Impact of Steam Processing on the Physicochemical Properties and Flavor Profile of Takifugu flavidus: A Comprehensive Quality Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Sample
2.3. Core Temperature
2.4. Water Loss Rate
2.5. Mass Loss Rate
2.6. Water Distribution and Migration
2.7. Texture Properties
2.8. Color
2.9. Free Amnio Acid Analysis
2.10. Electronic Nose Analysis
2.11. Electronic Tongue Analysis
2.12. HS-GC-IMS Analysis
2.13. Sensory Evaluation
2.14. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
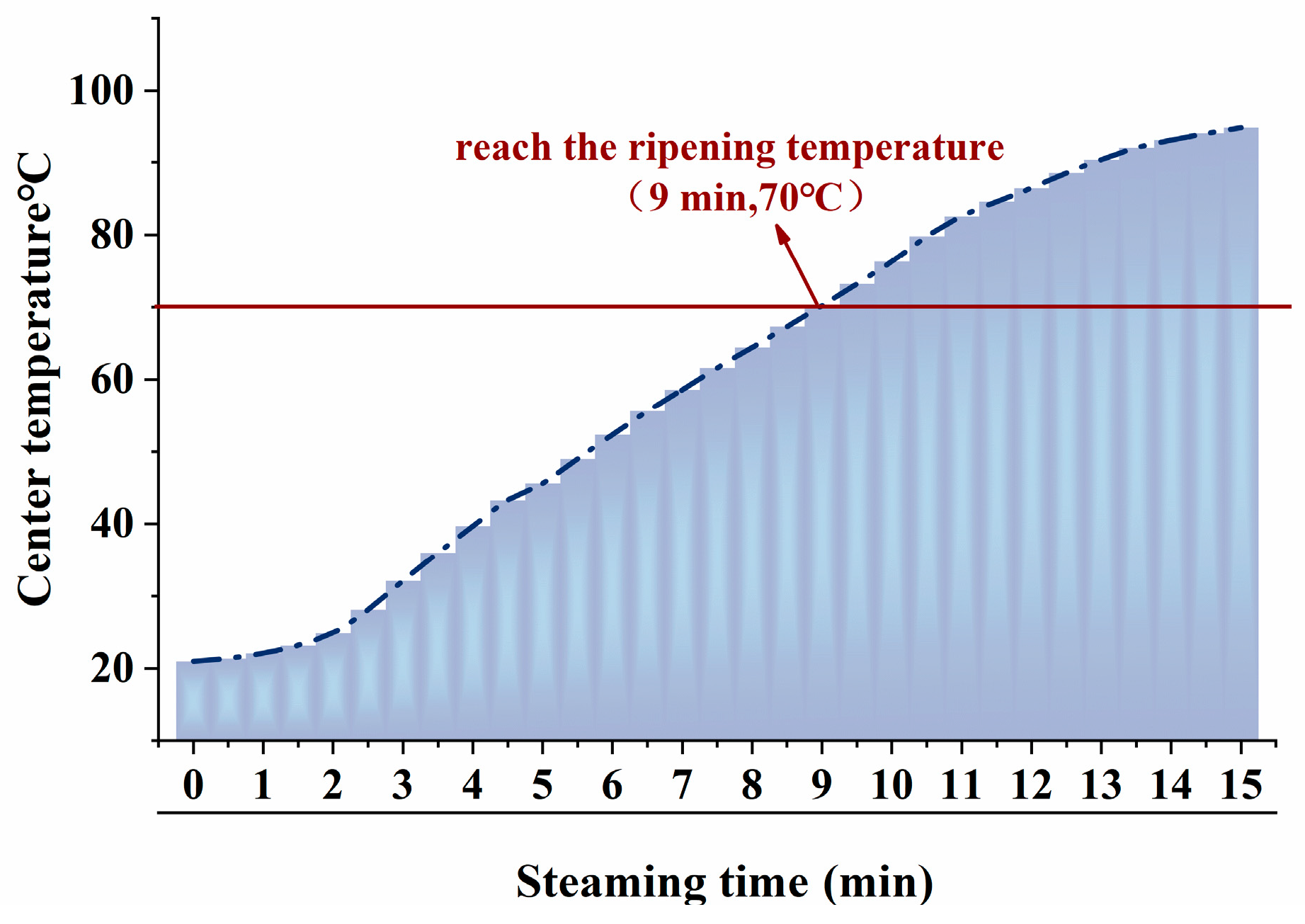
3.1. Changes in Core Temperature
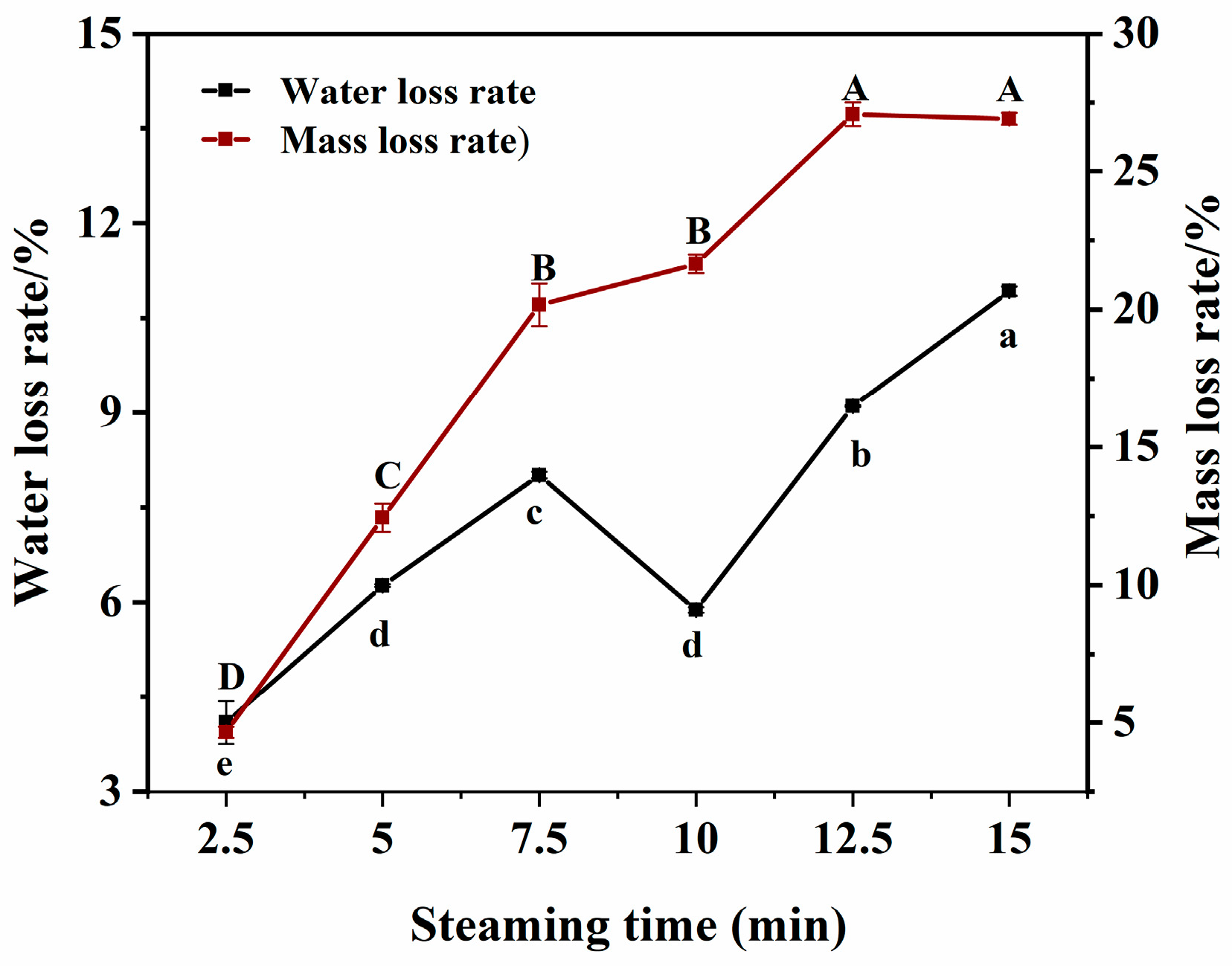
3.2. Changes in Water Loss Rate and Mass Loss Rate
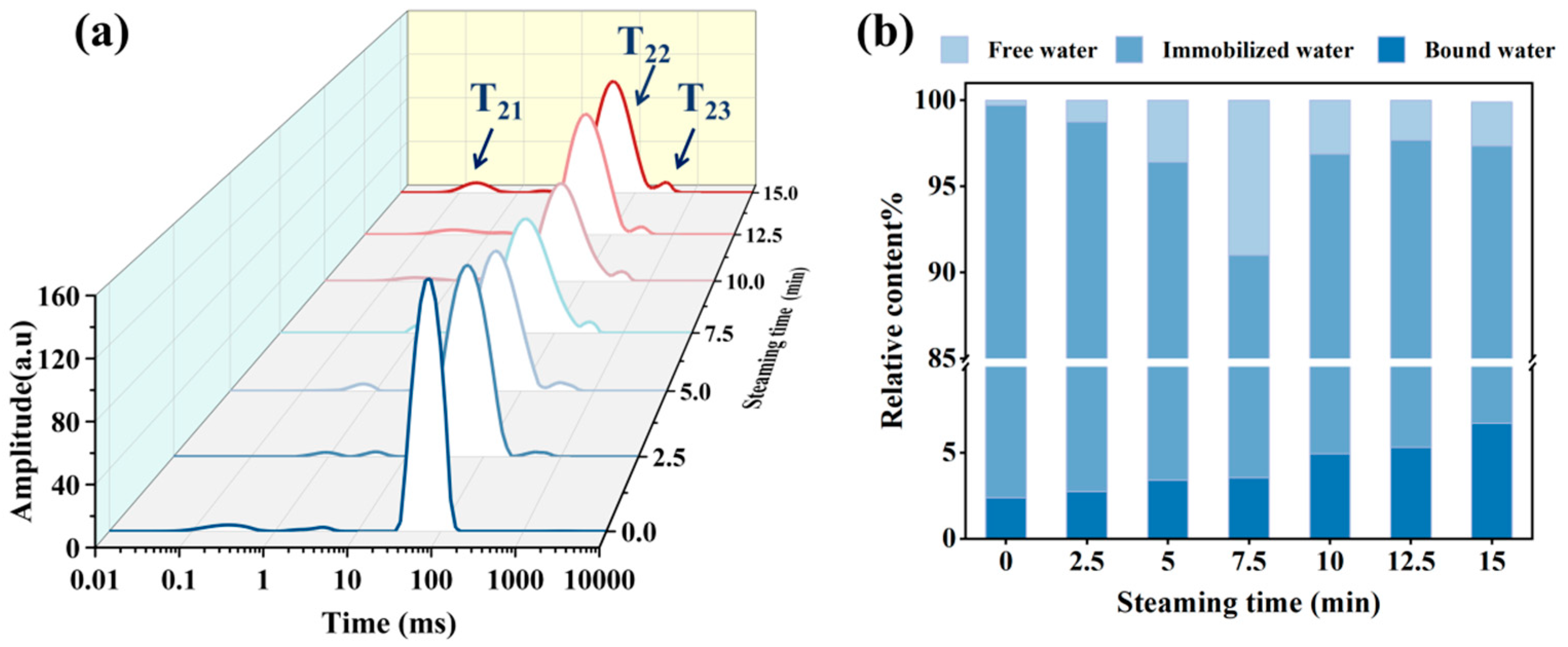
3.3. Changes in Water Distribution
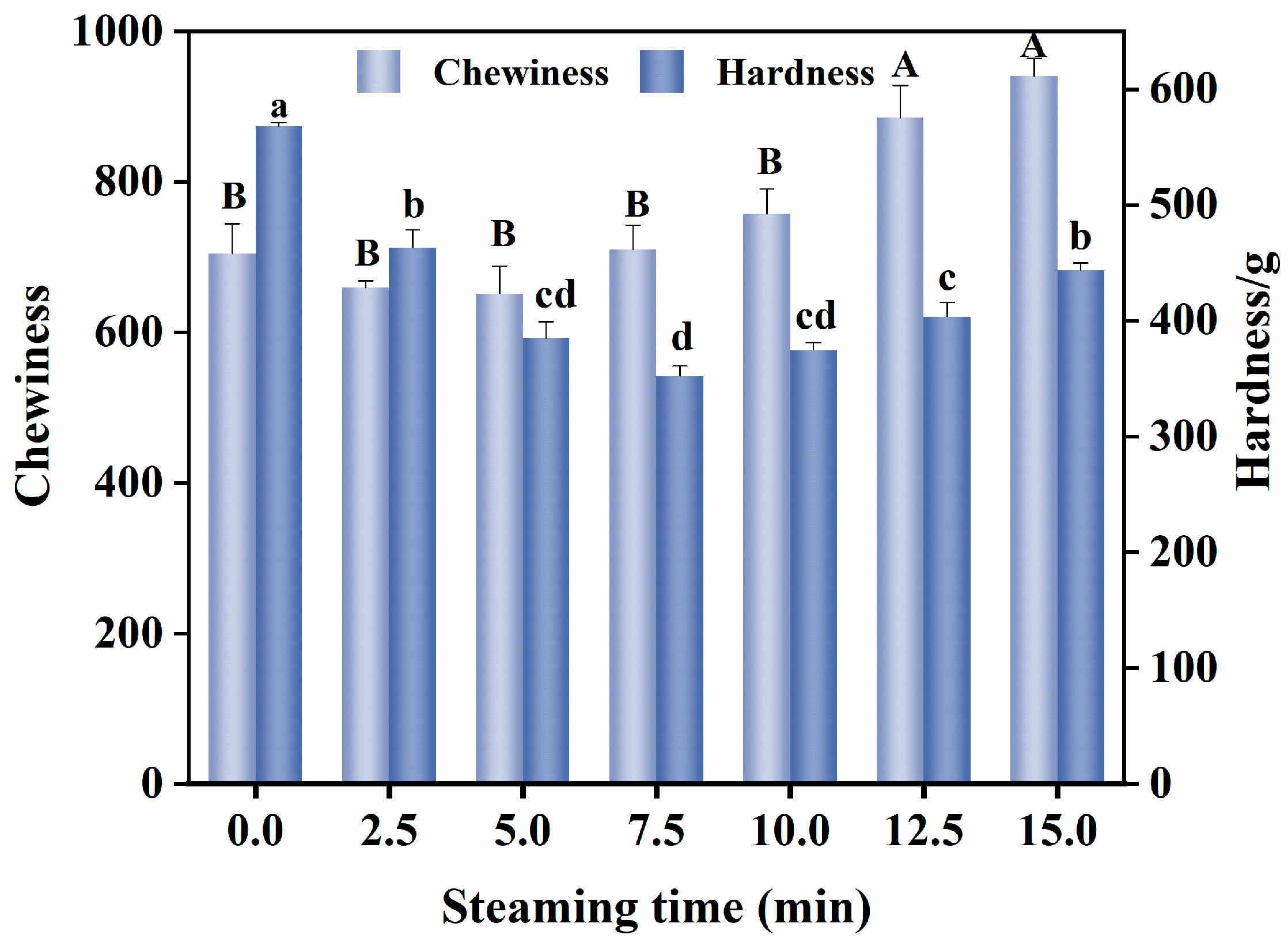
3.4. Changes in Textural Properties
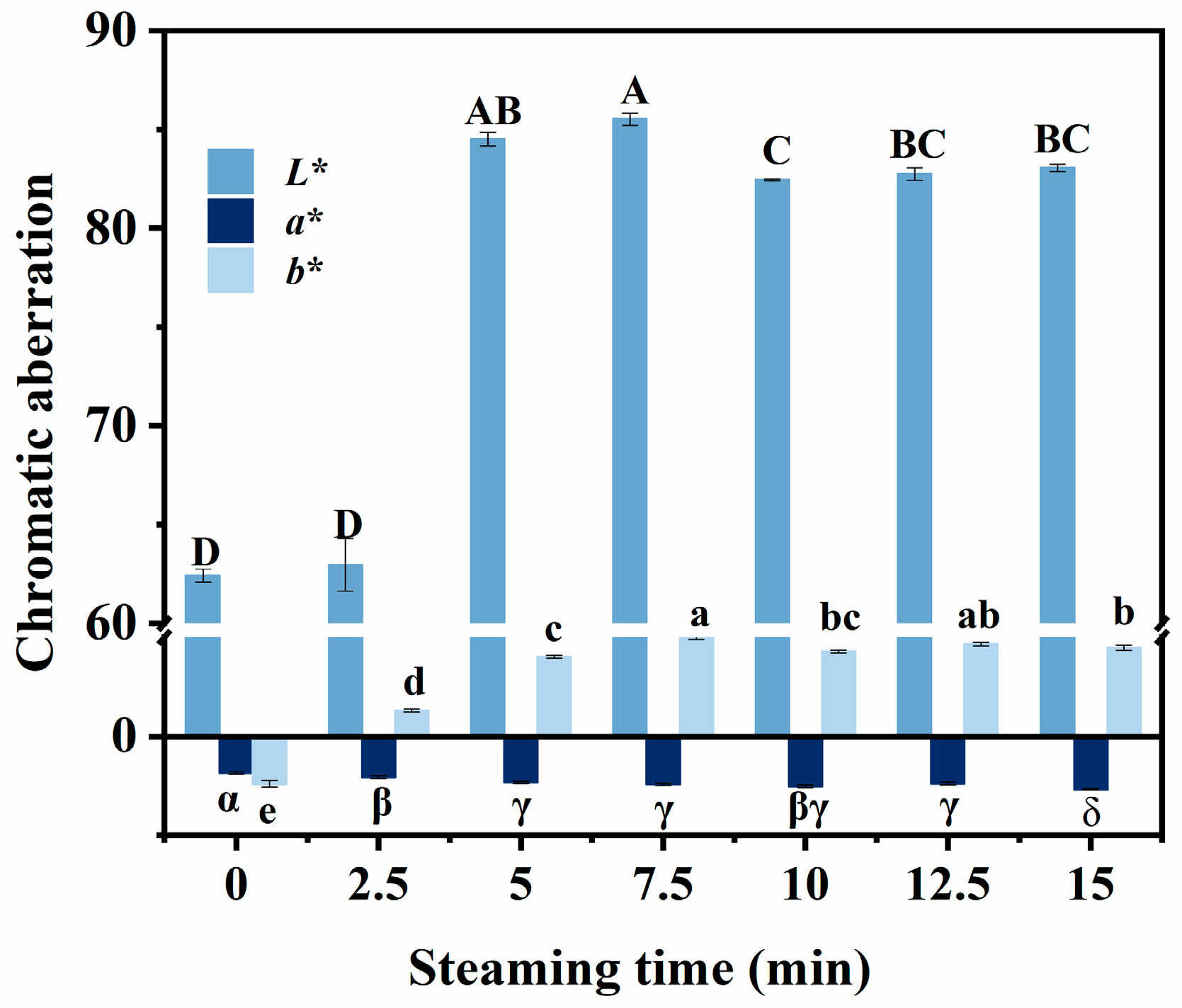
3.5. Changes in Color
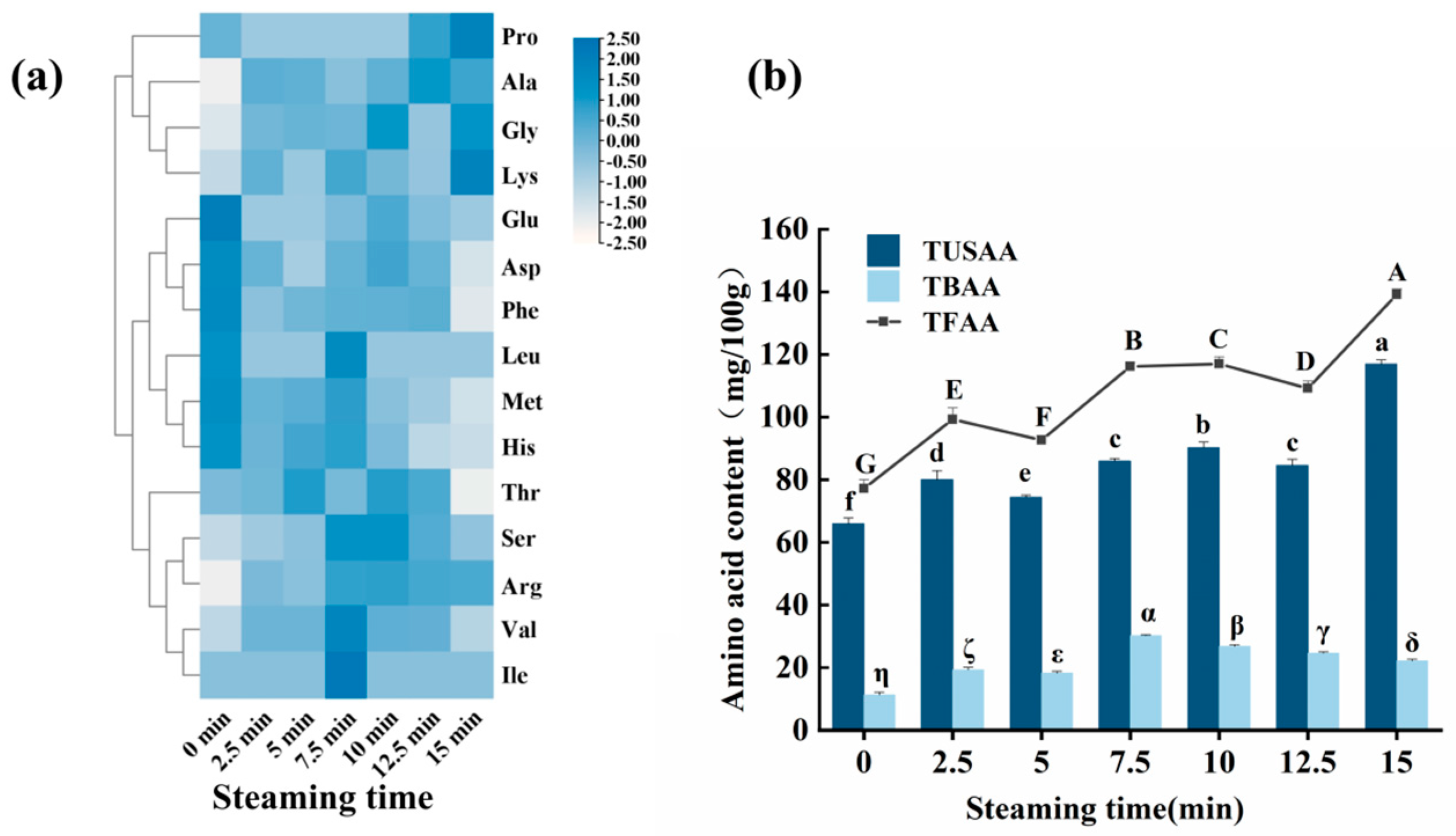
3.6. Changes in Free Amino Acids
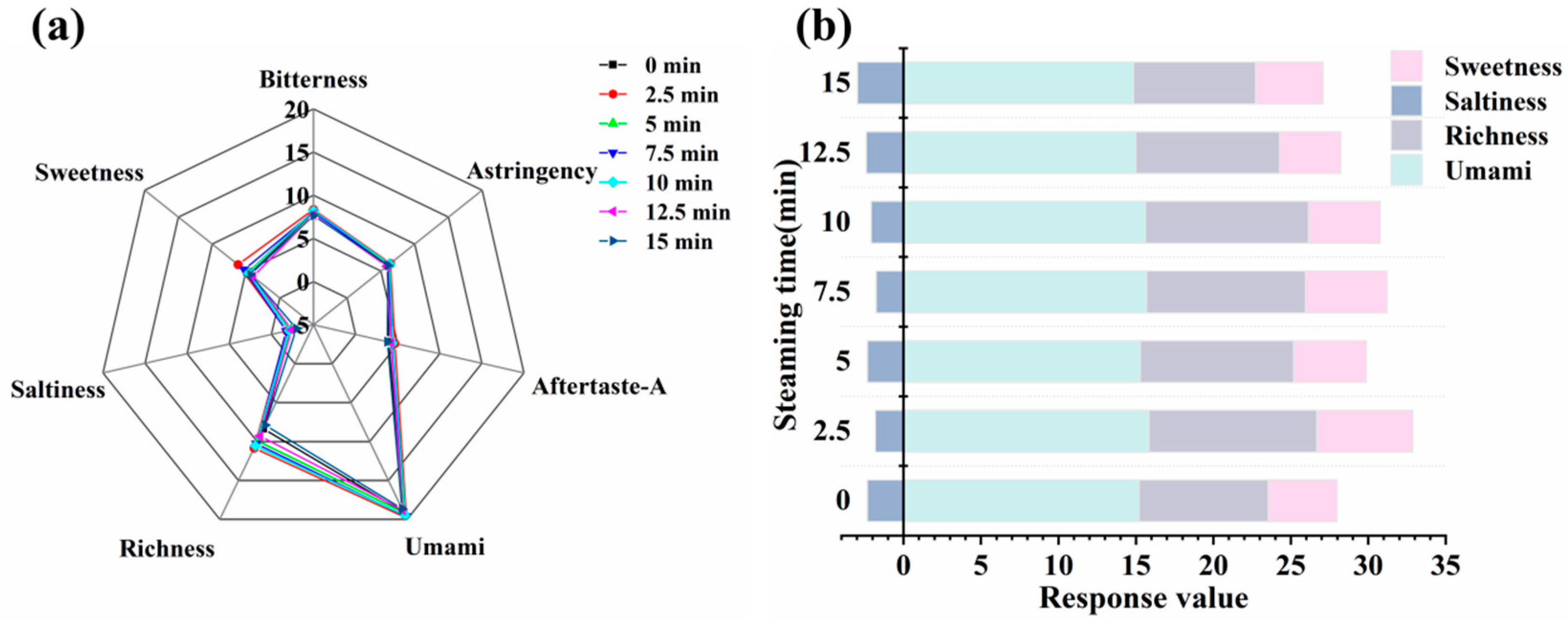
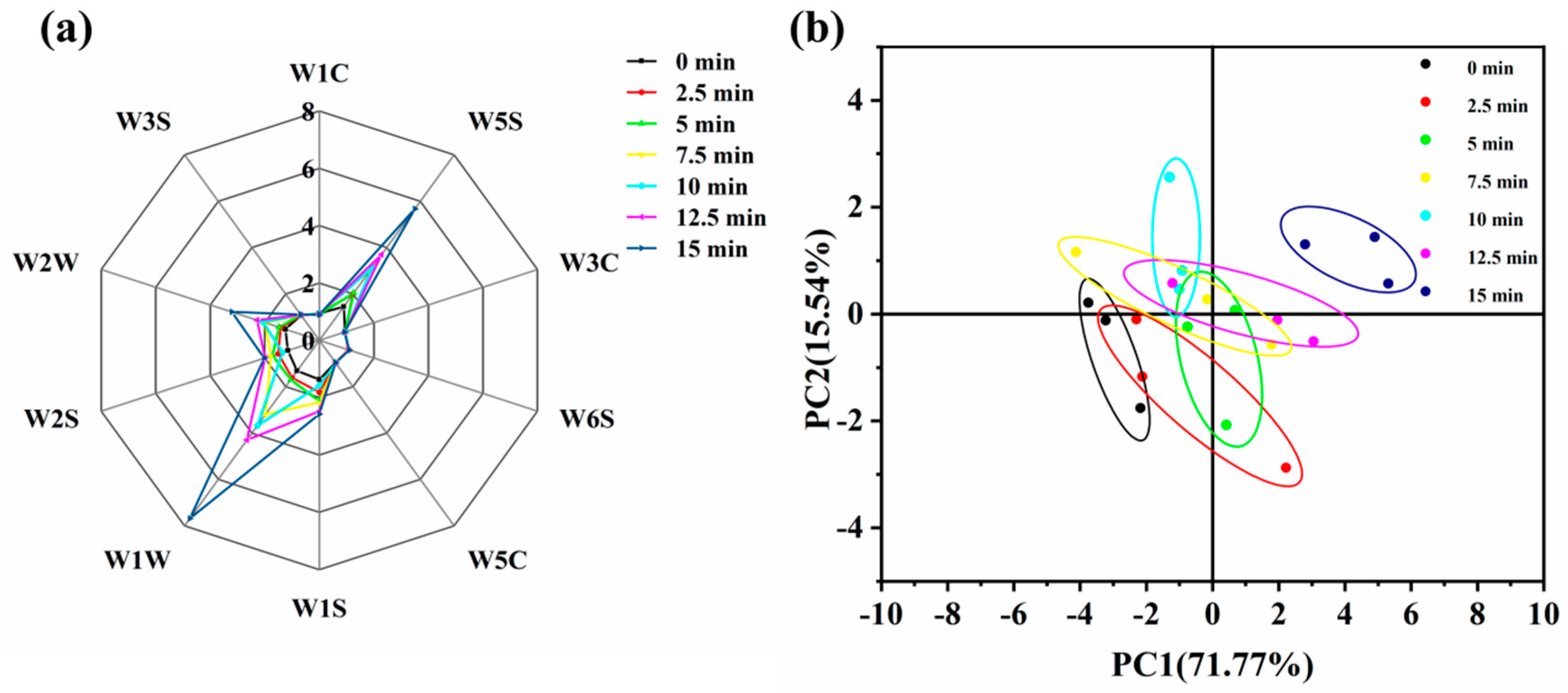
3.7. Analysis of Electronic Tongue Results
3.8. Analysis of Volatile Flavor Compounds by Electronic Nose
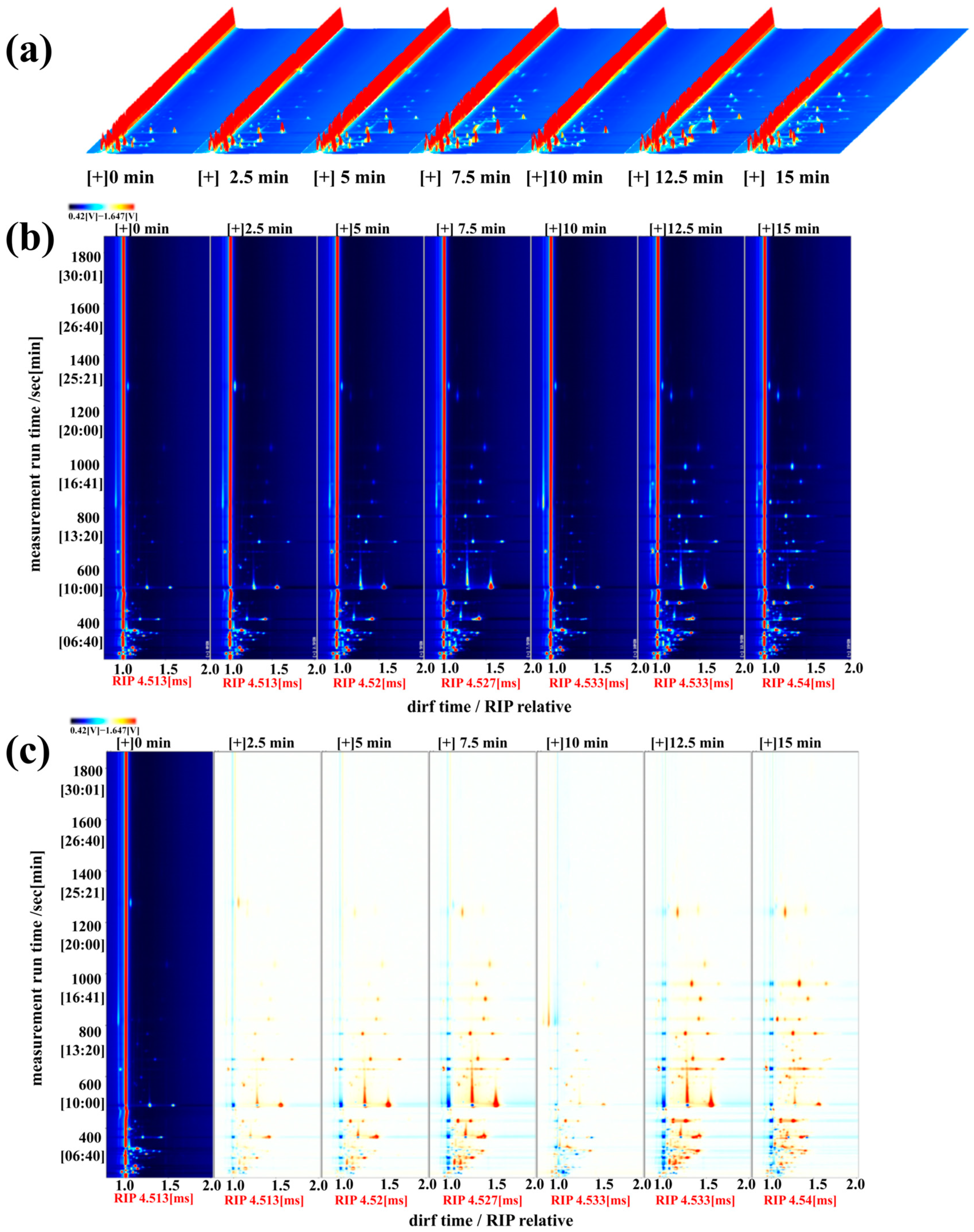
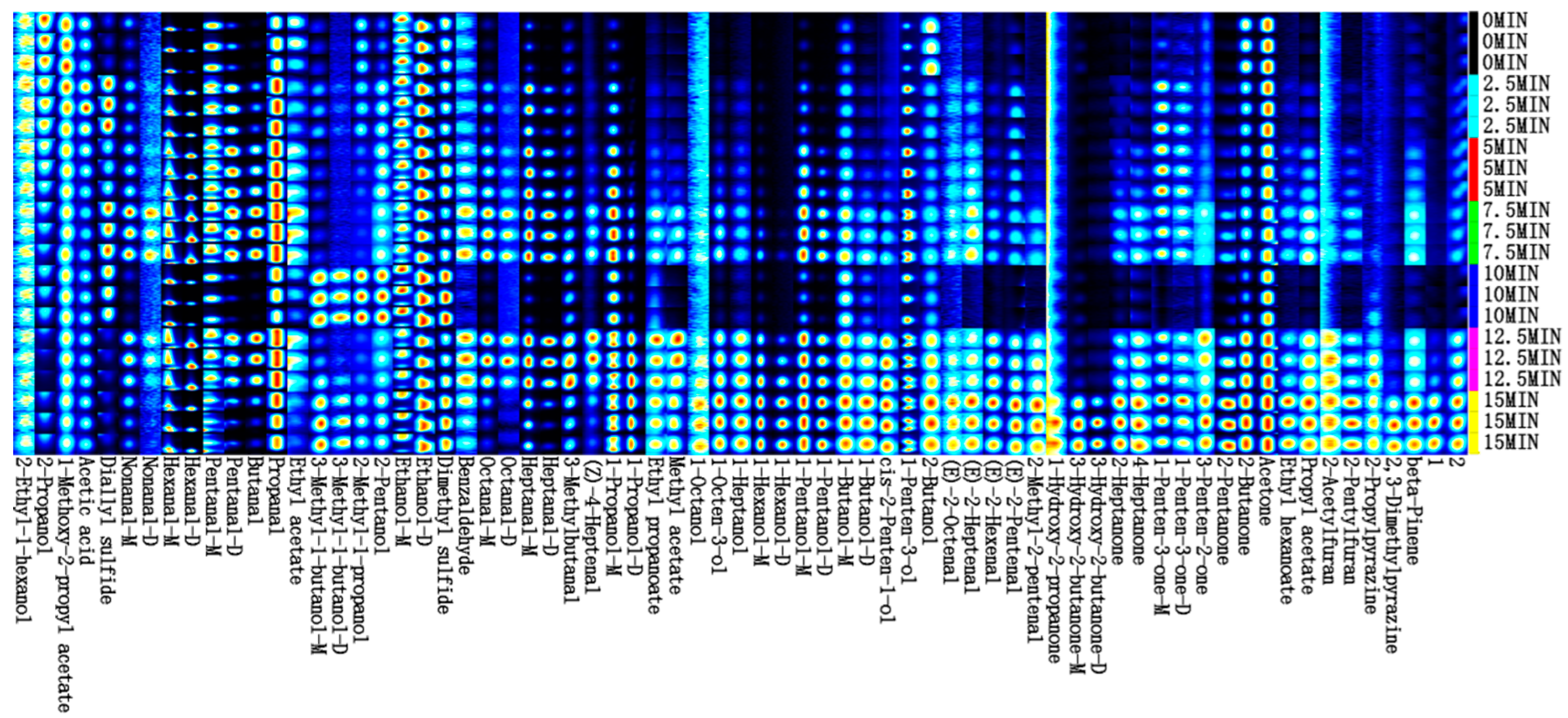
3.9. HS-GC-IMS Analysis
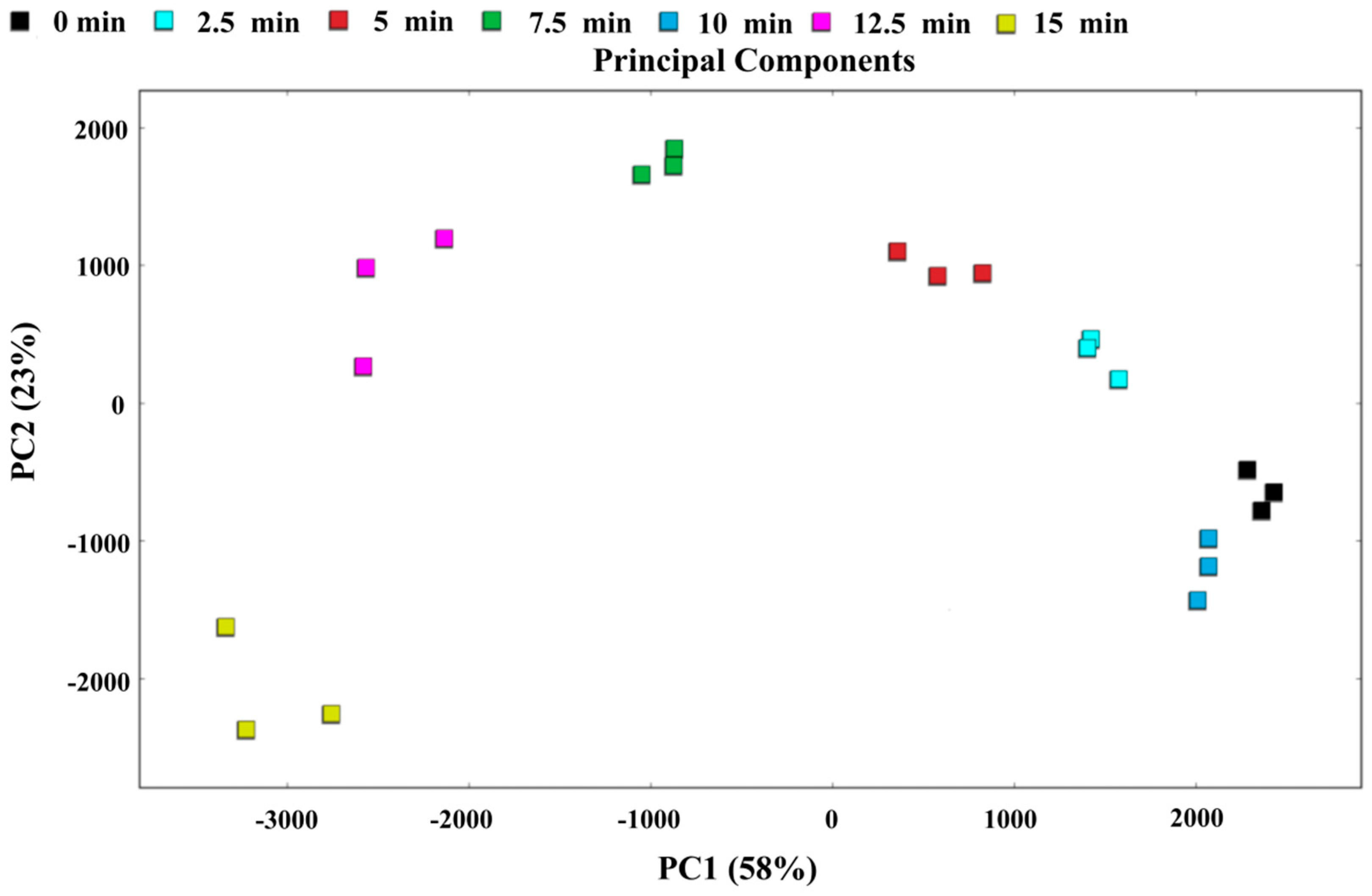
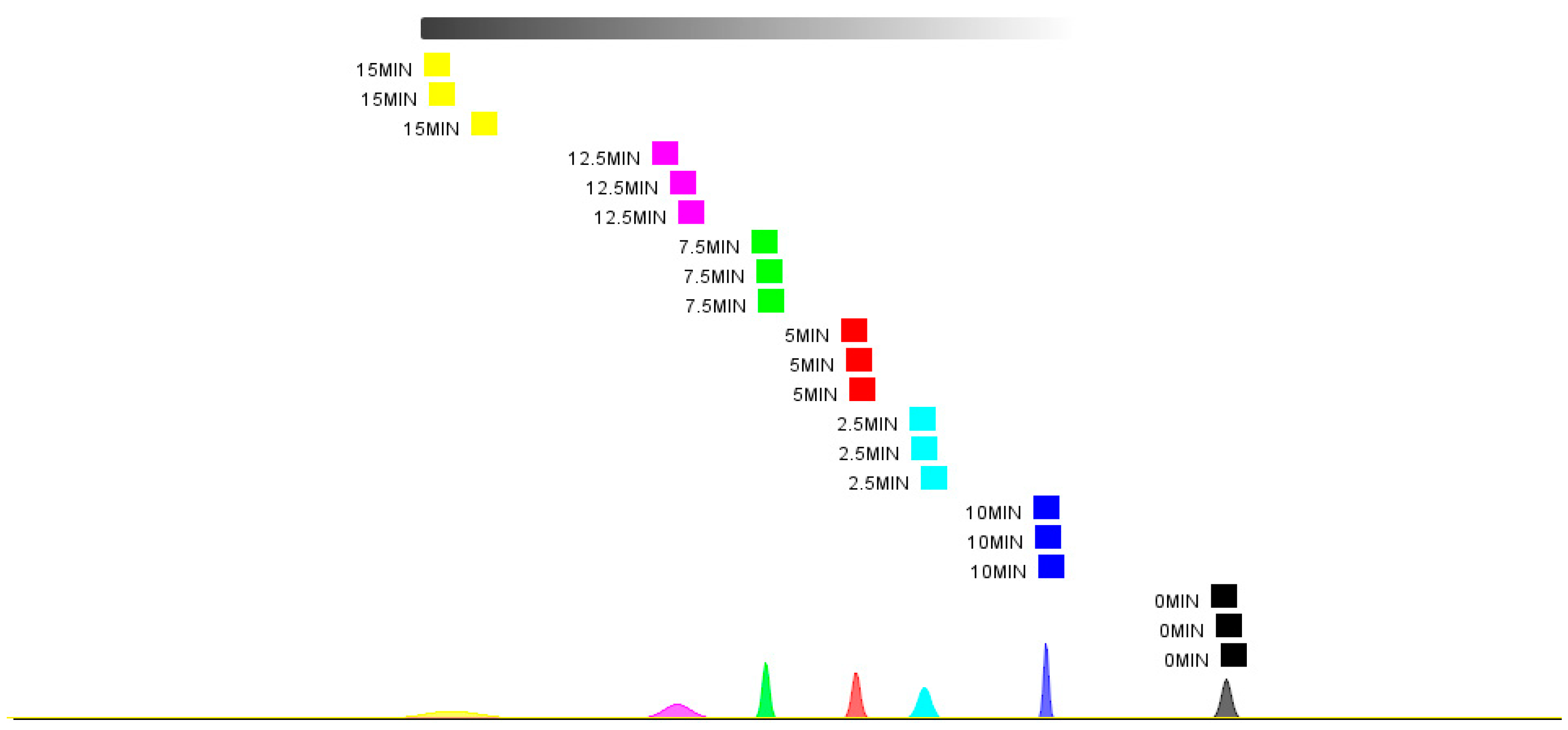
3.10. PCA and Nearest Neighbor Distance Analysis
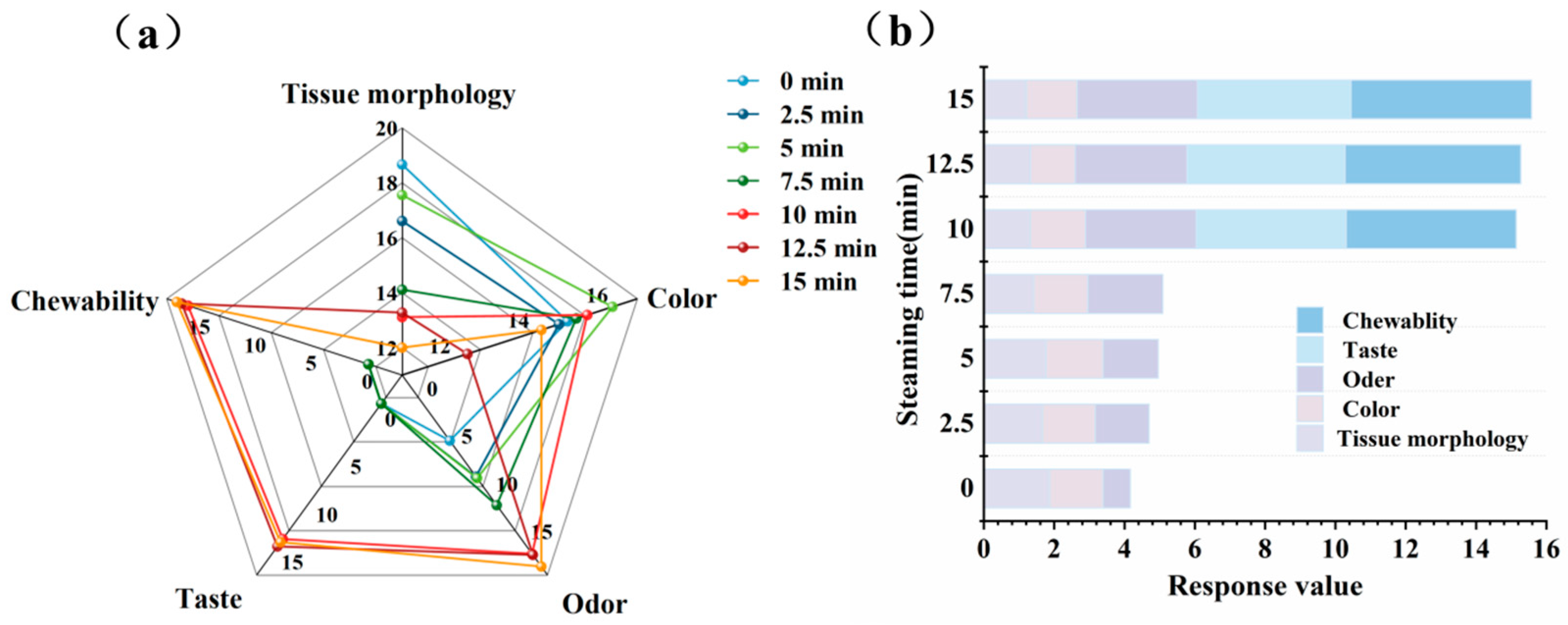
3.11. Sensory Evaluation Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ji, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gong, Q.L.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z.P. Toxicity of cultured puffer fish and seasonal variations in China. Aquac. Res. 2011, 42, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.F.; Chen, T.Y.; Shiau, C.Y.; Jeng, S.S. Seasonal variations of free amino acids and nucleotide-related compounds in the muscle of cultured Taiwanese puffer Takifugu rubripes. Fish. Sci. 2000, 66, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.T.; Wu, J.N.; Xu, M.; Liu, S.; Su, Y.; Qiao, K.; Liu, Z. Analysis and evaluation of the nutritional components in fish skin and fish meat of four species of puffer fish. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 36, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Wereńska, M.; Haraf, G.; Okruszek, A.; Marcinkowska, W.; Wołoszyn, J. The effects of sous vide, microwave cooking, and stewing on some quality criteria of goose meat. Foods 2022, 12, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Lin, X.; Zhao, W.; Fan, X.; Yu, W.; Ma, Z.; Yu, C.; Dong, X. Low-temperature steaming improves eating quality of whitefish. J. Texture Stud. 2020, 51, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhijian, D.; Qingjun, W.; Jingya, H.; Jianrong, L. Change of Moisture Status and Texture for shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) during Steaming. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 15, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Fan, X.; Dong, X.; Xin, Q.; Pan, J. Study on the quality changes of carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) muscle during steam cooking. Food Ferment. Ind. 2015, 41, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, S.; Wang, B.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Huang, X.; Qin, L. Integrated volatolomics and lipidomics analysis reveal the characteristic flavor formation mechanism in steamed large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Xiao, N.; Guo, Q.; Shi, W. Identification of changes in volatile compounds in grass carp during steaming by headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry. Food Ferment. Ind. 2023, 49, 241–250. [Google Scholar]
- GB 5009.3-2016; National Food Safety Standard—Determination of Moisture in Foods. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Ge, Z.; Xu, Y.; Yu, D.; Xia, W. Effects of doneness and frying process on the quality of frozen cooked grass carp fillets. Fish. Res. 2024, 46, 436–447. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Wang, H. Effect of different inoculum levels of Lactobacillus plantarum on quality characteristics and flavor profile of low-sodium dry sausage. Food Chem. 2022, 43, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.L.; Tu, Z.C.; Sha, X.M.; Zhang, L.; Lin, D.R.; Zeng, K.; Wang, H.; Pang, J.J.; Tang, P.P. Effect of frying on fatty acid profile, free amino acids and volatile compounds of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) fillets. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2016, 41, e13088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Liao, E.; Chen, J. Effect of Variable Temperature Liquid Nitrogen Quick-Freezing Combined with Composite Cryoprotectant on the Quality of Frozen Prepared Monopterus albus. Food Chem. 2024, 45, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jing, L.; Xiao, N.; Wu, X.; Shi, W. Changes in Protein Degradation and Non-Volatile Flavor Substances of Swimming Crab (Portunus trituberculatus) during Steaming. Foods 2022, 11, 3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.-X.; Bai, X.-T.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, H.-L.; Li, X.-P.; Li, J.-R.; Yi, S.-M.; Xie, J.; Guo, X.