Physical, Mechanical, Barrier, and Optical Properties of Sodium Alginate/Gum Arabic/Gluten Edible Films Plasticized with Glycerol and Sorbitol
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
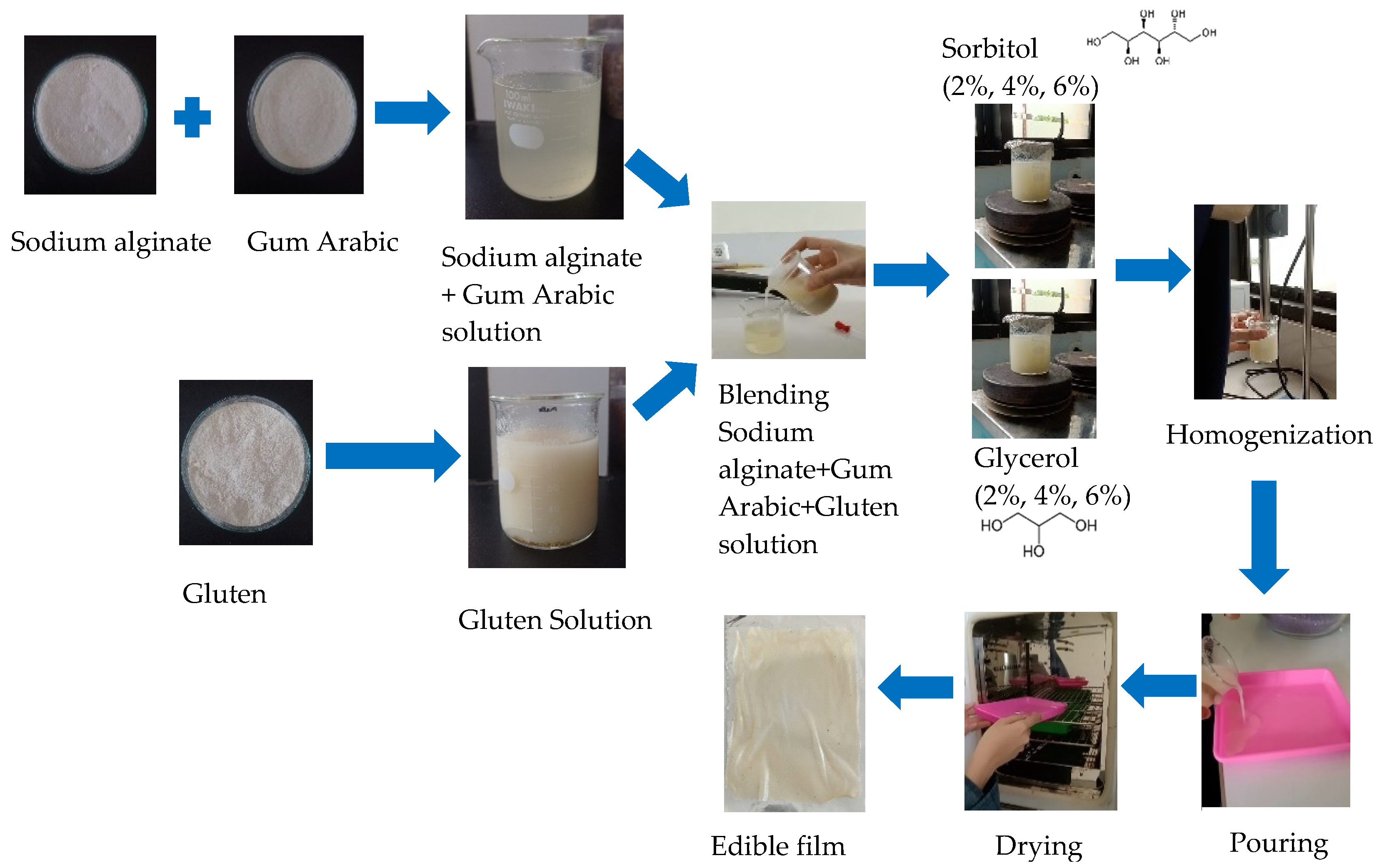
2.2. Preparation of Wheat Gluten Solution
2.3. Preparation of Sodium Alginate and Gum Arabic Solution
2.4. Preparation of Edible Film
2.5. Film Characterization
2.5.1. Thickness
2.5.2. Water Solubility
2.5.3. Tensile Strength
2.5.4. Water Vapor Transmission Rate
2.5.5. Color
2.5.6. Transparency
2.5.7. Determination of the Films’ Functional Groups
2.5.8. Microstructures of the Films
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thickness of Edible Films
3.2. Color of the Edible Films
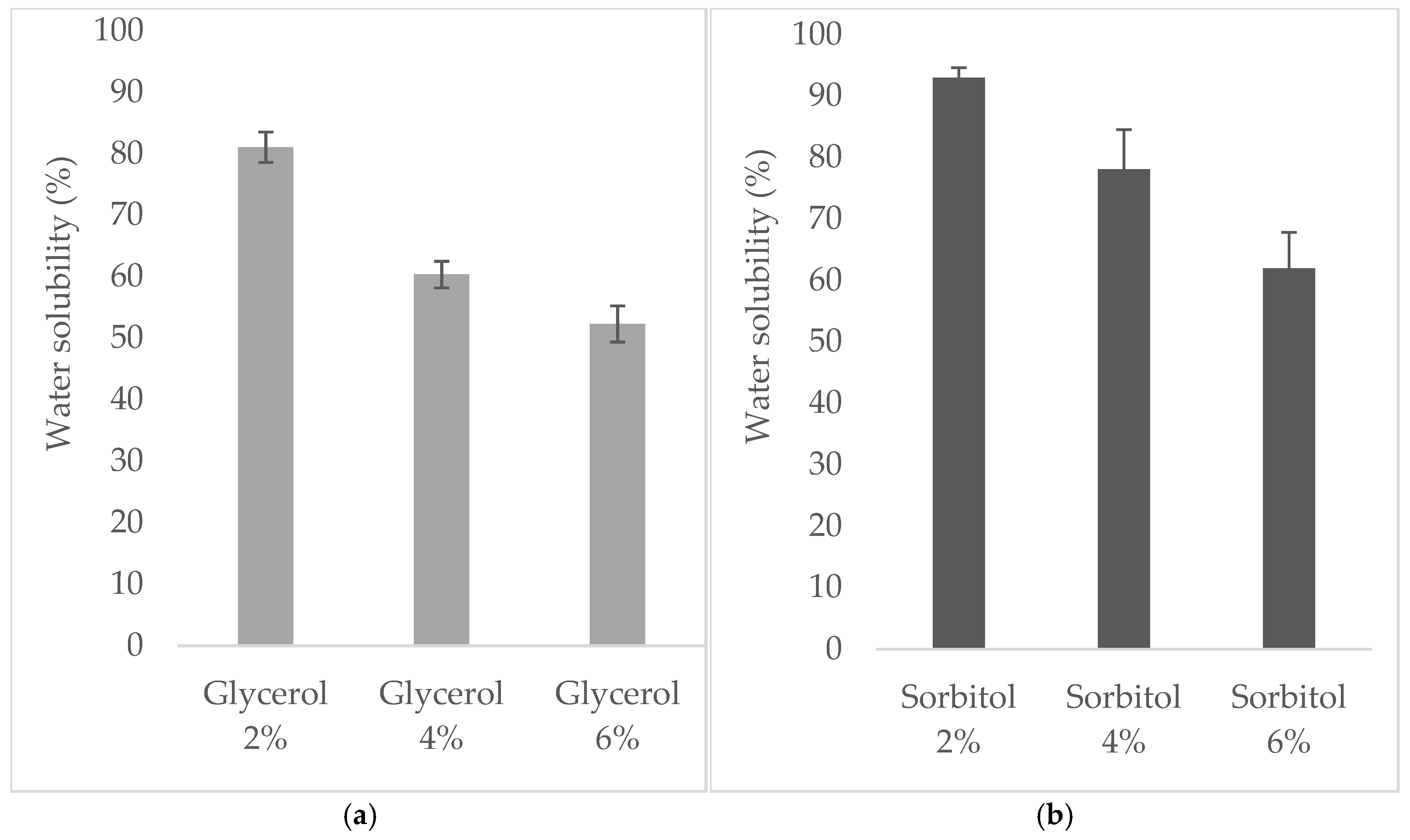
3.3. Water Solubility of Edible Films
3.4. Tensile Strength of Edible Films
3.5. Transparency of Edible Films
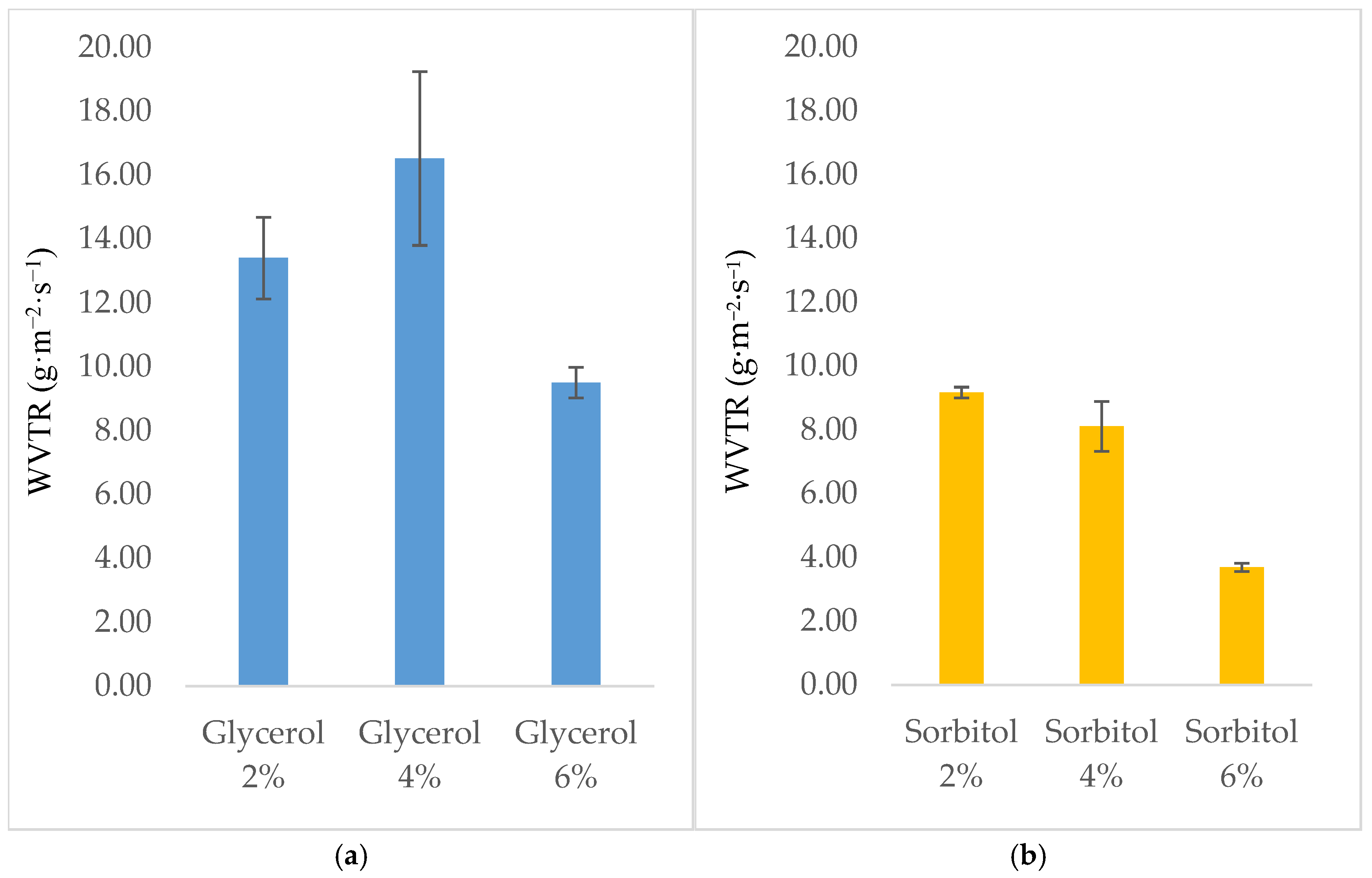
3.6. Water Vapor Transmission Rate of Edible Films
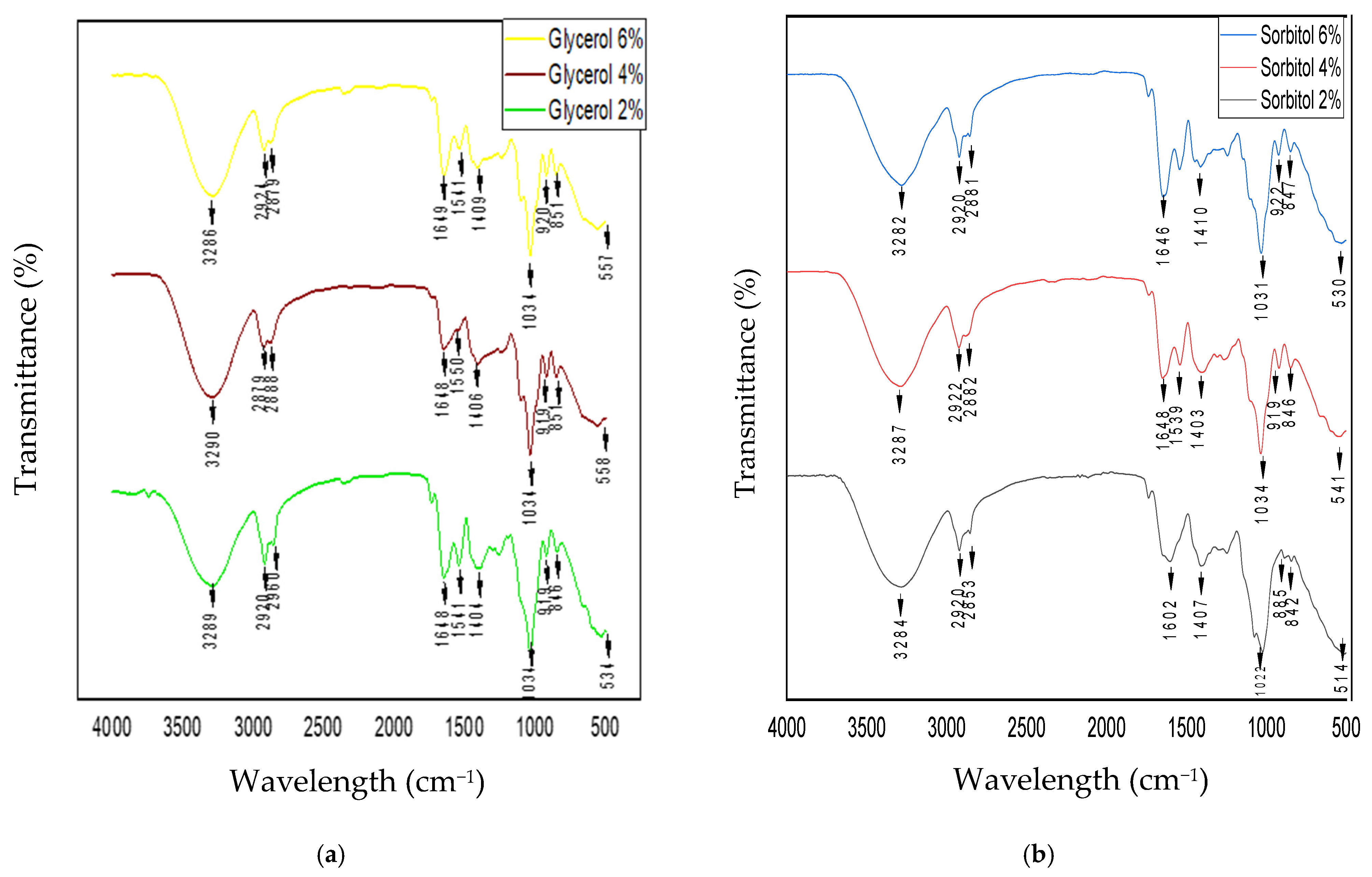
3.7. Fourier-Transform Infrared Analysis of Edible Films
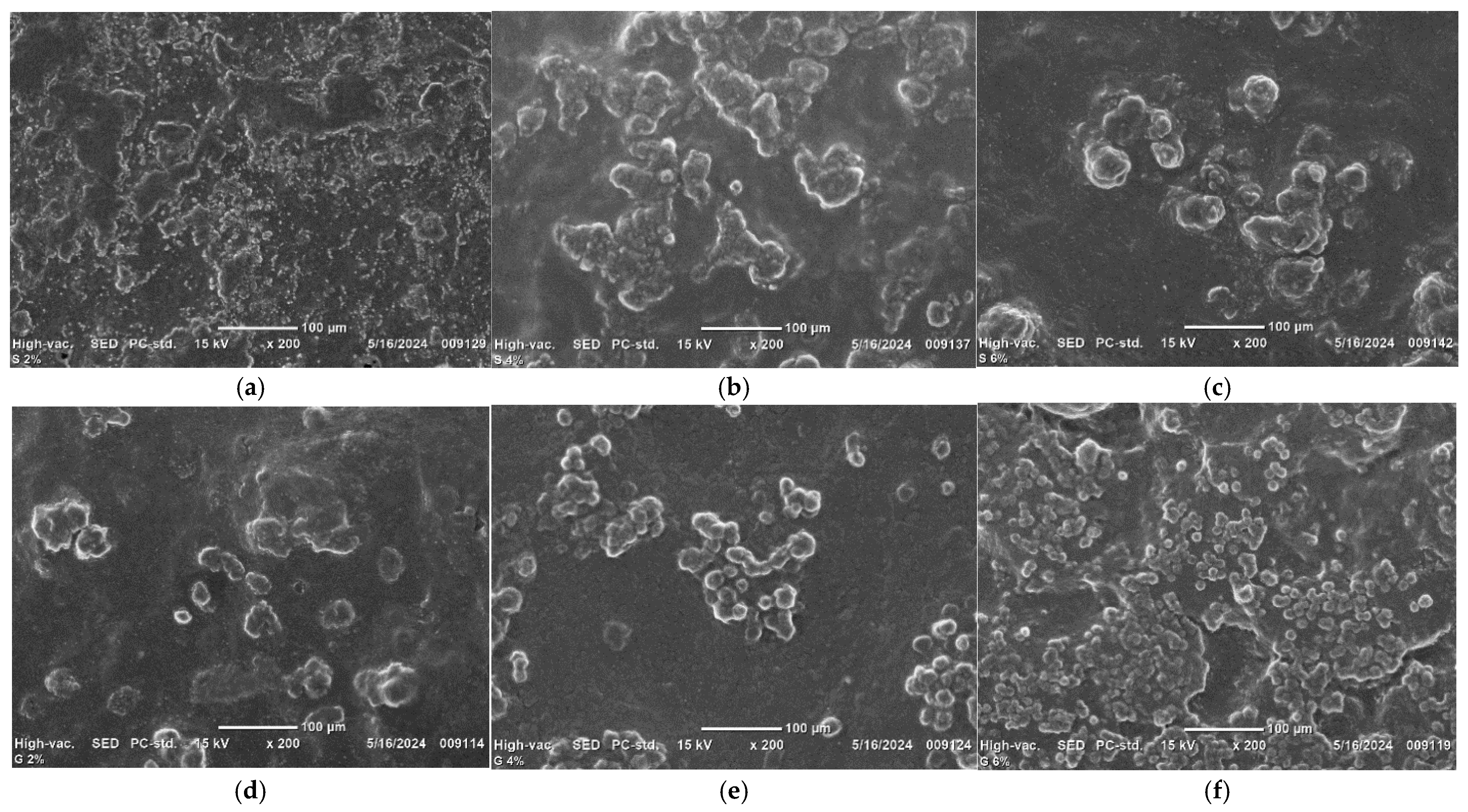
3.8. Morphologies of Edible Films
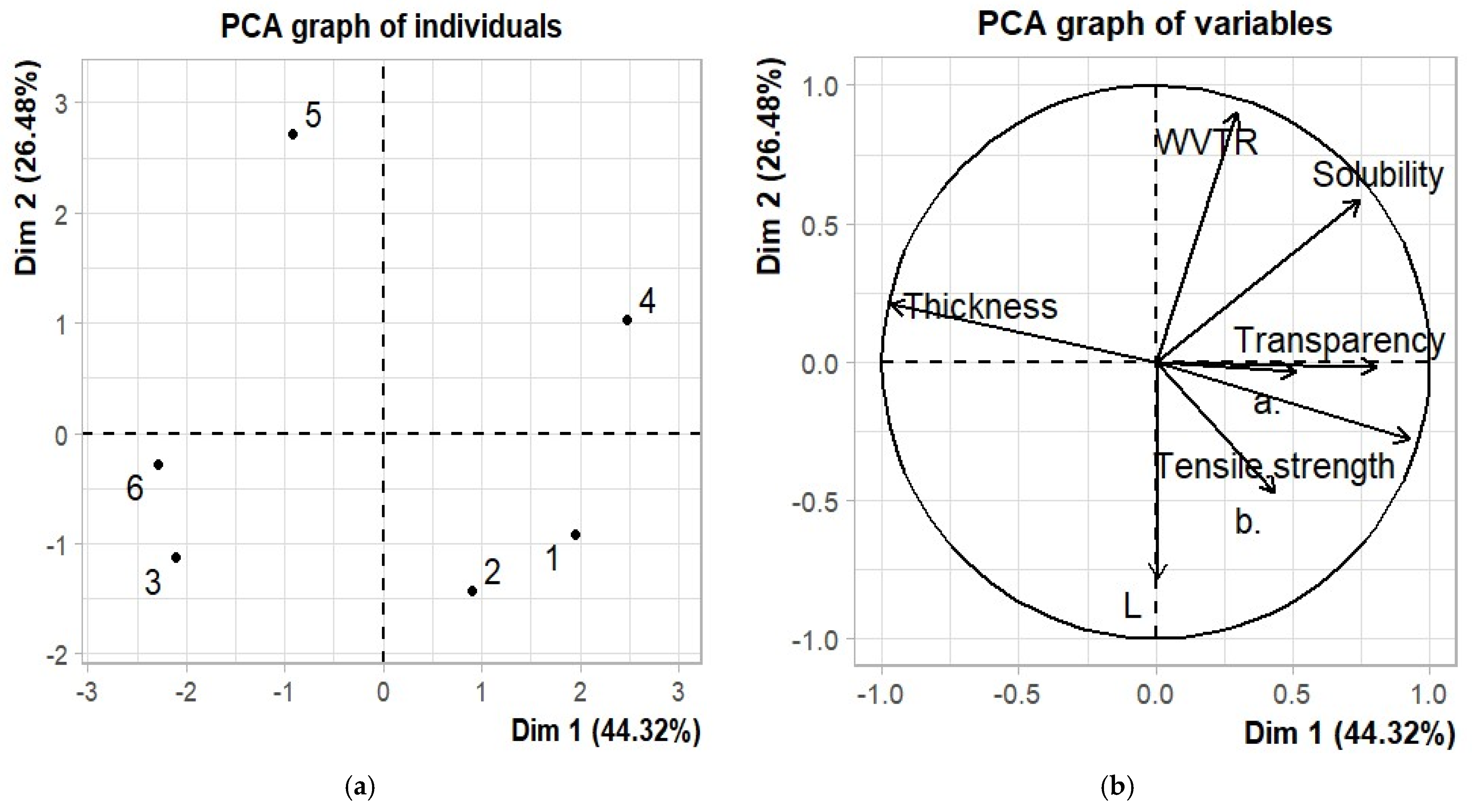
3.9. Principal Component Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, L. Developing a green and edible film from Cassia gum: The effects of glycerol and sorbitol. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 175, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, U.; Khan, M.U.; Majeed, Y.; Rebezov, M.; Khayrullin, M.; Bobkova, E.; Shariati, M.A.; Chung, I.M.; Thiruvengadam, M. Potentials of polysaccharides, lipids and proteins in biodegradable food packaging applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 2184–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metha, C.; Pawar, S.; Suvarna, V. Recent advancements in alginate-based films for active food packaging applications. Sustain. Food Technol. 2024, 2, 1246–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janik, W.; Nowotarski, M.; Ledniowska, K.; Shyntum, D.Y.; Krukiewicz, K.; Turczyn, R.; Sabura, E.; Furgoł, S.; Kudła, S.; Dudek, G. Modulation of physicochemical properties and antimicrobial activity of sodium alginate films through the use of chestnut extract and plasticizers. