04 | 2.33 ± 0.04 | 2.78 ± 0.02 | |
| Na | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.00 | 0.12 ± 0.00 | 0.13 ± 0.00 | |
| P | 8.50 ± 0.05 | 8.27 ± 0.06 | 6.97 ± 0.06 | 8.72 ± 0.05 | |
| S | 4.49 ± 0.07 | 5.05 ± 0.06 | 5.18 ± 0.09 | 4.81 ± 0.01 | |
| MICROELEMENTS (mg/kg) | Al | 4.10 ± 0.16 | 4.32 ± 0.01 | 4.09 ± 0.01 | 4.17 ± 0.29 |
| Cr | 0.13 ± 0.12 | 0.17 ± 0.03 | 0.19 ± 0.07 | 0.17 ± 0.02 | |
| Fe | 147 ± 0.08 | 194 ± 3.9 | 200 ± 0.07 | 161 ± 3.69 | |
| Mn | 6.29 ± 0.08 | 5.86 ± 0.07 | 5.29 ± 0.00 | 5.78 ± 0.01 | |
| Ni | 1.41 ± 0.01 | 0.97 ± 0.04 | 1.02 ± 0.11 | 0.70 ± 0.00 | |
| Cu | 12.0 ± 0.11 | 8.52 ± 0.04 | 10.4 ± 0.05 | 11.5 ± 0.04 | |
| Zn | 38.2 ± 0.48 | 36.9 ± 0.20 | 41.3 ± 0.14 | 39.8 ± 0.16 | |
| Sr | 10.6 ± 0.11 | 7.60 ± 0.03 | 6.11 ± 0.02 | 8.35 ± 0.07 | |
| Ba | 0.99 ± 0.00 | 0.85 ± 0.04 | 0.62 ± 0.02 | 0.78 ± 0.00 |
| V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 | EAA req* | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EAA | mg/100 g (DM) | % of Total | mg/g Protein | EAA Score * | mg/100 g (DM) | % of Total | mg/g Protein | EAA Score * | mg/100 g (DM) | % of Total | mg/g Protein | EAA Score * | mg/100 g (DM) | % of Total | mg/g Protein | EAA Score * | mg/g Protein |
| HIS | 22.1 ± 1.4 | 2.7 | 23.5 | 1.57 | 23.2 ± 1.0 | 3.0 | 23.5 | 1.57 | 22.7 ± 1.1 | 2.7 | 23.1 | 1.54 | 23.3 ± 0.5 | 2.7 | 23.9 | 1.59 | 15 |
| ILE | 39.1 ± 2.6 | 4.7 | 41.7 | 1.39 | 40.3 ± 2.4 | 5.1 | 40.8 | 1.36 | 42.1 ± 1.2 | 5.0 | 42.9 | 1.43 | 40.4 ± 1.5 | 4.7 | 41.4 | 1.38 | 30 |
| LEU | 73.7 ± 4.0 | 8.9 | 78.6 | 1.33 | 76.0 ± 3.2 | 9.7 | 77.0 | 1.31 | 76.3 ± 3.2 | 9.0 | 77.6 | 1.32 | 75.8 ± 1.4 | 8.9 | 77.6 | 1.31 | 59 |
| LYS | 66.5 ± 2.8 | 8.0 | 70.9 | 1.58 | 68.1 ± 6.2 | 8.7 | 69.0 | 1.53 | 71.8 ± 2.2 | 8.5 | 73.0 | 1.62 | 66.9 ± 2.7 | 7.9 | 68.5 | 1.52 | 45 |
| MET + CYS | 8.9 | 1.1 | 9.5 | 0.43 | 9.6 | 1.2 | 9.8 | 0.44 | 11.4 | 1.3 | 11.6 | 0.53 | 7.5 | 0.9 | 7.7 | 0.35 | 22 |
| MET | 3.0 ± 1.8 | 0.4 | 3.2 | 0.20 | 4.0 ± 2.8 | 0.5 | 4.0 | 0.25 | 4.9 ± 2.0 | 0.6 | 4.9 | 0.31 | 2.3 ± 1.9 | 0.3 | 2.3 | 0.14 | 16 |
| CYS | 6.0 ± 0.5 | 0.7 | 6.3 | 1.06 | 5.7 ± 0.8 | 0.7 | 5.7 | 0.96 | 6.5 ± 0.5 | 0.8 | 6.6 | 1.11 | 5.3 ± 0.5 | 0.6 | 5.4 | 0.90 | 6 |
| PHE + TYR | 67.5 | 8.2 | 72.0 | 1.89 | 68.6 | 8.7 | 69.5 | 1.83 | 55.8 | 6.6 | 72.4 | 1.91 | 68.9 | 8.1 | 70.5 | 1.86 | 38 |
| PHE | 38.2 ± 1.8 | 4.6 | 40.7 | - | 38.5 ± 2.3 | 4.9 | 39.0 | - | 39.8 ± 1.2 | 4.7 | 40.4 | - | 38.8 ± 0.9 | 4.6 | 39.7 | - | - |