-H. Changes of Flavor compounds in Sea Bass during Steaming Process as Analyzed by Gas Chromatography-Ion Mobility Spectroscopy and Chemometrics. Food Chem. 2021, 42, 270–275. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, Y.; Tan, C.; Nie, S.; Wen, Q.; Tu, Z. Exploration of changes in sensory, physicochemical properties and microbial metabolic activities of grass carp meat with five thermal processing treatments during refrigerated storage. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China; State Administration for Market Regulation. National Food Safety Standard: General Hygiene Specifications for Catering Services; China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2021; p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, S.K.; Ganesan, P.; Kishore, P.; Remya, S.; Mohan, C.O.; Padmavathy, P.; Muralidhran, N.; Bindu, J. Effects of different cooking methods on the proximate composition and physical properties of Brown shrimp (Metapenaeus dobsonii) during cooking and freezing cycle. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2024, 30, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Li, Z.; Xie, T.; Feng, J.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, X. Effects of sous-vide on quality, structure and flavor characteristics of tilapia fillets. Molecules 2023, 28, 8075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Huang, F.; Li, X.; Han, D.; Zhao, L.; Liang, H.; Rui, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C. Water status evolution of pork blocks at different cooking procedures: A two-dimensional LF-NMR T(1)-T(2) relaxation study. Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Covalent chemical modification of myofibrillar proteins to improve their gelation properties: A systematic review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 924–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Huang, Y.; Gu, X.; Meng, Z. Spirulina platensis protein-based emulsion gel as fat substitute in meat analogs: Evaluation performance across post-processing. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.L.; Feng, Y.; Xu, Y.X.; Yi, S.M.; Li, X.P.; Bu, Y.; Li, J.R. Changes in quality and flavor characteristics of sea bass muscle during steaming. Food Chem. 2021, 42, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Du, D.; Xu, Y. Dynamic changes of tenderness, moisture and protein in marinated chicken: The effect of different steaming temperatures. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 12, 7668–7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gu, Q.; Huang, M.; Guo, Z.; Zuo, H.