A Novel Cystatin Gene from Sea Cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus): Characterization and Comparative Expression with Cathepsin L During Early Stage of Hypoxic Exposure-Induced Autolysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animal and Hypoxia Exposure Experiment
2.2. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis for Cloning of SjCyt
2.3. Bioinformatic and Phylogenetic Analyses
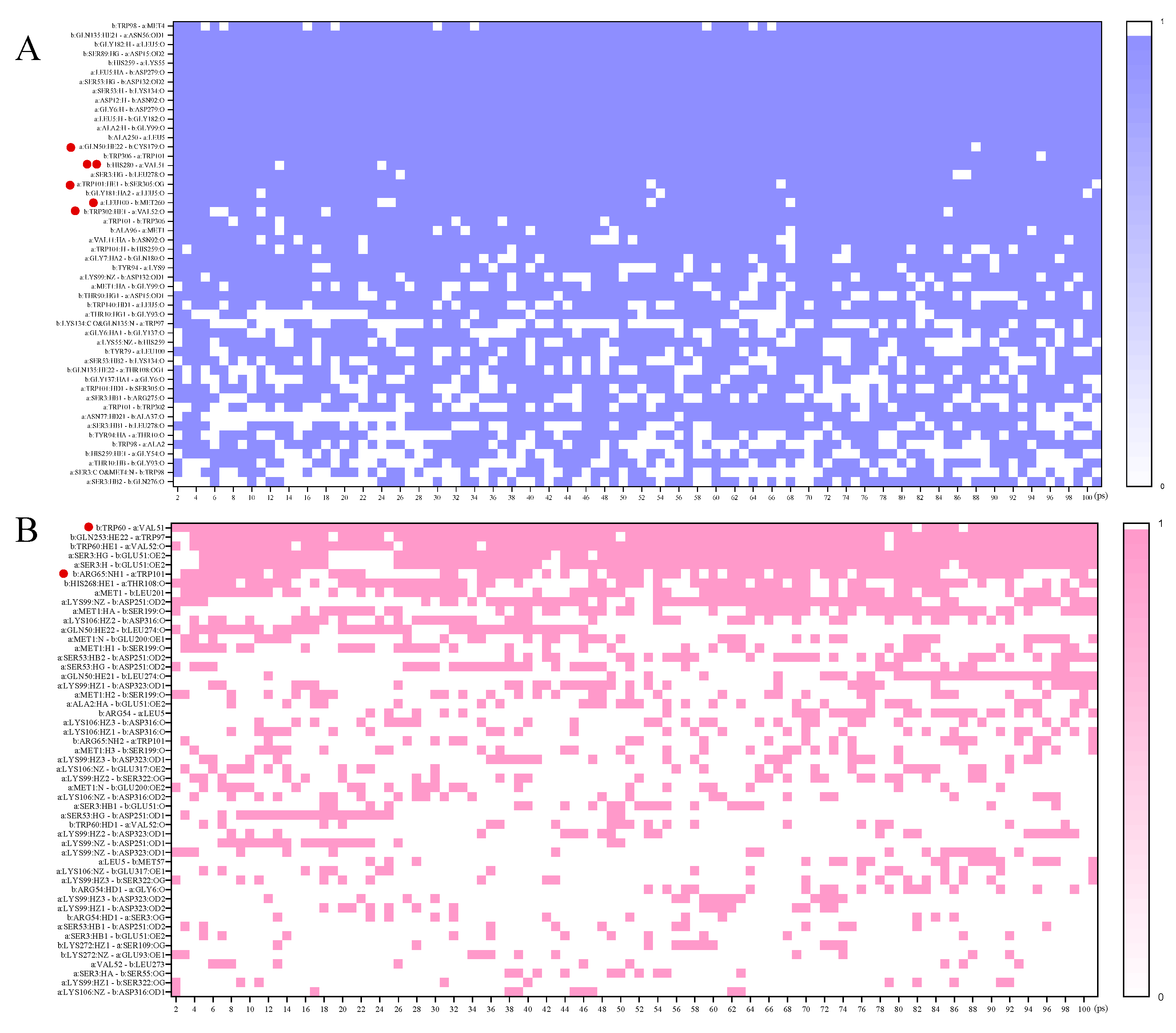
2.4. Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Free Energy Calculation
2.5. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.6. Western Blotting
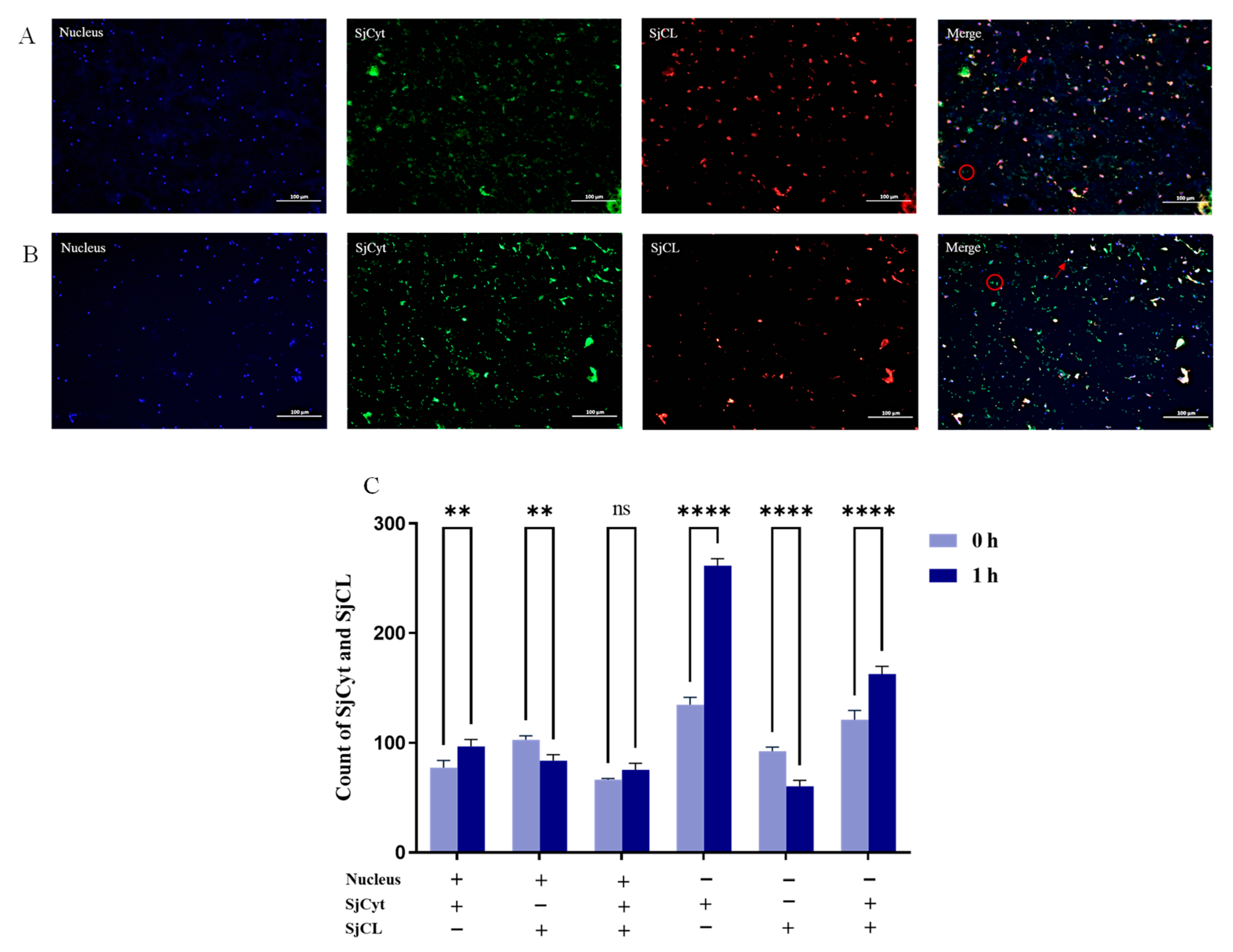
2.7. Double-Label Immunofluorescence Assays
2.8. Expression and Purification of Recombinant SjCyt (rSjCyt)
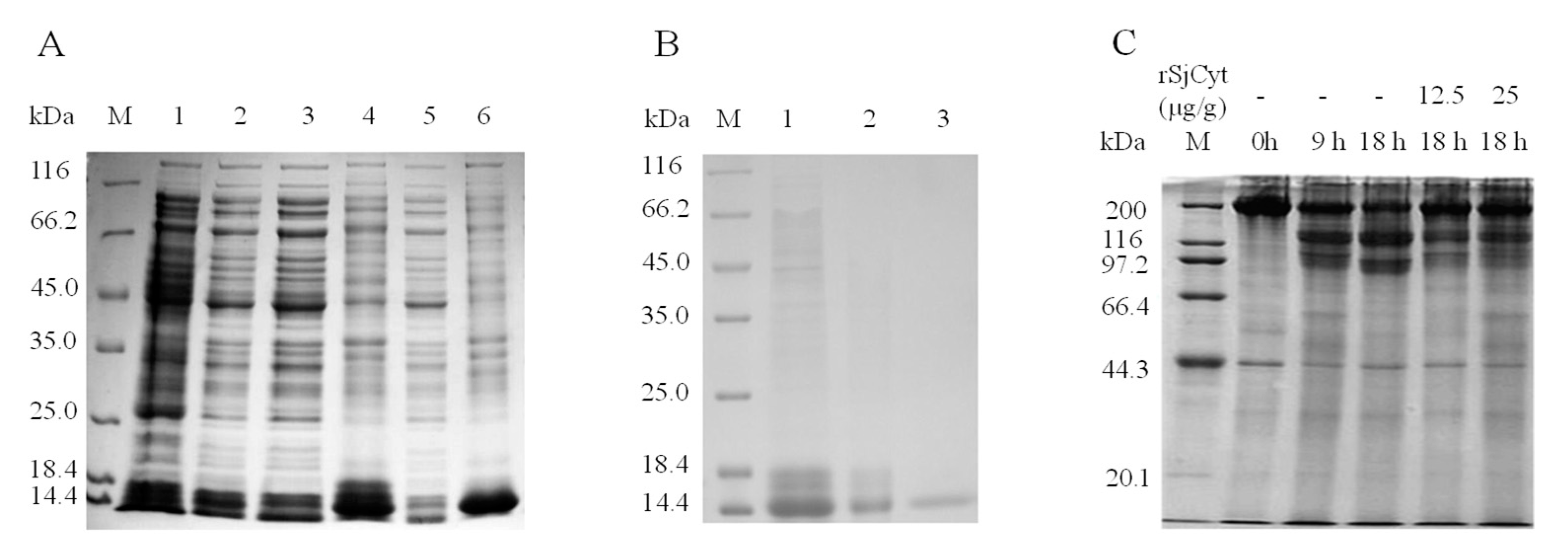
2.9. Effect of Recombinant SjCyt on Autolysis in Sea Cucumber by SDS-PAGE
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Bioinformatic Analysis of SjCyt
3.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
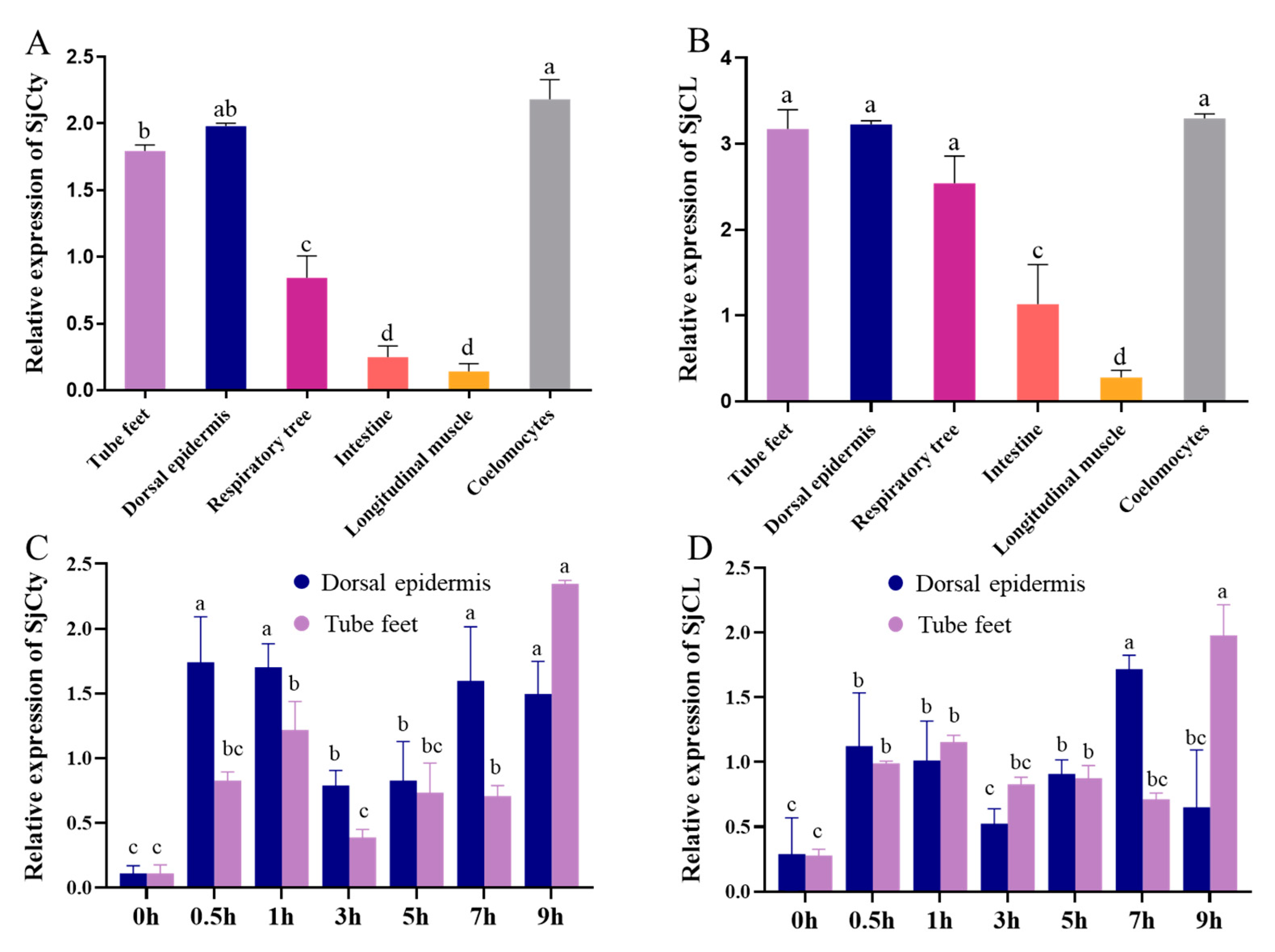
3.3. Tissue Distribution of SjCyt and SjCL
3.4. Temporal Expression of SjCyt and SjCL
3.5. Distribution of SjCyt and SjCL in the Dorsum
3.6. Overexpression, Purification, and Activity Validation of Recombinant SjCyt
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, H.T.; Li, D.M.; Zhu, B.W.; Sun, J.J.; Zheng, J.; Wang, F.L.; Kunihiko, K.; Jiang, X. Proteolysis of noncollagenous proteins in sea cucumber, Stichopus japonicus, body wall: Characterisation and the effects of cysteine protease inhibitors. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.X.; Zhou, D.Y.; Ma, D.D.; Liu, Y.F.; Li, D.M.; Dong, X.P.; Tan, M.Q.; Du, M.; Zhu, B.W. Changes in collagenous tissue microstructures and distributions of cathepsin L in body wall of autolytic sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicus). Food Chem. 2016, 212, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Tuo, F.Y.; Song, L.; Liu, Y.X.; Dong, X.P.; Li, D.M.; Zhou, D.Y.; Shahidi, F. Action of trypsin on structural changes of collagen fibres from sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicus). Food Chem. 2018, 256, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhou, D.