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Ding, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, Y. Developing sodium alginate based edible film incorporated with potassium sorbate and application for fresh cold pork preservation. Food Control 2025, 172, 111154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Fan, Y.; Cui, J.; Yang, L.; Su, H.; Yang, P.; Pan, J. Colorimetric films based on pectin/sodium alginate/xanthan gum incorporated with raspberry pomace extract for monitoring protein-rich food freshness. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.M.; Bindhu, B.; Reena, V.L. A polymer blend from Gum Arabic and Sodium Alginate—Preparation and characterization. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, H.; Fu, Y.; Chang, C.; Wu, J. Sodium alginate/gum arabic/glycerol multicomponent edible films loaded with natamycin: Study on physicochemical, antibacterial, and sweet potatoes preservation properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 213, 1068–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Yang, J.; Duan, A.; Li, X. Pectin/sodium alginate/xanthan gum edible composite films as the fresh-cut package. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 181, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dursun Capar, T. Characterization of sodium alginate-based biodegradable edible film incorporated with Vitis vinifera leaf extract: Nano-scaled by ultrasound-assisted technology. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2023, 37, 101068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopi, S.; Amalraj, A.; Kalarikkal, N.; Zhang, J.; Thomas, S. Materials Science & Engineering C Preparation and characterization of nanocomposite films based on gum arabic, maltodextrin and polyethylene glycol reinforced with turmeric nanofiber isolated from turmeric spent. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 97, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Gao, C.; Feng, X.; Yang, Y.; Shen, X.; Tang, X. Structure, physical and antioxidant properties of chitosan-gum arabic edible films incorporated with cinnamon essential oil. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawhena, T.G.; Opara, U.L.; Fawole, O.A. Optimization of gum arabic and starch-based edible coatings with lemongrass oil using response surface methodology for improving postharvest quality of whole “wonderful” pomegranate fruit. Coatings 2021, 11, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, F.; Ma, R.; Tian, Y. Advances in gum Arabic utilization for sustainable applications as food packaging: Reinforcement strategies and applications in food preservation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 142, 104215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahsiri, Z.; Mirzaei, H.; Hosseini, S.M.H.; Khalesi, M. Gum arabic improves the mechanical properties of wild almond protein film. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 114994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seididamyeh, M.; Mantilla, S.M.O.; Netzel, M.E.; Mereddy, R.; Sultanbawa, Y. Gum Arabic edible coating embedded aqueous plant extracts: Interactive effects of partaking components and its effectiveness on cold storage of fresh-cut capsicum. Food Control 2024, 159, 110267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erben, M.; Pérez, A.A.; Osella, C.A.; Alvarez, V.A.; Santiago, L.G. Impact of gum arabic and sodium alginate and their interactions with whey protein aggregates on bio-based films characteristics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Yu, D.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xia, W. Thermally-induced crosslinking altering the properties of chitosan films: Structure, physicochemical characteristics and antioxidant activity. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 34, 100948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanada-Palmu, P.S.; Grosso, C.R.F. Effect of edible wheat gluten-based films and coatings on refrigerated strawberry (Fragaria ananassa) quality. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2005, 36, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafian, N.; Aarabi, A.; Nezamzadeh-ejhieh, A. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules Evaluation of physicomechanical properties of gluten-based film incorporated with Persian gum and Guar gum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 223, 1257–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Song, Y.; Thakur, K.; Zhang, J.; Rizwan, M. Blueberry anthocyanin based active intelligent wheat gluten protein films: Preparation, characterization, and applications for shrimp freshness monitoring. Food Chem. 2024, 453, 139676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sothornvit, R.; Krochta, J.M. Plasticizers in edible films and coatings. In Innovations in Food Packaging; Academic Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; pp. 403–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, A.; Hani, N.M. Characterization of edible packaging films based on semi-refined kappa-carrageenan plasticized with glycerol and sorbitol. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 64, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, Z.; Rao, Z.; Zheng, X.; Tang, K.; Liu, J. Effect of polyol plasticizers on properties and microstructure of soluble soybean polysaccharide edible films. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2023, 35, 101023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Khatkar, B.S.; Kaushik, R.; Sharma, P.; Sharma, R. Isolation and development of wheat based gluten edible film and its physicochemical properties. Int. Food Res. J. 2017, 24, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Abotbina, W.; Sapuan, S.M.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Alkbir, M.F.M.; Ilyas, R.A. Development and Characterization of Cornstarch-Based Bioplastics Packaging Film Using a Combination of Different Plasticizers. Polymers 2021, 13, 3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, O.A.; Pellá, M.G.; Pellá, M.G.; Caetano, J.; Simões, M.R.; Bittencourt, P.R.S.; Dragunski, D.C. Synthesis