Synergistic Antibacterial Mechanism of Benzyl Isothiocyanate and Resveratrol Against Staphylococcus aureus Revealed by Transcriptomic Analysis and Their Application in Beef
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Chemicals
2.2. Fractional Inhibitory Concentration Index (FICI)
2.3. Time-Dependent Killing Curve
2.4. Antibiofilm Formation
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.6. Cell Membrane Analysis
2.6.1. Integrity of the Cell Membrane
2.6.2. Nucleic Acid and Protein Concentrations
2.6.3. Intimal Permeability
2.6.4. Plasma Membrane Potential
2.7. Synergistic Effects of BITC and RES on S. aureus at the Transcriptional Level
2.7.1. Sample Preparation
2.7.2. Library Construction and Sequencing
2.7.3. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.9. Synergistic Effect of BITC and RES on S. aureus on Lean Beef
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
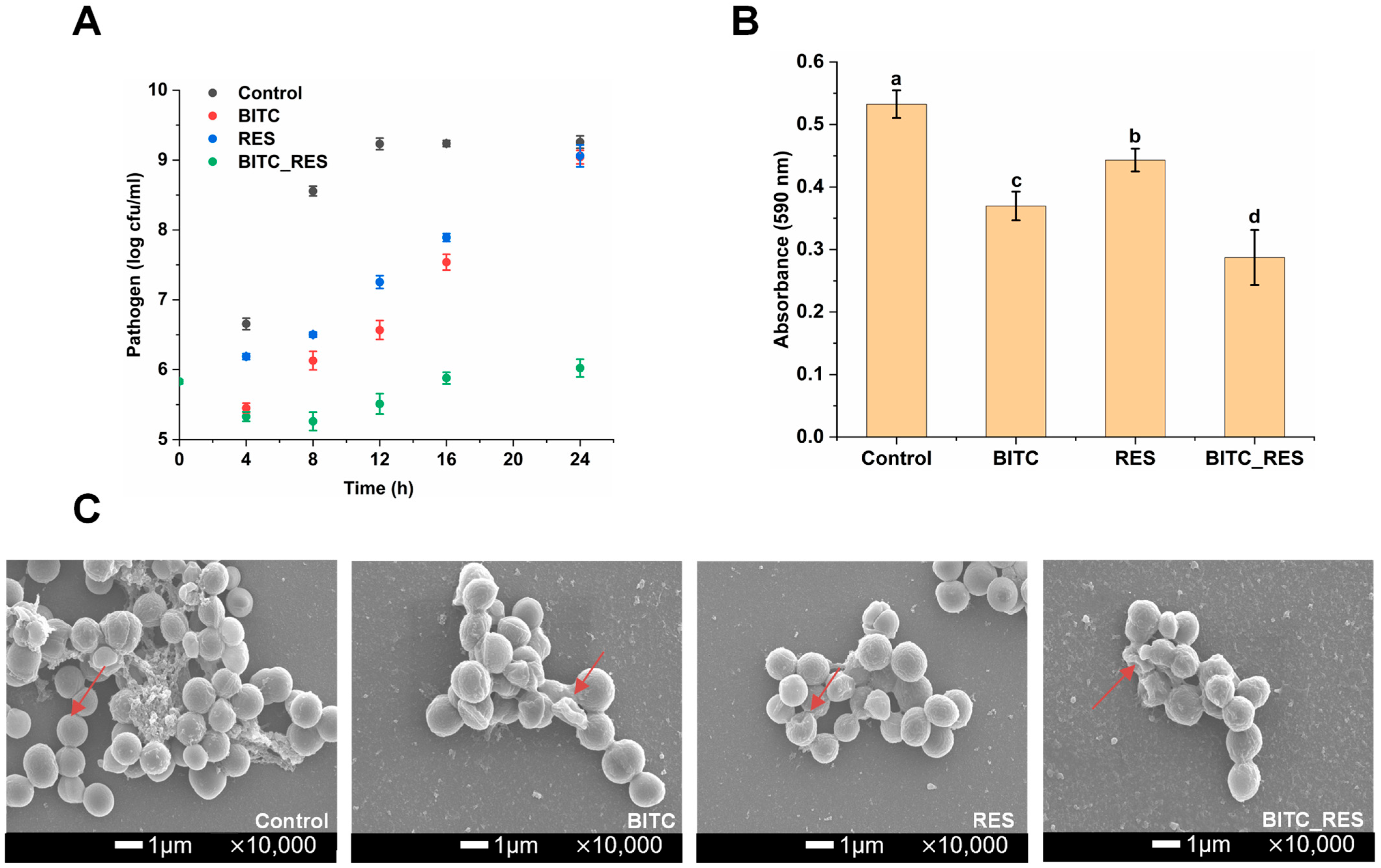
3.1. Synergistic Effects of BITC and RES on the Growth Inhibition of S. aureus
3.2. Synergistic Effects of BITC and RES on S. aureus Biofilm Formation
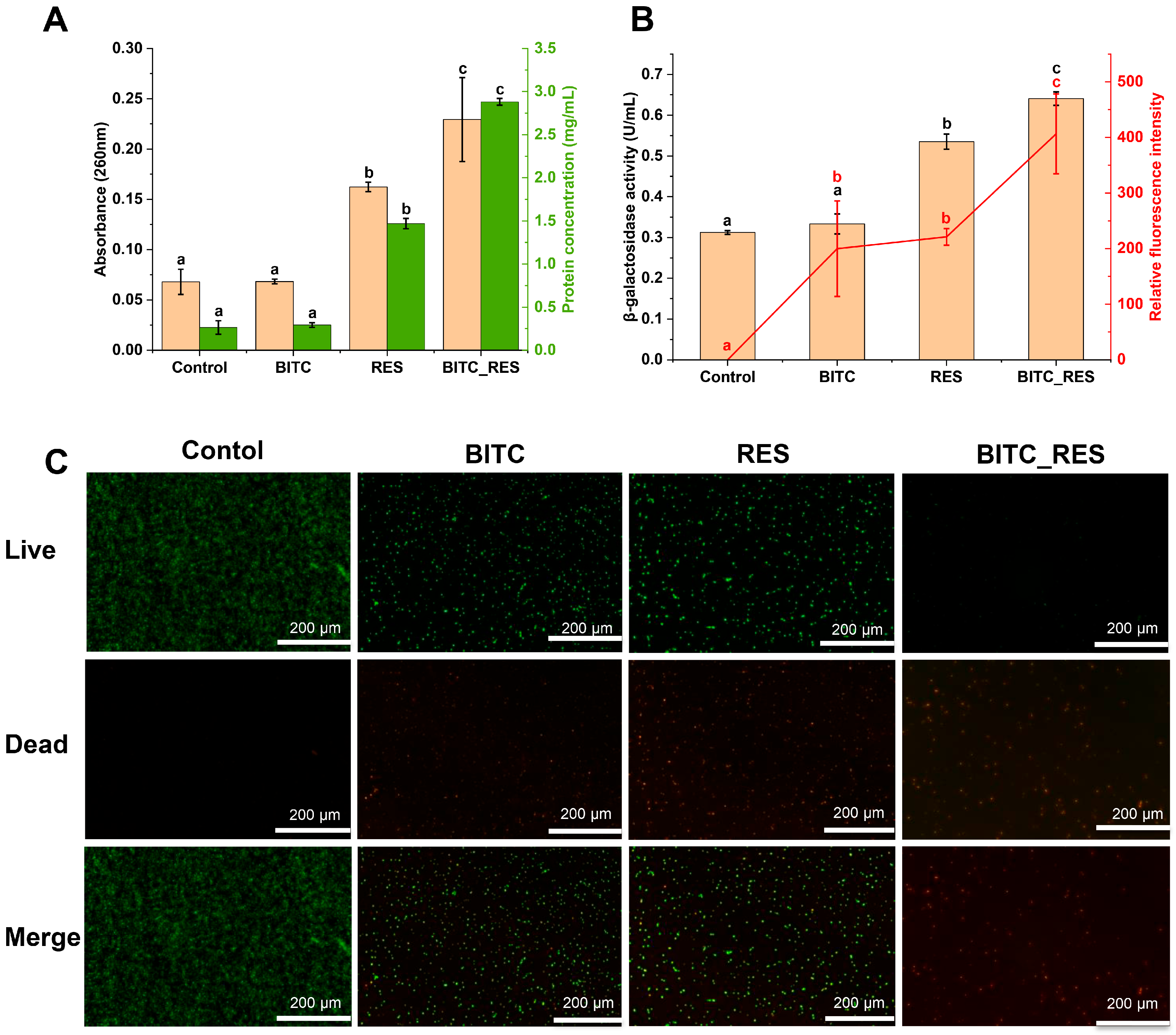
3.3. Synergistic Effects of BITC and RES on the Cell Membrane Permeability of S. aureus
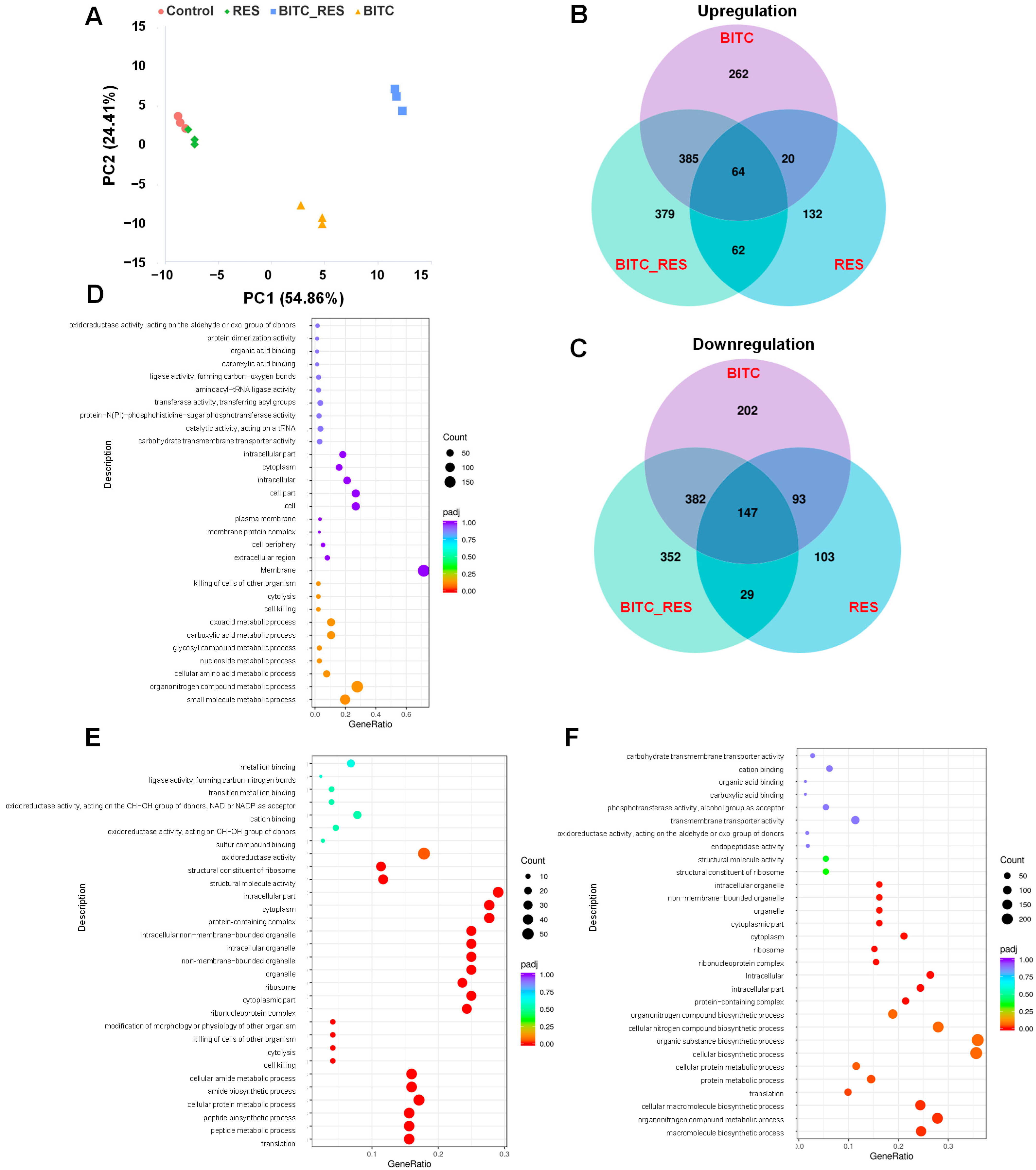
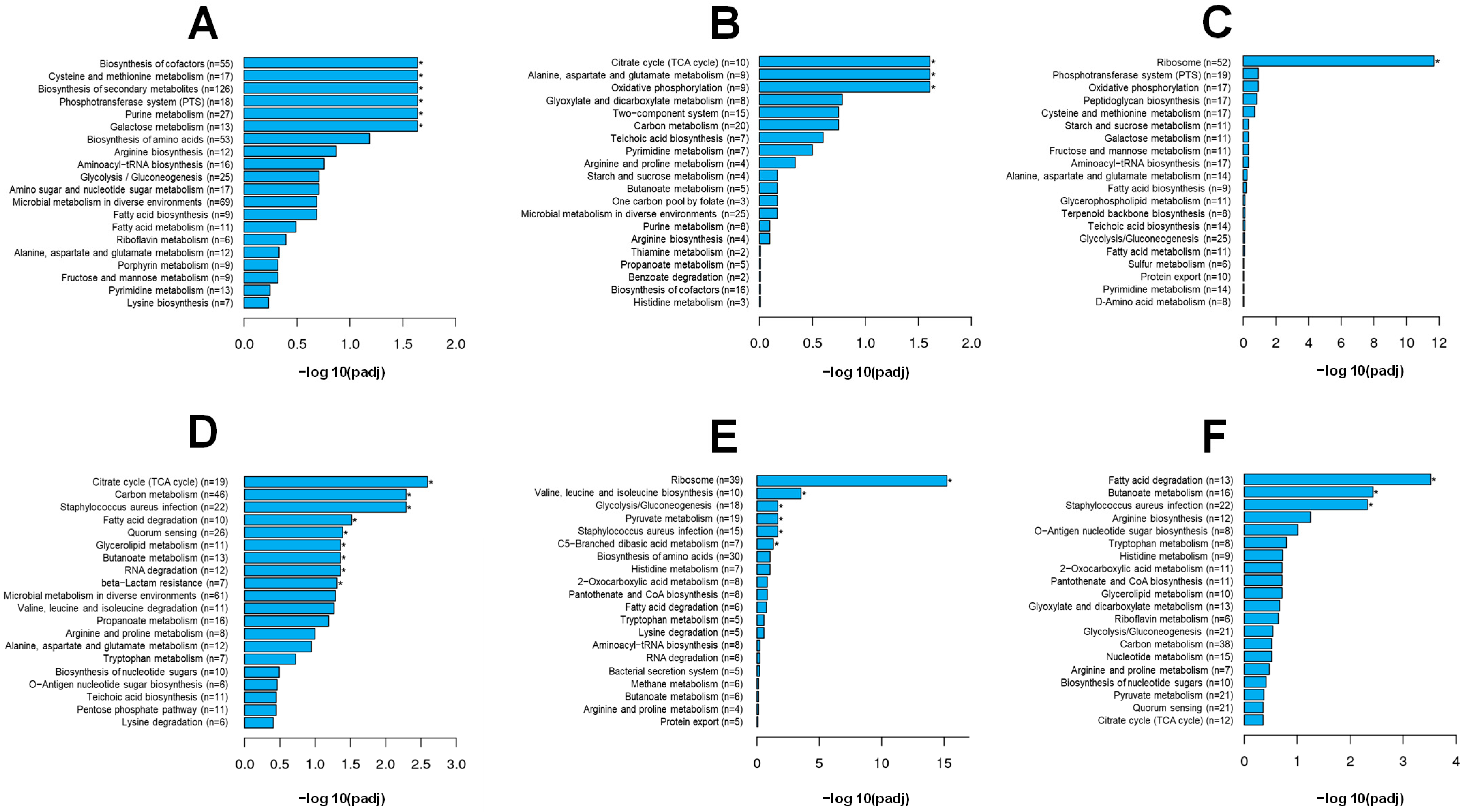
3.4. Synergistic Effects of BITC and RES on the DEGs of S. aureus
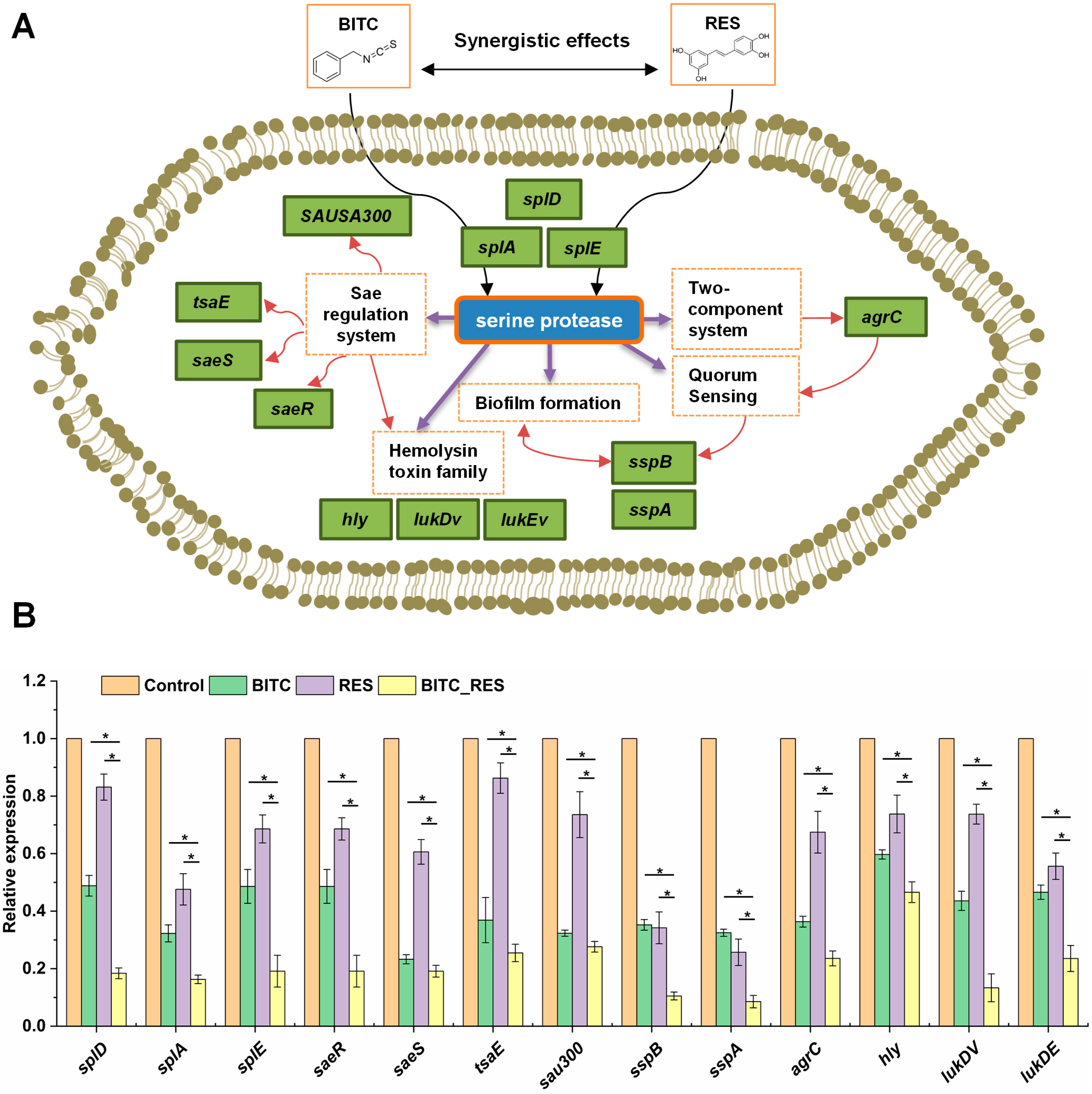
3.5. Synergistic Effects of BITC and RES on Some Key Genes in S. aureus
3.6. Synergistic Effects of BITC and RES on S. aureus in Beef at 4 °C and 25 °C
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, Z.; Wang, J.; Qu, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, M.; Zhao, M.; Sun, C.; Peng, H.; Huang, X.; Dong, Y. Celastrol combats methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by Targeting Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2302459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Cheng, W. Determination of cinnamaldehyde, thymol and eugenol in essential oils by LC–MS/MS and antibacterial activity of them against bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.U.; Park, Y.J.; Kang, C.E.; Cui, C.H.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, N.K.; Paik, H.D. Synergistic antimicrobial activity of ε-polylysine, chestnut extract, and cinnamon extract against Staphylococcus aureus. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 31, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, K.; Wu, H.; Zhu, J.; Hao, H.; Bi, J.; Hou, H.; Zhang, G. Label-free quantitative proteomics reveals the antibacterial effects of benzyl isothiocyanate against Vibrio parahaemolyticus. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 170, 114050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, H.; Ao, X.; Hao, H.; Bi, J.; Hou, H.; Zhang, G. Characterization of the inclusion complexes of isothiocyanates with γ-cyclodextrin for improvement of antibacterial activities against Staphylococcus aureus. Foods 2021, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Ming, X.; Xu, D.; Mo, H.; Liu, Z.; Hu, L.; Zhou, X. Transcriptome analysis and weighted gene co-expression network reveal multitarget-directed antibacterial mechanisms of benzyl isothiocyanate against Staphylococcus aureus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 11733–11741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, T.X.; Wang, X.N.; Wu, H.Y.; Bi, J.R.; Hao, H.S.; Hou, H.-M.; Zhang, G.L. Transcriptomic analysis, motility and biofilm formation characteristics of Salmonella typhimurium exposed to benzyl isothiocyanate treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.X.; Wu, H.T.; Li, X.-X.; Wu, H.Y.; Niu, T.X.; Wang, X.N.; Lian, R.; Zhang, G.L.; Hou, H.M. Comparison of the inhibitory potential of benzyl isothiocyanate and phenethyl isothiocyanate on Shiga toxin-producing and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 118, 108806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, M.; Ingmer, H. Antibacterial and antifungal properties of resveratrol. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 53, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulo, L.; Ferreira, S.; Gallardo, E.; Queiroz, J.A.; Domingues, F. Antimicrobial activity and effects of resveratrol on human pathogenic bacteria. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 1533–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.; Cho, T.J.; Rhee, M.S. Citrus fruit extracts with carvacrol and thymol eliminated 7-log acid-adapted Escherichia coli 0157:H7, Salmonella typhimurium, and Listeria monocytogenes: A potential of effective natural antibacterial agents. Food Res. Int. 2018, 107, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Han, Y.; Jian, L.; Liao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y. Fabrication, characterization, physicochemical stability of zein-chitosan nanocomplex for co-encapsulating curcumin and resveratrol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 116090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.; Hou, L.; Ma, M.; Li, M.