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L. The impact of different cooking temperatures on the quality and moisture distribution of beef. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2025, 104, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Peng, H.; Chen, Q.; Jiao, X.; Jia, J.; Pan, Z.; Cheng, J.; Wang, L. Effects of cooking processes on protein nutritional values and volatile flavor substances of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix). Foods 2023, 12, 3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Xue, G.; Liu, Y.; Ye, B.; Li, M.; Xu, Q. Optimization of the vacuum microwave drying of tilapia fillets using response surface analysis. Foods 2025, 14, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.X.; Li, D.Y.; Shen, M.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, Z.W.; Liu, Y.X.; Bai, Y.H.; Zhou, D.Y. Effect of different sous-vide cooking conditions on textural properties, protein physiochemical properties and microstructure of scallop (Argopecten irradians) adductor muscle. Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combes, S.; Lepetit, J.; Darche, B.; Lebas, F. Effect of cooking temperature and cooking time on Warner-Bratzler tenderness measurement and collagen content in rabbit meat. Meat Sci. 2004, 66, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Huang, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, Q.; Bai, W. Effects of Different Cooking Methods on the Physicochemical Properties and Taste Quality of Mud Carp. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 49, 114–122. [Google Scholar]
- Thiansilakul, Y.; Benjakul, S.; Richards, M.P. Isolation, characterisation and stability of myoglobin from Eastern little tuna (Euthynnus affinis) dark muscle. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhao, W.; Ma, J.; Fan, X.; Liu, Z.; Dong, X. Modifying yellowfin tuna myofibrillar proteins under ultra-high pressure auxiliary heat treatment: Impact on the conformation, gel properties and digestive characteristics. Food Chem. 2025, 475, 143365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Shahidi, F.; Heu, M.S. Characteristics of salt-fermented sauces from shrimp processing byproducts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, M.; Xie, J.; Zhao, M.; Hou, L.; Liang, J.; Wang, S.; Cheng, J. Volatile flavor constituents in the pork broth of black-pig. Food Chem. 2017, 226, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wu, J.; Qiu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Lin, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Evaluation of edible quality and processing suitability