Decoding Light-Spreading Intensity Effects on the Sensory Quality and Volatile Compounds of Green Tea: An Integrated GC-E-Nose and Targeted Metabolomics Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Tea Samples
2.3. Sensory Evaluation
2.4. GC-E-Nose Analysis
2.5. HS-SPME Coupled to GC-MS/MS Analysis
2.6. Odor Activity Value (OAV) Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sensory Evaluation Analysis on Tea Samples Exposed to YLDI
3.2. Analysis of the Effects of YLDI on the Volatile Fingerprints of Green Tea Using GC-E-Nose
3.3. Analysis of the Effects of YLDI on the Volatile Compounds of Green Tea Using GC-MS/MS
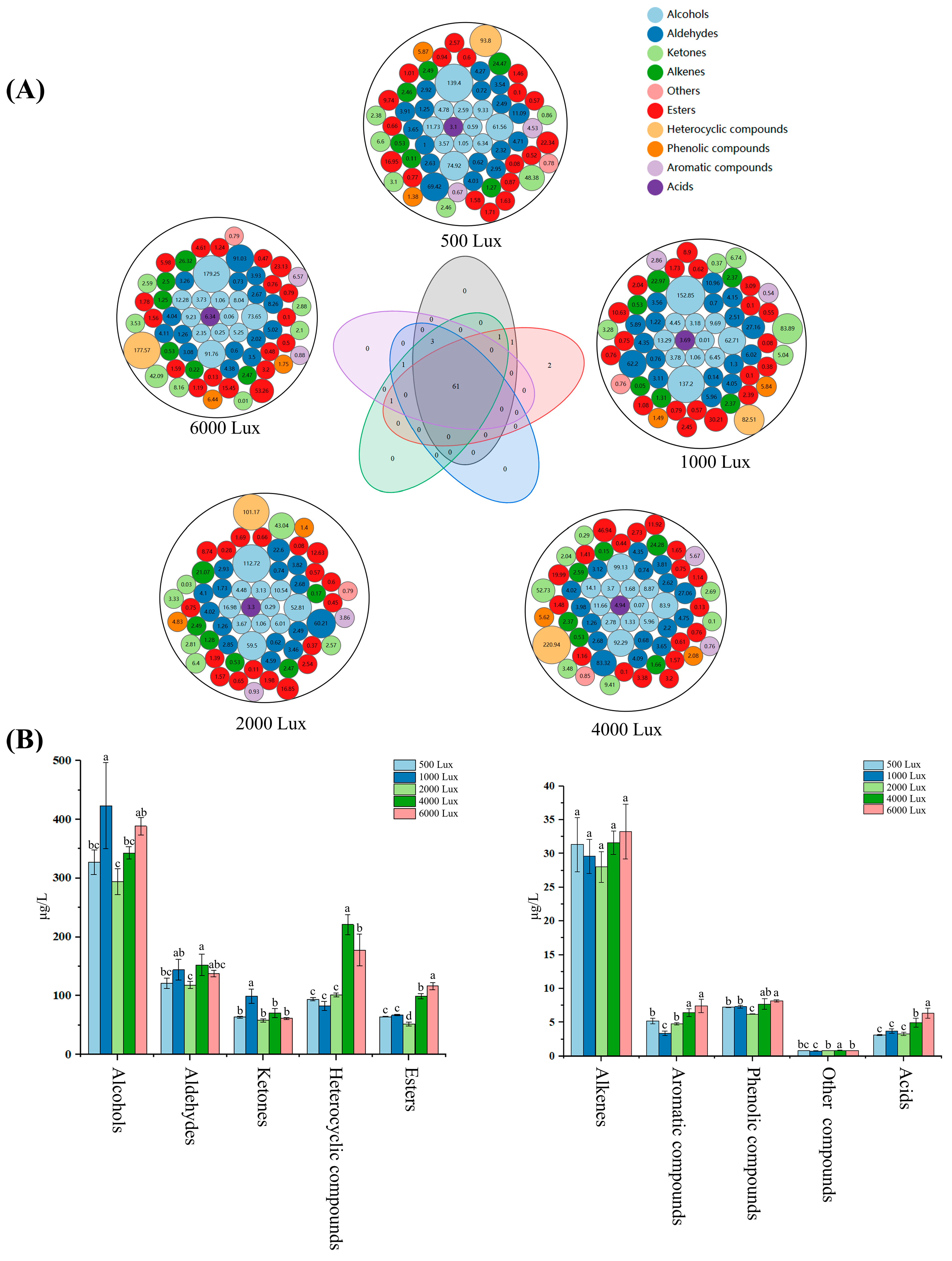
3.3.1. Comparative Analysis of the Volatile Compounds in Tea Samples
3.3.2. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
3.3.3. OAV Analysis
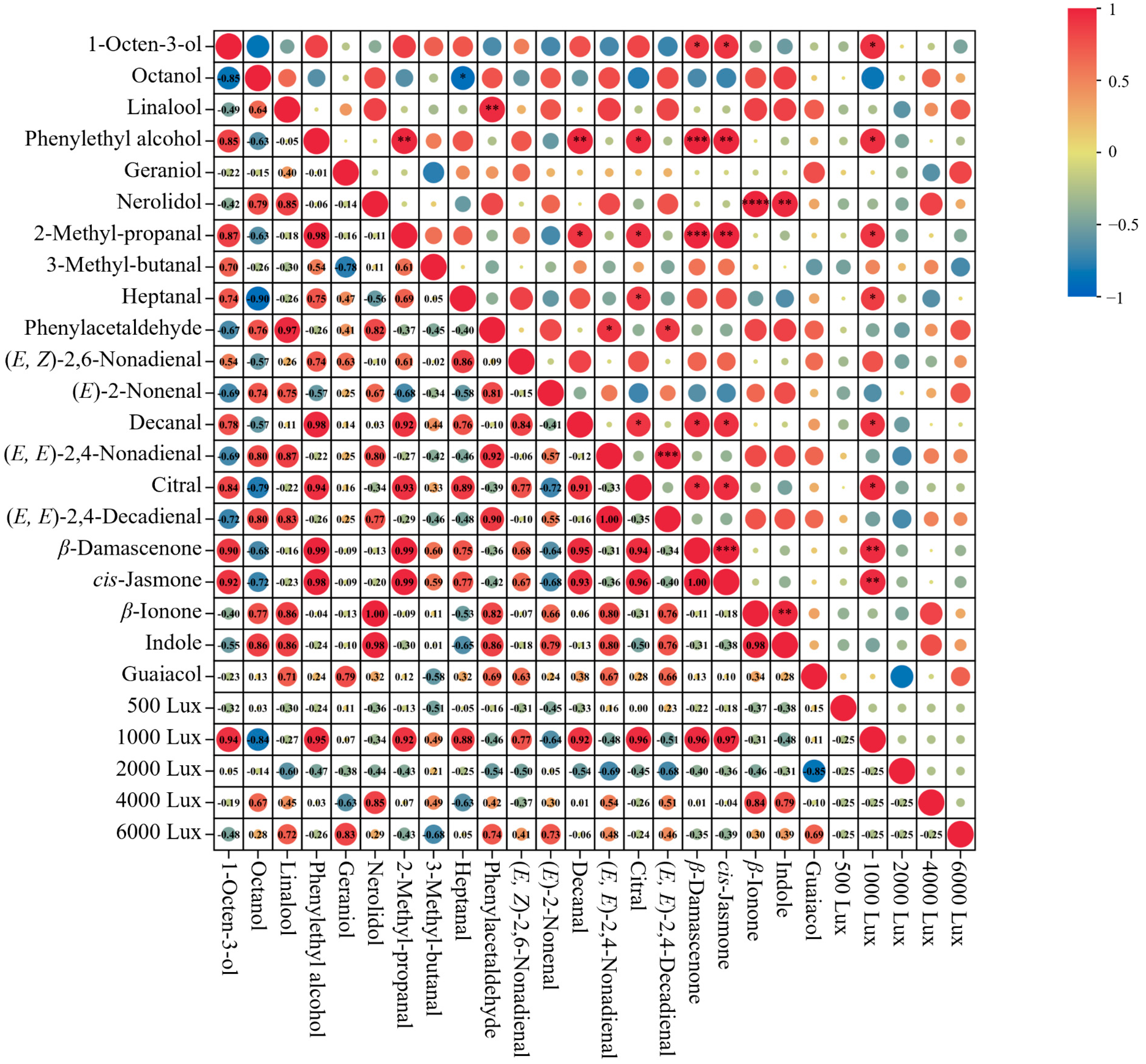
3.3.4. Analysis of the Correlations Between Key Volatile Components and Aroma Quality
3.3.5. Analysis of the Metabolic Pathways of Key Volatile Compounds
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, P.; Kong, Y.-S.; Liu, P.-P.; Wang, J.-J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, G.-M.; Sun, M.-F.; Chen, Y.; Guo, G.-Y.; Liu, Z.-H. A Critical Review of Key Odorants in Green Tea: Identification and Biochemical Formation Pathway. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 129, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Zhang, L.; Granvogl, M.; Ho, C.; Wan, X. Flavor of Tea (Camellia sinensis): A Review on Odorants and Analytical Techniques. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 3867–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Guo, L.; Zhou, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Sun, M.; Zeng, W.; Wu, H. Absolute Quantitative Volatile Measurement from Fresh Tea Leaves and the Derived Teas Revealed Contributions of Postharvest Synthesis of Endogenous Volatiles for the Aroma Quality of Made Teas. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Wang, F.; Luo, B.; Li, A.; Wang, C.; Shabala, L.; Ahmed, H.A.I.; Deng, S.; Zhang, H.; Song, P.; et al. Antioxidant Enzymatic Activity and Osmotic Adjustment as Components of the Drought Tolerance Mechanism in Carex Duriuscula. Plants 2021, 10, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, Y.; He, C.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Wang, P.; Ni, D. Nonvolatile Metabolism in Postharvest Tea (Camellia sinensis L.) Leaves: Effects of Different Withering Treatments on Nonvolatile Metabolites, Gene Expression Levels, and Enzyme Activity. Food Chem. 2020, 327, 126992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, C.; Yu, X.; Zhou, J.; Ntezimana, B.; Yu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ni, D. Study on Improving Aroma Quality of Summer-Autumn Black Tea by Red-Light Irradiation during Withering. LWT 2022, 154, 112597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; He, C.