| TYR | 29.3 ± 2.3 | 3.5 | 31.3 | - | 30.1 ± 2.4 | 3.8 | 30.5 | - | 16.0 ± 2.5 | 1.9 | 32.0 | - | 30.1 ± 1.2 | 3.5 | 30.8 | - | - |
| THR | 29.3 ± 1.9 | 3.5 | 31.2 | 1.36 | 30.5 ± 1.7 | 3.9 | 30.9 | 1.35 | 30.7 ± 0.9 | 3.6 | 31.2 | 1.36 | 30.2 ± 0.6 | 3.6 | 30.9 | 1.35 | 23 |
| VAL | 42.3 ± 3.1 | 5.1 | 45.1 | 1.16 | 44.2 ± 1.5 | 5.6 | 44.8 | 1.15 | 44.3 ± 1.5 | 5.2 | 45.1 | 1.16 | 44.3 ± 1.2 | 5.2 | 45.4 | 1.16 | 39 |
| Sub-total | 349.4 | 42.2 | 372.5 | 360.6 | 46.0 | 365.3 | 355.0 | 42.0 | 376.9 | 357.5 | 42.0 | 365.9 | |||||
| NON-ESSENTIAL AMINO ACIDS | |||||||||||||||||
| ALA | 35.2 ± 1.6 | 4.2 | 37.5 | 36.3 ± 1.7 | 4.6 | 36.8 | 36.9 ± 1.2 | 4.4 | 37.5 | 36.4 ± 0.9 | 4.3 | 37.3 | |||||
| ARG | 76.7 ± 5.3 | 9.3 | 81.8 | 11.0 ± 2.2 | 1.4 | 80.5 | 78.3 ± 5.0 | 9.3 | 79.7 | 80.6 ± 1.0 | 9.5 | 82.5 | |||||
| APS | 97.9 ± 4.1 | 11.8 | 104.4 | 99.2 ± 3.0 | 12.6 | 100.5 | 99.6 ± 3.8 | 11.8 | 101.4 | 99.8 ± 2.8 | 11.7 | 102.1 | |||||
| GLU | 151.8 ± 6.3 | 18.3 | 161.9 | 156.6 ± 5.7 | 20.0 | 158.7 | 156.4 ± 6.6 | 18.5 | 159.1 | 156.8 ± 3.7 | 18.4 | 160.5 | |||||
| GLY | 33.8 ± 1.3 | 4.1 | 36.1 | 35.0 ± 1.6 | 4.5 | 35.4 | 35.3 ± 1.4 | 4.2 | 35.9 | 34.7 ± 0.9 | 4.1 | 35.5 | |||||
| PRO | 38.3 ± 2.2 | 4.6 | 40.8 | 39.2 ± 1.2 | 5.0 | 39.7 | 39.1 ± 1.9 | 4.6 | 39.8 | 39.1 ± 0.6 | 4.6 | 40.1 | |||||
| SER | 45.3 ± 1.8 | 5.5 | 48.3 | 46.3 ± 1.7 | 5.9 | 46.9 | 45.5 ± 2.6 | 5.4 | 46.3 | 46.0 ± 0.8 | 5.4 | 47.1 | |||||
| Total | 828.5 | 784.1 | 846.2 | 851.0 | |||||||||||||
| VARIETY | L* | a* | b* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-PPIs | V1 | 71.37 ± 0.00 b | −0.67 ± 0.04 b | 36.42 ± 0.01 a |
| V2 | 70.86 ± 0.00 b | 0.35 ± 0.03 a | 33.83 ± 0.00 b | |
| V3 | 69.05 ± 0.00 b | 0.24 ± 0.01 a | 31.96 ± 0.00 b | |
| V4 | 64.31 ± 0.00 c | −5.73 ± 0.01 d | 29.94 ± 0.01 b | |
| US-PPIs | V1 | 77.25 ± 0.00 a | −2.18 ± 0.02 c | 29.25 ± 0.00 b |
| V2 | 78.81 ± 0.01 a | −2.96 ± 0.04 c | 24.42 ± 0.02 c | |
| V3 | 79.93 ± 0.00 a | −2.78 ± 0.00 c | 22.80 ± 0.00 c | |
| V4 | 78.22 ± 0.00 a | −4.92 ± 0.01 d | 23.16 ± 0.02 c |
| Samples | Secondary Structure Composition (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-Sheet Aggregates | β-Sheet | Random Coil | α-Helix | β-Turn | |
| V1-ST | 12.7 ± 1.2 b | 34.5 ± 2.2 b | 8.9 ± 1.8 c | 21.4 ± 2.3 a | 20.9 ± 1.9 b,c |
| V2-ST | 10.5 ± 1.4 b | 39.4 ± 3.1 c | 7.8 ± 1.5 c | 19.5 ± 3.4 a | 19.1 ± 2.2 c |
| V3-ST | 14.7 ± 0.8 a | 34.4 ± 1.8 b | 3.8 ± 0.5 c | 21.2 ± 1.2 a | 25.1 ± 0.8 a |
| V4-ST | 9.3 ± 0.9 c | 42.7 ± 2.4 a | 8.3 ± 0.7 c | 19.5 ± 2.1 a | 19.3 ± 2.4 c |
