Predicting the Degree of Fresh Tea Leaves Withering Using Image Classification Confidence
Abstract
1. Introduction
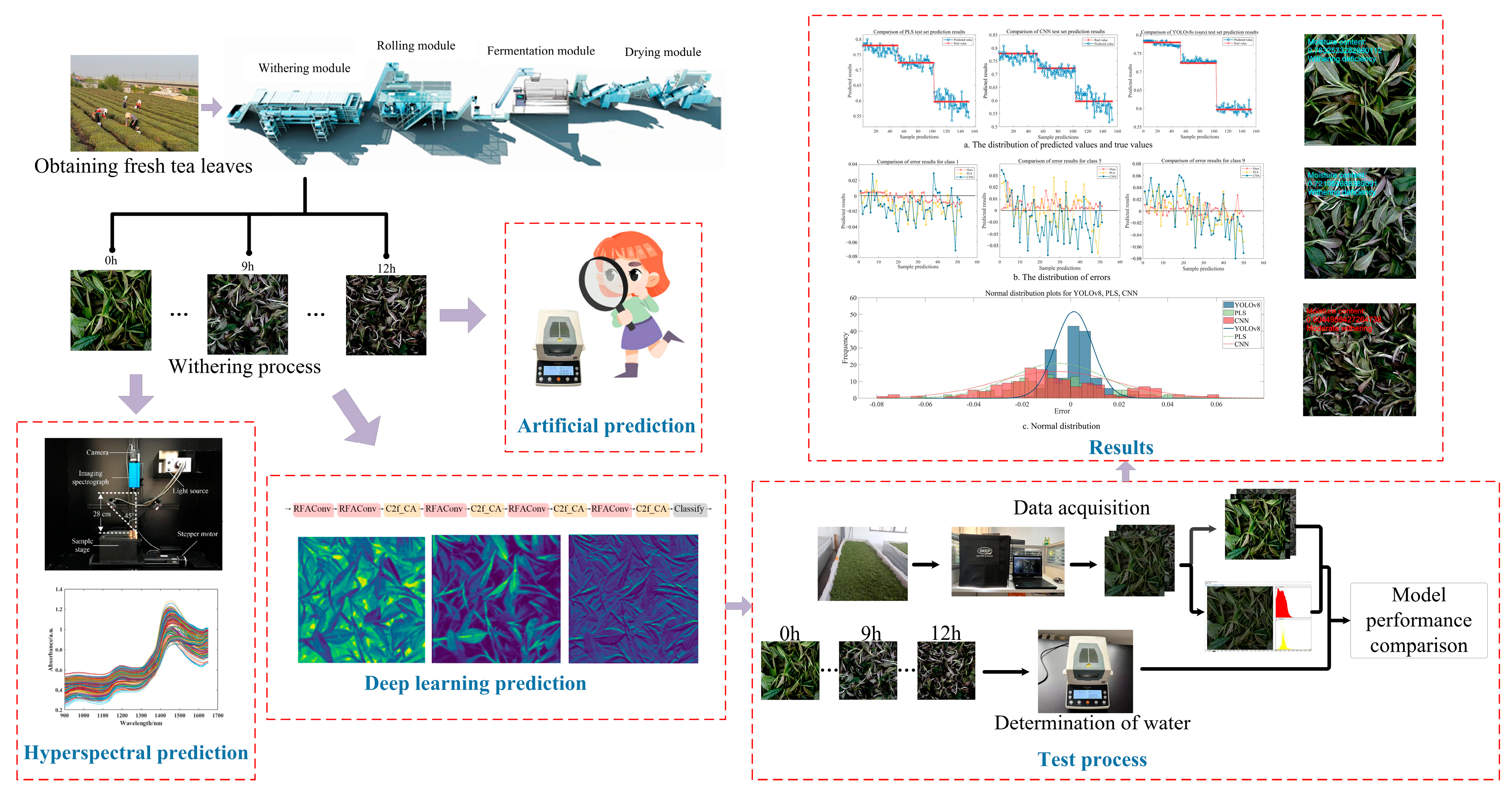
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Image Acquisition and Preprocessing
2.2. Model Selection and Optimization for Judging the Degree of Withering
2.2.1. Model Selection
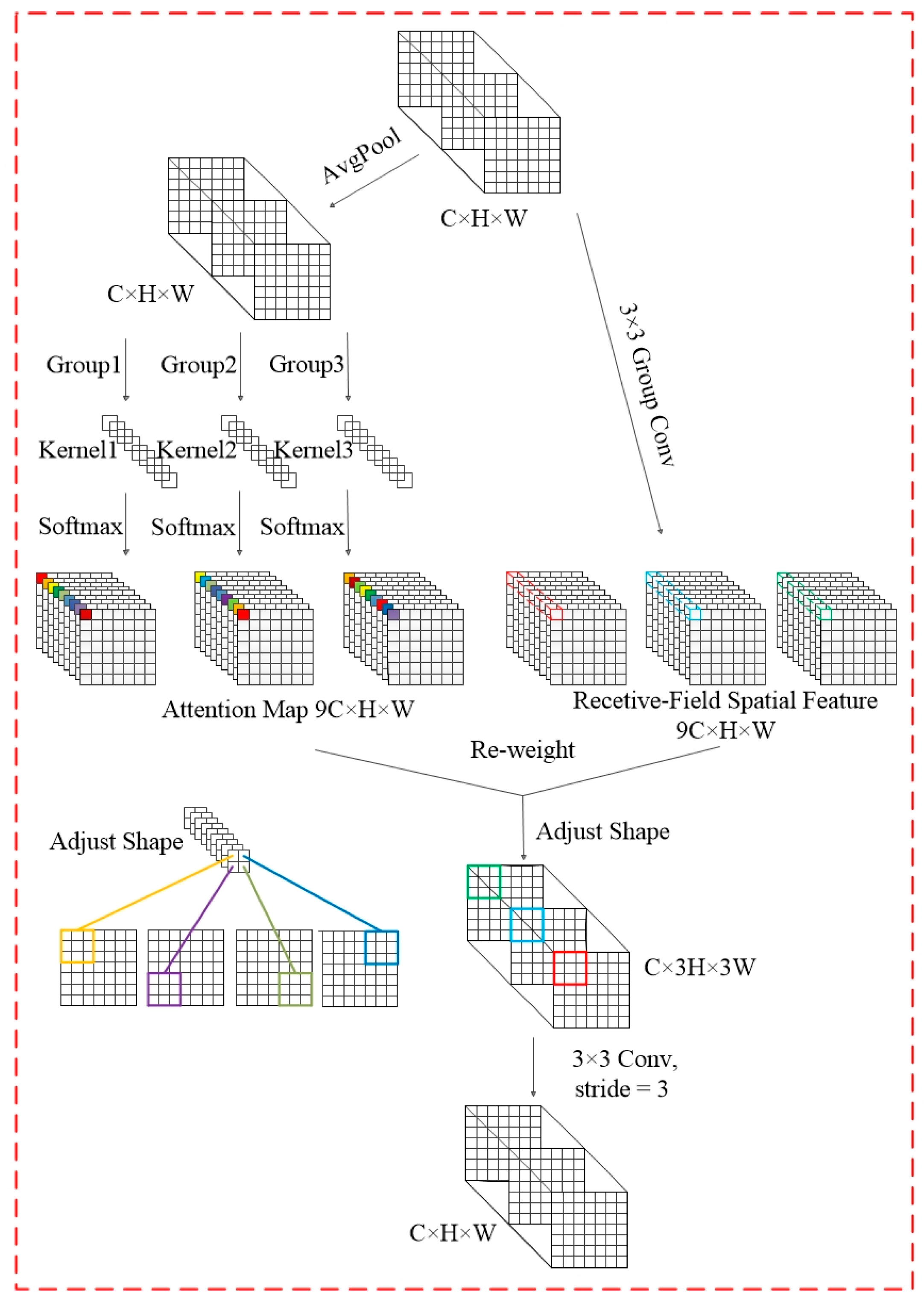
Perceived Field Attention Convolutional RFAConv
Cross-Stage Feature Fusion Coordinate Attention
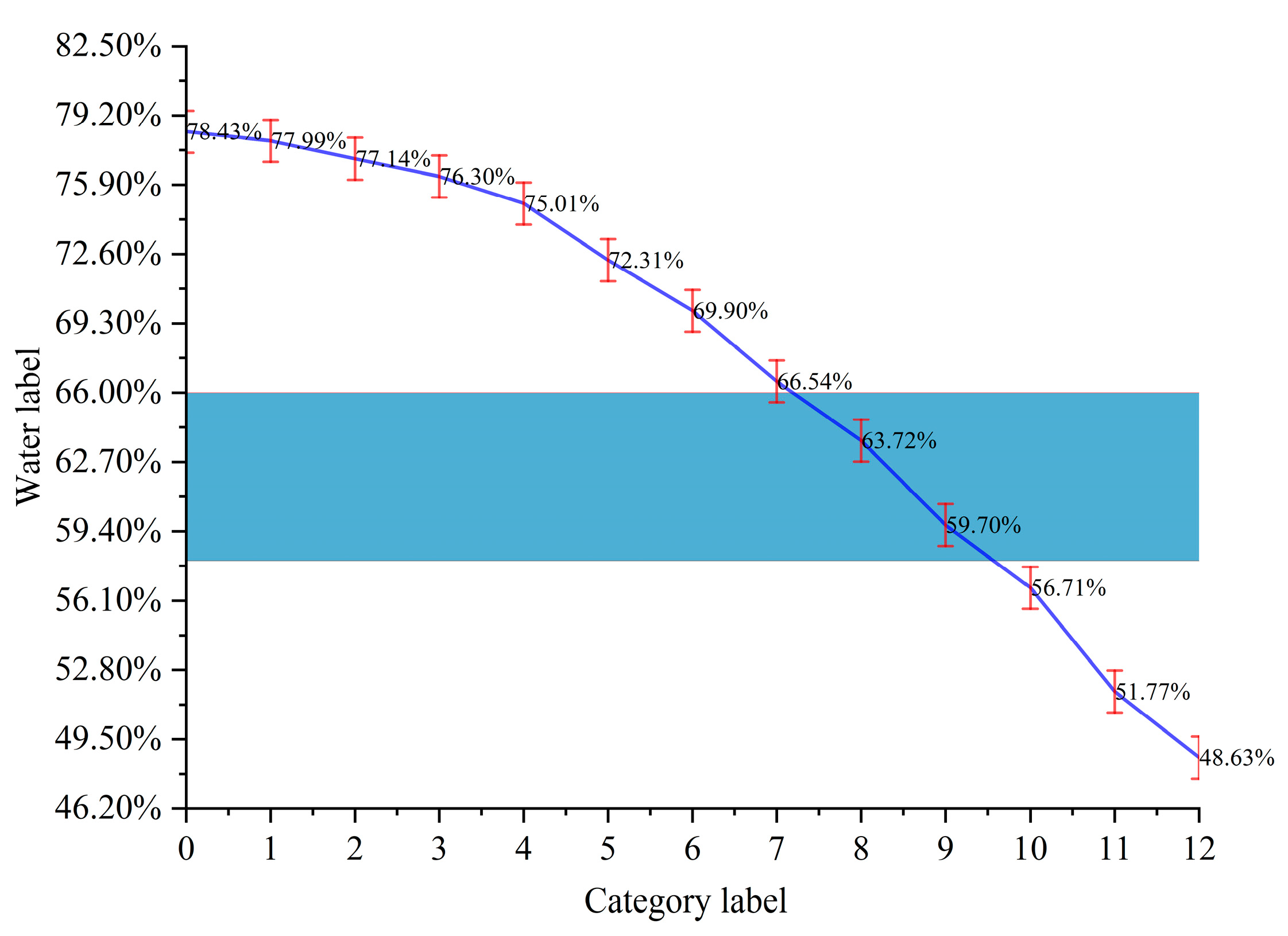
2.3. Quantitative Prediction of Moisture Content and Determination of Wilting Degree Based on Classification Confidence
2.4. Evaluation
2.5. Implementation Details
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparison Between Different Versions of YOLOv8
3.2. Comparative Experiments Before and After Model Optimization
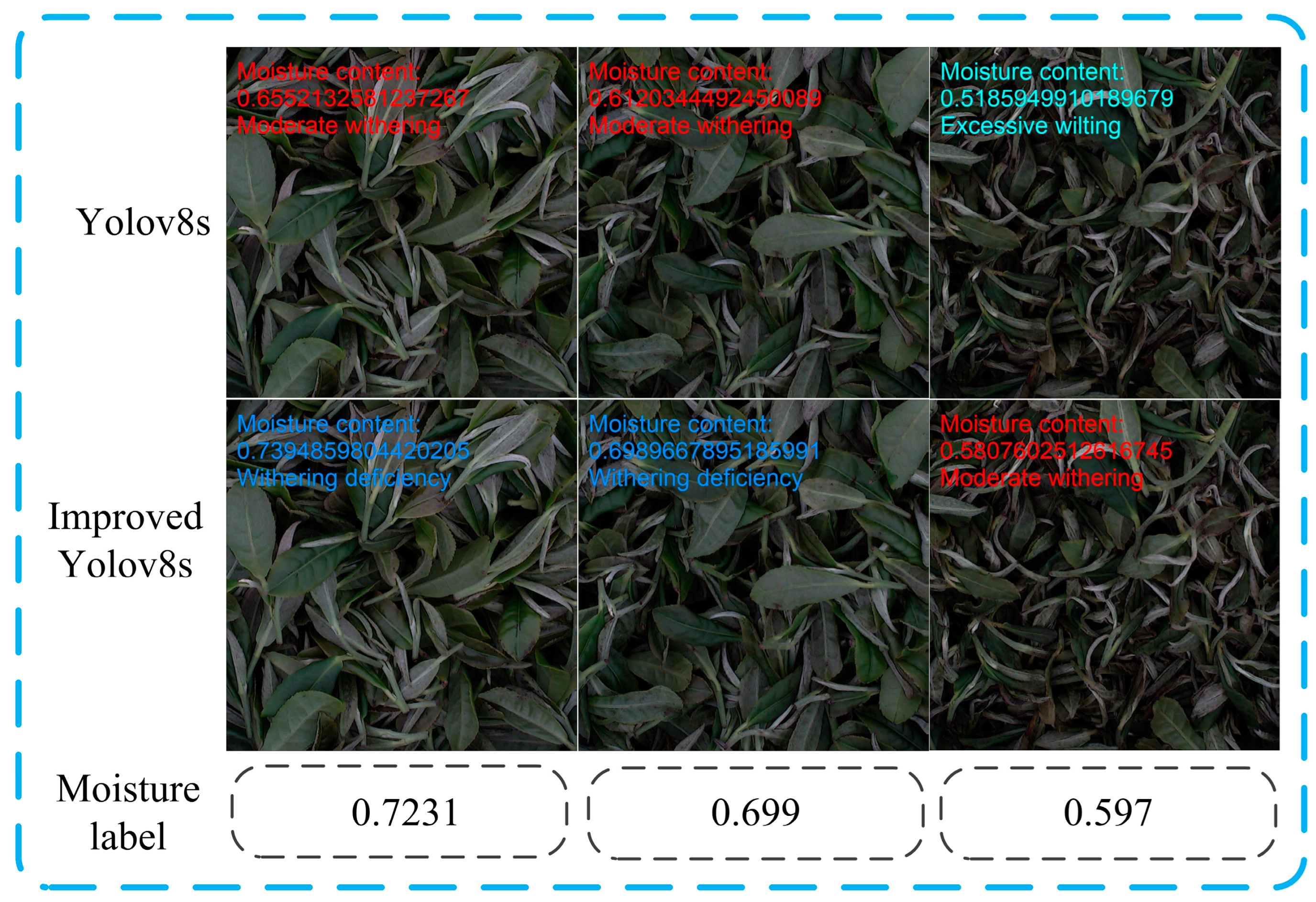
3.3. Improve the Model to Predict Moisture Content and Wilting Degree
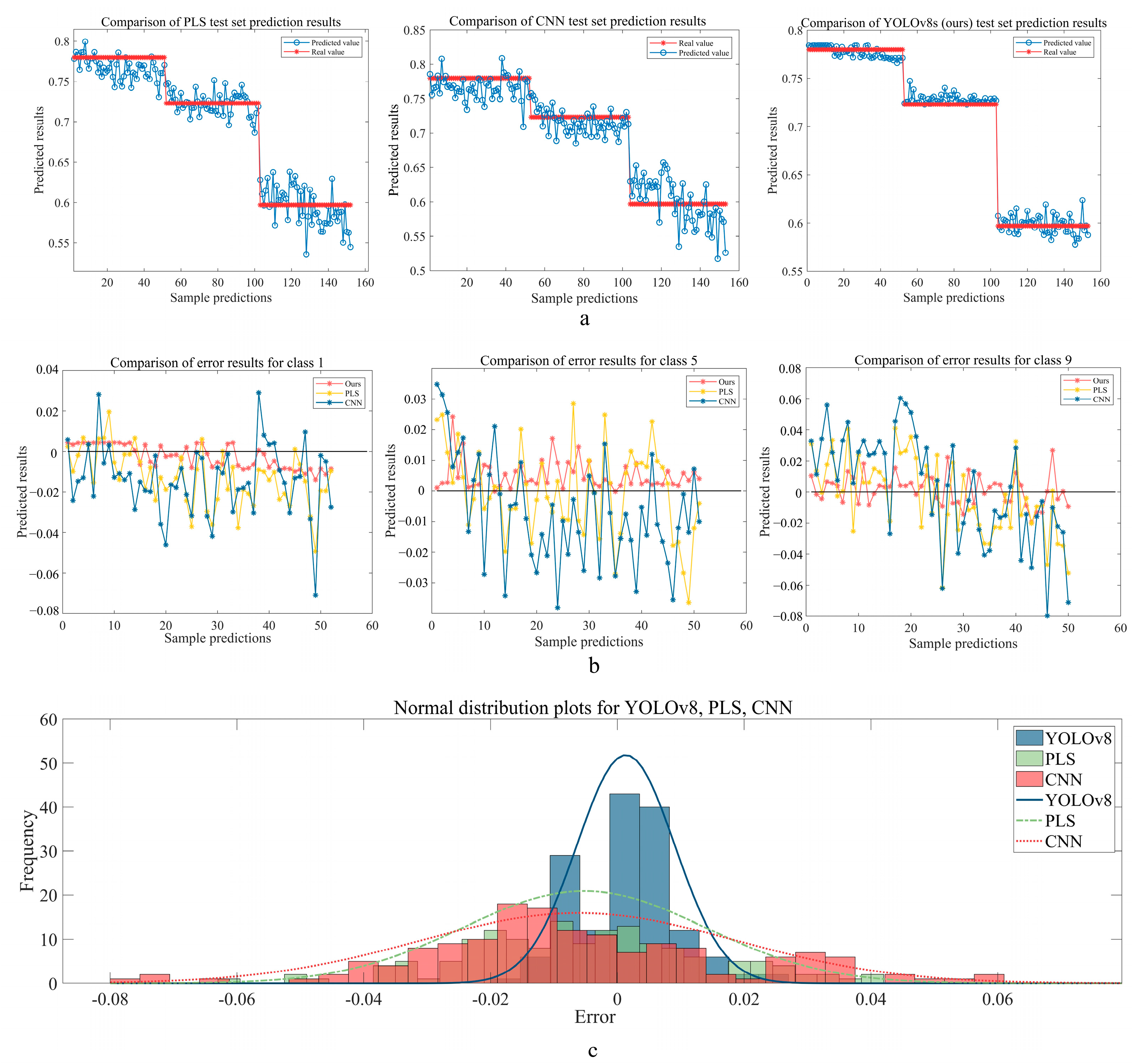
3.4. Comparison of Moisture Content Prediction Using Different Models