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ni, D. Effects of Different Spreading Treatments on the Formation of Aroma Quality in Green Tea. Beverage Plant Res. 2021, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Z.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Chen, H.; Ni, D. Impact of Light Irradiation on Black Tea Quality during Withering. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 1212–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Lin, F.; Sun, W.; Wu, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, L.; Weng, R. Effects of LED Yellow Light on the Expression Levels of Aroma Related Genes and the Enzyme Activity in Withering Process of Congou Black Tea. J. Tea Sci. 2015, 35, 559–566. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Z.-T.; Jin, J.; Ye, Y.; He, W.-Z.; Shu, Z.-F.; Shao, J.-N.; Fu, Z.-S.; Lu, J.-L.; Ye, J.-H. Effects of Different Shading Treatments on the Biomass and Transcriptome Profiles of Tea Leaves (Camellia sinensis L.) and the Regulatory Effect on Phytohormone Biosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 909765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Wang, Q.; Hu, J.; Wang, L.; Yu, X.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Y. Uncovering the Effects of Spreading under Different Light Irradiation on the Volatile and Non-Volatile Metabolites of Green Tea by Intelligent Sensory Technologies Integrated with Targeted and Non-Targeted Metabolomics Analyses. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Zhou, H.; Yao, X.; Lu, L. Finding the Optimal Light Quality and Intensity for the Withering Process of Fuding Dabai Tea and Its Impact on Quality Formation. LWT 2024, 193, 115713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Xie, J.; Yuan, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, F.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Y. Characterization of Volatile Metabolites in Pu-Erh Teas with Different Storage Years by Combining GC-E-Nose, GC–MS, and GC-IMS. Food Chem. X 2023, 18, 100693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qian, M.C.; Deng, Y.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, Y. Insight into Aroma Dynamic Changes during the Whole Manufacturing Process of Chestnut-like Aroma Green Tea by Combining GC-E-Nose, GC-IMS, and GC × GC-TOFMS. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Hua, J.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Yuan, H.; Dong, C. Quantitation of Pyrazines in Roasted Green Tea by Infrared-Assisted Extraction Coupled to Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction in Combination with GC-QqQ-MS/MS. Food Res. Int. 2020, 134, 109167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, J.; Chen, J.; Deng, Y.; Shen, S.; Hua, J.; Wang, J.