of segmented products from silver carp under different thermal processing methods. Food Res. Int. 2025, 201, 115623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felisiak, K.; Szymczak, M. Use of rapid capillary zone electrophoresis to determine amino acids indicators of herring ripening during salting. Foods 2021, 10, 2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, L.; Verneuil, B.; Wallach, J.; Julien, R. Purification and characterization of an alkaline elastase from Myxococcus xanthus. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 223, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Shi, W.; Zhou, S.; Qu, Y.; Wang, Z. Research on the changes of water-soluble flavor substances in grass carp during steaming. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tan, J.; He, J.; Hu, Q.; Li, J.; Xie, J. Effect of lysine on the cysteine-xylose Maillard reaction to form flavor compounds. Food Chem. 2025, 469, 142529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.X.; Zhang, X.; Fu, B.F.; Qiao, X.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Xu, X.B.; Cheng, S.Z.; Du, M. Impact of cooking processes on volatile flavor compounds and free amino acids in fish sauce. Foods 2025, 14, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, M.; Tomassini Barbarossa, I.T. Taste perception of sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami and changes due to l-arginine supplementation, as a function of genetic ability to taste 6-n-Propylthiouracil. Nutrients 2017, 9, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.W.; Zhang, M. Non-volatile taste active compounds in the meat of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.F.; Feng, L.; Jiang, W.D.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y.; Tang, L.; Li, S.W.; Zhong, C.B.; Zhou, X.Q. Exploring the dietary strategies of phenylalanine: Improving muscle nutraceutical quality as well as muscle glycogen and protein deposition in adult grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Ren, S.; Shen, Q.; Ye, X.; Chen, J.; Ling, J. Protein oxidation and proteolysis during roasting and in vitro digestion of fish (Acipenser gueldenstaedtii). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 5344–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, J.; Pei, Z.; Wei, P.; Xiang, D.; Cao, X.; Shen, X.; Li, C. Volatile flavour components and the mechanisms underlying their production in golden pompano (Trachinotus blochii) fillets subjected to different drying methods: A comparative study using an electronic nose, an electronic tongue and SDE-GC-MS. Food Res. Int. 2019, 123, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.T.; Wu, J.N.; Lu, H.X.; Liu, Z.Y.; Chen, Y.H. Optimization of Base Seasoning Preparation from Decapterus maruadsi Based on Electronic Nose and Electronic Tongue. Food Chem. 2018, 39, 282–289. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, F.; Guo, Y.; Mao, N.; Ding, Q.; Gao, J.; Sang, Y.; Tian, G. Steam explosion treatment for improving the quality of Xuehua pear soup: Components profile, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity in vitro, its flavor and metabolomics study. Food Chem. 2025, 471, 142863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, X. Effect of Aroma-improving Processing on Aroma Characteristics of Black Tea Based on Electronic Nose Analysis, Food Industry. Sci. Technol. 2019, 40, 234–237, 242. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Lei, Y.; Huang, S.; Huang, M. Effect of ageing time on the flavour compounds in Nanjing water-boiled salted duck detected by HS-GC-IMS. LWT 2022, 155, 112870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Z.; Mowafy, S.; Liu, Y. Comparative analyses of five drying techniques on drying attributes, physicochemical aspects, and flavor components of Amomum villosum fruits. LWT 2022, 154, 112879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, P.; Qi, L.; Lin, S. Identification of changes in volatile compounds in sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus during seasonings soaking using HS-GC-IMS. LWT 2022, 154, 112695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Cheng, K.; He, J.; Jin, W. Changes in Volatile Components during the Steaming Process of Giant Salamander Tails Analyzed by Gas Chromatography-Ion Mobility Spectrometry and Chemometrics. Meat Res. 2023, 37, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Al-Dalali, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, J.; He, Z. Effect of different processing steps in the production of beer fish on volatile flavor profile and their precursors determined by HS-GC-IMS, HPLC, E-nose, and E-tongue. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Baker, S.M.; Goodrich-Schneider, R.M.; Montazeri, N.; Sarnoski, P.J. Aroma profile characterization of Mahi-Mahi and tuna for determining spoilage using purge and trap gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siewe, F.B.; Kudre, T.G.; Bettadaiah, B.K.; Narayan, B. Effects of ultrasound-assisted heating on aroma profile, peptide structure, peptide molecular weight, antioxidant activities and sensory characteristics of natural fish flavouring. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 65, 105055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Lv, Y.; Wen, R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Characterization of selected Harbin red sausages on the basis of their flavour profiles using HS-SPME-GC/MS combined with electronic nose and electronic tongue. Meat Sci. 2021, 172, 108345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Shang, S.; Fu, B.; Wang, L.; Dong, X.; Jiang, P. Ready-to-eat fish cake processing methods and the impacts on quality and flavor. Foods 2022, 11, 3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yang, X.; Hong, P.; Liu, M.; Li, Z.; Zhou, C.; Zhong, S.; Liu, S. GC-MS. GC-MS, GC-IMS, and E-nose analysis of volatile aroma compounds in wet-marinated fermented golden pomfret prepared using different cooking methods. Foods 2024, 13, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Array Number | Sensor Name | Representative Substance Categories | Performance Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | W1C | Aromatic | Aromatic constituents, benzene |
| 2 | W5S | Broadrange | High sensitivity and sensitive to nitrogen oxides |
| 3 | W3C | Aromatic | Sensitive aroma, ammonia |
| 4 | W6S | Hydrogen | Mainly selective for hydrides |
| 5 | W5C | Arom-aliph | Short-chain alkane aromatic component |
| 6 | W1S | Broad-methane | Sensitive to methyl |
| 7 | W1W | Sulphur-organic | Sensitive to sulfides |
| 8 | W2S | Broad-alcohol | Sensitive to alcohols, aldehydes and ketones |
| 9 | W2W | Sulph-chlor | Aromatic ingredients, sensitive to organic sulfides |
| 10 | W3S | Methane-aliph | Sensitive to long-chain alkanes |
| Time | E1 (Drift Gas Flow Rate) | E2 (Carrier Gas Flow Rate) | R (Data Acquisition) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 00:00,000 | 75.0 mL/min | 2.0 mL/min | recording |
| 02:00,000 | 75.0 mL/min | 2.0 mL/min | - |
| 10:00,000 | 75.0 mL/min | 10.0 mL/min | - |
| 20:00,000 | 75.0 mL/min | 100.0 mL/min | - |
| 40:00,000 | 75.0 mL/min | 100.0 mL/min | stop |
| Scores | Tissue Morphology (10%) | Color (10%) | Odor (20%) | Taste (30%) | Chewiness (30%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17–20 | Maintaining the original morphology of the fish meat with a uniform and compact tissue structure | Bright and uniform color | Distinct steamed fish aroma, free from fishy or rancid odors | Strong umami characteristic of T. flavidus, free from bitter or fishy odors | Significant meat elasticity and chewiness, no sense of crumbling |