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Dong, X.P.; Li, D.M.; Shahidi, F. The role of matrix metalloprotease (MMP) to the autolysis of sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicus). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 5752–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magister, S.; Kos, J. Cystatins in Immune System. J. Cancer. 2013, 4, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.; Zhang, S.R.; Zhong, P.T.; Zhu, Z.T.; Chen, Y.P.; Huang, W.Y.; Wang, W. Serum cystatin C for risk stratification of prediabetes and diabetes populations. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2023, 17, 102882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Lin, Y.; He, Z.Y.; Li, J.; Xiang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z.N. Dual roles of cystatin A in the immune defense of the pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 75, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, P.; Kwon, H.; Elvitigala, D.; Wan, Q.; Lee, J. Identification and characterization of cystatin B from black rockfish, Sebastes schlegelii, indicating its potent immunological importance. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 104, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genetics, K.; Breeding, M. Molecular characterization, expression and immune functions of cystatin B in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 81, 463–469. [Google Scholar]
- Kavindi, K.Y.; Liyanage, D.S.; Omeka, W.K.M.; Hyukjae, H.; Don, H.S.; Jehee, L. Molecular characterization, expression, and functional analysis of cystatin B in the big–belly seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis). Fish shellfish Immunol. 2022, 124, 442–453. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Wang, X.B. Molecular characterization, expression and functional analysis of cystatin C in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 86, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.; Case, D. Development and testing of a general amber force field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamoureux, G.; Harder, E.; Vorobyov, I.; Roux, B.; MacKerell, A., Jr. A polarizable model of water for molecular dynamics simulations of biomolecules. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2016, 418, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennberg, C.; Murtola, T.; Pall, S. Direct-space corrections enable fast and accurate lorentz-berthelot combination rule lennard-jones lattice summation. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 5737–5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouamrane, S.; Khaldan, A.; Hajji, H.; El-Mernissi, R.; Alaqarbeh, M.; Alsakhen, N.; Maghat, H.; Ajana, M.A.; Sbai, A.; Bouachrine, M.; et al. In silico identification of 1, 2, 4–triazoles as potential Candida Albicans inhibitors using 3D–QSAR, molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations, and ADMET profiling. Mol. Divers. 2023, 27, 2111–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mernissi, R.; Khaldan, A.; Bouamrane, S.; Rehman, H.M.; Alaqarbeh, M.; Ajana, M.A.; Lakhlifi, T.; Bouachrine, M. 3D-QSAR, molecular docking, simulation dynamic and ADMET studies on new quinolines derivatives against colorectal carcinoma activity. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2024, 42, 3682–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.Y. Molecular modeling and molecular dynamics simulation studies on the selective binding mechanism of MTHFD2 inhibi tors. Comput. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Z.; Cun, S.J.; Peng, L.S.; Xie, X.J.; Wei, H.Y.; Yang, W.L.; Xu, A.L. cDNA cloning, identification and characterization of a novel cystatin from the tentacle of Cyanea capillata. Biochimie. 2003, 85, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzonka, Z.; Jankowska, E.; Kasprzykowski, F.; Kasprzykowska, R.; Łankiewicz, L.; Wiczk, W.; Wieczerzak, E.; Ciarkowski, J.; Drabik, P.; Janowski, R.; et al. Structural studies of cysteine proteases and their inhibitors. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2001, 48, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.M.; Zhu, B.W.; Wu, H.T.; Yu, L.; Zhou, D.Y.; Dong, X.P.; Yang, J.F.; Li, D.M.; Ye, W.X.; Murata, Y. Purification and characterization of cathepsin B from the gut of the sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicus). Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 20, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.W.; Liu, H.; Zheng, G.; Xiang, X.W.; Lv, Z.M.; Wang, T.M. Cathepsin L of the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus–molecular characterization and transcriptional response to Vibrio splendidus infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 49, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.Y.; Chang, X.N.; Bao, S.S.; Song, L.; Zhu, B.W.; Dong, X.P.; Zong, Y.; Li, D.M.; Zhang, M.M.; Liu, Y.X. Purification and partial characterisation of a cathepsin L-like proteinase from sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicus) and its tissue distribution in body wall. Food Chem. 2014, 158, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.F.; Guo, J.; Lian, J.Q.; Gao, F.; Khan, A.J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, F. Molecular simulation study on the interaction between tyrosinase and flavonoids from sea buckthorn. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 21579–21585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, N.; Singh, A.; Shuaib, M. Drug resistance mechanism of m46i-mutation-induced saquinavir resistance in HIV-1 protease using molecular dynamics simulation and binding energy calculation. Viruses 2022, 14, 697–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.N.; Guo, X.K.; Tang, Y.; Li, A.T.; Zhu, Z.M.; Chai, X.Q.; Duan, X.H.; Wu, H.T. Contribution of cathepsin L to autolysis of sea cucumber Stichopus japonicus intestines. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2019, 28, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, V.; Stoka, V.; Vasiljeva, O.; Renko, M.; Sun, T.; Turk, B.; Turk, D. Cysteine cathepsins: From structure, function and regulation to new frontiers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2011, 1824, 68–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulet, B.; Baruch, A.; Moon, N.S.; Poirier, M.; Sansregret, L.L.; Erickson, A.; Nepveu, A. A cathepsin L isoform that is devoid of a signal peptide localizes to the nucleus in S phase and processes the CDP/Cux transcription factor. Mol. Cell 2004, 14, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripti, T.; Rukshala, L.; Lu, S.; Gunhild, M.M.; Mads, H.H.; Klaudia, B. Nuclear cathepsin L activity is required for cell cycle progression of colorectal carcinoma cells. Biochimie 2016, 122, 208–218. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.F.; He, B.Y.; Jiang, D.; Yu, C.X.; Zhu, B.W.; Qi, H. Proteome analysis reveals the important roles of protease during tenderization of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus using Itraq. Food Res. Int. 2020, 131, 108632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.H.; Yan, T.T.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, Y.M.; Yang, J.F. Signaling transduction network elucidation of ACE 2 regulating Apostichopus japonicus autolysis by using integrative TMT proteomics and transcriptomics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 2197–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Tan, X.Q.; Li, S.H.; Jin, Y.; Li, S.; Li, S.L.; Takala, T.M.; Saris, P.E.J. Cloning, expression, characterization, and tissue distribution of cystatin C from silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 5144–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodagoda, Y.K.; Liyanage, D.S.; Omeka, W.K.M.; Kim, G.; Kim, J.; Lee, J. Identification, expression profiling, and functional characterization of cystatin C from big-belly seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 138, 108804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Wang, J.; Mao, Y.; Liu, M.; Song, X.H.; Su, Y.Q.; Wang, C.Z.; Zheng, Z.P. Identification and molecular characterization of Cathepsin L gene and its expression analysis during early ontogenetic development of kuruma shrimp Marsupenaeus japonicus. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2017, 36, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.H.; Sun, B.G. Identification, mRNA expression profiling and activity characterization of cathepsin L from red drum (Sciaenops ocellatus). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 41, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar]
- Nakano, H.; Murabe, N.; Amemiya, S.; Nakajima, Y. Nervous system development of the sea cucumber Stichopus japonicus. Dev. Biol. 2006, 292, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashanov, V.S.; Zueva, O.R.; Heinzeller, T.; Aschauer, B.; Naumann, W.W.; Grondona, J.M.; Garcia–Arraras, J.E. The central nervous system of sea cucumbers (Echinodermata: Holothuroidea) shows positive immunostaining for a chordate glial secretion. Front. Zool. 