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, Y. Characterization of N,O-Heterocycles in Green Tea during the Drying Process and Unraveling the Formation Mechanism. Food Control 2022, 139, 109079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 23776-2018; Methodology for Sensory Evaluation of Tea. Chinese National Standard: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Xie, J.; Miao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Tong, H.; Yuan, H. Aroma Quality Evaluation of High-Quality and Quality-Deficient Black Tea by Electronic Nose Coupled with Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Food Sci. 2024, 45, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Xie, J.; Wang, Q.; Tang, J.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Y. Unraveling the Dynamic Variations of Volatile and Non-Volatile Metabolites in Green Tea during the Yellow-Light Irradiation Spreading Process by Targeted and Untargeted Metabolomics. LWT 2025, 215, 117152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shi, D.; Hu, J.; Wang, L.; Xie, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Yang, Y. Unraveling the Dynamic Changes of Volatile Compounds during the Rolling Process of Congou Black Tea via GC-E-Nose and GC-MS. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1436542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Machine Learning Technique Combined with Data Fusion Strategies: A Tea Grade Discrimination Platform. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 203, 117127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xie, J.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, H.; Yang, Y. Comprehensive Investigation on the Dynamic Changes of Volatile Metabolites in Fresh Scent Green Tea during Processing by GC-E-Nose, GC–MS, and GC × GC-TOFMS. Food Res. Int. 2024, 187, 114330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Wang, L.; Deng, Y.; Yuan, H.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Y. Characterization of the Key Odorants in Floral Aroma Green Tea Based on GC-E-Nose, GC-IMS, GC-MS and Aroma Recombination and Investigation of the Dynamic Changes and Aroma Formation during Processing. Food Chem. 2023, 427, 136641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ouyang, W.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Chen, M.; Yuan, H.; Hua, J. Effect of Shaking on the Improvement of Aroma Quality and Transformation of Volatile Metabolites in Black Tea. Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 101007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, K.; Wu, W.; Huang, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, S. Effect of Shaking Manners on Floral Aroma Quality and Identification of Key Floral-Aroma-Active Compounds in Hunan Black Tea. Food Res. Int. 2023, 174, 113515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Sheng, C.; Ke, H.; Li, T.