and characterization of a low solubility edible film based on native cassava starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 128, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-De-benito, L.F.; Escamilla-García, M.; García-Almendárez, B.; Amaro-Reyes, A.; Di Pierro, P.; Regalado-González, C. Design of an active edible coating based on sodium caseinate, chitosan and oregano essential oil reinforced with silica particles and its application on panela cheese. Coatings 2021, 11, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Auty, M.A.E.; Kerry, J.P. Physical assessment of composite biodegradable films manufactured using whey protein isolate, gelatin and sodium alginate. J. Food Eng. 2010, 96, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, M.; Costa, T.M.H.; Gomaa, A.; Subirade, M.; Rios, A.D.O.; Flôres, S.H. Edible film production from chia seed mucilage: Effect of glycerol concentration on its physicochemical and mechanical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 130, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petry, J.M.; Pellá, M.C.G.; Silva, O.A.; Caetano, J.; Dragunski, D.C. Plasticizer concentration effect on films and coatings based on poly(vinyl alcohol) and cationic starch blends. Food Chem. 2024, 438, 137977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paidari, S.; Zamindar, N.; Tahergorabi, R.; Kargar, M.; Ezzati, S.; Shirani, N.; Musavi, S.H. Edible coating and films as promising packaging: A mini review. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 4205–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, K.C.; Embuscado, M.E. (Eds.) Edible Films and Coatings for Food Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-387-92823-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ballesteros-Mártinez, L.; Pérez-Cervera, C.; Andrade-Pizarro, R. Effect of glycerol and sorbitol concentrations on mechanical, optical, and barrier properties of sweet potato starch film. NFS J. 2020, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaderi, Z.; Tabatabaee Yazdi, F.; Mortazavi, S.A.; Koocheki, A. Effects of glycerol and sorbitol on a novel biodegradable edible film based on Malva sylvestris flower gum. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudel, S.; Regmi, S.; Janaswamy, S. Effect of glycerol and sorbitol on cellulose-based biodegradable films. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2023, 37, 101090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehra, A.; Biswas, D.; Siracusa, V.; Roy, S. Natural Gum-Based Functional Bioactive Films and Coatings: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xu, X.; Fang, Y.; Yan, S.; Cui, B.; Abd El-Aty, A.M. Effect of Different Ratios of Glycerol and Erythritol on Properties of Corn Starch-Based Films. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 882682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y. A novel high water-soluble antibacterial films-based guar gum incorporated with Aloe vera gel and ε-polylysine. Food Chem. 2023, 427, 136686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, S.; Foerster, J.; Lindner, M.; Schmid, M. Effect of glycerol and sorbitol on the mechanical and barrier properties of films based on pea protein isolate produced by high-moisture extrusion processing. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 62, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazrati, K.Z.; Sapuan, S.M.; Zuhri, M.Y.M.; Jumaidin, R. Effect of plasticizers on physical, thermal, and tensile properties of thermoplastic films based on Dioscorea hispida starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontard, N.; Duchez, C.; Cuq, J.-L.; Guilbert, S. Edible composite films of wheat gluten and lipids: Water vapour permeability and other physical properties. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1994, 29, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, Z.X.; Ismail, H.; Bakar, A.A.; Aziz, N.A.A. The Comparison Effect of Sorbitol and Glycerol as Plasticizing Agents on the Properties of Biodegradable Polyvinyl Alcohol/Rambutan Skin Waste Flour Blends. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2012, 51, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Núñez, J.R.; Madera-Santana, T.J.; Sánchez-Machado, D.I.; López-Cervantes, J.; Soto Valdez, H. Chitosan/Hydrophilic Plasticizer-Based Films: Preparation, Physicochemical and Antimicrobial Properties. J. Polym. Environ. 2014, 22, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Azmat, R.; Khojah, E.; Ahmed, R.; Qayyum, A.; Shah, A.N.; Abbas, A.; Moin, S.; Samra, B.N. The Development of a Green Innovative Bioactive Film for Industrial Application as a New Emerging Technology to Protect the Quality of Fruits. Molecules 2022, 27, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirbu, E.-E.; Dinita, A.; Tănase, M.; Portoacă, A.-I.; Bondarev, A.; Enascuta, C.-E.; Calin, C. Influence of Plasticizers Concentration on Thermal, Mechanical, and Physicochemical Properties on Starch Films. Processes 2024, 12, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourfarzad, A.; Ahmadian, Z.; Habibi-Najafi, M.B. Interactions between polyols and wheat biopolymers in a bread model system fortified with inulin: A Fourier transform infrared study. Heliyon 2018, 4, e01017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hassan, A.A. Development and characterization of camel gelatin films: Influence of camel bone age and glycerol or sorbitol on film properties. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basiak, E.; Lenart, A.; Debeaufort, F. Effect of starch type on the physico-chemical properties of edible films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tang, Z.; Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Lv, Y.; Qian, F.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, H. Improving air barrier, water vapor permeability properties of cellulose paper by layer-by-layer assembly of graphene oxide. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 253, 117227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Samples | Thickness (mm) | Color | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | a* | b* | ||
| Glycerol | ||||
| Glycerol 2% | 0.14 ± 0.01 a | 58.66 ± 0.64 a | −5.36 ± 0.20 a | 11.11 ± 1.26 a |