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, W.; Fang, S.; Su, Y.; Xia, D.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zou, L.; Lu, C.; Deng, W.-W.; Ning, J. Insights into the mechanism of different withering methods on flavor formation of black tea based on target metabolomics and transcriptomics. LWT 2023, 189, 115537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, S.; Jolvis Pou, K.R. A review of withering in the processing of black tea. J. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 41, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, Y.; Feng, W.; Shen, S.; Wei, Y.; Jia, H.; Wang, Y.; Deng, W.; Ning, J. Effects of three different withering treatments on the aroma of white tea. Foods 2022, 11, 2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Fang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhuo, C.; Luo, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Deng, W.-W.; Ning, J. Sensomics analysis of the effect of the withering method on the aroma components of Keemun black tea. Food Chem. 2022, 395, 133549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, G.; Dong, C.; Hu, B.; Zhu, H.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, Y.; Hao, G. Prediction of moisture content for congou black tea withering leaves using image features and nonlinear method. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, S.; Alam, S.; Saleem, M.; Ahmad, W.; Bibi, R.; Hamid, F.S.; Shah, H.U. Withering timings affect the total free amino acids and mineral contents of tea leaves during black tea manufacturing. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 2411–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavi, K.V.; Tamilkodi, R.; Dinakar, R.B.; JayaSudha, K. An innovative technique for content based image retrieval using color and texture features. Int. J. Innov. Res. Comput. Commun. Eng. 2013, 1, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, A.; Chen, H.Y.; Chen, C. Use of temperature and humidity sensors to determine moisture content of oolong tea. Sensors 2014, 14, 15593–15609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steger, C.; Ulrich, M.; Wiedemann, C. Machine Vision Algorithms and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wijaya, D.R.; Handayani, R.; Fahrudin, T.; Kusuma, G.P.; Afianti, F. Electronic Nose and Optimized Machine Learning Algorithms for Non-infused Aroma-based Quality Identification of Gambung Green Tea. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 24, 1880–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Lu, C.; Huang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ning, J. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the pile fermentation degree of Pu-erh tea. LWT 2023, 173, 114327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Deng, L. An Adaptive Genetic Algorithm Optimizes Double-Hidden Layer BPNN for Rapid Detection of Moisture Content of Green Tea in Processing. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2024, 2024, 5876051. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Xie, B.; Lü, E.; Zeng, Z.; Mei, S.; Ma, C.; Guo, J. Design of a Moisture content detection system for yinghong no. 9 tea leaves based on machine vision. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Zeng, Z.; Han, C.; Wu, W. Detection network for multi-size and multi-target tea bud leaves in the field of view via improved YOLOv7. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 218, 108700. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, W.; Wang, R.; Wan, S.; Rao, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Gu, L. Tea picking point detection and location based on Mask-RCNN. Inf. Process. Agric. 2023, 10, 267–275. [Google Scholar]
- An, T.; Yu, H.; Yang, C.; Liang, G.; Chen, J.; Hu, Z.; Hu, B.; Dong, C. Black tea withering moisture detection method based on convolution neural network confidence. J. Food Process Eng. 2020, 43, e13428. [Google Scholar]
- Bastien, P.; Vinzi, V.E.; Tenenhaus, M. PLS generalised linear regression. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2005, 48, 17–46. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Li, S.; Bai, Q.; Yang, J.; Jiang, S.; Miao, Y. Review of image classification algorithms based on convolutional neural networks. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terven, J.; Córdova-Esparza, D.M.; Romero-González, J.A. A comprehensive review of yolo architectures in computer vision: From yolov1 to yolov8 and yolo-nas. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2023, 5, 1680–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, D.; Song, T.; Ye, Y.; Li, K.; Song, Y. Rfaconv: Innovating spatital attention and standard convolutional operation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.03198. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13713–13722. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, D.; Pan, W.; Ouyang, Q.; Li, H.; Urmila, K.; Zhao, J. Recent developments of green analytical techniques in analysis of tea’s quality and nutrition. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 43, 63–82. [Google Scholar]