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.; Jia, Y. Synergistic antibacterial mechanism of sucrose laurate combined with nisin against Staphylococcus aureus and its application in milk beverage. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 158, 113145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Hao, H.; Bi, J.; Hou, H.; Zhang, G. Synergistic effects of benzyl isothiocyanate and resveratrol against Listeria monocytogenes and their application in chicken meat preservation. Food Chem. 2023, 419, 135984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEQC/MAQC-III Consortium. A comprehensive assessment of RNA-seq accuracy, reproducibility and information content by the Sequencing Quality Control Consortium. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, Q.; Hasted, T.-L.; Lepp, D.; Yin, X.; Tang, J.; Chalmers, G.; Ross, K.; Boerlin, P.; Diarra, M.S. Transcriptional profiling of extraintestinal Escherichia coli exposed to cranberry pomace extracts alone or in combination with ceftriaxone. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 6, 957099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewunmi, Y.; Namjilsuren, S.; Walker, W.D.; Amato, D.N.; Amato, D.V.; Mavrodi, O.V.; Patton, D.L.; Mavrodi, D.V. Antimicrobial activity of, and cellular pathways targeted by, p-anisaldehyde and epigallocatechin gallate in the opportunistic human pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am. Soc. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02482-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamad Maifiah, M.H.; Zhu, Y.; Tsuji, B.T.; Creek, D.J.; Velkov, T.; Li, J. Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses of the synergistic effect of polymyxin–rifampicin combination against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Biomed. Sci. 2022, 29, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Luo, L.; Wang, W.; Hong, B.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J. Synergistic antibacterial activity of cell wall hydrolase Lys14579 combined with cinnamaldehyde against emetic Bacillus cereus and their application in foods. Food Control 2024, 164, 110562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Yoon, H.; Kang, D.