| Glycerol 4% | 0.17 ± 0.02 a | 57.98 ± 0.41 a | −6.24 ± 0.72 a | 7.66 ± 3.41 b |
| Glycerol 6% | 0.17 ± 0.02 a | 59.98 ± 4.30 a | −6.42 ± 0.38 a | 8.62 ± 1.30 a |
| Sorbitol | ||||
| Sorbitol 2% | 0.14 ± 0.01 a | 60.37 ± 0.72 a | −6.67 ± 0.15 a | 8.84 ± 0.29 a |
| Sorbitol 4% | 0.15 ± 0.01 a | 59.27 ± 0.69 a | −4.51 ± 0.42 b | 14.96 ± 1.52 b |
| Sorbitol 6% | 0.17 ± 0.01 a | 59.33 ± 0.42 a | −7.01 ± 0.27 a | 9.19 ± 0.43 a |
| Samples | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Transparency |
|---|---|---|
| Glycerol | ||
| Glycerol 2% | 0.10 ± 0.00 a | 17.85 ± 1.07 a |
| Glycerol 4% | 0.01 ± 0.01 b | 13.58 ± 0.73 b |
| Glycerol 6% | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 6.39 ± 0.35 c |
| Sorbitol | ||
| Sorbitol 2% | 0.13 ± 0.07 a | 20.89 ± 2.57 a |
| Sorbitol 4% | 0.07 ± 0.03 a | 13.61 ± 0.81 b |
| Sorbitol 6% | 0.02 ± 0.01 b | 13.91 ± 0.83 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Syarifuddin, A.; Haliza, N.; Izzah, N.; Tahir, M.M.; Dirpan, A. Physical, Mechanical, Barrier, and Optical Properties of Sodium Alginate/Gum Arabic/Gluten Edible Films Plasticized with Glycerol and Sorbitol. Foods 2025, 14, 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071219
Syarifuddin A, Haliza N, Izzah N, Tahir MM, Dirpan A. Physical, Mechanical, Barrier, and Optical Properties of Sodium Alginate/Gum Arabic/Gluten Edible Films Plasticized with Glycerol and Sorbitol. Foods. 2025; 14(7):1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071219
Chicago/Turabian StyleSyarifuddin, Adiansyah, Nur Haliza, Nur Izzah, Mulyati Muhammad Tahir, and Andi Dirpan. 2025. "Physical, Mechanical, Barrier, and Optical Properties of Sodium Alginate/Gum Arabic/Gluten Edible Films Plasticized with Glycerol and Sorbitol" Foods 14, no. 7: 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071219
APA StyleSyarifuddin, A., Haliza, N., Izzah, N., Tahir, M. M., & Dirpan, A. (2025). Physical, Mechanical, Barrier, and Optical Properties of Sodium Alginate/Gum Arabic/Gluten Edible Films Plasticized with Glycerol and Sorbitol. Foods, 14(7), 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071219