2009, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Fan, X.; Li, Z.; Guo, L.; Ren, Y.; Li, Q. Comparative analysis for immune response of coelomic fluid from coelom and polian vesicle in Apostichopus japonicus to Vibrio splendidus infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 4, 100074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ton, C.; Stamatiou, D.; Liew, C.C. Gene expression profile of zebrafish exposed to hypoxia during development. Physiol. Genom. 2003, 13, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohindra, V.; Tripathi, R.K.; Singh, A.; Singh, B.J. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of a novel cystatin–like gene in a hypoxia–tolerant Indian catfish, Clarias batrachus [Linnaeus, 1758]. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.J.; Bak, H.J.; Park, J.H. Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) Cystatin C: Cloning, mRNA Expression, and Enzymatic Characterization of Olive Flounder Cystatin C. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 170, 1216–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Gai, X.; Wang, L.; Song, L.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, L.; Wang, M.; Siva, V.S. Identification and characterization of a cystatin gene from Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Liang, S.Y.; Nian, R.; Li, H.; Li, P.; Qu, Y.F.; Wu, T.; Meng, Q.G.; Ji, X. Molecular cloning and characterization of the cathepsin L gene in Pelodiscus sinensis and its expression in response to bacterial challenge. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 3071–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.R.; Hong, Y.H.; Ye, C.C.; Deng, H.L.; Yuan, J.P.; Hao, Y.F.; Wang, J.H. Molecular characterization and gene expression of cathepsin L in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 67, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlame, S.; Pauline, G.; Anne–Christine, L.; Lise, V.; Aurélie, F.; Pauline, V.; Geneviève, F.; Rodrigo, G.; Catherine, S.; Fabrice, L.; et al. Upregulation of gut cathepsin L during Eimeria tenella infection. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 140, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- De Sousa Abreu, R.; Penalva, L.O.; Marcotte, E.M.; Vogel, C. Global signatures of protein and mRNA expression levels. Mol. Biosyst. 