-H.; Chang, P.-S.; Ryu, S. Endolysin LysSA97 is synergistic with carvacrol in controlling Staphylococcus aureus in foods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 244, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yu, S.; Han, J.; Wu, J.; You, L.; Shi, X.; Wang, S. Synergistic antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of nisin/carvacrol combination against Staphylococcus aureus and their application in the infecting pasteurized milk. Food Chem. 2022, 38, 132009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, D.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Liu, F.; Yu, Y. Synergistic inactivation of Escherichia coli O157: H7 and Staphylococcus aureus by gallic acid and thymol and its potential application on fresh-cut tomatoes. Food Microbiol. 2022, 102, 103925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, L.; Jin, W.; Sun, Y. The specific effect of gallic acid on Escherichia coli biofilm formation by regulating pgaABCD genes expression. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Zhao, J.; Yan, X.; Zeng, Z.; Gong, D. Synergistic effects of monocaprin and carvacrol against Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella typhimurium in chicken meat preservation. Food Control 2021, 132, 108480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.X. Synergistic effects of endolysin Lysqdvp001 and epsilon-poly-lysine in controlling Vibrio parahaemolyticus and its biofilms. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 343, 109112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods Companion Methods Enzymol. 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassolé, I.H.N.; Juliani, H.R. Essential oils in combination and their antimicrobial properties. Molecules 2012, 17, 3989–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Jung, L.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.; Cho, Y.; Ahn, J. Enhanced antimicrobial activity of nisin in combination with allyl isothiocyanate against Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella Typhimurium and Shigella boydii. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opanasopit, S.P. Synergistic antibacterial activity of alpha mangostin and resveratrol loaded polymer-based films against bacteria infected wound. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 101629. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, L.; Liang, R.; Duan, J.; Song, S.; Pan, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhu, M.; Li, L. Synergistic antibacterial and anti-biofilm activities of resveratrol and polymyxin B against multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Antibiot. 2022, 75, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, N.; Yu, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, M.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, J. Synergistic microbicidal effect of AUR and PEITC against Staphylococcus aureus skin infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 927289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Q.; Niu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Chen, Q. Antibacterial activity and mannosylerythritol lipids against vegetative cells and spores of Bacillus cereus. Food Control 2019, 106, 106711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derde, M.; Guerin-Dubiard, C.; Lechevalier, V.; Cochet, M.-F.; Nau, F. Dry-heating of lysozyme increases its activity against Escherichia coli membranes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1692–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Zhao, X.C.; Meng, R.Z.; Liu, Z.J.; Zhang, G.N.; Guo, N. Synergistic antimicrobial effects of nisin and p-Anisaldehyde on Staphylococcus aureus in pasteurized milk. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 84, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, P.; Quek, S. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of cinnamon essential oil against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Food Control 2016, 59, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, R.Y.; Li, P.L. Antibacterial mechanism of plantaricin LPL-1, a novel class IIa bacteriocin against Listeria monocytogenes. Food Control 2019, 97, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Sheng, M.; Tian, Y.; Li, B.; Kang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Soteyome, T.; Guo, L.; Sun, H. Antibiofilm activity and synergistic effects of DNase I and Lysostaphin against Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Food Qual. Saf. 2024, 8, fyae024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Li, M.; Hao, Z.H.; Shen, X.F.; Liu, L.; Jin, Y.; Wang, S.S.; Guo, Y.J.; Yang, L.H.; Wang, L.X.; et al. Subinhibitory concentrations of resveratrol reduce alpha-hemolysin production in Staphylococcus aureus isolates by downregulating saeRS. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan-Krohn, T.; Grote, A.; Rodriguez, S.; Kirby, J.E.; Earl, A.M. Transcriptomics reveals how minocycline-colistin synergy overcomes antibiotic resistance in multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0196921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Chen, J.; Du, X.; Zhang, Y.J.; Qi, J.F.; He, Y.J.; An, Z.L.; Lu, Y.Y.; Ge, C.; Wang, Y. Unveiling synergistic potency: Exploring butyrolactone I to enhance gentamicin efficacy against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strain USA300. ACS Infect. Dis. 2023, 10, 196–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, T.; Bae, T.; Schneewind, O.; Takeuchi, F.; Hiramatsu, K. Genome sequence of Staphylococcus aureus strain newman and comparative analysis of staphylococcal genomes: Polymorphism and evolution of two major pathogenicity islands. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, S.B.; Wesson, C.A.; Liou, L.E.; Trumble, W.R.; Schlievert, P.M.; Bohach, G.A.; Bayles, K.W. Molecular characterization of a novel Staphylococcus aureus serine protease operon. Infect. Immun. 2015, 69, 1521–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.; Vijay, A.K.; Stapleton, F.; Willcox, M.D. Genomics of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from infectious and non-infectious ocular conditions. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygaard, T.K.; Pallister, K.B.; Ruzevich, P.; Griffith, S.; Vuong, C.; Voyich, J.M. SaeR binds a consensus sequence within virulence gene promoters to advance USA300 pathogenesis. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraudo, A.T.; Aldo, C.; Cataldi, A.A.; Cristina, B.; Rosa, N. The sae locus of Staphylococcus aureus encodes a two-component regulatory system. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 177, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JovVoyich, J.M.; Vuong, C.; DeWald, M.; Nygaard, T.K.; Kocianova, S.; Griffith, S.; Jones, J.; Iverson, C.; Sturdevant, D.E.; Braughton, K.R.; et al. The SaeR/S gene regulatory system is essential for innate immune evasion by Staphylococcus aureus. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 1698–1706. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Z.; Wang, H.; Ke, K.; Shi, D.; Zhu, L. Flavone inhibits Staphylococcus aureus virulence via inhibiting the sae two component system. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 180, 106128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Phukan, U. Interaction of host and Staphylococcus aureus protease-system regulates virulence and pathogenicity. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 208, 585–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loughran, A.J.; Atwood, D.N.; Anthony, A.C.; Harik, N.S.; Spencer, H.J.; Beenken, K.E.; Smeltzer, M.S. Impact of individual extracellular proteases on Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation in diverse clinical isolates and their isogenic sarA mutants. Microbiologyopen 2014, 3, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, C.; Shi, C.; Sameeh, M.Y.; Al-Asmari, F.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. Transcriptome analysis reveals the inhibitory mechanism of phloretin on virulence expression of Staphylococcus aureus and its application in cooked chicken. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 415, 110647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.; Hill, P.; Bonev, B.; Chan, W.C. Quorum-sensing, intra-and inter-species competition in the staphylococci. Microbiology 2023, 169, 001381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, K.Y.; Otto, M. Quorum-sensing regulation in staphylococci—An overview. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solano Goñi, C.; Echeverz Sarasúa, M.; Lasa Uzcudun, Í. Biofilm dispersion and quorum sensing. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2014, 18, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morfeldt, E.; Taylor, D.; von Gabain, A.; Arvidson, S. Activation of alpha-toxin translation in Staphylococcus aureus by the trans-encoded antisense RNA, RNAIII. Embo J. 1995, 14, 4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, J.; Li, R.; Ye, K. High-throughput sequencing analysis of the bacterial community for assessing the differences in extraction methods of bacteria separation from chilled pork. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 134, 110213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene ID | Gene Name | Protein Function | Log2 Fold Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BITC | RES | BITC_RES | |||
| Serine Protease | |||||
| SAOUHSC_01938 | splD | serine protease SplD | −1.5665 | −8.0212 | |