| V1-US | 11.9 ± 1.5 b | 25.1 ± 1.7 d | 14.1 ± 1.1 a | 21.5 ± 1.6 a | 19.9 ± 1.3 c |
| V2-US | 11.2 ± 1.1 b | 23.8 ± 2.3 d | 15.0 ± 1.5 a | 21.0 ± 1.4 a | 18.7 ± 3.1 c |
| V3-US | 12.3 ± 1.9 b | 24.8 ± 1.3 d | 16.3 ± 1.7 a | 22.6 ± 1.6 a | 21.2 ± 2.6 b |
| V4-US | 9.2 ± 0.7 c | 35.2 ± 3.5 b | 11.0 ± 1.3 b | 21.2 ± 2.4 a | 18.7 ± 1.6 c |
| Band frequency (cm−1) | 1688–1700 | 1610–1642 and 1681–1687 | 1630–1645 | 1650–1663 | 1663–1680 |
| Sample | d4,3 (µm) | ζ-Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|
| V1-ST | 14.78 ± 0.46 d | −23.06 ± 1.33 c |
| V2-ST | 11.50 ± 0.20 f | −22.18 ± 1.30 c |
| V3-ST | 10.66 ± 0.70 g | −22.15 ± 2.09 c |
| V4-ST | 13.16 ± 0.46 e | −21.30 ± 1.11 b |
| V1-US | 19.33 ± 1.23 b | −21.77 ± 0.68 b |
| V2-US | 17.36 ± 0.39 c | −19.71 ± 1.78 a |
| V3-US | 21.02 ± 0.26 a | −19.20 ± 1.27 a |
| V4-US | 15.07 ± 0.48 d | −19.77 ± 1.38 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dadi, F.; Taha, A.; Sales Queiroz, L.; Nogueira Silva, N.F.; Altay, I.; Kominami, Y.; Marie, R.; Feyissa, A.H.; Sloth, J.J.; Petersen, H.O.; et al. Effects of Ultrasound Treatment on Emulsifying Properties of Pea Protein Isolates Obtained from Four Different Pea Flour Varieties. Foods 2025, 14, 1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091634
Dadi F, Taha A, Sales Queiroz L, Nogueira Silva NF, Altay I, Kominami Y, Marie R, Feyissa AH, Sloth JJ, Petersen HO, et al. Effects of Ultrasound Treatment on Emulsifying Properties of Pea Protein Isolates Obtained from Four Different Pea Flour Varieties. Foods. 2025; 14(9):1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091634
Chicago/Turabian StyleDadi, Fatma, Ahmed Taha, Lucas Sales Queiroz, Naaman Francisco Nogueira Silva, Ipek Altay, Yuri Kominami, Rodolphe Marie, Aberham Hailu Feyissa, Jens J. Sloth, Heidi Olander Petersen, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Ultrasound Treatment on Emulsifying Properties of Pea Protein Isolates Obtained from Four Different Pea Flour Varieties" Foods 14, no. 9: 1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091634
APA StyleDadi, F., Taha, A., Sales Queiroz, L., Nogueira Silva, N. F., Altay, I., Kominami, Y., Marie, R., Feyissa, A. H., Sloth, J. J., Petersen, H. O., Grandi, M., Spigno, G., & Casanova, F. (2025). Effects of Ultrasound Treatment on Emulsifying Properties of Pea Protein Isolates Obtained from Four Different Pea Flour Varieties. Foods, 14(9), 1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091634