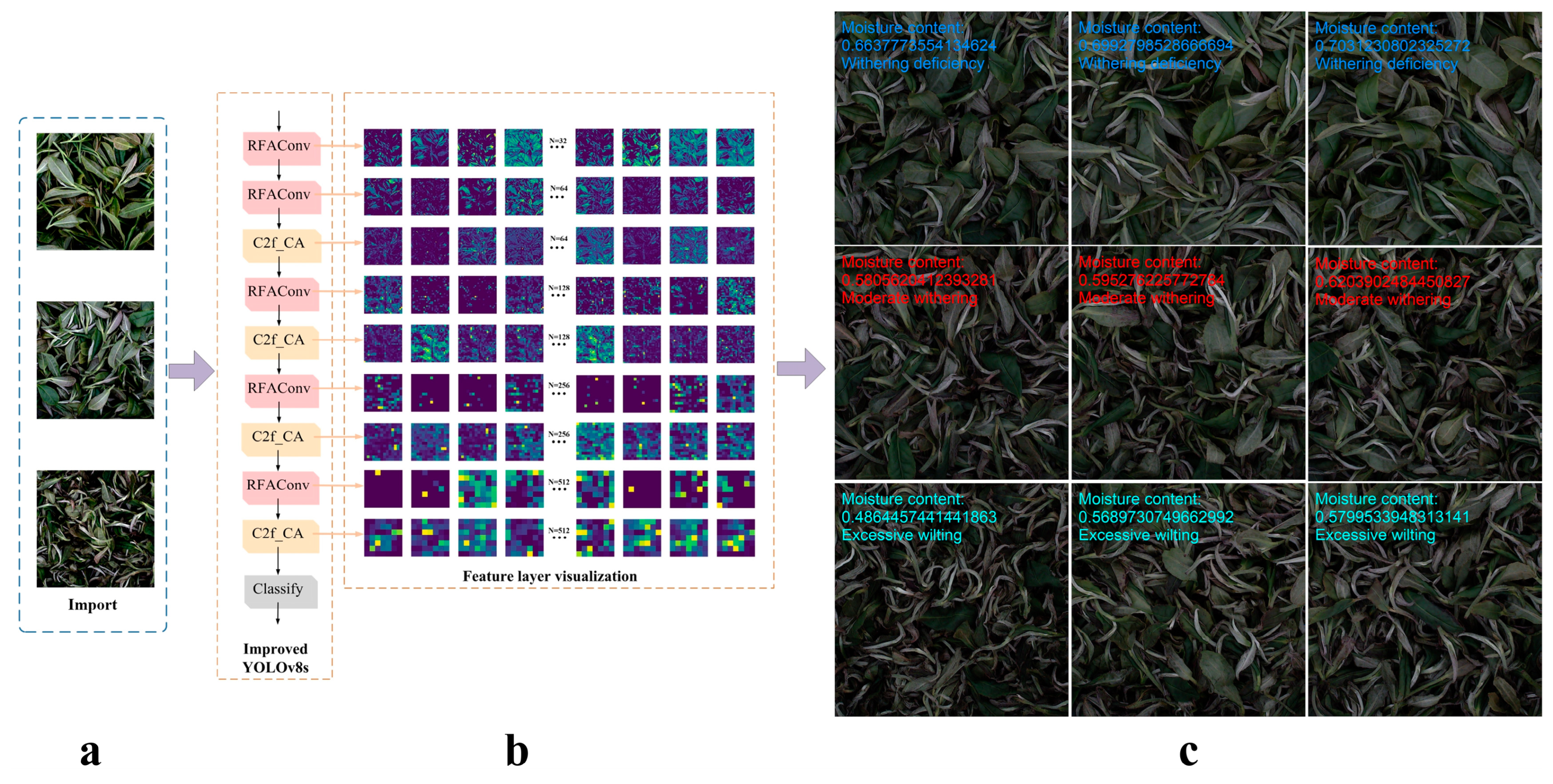
| Network Structure | Network Layer Before Optimization | Improved Network Layer | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Backbone | Layer number | Network Layer | Repeats | Kernels size | Network Layer | Repeats | Kernels size |
| (1) | Conv | 1 | 64 | RFAConv | 1 | 64 | |
| (2) | Conv | 1 | 128 | RFAConv | 1 | 128 | |
| (3) | C2f | 3 | 128 | C2f_CA | 3 | 128 | |
| (4) | Conv | 1 | 256 | RFAConv | 1 | 256 | |
| (5) | C2f | 6 | 256 | C2f_CA | 6 | 256 | |
| (6) | Conv | 1 | 512 | RFAConv | 1 | 512 | |
| (7) | C2f | 6 | 512 | C2f_CA | 6 | 512 | |
| (8) | Conv | 1 | 1024 | RFAConv | 1 | 1024 | |
| (9) | C2f | 3 | 1024 | C2f_CA | 3 | 1024 | |
| Head | Layer number | Network Layer | Repeats | Output | Network Layer | Repeats | Output |
| (1) | Classify | 1 | 10 | Classify | 1 | 10 | |
| Model | Acc | Para (MB) | GFLOPs (G) | Speed (ms) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preprocessing | Inference | ||||
| YOLOv8n | 0.729 | 1.384 | 3.3 | 0.2 | 1.3 |
| YOLOv8s | 0.771 | 4.856 | 12.5 | 0.1 | 1.4 |
| YOLOv8m | 0.771 | 15.048 | 41.6 | 0.2 | 1.7 |
| YOLOv8l | 0.786 | 34.524 | 98.7 | 0.2 | 1.9 |
| YOLOv8x | 0.786 | 53.539 | 153.8 | 0.3 | 2.5 |