| SAOUHSC_01942 | splA | serine protease SplA | −1.4534 | −0.5767 | −7.3169 |
| SAOUHSC_01936 | splE | serine protease SplE | −0.6263 | −5.8138 | |
| Sae regulation system | |||||
| SAOUHSC_00715 | saeR | response regulator | 0.5030 | −2.1426 | |
| SAOUHSC_00714 | saeS | sensor histidine kinase SaeS | −0.3589 | 0.4733 | −2.0228 |
| SAOUHSC_02280 | tsaE | threonylcarbamoyladenosine biosynthesis protein | 0.4837 | −1.1128 | |
| SAOUHSC_00266 | sau300 | Type VII secretion system protein | −2.3866 | −3.1303 | |
| Two- component system | |||||
| SAOUHSC_02264 | agrC | accessory gene regulator protein C | −2.2806 | −2.5308 | |
| Quorum Sensing | |||||
| SAOUHSC_00987 | sspB | cysteine protease | −1.2682 | −1.636 | |
| Biofilm formation | |||||
| SAOUHSC_00988 | sspA | glutamyl endopeptidase | −1.1754 | −1.5138 | |
| Hemolysin toxin family | |||||
| SAOUHSC_01121 | hly | alpha-hemolysin | −2.5263 | 0.2595 | −5.2095 |
| SAOUHSC_01954 | lukDv | leukotoxin LukD | −0.7223 | −2.3529 | |
| SAOUHSC_01955 | lukEv | leukotoxin LukE | −0.9734 | −2.8215 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Hao, H.; Bi, J.; Hou, H.; Zhang, G. Synergistic Antibacterial Mechanism of Benzyl Isothiocyanate and Resveratrol Against Staphylococcus aureus Revealed by Transcriptomic Analysis and Their Application in Beef. Foods 2025, 14, 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091610
Liu J, Ma J, Wang Y, Hao H, Bi J, Hou H, Zhang G. Synergistic Antibacterial Mechanism of Benzyl Isothiocyanate and Resveratrol Against Staphylococcus aureus Revealed by Transcriptomic Analysis and Their Application in Beef. Foods. 2025; 14(9):1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091610
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jianan, Jinle Ma, Yingrui Wang, Hongshun Hao, Jingran Bi, Hongman Hou, and Gongliang Zhang. 2025. "Synergistic Antibacterial Mechanism of Benzyl Isothiocyanate and Resveratrol Against Staphylococcus aureus Revealed by Transcriptomic Analysis and Their Application in Beef" Foods 14, no. 9: 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091610
APA StyleLiu, J., Ma, J., Wang, Y., Hao, H., Bi, J., Hou, H., & Zhang, G. (2025). Synergistic Antibacterial Mechanism of Benzyl Isothiocyanate and Resveratrol Against Staphylococcus aureus Revealed by Transcriptomic Analysis and Their Application in Beef. Foods, 14(9), 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091610