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Ning, J. Revealing the Differences in Aroma of Black Tea under Different Drying Methods Based on GC–MS, GC-O. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, T.; Huang, W.; Liu, Q.; Deng, G.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ning, J. Investigation of the Aroma Profile and Blending Strategy of Lu’an Guapian Teas during Grain Rain Period by Sensory Evaluation Combined with SBSE-GC–MS, GC–O and OAV. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Yao, H.; Hou, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, M.; Wu, C.; Zhang, L.; Xu, C.; Su, H. Sensomics-Assisted Analysis Unravels the Formation of the Fungus Aroma of Fu Brick Tea. Food Chem. 2024, 458, 140174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Li, X.; Tao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Feng, X.; Guo, H.; Chen, P.; Chu, Q. A Newly-Discovered Tea Population Variety Processed Bai Mu Dan White Tea: Flavor Characteristics and Chemical Basis. Food Chem. 2024, 446, 138851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ho, C.-T.; Schwab, W.; Wan, X. Effect of the Roasting Degree on Flavor Quality of Large-Leaf Yellow Tea. Food Chem. 2021, 347, 129016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ho, C.-T.; Wan, X.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Q.; Wen, Z. Changes of Volatile Compounds and Odor Profiles in Wuyi Rock Tea during Processing. Food Chem. 2021, 341, 128230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.-T.; Zheng, X.; Li, S. Tea Aroma Formation. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2015, 4, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Li, L.; Chen, F.; Rong, B.; Ni, H.; Zheng, F. β-Glucosidase Improve the Aroma of the Tea Infusion Made from a Spray-Dried Oolong Tea Instant. LWT 2022, 159, 113175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yin, H.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Dong, C.; Li, J.; Hua, J.; Wang, J. Rapid Profiling of Volatile Compounds in Green Teas Using Micro-Chamber/Thermal Extractor Combined with Thermal Desorption Coupled to Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Followed by Multivariate Statistical Analysis. LWT 2018, 96, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, J.; Mei, H.; Zhuang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Jeyaraj, A.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Z. Effects of Leaf-Spreading on the Volatile Aroma Components of Green Tea under Red Light of Different Intensities. Food Res. Int. 2023, 168, 112759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Shen, S.