2009, 5, 1512–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.F.; Qi, H.; Feng, D.D.; He, B.Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Yu, C.X.; Zhu, B.W. Oxidative stress involved in textural changes of sea cucumber Stichopus japonicus body wall during low-temperature treatment. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 2646–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilder, C.L.; Walton, C.; Watson, V.; Stewart, F.A.A.; Johnson, J.; Peyton, S.R.; Payne, C.K.; Odero-Marah, V.; Platt, M.O. Differential cathepsin responses to inhibitor-induced feedback: E–64 and cystatin C elevate active cathepsin S and suppress active cathepsin L in breast cancer cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 79, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caglic, D.; Pungercar, J.R.; Pejler, G.; Turk, V.; Turk, B. Glycosaminoglycans facilitate procathepsin B activation through disruption of propeptide–mature enzyme interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 33076–33085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, T.; Cimerman, N.; Dolenc, I.; Ritonja, A.; Brzin, J. Cathepsin L is capable of truncating cystatin C of 11 N-terminal amino acids. FEBS Lett. 1999, 455, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, P.J.; Storer, A.C. Local pH-dependent conformational changes leading to proteolytic susceptibility of cystatin C. Biochem. J. 1994, 302, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
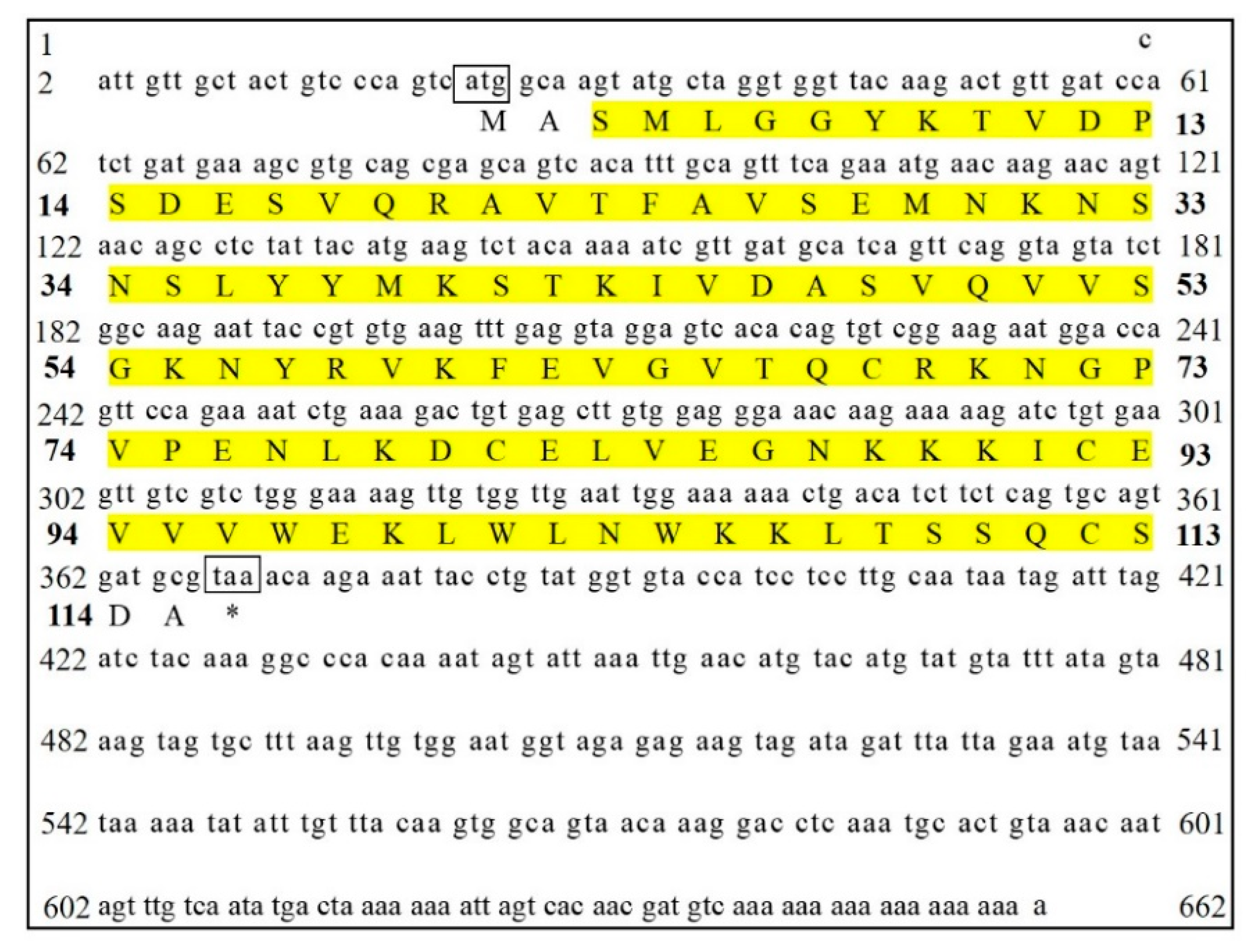
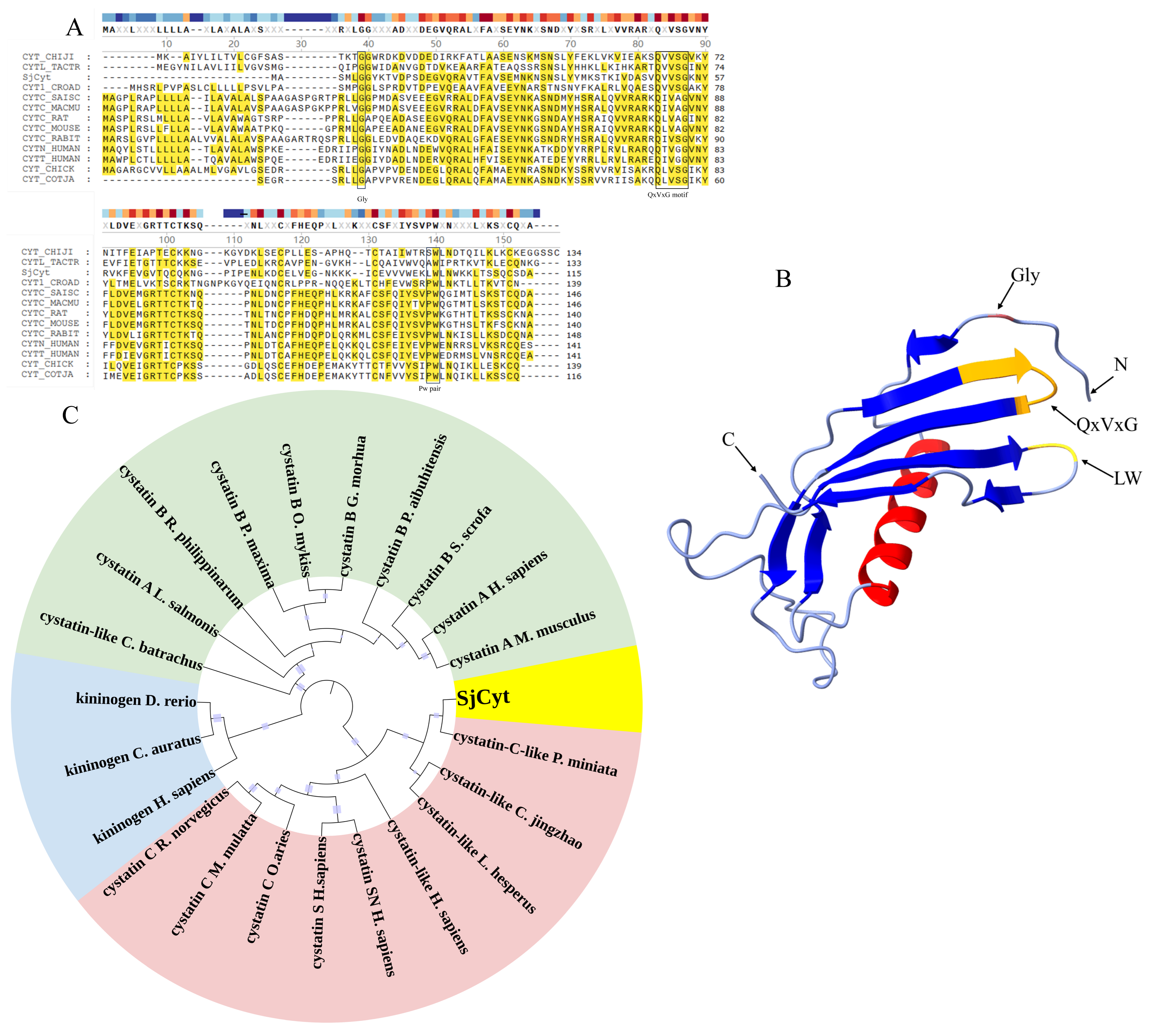

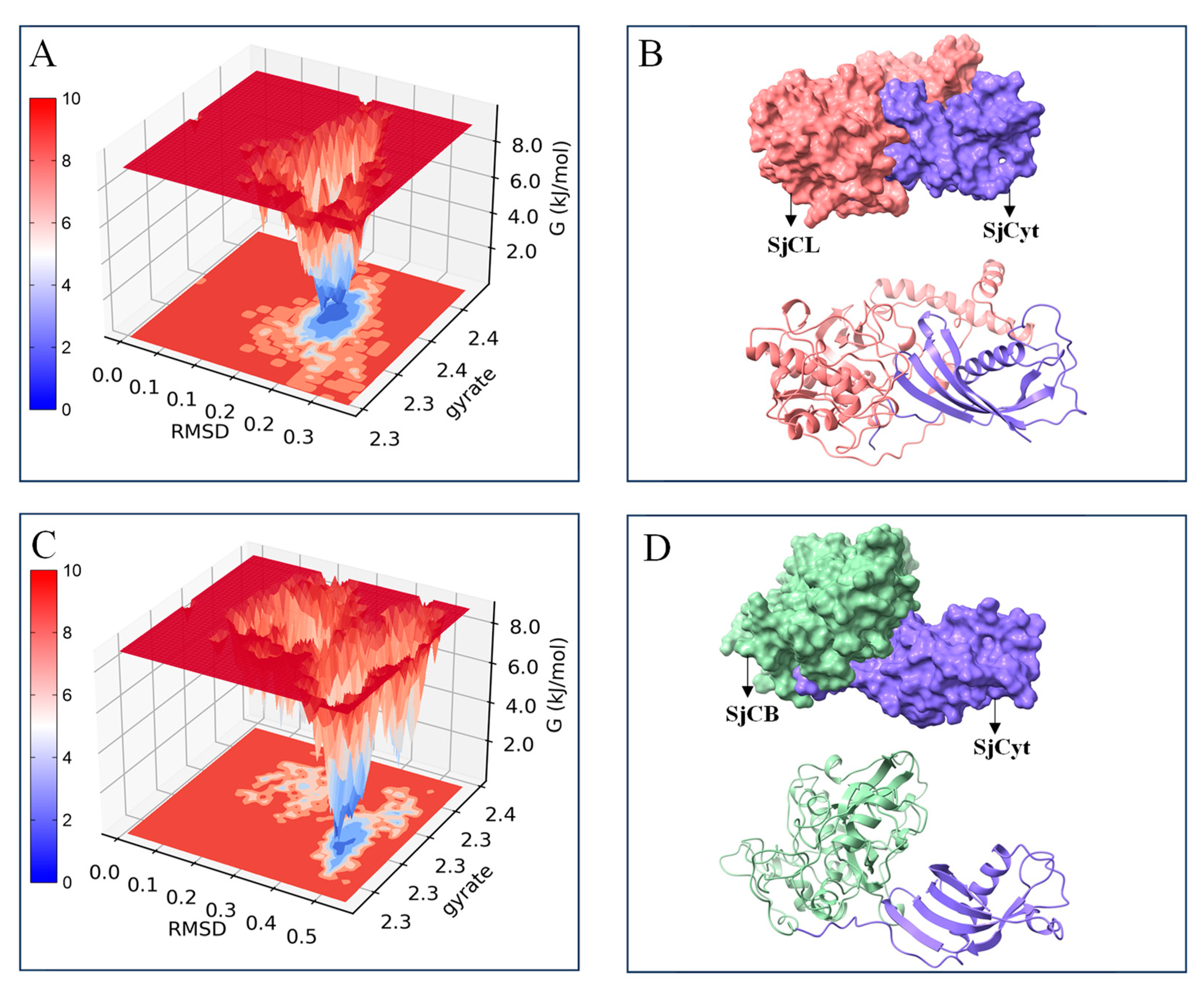
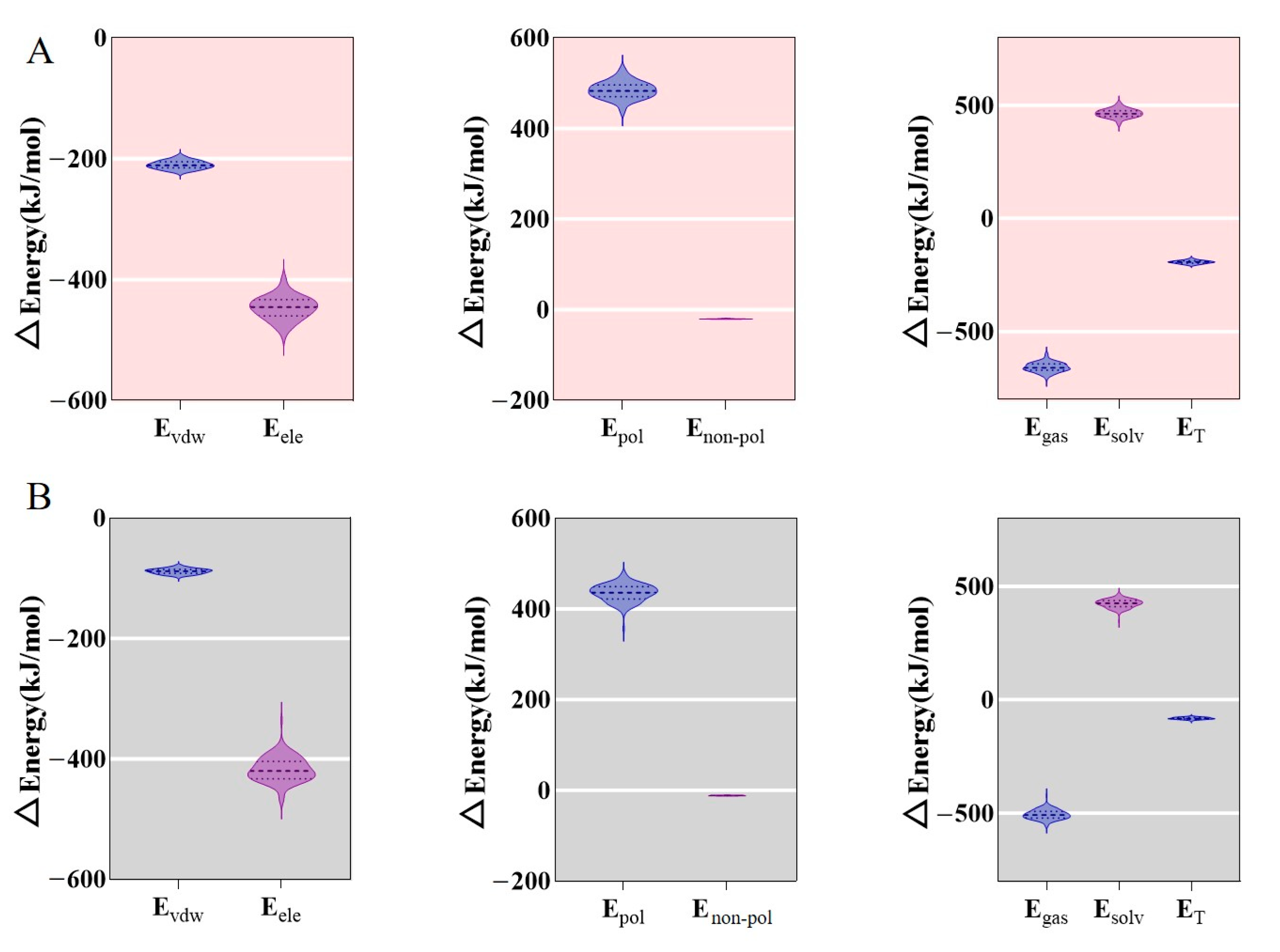

| Name | GenBank | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Purpose | Tm (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SjCyt–F | / | TGCTACTGTCCCAGTCATGG | Homologous cloning | / |
| SjCyt–R | TAATACTATTTTGTGGGCCTTTG | |||
| SjCyt–O | / | GTTGTCGTCTGGGAAAAGTTGTG | 3′RACE | / |
| SjCyt–I | GATGCGTAAACAAGAAATTACCTGT | |||
| SjCyt–RTF | KR872411 | GTGAAGTTGTCGTCTGGGAAAAG | Real-time PCR | 79 |
| SjCyt–RTR | AGGAGGATGGTACACCATACAGG | |||
| SjCL–RTF | EU143709 | GCCAGCCACGAGTCTTTCCAA | Real-time PCR | 85 |
| SjCL–RTR | CGATCCAGTAATCACCACCCACAG | |||
| Cytochrome–RTF | FJ594967 | TGAGCCGCAACAGTAATC | Real-time PCR | 80 |