| 13–16 | The original morphology of the fish meat is preserved, with a relatively compact tissue structure | Bright color with good appearance | Fresh steamed aroma, free from fishy or rancid odors | Distinct umami characteristic of T. flavidus, free from bitter or fishy odors | Noticeable meat elasticity with moderate chewiness, no sense of crumbling |
| 9–12 | The morphology is slightly loose, with moderate uniformity and compactness of the tissue | Dull color with a slightly grayish-white appearance | Moderate aroma with slight fishy or rancid odors | Moderate umami characteristic of T. flavidus, with slight bitter or fishy odors | Moderate meat elasticity and chewiness, with a slight sense of crumbling |
| 5–8 | The morphology is loose, with poor tissue uniformity | Dull color with a distinctly grayish-white appearance | Weak aroma with noticeable fishy or rancid odors | Weak umami characteristic of T. flavidus, with noticeable bitter or fishy odors | Poor elasticity and chewiness, loose texture with a sense of crumbling |
| 1–4 | The integrity of the morphology cannot be maintained, and the tissue exhibits significant fragmentation | Uneven and grayish color with dark gray or black spots | Almost no aroma, with prominent fishy or rancid odors | No umami characteristic of T. flavidus, with prominent bitter or fishy odors | Low elasticity, loose texture, and a pronounced sense of crumbling |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, B.; Qu, Y.; Tang, H.; Wu, R.; Qiao, K.; Su, Y.; Pan, N.; Chen, T.; et al. Impact of Steam Processing on the Physicochemical Properties and Flavor Profile of Takifugu flavidus: A Comprehensive Quality Evaluation. Foods 2025, 14, 1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091537
Liu Z, Chen X, Chen B, Qu Y, Tang H, Wu R, Qiao K, Su Y, Pan N, Chen T, et al. Impact of Steam Processing on the Physicochemical Properties and Flavor Profile of Takifugu flavidus: A Comprehensive Quality Evaluation. Foods. 2025; 14(9):1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091537
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhihui, Xiaoting Chen, Bei Chen, Yinghong Qu, Haiyan Tang, Ruowen Wu, Kun Qiao, Yongchang Su, Nan Pan, Tingru Chen, and et al. 2025. "Impact of Steam Processing on the Physicochemical Properties and Flavor Profile of Takifugu flavidus: A Comprehensive Quality Evaluation" Foods 14, no. 9: 1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091537
APA StyleLiu, Z., Chen, X., Chen, B., Qu, Y., Tang, H., Wu, R., Qiao, K., Su, Y., Pan, N., Chen, T., Shi, W., & Liu, Z. (2025). Impact of Steam Processing on the Physicochemical Properties and Flavor Profile of Takifugu flavidus: A Comprehensive Quality Evaluation. Foods, 14(9), 1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091537