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, Y. Characterization of the Key Differential Volatile Components in Different Grades of Dianhong Congou Tea Infusions by the Combination of Sensory Evaluation, Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography-Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry, and Odor Activity Value. LWT 2022, 165, 113755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Chen, J.; Xie, J.; Shen, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, Y. Characterization of the Key Aroma Compounds in Black Teas with Different Aroma Types by Using Gas Chromatography Electronic Nose, Gas Chromatography-Ion Mobility Spectrometry, and Odor Activity Value Analysis. LWT 2022, 163, 113492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Wang, Q.; Cui, H.; Wang, L.; Deng, Y.; Yuan, H.; Zhu, J.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, Y. Characterization of Gardenia Tea Based on Aroma Profiles Using GC-E-Nose, GC-O-MS and GC × GC-TOFMS Combined with Chemometrics. Beverage Plant Res. 2024, 4, e001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambla, J.L.; Tikunov, Y.M.; Monforte, A.J.; Bovy, A.G.; Granell, A. The Expanded Tomato Fruit Volatile Landscape. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 65, 4613–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Lin, J.; Lin, H.; Hao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Y. Dynamic Change of the Carotenoid Metabolic Pathway Profile during Oolong Tea Processing with Supplementary LED Light. Food Res. Int. 2023, 169, 112839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gemert, L.J. ODOUR THRESHOLDS—Compilations of Odour Threshold Values in Air, Water and Other Media; Oliemans Punter& Partners BV: Zeist, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Hu, J.; Tang, J.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, Y.; Xie, J.; Yang, Y. Decoding Light-Spreading Intensity Effects on the Sensory Quality and Volatile Compounds of Green Tea: An Integrated GC-E-Nose and Targeted Metabolomics Analysis. Foods 2025, 14, 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081313
Wang Q, Hu J, Tang J, Zhou X, Yuan H, Jiang Y, Xie J, Yang Y. Decoding Light-Spreading Intensity Effects on the Sensory Quality and Volatile Compounds of Green Tea: An Integrated GC-E-Nose and Targeted Metabolomics Analysis. Foods. 2025; 14(8):1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081313
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qiwei, Jiajing Hu, Jiahao Tang, Xianxiu Zhou, Haibo Yuan, Yongwen Jiang, Jialing Xie, and Yanqin Yang. 2025. "Decoding Light-Spreading Intensity Effects on the Sensory Quality and Volatile Compounds of Green Tea: An Integrated GC-E-Nose and Targeted Metabolomics Analysis" Foods 14, no. 8: 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081313
APA StyleWang, Q., Hu, J., Tang, J., Zhou, X., Yuan, H., Jiang, Y., Xie, J., & Yang, Y. (2025). Decoding Light-Spreading Intensity Effects on the Sensory Quality and Volatile Compounds of Green Tea: An Integrated GC-E-Nose and Targeted Metabolomics Analysis. Foods, 14(8), 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081313