| Model | top1_acc | top5_acc: | Params (M) | GFLOPs (G) | Speed (ms) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preprocessing | Inference | |||||
| YOLOv8s | 0.771 | 1 | 4.856 | 12.5 | 0.1 | 1.4 |
| Ours | 0.927 | 1 | 5.08 | 13.7 | 0.3 | 5 |
| Training Set Category | Moisture Label | Test Set Confidence | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 9 | ||
| 0 | 0.7843 | 0.91888142 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0.7714 | 0.08109235 | 0.00000007 | 0 |
| 2 | 0.763 | 0.00002619 | 0.00961427 | 0 |
| 3 | 0.7501 | 0.00000001 | 0.41952419 | 0 |
| 4 | 0.699 | 0 | 0.57085168 | 0.00000004 |
| 5 | 0.6654 | 0 | 0.00000980 | 0.00098720 |
| 6 | 0.6372 | 0 | 0 | 0.53591472 |
| 7 | 0.5671 | 0 | 0 | 0.45765832 |
| 8 | 0.5177 | 0 | 0 | 0.00543968 |
| 9 | 0.4863 | 0 | 0 | 0.00000003 |
| Sum of Confidence | 0.99999997 | 1.00000001 | 0.99999999 | |
| Predictive value | 0.78325333 | 0.72105269 | 0.60449594 | |
| True value | 0.7799 | 0.7231 | 0.597 | |
| Ours | PLS | CNN | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 9 | 1 | 5 | 9 | 1 | 5 | 9 | |
| Rp | 0.9983 | 0.993 | 0.9474 | 0.982 | 0.966 | 0.9488 | 0.9726 | 0.9277 | 0.905 |
| RMSEP | 0.006278 | 0.00694 | 0.018411 | 0.018615 | 0.014287 | 0.024974 | 0.022124 | 0.018567 | 0.03413 |
| RPD | 39.2513 | 20.1693 | 7.363 | 12.0667 | 7.974 | 6.4651 | 9.8045 | 5.5216 | 4.7987 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Meng, H.; Ding, Z.; Tian, Z.; Dong, C.; Chen, Z. Predicting the Degree of Fresh Tea Leaves Withering Using Image Classification Confidence. Foods 2025, 14, 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071125
Wang M, Shi Y, Li Y, Meng H, Ding Z, Tian Z, Dong C, Chen Z. Predicting the Degree of Fresh Tea Leaves Withering Using Image Classification Confidence. Foods. 2025; 14(7):1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071125
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Mengjie, Yali Shi, Yaping Li, Hewei Meng, Zezhong Ding, Zhengrui Tian, Chunwang Dong, and Zhiwei Chen. 2025. "Predicting the Degree of Fresh Tea Leaves Withering Using Image Classification Confidence" Foods 14, no. 7: 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071125
APA StyleWang, M., Shi, Y., Li, Y., Meng, H., Ding, Z., Tian, Z., Dong, C., & Chen, Z. (2025). Predicting the Degree of Fresh Tea Leaves Withering Using Image Classification Confidence. Foods, 14(7), 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071125