| Cytochrome–RTR | AAGGGAAAAGGAAGTGAAAG |
| Abbreviation | Species | Accession No. |
|---|---|---|
| CYT_CHIJI | Chilobrachysguangxiensis | B1P1J3 |
| CYTL_TACTR | Tachypleustridentatus | Q7M429 |
| CYTC_MACMU | Macaca mulatta | O19092 |
| CYTC_SAISC | Saimiri sciureus | O19093 |
| CYTC_RAT | Rattus norvegicus | P14841 |
| CYTC_MOUSE | Mus musculus | P21460 |
| CYTN_HUMAN | Homo sapiens | P01037 |
| CYT_CHICK | Gallus gallus | P01038 |
| CYT1_CROAD | Crotalus adamanteus | J3RYX9 |
| CYT_COTJA | Coturnix japonica | P81061 |
| CYTC_RABIT | Oryctolagus cuniculus | O97862 |
| CYTT_HUMAN | Homo sapiens | P09228 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, S.; Zhang, R.; Ma, S.; Zhao, T.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, L.; Liu, C.; Sun, L.; Du, M. A Novel Cystatin Gene from Sea Cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus): Characterization and Comparative Expression with Cathepsin L During Early Stage of Hypoxic Exposure-Induced Autolysis. Foods 2025, 14, 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081404
Yao S, Zhang R, Ma S, Zhao T, Liu Q, Zhu L, Liu C, Sun L, Du M. A Novel Cystatin Gene from Sea Cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus): Characterization and Comparative Expression with Cathepsin L During Early Stage of Hypoxic Exposure-Induced Autolysis. Foods. 2025; 14(8):1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081404
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Siyu, Rui Zhang, Siyuan Ma, Ting Zhao, Qinhao Liu, Lin Zhu, Chang Liu, Liming Sun, and Ming Du. 2025. "A Novel Cystatin Gene from Sea Cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus): Characterization and Comparative Expression with Cathepsin L During Early Stage of Hypoxic Exposure-Induced Autolysis" Foods 14, no. 8: 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081404
APA StyleYao, S., Zhang, R., Ma, S., Zhao, T., Liu, Q., Zhu, L., Liu, C., Sun, L., & Du, M. (2025). A Novel Cystatin Gene from Sea Cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus): Characterization and Comparative Expression with Cathepsin L During Early Stage of Hypoxic Exposure-Induced Autolysis. Foods, 14(8), 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081404






